506:) and can go back and forth in the metabolic chain. These are found in humans, animals, plants, and bacteria. In plants, they are located in the chloroplasts in order to help with the metabolic processes. In baker's yeast, they are located in the mitochondria. In several experiments, it has been shown that mutated strains of Escherichia coli K-12 without the enzyme were not able to grow in the presence of only acetate or oleate as the only carbon sources.
645:>sp|P1759|86-667 TFISRFAPDQPRKGADILVEALERQGVETVFAYPGGASMEIHQALTRSSSIRNVLPRHEQGGVFAAEGYARSSGKPGICIATSGPGATNLVSGLADALLD SVPLVAITGQVPRRMIGTDAFQETPIVEVTRSITKHNYLVMDVEDIPRIIEEAFFLATSGRPGPVLVDVPKDIQQQLAIPNWEQAMRLPGYMSRMPKPPE DSHLEQIVRLISESKKPVLYVGGGCLNSSDELGRFVELTGIPVASTLMGLGSYPXDDELSLHMLGMHGTVYANYAVEHSDLLLAFGVRFDDRVTGKLEAF ASRAKIVHIDIDSAEIGKNKTPHVSVCGDVKLALQGMNKVLENRAEELKLDFGVWRNELNVQKQKFPLSFKTFGEAIPPQYAIKVLDELTDGKAIISTG
31:
2255:
567:. This enzyme is the first of several enzymes in the biosynthesis cycle for leucine and valine, taking the initial pyruvate molecules and starting the conversion from pyruvic acid to the amino acids. The specific residue that is responsible for this is a glycine at position 511 in the protein. This is the one that requires a cofactor of TPP for its function.
501:
involved in the biosynthesis of various amino acids. This enzyme has the Enzyme
Commission Code is 2.2.1.6, which means that the enzyme is a transketolase or a transaldolase, which is classified under the transferases that transfer aldehyde or ketone residues. In this case, acetolactate synthase is a
350:
The structure of acetolactate synthase that was used for the picture on this page was determined using X-ray diffraction at 2.70 angstroms. X-ray diffraction uses X-rays at specified wavelengths to produce patterns, as the X–ray is scattered in certain ways that give an idea to the structure of the
636:
is listed below. Residues involved in catalytic activity are bolded. Mutagenesis of Asp428, which is crucial carboxylate ligand to Mg(2+) in the "ThDP motif", leads to a decrease in the affinity of AHAS II for Mg(2+). While mutant D428N shows ThDP affinity close to that of the wild-type on
916:, was previously mapped to “ILVBL” gene within a 2-cM interval, D19S226–D19S199. This gene encodes a protein highly similar to the acetolactate synthase of other organisms. No recombination event was observed with D19S841, a highly polymorphic microsatellite marker isolated from a
1110:
Joutel A, Ducros A, Alamowitch S, Cruaud C, Domenga V, Maréchal E, Vahedi K, Chabriat H, Bousser MG, Tournier-Lasserve E (December 1996). "A human homolog of bacterial acetolactate synthase genes maps within the CADASIL critical region".
558:
The reaction uses thiamine pyrophosphate in order to link the two pyruvate molecules. The resulting product of this reaction, acetolactate, eventually becomes valine, leucine, and isoleucine. All three of these amino acids are
867:. As of March 2022, the ALS inhibitors suffer the worst (known) resistance problem of all herbicide classes, having 169 known resistant target species. The structures of ALS herbicides are radically different from the normal
753:, ilvBN, ilvGM and ilvIH (where ilvN regulated ilvB, and vice versa). Together, these operons code for several enzymes involved in branched-chain amino acid biosynthesis. Regulation is different for each operon.
879:
are expected to have widely varying effects on normal ALS catalysis activity, positive, negative and neutral. Unsurprisingly that is exactly what experiments have shown, including Yu
1888:
1258:
Bar-Ilan A, Balan V, Tittmann K, Golbik R, Vyazmensky M, Hübner G, Barak Z, Chipman DM (October 2001). "Binding and activation of thiamin diphosphate in acetohydroxyacid synthase".
1381:
Mohammad
Dezfulian, Curtis Foreman, Espanta Jalili, Mrinal Pal, Rajdeep K. Dhaliwal, Don Karl A. Roberto, Kathleen M. Imre, Susanne E. Kohalmi, and William L. Crosby. (2017).
1346:
Lee YT, Duggleby RG (June 2001). "Identification of the regulatory subunit of
Arabidopsis thaliana acetohydroxyacid synthase and reconstitution with its catalytic subunit".
1192:"ILV2 - Acetolactate synthase catalytic subunit, mitochondrial precursor - Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) - ILV2 gene & protein"
1432:
218:
1211:"Acetohydroxy acid synthase I, a required enzyme for isoleucine and valine biosynthesis in Escherichia coli K-12 during growth on acetate as the sole carbon source"
812:
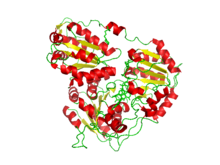
operons are derepressed during shortages of the branched-chain amino acids by the same mechanism that represses them. Both of these operons as well as the third,
347:
sandwiching a DHS-like NAD/FAD-binding domain. In SCOP assignment, these subunits are named d1yhya1, d1yhya2, and d1yhya3 from the N-terminal to the C-terminal.
1311:
Chen H, Saksa K, Zhao F, Qiu J, Xiong L (August 2010). "Genetic analysis of pathway regulation for enhancing branched-chain amino acid biosynthesis in plants".
237:
702:. Such an arrangement is widespread in both bacterial and eukaryotic ALS. The hetromeric structure was demonstrated in E. coli in 1984 and in eukaryotes (
1881:
1383:"Acetolactate synthase regulatory subunits play divergent and overlapping roles in branched-chain amino acid synthesis and Arabidopsis development"
527:
Acetolactate synthase, also known as acetohydroxy acid synthase, is an enzyme specifically involved in the conversion of pyruvate to acetolactate:
1756:
767:
1072:
Chipman D, Barak Z, Schloss JV (June 1998). "Biosynthesis of 2-aceto-2-hydroxy acids: acetolactate synthases and acetohydroxyacid synthases".
1874:
1654:
1598:
839:, which eventually leads to inhibition of DNA synthesis. They affect grasses and dicots alike. They are not a chemistry class but rather a
876:
1675:
Mitra A, Sarma SP (February 2008). "Escherichia coli ilvN interacts with the FAD binding domain of ilvB and activates the AHAS I enzyme".
741:)), Acetolactate synthase consists of three pairs of isoforms. Each pair includes a large subunit, which is thought to be responsible for
570:
Four specific residues are responsible for catalytic activity in this enzyme. They are listed here with cofactors required written after.
1830:
1974:
657:
GFGLPAAIGASVANPDAIVVDIDGDGSFIMNVQELATIRVENLPVKVLLLNNQHLGMVMQWEDRFYKANRAH TFLGDPAQEDEIFPNMLLFAAACGIPAARVTKKADLREAIQTMLDTPGPYLLDVICP
637:
saturation with Mg(2+), D428E has a decreased affinity for ThDP. These mutations also lead to dependence of the enzyme on K(+).
230:
1726:
1815:
157:
2130:
181:
2245:
864:
1294:"ALS - Acetolactate synthase, chloroplastic precursor - Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) - ALS gene & protein"
856:
1730:
1749:
941:
937:
798:
783:
1042:
817:
771:
275:
2115:
801:(ilvC). It is similarly regulated, but is specific to isoleucine and leucine; valine does not affect it directly.
2231:
2218:
2205:
2192:
2179:
2166:
2153:
1918:
1795:
1790:
757:
2125:
912:, an identified autosomal dominant condition characterized by the recurrence of subcortical infarcts leading to
293:
A human protein of yet unknown function, sharing some sequence similarity with bacterial ALS, is encoded by the
2079:
2022:
1909:
1717:
1614:
Zhou Q, Liu W, Zhang Y, Liu KK (Oct 2007). "Action mechanisms of acetolactate synthase-inhibiting herbicides".
868:
343:
consisting of 670 residues, the last 615 of which form the active form. Three main domains are found, with two
175:
60:
860:
2027:
1825:
1810:
1805:
848:
787:
775:
502:
transketolase, which moves back and forth, having both catabolic and anabolic forms. These act on a ketone (
162:
1446:
Duggleby RG (May 1997). "Identification of an acetolactate synthase small subunit gene in two eukaryotes".
1785:
1742:
344:
274:) is a protein found in plants and micro-organisms. ALS catalyzes the first step in the synthesis of the
42:
2048:
1967:
1855:
1426:
852:
242:
2120:
150:
924:
was detected on this gene in CADASIL patients, suggesting that it is not implicated in this disorder.
1623:
984:
560:
332:
77:
37:
2084:
840:
779:
746:
72:
178:
2017:
1835:
1713:
1532:"The leucine-responsive regulatory protein, a global regulator of metabolism in Escherichia coli"
102:
46:
2275:
1850:
1845:
1723:
1692:
1594:
1563:
1512:
1463:
1414:
1363:
1328:
1275:
1240:
1128:
1089:
1054:
1012:
961:
169:
2063:
2058:
2032:
1960:
1684:
1631:
1586:
1553:
1543:
1502:
1494:
1455:
1404:
1394:
1355:
1320:
1267:
1230:
1222:
1120:
1081:
1046:
1002:
992:
933:
828:
354:
There are five specific ligands that interact with this protein. The five are listed below.
2110:
2094:
2007:
1050:
885:
790:
is reduced in the presence of the pathway's end-products, the branched-chain amino acids.
633:
138:
1866:
1627:
1585:. Microbiology Monographs. Vol. 5. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer. pp. 129–162.
988:
114:
2259:
2148:
2089:
1507:
1482:
1409:
1382:
1007:
972:
872:
213:
65:
1558:
1531:
1459:
1235:
1210:
1085:
973:"Herbicide-binding sites revealed in the structure of plant acetohydroxyacid synthase"
193:
30:
2269:
2053:
2012:
1936:
1931:
1840:
1324:
1033:
Powles SB, Yu Q (2010-06-02). "Evolution in action: plants resistant to herbicides".
319:
188:
1650:
2002:
1941:
1800:
1769:
1548:
844:
699:
1226:
1635:
730:
716:
690:
680:
515:
2226:
2161:
1997:
1897:
1163:
1074:
Biochimica et
Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Protein Structure and Molecular Enzymology
337:
197:
2254:
977:
Proceedings of the
National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
749:. Each subunit pair, or ALS I, II, and III respectively, is located on its own
695:
1820:
1399:
836:
721:
287:
2200:
2174:
997:
832:
742:
1696:
1516:
1418:
1367:
1332:
1279:
1164:"Acetolactate synthase, chloroplastic (P17597) < InterPro < EMBL-EBI"
1124:
1058:
1016:
1590:
1567:
1467:
1244:
1146:
1132:
1093:
971:
McCourt JA, Pang SS, King-Scott J, Guddat LW, Duggleby RG (January 2006).
563:
and cannot be synthesized by humans. This also leads to the systemic name
1901:
1734:
1483:"The amino acid valine is secreted in continuous-flow bacterial biofilms"
1481:
Valle J, Da Re S, Schmid S, Skurnik D, D'Ari R, Ghigo JM (January 2008).
1293:
1191:
1177:
921:
913:
725:
711:
685:
675:
510:
503:
1498:
1765:
1583:
Amino Acid
Biosynthesis: Pathways, Regulation and Metabolic Engineering
909:
890:
340:
283:
145:
126:
1688:
1359:
1271:
965:
2213:
1983:
1905:
917:
894:
750:
498:
279:
225:
121:
109:
97:
2187:
843:
class with diverse chemistries. The ALS inhibitor family includes
666:
Because of inhibition and several factors it is a slow procedure.
315:
298:
133:
1956:
1870:
1738:
1651:"List of Herbicide Resistant Weeds by Herbicide Mode of Action"
1147:"Entrez Gene:ILVBL ilvB (bacterial acetolactate synthase)-like"
875:
but instead at a site specific to herbicidal action. Therefore
710:) in 1997. Most of the regulatory proteins have an ACT domain (
1178:"SCOPe 2.07: Structural Classification of Proteins — extended"
565:
pyruvate:pyruvate acetaldehydetransferase (decarboxylating)
87:
pyruvate:pyruvate acetaldehydetransferase (decarboxylating)
1952:
2243:
766:
operon encodes the ilvGM (ALS II) pair as well as a
2139:
2103:
2072:
2041:
1990:
1917:
684:) is complexed with two regulatory small subunits (
572:
356:
236:
224:
212:
207:
187:
168:
156:
144:
132:
120:
108:
96:
91:
83:
71:
59:
54:
23:
1028:
1026:
1581:Pátek M (2007). "Branched-chain amino acids.".
1968:
1882:
1750:
1105:
1103:
674:In Arabidopsis, two chains of catalytic ALS (
641:Primary sequence. Catalytic residues are bold
8:
1431:: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (
1158:
1156:
835:that slowly starve affected plants of these
797:operon encodes the ilvBN (ALS I) pair and a
509:A catabolic version that does not bind FAD (
41:acetohydroxyacid synthase complexed with a
1975:
1961:
1953:
1889:
1875:
1867:
1757:
1743:
1735:
944:with ilvN and activate the AHAS I enzyme.
758:Branched-chain amino acid § Synthesis
464:METHYL 2-CARBONYL}AMINO)SULFONYL]BENZOATE
204:
29:
1716:at the U.S. National Library of Medicine
1557:
1547:
1506:
1408:
1398:
1234:
1006:
996:
940:binding domain of ilvB has been shown to
1530:Calvo JM, Matthews RG (September 1994).
632:The primary sequence of this protein in
2250:
953:
1424:
1209:Dailey FE, Cronan JE (February 1986).
768:branched-chain-amino-acid transaminase
20:
1655:Herbicide Resistance Action Committee
1616:Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology
1051:10.1146/annurev-arplant-042809-112119
7:
865:sulfonylamino carbonyl triazolinones
1831:Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase
497:Acetolactate synthase is catalytic
897:substitution at amino acid 197 to
14:
2253:
1325:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04261.x
871:and so none of them bind at the
489:The FAD bound is not catalytic.
330:The catalytic peptide of ALS in
1816:Dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase
1549:10.1128/mmbr.58.3.466-490.1994
1035:Annual Review of Plant Biology
1:
1460:10.1016/s0378-1119(97)00002-4
1227:10.1128/jb.165.2.453-460.1986
1086:10.1016/S0167-4838(98)00083-1
883:, 2007 finding resistance in
519:) is found in some bacteria.
374:ETHYL DIHYDROGEN DIPHOSPHATE
1636:10.1016/j.pestbp.2007.04.004
857:Category:Triazolopyrimidines
434:FLAVIN-ADENINE DINUCLEOTIDE
799:ketol-acid reductoisomerase
784:transcriptional attenuation
778:(ilvA). It is regulated by
2292:
920:mapped to this region. No
818:leucine-responsive protein
772:dihydroxy-acid dehydratase
755:
745:, and a small subunit for
720:) and some of them have a
276:branched-chain amino acids
2131:Michaelis–Menten kinetics
1796:Butyryl CoA dehydrogenase
1791:Apoptosis-inducing factor
1776:
1400:10.1186/s12870-017-1022-6
661:QEHVLPMIPSGGTFNDVITEGDGR
649:GQHQMWAAQFYNYKKPRQWLSSGGL
351:molecule being analyzed.
336:(mouse-eared cress) is a
268:acetohydroxyacid synthase
203:
28:
2023:Diffusion-limited enzyme
1718:Medical Subject Headings
861:pyrimidinyl oxybenzoates
314:Human ILVBL gene has 17
262:) enzyme (also known as
1826:Methemoglobin reductase
1811:Cytokinin dehydrogenase
1806:Cytochrome b5 reductase
1536:Microbiological Reviews
1487:Journal of Bacteriology
1215:Journal of Bacteriology
998:10.1073/pnas.0508701103
901:ALS activity by 2x-3x.
776:threonine ammonia-lyase
400:2-ETHANE SULFONIC ACID
1786:Acyl CoA dehydrogenase
1125:10.1006/geno.1996.0615
345:thiamine pyrophosphate
43:sulfonylurea herbicide
2116:Eadie–Hofstee diagram
2049:Allosteric regulation
1927:Acetolactate synthase
1856:Thioredoxin reductase
1781:Acetolactate synthase
1714:Acetolactate+synthase
1591:10.1007/7171_2006_070
905:Clinical significance
561:essential amino acids
256:acetolactate synthase
35:Crystal structure of
24:acetolactate synthase
2126:Lineweaver–Burk plot
877:resistance mutations
333:Arabidopsis thaliana
38:Arabidopsis thaliana
1628:2007PBioP..89...89Z
1499:10.1128/JB.01405-07
989:2006PNAS..103..569M
853:triazolopyrimidines
841:mechanism of action
831:of ALS are used as
816:, are regulated by
780:feedback inhibition
747:feedback inhibition
2085:Enzyme superfamily
2018:Enzyme promiscuity
1836:NADH dehydrogenase
724:-like C-terminal (
523:Catalytic activity
360:Ligand Identifier
47:metsulfuron-methyl
2241:
2240:
1950:
1949:
1864:
1863:
1851:Sarcosine oxidase
1846:Nitrate reductase
1724:Ramachandran plot
1689:10.1021/bi701893b
1600:978-3-540-48596-4
1387:BMC Plant Biology
1360:10.1021/bi002775q
1313:The Plant Journal
1272:10.1021/bi0104524
708:Porphyra purpurea
630:
629:
487:
486:
264:acetohydroxy acid
252:
251:
248:
247:
151:metabolic pathway
2283:
2258:
2257:
2249:
2121:Hanes–Woolf plot
2064:Enzyme activator
2059:Enzyme inhibitor
2033:Enzyme catalysis
1977:
1970:
1963:
1954:
1891:
1884:
1877:
1868:
1759:
1752:
1745:
1736:
1701:
1700:
1672:
1666:
1665:
1663:
1662:
1646:
1640:
1639:
1611:
1605:
1604:
1578:
1572:
1571:
1561:
1551:
1527:
1521:
1520:
1510:
1478:
1472:
1471:
1443:
1437:
1436:
1430:
1422:
1412:
1402:
1378:
1372:
1371:
1343:
1337:
1336:
1308:
1302:
1301:
1290:
1284:
1283:
1266:(39): 11946–54.
1255:
1249:
1248:
1238:
1206:
1200:
1199:
1188:
1182:
1181:
1174:
1168:
1167:
1160:
1151:
1150:
1143:
1137:
1136:
1107:
1098:
1097:
1069:
1063:
1062:
1030:
1021:
1020:
1010:
1000:
968:
958:
934:Escherichia coli
932:In the study of
573:
357:
205:
33:
21:
16:Class of enzymes
2291:
2290:
2286:
2285:
2284:
2282:
2281:
2280:
2266:
2265:
2264:
2252:
2244:
2242:
2237:
2149:Oxidoreductases
2135:
2111:Enzyme kinetics
2099:
2095:List of enzymes
2068:
2037:
2008:Catalytic triad
1986:
1981:
1951:
1946:
1913:
1895:
1865:
1860:
1772:
1763:
1710:
1705:
1704:
1674:
1673:
1669:
1660:
1658:
1648:
1647:
1643:
1613:
1612:
1608:
1601:
1580:
1579:
1575:
1529:
1528:
1524:
1480:
1479:
1475:
1445:
1444:
1440:
1423:
1380:
1379:
1375:
1354:(23): 6836–44.
1345:
1344:
1340:
1310:
1309:
1305:
1298:www.uniprot.org
1292:
1291:
1287:
1257:
1256:
1252:
1208:
1207:
1203:
1196:www.uniprot.org
1190:
1189:
1185:
1176:
1175:
1171:
1162:
1161:
1154:
1145:
1144:
1140:
1109:
1108:
1101:
1071:
1070:
1066:
1032:
1031:
1024:
970:
960:
959:
955:
950:
930:
907:
886:Hordeum murinum
826:
782:in the form of
760:
672:
664:
663:
662:
642:
554:
550:
546:
542:
538:
534:
525:
495:
482:
478:
474:
470:
456:
452:
448:
444:
440:
414:
410:
406:
392:
388:
384:
380:
328:
312:
307:
50:
17:
12:
11:
5:
2289:
2287:
2279:
2278:
2268:
2267:
2263:
2262:
2239:
2238:
2236:
2235:
2222:
2209:
2196:
2183:
2170:
2157:
2143:
2141:
2137:
2136:
2134:
2133:
2128:
2123:
2118:
2113:
2107:
2105:
2101:
2100:
2098:
2097:
2092:
2087:
2082:
2076:
2074:
2073:Classification
2070:
2069:
2067:
2066:
2061:
2056:
2051:
2045:
2043:
2039:
2038:
2036:
2035:
2030:
2025:
2020:
2015:
2010:
2005:
2000:
1994:
1992:
1988:
1987:
1982:
1980:
1979:
1972:
1965:
1957:
1948:
1947:
1945:
1944:
1939:
1934:
1929:
1923:
1921:
1915:
1914:
1896:
1894:
1893:
1886:
1879:
1871:
1862:
1861:
1859:
1858:
1853:
1848:
1843:
1838:
1833:
1828:
1823:
1818:
1813:
1808:
1803:
1798:
1793:
1788:
1783:
1777:
1774:
1773:
1764:
1762:
1761:
1754:
1747:
1739:
1733:
1732:
1728:
1721:
1709:
1708:External links
1706:
1703:
1702:
1683:(6): 1518–31.
1667:
1641:
1606:
1599:
1573:
1522:
1473:
1438:
1373:
1338:
1303:
1285:
1250:
1201:
1183:
1169:
1152:
1138:
1099:
1064:
1043:Annual Reviews
1022:
952:
951:
949:
946:
929:
926:
906:
903:
873:catalytic site
849:imidazolinones
825:
822:
671:
668:
644:
643:
640:
639:
628:
627:
624:
621:
617:
616:
613:
610:
606:
605:
602:
599:
595:
594:
591:
588:
584:
583:
580:
577:
556:
555:
552:
548:
544:
540:
536:
532:
524:
521:
494:
491:
485:
484:
480:
476:
472:
468:
465:
462:
458:
457:
454:
450:
446:
442:
438:
435:
432:
428:
427:
424:
423:Magnesium Ion
421:
417:
416:
412:
408:
404:
401:
398:
394:
393:
390:
386:
382:
378:
375:
372:
368:
367:
364:
361:
327:
324:
311:
308:
306:
303:
250:
249:
246:
245:
240:
234:
233:
228:
222:
221:
216:
210:
209:
201:
200:
191:
185:
184:
173:
166:
165:
160:
154:
153:
148:
142:
141:
136:
130:
129:
124:
118:
117:
112:
106:
105:
100:
94:
93:
89:
88:
85:
81:
80:
75:
69:
68:
63:
57:
56:
52:
51:
34:
26:
25:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2288:
2277:
2274:
2273:
2271:
2261:
2256:
2251:
2247:
2233:
2229:
2228:
2223:
2220:
2216:
2215:
2210:
2207:
2203:
2202:
2197:
2194:
2190:
2189:
2184:
2181:
2177:
2176:
2171:
2168:
2164:
2163:
2158:
2155:
2151:
2150:
2145:
2144:
2142:
2138:
2132:
2129:
2127:
2124:
2122:
2119:
2117:
2114:
2112:
2109:
2108:
2106:
2102:
2096:
2093:
2091:
2090:Enzyme family
2088:
2086:
2083:
2081:
2078:
2077:
2075:
2071:
2065:
2062:
2060:
2057:
2055:
2054:Cooperativity
2052:
2050:
2047:
2046:
2044:
2040:
2034:
2031:
2029:
2026:
2024:
2021:
2019:
2016:
2014:
2013:Oxyanion hole
2011:
2009:
2006:
2004:
2001:
1999:
1996:
1995:
1993:
1989:
1985:
1978:
1973:
1971:
1966:
1964:
1959:
1958:
1955:
1943:
1940:
1938:
1937:Transketolase
1935:
1933:
1932:Transaldolase
1930:
1928:
1925:
1924:
1922:
1920:
1916:
1911:
1907:
1903:
1899:
1892:
1887:
1885:
1880:
1878:
1873:
1872:
1869:
1857:
1854:
1852:
1849:
1847:
1844:
1842:
1841:NADPH oxidase
1839:
1837:
1834:
1832:
1829:
1827:
1824:
1822:
1819:
1817:
1814:
1812:
1809:
1807:
1804:
1802:
1799:
1797:
1794:
1792:
1789:
1787:
1784:
1782:
1779:
1778:
1775:
1771:
1770:flavoproteins
1767:
1760:
1755:
1753:
1748:
1746:
1741:
1740:
1737:
1731:
1729:
1727:
1725:
1722:
1719:
1715:
1712:
1711:
1707:
1698:
1694:
1690:
1686:
1682:
1678:
1671:
1668:
1656:
1652:
1645:
1642:
1637:
1633:
1629:
1625:
1621:
1617:
1610:
1607:
1602:
1596:
1592:
1588:
1584:
1577:
1574:
1569:
1565:
1560:
1555:
1550:
1545:
1542:(3): 466–90.
1541:
1537:
1533:
1526:
1523:
1518:
1514:
1509:
1504:
1500:
1496:
1493:(1): 264–74.
1492:
1488:
1484:
1477:
1474:
1469:
1465:
1461:
1457:
1453:
1449:
1442:
1439:
1434:
1428:
1420:
1416:
1411:
1406:
1401:
1396:
1392:
1388:
1384:
1377:
1374:
1369:
1365:
1361:
1357:
1353:
1349:
1342:
1339:
1334:
1330:
1326:
1322:
1319:(4): 573–83.
1318:
1314:
1307:
1304:
1299:
1295:
1289:
1286:
1281:
1277:
1273:
1269:
1265:
1261:
1254:
1251:
1246:
1242:
1237:
1232:
1228:
1224:
1221:(2): 453–60.
1220:
1216:
1212:
1205:
1202:
1197:
1193:
1187:
1184:
1179:
1173:
1170:
1165:
1159:
1157:
1153:
1148:
1142:
1139:
1134:
1130:
1126:
1122:
1118:
1114:
1106:
1104:
1100:
1095:
1091:
1087:
1083:
1080:(2): 401–19.
1079:
1075:
1068:
1065:
1060:
1056:
1052:
1048:
1044:
1040:
1036:
1029:
1027:
1023:
1018:
1014:
1009:
1004:
999:
994:
990:
986:
983:(3): 569–73.
982:
978:
974:
967:
963:
957:
954:
947:
945:
943:
939:
935:
927:
925:
923:
919:
915:
911:
904:
902:
900:
896:
892:
888:
887:
882:
878:
874:
870:
866:
862:
858:
854:
850:
846:
845:sulfonylureas
842:
838:
834:
830:
823:
821:
819:
815:
811:
807:
802:
800:
796:
791:
789:
788:transcription
785:
781:
777:
773:
769:
765:
759:
754:
752:
748:
744:
740:
737:In bacteria (
735:
733:
732:
727:
723:
719:
718:
713:
709:
705:
704:S. cerevisiae
701:
697:
693:
692:
687:
683:
682:
677:
669:
667:
660:
656:
652:
648:
638:
635:
625:
622:
619:
618:
614:
611:
608:
607:
603:
600:
597:
596:
592:
589:
586:
585:
581:
578:
575:
574:
571:
568:
566:
562:
530:
529:
528:
522:
520:
518:
517:
512:
507:
505:
500:
492:
490:
466:
463:
460:
459:
436:
433:
430:
429:
425:
422:
419:
418:
402:
399:
396:
395:
376:
373:
370:
369:
365:
362:
359:
358:
355:
352:
348:
346:
342:
339:
338:chloroplastic
335:
334:
325:
323:
321:
320:chromosome 19
317:
309:
304:
302:
300:
296:
291:
289:
285:
281:
277:
273:
269:
265:
261:
257:
244:
241:
239:
235:
232:
229:
227:
223:
220:
217:
215:
211:
206:
202:
199:
195:
192:
190:
189:Gene Ontology
186:
183:
180:
177:
174:
171:
167:
164:
161:
159:
155:
152:
149:
147:
143:
140:
137:
135:
131:
128:
127:NiceZyme view
125:
123:
119:
116:
113:
111:
107:
104:
101:
99:
95:
90:
86:
82:
79:
76:
74:
70:
67:
64:
62:
58:
53:
48:
44:
40:
39:
32:
27:
22:
19:
2227:Translocases
2224:
2211:
2198:
2185:
2172:
2162:Transferases
2159:
2146:
2003:Binding site
1942:DXP synthase
1926:
1898:Transferases
1801:Cryptochrome
1780:
1680:
1677:Biochemistry
1676:
1670:
1659:. Retrieved
1644:
1622:(2): 89–96.
1619:
1615:
1609:
1582:
1576:
1539:
1535:
1525:
1490:
1486:
1476:
1454:(2): 245–9.
1451:
1447:
1441:
1427:cite journal
1390:
1386:
1376:
1351:
1348:Biochemistry
1347:
1341:
1316:
1312:
1306:
1297:
1288:
1263:
1260:Biochemistry
1259:
1253:
1218:
1214:
1204:
1195:
1186:
1172:
1141:
1119:(2): 192–8.
1116:
1112:
1077:
1073:
1067:
1038:
1034:
980:
976:
956:
931:
928:Interactions
908:
898:
884:
880:
827:
813:
809:
805:
803:
794:
792:
774:(ilvD), and
763:
761:
738:
736:
729:
715:
707:
703:
689:
679:
673:
665:
658:
654:
650:
646:
631:
569:
564:
557:
526:
514:
508:
496:
488:
353:
349:
331:
329:
313:
297:(ilvB-like)
294:
292:
271:
267:
263:
259:
255:
253:
115:BRENDA entry
36:
18:
1998:Active site
837:amino acids
786:. That is,
634:Arabidopsis
598:Methionine
318:resides on
103:IntEnz view
55:Identifiers
2201:Isomerases
2175:Hydrolases
2042:Regulation
1821:Flavodoxin
1661:2022-03-30
1045:: 317–47.
948:References
833:herbicides
829:Inhibitors
824:Inhibitors
756:See also:
670:Regulation
609:Histidine
582:Cofactors
366:Structure
322:at q13.1.
288:isoleucine
172:structures
139:KEGG entry
84:Alt. names
78:9027-45-6
2080:EC number
969:;
889:due to a
869:substrate
804:Both the
743:catalysis
731:IPR027271
717:IPR002912
691:IPR004789
681:IPR012846
579:Position
543:CC(OH)(CH
516:IPR012782
305:Structure
92:Databases
2276:EC 2.2.1
2270:Category
2104:Kinetics
2028:Cofactor
1991:Activity
1902:aldehyde
1697:18193896
1653:. HRAC (
1649:Heap I.
1517:17981982
1419:28388946
1368:11389597
1333:20497381
1280:11570896
1113:Genomics
1059:20192743
1017:16407096
942:interact
922:mutation
914:dementia
899:increase
806:ilvGMEDA
770:(ilvE),
764:ilvGMEDA
726:InterPro
712:InterPro
686:InterPro
676:InterPro
620:Glycine
576:Residue
511:InterPro
504:pyruvate
493:Function
270:, abbr.
243:proteins
231:articles
219:articles
176:RCSB PDB
2260:Biology
2214:Ligases
1984:Enzymes
1766:Protein
1624:Bibcode
1568:7968922
1508:2223729
1468:9197540
1410:5384131
1245:3511034
1133:8954801
1094:9655946
1008:1334660
985:Bibcode
910:CADASIL
891:proline
847:(SUs),
820:(Lrp).
739:E. coli
728::
714::
688::
678::
587:Valine
513::
341:protein
326:Protein
284:leucine
198:QuickGO
163:profile
146:MetaCyc
73:CAS no.
66:2.2.1.6
2246:Portal
2188:Lyases
1906:ketone
1720:(MeSH)
1695:
1597:
1566:
1559:372976
1556:
1515:
1505:
1466:
1417:
1407:
1366:
1331:
1278:
1243:
1236:214440
1233:
1131:
1092:
1057:
1015:
1005:
936:, the
918:cosmid
895:serine
881:et al.
863:, and
810:ilvBNC
795:ilvBNC
751:operon
700:AHASS1
696:AHASS2
499:enzyme
286:, and
280:valine
226:PubMed
208:Search
194:AmiGO
182:PDBsum
122:ExPASy
110:BRENDA
98:IntEnz
61:EC no.
2140:Types
1919:2.2.1
1041:(1).
855:(see
814:ilvIH
547:)COCH
363:Name
316:exons
295:ILVBL
158:PRIAM
2232:list
2225:EC7
2219:list
2212:EC6
2206:list
2199:EC5
2193:list
2186:EC4
2180:list
2173:EC3
2167:list
2160:EC2
2154:list
2147:EC1
1912:2.2)
1693:PMID
1595:ISBN
1564:PMID
1513:PMID
1464:PMID
1448:Gene
1433:link
1415:PMID
1364:PMID
1329:PMID
1276:PMID
1241:PMID
1129:PMID
1090:PMID
1078:1385
1055:PMID
1013:PMID
966:1YHY
808:and
793:The
762:The
722:NiKR
706:and
698:and
626:TPP
623:511
612:643
604:HE3
601:513
593:HE3
590:485
551:+ CO
535:COCO
531:2 CH
461:1SM
431:FAD
397:NHE
371:P22
310:Gene
299:gene
272:AHAS
254:The
238:NCBI
179:PDBe
134:KEGG
1685:doi
1632:doi
1587:doi
1554:PMC
1544:doi
1503:PMC
1495:doi
1491:190
1456:doi
1452:190
1405:PMC
1395:doi
1356:doi
1321:doi
1268:doi
1231:PMC
1223:doi
1219:165
1121:doi
1082:doi
1047:doi
1003:PMC
993:doi
981:103
962:PDB
938:FAD
859:),
694:),
539:→ O
426:Mg
420:Mg
290:).
266:or
260:ALS
214:PMC
170:PDB
2272::
1910:EC
1900::
1768::
1691:.
1681:47
1679:.
1630:.
1620:89
1618:.
1593:.
1562:.
1552:.
1540:58
1538:.
1534:.
1511:.
1501:.
1489:.
1485:.
1462:.
1450:.
1429:}}
1425:{{
1413:.
1403:.
1393:.
1391:17
1389:.
1385:.
1362:.
1352:40
1350:.
1327:.
1317:63
1315:.
1296:.
1274:.
1264:40
1262:.
1239:.
1229:.
1217:.
1213:.
1194:.
1155:^
1127:.
1117:38
1115:.
1102:^
1088:.
1076:.
1053:.
1039:61
1037:.
1025:^
1011:.
1001:.
991:.
979:.
975:.
964::
851:,
734:)
615:-
483:S
473:16
469:15
451:15
443:33
439:27
415:S
411:NO
409:17
301:.
282:,
196:/
45:,
2248::
2234:)
2230:(
2221:)
2217:(
2208:)
2204:(
2195:)
2191:(
2182:)
2178:(
2169:)
2165:(
2156:)
2152:(
1976:e
1969:t
1962:v
1908:(
1904:-
1890:e
1883:t
1876:v
1758:e
1751:t
1744:v
1699:.
1687::
1664:.
1657:)
1638:.
1634::
1626::
1603:.
1589::
1570:.
1546::
1519:.
1497::
1470:.
1458::
1435:)
1421:.
1397::
1370:.
1358::
1335:.
1323::
1300:.
1282:.
1270::
1247:.
1225::
1198:.
1180:.
1166:.
1149:.
1135:.
1123::
1096:.
1084::
1061:.
1049::
1019:.
995::
987::
893:→
659:H
655:M
653:A
651:G
647:V
553:2
549:3
545:3
541:2
537:2
533:3
481:5
479:O
477:4
475:N
471:H
467:C
455:2
453:P
449:O
447:9
445:N
441:H
437:C
413:3
407:H
405:8
403:C
391:2
389:P
387:7
385:O
383:8
381:H
379:2
377:C
278:(
258:(
49:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.