229:
217:
197:
31:
180:
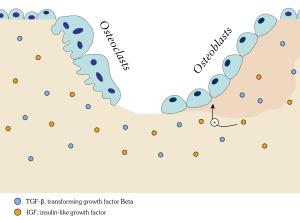
Subsequent to appropriate signaling, osteoclasts move to resorb the surface of the bone, followed by deposition of bone by osteoblasts. Together, the cells that are responsible for bone remodeling are known as the basic multicellular unit (BMU), and the temporal duration (i.e. lifespan) of the BMU
124:
requires close cooperation between these two cell types and other cell populations present at the bone remodeling sites (e.g. immune cells). Bone metabolism relies on complex signaling pathways and control mechanisms to achieve proper rates of growth and differentiation. These controls include the
228:
216:
177:
required for physiological processes. Thus bone remodeling is not just occasional "repair of bone damage" but rather an active, continual process that is always happening in a healthy body.
493:
196:
96:
An imbalance in the regulation of bone remodeling's two sub-processes, bone resorption and bone formation, results in many metabolic bone diseases, such as
486:
479:
222:
Osteoclast, with bone below it, showing typical distinguishing characteristics: a large cell with multiple nuclei and a "foamy" cytosol.
462:
112:
involves multiple but coordinated cellular and molecular events. Two main types of cells are responsible for bone metabolism:
34:
Bone tissue is removed by osteoclasts, and then new bone tissue is formed by osteoblasts. Both processes utilize cytokine (
93:
In the first year of life, almost 100% of the skeleton is replaced. In adults, remodeling proceeds at about 10% per year.
354:"Coupling the activities of bone formation and resorption: a multitude of signals within the basic multicellular unit"
645:
39:
90:, which occurs during normal activity. Remodeling responds also to functional demands of the mechanical loading.
182:
457:
Pietrzak, WS. Musculoskeletal tissue regeneration: biological materials and methods, Humana Press, 2008.
565:
249:
126:
87:
458:
440:
422:
383:
334:
254:
245:
82:). These processes also control the reshaping or replacement of bone following injuries like
543:
430:
414:
373:
365:
324:
314:
601:
538:
68:
289:
435:
402:
650:
624:
583:
418:
378:
353:
329:
302:
259:
154:
134:
59:
278:
639:
611:
170:
83:
548:
533:
523:
471:
97:
74:
146:
109:
17:
553:
173:
family). It is in this way that the body is able to maintain proper levels of
142:
120:(which break bone down). The structure of bones as well as adequate supply of
117:
113:
426:
369:
575:
507:
319:
207:
150:
130:
47:
30:
444:
387:
338:
560:
403:"Topography-mediated immunomodulation in osseointegration; Ally or Enemy"
138:
63:
35:
619:
203:
174:
121:
401:
Shirazi, Sajjad; Ravindran, Sriram; Cooper, Lyndon F. (2022-11-09).
593:
162:
158:
29:
515:
503:
166:
475:
303:"Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Bone Remodeling"
610:
592:
574:
514:
72:) and new bone tissue is formed (a process called
248:, the general class of forming and maintaining
27:Continuous turnover of bone matrix and mineral
487:
8:
301:Raggatt, L. J.; et al. (May 25, 2010).
352:Sims, N. A.; et al. (8 January 2014).
234:Illustration showing bone remodelling cycle
494:
480:
472:
434:
377:
328:
318:
271:
192:
125:action of several hormones, including
7:
307:The Journal of Biological Chemistry
58:is a lifelong process where mature
419:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2022.121903
202:Osteoblasts actively synthesizing
25:
227:
215:
195:
149:-derived membrane and soluble
116:(which secrete new bone), and
1:
667:
290:Online Medical Dictionary
370:10.1038/bonekey.2013.215
320:10.1074/jbc.R109.041087
183:bone remodeling period
181:is referred to as the
43:
145:, as well as several
33:
62:is removed from the
566:Periosteal reaction
313:(33): 25103–25108.
250:mineralized tissues
127:parathyroid hormone
80:new bone formation
66:(a process called
44:
646:Animal physiology
633:
632:
279:Wheeless Textbook
255:Tissue remodeling
246:Biomineralization
16:(Redirected from
658:
544:Osseointegration
496:
489:
482:
473:
466:
455:
449:
448:
438:
398:
392:
391:
381:
349:
343:
342:
332:
322:
298:
292:
287:
281:
276:
231:
219:
199:
21:
666:
665:
661:
660:
659:
657:
656:
655:
636:
635:
634:
629:
606:
602:Range of motion
588:
570:
539:Bone resorption
529:Bone remodeling
510:
500:
470:
469:
456:
452:
400:
399:
395:
358:BoneKEy Reports
351:
350:
346:
300:
299:
295:
288:
284:
277:
273:
268:
242:
235:
232:
223:
220:
211:
206:containing two
200:
191:
106:
69:bone resorption
56:bone metabolism
52:bone remodeling
28:
23:
22:
18:Bone metabolism
15:
12:
11:
5:
664:
662:
654:
653:
648:
638:
637:
631:
630:
628:
627:
625:Cementogenesis
622:
616:
614:
608:
607:
605:
604:
598:
596:
590:
589:
587:
586:
584:Chondrogenesis
580:
578:
572:
571:
569:
568:
563:
558:
557:
556:
551:
546:
541:
536:
526:
520:
518:
512:
511:
502:Physiology of
501:
499:
498:
491:
484:
476:
468:
467:
450:
393:
344:
293:
282:
270:
269:
267:
264:
263:
262:
257:
252:
241:
238:
237:
236:
233:
226:
224:
221:
214:
212:
201:
194:
190:
187:
155:growth factors
135:growth hormone
105:
102:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
663:
652:
649:
647:
644:
643:
641:
626:
623:
621:
618:
617:
615:
613:
609:
603:
600:
599:
597:
595:
591:
585:
582:
581:
579:
577:
573:
567:
564:
562:
559:
555:
552:
550:
547:
545:
542:
540:
537:
535:
532:
531:
530:
527:
525:
522:
521:
519:
517:
513:
509:
505:
497:
492:
490:
485:
483:
478:
477:
474:
464:
463:1-58829-909-0
460:
454:
451:
446:
442:
437:
432:
428:
424:
420:
416:
412:
408:
404:
397:
394:
389:
385:
380:
375:
371:
367:
363:
359:
355:
348:
345:
340:
336:
331:
326:
321:
316:
312:
308:
304:
297:
294:
291:
286:
283:
280:
275:
272:
265:
261:
258:
256:
253:
251:
247:
244:
243:
239:
230:
225:
218:
213:
209:
205:
198:
193:
188:
186:
184:
178:
176:
172:
168:
164:
160:
156:
152:
148:
144:
140:
136:
132:
128:
123:
119:
115:
111:
103:
101:
99:
94:
91:
89:
85:
81:
77:
76:
71:
70:
65:
61:
57:
53:
49:
42:) signalling.
41:
37:
32:
19:
549:Ossification
534:Bone healing
528:
524:Bone density
453:
410:
407:Biomaterials
406:
396:
361:
357:
347:
310:
306:
296:
285:
274:
179:
107:
98:osteoporosis
95:
92:
88:micro-damage
79:
75:ossification
73:
67:
55:
51:
45:
260:Wolff's law
147:bone marrow
118:osteoclasts
114:osteoblasts
110:homeostasis
60:bone tissue
640:Categories
554:Osteolysis
413:: 121903.
266:References
208:osteocytes
143:calcitonin
104:Physiology
576:Cartilage
508:cartilage
427:0142-9612
151:cytokines
131:vitamin D
86:but also
84:fractures
48:osteology
561:Bone age
445:36410109
436:10148651
388:24466412
339:20501658
240:See also
139:steroids
64:skeleton
620:Chewing
465:page 48
379:3899560
364:: 481.
330:2919071
204:osteoid
189:Gallery
175:calcium
129:(PTH),
122:calcium
461:
443:
433:
425:
386:
376:
337:
327:
157:(e.g.
141:, and
651:Bones
612:Teeth
594:Joint
163:RANKL
159:M-CSF
108:Bone
36:TGF-β
516:Bone
506:and
504:bone
459:ISBN
441:PMID
423:ISSN
384:PMID
335:PMID
171:IL-6
169:and
167:VEGF
153:and
431:PMC
415:doi
411:291
374:PMC
366:doi
325:PMC
315:doi
311:285
78:or
54:or
46:In
40:IGF
642::
439:.
429:.
421:.
409:.
405:.
382:.
372:.
360:.
356:.
333:.
323:.
309:.
305:.
185:.
165:,
161:,
137:,
133:,
100:.
50:,
38:,
495:e
488:t
481:v
447:.
417::
390:.
368::
362:3
341:.
317::
210:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.