292:(180° rotation of the CONH peptide plane with little positional alteration to side chains and surrounding peptides). The same relationship exists between type I’ and II’ β turns. Some evidence has indicated that these interconversions occur in beta turns in proteins such that crystal or NMR structures merely provide a snapshot of β turns that are, in reality, interchanging. In proteins in general all four beta turn types occur frequently but I is most common, followed by II, I' and II' in that order. Beta turns are especially common at the loop ends of
133:
322:. The main chain–main chain hydrogen bond is replaced by a side chain–main chain hydrogen bond. 3D computer superimposition shows that, in proteins, they occur as one of the same four types that beta turns do, except that their relative frequency of occurrence differs: type II’ is the most common, followed by types I, II and I’.
141:
The hydrogen bond criterion for beta turns, applied to polypeptides whose amino acids are linked by trans peptide bonds, gives rise to just four categories, as shown by
Venkatachalam in 1968. They are called types I, II, I’ and II’. All occur regularly in proteins and polypeptides but type I is most
330:
Apart from the type I, I’,II and II’ beta turns as identified via the hydrogen bond criterion, non-hydrogen-bonded beta-turns named type VIII often occur. Three other, fairly rare, types of beta turn have been identified in which the peptide bond between residues
296:; they have a different distribution of types from the others; type I' is the most common, followed by types II', I and II. Additional turn types have been defined by clustering turn conformations within very high-resolution protein structures.
136:
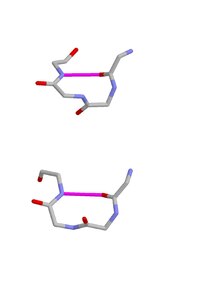
Two beta turns, type I above and type II below. Each image shows the main chain atoms of a tetrapeptide excluding hydrogen atoms. Carbon atoms grey, oxygen atoms red and nitrogen atoms blue. The defining hydrogen bond is shown as a magenta
118:
The hydrogen bond criterion is the one most appropriate for everyday use, partly because it gives rise to four distinct categories; the distance criterion gives rise to the same four categories but yields additional turn types.
670:
Sibanda, BL; Blundell TL (1989). "Conformation of β-hairpins in protein structures: A systematic classification with applications to modelling by homology, electron density fitting and protein engineering".
1032:
347:; these are named types VIa1, VIa2 and VIb. Another category, type IV, was used for turns not belonging to any of the above. Further details of these turns are given in
1025:
150:
helices and at the ends of some classic alpha helices. Type II beta turns, on the other hand, often occur in association with beta-sheet as part of
1018:
1180:
584:
539:
1047:
40:
288:
Type I and II β turns exhibit a relationship to one another because they potentially interconvert by the process of
177:
such a conformation is sterically impossible but they occur frequently at amino acid positions where φ is negative.
390:"Stereochemical criteria for polypeptides and proteins. V. Conformation of a system of three linked peptide units"
389:
635:
Wilmot, CM; Thornton JM (1988). "Analysis and prediction of the different types of beta-turn in proteins".
289:
103:
817:
1112:
348:
36:
806:"A new clustering and nomenclature for beta turns derived from high-resolution protein structures"
430:
151:
1086:
996:
945:
894:
845:
786:
737:
688:
652:
590:
580:
545:
535:
500:
465:
422:
359:
Two websites are available for finding and examining hydrogen-bonded beta turns in proteins:
1155:
986:
976:
935:
925:
884:
876:
835:
825:
776:
768:
727:
719:
680:
644:
617:
572:
527:
492:
457:
412:
404:
914:"Motivated Proteins: A web application for studying small three-dimensional protein motifs"
483:
Toniolo, C; Benedetti E (1980). "Intramolecularly hydrogen-bonded peptide conformations".
821:
1091:
991:
964:
940:
913:
889:
864:
840:
805:
781:
756:
732:
707:
84:
576:
531:
1174:
684:
648:
621:
461:
293:
80:
1124:
434:
52:
608:
Milner-White, EJ; Poet R (1987). "Loops, bulges, turns and hairpins in proteins".
830:
1150:
1134:
1062:
143:
92:
408:
1129:
1107:
1081:
1010:
496:
315:
170:
157:
The four types of beta turn are distinguished by the φ, ψ angles of residues
56:
1067:
981:
930:
368:
319:
311:
132:
1000:
949:
898:
865:"Mimicry by asx- and ST-turns of the four main types of β turn in proteins"
849:
790:
723:
741:
692:
656:
594:
549:
504:
469:
426:
363:
1076:
417:
299:
48:
880:
518:
Richardson, JS (1981). "The anatomy and taxonomy of protein structure".
303:
174:
166:
44:
772:
131:
563:
Rose, GD; Gierasch LM (1985). "Turns in peptides and proteins".
1014:
165:
as shown in the table below giving the typical average values.
708:"A revised set of potentials for β-turn formation in proteins"
448:
Lewis, PN; Momany FA (1973). "Chain reversal in proteins".
804:
Shapovalov, M; Vucetic, S; Dunbrack RL, Jr (March 2019).
1143:
1100:
1055:
1046:
102:By having a distance of less than 7Å between the
965:"MSDmotif: exploring protein sites and motifs"
1026:
8:
1052:
1033:
1019:
1011:
990:
980:
939:
929:
888:
839:
829:
780:
731:
416:
79:By the possession of an intra-main-chain
306:resemble beta turns except that residue
179:
43:that cause a change in direction of the
380:
142:common, because it most resembles an
7:
912:Leader, DP; Milner-White EJ (2009).
757:"Peptide plane flipping in proteins"
706:Hutchinson, EG; Thornton JM (1994).
310:is replaced by the side chain of an
75:). They can be defined in two ways:
14:
567:. Advances in Protein Chemistry.
522:. Advances in Protein Chemistry.
47:. They are very common motifs in
863:Duddy, WM; Nissink JWM (2004).
41:secondary structure in proteins
963:Golovin, A; Henrick K (2008).
35:) are the most common form of
1:
577:10.1016/S0065-3233(08)60063-7
532:10.1016/S0065-3233(08)60520-3
831:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006844
685:10.1016/0022-2836(89)90583-4
649:10.1016/0022-2836(88)90103-9
622:10.1016/0968-0004(87)90091-0
462:10.1016/0005-2795(73)90350-4
173:with positive φ angles; for
1048:Protein secondary structure
1041:Protein secondary structure
1197:
810:PLOS Computational Biology
409:10.1002/bip.1968.360061006
388:Venkatachalam, CM (1968).
1181:Protein structural motifs
497:10.3109/10409238009105471
169:are especially common as
55:. Each consists of four
982:10.1186/1471-2105-9-312
931:10.1186/1471-2105-10-60
128:Hydrogen bond criterion
39:—a type of non-regular
724:10.1002/pro.5560031206
290:peptide plane flipping
138:
135:
485:CRC Crit Rev Biochem
450:Biochim Biophys Acta
146:, occurring within 3
881:10.1110/ps.04920904
822:2019PLSCB..15E6844S
755:Hayward, S (2001).
349:turn (biochemistry)
59:residues (labelled
33:Venkatachalam turns
969:BMC Bioinformatics
918:BMC Bioinformatics
610:Trends Biochem Sci
364:Motivated Proteins
326:Distance criterion
139:
106:atoms of residues
1168:
1167:
1164:
1163:
1087:Polyproline helix
875:(11): 3051–3055.
767:(11): 2219–2227.
718:(12): 2207–2216.
403:(10): 1425–1436.
286:
285:
45:polypeptide chain
1188:
1156:Helix-turn-helix
1053:
1035:
1028:
1021:
1012:
1005:
1004:
994:
984:
960:
954:
953:
943:
933:
909:
903:
902:
892:
860:
854:
853:
843:
833:
801:
795:
794:
784:
773:10.1110/ps.23101
752:
746:
745:
735:
703:
697:
696:
667:
661:
660:
632:
626:
625:
605:
599:
598:
560:
554:
553:
515:
509:
508:
480:
474:
473:
445:
439:
438:
420:
394:
385:
180:
1196:
1195:
1191:
1190:
1189:
1187:
1186:
1185:
1171:
1170:
1169:
1160:
1144:Supersecondary:
1139:
1096:
1071:
1042:
1039:
1009:
1008:
962:
961:
957:
911:
910:
906:
869:Protein Science
862:
861:
857:
816:(3): e1006844.
803:
802:
798:
761:Protein Science
754:
753:
749:
705:
704:
700:
669:
668:
664:
634:
633:
629:
607:
606:
602:
587:
562:
561:
557:
542:
517:
516:
512:
482:
481:
477:
447:
446:
442:
392:
387:
386:
382:
377:
357:
328:
214:
206:
198:
189:
149:
130:
125:
12:
11:
5:
1194:
1192:
1184:
1183:
1173:
1172:
1166:
1165:
1162:
1161:
1159:
1158:
1153:
1147:
1145:
1141:
1140:
1138:
1137:
1132:
1127:
1122:
1121:
1120:
1110:
1104:
1102:
1098:
1097:
1095:
1094:
1092:Collagen helix
1089:
1084:
1079:
1074:
1069:
1065:
1059:
1057:
1050:
1044:
1043:
1040:
1038:
1037:
1030:
1023:
1015:
1007:
1006:
955:
904:
855:
796:
747:
698:
679:(4): 759–777.
662:
643:(1): 221–232.
627:
600:
585:
555:
540:
510:
475:
440:
379:
378:
376:
373:
372:
371:
366:
356:
355:External links
353:
327:
324:
284:
283:
280:
277:
274:
271:
267:
266:
263:
260:
257:
254:
250:
249:
246:
243:
240:
237:
233:
232:
229:
226:
223:
220:
216:
215:
210:
207:
202:
199:
194:
191:
187:
183:
147:
129:
126:
124:
121:
116:
115:
100:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1193:
1182:
1179:
1178:
1176:
1157:
1154:
1152:
1149:
1148:
1146:
1142:
1136:
1133:
1131:
1128:
1126:
1123:
1119:
1116:
1115:
1114:
1111:
1109:
1106:
1105:
1103:
1099:
1093:
1090:
1088:
1085:
1083:
1080:
1078:
1075:
1073:
1066:
1064:
1061:
1060:
1058:
1054:
1051:
1049:
1045:
1036:
1031:
1029:
1024:
1022:
1017:
1016:
1013:
1002:
998:
993:
988:
983:
978:
974:
970:
966:
959:
956:
951:
947:
942:
937:
932:
927:
923:
919:
915:
908:
905:
900:
896:
891:
886:
882:
878:
874:
870:
866:
859:
856:
851:
847:
842:
837:
832:
827:
823:
819:
815:
811:
807:
800:
797:
792:
788:
783:
778:
774:
770:
766:
762:
758:
751:
748:
743:
739:
734:
729:
725:
721:
717:
713:
709:
702:
699:
694:
690:
686:
682:
678:
674:
666:
663:
658:
654:
650:
646:
642:
638:
631:
628:
623:
619:
615:
611:
604:
601:
596:
592:
588:
586:9780120342372
582:
578:
574:
570:
566:
565:Adv Prot Chem
559:
556:
551:
547:
543:
541:9780120342341
537:
533:
529:
525:
521:
520:Adv Prot Chem
514:
511:
506:
502:
498:
494:
490:
486:
479:
476:
471:
467:
463:
459:
456:(2): 211–29.
455:
451:
444:
441:
436:
432:
428:
424:
419:
418:2027.42/37819
414:
410:
406:
402:
398:
391:
384:
381:
374:
370:
367:
365:
362:
361:
360:
354:
352:
350:
346:
342:
338:
334:
325:
323:
321:
317:
313:
309:
305:
301:
297:
295:
294:beta hairpins
291:
281:
278:
275:
272:
269:
268:
264:
261:
258:
255:
252:
251:
247:
244:
241:
238:
235:
234:
230:
227:
224:
221:
218:
217:
213:
208:
205:
200:
197:
192:
190:
184:
182:
181:
178:
176:
172:
168:
164:
160:
155:
153:
145:
134:
127:
122:
120:
113:
109:
105:
101:
98:
94:
90:
86:
82:
81:hydrogen bond
78:
77:
76:
74:
70:
66:
62:
58:
54:
50:
46:
42:
38:
34:
30:
29:reverse turns
26:
22:
18:
1125:Beta hairpin
1117:
972:
968:
958:
921:
917:
907:
872:
868:
858:
813:
809:
799:
764:
760:
750:
715:
711:
701:
676:
672:
665:
640:
636:
630:
613:
609:
603:
568:
564:
558:
523:
519:
513:
488:
484:
478:
453:
449:
443:
400:
396:
383:
358:
344:
343:rather than
340:
336:
332:
329:
318:, serine or
307:
298:
287:
211:
203:
195:
186:
162:
158:
156:
140:
117:
111:
107:
96:
88:
83:between the
72:
68:
64:
60:
53:polypeptides
32:
28:
24:
20:
16:
15:
1151:Coiled coil
616:: 189–192.
526:: 167–339.
491:(1): 1–44.
397:Biopolymers
171:amino acids
144:alpha helix
95:of residue
87:of residue
25:tight turns
1130:Beta bulge
975:(1): 312.
712:J Mol Biol
673:J Mol Biol
637:J Mol Biol
375:References
316:asparagine
152:beta-links
123:Definition
57:amino acid
1118:Beta turn
1101:Extended:
924:(1): 60.
571:: 1–109.
369:PDBeMotif
320:threonine
312:aspartate
300:Asx turns
1175:Category
1135:α-strand
1108:β-strand
1056:Helices:
1001:18637174
950:19210785
899:15459339
850:30845191
791:11604529
304:ST turns
270:type II'
175:prolines
167:Glycines
91:and the
49:proteins
1082:β-helix
1077:π-helix
1063:α-helix
992:2491636
941:2651126
890:2286581
841:6424458
818:Bibcode
782:2374056
742:7756980
733:2142776
693:2500530
657:3184187
595:2865874
550:7020376
505:6254725
470:4351002
435:5873535
427:5685102
253:type I'
236:type II
21:β-bends
17:β turns
999:
989:
948:
938:
897:
887:
848:
838:
789:
779:
740:
730:
691:
655:
593:
583:
548:
538:
503:
468:
433:
425:
219:type I
19:(also
1072:helix
431:S2CID
393:(PDF)
345:trans
137:line.
37:turns
1113:Turn
997:PMID
946:PMID
895:PMID
846:PMID
787:PMID
738:PMID
689:PMID
653:PMID
591:PMID
581:ISBN
546:PMID
536:ISBN
501:PMID
466:PMID
423:PMID
335:and
302:and
276:-120
161:and
110:and
71:and
51:and
987:PMC
977:doi
936:PMC
926:doi
885:PMC
877:doi
836:PMC
826:doi
777:PMC
769:doi
728:PMC
720:doi
681:doi
677:206
645:doi
641:203
618:doi
573:doi
528:doi
493:doi
458:doi
454:303
413:hdl
405:doi
341:cis
339:is
337:i+2
333:i+1
279:-80
242:120
239:-60
228:-90
225:-30
222:-60
212:i+2
204:i+2
196:i+1
188:i+1
163:i+2
159:i+1
112:i+3
97:i+3
73:i+3
69:i+2
65:i+1
1177::
1070:10
995:.
985:.
971:.
967:.
944:.
934:.
922:10
920:.
916:.
893:.
883:.
873:13
871:.
867:.
844:.
834:.
824:.
814:15
812:.
808:.
785:.
775:.
765:10
763:.
759:.
736:.
726:.
714:.
710:.
687:.
675:.
651:.
639:.
614:12
612:.
589:.
579:.
569:37
544:.
534:.
524:34
499:.
487:.
464:.
452:.
429:.
421:.
411:.
399:.
395:.
351:.
314:,
282:0
273:60
265:0
262:90
259:30
256:60
248:0
245:80
231:0
154:.
148:10
104:Cα
93:NH
85:CO
67:,
63:,
31:,
27:,
23:,
1068:3
1034:e
1027:t
1020:v
1003:.
979::
973:9
952:.
928::
901:.
879::
852:.
828::
820::
793:.
771::
744:.
722::
716:3
695:.
683::
659:.
647::
624:.
620::
597:.
575::
552:.
530::
507:.
495::
489:9
472:.
460::
437:.
415::
407::
401:6
308:i
209:ψ
201:φ
193:ψ
185:φ
114:.
108:i
99:;
89:i
61:i
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.