239:
111:
400:– by some estimates more than 60% of human protein-coding genes are likely to be regulated by miRNA, though the quality of experimental evidence for miRNA-target interactions is often weak. Because processing by microprocessor is a major determinant of miRNA abundance, microprocessor itself is then an important target of regulation.
27:
415:
modulating stability, intracellular localization, and activity levels. Activity against particular substrates may be regulated by additional protein cofactors interacting with the microprocessor complex. The loop region of the pri-miRNA stem-loop is also a recognition element for regulatory proteins,
550:
The involvement of miRNAs in diseases has led scientists to become more interested in the role of additional protein complexes, like microprocessor, that have the ability to influence or modulate the function and expression of miRNAs. Microprocessor complex component, DGCR8, is affected through the
1135:
Okada, Chimari; Yamashita, Eiki; Lee, Soo Jae; Shibata, Satoshi; Katahira, Jun; Nakagawa, Atsushi; Yoneda, Yoshihiro; Tsukihara, Tomitake (2009-11-27). "A High-Resolution
Structure of the Pre-microRNA Nuclear Export Machinery".
364:
have been described; these are very small introns which, after splicing, have the appropriate size and stem-loop structure to serve as a pre-miRNA. The processing pathways for microRNA and for exogenously derived
280:(pre-miRNA). Its two subunits have been determined as necessary and sufficient for the mediation of the development of miRNAs from the pri-miRNAs. These molecules of around 70 nucleotides contain a
341:
allows for the increased processing of pri-miRNAs through an induced conformational change of the DGCR8 subunit, and also enhances DGCR8's binding specificity for RNA.
898:
Gregory RI, Yan KP, Amuthan G, Chendrimada T, Doratotaj B, Cooch N, Shiekhattar R (November 2004). "The
Microprocessor complex mediates the genesis of microRNAs".
637:
Gregory RI, Yan KP, Amuthan G, Chendrimada T, Doratotaj B, Cooch N, Shiekhattar R (November 2004). "The
Microprocessor complex mediates the genesis of microRNAs".
223:
1443:
Winter J, Jung S, Keller S, Gregory RI, Diederichs S (March 2009). "Many roads to maturity: microRNA biogenesis pathways and their regulation".
1635:"MicroRNAs and essential components of the microRNA processing machinery are not encoded in the genome of the ctenophore Mnemiopsis leidyi"
481:
428:
424:
408:
342:
688:
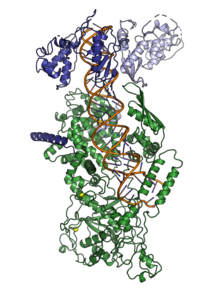
Denli AM, Tops BB, Plasterk RH, Ketting RF, Hannon GJ (November 2004). "Processing of primary microRNAs by the
Microprocessor complex".
1837:"Deficiency of Dgcr8, a gene disrupted by the 22q11.2 microdeletion, results in altered short-term plasticity in the prefrontal cortex"
137:
domains (blue and orange); a double-stranded RNA binding domain (yellow); and a connector/platform domain (gray) containing two bound
412:
588:
Partin, Alexander C.; Zhang, Kaiming; Jeong, Byung-Cheon; Herrell, Emily; Li, Shanshan; Chiu, Wah; Nam, Yunsun (May 2020).
211:
of the minimal complex was at one point experimentally difficult to determine, but it has been demonstrated to be a
1914:
357:
away from the junctions, and remains in contact with the pri-miRNAs following cleavage and dissociation of Drosha.
1904:
360:
Although the large majority of miRNAs undergo processing by microprocessor, a small number of exceptions called
1909:
31:
1486:
Jiang X, Prabhakar A, Van der Voorn SM, Ghatpande P, Celona B, Venkataramanan S, et al. (February 2021).
454:
and related enzymes are found only in animals while Dicer relatives are widely distributed, including among
308:
188:
997:"A heterotrimer model of the complete Microprocessor complex revealed by single-molecule subunit counting"
219:
192:
523:
459:
366:
285:
115:
96:
1848:
1391:
Bellemer C, Bortolin-Cavaillé ML, Schmidt U, Jensen SM, Kjems J, Bertrand E, Cavaillé J (June 2012).
1347:
1145:
907:
697:
646:
539:
542:. Elaboration of this pathway for miRNA-mediated gene regulation is thought to have evolved later.
378:
218:
In addition to the minimal catalytically active microprocessor components, other cofactors such as
176:
173:
89:
1468:
1422:
1169:
1117:
931:
721:
670:
493:
492:. In plants, the miRNA biogenesis pathway is somewhat different; neither Drosha nor DGCR8 has a
995:
Herbert KM, Sarkar SK, Mills M, Delgado De la Herran HC, Neuman KC, Steitz JA (February 2016).
1899:
1876:
1817:
1766:
1717:
1666:
1615:
1566:
1517:
1460:
1414:
1373:
1316:
1267:
1218:
1161:
1109:
1067:
1026:
977:
923:
877:
827:
769:
713:
662:
619:
564:
468:
420:
256:
180:
143:
52:
850:
Macias S, Cordiner RA, Cáceres JF (August 2013). "Cellular functions of the microprocessor".
416:
which may up- or down-regulate microprocessor processing of the specific miRNAs they target.
315:
overhang of 2-3 nucleotides, which serves as a recognition element for the transport protein
1866:
1856:
1807:
1797:
1756:
1748:
1707:
1697:
1656:
1646:
1605:
1597:
1556:
1548:
1507:
1499:
1452:
1404:
1363:
1355:
1306:
1298:
1257:
1249:
1208:
1200:
1153:
1101:
1057:
1016:
1008:
967:
915:
867:
859:
817:
809:
759:
705:
654:
609:
601:
519:
496:
in plant cells, where the first step in miRNA processing is usually executed by a different
374:
328:
165:
134:
77:
39:
373:
processing and are largely identical downstream. Broadly defined, both pathways constitute
296:. In the latter case, there is evidence that the microprocessor complex interacts with the
103:. Microprocessor is also the smaller of the two multi-protein complexes that contain human
813:
393:
346:
312:
230:. Some miRNAs are processed by microprocessor only in the presence of specific cofactors.
69:
1852:
1351:
1149:
911:
701:
650:
1871:
1836:
1812:
1785:
1761:
1736:
1712:
1685:
1661:
1634:
1610:
1585:
1561:
1536:
1512:
1487:
1393:"Microprocessor dynamics and interactions at endogenous imprinted C19MC microRNA genes"
1368:
1335:
1311:
1286:
1285:
Morlando M, Ballarino M, Gromak N, Pagano F, Bozzoni I, Proudfoot NJ (September 2008).
1262:
1237:
1213:
1188:
1021:
996:
822:
797:
614:
589:
289:
277:
212:
184:
20:
1893:
1472:
1173:
1121:
560:
552:
273:
208:
1835:
Fénelon K, Mukai J, Xu B, Hsu PK, Drew LJ, Karayiorgou M, et al. (March 2011).
1786:"Microprocessor of microRNAs: regulation and potential for therapeutic intervention"
1426:
935:
725:
674:
515:
500:
497:
301:
269:
238:
100:
81:
1686:"Vive la différence: biogenesis and evolution of microRNAs in plants and animals"
764:
747:
605:
297:
126:
110:
1841:
Proceedings of the
National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
1359:
1062:
1045:
972:
955:
590:"Cryo-EM Structures of Human Drosha and DGCR8 in Complex with Primary MicroRNA"
1752:
1503:
1044:
Nguyen TA, Jo MH, Choi YG, Park J, Kwon SC, Hohng S, et al. (June 2015).
473:
354:
316:
251:
123:
1737:"On the origin and functions of RNA-mediated silencing: from protists to man"
1702:
1651:
1633:
Maxwell EK, Ryan JF, Schnitzler CE, Browne WE, Baxevanis AD (December 2012).
1861:
1802:
1157:
954:
Kwon SC, Nguyen TA, Choi YG, Jo MH, Hohng S, Kim VN, Woo JS (January 2016).
527:
455:
320:
281:
1880:
1821:
1770:
1721:
1670:
1619:
1570:
1521:
1464:
1418:
1377:
1320:
1271:
1238:"Functional association of the Microprocessor complex with the spliceosome"
1222:
1204:
1165:
1113:
1071:
1030:
1012:
981:
927:
881:
831:
773:
717:
666:
623:
19:
This article is about the protein complex. For the computer processor, see
1552:
1336:"Heme enables proper positioning of Drosha and DGCR8 on primary microRNAs"
1253:
485:
463:
423:
through association with a pri-miRNA-like hairpin structure found in the
361:
247:
73:
47:
1456:
919:
863:
709:
658:
1409:
1392:
556:
446:
shares striking structural similarity with the downstream ribonuclease
243:
1601:
1488:"Control of ribosomal protein synthesis by the Microprocessor complex"
1334:
Partin AC, Ngo TD, Herrell E, Jeong BC, Hon G, Nam Y (November 2017).
1302:
872:
260:
147:
95:(also known as Pasha in non-human animals), and cleaves primary miRNA
56:
563:. This deletion causes irregular processing of miRNAs which leads to
531:
489:
477:
451:
443:
404:
397:
382:
350:
324:
293:
227:
161:
119:
104:
85:
46:(dark and light blue) interacting with and ready to cleave a primary
35:
1105:
179:. (DGCR8 is the name used in mammalian genetics, abbreviated from "
748:"Posttranscriptional regulation of microRNA biogenesis in animals"
535:
508:
447:
385:
and activating transcription of ribosomal protein encoding genes.
370:
338:
332:
237:
169:
130:
109:
92:
43:
25:
1287:"Primary microRNA transcripts are processed co-transcriptionally"
1092:
Ha M, Kim VN (August 2014). "Regulation of microRNA biogenesis".
80:(RNAi) in animal cells. The complex is minimally composed of the
504:
484:
homologs, as well as recognizable miRNAs, and is the only known
432:
138:
160:
The microprocessor complex consists minimally of two proteins:
26:
435:
and is unlikely to itself function as miRNA in its own right.
327:-dependent manner and are further processed, typically by the
1535:
Friedman RC, Farh KK, Burge CB, Bartel DP (January 2009).
307:
Microprocessor cleavage of pri-miRNAs typically occurs co-
1537:"Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs"
226:
may be present in the complex to mediate the activity of
431:
expression. The structure in this case is located in an
345:
recognizes the junctions between hairpin structures and
34:
structure of the microprocessor complex, showing human
1586:"Validated MicroRNA Target Databases: An Evaluation"
458:. Both components of the microprocessor complex are
1584:Lee YJ, Kim V, Muth DC, Witwer KW (November 2015).
242:The human exportin-5 protein (red) in complex with
1189:"Post-transcriptional control of miRNA biogenesis"
450:, suggesting an evolutionary relationship, though
319:. Pre-miRNAs are exported from the nucleus to the
300:and that the pri-miRNA processing occurs prior to
16:Protein involved in processing RNA in animal cells
377:. Microprocessor is also found to be involved in
1046:"Functional Anatomy of the Human Microprocessor"
1784:Beezhold KJ, Castranova V, Chen F (June 2010).
183:critical region 8"; the homologous protein in
583:
581:
8:
254:overhang recognition element (orange). From
1735:Cerutti H, Casas-Mollano JA (August 2006).
419:Microprocessor itself is auto-regulated by
72:involved in the early stages of processing
798:"Molecular mechanisms of RNA interference"
133:molecules (green). Drosha consists of two
1870:
1860:
1811:
1801:
1760:
1711:
1701:
1660:
1650:
1609:
1560:
1511:
1438:
1436:
1408:
1367:
1310:
1291:Nature Structural & Molecular Biology
1261:
1236:Kataoka N, Fujita M, Ohno M (June 2009).
1212:
1187:Michlewski G, Cáceres JF (January 2019).
1061:
1020:
971:
871:
821:
763:
613:
845:
843:
841:
791:
789:
787:
785:
783:
224:heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins
1684:Axtell MJ, Westholm JO, Lai EC (2011).
741:
739:
737:
735:
577:
488:with no detectable genomic evidence of
1094:Nature Reviews. Molecular Cell Biology
949:
947:
945:
311:and leaves a characteristic RNase III
215:of two DGCR8 proteins and one Drosha.
1087:
1085:
1083:
1081:
814:10.1146/annurev-biophys-083012-130404
272:, the microprocessor complex cleaves
7:
893:
891:
518:analysis that the key components of
396:by miRNA is widespread across many
14:
427:mRNA, which when cleaved reduces
852:Biochemical Society Transactions
413:post-translational modifications
284:or hairpin structure. Pri-miRNA
514:It has been suggested based on
381:specifically in the removal of
1242:Molecular and Cellular Biology
746:Siomi H, Siomi MC (May 2010).
526:were present in the ancestral
1:
796:Wilson RC, Doudna JA (2013).
411:are subject to regulation by
42:, green) and two subunits of
765:10.1016/j.molcel.2010.03.013
606:10.1016/j.molcel.2020.02.016
122:protein in complex with the
956:"Structure of Human DROSHA"
802:Annual Review of Biophysics
462:among the vast majority of
288:can be derived either from
1931:
1360:10.1038/s41467-017-01713-y
1063:10.1016/j.cell.2015.05.010
973:10.1016/j.cell.2015.12.019
18:
1753:10.1007/s00294-006-0078-x
1590:Drug Development Research
1504:10.1126/scisignal.abd2639
369:converge at the point of
349:RNA and serves to orient
1703:10.1186/gb-2011-12-4-221
1652:10.1186/1471-2164-13-714
32:cryo-electron microscopy
1862:10.1073/pnas.1101219108
1803:10.1186/1476-4598-9-134
1397:Journal of Cell Science
1158:10.1126/science.1178705
1205:10.1261/rna.068692.118
1013:10.1261/rna.054684.115
265:
220:DEAD box RNA helicases
152:
66:microprocessor complex
61:
1553:10.1101/gr.082701.108
1340:Nature Communications
559:, a small portion of
546:Clinical significance
540:transposable elements
367:small interfering RNA
250:(green), showing two-
241:
113:
29:
1254:10.1128/MCB.00360-09
466:with known genomes.
379:ribosomal biogenesis
353:to cleave around 11
141:ion (spheres). From
99:to pre-miRNA in the
1853:2011PNAS..108.4447F
1457:10.1038/ncb0309-228
1445:Nature Cell Biology
1352:2017NatCo...8.1737P
1150:2009Sci...326.1275O
1144:(5957): 1275–1279.
920:10.1038/nature03120
912:2004Natur.432..235G
864:10.1042/BST20130011
710:10.1038/nature03049
702:2004Natur.432..231D
659:10.1038/nature03120
651:2004Natur.432..235G
522:based on exogenous
246:(yellow) and a pre-
174:double-stranded RNA
90:RNA-binding protein
1410:10.1242/jcs.100354
1403:(Pt 11): 2709–20.
534:mechanism against
266:
153:
62:
1915:Protein complexes
1602:10.1002/ddr.21278
1498:(671): eabd2639.
1492:Science Signaling
1303:10.1038/nsmb.1475
600:(3): 411–422.e4.
565:DiGeorge Syndrome
469:Mnemiopsis leidyi
421:negative feedback
309:transcriptionally
276:(pri-miRNA) into
181:DiGeorge syndrome
116:crystal structure
88:and the dimeric
1922:
1905:RNA interference
1885:
1884:
1874:
1864:
1832:
1826:
1825:
1815:
1805:
1790:Molecular Cancer
1781:
1775:
1774:
1764:
1741:Current Genetics
1732:
1726:
1725:
1715:
1705:
1681:
1675:
1674:
1664:
1654:
1630:
1624:
1623:
1613:
1581:
1575:
1574:
1564:
1532:
1526:
1525:
1515:
1483:
1477:
1476:
1440:
1431:
1430:
1412:
1388:
1382:
1381:
1371:
1331:
1325:
1324:
1314:
1282:
1276:
1275:
1265:
1233:
1227:
1226:
1216:
1184:
1178:
1177:
1132:
1126:
1125:
1089:
1076:
1075:
1065:
1041:
1035:
1034:
1024:
992:
986:
985:
975:
951:
940:
939:
906:(7014): 235–40.
895:
886:
885:
875:
847:
836:
835:
825:
793:
778:
777:
767:
743:
730:
729:
685:
679:
678:
645:(7014): 235–40.
634:
628:
627:
617:
585:
520:RNA interference
329:endoribonuclease
263:
166:ribonuclease III
150:
135:ribonuclease III
78:RNA interference
59:
40:ribonuclease III
1930:
1929:
1925:
1924:
1923:
1921:
1920:
1919:
1910:Gene expression
1890:
1889:
1888:
1847:(11): 4447–52.
1834:
1833:
1829:
1783:
1782:
1778:
1734:
1733:
1729:
1683:
1682:
1678:
1632:
1631:
1627:
1583:
1582:
1578:
1541:Genome Research
1534:
1533:
1529:
1485:
1484:
1480:
1442:
1441:
1434:
1390:
1389:
1385:
1333:
1332:
1328:
1284:
1283:
1279:
1248:(12): 3243–54.
1235:
1234:
1230:
1186:
1185:
1181:
1134:
1133:
1129:
1106:10.1038/nrm3838
1091:
1090:
1079:
1043:
1042:
1038:
994:
993:
989:
953:
952:
943:
897:
896:
889:
849:
848:
839:
795:
794:
781:
745:
744:
733:
696:(7014): 231–5.
687:
686:
682:
636:
635:
631:
587:
586:
579:
575:
548:
530:, likely as an
507:, a homolog of
441:
394:Gene regulation
391:
347:single-stranded
313:single-stranded
278:precursor miRNA
268:Located in the
255:
236:
185:model organisms
177:binding protein
158:
142:
70:protein complex
51:
24:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1928:
1926:
1918:
1917:
1912:
1907:
1902:
1892:
1891:
1887:
1886:
1827:
1776:
1727:
1690:Genome Biology
1676:
1625:
1576:
1527:
1478:
1432:
1383:
1326:
1277:
1228:
1179:
1127:
1077:
1056:(6): 1374–87.
1036:
987:
966:(1–2): 81–90.
941:
887:
837:
779:
752:Molecular Cell
731:
680:
629:
594:Molecular Cell
576:
574:
571:
553:micro-deletion
547:
544:
440:
437:
390:
387:
292:genes or from
290:non-coding RNA
235:
232:
157:
154:
21:Microprocessor
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1927:
1916:
1913:
1911:
1908:
1906:
1903:
1901:
1898:
1897:
1895:
1882:
1878:
1873:
1868:
1863:
1858:
1854:
1850:
1846:
1842:
1838:
1831:
1828:
1823:
1819:
1814:
1809:
1804:
1799:
1795:
1791:
1787:
1780:
1777:
1772:
1768:
1763:
1758:
1754:
1750:
1746:
1742:
1738:
1731:
1728:
1723:
1719:
1714:
1709:
1704:
1699:
1695:
1691:
1687:
1680:
1677:
1672:
1668:
1663:
1658:
1653:
1648:
1644:
1640:
1636:
1629:
1626:
1621:
1617:
1612:
1607:
1603:
1599:
1596:(7): 389–96.
1595:
1591:
1587:
1580:
1577:
1572:
1568:
1563:
1558:
1554:
1550:
1547:(1): 92–105.
1546:
1542:
1538:
1531:
1528:
1523:
1519:
1514:
1509:
1505:
1501:
1497:
1493:
1489:
1482:
1479:
1474:
1470:
1466:
1462:
1458:
1454:
1451:(3): 228–34.
1450:
1446:
1439:
1437:
1433:
1428:
1424:
1420:
1416:
1411:
1406:
1402:
1398:
1394:
1387:
1384:
1379:
1375:
1370:
1365:
1361:
1357:
1353:
1349:
1345:
1341:
1337:
1330:
1327:
1322:
1318:
1313:
1308:
1304:
1300:
1296:
1292:
1288:
1281:
1278:
1273:
1269:
1264:
1259:
1255:
1251:
1247:
1243:
1239:
1232:
1229:
1224:
1220:
1215:
1210:
1206:
1202:
1198:
1194:
1190:
1183:
1180:
1175:
1171:
1167:
1163:
1159:
1155:
1151:
1147:
1143:
1139:
1131:
1128:
1123:
1119:
1115:
1111:
1107:
1103:
1100:(8): 509–24.
1099:
1095:
1088:
1086:
1084:
1082:
1078:
1073:
1069:
1064:
1059:
1055:
1051:
1047:
1040:
1037:
1032:
1028:
1023:
1018:
1014:
1010:
1007:(2): 175–83.
1006:
1002:
998:
991:
988:
983:
979:
974:
969:
965:
961:
957:
950:
948:
946:
942:
937:
933:
929:
925:
921:
917:
913:
909:
905:
901:
894:
892:
888:
883:
879:
874:
869:
865:
861:
858:(4): 838–43.
857:
853:
846:
844:
842:
838:
833:
829:
824:
819:
815:
811:
807:
803:
799:
792:
790:
788:
786:
784:
780:
775:
771:
766:
761:
758:(3): 323–32.
757:
753:
749:
742:
740:
738:
736:
732:
727:
723:
719:
715:
711:
707:
703:
699:
695:
691:
684:
681:
676:
672:
668:
664:
660:
656:
652:
648:
644:
640:
633:
630:
625:
621:
616:
611:
607:
603:
599:
595:
591:
584:
582:
578:
572:
570:
569:
566:
562:
561:chromosome 22
558:
554:
545:
543:
541:
537:
533:
529:
525:
521:
517:
512:
510:
506:
502:
499:
495:
491:
487:
483:
479:
476:, lacks both
475:
471:
470:
465:
461:
457:
453:
449:
445:
438:
436:
434:
430:
426:
422:
417:
414:
410:
406:
401:
399:
395:
388:
386:
384:
380:
376:
372:
368:
363:
358:
356:
352:
348:
344:
340:
336:
334:
330:
326:
322:
318:
314:
310:
305:
303:
299:
295:
291:
287:
283:
279:
275:
274:primary miRNA
271:
262:
258:
253:
249:
245:
240:
233:
231:
229:
225:
221:
216:
214:
210:
209:stoichiometry
206:
202:
198:
194:
190:
186:
182:
178:
175:
171:
167:
163:
155:
149:
145:
140:
136:
132:
128:
125:
121:
118:of the human
117:
112:
108:
106:
102:
98:
94:
91:
87:
83:
79:
75:
71:
67:
58:
54:
49:
45:
41:
37:
33:
28:
22:
1844:
1840:
1830:
1793:
1789:
1779:
1747:(2): 81–99.
1744:
1740:
1730:
1693:
1689:
1679:
1642:
1639:BMC Genomics
1638:
1628:
1593:
1589:
1579:
1544:
1540:
1530:
1495:
1491:
1481:
1448:
1444:
1400:
1396:
1386:
1343:
1339:
1329:
1297:(9): 902–9.
1294:
1290:
1280:
1245:
1241:
1231:
1196:
1192:
1182:
1141:
1137:
1130:
1097:
1093:
1053:
1049:
1039:
1004:
1000:
990:
963:
959:
903:
899:
855:
851:
805:
801:
755:
751:
693:
689:
683:
642:
638:
632:
597:
593:
567:
549:
516:phylogenetic
513:
501:ribonuclease
467:
442:
418:
402:
392:
359:
337:
306:
270:cell nucleus
267:
217:
213:heterotrimer
204:
203:rtner of Dro
200:
196:
168:enzyme; and
159:
101:cell nucleus
82:ribonuclease
76:(miRNA) and
65:
63:
1346:(1): 1737.
1199:(1): 1–16.
355:nucleotides
298:spliceosome
156:Composition
1894:Categories
1796:(1): 134.
1696:(4): 221.
873:1842/25877
808:: 217–39.
573:References
524:substrates
474:ctenophore
456:protozoans
389:Regulation
317:exportin-5
286:substrates
252:nucleotide
195:is called
124:C-terminal
97:substrates
1473:205286318
1174:206522317
1122:205495632
528:eukaryote
464:metazoans
460:conserved
439:Evolution
321:cytoplasm
282:stem-loop
38:protein (
1900:MicroRNA
1881:21368174
1822:20515486
1771:16691418
1722:21554756
1671:23256903
1620:26286669
1571:18955434
1522:33622983
1465:19255566
1427:19121670
1419:22393237
1378:29170488
1321:19172742
1272:19349299
1223:30333195
1166:19965479
1114:25027649
1072:26027739
1031:26683315
982:26748718
928:15531877
882:23863141
832:23654304
774:20471939
718:15531879
667:15531877
624:32220646
486:metazoan
362:mirtrons
302:splicing
264:.
248:microRNA
234:Function
187:such as
151:.
74:microRNA
60:.
48:microRNA
1872:3060227
1849:Bibcode
1813:2887798
1762:2583075
1713:3218855
1662:3563456
1645:: 714.
1611:4777876
1562:2612969
1513:8012103
1369:5700927
1348:Bibcode
1312:6952270
1263:2698730
1214:6298569
1146:Bibcode
1138:Science
1022:4712668
936:4389261
908:Bibcode
823:5895182
726:4425505
698:Bibcode
675:4389261
647:Bibcode
615:7214211
557:22q11.2
536:viruses
498:nuclear
494:homolog
398:genomes
383:R-loops
331:enzyme
294:introns
244:Ran-GTP
207:.) The
129:of two
127:helices
84:enzyme
50:. From
1879:
1869:
1820:
1810:
1769:
1759:
1720:
1710:
1669:
1659:
1618:
1608:
1569:
1559:
1520:
1510:
1471:
1463:
1425:
1417:
1376:
1366:
1319:
1309:
1270:
1260:
1221:
1211:
1172:
1164:
1120:
1112:
1070:
1029:
1019:
980:
934:
926:
900:Nature
880:
830:
820:
772:
724:
716:
690:Nature
673:
665:
639:Nature
622:
612:
532:immune
490:Drosha
478:Drosha
452:Drosha
444:Drosha
405:Drosha
351:Drosha
325:RanGTP
228:Drosha
199:, for
162:Drosha
120:Drosha
105:Drosha
86:Drosha
36:Drosha
1469:S2CID
1423:S2CID
1170:S2CID
1118:S2CID
932:S2CID
722:S2CID
671:S2CID
509:Dicer
482:DGCR8
448:Dicer
429:DGCR8
425:DGCR8
409:DGCR8
403:Both
371:Dicer
343:DGCR8
339:Hemin
333:Dicer
323:in a
197:Pasha
193:worms
189:flies
170:DGCR8
131:DGCR8
93:DGCR8
68:is a
44:DGCR8
1877:PMID
1818:PMID
1767:PMID
1718:PMID
1667:PMID
1616:PMID
1567:PMID
1518:PMID
1461:PMID
1415:PMID
1374:PMID
1317:PMID
1268:PMID
1219:PMID
1162:PMID
1110:PMID
1068:PMID
1050:Cell
1027:PMID
978:PMID
960:Cell
924:PMID
878:PMID
828:PMID
770:PMID
714:PMID
663:PMID
620:PMID
538:and
505:DCL1
480:and
472:, a
433:exon
407:and
375:RNAi
261:3A6P
222:and
191:and
172:, a
164:, a
148:5B16
139:zinc
64:The
57:6V5B
1867:PMC
1857:doi
1845:108
1808:PMC
1798:doi
1757:PMC
1749:doi
1708:PMC
1698:doi
1657:PMC
1647:doi
1606:PMC
1598:doi
1557:PMC
1549:doi
1508:PMC
1500:doi
1453:doi
1405:doi
1401:125
1364:PMC
1356:doi
1307:PMC
1299:doi
1258:PMC
1250:doi
1209:PMC
1201:doi
1193:RNA
1154:doi
1142:326
1102:doi
1058:doi
1054:161
1017:PMC
1009:doi
1001:RNA
968:doi
964:164
916:doi
904:432
868:hdl
860:doi
818:PMC
810:doi
760:doi
706:doi
694:432
655:doi
643:432
610:PMC
602:doi
555:of
257:PDB
205:sha
144:PDB
53:PDB
1896::
1875:.
1865:.
1855:.
1843:.
1839:.
1816:.
1806:.
1792:.
1788:.
1765:.
1755:.
1745:50
1743:.
1739:.
1716:.
1706:.
1694:12
1692:.
1688:.
1665:.
1655:.
1643:13
1641:.
1637:.
1614:.
1604:.
1594:76
1592:.
1588:.
1565:.
1555:.
1545:19
1543:.
1539:.
1516:.
1506:.
1496:14
1494:.
1490:.
1467:.
1459:.
1449:11
1447:.
1435:^
1421:.
1413:.
1399:.
1395:.
1372:.
1362:.
1354:.
1342:.
1338:.
1315:.
1305:.
1295:15
1293:.
1289:.
1266:.
1256:.
1246:29
1244:.
1240:.
1217:.
1207:.
1197:25
1195:.
1191:.
1168:.
1160:.
1152:.
1140:.
1116:.
1108:.
1098:15
1096:.
1080:^
1066:.
1052:.
1048:.
1025:.
1015:.
1005:22
1003:.
999:.
976:.
962:.
958:.
944:^
930:.
922:.
914:.
902:.
890:^
876:.
866:.
856:41
854:.
840:^
826:.
816:.
806:42
804:.
800:.
782:^
768:.
756:38
754:.
750:.
734:^
720:.
712:.
704:.
692:.
669:.
661:.
653:.
641:.
618:.
608:.
598:78
596:.
592:.
580:^
511:.
503:,
335:.
304:.
259::
201:Pa
146::
114:A
107:.
55::
30:A
1883:.
1859::
1851::
1824:.
1800::
1794:9
1773:.
1751::
1724:.
1700::
1673:.
1649::
1622:.
1600::
1573:.
1551::
1524:.
1502::
1475:.
1455::
1429:.
1407::
1380:.
1358::
1350::
1344:8
1323:.
1301::
1274:.
1252::
1225:.
1203::
1176:.
1156::
1148::
1124:.
1104::
1074:.
1060::
1033:.
1011::
984:.
970::
938:.
918::
910::
884:.
870::
862::
834:.
812::
776:.
762::
728:.
708::
700::
677:.
657::
649::
626:.
604::
568:.
23:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.