334:
241:
510:
725:, it does not inhibit glucose transport. Cytochalasin E, however, was noted to decrease glucose absorption in mice around the intestinal tissues by increasing the Km needed for glucose to reach the Vmax, which meant that a higher concentration of glucose was required in its presence to attain Vmax. Since Vmax remained the same according to another study, it is evident that CE is indeed a competitive inhibitor at the intestinal receptor sites for glucose.
505:
747:, which is required for specificity and potency. Cytochalasin E is a potent antiangiogenic agent that may be useful for treatments of cancer and other pathologic angiogenesis. Cytochalasin E was also found to inhibit autophagy, a process vital in recycling dysfunctional cells and cellular components. Cancer cells thus favor autophagy due to its role in countering metabolic stresses induced by anti-cancer drugs such as
24:
674:
140:
751:
in order to regenerate healthier cancer cells for continued proliferation and growth. In a study, it was confirmed that when CE was used, fusion of autophagosomes with lysozyme was inhibited and so cell death due to bortezomib, a proteasome inhibitor, was amplified as unnecessary proteins would
357:
InChI=1S/C28H33NO7/c1-16-9-8-12-19-23-27(4,35-23)17(2)21-20(15-18-10-6-5-7-11-18)29-24(31)28(19,21)36-25(32)34-14-13-26(3,33)22(16)30/h5-8,10-14,16-17,19-21,23,33H,9,15H2,1-4H3,(H,29,31)/b12-8+,14-13+/t16-,17-,19-,20-,21-,23-,26+,27+,28+/m0/s1
367:
InChI=1/C28H33NO7/c1-16-9-8-12-19-23-27(4,35-23)17(2)21-20(15-18-10-6-5-7-11-18)29-24(31)28(19,21)36-25(32)34-14-13-26(3,33)22(16)30/h5-8,10-14,16-17,19-21,23,33H,9,15H2,1-4H3,(H,29,31)/b12-8+,14-13+/t16-,17-,19-,20-,21-,23-,26+,27+,28+/m0/s1
518:
485:
687:
834:
383:
768:
612:
348:
733:
466:
592:
694:
568:
838:
604:
558:
509:
312:
861:"Cytochalasin E, an epoxide containing Aspergillus-derived fungal metabolite, inhibits angiogenesis and tumor growth"
648:
900:"Cytochalasin E increased the sensitivity of human lung cancer A549 cells to bortezomib via inhibition of autophagy"
898:
Takanezawa, Yasukazu; Nakamura, Ryosuke; Kojima, Yuka; Sone, Yuka; Uraguchi, Shimpei; Kiyono, Masako (2018-04-06).
983:
978:
248:
752:
continue to build up inside cancer cells unable to be further recycled through autophagy, leading to apoptosis.
959:
616:
236:
198:
532:
504:
497:
739:
Cytochalasin E was found to be a potent and selective inhibitor of bovine capillary endothelial (BCE)
640:
624:
620:
36:
718:
329:
973:
584:
550:
106:
955:
740:
608:
572:
158:
588:
993:
988:
927:
919:
880:
872:
816:
808:
596:
218:
911:
800:
576:
406:
859:
Udagawa, T.; Yuan, J.; Panigrahy, D.; Chang, Y. H.; Shah, J.; D'Amato, R. J. (2000-08-01).
628:
116:
632:
333:
240:
644:
178:
736:, a kind of blindness caused by an abnormal proliferation of blood vessels in the eye.
729:
722:
665:
564:
967:
804:
775:
229:
656:
300:
714:
710:
580:
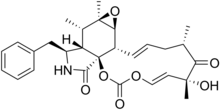
81:)-14-Benzyl-6-hydroxy-6,8,12a,13-tetramethyl-9,11a,11b,12a,13,13a,14,15-octahydro-2
947:
915:
713:
group, is an inhibitor of actin polymerization in blood platelets. It inhibits
748:
437:
209:
923:
876:
812:
787:
Glinsukon, T.; Kongsuktrakoon, B.; Toskulkao, C.; Sophasan, S. (1983-03-01).
951:
899:
860:
600:
23:
931:
884:
788:
820:
789:"Cytochalasin E: inhibition of intestinal glucose absorption in the mouse"
542:
743:. Cytochalasin E differs from other cytochalasin molecules by having an
744:
450:
287:
249:
189:
664:
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their
275:
538:
169:
139:
129:
391:
C1C/C=C/23(O3)((42(C(=O)N4CC5=CC=CC=C5)OC(=O)O/C=C/(C1=O)(C)O)C)C
652:
546:
266:
636:
317:
865:
The
Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics
682:
904:
157:
299:
732:effect, cytochalasin E is a potential drug for
115:
85:-dioxacyclotridecinooxirenoisoindole-2,7,16(6
8:
332:
239:
217:
15:
761:
388:
353:
328:
230:
360:Key: LAJXCUNOQSHRJO-ZYGJITOWSA-N
197:
177:
7:
370:Key: LAJXCUNOQSHRJO-ZYGJITOWBM
290:
274:
14:
734:age-related macular degeneration
672:
508:
503:
424:
418:
22:
668:(at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
467:Occupational safety and health
427:
412:
1:
837:. 2006-05-19. Archived from
805:10.1016/0378-4274(83)90154-6
1010:
916:10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.03.029
717:and tumor growth. Unlike
662:
484:
464:
459:
399:
379:
344:
99:
35:
30:
21:
559:Precautionary statements
771:Aspergillus clavatus
769:Cytochalasin E from
37:Preferred IUPAC name
445: g·mol
18:
793:Toxicology Letters
741:cell proliferation
709:, a member of the
695:Infobox references
16:
703:Chemical compound
701:
700:
533:Hazard statements
313:CompTox Dashboard
141:Interactive image
1001:
984:Carbonate esters
979:Actin inhibitors
936:
935:
895:
889:
888:
856:
850:
849:
847:
846:
835:"Cytochalasin E"
831:
825:
824:
784:
778:
766:
685:
679:
676:
675:
658:
654:
650:
646:
642:
638:
634:
630:
626:
622:
618:
614:
610:
606:
602:
598:
594:
590:
586:
582:
578:
574:
570:
566:
552:
548:
544:
540:
512:
507:
444:
429:
426:
420:
414:
407:Chemical formula
337:
336:
321:
319:
303:
292:
278:
251:
243:
232:
221:
201:
181:
161:
143:
119:
26:
19:
1009:
1008:
1004:
1003:
1002:
1000:
999:
998:
964:
963:
960:Cayman Chemical
954:
945:
940:
939:
897:
896:
892:
858:
857:
853:
844:
842:
833:
832:
828:
786:
785:
781:
767:
763:
758:
728:Because of its
704:
697:
692:
691:
690: ?)
681:
677:
673:
669:
561:
535:
521:
500:
477:
442:
432:
423:
417:
409:
395:
392:
387:
386:
375:
372:
371:
368:
362:
361:
358:
352:
351:
340:
322:
315:
306:
293:
281:
261:
224:
204:
184:
164:
146:
133:
122:
109:
95:
94:
17:Cytochalasin E
12:
11:
5:
1007:
1005:
997:
996:
991:
986:
981:
976:
966:
965:
956:Cytochalasin E
948:Cytochalasin E
944:
943:External pages
941:
938:
937:
910:(3): 603–608.
890:
871:(2): 421–427.
851:
841:on 19 May 2006
826:
799:(4): 341–348.
779:
760:
759:
757:
754:
730:antiangiogenic
723:cytochalasin B
719:cytochalasin A
707:Cytochalasin E
702:
699:
698:
693:
671:
670:
666:standard state
663:
660:
659:
562:
557:
554:
553:
536:
531:
528:
527:
522:
517:
514:
513:
501:
496:
493:
492:
482:
481:
478:
475:
472:
471:
462:
461:
457:
456:
453:
447:
446:
440:
434:
433:
430:
421:
415:
410:
405:
402:
401:
397:
396:
394:
393:
390:
382:
381:
380:
377:
376:
374:
373:
369:
366:
365:
363:
359:
356:
355:
347:
346:
345:
342:
341:
339:
338:
330:DTXSID60894866
325:
323:
311:
308:
307:
305:
304:
296:
294:
286:
283:
282:
280:
279:
271:
269:
263:
262:
260:
259:
255:
253:
245:
244:
234:
226:
225:
223:
222:
214:
212:
206:
205:
203:
202:
194:
192:
186:
185:
183:
182:
174:
172:
166:
165:
163:
162:
154:
152:
148:
147:
145:
144:
136:
134:
127:
124:
123:
121:
120:
112:
110:
105:
102:
101:
97:
96:
40:
39:
33:
32:
28:
27:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1006:
995:
992:
990:
987:
985:
982:
980:
977:
975:
972:
971:
969:
962:
961:
957:
953:
949:
942:
933:
929:
925:
921:
917:
913:
909:
905:
901:
894:
891:
886:
882:
878:
874:
870:
866:
862:
855:
852:
840:
836:
830:
827:
822:
818:
814:
810:
806:
802:
798:
794:
790:
783:
780:
777:
776:Sigma-Aldrich
773:
772:
765:
762:
755:
753:
750:
746:
742:
737:
735:
731:
726:
724:
720:
716:
712:
708:
696:
689:
684:
667:
661:
563:
560:
556:
555:
537:
534:
530:
529:
526:
523:
520:
516:
515:
511:
506:
502:
499:
495:
494:
490:
488:
483:
479:
474:
473:
469:
468:
463:
458:
454:
452:
449:
448:
441:
439:
436:
435:
411:
408:
404:
403:
398:
389:
385:
378:
364:
354:
350:
343:
335:
331:
327:
326:
324:
314:
310:
309:
302:
298:
297:
295:
289:
285:
284:
277:
273:
272:
270:
268:
265:
264:
257:
256:
254:
252:
247:
246:
242:
238:
235:
233:
231:ECHA InfoCard
228:
227:
220:
216:
215:
213:
211:
208:
207:
200:
196:
195:
193:
191:
188:
187:
180:
176:
175:
173:
171:
168:
167:
160:
156:
155:
153:
150:
149:
142:
138:
137:
135:
131:
126:
125:
118:
114:
113:
111:
108:
104:
103:
98:
92:
88:
84:
80:
76:
72:
68:
64:
60:
56:
52:
48:
44:
38:
34:
29:
25:
20:
946:
907:
903:
893:
868:
864:
854:
843:. Retrieved
839:the original
829:
796:
792:
782:
770:
764:
738:
727:
715:angiogenesis
711:cytochalasin
706:
705:
524:
486:
476:Main hazards
465:
199:ChEMBL494856
100:Identifiers
90:
86:
82:
78:
74:
70:
66:
62:
58:
54:
50:
46:
42:
519:Signal word
470:(OHS/OSH):
455:1.309 g/ml
400:Properties
237:100.048.018
179:CHEBI:68201
974:Mycotoxins
968:Categories
845:2022-05-12
756:References
749:bortezomib
498:Pictograms
438:Molar mass
210:ChemSpider
128:3D model (
117:36011-19-5
107:CAS Number
952:Fermentek
924:1090-2104
877:0022-3565
813:0378-4274
649:P403+P233
617:P308+P313
613:P304+P340
609:P302+P350
605:P301+P310
489:labelling
258:252-835-7
250:EC Number
994:Lactones
989:Epoxides
932:29524420
885:10900214
460:Hazards
93:)-trione
821:6836602
745:epoxide
688:what is
686: (
451:Density
443:495.572
301:5458385
288:PubChem
219:4572350
930:
922:
883:
875:
819:
811:
683:verify
680:
525:Danger
480:Toxic
384:SMILES
276:C19953
190:ChEMBL
159:L06226
151:3DMet
31:Names
958:from
950:from
349:InChI
170:ChEBI
130:JSmol
928:PMID
920:ISSN
881:PMID
873:ISSN
817:PMID
809:ISSN
721:and
657:P501
653:P405
645:P363
641:P361
637:P330
633:P322
629:P321
625:P320
621:P310
601:P284
597:P281
593:P280
589:P271
585:P270
581:P264
577:P262
573:P260
569:P202
565:P201
551:H361
547:H330
543:H310
539:H300
267:KEGG
73:,13a
65:,12a
61:,11b
57:,11a
912:doi
908:498
869:294
801:doi
774:at
487:GHS
318:EPA
291:CID
77:,14
69:,13
53:,10
970::
926:.
918:.
906:.
902:.
879:.
867:.
863:.
815:.
807:.
797:15
795:.
791:.
655:,
651:,
647:,
643:,
639:,
635:,
631:,
627:,
623:,
619:,
615:,
611:,
607:,
603:,
599:,
595:,
591:,
587:,
583:,
579:,
575:,
571:,
567:,
549:,
545:,
541:,
491::
422:33
416:28
89:,8
49:,8
45:,6
41:(4
934:.
914::
887:.
848:.
823:.
803::
678:N
431:7
428:O
425:N
419:H
413:C
320:)
316:(
132:)
91:H
87:H
83:H
79:S
75:S
71:S
67:R
63:S
59:S
55:E
51:S
47:R
43:E
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.