17:
217:
483:
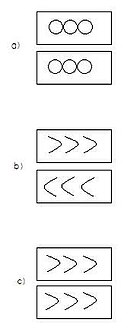
will result elongated dimples, which are parabolic depressions that coalesce in planes of maximum shear stress. The depressions point back to the crack origin, and shear influenced failure will produce depressions that point in opposite directions on opposing fracture surfaces. Combined tension and
66:
and the matrix. Additionally, microvoids often form at grain boundaries or inclusions within the material. Microvoids grow during plastic flow of the matrix, and microvoids coalesce when adjacent microvoids link together or the material between microvoids experiences
76:
50:
466:
62:
MVC proceeds in three stages: nucleation, growth, and coalescence of microvoids. The nucleation of microvoids can be caused by particle cracking or interfacial failure between
331:
269:
300:
387:
358:
538:
212:{\displaystyle \ln \left({\frac {\bar {R}}{R_{0}}}\right)=\int \limits _{0}^{\epsilon _{q}}A\left({\frac {3\sigma _{m}}{2\sigma _{ys}}}\right)d\epsilon _{v}^{p}}
239:
488:
will also produce the elongated dimple morphology, but the directions of the depressions will be in the same direction on both fracture surfaces.
611:
514:
71:. Microvoid coalescence leads to fracture. Void growth rates can be predicted assuming continuum plasticity using the Rice-Tracey model:
479:
results in equiaxed dimples, which are spherical depressions a few micrometres in diameter that coalesce normal to the loading axis.
564:
394:
660:
20:
655:
606:. Milne, I., Ritchie, R. O., Karihaloo, B. L. (1st ed.). Amsterdam: Elsevier/Pergamon. 2003. pp. 186–192.
635:
16:
63:
68:
309:
244:
629:
532:
475:
MVC can result in three distinct fracture morphologies based on the type of loading at failure.
303:
278:
363:
617:
607:
570:
560:
520:
510:
476:
336:
224:
649:
241:
is a constant typically equal to 0.283 (but dependent upon the stress triaxiality),
480:
272:
53:
MVC fracture surface morphologies for a) tension, b) shear, and c) bending failures
23:
image of microvoid coalescence seen on a ductile fracture surface of 6061-T6 Al
621:
524:
574:
589:
Deformation and
Fracture Mechanics of Engineering Materials, Fourth Edition
601:
43:
35:
509:. Wright, Wendelin J. (Seventh ed.). Boston, MA. pp. 236–237.
485:
49:
48:
39:
15:
461:{\displaystyle {\bar {R}}={\frac {R_{1}+R_{2}+R_{3}}{3}}}
397:
366:
339:
312:
281:
247:
227:
79:
460:
381:
352:
325:
294:
263:
233:
211:
591:. John Wiley and Sons, Inc, Hoboken, NJ: 1996.
557:Mechanical properties of engineered materials
8:
333:is the equivalent Von Mises plastic strain,
537:: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (
446:
433:
420:
413:
399:
398:
396:
368:
367:
365:
344:
338:
317:
311:
286:
280:
252:
246:
226:
203:
198:
175:
160:
150:
135:
130:
125:
106:
92:
90:
78:
507:The science and engineering of materials
497:
627:
530:
38:mechanism observed in the majority of
7:
550:
548:
505:Askeland, Donald R. (January 2015).
559:. Marcel Dekker. pp. 393–394.
389:produced by the stress triaxality:
603:Comprehensive structural integrity
14:
34:) is a high energy microscopic
404:
373:
97:
1:
471:Fracture surface morphologies
326:{\displaystyle \epsilon _{q}}
264:{\displaystyle \sigma _{ys}}
295:{\displaystyle \sigma _{m}}
677:
382:{\displaystyle {\bar {R}}}
360:is the particle size, and
42:and in some engineering
587:Hertzberg, Richard W.
634:: CS1 maint: others (
555:Soboyejo, W.O (2003).
462:
383:
354:
327:
296:
265:
235:
213:
142:
54:
24:
661:Materials degradation
463:
384:
355:
353:{\displaystyle R_{o}}
328:
297:
266:
236:
214:
121:
64:precipitate particles
52:
28:Microvoid coalescence
19:
395:
364:
337:
310:
279:
245:
225:
77:
208:
656:Fracture mechanics
458:
379:
350:
323:
292:
261:
231:
209:
194:
55:
25:
613:978-0-08-049073-1
516:978-1-305-07676-1
456:
407:
376:
234:{\displaystyle A}
185:
112:
100:
668:
640:
639:
633:
625:
598:
592:
585:
579:
578:
552:
543:
542:
536:
528:
502:
467:
465:
464:
459:
457:
452:
451:
450:
438:
437:
425:
424:
414:
409:
408:
400:
388:
386:
385:
380:
378:
377:
369:
359:
357:
356:
351:
349:
348:
332:
330:
329:
324:
322:
321:
301:
299:
298:
293:
291:
290:
270:
268:
267:
262:
260:
259:
240:
238:
237:
232:
218:
216:
215:
210:
207:
202:
190:
186:
184:
183:
182:
166:
165:
164:
151:
141:
140:
139:
129:
117:
113:
111:
110:
101:
93:
91:
58:Fracture process
676:
675:
671:
670:
669:
667:
666:
665:
646:
645:
644:
643:
626:
614:
600:
599:
595:
586:
582:
567:
554:
553:
546:
529:
517:
504:
503:
499:
494:
477:Tensile loading
473:
442:
429:
416:
415:
393:
392:
362:
361:
340:
335:
334:
313:
308:
307:
282:
277:
276:
248:
243:
242:
223:
222:
171:
167:
156:
152:
146:
131:
102:
86:
75:
74:
60:
40:metallic alloys
12:
11:
5:
674:
672:
664:
663:
658:
648:
647:
642:
641:
612:
593:
580:
565:
544:
515:
496:
495:
493:
490:
481:Shear stresses
472:
469:
455:
449:
445:
441:
436:
432:
428:
423:
419:
412:
406:
403:
375:
372:
347:
343:
320:
316:
289:
285:
258:
255:
251:
230:
206:
201:
197:
193:
189:
181:
178:
174:
170:
163:
159:
155:
149:
145:
138:
134:
128:
124:
120:
116:
109:
105:
99:
96:
89:
85:
82:
59:
56:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
673:
662:
659:
657:
654:
653:
651:
637:
631:
623:
619:
615:
609:
605:
604:
597:
594:
590:
584:
581:
576:
572:
568:
566:0-203-91039-7
562:
558:
551:
549:
545:
540:
534:
526:
522:
518:
512:
508:
501:
498:
491:
489:
487:
482:
478:
470:
468:
453:
447:
443:
439:
434:
430:
426:
421:
417:
410:
401:
390:
370:
345:
341:
318:
314:
305:
287:
283:
274:
256:
253:
249:
228:
219:
204:
199:
195:
191:
187:
179:
176:
172:
168:
161:
157:
153:
147:
143:
136:
132:
126:
122:
118:
114:
107:
103:
94:
87:
83:
80:
72:
70:
65:
57:
51:
47:
45:
41:
37:
33:
29:
22:
18:
602:
596:
588:
583:
556:
506:
500:
474:
391:
273:yield stress
220:
73:
61:
31:
27:
26:
304:mean stress
650:Categories
492:References
630:cite book
622:190802556
533:cite book
525:903959750
405:¯
374:¯
315:ϵ
284:σ
250:σ
196:ϵ
173:σ
158:σ
133:ϵ
123:∫
98:¯
84:
575:54091550
44:plastics
36:fracture
486:bending
302:is the
271:is the
69:necking
620:
610:
573:
563:
523:
513:
221:where
636:link
618:OCLC
608:ISBN
571:OCLC
561:ISBN
539:link
521:OCLC
511:ISBN
32:MVC
21:SEM
652::
632:}}
628:{{
616:.
569:.
547:^
535:}}
531:{{
519:.
306:,
275:,
81:ln
46:.
638:)
624:.
577:.
541:)
527:.
454:3
448:3
444:R
440:+
435:2
431:R
427:+
422:1
418:R
411:=
402:R
371:R
346:o
342:R
319:q
288:m
257:s
254:y
229:A
205:p
200:v
192:d
188:)
180:s
177:y
169:2
162:m
154:3
148:(
144:A
137:q
127:0
119:=
115:)
108:0
104:R
95:R
88:(
30:(
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.