1518:, which induce the production of interferons and other cytokines increasing resistance of cells such as monocytes to infections. Cytokines produced during innate immune responses are among the activators of adaptive immune responses. Antibodies exert additive or synergistic effects with mechanisms of innate immunity. Unstable HbS clusters Band-3, a major integral red cell protein; antibodies recognize these clusters and accelerate their removal by phagocytic cells. Clustered Band 3 proteins with attached antibodies activate complement, and complement C3 fragments are opsonins recognized by the CR1 complement receptor on phagocytic cells.
186:
1210:. Throughout the lifetime of an animal these memory cells form a database of effective B and T lymphocytes. Upon interaction with a previously encountered antigen, the appropriate memory cells are selected and activated. In this manner, the second and subsequent exposures to an antigen produce a stronger and faster immune response. This is "adaptive" in the sense that the body's immune system prepares itself for future challenges, but is "maladaptive" of course if the receptors are autoimmune. Immunological memory can be in the form of either
1388:, in which one gene segment recombines with other gene segments to form a single unique gene. This assembly process generates the enormous diversity of receptors and antibodies, before the body ever encounters antigens, and enables the immune system to respond to an almost unlimited diversity of antigens. Throughout an animal's lifetime, lymphocytes that can react against the antigens an animal actually encounters are selected for action—directed against anything that expresses that antigen.
1133:
377:
368:(NK) cells with so-far unexplained specificity for antigens, expansion of NK cells expressing germ-line encoded receptors, and activation of other innate immune cells to an activated state that confers a short-term "immune memory". In this sense, "adaptive immunity" more closely resembles the concept of "activated state" or "heterostasis", thus returning in sense to the physiological sense of "adaptation" to environmental changes.
560:
900:
724:
1346:
43:
1404:(which is considered "non-self") from attack by the immune system, are particularly interesting. Although no comprehensive explanation has emerged to explain this mysterious, and often repeated, lack of rejection, two classical reasons may explain how the fetus is tolerated. The first is that the fetus occupies a portion of the body protected by a non-immunological barrier, the
352:, a previously marginal organism for the study of immunology. The term "adaptive" as used in immunology is problematic as acquired immune responses can be both adaptive and maladaptive in the physiological sense. Indeed, both acquired and innate immune responses can be both adaptive and maladaptive in the evolutionary sense. Most textbooks today, following the early use by
140:
1101:. Those domains can be alternatively spliced reaching high numbers of variations. It was shown that after exposure to different pathogens there are different splice forms of dscam produced. After the animals with different splice forms are exposed to the same pathogen only the individuals with the splice form specific for that pathogen survive.
1365:, or antigenic determinants. Most antigens contain a variety of epitopes and can stimulate the production of antibodies, specific T cell responses, or both. A very small proportion (less than 0.01%) of the total lymphocytes are able to bind to a particular antigen, which suggests that only a few cells respond to each antigen.
1369:
different pathogen that might ever be encountered. Even in the absence of antigen stimulation, a human can produce more than 1 trillion different antibody molecules. Millions of genes would be required to store the genetic information that produces these receptors, but, the entire human genome contains fewer than 25,000
1408:, which the immune system does not routinely patrol. The second is that the fetus itself may promote local immunosuppression in the mother, perhaps by a process of active nutrient depletion. A more modern explanation for this induction of tolerance is that specific glycoproteins expressed in the uterus during
1391:
The innate and acquired portions of the immune system work together, not in spite of each other. The acquired arm, B, and T cells could not function without the innate system input. T cells are useless without antigen-presenting cells to activate them, and B cells are disabled without T cell help. On
962:
Like the T cell, B cells express a unique B cell receptor (BCR), in this case, a membrane-bound antibody molecule. All the BCR of any one clone of B cells recognizes and binds to only one particular antigen. A critical difference between B cells and T cells is how each cell "sees" an antigen. T cells
363:
discovery, "antigen-specific immunity mediated by somatic gene rearrangements that create clone-defining antigen receptors". In the last decade, the term "adaptive" has been increasingly applied to another class of immune response not so-far associated with somatic gene rearrangements. These include
1651:
Immunity can be acquired either actively or passively. Immunity is acquired actively when a person is exposed to foreign substances and the immune system responds. Passive immunity is when antibodies are transferred from one host to another. Both actively acquired and passively acquired immunity can
1368:
For the acquired response to "remember" and eliminate a large number of pathogens the immune system must be able to distinguish between many different antigens, and the receptors that recognize antigens must be produced in a huge variety of configurations, in essence one receptor (at least) for each
731:
CD4+ lymphocytes, also called "helper" T cells, are immune response mediators, and play an important role in establishing and maximizing the capabilities of the acquired immune response. These cells have no cytotoxic or phagocytic activity; and cannot kill infected cells or clear pathogens, but, in
550:
Several T cells subgroups can be activated by professional APCs, and each type of T cell is specially equipped to deal with each unique toxin or microbial pathogen. The type of T cell activated, and the type of response generated, depends, in part, on the context in which the APC first encountered
342:
in reference to antibody responses in frogs as a synonym for "acquired immune response" in 1964. Good acknowledged he used the terms as synonyms but explained only that he preferred to use the term "adaptive". He might have been thinking of the then not implausible theory of antibody formation in
1443:
cannot do sufficiently, as certain blood cells specialize to insert themselves between adjacent epithelial cells). The immunodepressive action was the initial normal behavior of the virus, similar to HIV. The fusion proteins were a way to spread the infection to other cells by simply merging them
744:
Classically, two types of effector CD4 T helper cell responses can be induced by a professional APC, designated Th1 and Th2, each designed to eliminate different types of pathogens. The factors that dictate whether an infection triggers a Th1 or Th2 type response are not fully understood, but the
347:
in bacteria, that is, enzymes whose expression could be induced by their substrates. The phrase was used almost exclusively by Good and his students and a few other immunologists working with marginal organisms until the 1990s when it became widely used in tandem with the term "innate immunity"
1380:. According to the clonal selection theory, at birth, an animal randomly generates a vast diversity of lymphocytes (each bearing a unique antigen receptor) from information encoded in a small family of genes. To generate each unique antigen receptor, these genes have undergone a process called
735:
Helper T cells express T cell receptors (TCR) that recognize antigen bound to Class II MHC molecules. The activation of a naive helper T-cell causes it to release cytokines, which influences the activity of many cell types, including the APC (Antigen-Presenting Cell) that activated it. Helper
657:
Naive cytotoxic T cells are activated when their T-cell receptor (TCR) strongly interacts with a peptide-bound MHC class I molecule. This affinity depends on the type and orientation of the antigen/MHC complex, and is what keeps the CTL and infected cell bound together. Once activated, the CTL
223:
are a critical part of the adaptive immune system. Adaptive immunity can provide long-lasting protection, sometimes for the person's entire lifetime. For example, someone who recovers from measles is now protected against measles for their lifetime; in other cases it does not provide lifetime
1553:
receptors, Ig and TCR, are found in all jawed vertebrates. The most ancient Ig class, IgM, is membrane-bound and then secreted upon stimulation of cartilaginous fish B cells. Another isotype, shark IgW, is related to mammalian IgD. TCRs, both α/β and γ/δ, are found in all animals from
309:
and discards the rest, which produces a highly unique combination of antigen-receptor gene segments in each lymphocyte. This mechanism allows a small number of genetic segments to generate a vast number of different antigen receptors, which are then uniquely expressed on each individual
615:
antigens are produced by intracellular bacteria and viruses replicating within a host cell. The host cell uses enzymes to digest virally associated proteins and displays these pieces on its surface to T-cells by coupling them to MHC. Endogenous antigens are typically displayed on
528:. These antigens are different from those on the surface of bacteria or on the surface of virus-infected host cells ("non-self" or "foreign" antigens). The acquired immune response is triggered by recognizing foreign antigen in the cellular context of an activated dendritic cell.
1288:) is the deliberate induction of an immune response, and represents the single most effective manipulation of the immune system that scientists have developed. Immunizations are successful because they utilize the immune system's natural specificity as well as its inducibility.
1071:
they are able to develop a memory of that infection that allows them to withstand otherwise lethal dose of the same bacteria they were exposed to before. Unlike in vertebrates, insects do not possess cells specific for adaptive immunity. Instead those mechanisms are mediated by
1521:
A population study has shown that the protective effect of the sickle-cell trait against falciparum malaria involves the augmentation of acquired as well as innate immune responses to the malaria parasite, illustrating the expected transition from innate to acquired immunity.
835:
infection. HIV is able to subvert the immune system by specifically attacking the CD4 T cells, precisely the cells that could drive the clearance of the virus, but also the cells that drive immunity against all other pathogens encountered during an organism's lifetime.
1291:
The principle behind immunization is to introduce an antigen, derived from a disease-causing organism, that stimulates the immune system to develop protective immunity against that organism, but that does not itself cause the pathogenic effects of that organism. An
1529:. By school age most children have developed efficacious adaptive immunity against malaria. These observations raise questions about mechanisms that favor the survival of most children in Africa while allowing some to develop potentially lethal infections.
963:
recognize their cognate antigen in a processed form – as a peptide in the context of an MHC molecule, whereas B cells recognize antigens in their native form. Once a B cell encounters its cognate (or specific) antigen (and receives additional signals from a
1627:. Though the molecules of the AIS are well-conserved, they are also rapidly evolving. Yet, a comparative approach finds that many features are quite uniform across taxa. All the major features of the AIS arose early and quickly. Jawless fishes have a
575:
signals, to the T cell-enriched lymph nodes. During migration, dendritic cells undergo a process of maturation in which they lose most of their ability to engulf other pathogens, and develop an ability to communicate with T-cells. The dendritic cell uses
701:(cell death). To limit extensive tissue damage during an infection, CTL activation is tightly controlled and in general requires a very strong MHC/antigen activation signal, or additional activation signals provided by "helper" T-cells (see below).
708:
clear them away—but a few of these cells remain as memory cells. On a later encounter with the same antigen, these memory cells quickly differentiate into effector cells, dramatically shortening the time required to mount an effective response.
1431:(ERVs) are activated and produced in high quantities during the implantation of the embryo. They are currently known to possess immunosuppressive properties, suggesting a role in protecting the embryo from its mother's immune system. Also,
653:
Cytotoxic T cells (also known as TC, killer T cell, or cytotoxic T-lymphocyte (CTL)) are a sub-group of T cells that induce the death of cells that are infected with viruses (and other pathogens), or are otherwise damaged or dysfunctional.
1544:
The acquired immune system, which has been best-studied in mammals, originated in jawed fish approximately 500 million years ago. Most of the molecules, cells, tissues, and associated mechanisms of this system of defense are found in
3466:
Rogozin IB, Iyer LM, Liang L, Glazko GV, Liston VG, Pavlov YI, Aravind L, Pancer Z (June 2007). "Evolution and diversification of lamprey antigen receptors: evidence for involvement of an AID-APOBEC family cytosine deaminase".
1076:. Hemocytes function similarly to phagocytes and after priming they are able to more effectively recognize and engulf the pathogen. It was also shown that it is possible to transfer the memory into offspring. For example, in
2970:
Mi S, Lee X, Li X, Veldman GM, Finnerty H, Racie L, LaVallie E, Tang XY, Edouard P, Howes S, Keith JC, McCoy JM (February 2000). "Syncytin is a captive retroviral envelope protein involved in human placental morphogenesis".
939:, differing in biological properties; each has evolved to handle different kinds of antigens. Upon activation, B cells produce antibodies, each of which recognize a unique antigen, and neutralizing specific pathogens.
1665:– involves a natural transfer of antibodies from a mother to her infant. The antibodies cross the woman's placenta to the fetus. Antibodies can also be transferred through breast milk with the secretions of colostrum.
865:, γδ T cells exhibit characteristics that place them at the border between innate and acquired immunity. On one hand, γδ T cells may be considered a component of adaptive immunity in that they rearrange TCR genes via
1444:
with the infected one (HIV does this too). It is believed that the ancestors of modern viviparous mammals evolved after an infection by this virus, enabling the fetus to survive the immune system of the mother.
1509:
One of the most interesting developments in biomedical science during the past few decades has been elucidation of mechanisms mediating innate immunity. One set of innate immune mechanisms is humoral, such as
1255:
because the fetus does not actually make any memory cells or antibodies: It only borrows them. Short-term passive immunity can also be transferred artificially from one individual to another via antibody-rich
857:(TCR) as opposed to CD4+ and CD8+ αβ T cells and share characteristics of helper T cells, cytotoxic T cells and natural killer cells. Like other 'unconventional' T cell subsets bearing invariant TCRs, such as
1532:
In malaria, as in other infections, innate immune responses lead into, and stimulate, adaptive immune responses. The genetic control of innate and acquired immunity is now a large and flourishing discipline.
662:, in which it gains functions and divides rapidly to produce an army of "armed" effector cells. Activated CTL then travels throughout the body searching for cells that bear that unique MHC Class I + peptide.
251:, which are proteins also known as immunoglobulins. Antibodies travel through the bloodstream and bind to the foreign antigen causing it to inactivate, which does not allow the antigen to bind to the host.
535:), all cells are capable of presenting antigen through the function of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules. Some cells are specially equipped to present antigen, and to prime naive T cells.
384:
Acquired immunity is triggered in vertebrates when a pathogen evades the innate immune system and (1) generates a threshold level of antigen and (2) generates "stranger" or "danger" signals activating
1562:
differs in cartilaginous fishes, which have a cluster form as compared to the translocon form in bony fish to mammals. Like TCR and Ig, the MHC is found only in jawed vertebrates. Genes involved in
3354:
Hibino T, Loza-Coll M, Messier C, Majeske AJ, Cohen AH, Terwilliger DP, Buckley KM, Brockton V, Nair SV, Berney K, Fugmann SD, Anderson MK, Pancer Z, Cameron RA, Smith LC, Rast JP (December 2006).
2763:
Rubio M, Maestro JL, Piulachs MD, Belles X (June 2018). "Conserved association of
Argonaute 1 and 2 proteins with miRNA and siRNA pathways throughout insect evolution, from cockroaches to flies".
873:, and develop a memory phenotype. On the other hand, however, the various subsets may also be considered part of the innate immune system where a restricted TCR or NK receptors may be used as a
919:. Antibodies (also known as immunoglobulin, Ig), are large Y-shaped proteins used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects. In mammals, there are five types of antibody:
727:
The T lymphocyte activation pathway. T cells contribute to immune defenses in two major ways: some direct and regulate immune responses; others directly attack infected or cancerous cells.
985:. Already primed to produce specific antibodies, these cells can be called upon to respond quickly if the same pathogen re-infects the host, while the host experiences few, if any, symptoms.
2028:. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases National Cancer Institute, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Institutes of Health. September 2003. Archived from
1268:
In general, active immunity is long-term and can be acquired by infection followed by B cell and T cell activation, or artificially acquired by vaccines, in a process called immunization.
1536:
Humoral and cell-mediated immune responses limit malaria parasite multiplication, and many cytokines contribute to the pathogenesis of malaria as well as to the resolution of infections.
459:. In humans, approximately 1–2% of the lymphocyte pool recirculates each hour to increase the opportunity for the cells to encounter the specific pathogen and antigen that they react to.
1481:
of the variable portion of an antibody) and 'anti-idiotypes' (antigen receptors that react with the idiotype as if it were a foreign antigen). This theory, which builds on the existing
255:
are any substances that elicit the adaptive immune response. Sometimes the adaptive system is unable to distinguish harmful from harmless foreign molecules; the effects of this may be
1276:
Historically, infectious disease has been the leading cause of death in the human population. Over the last century, two important factors have been developed to combat their spread:
1108:(RNAi). RNAi is a form of antiviral immunity with high specificity. It has several different pathways that all end with the virus being unable to replicate. One of the pathways is
247:, two different types of lymphocytes, carry out the main activities: antibody responses, and cell-mediated immune response. In antibody responses, B cells are activated to secrete
1016:, have an adaptive immune system that shows 3 different cell lineages, each sharing a common origin with B cells, αβ T cells, and innate-like γΔ T cells. Instead of the classical
439:
are the cells of the adaptive immune system. The human body has about 2 trillion lymphocytes, which are 20–40% of white blood cells; their total mass is about the same as the
212:, which is pre-programmed to react to common broad categories of pathogen, the adaptive immune system is highly specific to each particular pathogen the body has encountered.
3570:
1248:
contains antibodies (mainly IgA) that are transferred to the gut of the infant, protecting against bacterial infections, until the newborn can synthesize its own antibodies.
903:
The B lymphocyte activation pathway. B cells function to protect the host by producing antibodies that identify and neutralize foreign objects like bacteria and viruses.
4314:
1677:– This involves the introduction of antibodies rather than antigens to the human body. These antibodies are from an animal or person who is already immune to the disease.
1112:
in which long double stranded RNA is cut into pieces that serve as templates for protein complex Ago2-RISC that finds and degrades complementary RNA of the virus.
1080:
if the queen is infected with bacteria then the newly born workers have enhanced abilities in fighting with the same bacteria. Other experimental model based on
2833:
Gesner E.M; Schellenberg M.J; Garside E.L; George M.M. & Macmillan A.M. 2011. Recognition and maturation of effector RNAs in a CRISPR interference pathway.
1184:
CRISPR has a lot of short repeated sequences. These sequences are part of an adaptive immune system for prokaryotes. It allows them to remember and counter the
812:
are another distinct population of effector CD4 T cells that develop from naive T cells post-antigen activation. Tfh cells are specialized in helping B cell
524:
Acquired immunity relies on the capacity of immune cells to distinguish between the body's own cells and unwanted invaders. The host's cells express "self"
1323:
components. Many antigens derived from acellular vaccines do not strongly induce an adaptive response, and most bacterial vaccines require the addition of
1073:
736:
T-cells require a much milder activation stimulus than cytotoxic T cells. Helper T cells can provide extra signals that "help" activate cytotoxic cells.
343:
which antibodies were plastic and could adapt themselves to the molecular shape of antigens, and/or to the concept of "adaptive enzymes" as described by
977:
are short-lived cells (2–3 days) that secrete antibodies. These antibodies bind to antigens, making them easier targets for phagocytes, and trigger the
1124:
and other mobile elements. Despite the research the exact mechanisms responsible for immune priming and specificity in insects are not well described.
808:
the immune system to control aberrant immune responses to self-antigens; an important mechanism in controlling the development of autoimmune diseases.
4011:
1230:
have had no prior exposure to microbes and are particularly vulnerable to infection. Several layers of passive protection are provided by the mother.
2815:
Grissa I; Vergnaud G. & Pourcel C. 2007. The CRISPRdb database and tools to display CRISPRs and to generate dictionaries of spacers and repeats.
828:
as an abnormal expansion of Tfh cell numbers can lead to unrestricted autoreactive antibody production causing severe systemic autoimmune disorders.
999:
800:
Increasingly, there is strong evidence from mouse and human-based scientific studies of a broader diversity in CD4 effector T helper cell subsets.
3563:
278:). This acquired response is called "adaptive" because it prepares the body's immune system for future challenges (though it can actually also be
60:
1616:
The evolution of the AIS, based on Ig, TCR, and MHC molecules, is thought to have arisen from two major evolutionary events: the transfer of the
1349:
An antibody is made up of two heavy chains and two light chains. The unique variable region allows an antibody to recognize its matching antigen.
2018:
4307:
955:
Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity: Antibodies attached to target cell cause destruction by macrophages, eosinophils, and NK cells
1631:
that relies on gene rearrangement to generate diverse immune receptors with a functional dichotomy that parallels Ig and TCR molecules. The
3023:
1392:
the other hand, the innate system would likely be overrun with pathogens without the specialized action of the adaptive immune response.
820:
in secondary lymphoid organs and provide them positive paracrine signals to enable the generation and recall production of high-quality
463:
3556:
1400:
The cornerstone of the immune system is the recognition of "self" versus "non-self". Therefore, the mechanisms that protect the human
1067:
Immune memory in insects was discovered through the phenomenon of priming. When insects are exposed to non-lethal dose or heat killed
592:(HLA)). This MHC-antigen complex is recognized by T-cells passing through the lymph node. Exogenous antigens are usually displayed on
274:
are "acquired" during the lifetime of the organism (whereas in innate immunity pathogen-specific receptors are already encoded in the
107:
4300:
4259:
2904:
Mojica F.J.M. et al 2000. Biological significance of regularly spaced repeats in the genomes of
Archaea, Bacteria and mitochondria.
1997:
1914:
1836:
1628:
192:
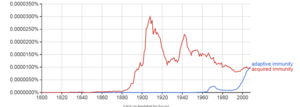
of "acquired immunity " vs. "adaptive immunity". The peak for "adaptive" in the 1960s reflects its introduction to immunology by
126:
31:
584:. In the lymph node, the dendritic cell displays these non-self antigens on its surface by coupling them to a receptor called the
489:
In an adult animal, the peripheral lymphoid organs contain a mixture of B and T cells in at least three stages of differentiation:
79:
543:
are equipped with special "co-stimulatory" ligands recognized by co-stimulatory receptors on T cells, and are termed professional
3902:
1826:
797:. Like cytotoxic T cells, most of the CD4 helper cells die on resolution of infection, with a few remaining as CD4 memory cells.
585:
482:, B cells and T cells are produced by stem cells in the bone marrow. T cell progenitors then migrate from the bone marrow to the
1904:
1525:
Repeated malaria infections strengthen acquired immunity and broaden its effects against parasites expressing different surface
1244:, so that, at birth, human babies have high levels of antibodies, with the same range of antigen specificities as their mother.
4132:
2403:"Insect immunity: oral exposure to a bacterial pathogen elicits free radical response and protects from a recurring infection"
1949:
1361:, can serve as antigens. The parts of an antigen that interact with an antibody molecule or a lymphocyte receptor, are called
1056:. However, in recent years some of the basic hallmarks of adaptive immunity have been discovered in insects. Those traits are
1028:(VLRs for short) that, like the antigen receptors of jawed vertebrates, are produced from only a small number (one or two) of
500:, which have left the bone marrow or thymus and entered the lymphatic system, but have yet to encounter their matching antigen
86:
4267:
3897:
786:
219:
after an initial response to a specific pathogen, and leads to an enhanced response to future encounters with that pathogen.
64:
3049:
4004:
3840:
1617:
1610:
471:
4335:
4197:
1586:
1025:
874:
447:. The peripheral bloodstream contains only 2% of all circulating lymphocytes; the other 98% move within tissues and the
144:
93:
196:
and use by colleagues; the explosive increase in the 1990s was correlated with the use of the phrase "innate immunity".
2714:"RNA interference-based antiviral immune response against the salivary gland hypertrophy virus in Glossina pallidipes"
1494:
809:
185:
5036:
3726:
1116:
pathway in cytoplasm binds to Ago1-RISC complex and functions as a template for viral RNA degradation. Last one is
75:
3202:
Williams TN, Mwangi TW, Roberts DJ, Alexander ND, Weatherall DJ, Wambua S, Kortok M, Snow RW, Marsh K (May 2005).
2663:"AgDscam, a hypervariable immunoglobulin domain-containing receptor of the Anopheles gambiae innate immune system"
53:
4996:
4078:
1304:
erator), is defined as any substance that binds to a specific antibody and elicits an adaptive immune response.
5004:
4225:
3997:
2851:
1624:
968:
544:
402:
Generation of responses that are tailored to maximally eliminate specific pathogens or pathogen-infected cells.
3163:"Band 3/complement-mediated recognition and removal of normally senescent and pathological human erythrocytes"
2823:
881:
produced by microbes, and highly restricted intraepithelial Vδ1 T cells respond to stressed epithelial cells.
2871:
Wiedenheft B; Sternberg S.H; Doudna J.A. 2012. RNA-guided genetic silencing systems in bacteria and archaea.
2097:"Single-cell transcriptomics of human T cells reveals tissue and activation signatures in health and disease"
4064:
4046:
4029:
3906:
3664:
1439:
to limit exchange of migratory cells between the developing embryo and the body of the mother (something an
1428:
589:
467:
3399:
5127:
4930:
4835:
4687:
3928:
3646:
2855:
1758:
1478:
762:
356:, use "adaptive" almost exclusively and noting in glossaries that the term is synonymous with "acquired".
205:
4737:
3875:
3731:
3709:
2712:
Meki IK, Kariithi HM, Parker AG, Vreysen MJ, Ros VI, Vlak JM, van Oers MM, Abd-Alla AM (November 2018).
1763:
1470:
1464:
1452:
1432:
1109:
1098:
862:
306:
294:
563:
Antigen presentation stimulates T cells to become either "cytotoxic" CD8+ cells or "helper" CD4+ cells.
506:
that have been activated by their matching antigen, and are actively involved in eliminating a pathogen
4966:
4702:
4103:
3892:
3825:
3736:
3660:
3414:
3118:
3027:
2980:
2934:
2622:
2465:
2365:
2108:
2029:
1632:
1590:
1567:
1546:
1490:
1448:
1330:
1325:
1252:
1117:
1053:
878:
870:
519:
466:, and look identical to one another until after they are activated. B cells play a large role in the
396:
216:
209:
179:
3548:
877:. For example, according to this paradigm, large numbers of Vγ9/Vδ2 T cells respond within hours to
301:
in the antibody-coding genes, which allows antibodies with novel specificity to be created. Second,
100:
4715:
4484:
4147:
3952:
3887:
3870:
3704:
3622:
1768:
1728:
1606:
1559:
1381:
1084:
also showed pathogen specific primed memory transfer into offspring from both mothers and fathers.
866:
821:
365:
302:
3024:"The Viruses That Make Us: A Role For Endogenous Retrovirus In The Evolution Of Placental Species"
4907:
4778:
4540:
4531:
4517:
3772:
3535:
3492:
3448:
3284:
3004:
2798:
2491:
1602:
1563:
1515:
1312:
1197:
978:
850:
845:
817:
801:
171:
1132:
322:(offspring) of that cell inherit genes that encode the same receptor specificity, including the
1060:
and specificity. Although the hallmarks are present the mechanisms are different from those in
804:, have been identified as important negative regulators of adaptive immunity as they limit and
5106:
5096:
4808:
4786:
4627:
4424:
4182:
4115:
3820:
3586:
3527:
3484:
3440:
3380:
3336:
3276:
3235:
3184:
3143:
3099:
2996:
2952:
2790:
2745:
2694:
2640:
2611:"Paternally derived immune priming for offspring in the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum"
2591:
2542:
2483:
2434:
2383:
2334:
2326:
2285:
2236:
2187:
2136:
2077:
1993:
1910:
1832:
1753:
1733:
1511:
256:
1469:
A theoretical framework explaining the workings of the acquired immune system is provided by
1226:
Passive memory is usually short-term, lasting between a few days and several months. Newborn
421:
In humans, it takes 4–7 days for the adaptive immune system to mount a significant response.
395:
Recognition of specific "non-self" antigens in the presence of "self", during the process of
5073:
4580:
4563:
4444:
4394:
4389:
4272:
4215:
4192:
4152:
4021:
3940:
3880:
3852:
3847:
3815:
3802:
3792:
3519:
3476:
3430:
3422:
3370:
3326:
3318:
3307:"Origin and evolution of the adaptive immune system: genetic events and selective pressures"
3266:
3225:
3215:
3174:
3133:
3089:
2988:
2942:
2780:
2772:
2735:
2725:
2684:
2674:
2630:
2581:
2573:
2532:
2522:
2473:
2424:
2414:
2373:
2316:
2275:
2267:
2226:
2218:
2177:
2167:
2126:
2116:
2067:
2059:
1748:
1482:
1377:
1105:
1081:
932:
916:
894:
825:
813:
805:
749:
659:
648:
448:
201:
1097:
gene also known as Down syndrome cell adhesive molecule is a gene that contains 3 variable
376:
5081:
5029:
4981:
4912:
4902:
4499:
4327:
4277:
4237:
4177:
4172:
4137:
3835:
3119:"Excess heme in sickle erythrocyte inside-out membranes: possible role in thiol oxidation"
2891:
2859:
1743:
1601:
use variable lymphocyte receptors (VLRs) for antigen binding. Diversity is generated by a
1021:
854:
694:
678:
536:
385:
360:
353:
271:
1635:, which has an important role in AIS activation, is the most important defense system of
3418:
2984:
2938:
2626:
2469:
2369:
2154:
Magen A, Nie J, Ciucci T, Tamoutounour S, Zhao Y, Mehta M, et al. (December 2019).
2112:
745:
response generated does play an important role in the clearance of different pathogens.
4958:
4848:
4692:
4670:
4643:
4489:
4344:
3862:
3807:
3748:
3668:
3641:
3355:
3331:
3306:
3230:
3203:
2740:
2713:
2689:
2662:
2586:
2561:
2537:
2510:
2429:
2402:
2280:
2255:
2231:
2206:
2182:
2155:
2131:
2096:
2095:
Szabo PA, Levitin HM, Miron M, Snyder ME, Senda T, Yuan J, et al. (October 2019).
2072:
2047:
1594:
1358:
1334:
732:
essence "manage" the immune response, by directing other cells to perform these tasks.
339:
327:
193:
3400:"Somatic diversification of variable lymphocyte receptors in the agnathan sea lamprey"
2609:
Roth O, Joop G, Eggert H, Hilbert J, Daniel J, Schmid-Hempel P, Kurtz J (March 2010).
571:
pathogens, such as bacteria, parasites or toxins in the tissues and then migrate, via
5121:
5101:
4941:
4766:
4754:
4741:
4725:
4479:
4414:
4247:
4120:
4098:
3830:
3719:
2635:
2610:
2321:
2304:
2222:
1582:
1207:
1203:
1185:
1137:
1057:
982:
964:
858:
790:
782:
774:
767:
718:
601:
414:
410:
344:
323:
305:
randomly selects one variable (V), one diversity (D), and one joining (J) region for
279:
235:
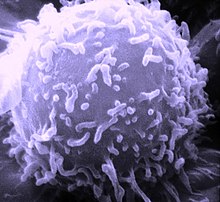
The cells that carry out the adaptive immune response are white blood cells known as
163:
3539:
3288:
2495:
1709:– Antibodies pass from mother to fetus via placenta or infant via the mother's milk.
559:
5086:
4409:
4357:
4187:
3797:
3782:
3777:
3714:
3612:
3496:
3008:
2802:
1953:
1671:– is done by vaccination (introducing dead or weakened antigen to the host's cell).
1636:
1575:
1555:
1281:
1257:
1162:
1049:
974:
912:
753:
666:
593:
497:
493:
283:
189:
3452:
3398:
Pancer Z, Amemiya CT, Ehrhardt GR, Ceitlin J, Gartland GL, Cooper MD (July 2004).
2454:"Insect immunity shows specificity in protection upon secondary pathogen exposure"
348:
which became a popular subject after the discovery of the Toll receptor system in
3989:
3220:
2776:
2679:
2527:
2172:
17:
5014:
4863:
4843:
4658:
4653:
4593:
4242:
4038:
3375:
3138:
3057:
1930:
Charles A Janeway, Jr; Travers, Paul; Walport, Mark; Shlomchik, Mark J. (2001).
1798:
1598:
1571:
1498:
1486:
1285:
1245:
1188:
which prey on them. They work as a kind of acquired immune system for bacteria.
1121:
899:
778:
723:
625:
617:
572:
540:
532:
452:
436:
229:
42:
2352:
Alder MN, Rogozin IB, Iyer LM, Glazko GV, Cooper MD, Pancer Z (December 2005).
2121:
1931:
942:
Antigen and antibody binding would cause five different protective mechanisms:
4922:
4791:
4761:
4710:
4615:
4323:
4207:
4127:
3920:
3673:
3579:
2894:
2730:
2560:
Hernández López J, Schuehly W, Crailsheim K, Riessberger-Gallé U (June 2014).
2478:
2453:
2271:
1620:
1550:
1440:
1420:
1345:
1277:
1166:
1136:
Bacteria use CRISPR as part of their adaptive immune system to defend against
1061:
908:
674:
612:
475:
430:
311:
290:
248:
236:
225:
175:
148:
2354:"Diversity and function of adaptive immune receptors in a jawless vertebrate"
2330:
1803:. Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG). 4 August 2016.
1659:– when a person is naturally exposed to antigens, becomes ill, then recovers.
166:
that is composed of specialized, systemic cells and processes that eliminate
4885:
4680:
4461:
3978:
3683:
2880:
2511:"A specific primed immune response in Drosophila is dependent on phagocytes"
2419:
2378:
2353:
1474:
1436:
1424:
1409:
1316:
1077:
705:
698:
568:
319:
139:
4292:
3531:
3488:
3444:
3384:
3340:
3280:
3239:
3188:
3103:
3094:
3077:
3000:
2956:
2794:
2749:
2698:
2644:
2595:
2577:
2546:
2487:
2438:
2387:
2338:
2289:
2240:
2191:
2140:
2081:
170:
or prevent their growth. The acquired immune system is one of the two main
3147:
981:. About 10% of plasma cells survive to become long-lived antigen-specific
760:(marking for phagocytosis) and complement-fixing antibodies, and leads to
624:+ cytotoxic T-cells. With the exception of non-nucleated cells (including
30:
This article is about human immunity. For the same concept in botany, see
5061:
5024:
5019:
4946:
4818:
4399:
4384:
4362:
4110:
3968:
3753:
3741:
3699:
3653:
3617:
3435:
2063:
1241:
1237:
1170:
1113:
1068:
1036:
in a similar way to antibodies, and with the same degree of specificity.
1017:
690:
670:
525:
298:
252:
220:
167:
3426:
2947:
2922:
2785:
2305:"Evolution of innate and adaptive immune systems in jawless vertebrates"
1578:
genes, are closely linked within the MHC of almost all studied species.
5091:
5009:
4986:
4890:
4880:
4875:
4813:
4796:
4749:
4454:
4404:
4379:
3973:
3787:
3636:
3607:
1526:
1413:
1362:
1354:
1308:
1293:
1178:
1174:
1033:
1013:
1009:
1005:
757:
581:
479:
264:
3179:
3162:
314:. Since the gene rearrangement leads to an irreversible change in the
5046:
5041:
4976:
4971:
4917:
4853:
4801:
4720:
4610:
4598:
4553:
4512:
4507:
4449:
4374:
4232:
4220:
4164:
4087:
4056:
3945:
3933:
3678:
3629:
2992:
1738:
1613:(RAGs) that rearrange Ig and TCR gene segments in jawed vertebrates.
1405:
1232:
1227:
1145:
1045:
890:
685:
and water to flow into the infected cell, and causing it to burst or
637:
577:
503:
483:
456:
275:
260:
244:
240:
3523:
3510:
Boehm T (May 2011). "Design principles of adaptive immune systems".
3356:"The immune gene repertoire encoded in the purple sea urchin genome"
3322:
3271:
3254:
1825:
Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, Raff M, Roberts K, Walters P (2002).
1715:– Preformed antibodies in immune serum are introduced by injection.
1477:(unique molecular features of one clonotype, i.e. the unique set of
3480:
1936:
Immunobiology: The Immune System in Health and
Disease. 5th Edition
5056:
5051:
4936:
4663:
4570:
4471:
4429:
4419:
4368:
3026:. University of California, Irvine (lecture notes). Archived from
1640:
1401:
1344:
1320:
1131:
1104:
Other mechanisms supporting the specificity of insect immunity is
1089:
946:
Agglutination: Reduces number of infectious units to be dealt with
898:
794:
722:
686:
558:
444:
440:
375:
184:
138:
3204:"An immune basis for malaria protection by the sickle cell trait"
2921:
International Human Genome
Sequencing Consortium (October 2004).
2207:"T cells that promote B-Cell maturation in systemic autoimmunity"
1952:. University of South Carolina School of Medicine. Archived from
1181:. Its structure and function was discovered in the 21st century.
958:
Neutralization: Blocks adhesion of bacteria and viruses to mucosa
952:
Opsonization: Coating antigen with antibody enhances phagocytosis
380:
Overview of the processes involved in the primary immune response
200:
Like the innate system, the adaptive immune system includes both
4823:
4558:
4434:
4352:
2765:
Biochimica et
Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Gene Regulatory Mechanisms
1370:
1029:
697:
encapsulated in a granule that enters cells via pores to induce
4296:
3993:
3552:
2509:
Pham LN, Dionne MS, Shirasu-Hiza M, Schneider DS (March 2007).
2401:
Mikonranta L, Mappes J, Kaukoniitty M, Freitak D (March 2014).
1514:. Another set comprises pattern recognition receptors such as
4858:
4675:
4439:
3050:"Persisting Viruses Could Play Role in Driving Host Evolution"
1154:
1120:
where small RNA binds to the Piwi protein family and controls
936:
928:
924:
920:
832:
682:
621:
597:
315:
36:
1087:
Most commonly accepted theory of the specificity is based on
831:
The relevance of CD4 T helper cells is highlighted during an
770:
pathogens (viruses and bacteria that are inside host cells).
359:
The classic sense of "acquired immunity" came to mean, since
1558:
to mammals. The organization of gene segments that undergo
824:
antibodies. Similar to Tregs, Tfh cells also play a role in
704:
On resolution of the infection, most effector cells die and
949:
Activation of complement: Cause inflammation and cell lysis
391:
The major functions of the acquired immune system include:
1024:, these animals possess a large array of molecules called
1376:
Myriad receptors are produced through a process known as
1159:
clustered regularly-interspaced short palindromic repeats
2923:"Finishing the euchromatic sequence of the human genome"
1581:
Lymphoid cells can be identified in some pre-vertebrate
1493:, is seen as being relevant to the understanding of the
907:
B Cells are the major cells involved in the creation of
1988:
Janeway CA, Travers P, Walport M, Shlomchik MJ (2005).
1903:
Janeway CA, Travers P, Walport M, Shlomchik MJ (2001).
1485:
hypothesis and since 1974 has been developed mainly by
789:. In general, Th2 responses are more effective against
766:. In general, Th1 responses are more effective against
756:
activities of macrophages, and induces B cells to make
748:
The Th1 response is characterized by the production of
208:
components and destroys invading pathogens. Unlike the
1909:(5th ed.). New York and London: Garland Science.
1831:(4th ed.). New York and London: Garland Science.
1315:
viruses, whereas many bacterial vaccines are based on
2048:"Eosinophils and Th2 immunity: contemporary insights"
531:
With the exception of non-nucleated cells (including
773:
The Th2 response is characterized by the release of
228:. This process of adaptive immunity is the basis of
5072:
4995:
4957:
4834:
4777:
4736:
4701:
4642:
4579:
4539:
4530:
4498:
4470:
4343:
4334:
4258:
4206:
4163:
4086:
4077:
4055:
4037:
4028:
3961:
3919:
3861:
3762:
3692:
3600:
3593:
1202:When B cells and T cells are activated some become
330:that are the keys to long-lived specific immunity.
67:. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
1609:-based DNA segments. There is no evidence for the
1329:that activate the antigen-presenting cells of the
1032:. These molecules are believed to bind pathogenic
677:: cytotoxins that form pores in the target cell's
162:, or specific immune system is a subsystem of the
3255:"Immunological processes in malaria pathogenesis"
1319:components of microorganisms, including harmless
580:to chop the pathogen into smaller pieces, called
2562:"Trans-generational immune priming in honeybees"
2205:Weinstein JS, Hernandez SG, Craft J (May 2012).
781:in the clearance of parasites. Th2 also produce
665:When exposed to these infected or dysfunctional
3300:
3298:
1177:have it. It is their defence against attack by
971:into an effector cell, known as a plasma cell.
628:), MHC class I is expressed by all host cells.
2019:"Understanding the Immune System How It Works"
1950:"Microbiology and Immunology On-Line Textbook"
1353:Most large molecules, including virtually all
509:Memory cells, the survivors of past infections
462:B cells and T cells are derived from the same
409:, in which pathogens are "remembered" through
4308:
4005:
3564:
2661:Dong Y, Taylor HE, Dimopoulos G (July 2006).
1585:(i.e., sea urchins). These bind antigen with
816:as they are uniquely capable of migrating to
470:, whereas T cells are intimately involved in
8:
3117:Kuross SA, Rank BH, Hebbel RP (April 1988).
3078:"Toll-like receptors and Type I interferons"
1932:"Principles of innate and adaptive immunity"
1652:be obtained by natural or artificial means.
793:bacteria, parasites including helminths and
1983:
297:is a process of accelerated random genetic
4536:
4340:
4315:
4301:
4293:
4083:
4034:
4012:
3998:
3990:
3597:
3571:
3557:
3549:
3071:
3069:
3067:
2256:"A cold-blooded view of adaptive immunity"
1981:
1979:
1977:
1975:
1973:
1971:
1969:
1967:
1965:
1963:
1898:
1896:
1894:
1892:
1890:
1888:
1886:
1884:
1882:
1880:
1878:
1876:
1874:
1872:
1870:
1868:
1412:suppress the uterine immune response (see
3434:
3374:
3330:
3270:
3229:
3219:
3178:
3137:
3093:
2946:
2835:Nature Structural & Molecular Biology
2784:
2739:
2729:
2688:
2678:
2634:
2585:
2536:
2526:
2477:
2428:
2418:
2377:
2320:
2279:
2230:
2181:
2171:
2130:
2120:
2071:
1866:
1864:
1862:
1860:
1858:
1856:
1854:
1852:
1850:
1848:
1820:
1818:
1816:
1814:
1812:
1810:
406:
127:Learn how and when to remove this message
3161:Arese P, Turrini F, Schwarzer E (2005).
1680:
1284:. Immunization (commonly referred to as
1000:Adaptive immunity in jawless vertebrates
270:In adaptive immunity, pathogen-specific
3305:Flajnik MF, Kasahara M (January 2010).
3253:Schofield L, Grau GE (September 2005).
2013:
2011:
2009:
1790:
1701:– Antigens are introduced in vaccines.
1240:IgG is transported directly across the
2452:Sadd BM, Schmid-Hempel P (June 2006).
1800:The innate and adaptive immune systems
1675:Artificially Acquired Passive Immunity
967:(predominately Th2 type)), it further
338:The term "adaptive" was first used by
2656:
2654:
1669:Artificially Acquired Active Immunity
1435:cause the formation of the placental
885:B lymphocytes and antibody production
7:
3167:Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry
2254:Flajnik, Martin F. (19 March 2018).
1044:For a long time it was thought that
853:(γδ T cells) possess an alternative
740:Th1 and Th2: helper T cell responses
464:multipotent hematopoietic stem cells
65:adding citations to reliable sources
3082:The Journal of Biological Chemistry
1695:– Antigen enters the body naturally
1663:Naturally Acquired Passive Immunity
1623:(possibly of viral origin) and two
643:CD8+ T lymphocytes and cytotoxicity
1657:Naturally Acquired Active Immunity
1396:Acquired immunity during pregnancy
588:, or MHC (also known in humans as
25:
1992:(6th ed.). Garland Science.
32:Plant-induced systemic resistance
2636:10.1111/j.1365-2656.2009.01617.x
2566:Proceedings. Biological Sciences
2322:10.1111/j.1348-0421.2012.00500.x
2223:10.1111/j.1600-065x.2012.01122.x
1505:Stimulation of adaptive immunity
1473:, based on interactions between
586:major histocompatibility complex
282:when it results in allergies or
41:
4133:Periarteriolar lymphoid sheaths
3076:Uematsu S, Akira S (May 2007).
2303:Kasamatsu, Jun (January 2013).
810:Follicular helper T (Tfh) cells
293:because of two factors. First,
52:needs additional citations for
3898:Immunoglobulin class switching
2046:Spencer LA, Weller PF (2010).
1611:recombination-activating genes
486:, where they develop further.
472:cell-mediated immune responses
27:Subsystem of the immune system
1:
2615:The Journal of Animal Ecology
1828:Molecular Biology of the Cell
1587:pattern recognition receptors
1455:classified into 24 families.
1386:combinatorial diversification
1026:variable lymphocyte receptors
3221:10.1371/journal.pmed.0020128
2777:10.1016/j.bbagrm.2018.04.001
2680:10.1371/journal.pbio.0040229
2528:10.1371/journal.ppat.0030026
2173:10.1016/j.celrep.2019.10.131
1423:mammals (all mammals except
875:pattern recognition receptor
145:scanning electron microscope
3376:10.1016/j.ydbio.2006.08.065
3139:10.1182/blood.V71.4.876.876
2309:Microbiology and Immunology
2052:Immunology and Cell Biology
2026:NIH Publication No. 03-5423
1605:-mediated rearrangement of
785:, which facilitates B cell
658:undergoes a process called
5144:
3727:Polyclonal B cell response
3512:Nature Reviews. Immunology
3259:Nature Reviews. Immunology
3048:Villarreal LP (Oct 2001).
2122:10.1038/s41467-019-12464-3
1647:Types of acquired immunity
1462:
1195:
1143:
997:
888:
843:
716:
646:
635:
596:molecules, which activate
517:
428:
215:Adaptive immunity creates
29:
4198:Waldeyer's tonsillar ring
2731:10.1186/s12866-018-1298-1
2479:10.1016/j.cub.2006.04.047
2272:10.1038/s41577-018-0003-9
2260:Nature Reviews Immunology
1625:whole genome duplications
802:Regulatory T (Treg) cells
4226:High endothelial venules
3311:Nature Reviews. Genetics
2852:Nobel Prize in Chemistry
1161:. These are part of the
1157:research. It stands for
620:molecules, and activate
545:antigen-presenting cells
147:image of a single human
76:"Adaptive immune system"
4047:Hematopoietic stem cell
2420:10.1186/1742-9994-11-23
2379:10.1126/science.1119420
1451:found several thousand
1429:endogenous retroviruses
1341:Immunological diversity
826:immunological tolerance
669:, effector CTL release
590:human leukocyte antigen
567:Dendritic cells engulf
468:humoral immune response
4767:Lymphoid immune system
4336:Musculoskeletal system
3841:Tolerance in pregnancy
3583:adaptive immune system
3095:10.1074/jbc.R700009200
2906:Molecular Microbiology
2856:Emmanuelle Charpentier
2578:10.1098/rspb.2014.0454
1759:Original antigenic sin
1687:Artificially acquired
1497:and the search for an
1479:antigenic determinants
1350:
1141:
994:In jawless vertebrates
904:
869:, which also produces
863:natural killer T cells
763:cell-mediated immunity
752:, which activates the
728:
564:
381:
206:cell-mediated immunity
197:
160:acquired immune system
156:adaptive immune system
151:
4755:Myeloid immune system
4541:Cardiovascular system
3876:Somatic hypermutation
3710:Polyclonal antibodies
3705:Monoclonal antibodies
3363:Developmental Biology
2211:Immunological Reviews
2101:Nature Communications
1764:Somatic hypermutation
1512:complement activation
1471:immune network theory
1465:Immune network theory
1459:Immune network theory
1433:viral fusion proteins
1348:
1214:short-term memory or
1196:Further information:
1135:
902:
726:
562:
451:, which includes the
379:
307:genetic recombination
295:somatic hypermutation
289:The system is highly
188:
178:(the other being the
142:
5107:Islets of Langerhans
4967:Genitourinary system
4703:Integumentary system
4065:Hassall's corpuscles
3893:Junctional diversity
3661:Antigen presentation
2407:Frontiers in Zoology
2166:(10): 3019–3032.e6.
2064:10.1038/icb.2009.115
1956:on 2 September 2008.
1776:Notes and references
1633:innate immune system
1591:innate immune system
1547:cartilaginous fishes
1491:Geoffrey W. Hoffmann
1449:human genome project
1419:During pregnancy in
1331:innate immune system
1192:Immunological memory
1054:innate immune system
915:and lymph, known as
871:junctional diversity
520:Antigen presentation
514:Antigen presentation
407:immunological memory
397:antigen presentation
224:protection, as with
217:immunological memory
210:innate immune system
180:innate immune system
174:strategies found in
158:, also known as the
61:improve this article
4997:Reproductive system
4716:Subcutaneous tissue
4485:Cartilaginous joint
4148:Trabecular arteries
3888:V(D)J recombination
3871:Affinity maturation
3623:Antigenic variation
3427:10.1038/nature02740
3419:2004Natur.430..174P
2985:2000Natur.403..785M
2948:10.1038/nature03001
2939:2004Natur.431..931H
2627:2010JAnEc..79..403R
2470:2006CBio...16.1206S
2370:2005Sci...310.1970A
2113:2019NatCo..10.4706S
1769:Polyclonal response
1729:Affinity maturation
1516:toll-like receptors
1382:V(D)J recombination
1006:jawless vertebrates
989:Alternative systems
867:V(D)J recombination
851:Gamma delta T cells
840:Gamma delta T cells
608:Endogenous antigens
303:V(D)J recombination
4779:Respiratory system
4532:Circulatory system
2817:BMC Bioinformatics
2572:(1785): 20140454.
1684:Naturally acquired
1603:cytosine deaminase
1564:antigen processing
1560:gene rearrangement
1351:
1311:are based on live
1218:long-term memory.
1198:Immunity (medical)
1142:
979:complement cascade
911:that circulate in
905:
846:Gamma delta T cell
818:follicular B cells
729:
565:
555:Exogenous antigens
382:
318:of each cell, all
198:
152:
5115:
5114:
4638:
4637:
4628:Glymphatic system
4526:
4525:
4290:
4289:
4286:
4285:
4116:Cords of Billroth
4073:
4072:
3987:
3986:
3915:
3914:
3665:professional APCs
3469:Nature Immunology
3180:10.1159/000089839
2364:(5756): 1970–73.
1754:Immunosuppression
1734:Allelic exclusion
1719:
1718:
1597:, two subsets of
1570:, as well as the
787:isotype switching
137:
136:
129:
111:
18:Adaptive immunity
16:(Redirected from
5135:
5074:Endocrine system
4836:Digestive system
4581:Lymphatic system
4564:Lymphatic vessel
4537:
4341:
4317:
4310:
4303:
4294:
4216:Lymphatic vessel
4193:Tonsillar crypts
4153:Trabecular veins
4084:
4079:Secondary organs
4035:
4022:lymphatic system
4014:
4007:
4000:
3991:
3881:Clonal selection
3853:Immune privilege
3848:Immunodeficiency
3803:Cross-reactivity
3793:Hypersensitivity
3598:
3573:
3566:
3559:
3550:
3544:
3543:
3507:
3501:
3500:
3463:
3457:
3456:
3438:
3413:(6996): 174–80.
3404:
3395:
3389:
3388:
3378:
3360:
3351:
3345:
3344:
3334:
3302:
3293:
3292:
3274:
3250:
3244:
3243:
3233:
3223:
3199:
3193:
3192:
3182:
3158:
3152:
3151:
3141:
3123:
3114:
3108:
3107:
3097:
3088:(21): 15319–23.
3073:
3062:
3061:
3056:. Archived from
3045:
3039:
3038:
3036:
3035:
3019:
3013:
3012:
2993:10.1038/35001608
2979:(6771): 785–89.
2967:
2961:
2960:
2950:
2933:(7011): 931–45.
2918:
2912:
2902:
2896:
2888:
2882:
2879:(7385): 331–338.
2869:
2863:
2848:
2842:
2831:
2825:
2813:
2807:
2806:
2788:
2760:
2754:
2753:
2743:
2733:
2724:(Suppl 1): 170.
2718:BMC Microbiology
2709:
2703:
2702:
2692:
2682:
2658:
2649:
2648:
2638:
2606:
2600:
2599:
2589:
2557:
2551:
2550:
2540:
2530:
2506:
2500:
2499:
2481:
2449:
2443:
2442:
2432:
2422:
2398:
2392:
2391:
2381:
2349:
2343:
2342:
2324:
2300:
2294:
2293:
2283:
2251:
2245:
2244:
2234:
2202:
2196:
2195:
2185:
2175:
2151:
2145:
2144:
2134:
2124:
2092:
2086:
2085:
2075:
2043:
2037:
2036:
2034:
2023:
2015:
2004:
2003:
1985:
1958:
1957:
1946:
1940:
1939:
1927:
1921:
1920:
1900:
1843:
1842:
1822:
1805:
1804:
1795:
1749:Immune tolerance
1681:
1495:HIV pathogenesis
1483:clonal selection
1378:clonal selection
1253:passive immunity
1106:RNA interference
1082:red flour beetle
1022:T cell receptors
917:humoral immunity
895:Humoral immunity
879:common molecules
822:affinity-matured
814:humoral immunity
777:, which induces
750:Interferon-gamma
660:clonal selection
649:Cytotoxic T cell
449:lymphatic system
202:humoral immunity
132:
125:
121:
118:
112:
110:
69:
45:
37:
21:
5143:
5142:
5138:
5137:
5136:
5134:
5133:
5132:
5118:
5117:
5116:
5111:
5068:
5030:Seminal vesicle
4991:
4953:
4903:Small intestine
4830:
4773:
4732:
4697:
4634:
4575:
4522:
4500:Muscular system
4494:
4466:
4345:Skeletal system
4330:
4321:
4291:
4282:
4278:Germinal center
4254:
4238:Germinal center
4202:
4159:
4138:Germinal center
4069:
4051:
4024:
4018:
3988:
3983:
3957:
3911:
3857:
3836:Clonal deletion
3764:
3758:
3688:
3589:
3577:
3547:
3524:10.1038/nri2944
3509:
3508:
3504:
3465:
3464:
3460:
3402:
3397:
3396:
3392:
3358:
3353:
3352:
3348:
3323:10.1038/nrg2703
3304:
3303:
3296:
3272:10.1038/nri1686
3252:
3251:
3247:
3201:
3200:
3196:
3173:(4–6): 133–46.
3160:
3159:
3155:
3121:
3116:
3115:
3111:
3075:
3074:
3065:
3047:
3046:
3042:
3033:
3031:
3022:Villarreal LP.
3021:
3020:
3016:
2969:
2968:
2964:
2920:
2919:
2915:
2903:
2899:
2892:Jennifer Doudna
2889:
2885:
2870:
2866:
2860:Jennifer Doudna
2849:
2845:
2832:
2828:
2814:
2810:
2762:
2761:
2757:
2711:
2710:
2706:
2660:
2659:
2652:
2608:
2607:
2603:
2559:
2558:
2554:
2508:
2507:
2503:
2464:(12): 1206–10.
2458:Current Biology
2451:
2450:
2446:
2400:
2399:
2395:
2351:
2350:
2346:
2302:
2301:
2297:
2253:
2252:
2248:
2204:
2203:
2199:
2153:
2152:
2148:
2094:
2093:
2089:
2045:
2044:
2040:
2032:
2021:
2017:
2016:
2007:
2000:
1987:
1986:
1961:
1948:
1947:
1943:
1929:
1928:
1924:
1917:
1902:
1901:
1846:
1839:
1824:
1823:
1808:
1797:
1796:
1792:
1778:
1773:
1744:Immune response
1724:
1649:
1542:
1507:
1467:
1461:
1398:
1359:polysaccharides
1343:
1274:
1266:
1224:
1200:
1194:
1148:
1130:
1042:
1002:
996:
991:
897:
889:Main articles:
887:
855:T cell receptor
848:
842:
742:
721:
715:
695:serine protease
679:plasma membrane
651:
645:
640:
634:
610:
557:
539:, B-cells, and
537:Dendritic cells
522:
516:
433:
427:
405:Development of
386:dendritic cells
374:
336:
263:, or any other
204:components and
133:
122:
116:
113:
70:
68:
58:
46:
35:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
5141:
5139:
5131:
5130:
5120:
5119:
5113:
5112:
5110:
5109:
5104:
5099:
5094:
5089:
5084:
5078:
5076:
5070:
5069:
5067:
5066:
5065:
5064:
5059:
5054:
5049:
5044:
5034:
5033:
5032:
5027:
5022:
5017:
5012:
5001:
4999:
4993:
4992:
4990:
4989:
4984:
4979:
4974:
4969:
4963:
4961:
4959:Urinary system
4955:
4954:
4952:
4951:
4950:
4949:
4944:
4939:
4927:
4926:
4925:
4920:
4915:
4910:
4905:
4895:
4894:
4893:
4888:
4883:
4881:Laryngopharynx
4878:
4868:
4867:
4866:
4861:
4856:
4851:
4849:Salivary gland
4840:
4838:
4832:
4831:
4829:
4828:
4827:
4826:
4821:
4816:
4806:
4805:
4804:
4799:
4794:
4783:
4781:
4775:
4774:
4772:
4771:
4770:
4769:
4759:
4758:
4757:
4746:
4744:
4742:immune systems
4738:Haematopoietic
4734:
4733:
4731:
4730:
4729:
4728:
4718:
4713:
4707:
4705:
4699:
4698:
4696:
4695:
4690:
4688:Somatic system
4685:
4684:
4683:
4678:
4671:Sensory system
4668:
4667:
4666:
4661:
4656:
4648:
4646:
4644:Nervous system
4640:
4639:
4636:
4635:
4633:
4632:
4631:
4630:
4623:CNS equivalent
4620:
4619:
4618:
4613:
4603:
4602:
4601:
4596:
4585:
4583:
4577:
4576:
4574:
4573:
4568:
4567:
4566:
4561:
4556:
4545:
4543:
4534:
4528:
4527:
4524:
4523:
4521:
4520:
4515:
4510:
4504:
4502:
4496:
4495:
4493:
4492:
4490:Synovial joint
4487:
4482:
4476:
4474:
4468:
4467:
4465:
4464:
4459:
4458:
4457:
4452:
4447:
4442:
4437:
4432:
4427:
4422:
4417:
4412:
4407:
4402:
4397:
4392:
4387:
4382:
4377:
4372:
4366:
4360:
4349:
4347:
4338:
4332:
4331:
4322:
4320:
4319:
4312:
4305:
4297:
4288:
4287:
4284:
4283:
4281:
4280:
4275:
4270:
4264:
4262:
4256:
4255:
4253:
4252:
4251:
4250:
4245:
4240:
4230:
4229:
4228:
4218:
4212:
4210:
4204:
4203:
4201:
4200:
4195:
4190:
4185:
4180:
4175:
4169:
4167:
4161:
4160:
4158:
4157:
4156:
4155:
4150:
4144:Blood vessels
4142:
4141:
4140:
4135:
4125:
4124:
4123:
4118:
4108:
4107:
4106:
4101:
4092:
4090:
4081:
4075:
4074:
4071:
4070:
4068:
4067:
4061:
4059:
4053:
4052:
4050:
4049:
4043:
4041:
4032:
4030:Primary organs
4026:
4025:
4020:Organs of the
4019:
4017:
4016:
4009:
4002:
3994:
3985:
3984:
3982:
3981:
3976:
3971:
3965:
3963:
3959:
3958:
3956:
3955:
3950:
3949:
3948:
3938:
3937:
3936:
3925:
3923:
3917:
3916:
3913:
3912:
3910:
3909:
3900:
3895:
3890:
3885:
3884:
3883:
3878:
3867:
3865:
3863:Immunogenetics
3859:
3858:
3856:
3855:
3850:
3845:
3844:
3843:
3838:
3833:
3828:
3823:
3811:
3810:
3808:Co-stimulation
3805:
3800:
3795:
3790:
3785:
3780:
3775:
3768:
3766:
3760:
3759:
3757:
3756:
3751:
3749:Immune complex
3745:
3744:
3739:
3734:
3729:
3724:
3723:
3722:
3717:
3712:
3707:
3696:
3694:
3690:
3689:
3687:
3686:
3681:
3676:
3671:
3669:Dendritic cell
3657:
3656:
3651:
3650:
3649:
3647:Conformational
3644:
3633:
3632:
3627:
3626:
3625:
3620:
3615:
3604:
3602:
3595:
3591:
3590:
3578:
3576:
3575:
3568:
3561:
3553:
3546:
3545:
3502:
3481:10.1038/ni1463
3458:
3390:
3346:
3294:
3245:
3194:
3153:
3109:
3063:
3060:on 2009-05-08.
3040:
3014:
2962:
2913:
2897:
2883:
2864:
2843:
2826:
2808:
2755:
2704:
2650:
2601:
2552:
2515:PLOS Pathogens
2501:
2444:
2393:
2344:
2295:
2246:
2197:
2146:
2087:
2038:
2035:on 2007-01-03.
2005:
1998:
1959:
1941:
1922:
1915:
1844:
1837:
1806:
1789:
1788:
1787:
1783:
1782:
1777:
1774:
1772:
1771:
1766:
1761:
1756:
1751:
1746:
1741:
1736:
1731:
1725:
1723:
1720:
1717:
1716:
1710:
1703:
1702:
1696:
1689:
1688:
1685:
1679:
1678:
1672:
1666:
1660:
1648:
1645:
1595:jawless fishes
1589:(PRRs) of the
1541:
1538:
1506:
1503:
1463:Main article:
1460:
1457:
1397:
1394:
1342:
1339:
1335:immunogenicity
1273:
1270:
1265:
1262:
1223:
1222:Passive memory
1220:
1208:memory T cells
1204:memory B cells
1193:
1190:
1186:bacteriophages
1144:Main article:
1138:bacteriophages
1129:
1126:
1041:
1038:
1008:, such as the
998:Main article:
995:
992:
990:
987:
983:memory B cells
969:differentiates
960:
959:
956:
953:
950:
947:
886:
883:
844:Main article:
841:
838:
741:
738:
717:Main article:
714:
713:Helper T-cells
711:
689:. CTL release
647:Main article:
644:
641:
636:Main article:
633:
630:
609:
606:
602:T helper cells
556:
553:
518:Main article:
515:
512:
511:
510:
507:
504:Effector cells
501:
429:Main article:
426:
423:
419:
418:
415:memory T cells
411:memory B cells
403:
400:
373:
370:
366:natural killer
335:
332:
328:memory T cells
324:memory B cells
194:Robert A. Good
135:
134:
49:
47:
40:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
5140:
5129:
5128:Immune system
5126:
5125:
5123:
5108:
5105:
5103:
5100:
5098:
5095:
5093:
5090:
5088:
5085:
5083:
5080:
5079:
5077:
5075:
5071:
5063:
5060:
5058:
5055:
5053:
5050:
5048:
5045:
5043:
5040:
5039:
5038:
5035:
5031:
5028:
5026:
5023:
5021:
5018:
5016:
5013:
5011:
5008:
5007:
5006:
5003:
5002:
5000:
4998:
4994:
4988:
4985:
4983:
4980:
4978:
4975:
4973:
4970:
4968:
4965:
4964:
4962:
4960:
4956:
4948:
4945:
4943:
4942:Biliary tract
4940:
4938:
4935:
4934:
4933:
4932:
4928:
4924:
4921:
4919:
4916:
4914:
4911:
4909:
4906:
4904:
4901:
4900:
4899:
4896:
4892:
4889:
4887:
4884:
4882:
4879:
4877:
4874:
4873:
4872:
4869:
4865:
4862:
4860:
4857:
4855:
4852:
4850:
4847:
4846:
4845:
4842:
4841:
4839:
4837:
4833:
4825:
4822:
4820:
4817:
4815:
4812:
4811:
4810:
4807:
4803:
4800:
4798:
4795:
4793:
4790:
4789:
4788:
4785:
4784:
4782:
4780:
4776:
4768:
4765:
4764:
4763:
4760:
4756:
4753:
4752:
4751:
4748:
4747:
4745:
4743:
4739:
4735:
4727:
4726:Mammary gland
4724:
4723:
4722:
4719:
4717:
4714:
4712:
4709:
4708:
4706:
4704:
4700:
4694:
4691:
4689:
4686:
4682:
4679:
4677:
4674:
4673:
4672:
4669:
4665:
4662:
4660:
4657:
4655:
4652:
4651:
4650:
4649:
4647:
4645:
4641:
4629:
4626:
4625:
4624:
4621:
4617:
4614:
4612:
4609:
4608:
4607:
4604:
4600:
4597:
4595:
4592:
4591:
4590:
4587:
4586:
4584:
4582:
4578:
4572:
4569:
4565:
4562:
4560:
4557:
4555:
4552:
4551:
4550:
4547:
4546:
4544:
4542:
4538:
4535:
4533:
4529:
4519:
4516:
4514:
4511:
4509:
4506:
4505:
4503:
4501:
4497:
4491:
4488:
4486:
4483:
4481:
4480:Fibrous joint
4478:
4477:
4475:
4473:
4469:
4463:
4460:
4456:
4453:
4451:
4448:
4446:
4443:
4441:
4438:
4436:
4433:
4431:
4428:
4426:
4423:
4421:
4418:
4416:
4413:
4411:
4408:
4406:
4403:
4401:
4398:
4396:
4393:
4391:
4388:
4386:
4383:
4381:
4378:
4376:
4373:
4370:
4367:
4364:
4361:
4359:
4356:
4355:
4354:
4351:
4350:
4348:
4346:
4342:
4339:
4337:
4333:
4329:
4325:
4324:Human systems
4318:
4313:
4311:
4306:
4304:
4299:
4298:
4295:
4279:
4276:
4274:
4273:Peyer's patch
4271:
4269:
4266:
4265:
4263:
4261:
4257:
4249:
4248:Marginal zone
4246:
4244:
4241:
4239:
4236:
4235:
4234:
4231:
4227:
4224:
4223:
4222:
4219:
4217:
4214:
4213:
4211:
4209:
4205:
4199:
4196:
4194:
4191:
4189:
4186:
4184:
4181:
4179:
4176:
4174:
4171:
4170:
4168:
4166:
4162:
4154:
4151:
4149:
4146:
4145:
4143:
4139:
4136:
4134:
4131:
4130:
4129:
4126:
4122:
4121:Marginal zone
4119:
4117:
4114:
4113:
4112:
4109:
4105:
4102:
4100:
4097:
4096:
4094:
4093:
4091:
4089:
4085:
4082:
4080:
4076:
4066:
4063:
4062:
4060:
4058:
4054:
4048:
4045:
4044:
4042:
4040:
4036:
4033:
4031:
4027:
4023:
4015:
4010:
4008:
4003:
4001:
3996:
3995:
3992:
3980:
3977:
3975:
3972:
3970:
3967:
3966:
3964:
3960:
3954:
3951:
3947:
3944:
3943:
3942:
3939:
3935:
3932:
3931:
3930:
3927:
3926:
3924:
3922:
3918:
3908:
3904:
3901:
3899:
3896:
3894:
3891:
3889:
3886:
3882:
3879:
3877:
3874:
3873:
3872:
3869:
3868:
3866:
3864:
3860:
3854:
3851:
3849:
3846:
3842:
3839:
3837:
3834:
3832:
3831:Clonal anergy
3829:
3827:
3824:
3822:
3819:
3818:
3817:
3813:
3812:
3809:
3806:
3804:
3801:
3799:
3796:
3794:
3791:
3789:
3786:
3784:
3781:
3779:
3776:
3774:
3770:
3769:
3767:
3761:
3755:
3752:
3750:
3747:
3746:
3743:
3740:
3738:
3735:
3733:
3730:
3728:
3725:
3721:
3720:Microantibody
3718:
3716:
3713:
3711:
3708:
3706:
3703:
3702:
3701:
3698:
3697:
3695:
3691:
3685:
3682:
3680:
3677:
3675:
3672:
3670:
3666:
3662:
3659:
3658:
3655:
3652:
3648:
3645:
3643:
3640:
3639:
3638:
3635:
3634:
3631:
3628:
3624:
3621:
3619:
3616:
3614:
3611:
3610:
3609:
3606:
3605:
3603:
3599:
3596:
3592:
3588:
3584:
3581:
3574:
3569:
3567:
3562:
3560:
3555:
3554:
3551:
3541:
3537:
3533:
3529:
3525:
3521:
3518:(5): 307–17.
3517:
3513:
3506:
3503:
3498:
3494:
3490:
3486:
3482:
3478:
3475:(6): 647–56.
3474:
3470:
3462:
3459:
3454:
3450:
3446:
3442:
3437:
3436:2027.42/62870
3432:
3428:
3424:
3420:
3416:
3412:
3408:
3401:
3394:
3391:
3386:
3382:
3377:
3372:
3369:(1): 349–65.
3368:
3364:
3357:
3350:
3347:
3342:
3338:
3333:
3328:
3324:
3320:
3316:
3312:
3308:
3301:
3299:
3295:
3290:
3286:
3282:
3278:
3273:
3268:
3265:(9): 722–35.
3264:
3260:
3256:
3249:
3246:
3241:
3237:
3232:
3227:
3222:
3217:
3213:
3209:
3208:PLOS Medicine
3205:
3198:
3195:
3190:
3186:
3181:
3176:
3172:
3168:
3164:
3157:
3154:
3149:
3145:
3140:
3135:
3132:(4): 876–82.
3131:
3127:
3120:
3113:
3110:
3105:
3101:
3096:
3091:
3087:
3083:
3079:
3072:
3070:
3068:
3064:
3059:
3055:
3051:
3044:
3041:
3030:on 2007-07-15
3029:
3025:
3018:
3015:
3010:
3006:
3002:
2998:
2994:
2990:
2986:
2982:
2978:
2974:
2966:
2963:
2958:
2954:
2949:
2944:
2940:
2936:
2932:
2928:
2924:
2917:
2914:
2910:
2907:
2901:
2898:
2895:
2893:
2887:
2884:
2881:
2878:
2874:
2868:
2865:
2861:
2857:
2853:
2847:
2844:
2841:(6): 688–692.
2840:
2836:
2830:
2827:
2824:
2821:
2818:
2812:
2809:
2804:
2800:
2796:
2792:
2787:
2782:
2778:
2774:
2771:(6): 554–60.
2770:
2766:
2759:
2756:
2751:
2747:
2742:
2737:
2732:
2727:
2723:
2719:
2715:
2708:
2705:
2700:
2696:
2691:
2686:
2681:
2676:
2672:
2668:
2664:
2657:
2655:
2651:
2646:
2642:
2637:
2632:
2628:
2624:
2621:(2): 403–13.
2620:
2616:
2612:
2605:
2602:
2597:
2593:
2588:
2583:
2579:
2575:
2571:
2567:
2563:
2556:
2553:
2548:
2544:
2539:
2534:
2529:
2524:
2520:
2516:
2512:
2505:
2502:
2497:
2493:
2489:
2485:
2480:
2475:
2471:
2467:
2463:
2459:
2455:
2448:
2445:
2440:
2436:
2431:
2426:
2421:
2416:
2412:
2408:
2404:
2397:
2394:
2389:
2385:
2380:
2375:
2371:
2367:
2363:
2359:
2355:
2348:
2345:
2340:
2336:
2332:
2328:
2323:
2318:
2314:
2310:
2306:
2299:
2296:
2291:
2287:
2282:
2277:
2273:
2269:
2266:(7): 438–53.
2265:
2261:
2257:
2250:
2247:
2242:
2238:
2233:
2228:
2224:
2220:
2217:(1): 160–71.
2216:
2212:
2208:
2201:
2198:
2193:
2189:
2184:
2179:
2174:
2169:
2165:
2161:
2157:
2150:
2147:
2142:
2138:
2133:
2128:
2123:
2118:
2114:
2110:
2106:
2102:
2098:
2091:
2088:
2083:
2079:
2074:
2069:
2065:
2061:
2058:(3): 250–56.
2057:
2053:
2049:
2042:
2039:
2031:
2027:
2020:
2014:
2012:
2010:
2006:
2001:
1999:0-443-07310-4
1995:
1991:
1990:Immunobiology
1984:
1982:
1980:
1978:
1976:
1974:
1972:
1970:
1968:
1966:
1964:
1960:
1955:
1951:
1945:
1942:
1937:
1933:
1926:
1923:
1918:
1916:0-8153-4101-6
1912:
1908:
1907:
1906:Immunobiology
1899:
1897:
1895:
1893:
1891:
1889:
1887:
1885:
1883:
1881:
1879:
1877:
1875:
1873:
1871:
1869:
1867:
1865:
1863:
1861:
1859:
1857:
1855:
1853:
1851:
1849:
1845:
1840:
1838:0-8153-3218-1
1834:
1830:
1829:
1821:
1819:
1817:
1815:
1813:
1811:
1807:
1802:
1801:
1794:
1791:
1785:
1784:
1780:
1779:
1775:
1770:
1767:
1765:
1762:
1760:
1757:
1755:
1752:
1750:
1747:
1745:
1742:
1740:
1737:
1735:
1732:
1730:
1727:
1726:
1721:
1714:
1711:
1708:
1705:
1704:
1700:
1697:
1694:
1691:
1690:
1686:
1683:
1682:
1676:
1673:
1670:
1667:
1664:
1661:
1658:
1655:
1654:
1653:
1646:
1644:
1642:
1638:
1637:invertebrates
1634:
1630:
1629:different AIS
1626:
1622:
1619:
1614:
1612:
1608:
1604:
1600:
1596:
1592:
1588:
1584:
1583:deuterostomes
1579:
1577:
1573:
1569:
1565:
1561:
1557:
1552:
1548:
1539:
1537:
1534:
1530:
1528:
1523:
1519:
1517:
1513:
1504:
1502:
1500:
1496:
1492:
1488:
1484:
1480:
1476:
1472:
1466:
1458:
1456:
1454:
1450:
1445:
1442:
1438:
1434:
1430:
1426:
1422:
1417:
1415:
1411:
1407:
1403:
1395:
1393:
1389:
1387:
1383:
1379:
1374:
1372:
1366:
1364:
1360:
1356:
1347:
1340:
1338:
1336:
1332:
1328:
1327:
1322:
1318:
1314:
1310:
1305:
1303:
1299:
1295:
1289:
1287:
1283:
1279:
1271:
1269:
1264:Active memory
1263:
1261:
1259:
1254:
1249:
1247:
1243:
1239:
1235:
1234:
1229:
1221:
1219:
1217:
1213:
1209:
1205:
1199:
1191:
1189:
1187:
1182:
1180:
1176:
1172:
1168:
1164:
1160:
1156:
1153:is a term in
1152:
1147:
1139:
1134:
1127:
1125:
1123:
1119:
1115:
1111:
1107:
1102:
1100:
1096:
1092:
1091:
1085:
1083:
1079:
1075:
1070:
1065:
1063:
1059:
1058:immune memory
1055:
1052:possess only
1051:
1050:invertebrates
1047:
1039:
1037:
1035:
1031:
1027:
1023:
1019:
1015:
1011:
1007:
1001:
993:
988:
986:
984:
980:
976:
972:
970:
966:
965:helper T cell
957:
954:
951:
948:
945:
944:
943:
940:
938:
934:
930:
926:
922:
918:
914:
910:
901:
896:
892:
884:
882:
880:
876:
872:
868:
864:
860:
856:
852:
847:
839:
837:
834:
829:
827:
823:
819:
815:
811:
807:
803:
798:
796:
792:
791:extracellular
788:
784:
783:Interleukin 4
780:
776:
775:Interleukin 5
771:
769:
768:intracellular
765:
764:
759:
755:
751:
746:
739:
737:
733:
725:
720:
719:T helper cell
712:
710:
707:
702:
700:
696:
692:
688:
684:
680:
676:
672:
668:
667:somatic cells
663:
661:
655:
650:
642:
639:
632:T lymphocytes
631:
629:
627:
623:
619:
614:
607:
605:
603:
599:
595:
591:
587:
583:
579:
574:
570:
561:
554:
552:
551:the antigen.
548:
546:
542:
538:
534:
529:
527:
521:
513:
508:
505:
502:
499:
498:naive T cells
495:
492:
491:
490:
487:
485:
481:
477:
473:
469:
465:
460:
458:
454:
450:
446:
442:
438:
432:
424:
422:
416:
412:
408:
404:
401:
398:
394:
393:
392:
389:
387:
378:
371:
369:
367:
364:expansion of
362:
357:
355:
351:
346:
341:
333:
331:
329:
325:
321:
317:
313:
308:
304:
300:
296:
292:
287:
285:
281:
277:
273:
268:
266:
262:
258:
254:
250:
246:
242:
238:
233:
231:
227:
222:
218:
213:
211:
207:
203:
195:
191:
187:
183:
181:
177:
173:
169:
165:
164:immune system
161:
157:
150:
146:
141:
131:
128:
120:
109:
106:
102:
99:
95:
92:
88:
85:
81:
78: –
77:
73:
72:Find sources:
66:
62:
56:
55:
50:This article
48:
44:
39:
38:
33:
19:
4929:
4897:
4870:
4622:
4605:
4588:
4548:
3798:Inflammation
3783:Alloimmunity
3778:Autoimmunity
3763:Immunity vs.
3715:Autoantibody
3613:Superantigen
3582:
3515:
3511:
3505:
3472:
3468:
3461:
3410:
3406:
3393:
3366:
3362:
3349:
3317:(1): 47–59.
3314:
3310:
3262:
3258:
3248:
3211:
3207:
3197:
3170:
3166:
3156:
3129:
3125:
3112:
3085:
3081:
3058:the original
3053:
3043:
3032:. Retrieved
3028:the original
3017:
2976:
2972:
2965:
2930:
2926:
2916:
2908:
2905:
2900:
2886:
2876:
2872:
2867:
2846:
2838:
2834:
2829:
2819:
2816:
2811:
2786:10261/168051
2768:
2764:
2758:
2721:
2717:
2707:
2670:
2667:PLOS Biology
2666:
2618:
2614:
2604:
2569:
2565:
2555:
2518:
2514:
2504:
2461:
2457:
2447:
2410:
2406:
2396:
2361:
2357:
2347:
2312:
2308:
2298:
2263:
2259:
2249:
2214:
2210:
2200:
2163:
2160:Cell Reports
2159:
2149:
2104:
2100:
2090:
2055:
2051:
2041:
2030:the original
2025:
1989:
1954:the original
1944:
1935:
1925:
1905:
1827:
1799:
1793:
1712:
1706:
1698:
1692:
1674:
1668:
1662:
1656:
1650:
1615:
1580:
1568:presentation
1556:gnathostomes
1543:
1535:
1531:
1524:
1520:
1508:
1468:
1446:
1418:
1399:
1390:
1385:
1375:
1367:
1352:
1324:
1306:
1301:
1297:
1290:
1282:immunization
1275:
1272:Immunization
1267:
1250:
1231:
1225:
1215:
1211:
1201:
1183:
1163:genetic code
1158:
1150:
1149:
1122:transposones
1103:
1094:
1088:
1086:
1066:
1043:
1003:
975:Plasma cells
973:
961:
941:
913:blood plasma
906:
861:-restricted
849:
830:
799:
772:
761:
754:bactericidal
747:
743:
734:
730:
703:
664:
656:
652:
626:erythrocytes
611:
594:MHC class II
566:
549:
533:erythrocytes
530:
523:
488:
461:
434:
420:
390:
383:
358:
349:
337:
288:
284:autoimmunity
269:
234:
214:
199:
190:Google Ngram
159:
155:
153:
123:
114:
104:
97:
90:
83:
71:
59:Please help
54:verification
51:
5097:Parathyroid
4797:Nasopharynx
4659:Spinal cord
4594:Bone marrow
4363:Collar bone
4243:Mantle zone
4208:Lymph nodes
4039:Bone marrow
3921:Lymphocytes
3580:Lymphocytic
3214:(5): e128.
2890:Lecture by
2673:(7): e229.
2315:(1): 1–12.
2156:"+ T Cells"
2107:(1): 4706.
1599:lymphocytes
1499:HIV vaccine
1487:Niels Jerne
1333:to enhance
1307:Most viral
1296:(short for
1286:vaccination
1246:Breast milk
1167:prokaryotes
1128:In bacteria
1062:vertebrates
779:eosinophils
681:, allowing
618:MHC class I
573:chemotactic
541:macrophages
476:vertebrates
453:lymph nodes
437:lymphocytes
425:Lymphocytes
340:Robert Good
280:maladaptive
237:lymphocytes
230:vaccination
176:vertebrates
4876:Oropharynx
4616:Lymph node
4549:peripheral
4395:Metatarsus
4390:Metacarpus
4369:Thigh bone
4365:(clavicle)
4183:Pharyngeal
4128:White pulp
4104:Trabeculae
3962:Substances
3826:Peripheral
3814:Inaction:
3693:Antibodies
3674:Macrophage
3587:complement
3034:2008-02-03
2911:: 244–246.
2521:(3): e26.
1786:References
1621:transposon
1551:Lymphocyte
1441:epithelium
1425:Monotremes
1421:viviparous
1313:attenuated
1278:sanitation
1099:Ig domains
1048:and other
1040:In insects
1018:antibodies
1004:Primitive
909:antibodies
758:opsonizing
706:phagocytes
675:granulysin
613:Endogenous
431:Lymphocyte
361:Tonegawa's
350:Drosophila
312:lymphocyte
249:antibodies
226:chickenpox
221:Antibodies
149:lymphocyte
117:March 2024
87:newspapers
5082:Pituitary
4931:accessory
4886:Esophagus
4606:secondary
4518:Diaphragm
4462:Cartilage
4410:Phalanges
3979:Cytolysin
3969:Cytokines
3816:Tolerance
3765:tolerance
3684:Immunogen
2413:(1): 23.
2331:0385-5600
1540:Evolution
1475:idiotypes
1437:syncytium
1410:pregnancy
1357:and many
1326:adjuvants
1317:acellular
1206:and some
1078:honeybees
1074:hemocytes
699:apoptosis
569:exogenous
474:. In all
372:Functions
299:mutations
291:adaptable
272:receptors
168:pathogens
5122:Category
5062:Placenta
5025:Testicle
5020:Prostate
4947:Pancreas
4908:Appendix
4898:lower GI
4871:upper GI
4819:Bronchus
4762:Lymphoid
4445:Vertebra
4400:Ossicles
4385:Mandible
4173:Palatine
4111:Red pulp
3929:Cellular
3773:Immunity
3771:Action:
3754:Paratope
3742:Idiotype
3732:Allotype
3700:Antibody
3654:Mimotope
3618:Allergen
3601:Antigens
3594:Lymphoid
3540:25989912
3532:21475308
3489:17468760
3445:15241406
3385:17027739
3341:19997068
3289:19594405
3281:16138104
3240:15916466
3189:16301814
3104:17395581
3054:ASM News
3001:10693809
2957:15496913
2795:29656113
2750:30470195
2699:16774454
2645:19840170
2596:24789904
2547:17352533
2496:14436004
2488:16782011
2439:24602309
2388:16373579
2339:22924515
2290:29556016
2241:22500839
2192:31801070
2141:31624246
2082:20065995
1722:See also
1576:class II
1527:antigens
1363:epitopes
1355:proteins
1309:vaccines
1251:This is
1242:placenta
1238:maternal
1233:In utero
1171:bacteria
1069:bacteria
1034:antigens
806:suppress
691:granzyme
671:perforin
582:antigens
547:(APCs).
526:antigens
435:T and B
257:hayfever
253:Antigens
172:immunity
5102:Adrenal
5092:Thyroid
5010:Scrotum
4987:Urethra
4982:Bladder
4891:Stomach
4814:Trachea
4750:Myeloid
4589:primary
4455:Sternum
4405:Patella
4380:Humerus
4371:(femur)
4233:B cells
4221:T cells
4178:Lingual
4165:Tonsils
3974:Opsonin
3953:NK cell
3941:Humoral
3821:Central
3788:Allergy
3737:Isotype
3637:Epitope
3608:Antigen
3497:3658963
3415:Bibcode
3332:3805090
3231:1140945
3148:3355895
3009:4367889
2981:Bibcode
2935:Bibcode
2862:, 2020.
2822:: 172.
2803:4890483
2741:6251114
2690:1479700
2623:Bibcode
2587:4024302
2538:1817657
2466:Bibcode
2430:3975449
2366:Bibcode
2358:Science
2281:6084782
2232:3334351
2183:6934378
2132:6797728
2109:Bibcode
2073:3589820
1713:Passive
1707:Passive
1572:class I
1414:eu-FEDS
1294:antigen
1228:infants
1212:passive
1179:viruses
1175:archaea
1169:: most
1046:insects
1014:hagfish
1010:lamprey
578:enzymes
494:Naive B
480:Agnatha
478:except
354:Janeway
320:progeny
265:allergy
245:T cells
241:B cells
101:scholar
5087:Pineal
5047:Vagina
5042:Uterus
5037:Female
4977:Ureter
4972:Kidney
4918:Rectum
4854:Tongue
4802:Larynx
4721:Breast
4693:Tissue
4611:Spleen
4599:Thymus
4554:Artery
4513:Tendon
4508:Muscle
4472:Joints
4450:Pelvis
4425:Tarsus
4415:Radius
4375:Fibula
4358:Carpus
4328:organs
4095:Parts
4088:Spleen
4057:Thymus
3946:B cell
3934:T cell
3679:B cell
3642:Linear
3630:Hapten
3538:
3530:
3495:
3487:
3453:876413
3451:
3443:
3407:Nature
3383:
3339:
3329:
3287:
3279:
3238:
3228:
3187:
3146:
3102:
3007:
2999:
2973:Nature
2955:
2927:Nature
2873:Nature
2801:
2793:
2748:
2738:
2697:
2687:
2643:
2594:
2584:
2545:
2535:
2494:
2486:
2437:
2427:
2386:
2337:
2329:
2288:
2278:
2239:
2229:
2190:
2180:
2139:
2129:
2080:
2070:
1996:
1913:
1835:
1739:Anergy
1699:Active
1693:Active
1641:plants
1593:. In
1406:uterus
1216:active
1151:CRISPR
1146:CRISPR
1093:gene.
935:, and
891:B cell
795:toxins
638:T cell
484:thymus
457:spleen
334:Naming
276:genome
261:asthma
103:
96:
89:
82:
74:
5057:Ovary
5052:Vulva
5015:Penis
4937:Liver
4913:Colon
4864:Tooth
4844:Mouth
4809:Lower
4787:Upper
4664:Nerve
4654:Brain
4571:Heart
4430:Tibia
4420:Skull
4188:Tubal
4099:Hilum
3536:S2CID
3493:S2CID
3449:S2CID
3403:(PDF)
3359:(PDF)
3285:S2CID
3126:Blood
3122:(PDF)
3005:S2CID
2799:S2CID
2492:S2CID
2033:(PDF)
2022:(PDF)
1781:Notes
1402:fetus
1384:, or
1371:genes
1321:toxin
1300:body
1258:serum
1118:piRNA
1114:MiRNA
1110:siRNA
1095:Dscam
1090:Dscam
1030:genes
445:liver
441:brain
345:Monod
108:JSTOR
94:books
5005:Male
4923:Anus
4824:Lung
4792:Nose
4740:and
4711:Skin
4559:Vein
4435:Ulna
4353:Bone
4326:and
4268:GALT
4260:MALT
3585:and
3528:PMID
3485:PMID
3441:PMID
3381:PMID
3337:PMID
3277:PMID
3236:PMID
3185:PMID
3144:PMID
3100:PMID
2997:PMID
2953:PMID
2858:and
2850:See
2791:PMID
2769:1861
2746:PMID
2695:PMID
2641:PMID
2592:PMID
2543:PMID
2484:PMID
2435:PMID
2384:PMID
2335:PMID
2327:ISSN
2286:PMID
2237:PMID
2188:PMID
2137:PMID
2078:PMID
1994:ISBN
1911:ISBN
1833:ISBN
1639:and
1574:and
1566:and
1489:and
1453:ERVs
1447:The
1298:anti
1280:and
1173:and
1020:and
1012:and
893:and
859:CD1d
693:, a
687:lyse
683:ions
673:and
496:and
455:and
413:and
326:and
243:and
154:The
80:news
4859:Lip
4681:Eye
4676:Ear
4440:Rib
3907:HLA
3903:MHC
3520:doi
3477:doi
3431:hdl
3423:doi
3411:430
3371:doi
3367:300
3327:PMC
3319:doi
3267:doi
3226:PMC
3216:doi
3175:doi
3134:doi
3090:doi
3086:282
2989:doi
2977:403
2943:doi
2931:431
2877:482
2854:to
2781:hdl
2773:doi
2736:PMC
2726:doi
2685:PMC
2675:doi
2631:doi
2582:PMC
2574:doi
2570:281
2533:PMC
2523:doi
2474:doi
2425:PMC
2415:doi
2374:doi
2362:310
2317:doi
2276:PMC
2268:doi
2227:PMC
2219:doi
2215:247
2178:PMC
2168:doi
2127:PMC
2117:doi
2068:PMC
2060:doi
1618:RAG
1607:LRR
1427:),
1416:).
1302:gen
1165:in
1155:DNA
937:IgM
933:IgG
929:IgE
925:IgD
921:IgA
833:HIV
622:CD8
598:CD4
443:or
316:DNA
286:).
182:).
63:by
5124::
3667::
3534:.
3526:.
3516:11
3514:.
3491:.
3483:.
3471:.
3447:.
3439:.
3429:.
3421:.
3409:.
3405:.
3379:.
3365:.
3361:.
3335:.
3325:.
3315:11
3313:.
3309:.
3297:^
3283:.
3275:.
3261:.
3257:.
3234:.
3224:.
3210:.
3206:.
3183:.
3171:16
3169:.
3165:.
3142:.
3130:71
3128:.
3124:.
3098:.
3084:.
3080:.
3066:^
3052:.
3003:.
2995:.
2987:.
2975:.
2951:.
2941:.
2929:.
2925:.
2909:36
2875:.
2839:18
2837:.
2797:.
2789:.
2779:.
2767:.
2744:.
2734:.
2722:18
2720:.
2716:.
2693:.
2683:.
2669:.
2665:.
2653:^
2639:.
2629:.
2619:79
2617:.
2613:.
2590:.
2580:.
2568:.
2564:.
2541:.
2531:.
2517:.
2513:.
2490:.
2482:.
2472:.
2462:16
2460:.
2456:.
2433:.
2423:.
2411:11
2409:.
2405:.
2382:.
2372:.
2360:.
2356:.
2333:.
2325:.
2313:57
2311:.
2307:.
2284:.
2274:.
2264:18
2262:.
2258:.
2235:.
2225:.
2213:.
2209:.
2186:.
2176:.
2164:29
2162:.
2158:.
2135:.
2125:.
2115:.
2105:10
2103:.
2099:.
2076:.
2066:.
2056:88
2054:.
2050:.
2024:.
2008:^
1962:^
1934:.
1847:^
1809:^
1643:.
1549:.
1501:.
1373:.
1337:.
1260:.
1236:,
1064:.
931:,
927:,
923:,
604:.
388:.
267:.
259:,
239:.
232:.
143:A
4316:e
4309:t
4302:v
4013:e
4006:t
3999:v
3905:/
3663:/
3572:e
3565:t
3558:v
3542:.
3522::
3499:.
3479::
3473:8
3455:.
3433::
3425::
3417::
3387:.
3373::
3343:.
3321::
3291:.
3269::
3263:5
3242:.
3218::
3212:2
3191:.
3177::
3150:.
3136::
3106:.
3092::
3037:.
3011:.
2991::
2983::
2959:.
2945::
2937::
2820:8
2805:.
2783::
2775::
2752:.
2728::
2701:.
2677::
2671:4
2647:.
2633::
2625::
2598:.
2576::
2549:.
2525::
2519:3
2498:.
2476::
2468::
2441:.
2417::
2390:.
2376::
2368::
2341:.
2319::
2292:.
2270::
2243:.
2221::
2194:.
2170::
2143:.
2119::
2111::
2084:.
2062::
2002:.
1938:.
1919:.
1841:.
1140:.
600:+
417:.
399:.
130:)
124:(
119:)
115:(
105:·
98:·
91:·
84:·
57:.
34:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.