1643:: A degree of matching is also possible and it is often done by only admitting certain age groups or a certain sex into the study population, creating a cohort of people who share similar characteristics and thus all cohorts are comparable in regard to the possible confounding variable. For example, if age and sex are thought to be confounders, only 40 to 50 years old males would be involved in a cohort study that would assess the myocardial infarct risk in cohorts that either are physically active or inactive. Drawback: In cohort studies, the overexclusion of input data may lead researchers to define too narrowly the set of similarly situated persons for whom they claim the study to be useful, such that other persons to whom the causal relationship does in fact apply may lose the opportunity to benefit from the study's recommendations. Similarly, "over-stratification" of input data within a study may reduce the sample size in a given stratum to the point where generalizations drawn by observing the members of that stratum alone are not
1664:: A method where the study population is divided randomly in order to mitigate the chances of self-selection by participants or bias by the study designers. Before the experiment begins, the testers will assign the members of the participant pool to their groups (control, intervention, parallel), using a randomization process such as the use of a random number generator. For example, in a study on the effects of exercise, the conclusions would be less valid if participants were given a choice if they wanted to belong to the control group which would not exercise or the intervention group which would be willing to take part in an exercise program. The study would then capture other variables besides exercise, such as pre-experiment health levels and motivation to adopt healthy activities. From the observer's side, the experimenter may choose candidates who are more likely to show the results the study wants to see or may interpret subjective results (more energetic, positive attitude) in a way favorable to their desires.
1589:, factors such as age, gender, and educational levels often affect health status and so should be controlled. Beyond these factors, researchers may not consider or have access to data on other causal factors. An example is on the study of smoking tobacco on human health. Smoking, drinking alcohol, and diet are lifestyle activities that are related. A risk assessment that looks at the effects of smoking but does not control for alcohol consumption or diet may overestimate the risk of smoking. Smoking and confounding are reviewed in occupational risk assessments such as the safety of coal mining. When there is not a large sample population of non-smokers or non-drinkers in a particular occupation, the risk assessment may be biased towards finding a negative effect on health.
148:
fuel and miles driven for a month and calculate the MPG for each truck. We then run the appropriate analysis, which determines that there is a statistically significant trend that A Trucks are more fuel efficient than B Trucks. Upon further reflection, however, we also notice that A Trucks are more likely to be assigned highway routes, and B Trucks are more likely to be assigned city routes. This is a confounding variable. The confounding variable makes the results of the analysis unreliable. It is quite likely that we are just measuring the fact that highway driving results in better fuel economy than city driving.
1742:
that are currently being performed regularly, but for which there is no concrete evidence of a genuine effect, there may be ethical issues to continue such surgeries. In such circumstances, many of people are exposed to the real risks of surgery yet these treatments may possibly offer no discernible benefit. Sham-surgery control is a method that may allow medical science to determine whether a surgical procedure is efficacious or not. Given that there are known risks associated with medical operations, it is questionably ethical to allow unverified surgeries to be conducted ad infinitum into the future.
5629:
5141:
97:
1517:. Because prognostic factors may influence treatment decisions (and bias estimates of treatment effects), controlling for known prognostic factors may reduce this problem, but it is always possible that a forgotten or unknown factor was not included or that factors interact complexly. Confounding by indication has been described as the most important limitation of observational studies. Randomized trials are not affected by confounding by indication due to
1306:
5127:
1670:: As in the example above, physical activity is thought to be a behaviour that protects from myocardial infarct; and age is assumed to be a possible confounder. The data sampled is then stratified by age group – this means that the association between activity and infarct would be analyzed per each age group. If the different age groups (or age strata) yield much different
5165:
5153:
1086:
152:
up with equal amounts of city and highway driving. That eliminates the confounding variable. Another choice is to quantify the amount of city driving and use that as a second independent variable. A third choice is to segment the study, first comparing MPG during city driving for all trucks, and then run a separate study comparing MPG during highway driving.
1502:, or new drug. For prospective studies, it is difficult to recruit and screen for volunteers with the same background (age, diet, education, geography, etc.), and in historical studies, there can be similar variability. Due to the inability to control for variability of volunteers and human studies, confounding is a particular challenge. For these reasons,
47:
1637:, 4) an avid football player, 5) vegetarian, and 6) working in education. A theoretically perfect control would be a person who, in addition to not having the disease being investigated, matches all these characteristics and has no diseases that the patient does not also have—but finding such a control would be an enormous task.
1616:
Confounding effects may be less likely to occur and act similarly at multiple times and locations. In selecting study sites, the environment can be characterized in detail at the study sites to ensure sites are ecologically similar and therefore less likely to have confounding variables. Lastly, the
151:
In statistics terms, the make of the truck is the independent variable, the fuel economy (MPG) is the dependent variable and the amount of city driving is the confounding variable. To fix this study, we have several choices. One is to randomize the truck assignments so that A trucks and B Trucks end
147:
Let's assume that a trucking company owns a fleet of trucks made by two different manufacturers. Trucks made by one manufacturer are called "A Trucks" and trucks made by the other manufacturer are called "B Trucks." We want to find out whether A Trucks or B Trucks get better fuel economy. We measure
1741:
and may be denied effective treatments. There is a possibility that patients only agree to invasive surgery (which carry real medical risks) under the understanding that they are receiving treatment. Although this is an ethical concern, it is not a complete account of the situation. For surgeries
1597:
A reduction in the potential for the occurrence and effect of confounding factors can be obtained by increasing the types and numbers of comparisons performed in an analysis. If measures or manipulations of core constructs are confounded (i.e. operational or procedural confounds exist), subgroup
1608:
is a process that can assist in reducing instances of confounding, either before study implementation or after analysis has occurred. Peer review relies on collective expertise within a discipline to identify potential weaknesses in study design and analysis, including ways in which results may
1766:
design. Within this design, "groups of people who are initially equivalent (at the pretest phase) are randomly assigned to receive the experimental treatment or a control condition and then assessed again after this differential experience (posttest phase)". Thus, any effects of artifacts are
1627:
assign confounders to both groups, cases and controls, equally. For example, if somebody wanted to study the cause of myocardial infarct and thinks that the age is a probable confounding variable, each 67-year-old infarct patient will be matched with a healthy 67-year-old "control" person. In
1433:
verb "confundere", which meant "mixing", and was probably chosen to represent the confusion (from Latin: con=with + fusus=mix or fuse together) between the cause one wishes to assess and other causes that may affect the outcome and thus confuse, or stand in the way of the desired assessment.
1301:{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}P(Y={\text{recovered}}\mid {\text{do}}(x={\text{give drug}}))={}&P(Y={\text{recovered}}\mid X={\text{give drug}},Z={\text{male}})P(Z={\text{male}})\\&{}+P(Y={\text{recovered}}\mid X={\text{give drug}},Z={\text{female}})P(Z={\text{female}})\end{aligned}}}
1617:
relationship between the environmental variables that possibly confound the analysis and the measured parameters can be studied. The information pertaining to environmental variables can then be used in site-specific models to identify residual variance that may be due to real effects.
1459:
who used the word "confounding" in the sense of "incomparability" of two or more groups (e.g., exposed and unexposed) in an observational study. Formal conditions defining what makes certain groups "comparable" and others "incomparable" were later developed in
1632:
persons whose status vis-à-vis all known potential confounding factors is the same as that of the case's patient: Suppose a case-control study attempts to find the cause of a given disease in a person who is 1) 45 years old, 2) African-American, 3) from
1524:
Confounding variables may also be categorised according to their source. The choice of measurement instrument (operational confound), situational characteristics (procedural confound), or inter-individual differences (person confound).
1452:, whereby certain interactions may be "confounded with blocks". This popularized the notion of confounding in statistics, although Fisher was concerned with the control of heterogeneity in experimental units, not with causal inference.
1733:
sample taken as a whole, such that all potential confounding variables (known and unknown) will be distributed by chance across all study groups and hence will be uncorrelated with the binary variable for inclusion/exclusion in any
1324:
In this way the physician can predict the likely effect of administering the drug from observational studies in which the conditional probabilities appearing on the right-hand side of the equation can be estimated by regression.
1657:
should be the same for the control and treatment groups. By preventing the observers from knowing of their membership, there should be no bias from researchers treating the groups differently or from interpreting the outcomes
1755:. Artifacts are factors that covary with the treatment and the outcome. Campbell and Stanley identify several artifacts. The major threats to internal validity are history, maturation, testing, instrumentation,
1555:
occurs when two or more groups of units are analyzed together (e.g., workers from different occupations), despite varying according to one or more other (observed or unobserved) characteristics (e.g., gender).
989:
730:
1653:: conceals from the trial population and the observers the experiment group membership of the participants. By preventing the participants from knowing if they are receiving treatment or not, the
807:
1613:
can test for the robustness of findings from one study under alternative study conditions or alternative analyses (e.g., controlling for potential confounds not identified in the initial study).
1091:
678:
531:
363:
1076:
1019:
of variables that would guarantee unbiased estimates must be done with caution. The criterion for a proper choice of variables is called the Back-Door and requires that the chosen set
1415:
885:
267:
1578:
Maternal age is directly associated with birth order (the 2nd child, except in the case of twins, is born when the mother is older than she was for the birth of the 1st child)
1537:
and non-experimental research designs. This type of confounding occurs when a measure designed to assess a particular construct inadvertently measures something else as well.
568:
1751:
Artifacts are variables that should have been systematically varied, either within or across studies, but that were accidentally held constant. Artifacts are thus threats to
65:
533:
can be verified from the data generating model, assuming we have all the equations and probabilities associated with the model. This is done by simulating an intervention
611:
430:
887:, can be obtained by "adjusting" for all confounding factors, namely, conditioning on their various values and averaging the result. In the case of a single confounder
2748:
1725:
The best available defense against the possibility of spurious results due to confounding is often to dispense with efforts at stratification and instead conduct a
4262:
1367:
In general, confounding can be controlled by adjustment if and only if there is a set of observed covariates that satisfies the Back-Door condition. Moreover, if
5203:
4767:
1674:, age must be viewed as a confounding variable. There exist statistical tools, among them Mantel–Haenszel methods, that account for stratification of data sets.
1575:
Higher maternal age is directly associated with Down
Syndrome, regardless of birth order (a mother having her 1st vs 3rd child at age 50 confers the same risk)
124:
concept, and as such, cannot be described in terms of correlations or associations. The existence of confounders is an important quantitative explanation why
132:
are explicitly designed to identify the existence, possible existence, or non-existence of confounders in causal relationships between elements of a system.
1628:
case-control studies, matched variables most often are the age and sex. Drawback: Case-control studies are feasible only when it is easy to find controls,
4917:
4541:
3182:
1479:
Graphical criteria were shown to be formally equivalent to the counterfactual definition but more transparent to researchers relying on process models.
5528:
841:
in a randomized experiment). It can be shown that, in cases where only observational data is available, an unbiased estimate of the desired quantity
2342:
Neyman, J., with cooperation of K. Iwaskiewics and St. Kolodziejczyk (1935). Statistical problems in agricultural experimentation (with discussion).
4315:
4754:
2754:(5th ed.). Wiley. pp. 287–302. This textbook has an overview of confounding factors and how to account for them in design of experiments.
1620:
Depending on the type of study design in place, there are various ways to modify that design to actively exclude or control confounding variables:
729:
2840:
1548:. This type of confound occurs when the researcher mistakenly allows another variable to change along with the manipulated independent variable.
452:
are not confounded whenever the observationally witnessed association between them is the same as the association that would be measured in a
2613:
2459:
3177:
2877:
125:
5552:
3781:
2929:
113:
5169:
899:
100:
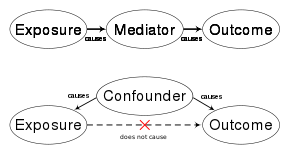
Whereas a mediator is a factor in the causal chain (above), a confounder is a spurious factor incorrectly implying causation (bottom)
5603:
5441:
5196:
4564:
4456:
2821:
2794:
1598:
analysis may not reveal problems in the analysis. Additionally, increasing the number of comparisons can create other problems (see
1031:
that contains an arrow into X. Such sets are called "Back-Door admissible" and may include variables which are not common causes of
83:
4742:
4616:
2605:
2410:
1737:
Ethical considerations: In double-blind and randomized controlled trials, participants are not aware that they are recipients of
1371:
is such a set, then the adjustment formula of Eq. (3) is valid. Pearl's do-calculus provides all possible conditions under which
5616:
5324:
5310:
4800:
4461:
4206:
3577:
3167:
2631:
3791:
2850:
5674:
5621:
4851:
4063:
3870:
3759:
3717:
2765:
2956:
745:
5664:
5094:
4053:
4103:
2047:"Should We Adjust for a Confounder if Empirical and Theoretical Criteria Yield Contradictory Results? A Simulation Study"
1440:
introduced the word "confounding" in his 1935 book "The Design of
Experiments" to refer specifically to a consequence of
1434:
Greenland, Robins and Pearl note an early use of the term "confounding" in causal inference by John Stuart Mill in 1843.
5522:
5487:
5419:
5275:
5189:
4645:
4594:
4579:
4569:
4438:
4310:
4277:
4058:
3888:
616:
469:
301:
4714:
4015:
5643:
5592:
5504:
4989:
4790:
3769:
3438:
2902:
2689:
1667:
1661:
4874:
4841:
5679:
5400:
4846:
4589:
4348:
4254:
4234:
4142:
3853:
3671:
3154:
3026:
2782:
1498:, it is important to control for confounding to isolate the effect of a particular hazard such as a food additive,
689:
4020:
3786:
3644:
2629:
Emanuel, Ezekiel J; Miller, Franklin G (Sep 20, 2001). "The Ethics of
Placebo-Controlled Trials—A Middle Ground".
1015:. The same adjustment formula works when there are multiple confounders except, in this case, the choice of a set
5669:
4606:
4374:
4095:
3949:
3878:
3798:
3656:
3637:
3345:
3066:
4719:
1049:
5578:
5573:
5538:
5422:
5340:
5295:
5290:
5089:
4856:
4404:
4369:
4333:
4118:
3560:
3469:
3428:
3340:
3031:
2870:
1702:
1697:
of the confounding variable than do stratification methods. For example, if multivariate analysis controls for
1644:
1610:
4126:
4110:
1374:
844:
226:
5546:
4998:
4611:
4551:
4488:
3848:
3710:
3700:
3550:
3464:
1682:
1353:
433:
5533:
4759:
4696:
5509:
5453:
5395:
5036:
4966:
4451:
4338:
3335:
3232:
3139:
3018:
2917:
2709:"Why there is no statistical test for confounding, why many think there is, and why they are almost right"
2307:
2298:
Greenland, S.; Robins, J. M. (1986). "Identifiability, exchangeability, and epidemiological confounding".
1788:
5157:
4035:
5638:
5482:
5382:
5356:
5335:
5315:
5252:
5235:
5212:
5061:
5003:
4946:
4772:
4665:
4574:
4300:
4184:
4043:
3925:
3917:
3732:
3628:
3606:
3565:
3530:
3497:
3443:
3418:
3373:
3312:
3272:
3074:
2897:
2356:
Rubin, D. B. (1974). "Estimating causal effects of treatments in randomized and nonrandomized studies".
1800:
1514:
1441:
453:
117:
5628:
5140:
4030:
2593:
1581:
Maternal age is not a consequence of birth order (having a 2nd child does not change the mother's age)
1564:
Say one is studying the relation between birth order (1st child, 2nd child, etc.) and the presence of
536:
5498:
5436:
5430:
4984:
4559:
4508:
4484:
4446:
4364:
4343:
4295:
4174:
4152:
4121:
3907:
3858:
3776:
3749:
3705:
3661:
3423:
3199:
3079:
2060:
1859:
1794:
1763:
1730:
1599:
1449:
1357:
165:
2773:
Brewer, M. B. (2000). "Research design and issues of validity". In Reis, H. T.; Judd, C. M. (eds.).
2312:
5598:
5563:
5472:
5131:
5056:
4979:
4660:
4424:
4417:
4379:
4287:
4267:
4239:
3972:
3838:
3833:
3823:
3815:
3633:
3594:
3484:
3474:
3383:
3162:
3118:
3036:
2961:
2863:
1756:
1686:
185:
4706:
96:
5633:
5240:
5145:
4956:
4810:
4655:
4531:
4428:
4412:
4389:
4166:
3900:
3883:
3843:
3754:
3649:
3611:
3582:
3542:
3502:
3448:
3365:
3051:
3046:
2841:
Tutorial: Confounding and Effect
Measure Modification (Boston University School of Public Health)
2759:
2373:
2280:
2245:
2157:
2051:
1889:
1776:
1624:
1445:
173:
31:
581:
400:
698:, from population data in which drug usage was a patient's choice. The data shows that gender (
5390:
5377:
5367:
5280:
5257:
5249:
5245:
5220:
5051:
5021:
5013:
4833:
4824:
4749:
4680:
4536:
4521:
4496:
4384:
4325:
4191:
4179:
3805:
3722:
3666:
3589:
3433:
3355:
3134:
3008:
2817:
2790:
2648:
2609:
2562:
2513:
2455:
2429:
2325:
2237:
2149:
2086:
1917:
1752:
1518:
136:
2813:
1472:(1974). These were later supplemented by graphical criteria such as the Back-Door condition (
613:. It turns out, however, that graph structure alone is sufficient for verifying the equality
5568:
5262:
5076:
5031:
4795:
4782:
4675:
4650:
4584:
4516:
4394:
4002:
3895:
3828:
3741:
3688:
3507:
3378:
3172:
2971:
2938:
2786:
2640:
2552:
2544:
2503:
2419:
2365:
2317:
2272:
2229:
2191:
2139:
2104:
Shpitser, I.; Pearl, J. (2008). "Complete identification methods for the causal hierarchy".
2076:
2068:
1973:
1948:
1907:
1899:
1785: – Branch of statistics concerned with inferring causal relationships between variables
1782:
1767:(ideally) equally distributed in participants in both the treatment and control conditions.
1545:
571:
105:
2726:
5584:
5514:
5467:
4993:
4737:
4599:
4526:
4201:
4075:
4048:
4025:
3994:
3621:
3616:
3570:
3300:
2951:
2845:
2684:
1650:
1586:
1488:
129:
2064:
5270:
4942:
4937:
3400:
3330:
2976:
2557:
2532:
2081:
2046:
1912:
1877:
1738:
1698:
1654:
1430:
1995:
In
Proceedings of the 49th Session of the International Statistical Science Institute,
825:
because the observational quantity contains information about the correlation between
5658:
5408:
5350:
5285:
5099:
5066:
4929:
4890:
4701:
4670:
4134:
4088:
3693:
3395:
3222:
2986:
2981:
2806:
2775:
2598:
2249:
2124:
1726:
1677:
Controlling for confounding by measuring the known confounders and including them as
1565:
1437:
3252:
2377:
1046:
complies with the Back-Door requirement (i.e., it intercepts the one Back-Door path
5558:
5041:
4974:
4951:
4866:
4196:
3492:
3390:
3325:
3267:
3189:
3144:
2161:
1640:
1510:
1469:
1465:
1461:
1348:
is not a confounder (i.e., the null set is Back-door admissible) and adjusting for
17:
5414:
5330:
5300:
5084:
5046:
4729:
4630:
4492:
4305:
3764:
3681:
3676:
3320:
3277:
3257:
3237:
3227:
2996:
2644:
2490:
Tjønneland, Anne; Grønbæk, Morten; Stripp, Connie; Overvad, Kim (January 1999).
1605:
1473:
1456:
1361:
2708:
2024:
5230:
3930:
3410:
3110:
3041:
2991:
2966:
2886:
2009:
Pearl, J. (2009). Causal
Diagrams and the Identification of Causal Effects In
1671:
1568:
in the child. In this scenario, maternal age would be a confounding variable:
1534:
1503:
702:) influences a patient's choice of drug as well as their chances of recovery (
2144:
1513:, one type is "confounding by indication", which relates to confounding from
5362:
4083:
3935:
3555:
3350:
3262:
3247:
3242:
3207:
2804:
Smith, E. R. (2000). "Research design". In Reis, H. T.; Judd, C. M. (eds.).
2424:
2405:
2196:
2179:
1970:
Experimental and quasi-experimental designs for generalized causal inference
1953:
1936:
1762:
One way to minimize the influence of artifacts is to use a pretest-posttest
1678:
1499:
460:
121:
35:
2652:
2508:
2491:
2433:
2321:
2241:
2153:
2090:
1993:
Pearl, J., (1993). "Aspects of
Graphical Models Connected With Causality",
1921:
2566:
2517:
2406:"Identifying Confounding by Indication through Blinded Prospective Review"
2329:
1572:
Higher maternal age is directly associated with Down
Syndrome in the child
3599:
3217:
3094:
3089:
3084:
3056:
2548:
1759:, selection, experimental mortality, and selection-history interactions.
1509:
In some disciplines, confounding is categorized into different types. In
5181:
5104:
4805:
2492:"Wine intake and diet in a random sample of 48763 Danish men and women"
2284:
2233:
1903:
2836:
These sites contain descriptions or examples of confounding variables.
2072:
5026:
4007:
3981:
3961:
3212:
3003:
2477:
Applied Social
Psychology: Understanding and managing social problems
2369:
1634:
1495:
694:
Consider a researcher attempting to assess the effectiveness of drug
2276:
1709:, then it will ignore that these two classes of antidepressant have
1464:
by
Greenland and Robins (1986) using the counterfactual language of
1328:
Contrary to common beliefs, adding covariates to the adjustment set
1894:
1492:
160:
Confounding is defined in terms of the data generating model. Let
95:
2808:
Handbook of research methods in social and personality psychology
984:{\displaystyle P(y\mid {\text{do}}(x))=\sum _{z}P(y\mid x,z)P(z)}
733:
Causal diagram of Gender as common cause of Drug use and Recovery
2946:
2263:
Kish, L (1959). "Some statistical problems in research design".
1706:
5185:
4915:
4482:
4229:
3528:
3298:
2915:
2859:
1689:. Multivariate analyses reveal much less information about the
1360:." Controls that are not good confounders are sometimes called
2475:
Steg, L.; Buunk, A. P.; Rothengatter, T. (2008). "Chapter 4".
2210:
Fisher, R. A. (1935). The design of experiments (pp. 114–145).
2173:
2171:
2125:"History of the modern epidemiological concept of confounding"
40:
2855:
728:
2723:
Montgomery, D. C. (2001). "Blocking and Confounding in the
2220:
Vandenbroucke, J. P. (2004). "The history of confounding".
2032:
UCLA Cognitive Systems Laboratory, Technical Report (R-493)
1007:
which gives an unbiased estimate for the causal effect of
30:"Confounding factor" redirects here. For the company, see
2005:
2003:
1332:
can introduce bias. A typical counterexample occurs when
2716:
UCLA Computer Science Department, Technical Report R-256
2668:
Experimental and quasi-experimental designs for research
2581:
Handbook of Environmental Risk Assessment and Management
2394:(2nd ed.). New York, NY, US: Cambridge University Press.
2013:(2nd ed.). New York, NY, US: Cambridge University Press.
2533:"Confounding from smoking in occupational epidemiology"
293:
are not confounded if and only if the following holds:
61:
1866:(2nd ed.). New York : Cambridge University Press.
802:{\displaystyle P(y\mid {\text{do}}(x))\neq P(y\mid x)}
2729:
1968:
Shadish, W. R.; Cook, T. D.; Campbell, D. T. (2002).
1377:
1089:
1052:
902:
847:
748:
619:
584:
539:
472:
403:
304:
229:
4768:
Autoregressive conditional heteroskedasticity (ARCH)
2180:"Confounding and Collapsibility in Causal Inference"
1937:"Confounding and Collapsibility in Causal Inference"
574:) and checking whether the resulting probability of
5481:
5376:
5309:
5219:
5075:
5012:
4965:
4928:
4883:
4865:
4832:
4823:
4781:
4728:
4689:
4638:
4629:
4550:
4507:
4437:
4403:
4357:
4324:
4286:
4253:
4165:
4074:
3993:
3948:
3916:
3869:
3814:
3740:
3731:
3541:
3483:
3457:
3409:
3364:
3311:
3198:
3153:
3127:
3109:
3065:
3017:
2937:
2928:
56:
may be too technical for most readers to understand
2805:
2774:
2742:
2597:
1797: – Error in statistical reasoning with groups
1713:effects on myocardial infarction, and one is much
1409:
1300:
1070:
983:
879:
833:, and the interventional quantity does not (since
801:
673:{\displaystyle P(y\mid {\text{do}}(x))=P(y\mid x)}
672:
605:
562:
526:{\displaystyle P(y\mid {\text{do}}(x))=P(y\mid x)}
525:
424:
358:{\displaystyle P(y\mid {\text{do}}(x))=P(y\mid x)}
357:
261:
2812:. New York: Cambridge University Press. pp.
2023:Cinelli, C.; Forney, A.; Pearl, J. (March 2022).
1417:can be estimated, not necessarily by adjustment.
2178:Greenland, S.; Robins, J. M.; Pearl, J. (1999).
1935:Greenland, S.; Robins, J. M.; Pearl, J. (1999).
1506:offer a way to avoid most forms of confounding.
184:, the statistician must suppress the effects of
4316:Multivariate adaptive regression splines (MARS)
1791: – Scientific method in the specific field
1701:, and it does not stratify antidepressants for
1491:evaluating the magnitude and nature of risk to
1779: – Evidence relying on personal testimony
1078:), the Back-Door adjustment formula is valid:
5197:
2871:
8:
2479:. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
2132:Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health
1989:
1987:
1985:
1983:
1023:"blocks" (or intercepts) every path between
114:dependent variable and independent variable
5204:
5190:
5182:
4925:
4912:
4829:
4635:
4504:
4479:
4250:
4226:
3954:
3737:
3538:
3525:
3308:
3295:
2934:
2925:
2912:
2878:
2864:
2856:
2496:The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition
2392:Causality: Models, Reasoning and Inference
2011:Causality: Models, Reasoning and Inference
1864:Causality: Models, Reasoning and Inference
1544:can occur in a laboratory experiment or a
1071:{\displaystyle X\leftarrow Z\rightarrow Y}
891:, this leads to the "adjustment formula":
2734:
2728:
2556:
2507:
2445:
2443:
2423:
2311:
2195:
2143:
2080:
2025:"A Crash Course in Good and Bad Controls"
1952:
1911:
1893:
1476:1993; Greenland, Robins and Pearl 1999).
1455:According to Vandenbroucke (2004) it was
1448:) the set of treatment combinations in a
1390:
1376:
1286:
1266:
1252:
1238:
1221:
1206:
1186:
1172:
1158:
1142:
1128:
1114:
1106:
1090:
1088:
1051:
1042:Returning to the drug use example, since
939:
915:
901:
860:
846:
761:
747:
632:
618:
583:
540:
538:
485:
471:
444:. Intuitively, this equality states that
402:
317:
303:
242:
228:
84:Learn how and when to remove this message
68:, without removing the technical details.
2666:Campbell, D. T.; Stanley, J. C. (1966).
2106:The Journal of Machine Learning Research
1876:VanderWeele, T.J.; Shpitser, I. (2013).
1721:All these methods have their drawbacks:
1593:Decreasing the potential for confounding
1851:
1815:
1410:{\displaystyle P(y\mid {\text{do}}(x))}
880:{\displaystyle P(y\mid {\text{do}}(x))}
262:{\displaystyle P(y\mid {\text{do}}(x))}
112:is a variable that influences both the
4842:Kaplan–Meier estimator (product limit)
2757:
2537:British Journal of Industrial Medicine
1425:According to Morabia (2011), the word
204:are confounded by some other variable
27:Variable or factor in causal inference
2851:Tutorial by University of New England
2300:International Journal of Epidemiology
1862:, Confounding, and Collapsibility In
66:make it understandable to non-experts
7:
5152:
4852:Accelerated failure time (AFT) model
2681:Crano, W. D.; Brewer, M. B. (2002).
1080:
893:
739:
466:In principle, the defining equality
295:
277:under the hypothetical intervention
126:correlation does not imply causation
5553:Generalized randomized block design
5164:
4447:Analysis of variance (ANOVA, anova)
2846:Linear Regression (Yale University)
1878:"On the definition of a confounder"
578:equals the conditional probability
34:. For the psychological state, see
4542:Cochran–Mantel–Haenszel statistics
3168:Pearson product-moment correlation
2752:Design and Analysis of Experiments
1609:depend on confounding. Similarly,
25:
5604:Sequential probability ratio test
2606:Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
2452:Conducting Research in Psychology
2358:Journal of Educational Psychology
5627:
5529:Polynomial and rational modeling
5163:
5151:
5139:
5126:
5125:
2411:American Journal of Epidemiology
563:{\displaystyle {\text{do}}(X=x)}
45:
4801:Least-squares spectral analysis
2632:New England Journal of Medicine
710:confounds the relation between
5296:Replication versus subsampling
3782:Mean-unbiased minimum-variance
1404:
1401:
1395:
1381:
1291:
1277:
1271:
1229:
1211:
1197:
1191:
1149:
1136:
1133:
1119:
1097:
1062:
1056:
1039:, but merely proxies thereof.
978:
972:
966:
948:
929:
926:
920:
906:
874:
871:
865:
851:
796:
784:
775:
772:
766:
752:
667:
655:
646:
643:
637:
623:
600:
588:
557:
545:
520:
508:
499:
496:
490:
476:
419:
407:
352:
340:
331:
328:
322:
308:
256:
253:
247:
233:
1:
5095:Geographic information system
4311:Simultaneous equations models
5523:Response surface methodology
5431:Analysis of variance (Anova)
4278:Coefficient of determination
3889:Uniformly most powerful test
2688:(2nd ed.). Mahwah, NJ:
1352:would create bias known as "
706:). In this scenario, gender
269:be the probability of event
176:. To estimate the effect of
5593:Randomized controlled trial
4847:Proportional hazards models
4791:Spectral density estimation
4773:Vector autoregression (VAR)
4207:Maximum posterior estimator
3439:Randomized controlled trial
2690:Lawrence Erlbaum Associates
2645:10.1056/nejm200109203451211
2344:Suppl J Roy Statist Soc Ser
1662:Randomized controlled trial
5696:
4607:Multivariate distributions
3027:Average absolute deviation
2835:
2783:Cambridge University Press
2764:: CS1 maint: postscript (
2707:Pearl, J. (January 1998).
2683:Principles and methods of
690:Controlling for a variable
687:
606:{\displaystyle P(y\mid x)}
425:{\displaystyle P(y\mid x)}
29:
5612:
5121:
4924:
4911:
4595:Structural equation model
4503:
4478:
4249:
4225:
3957:
3931:Score/Lagrange multiplier
3537:
3524:
3346:Sample size determination
3307:
3294:
2924:
2911:
2893:
1645:statistically significant
212:causally influences both
135:Confounds are threats to
5579:Repeated measures design
5291:Restricted randomization
5090:Environmental statistics
4612:Elliptical distributions
4405:Generalized linear model
4334:Simple linear regression
4104:Hodges–Lehmann estimator
3561:Probability distribution
3470:Stochastic approximation
3032:Coefficient of variation
2670:. Chicago: Rand McNally.
2600:Epidemiology in Medicine
2404:Johnston, S. C. (2001).
2145:10.1136/jech.2010.112565
4750:Cross-correlation (XCF)
4358:Non-standard predictors
3792:Lehmann–Scheffé theorem
3465:Adaptive clinical trial
2579:Calow, Peter P. (2009)
1531:operational confounding
837:is not correlated with
434:conditional probability
5634:Mathematics portal
5396:Ordinary least squares
5146:Mathematics portal
4967:Engineering statistics
4875:Nelson–Aalen estimator
4452:Analysis of covariance
4339:Ordinary least squares
4263:Pearson product-moment
3667:Statistical functional
3578:Empirical distribution
3411:Controlled experiments
3140:Frequency distribution
2918:Descriptive statistics
2744:
2454:. Belmont: Wadsworth.
2450:Pelham, Brett (2006).
1832:extraneous determinant
1789:Epidemiological method
1757:statistical regression
1683:multivariable analysis
1542:procedural confounding
1411:
1336:is a common effect of
1302:
1072:
985:
881:
803:
734:
674:
607:
564:
527:
426:
359:
263:
101:
5675:Design of experiments
5231:Scientific experiment
5213:Design of experiments
5062:Population statistics
5004:System identification
4738:Autocorrelation (ACF)
4666:Exponential smoothing
4580:Discriminant analysis
4575:Canonical correlation
4439:Partition of variance
4301:Regression validation
4145:(Jonckheere–Terpstra)
4044:Likelihood-ratio test
3733:Frequentist inference
3645:Location–scale family
3566:Sampling distribution
3531:Statistical inference
3498:Cross-sectional study
3485:Observational studies
3444:Randomized experiment
3273:Stem-and-leaf display
3075:Central limit theorem
2745:
2743:{\displaystyle 2^{k}}
2425:10.1093/aje/154.3.276
2197:10.1214/ss/1009211805
1954:10.1214/ss/1009211805
1801:Omitted-variable bias
1515:observational studies
1412:
1303:
1073:
986:
882:
804:
732:
675:
608:
565:
528:
454:controlled experiment
427:
360:
264:
99:
5665:Analysis of variance
5505:Fractional factorial
4985:Probabilistic design
4570:Principal components
4413:Exponential families
4365:Nonlinear regression
4344:General linear model
4306:Mixed effects models
4296:Errors and residuals
4273:Confounding variable
4175:Bayesian probability
4153:Van der Waerden test
4143:Ordered alternative
3908:Multiple comparisons
3787:Rao–Blackwellization
3750:Estimating equations
3706:Statistical distance
3424:Factorial experiment
2957:Arithmetic-Geometric
2777:Handbook of Research
2727:
2549:10.1136/oem.46.8.505
2531:Axelson, O. (1989).
2509:10.1093/ajcn/69.1.49
2322:10.1093/ije/15.3.413
1882:Annals of Statistics
1824:confounding variable
1625:Case-control studies
1600:multiple comparisons
1450:factorial experiment
1375:
1087:
1050:
900:
845:
746:
617:
582:
537:
470:
401:
302:
227:
188:that influence both
186:extraneous variables
166:independent variable
120:. Confounding is a
118:spurious association
5639:Statistical outline
5599:Sequential analysis
5564:Graeco-Latin square
5473:Multiple comparison
5420:Hierarchical model:
5057:Official statistics
4980:Methods engineering
4661:Seasonal adjustment
4429:Poisson regressions
4349:Bayesian regression
4288:Regression analysis
4268:Partial correlation
4240:Regression analysis
3839:Prediction interval
3834:Likelihood interval
3824:Confidence interval
3816:Interval estimation
3777:Unbiased estimators
3595:Model specification
3475:Up-and-down designs
3163:Partial correlation
3119:Index of dispersion
3037:Interquartile range
2750:Factorial Design".
2390:Pearl, J., (2009).
2184:Statistical Science
2123:Morabia, A (2011).
2065:2014NatSR...4E6085L
2045:Lee, P. H. (2014).
1941:Statistical Science
1858:Pearl, J., (2009).
1687:regression analysis
718:is a cause of both
5644:Statistical topics
5236:Statistical design
5077:Spatial statistics
4957:Medical statistics
4857:First hitting time
4811:Whittle likelihood
4462:Degrees of freedom
4457:Multivariate ANOVA
4390:Heteroscedasticity
4202:Bayesian estimator
4167:Bayesian inference
4016:Kolmogorov–Smirnov
3901:Randomization test
3871:Testing hypotheses
3844:Tolerance interval
3755:Maximum likelihood
3650:Exponential family
3583:Density estimation
3543:Statistical theory
3503:Natural experiment
3449:Scientific control
3366:Survey methodology
3052:Standard deviation
2740:
2234:10.1007/BF01326402
1904:10.1214/12-aos1058
1828:confounding factor
1777:Anecdotal evidence
1731:sufficiently large
1553:person confounding
1533:can occur in both
1407:
1344:, a case in which
1298:
1296:
1068:
981:
944:
877:
799:
735:
670:
603:
560:
523:
422:
355:
259:
174:dependent variable
102:
32:Confounding Factor
18:Confounding factor
5680:Experimental bias
5652:
5651:
5539:Central composite
5437:Cochran's theorem
5391:Linear regression
5368:Nuisance variable
5281:Random assignment
5258:Experimental unit
5179:
5178:
5117:
5116:
5113:
5112:
5052:National accounts
5022:Actuarial science
5014:Social statistics
4907:
4906:
4903:
4902:
4899:
4898:
4834:Survival function
4819:
4818:
4681:Granger causality
4522:Contingency table
4497:Survival analysis
4474:
4473:
4470:
4469:
4326:Linear regression
4221:
4220:
4217:
4216:
4192:Credible interval
4161:
4160:
3944:
3943:
3760:Method of moments
3629:Parametric family
3590:Statistical model
3520:
3519:
3516:
3515:
3434:Random assignment
3356:Statistical power
3290:
3289:
3286:
3285:
3135:Contingency table
3105:
3104:
2972:Generalized/power
2615:978-0-316-35636-7
2594:Mayrent, Sherry L
2461:978-0-534-53294-9
2073:10.1038/srep06085
1860:Simpson's Paradox
1795:Simpson's paradox
1753:external validity
1519:random assignment
1429:derives from the
1393:
1358:Berkson's paradox
1322:
1321:
1289:
1269:
1255:
1241:
1209:
1189:
1175:
1161:
1131:
1117:
1109:
1005:
1004:
935:
918:
863:
823:
822:
764:
635:
543:
488:
379:
378:
320:
245:
137:internal validity
94:
93:
86:
16:(Redirected from
5687:
5670:Causal inference
5632:
5631:
5569:Orthogonal array
5206:
5199:
5192:
5183:
5167:
5166:
5155:
5154:
5144:
5143:
5129:
5128:
5032:Crime statistics
4926:
4913:
4830:
4796:Fourier analysis
4783:Frequency domain
4763:
4710:
4676:Structural break
4636:
4585:Cluster analysis
4532:Log-linear model
4505:
4480:
4421:
4395:Homoscedasticity
4251:
4227:
4146:
4138:
4130:
4129:(Kruskal–Wallis)
4114:
4099:
4054:Cross validation
4039:
4021:Anderson–Darling
3968:
3955:
3926:Likelihood-ratio
3918:Parametric tests
3896:Permutation test
3879:1- & 2-tails
3770:Minimum distance
3742:Point estimation
3738:
3689:Optimal decision
3640:
3539:
3526:
3508:Quasi-experiment
3458:Adaptive designs
3309:
3296:
3173:Rank correlation
2935:
2926:
2913:
2880:
2873:
2866:
2857:
2827:
2811:
2800:
2780:
2769:
2763:
2755:
2749:
2747:
2746:
2741:
2739:
2738:
2719:
2713:
2694:
2693:
2678:
2672:
2671:
2663:
2657:
2656:
2626:
2620:
2619:
2603:
2590:
2584:
2577:
2571:
2570:
2560:
2528:
2522:
2521:
2511:
2487:
2481:
2480:
2472:
2466:
2465:
2447:
2438:
2437:
2427:
2401:
2395:
2388:
2382:
2381:
2370:10.1037/h0037350
2353:
2347:
2340:
2334:
2333:
2315:
2295:
2289:
2288:
2260:
2254:
2253:
2222:Soz Praventivmed
2217:
2211:
2208:
2202:
2201:
2199:
2175:
2166:
2165:
2147:
2129:
2120:
2114:
2113:
2101:
2095:
2094:
2084:
2042:
2036:
2035:
2029:
2020:
2014:
2007:
1998:
1991:
1978:
1977:
1974:Houghton-Mifflin
1965:
1959:
1958:
1956:
1932:
1926:
1925:
1915:
1897:
1873:
1867:
1856:
1839:
1836:lurking variable
1822:Also known as a
1820:
1783:Causal inference
1727:randomized study
1587:risk assessments
1546:quasi-experiment
1489:risk assessments
1416:
1414:
1413:
1408:
1394:
1391:
1316:
1307:
1305:
1304:
1299:
1297:
1290:
1287:
1270:
1267:
1256:
1253:
1242:
1239:
1222:
1217:
1210:
1207:
1190:
1187:
1176:
1173:
1162:
1159:
1143:
1132:
1129:
1118:
1115:
1110:
1107:
1081:
1077:
1075:
1074:
1069:
999:
990:
988:
987:
982:
943:
919:
916:
894:
886:
884:
883:
878:
864:
861:
817:
808:
806:
805:
800:
765:
762:
740:
679:
677:
676:
671:
636:
633:
612:
610:
609:
604:
572:Bayesian network
569:
567:
566:
561:
544:
541:
532:
530:
529:
524:
489:
486:
431:
429:
428:
423:
373:
364:
362:
361:
356:
321:
318:
296:
268:
266:
265:
260:
246:
243:
106:causal inference
89:
82:
78:
75:
69:
49:
48:
41:
21:
5695:
5694:
5690:
5689:
5688:
5686:
5685:
5684:
5655:
5654:
5653:
5648:
5626:
5608:
5585:Crossover study
5576:
5574:Latin hypercube
5510:Plackett–Burman
5489:
5486:
5485:
5477:
5380:
5372:
5313:
5305:
5222:
5215:
5210:
5180:
5175:
5138:
5109:
5071:
5008:
4994:quality control
4961:
4943:Clinical trials
4920:
4895:
4879:
4867:Hazard function
4861:
4815:
4777:
4761:
4724:
4720:Breusch–Godfrey
4708:
4685:
4625:
4600:Factor analysis
4546:
4527:Graphical model
4499:
4466:
4433:
4419:
4399:
4353:
4320:
4282:
4245:
4244:
4213:
4157:
4144:
4136:
4128:
4112:
4097:
4076:Rank statistics
4070:
4049:Model selection
4037:
3995:Goodness of fit
3989:
3966:
3940:
3912:
3865:
3810:
3799:Median unbiased
3727:
3638:
3571:Order statistic
3533:
3512:
3479:
3453:
3405:
3360:
3303:
3301:Data collection
3282:
3194:
3149:
3123:
3101:
3061:
3013:
2930:Continuous data
2920:
2907:
2889:
2884:
2837:
2834:
2824:
2803:
2797:
2772:
2756:
2730:
2725:
2724:
2722:
2711:
2706:
2703:
2701:Further reading
2698:
2697:
2685:social research
2680:
2679:
2675:
2665:
2664:
2660:
2628:
2627:
2623:
2616:
2592:
2591:
2587:
2578:
2574:
2530:
2529:
2525:
2489:
2488:
2484:
2474:
2473:
2469:
2462:
2449:
2448:
2441:
2403:
2402:
2398:
2389:
2385:
2355:
2354:
2350:
2341:
2337:
2313:10.1.1.157.6445
2297:
2296:
2292:
2277:10.2307/2089381
2262:
2261:
2257:
2219:
2218:
2214:
2209:
2205:
2177:
2176:
2169:
2127:
2122:
2121:
2117:
2103:
2102:
2098:
2044:
2043:
2039:
2027:
2022:
2021:
2017:
2008:
2001:
1992:
1981:
1967:
1966:
1962:
1934:
1933:
1929:
1875:
1874:
1870:
1857:
1853:
1848:
1843:
1842:
1821:
1817:
1812:
1806:
1773:
1749:
1739:sham treatments
1717:than the other.
1651:Double blinding
1595:
1562:
1487:In the case of
1485:
1423:
1373:
1372:
1314:
1295:
1294:
1215:
1214:
1144:
1085:
1084:
1048:
1047:
997:
898:
897:
843:
842:
815:
744:
743:
692:
686:
615:
614:
580:
579:
535:
534:
468:
467:
399:
398:
381:for all values
371:
300:
299:
225:
224:
158:
145:
90:
79:
73:
70:
62:help improve it
59:
50:
46:
39:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
5693:
5691:
5683:
5682:
5677:
5672:
5667:
5657:
5656:
5650:
5649:
5647:
5646:
5641:
5636:
5624:
5619:
5613:
5610:
5609:
5607:
5606:
5601:
5596:
5588:
5587:
5582:
5571:
5566:
5561:
5556:
5550:
5542:
5541:
5536:
5531:
5526:
5518:
5517:
5512:
5507:
5502:
5494:
5492:
5479:
5478:
5476:
5475:
5470:
5464:
5463:
5451:
5439:
5434:
5426:
5425:
5417:
5412:
5404:
5403:
5398:
5393:
5387:
5385:
5374:
5373:
5371:
5370:
5365:
5360:
5353:
5348:
5343:
5338:
5333:
5328:
5320:
5318:
5307:
5306:
5304:
5303:
5298:
5293:
5288:
5283:
5278:
5271:Optimal design
5266:
5265:
5260:
5255:
5243:
5238:
5233:
5227:
5225:
5217:
5216:
5211:
5209:
5208:
5201:
5194:
5186:
5177:
5176:
5174:
5173:
5161:
5149:
5135:
5122:
5119:
5118:
5115:
5114:
5111:
5110:
5108:
5107:
5102:
5097:
5092:
5087:
5081:
5079:
5073:
5072:
5070:
5069:
5064:
5059:
5054:
5049:
5044:
5039:
5034:
5029:
5024:
5018:
5016:
5010:
5009:
5007:
5006:
5001:
4996:
4987:
4982:
4977:
4971:
4969:
4963:
4962:
4960:
4959:
4954:
4949:
4940:
4938:Bioinformatics
4934:
4932:
4922:
4921:
4916:
4909:
4908:
4905:
4904:
4901:
4900:
4897:
4896:
4894:
4893:
4887:
4885:
4881:
4880:
4878:
4877:
4871:
4869:
4863:
4862:
4860:
4859:
4854:
4849:
4844:
4838:
4836:
4827:
4821:
4820:
4817:
4816:
4814:
4813:
4808:
4803:
4798:
4793:
4787:
4785:
4779:
4778:
4776:
4775:
4770:
4765:
4757:
4752:
4747:
4746:
4745:
4743:partial (PACF)
4734:
4732:
4726:
4725:
4723:
4722:
4717:
4712:
4704:
4699:
4693:
4691:
4690:Specific tests
4687:
4686:
4684:
4683:
4678:
4673:
4668:
4663:
4658:
4653:
4648:
4642:
4640:
4633:
4627:
4626:
4624:
4623:
4622:
4621:
4620:
4619:
4604:
4603:
4602:
4592:
4590:Classification
4587:
4582:
4577:
4572:
4567:
4562:
4556:
4554:
4548:
4547:
4545:
4544:
4539:
4537:McNemar's test
4534:
4529:
4524:
4519:
4513:
4511:
4501:
4500:
4483:
4476:
4475:
4472:
4471:
4468:
4467:
4465:
4464:
4459:
4454:
4449:
4443:
4441:
4435:
4434:
4432:
4431:
4415:
4409:
4407:
4401:
4400:
4398:
4397:
4392:
4387:
4382:
4377:
4375:Semiparametric
4372:
4367:
4361:
4359:
4355:
4354:
4352:
4351:
4346:
4341:
4336:
4330:
4328:
4322:
4321:
4319:
4318:
4313:
4308:
4303:
4298:
4292:
4290:
4284:
4283:
4281:
4280:
4275:
4270:
4265:
4259:
4257:
4247:
4246:
4243:
4242:
4237:
4231:
4230:
4223:
4222:
4219:
4218:
4215:
4214:
4212:
4211:
4210:
4209:
4199:
4194:
4189:
4188:
4187:
4182:
4171:
4169:
4163:
4162:
4159:
4158:
4156:
4155:
4150:
4149:
4148:
4140:
4132:
4116:
4113:(Mann–Whitney)
4108:
4107:
4106:
4093:
4092:
4091:
4080:
4078:
4072:
4071:
4069:
4068:
4067:
4066:
4061:
4056:
4046:
4041:
4038:(Shapiro–Wilk)
4033:
4028:
4023:
4018:
4013:
4005:
3999:
3997:
3991:
3990:
3988:
3987:
3979:
3970:
3958:
3952:
3950:Specific tests
3946:
3945:
3942:
3941:
3939:
3938:
3933:
3928:
3922:
3920:
3914:
3913:
3911:
3910:
3905:
3904:
3903:
3893:
3892:
3891:
3881:
3875:
3873:
3867:
3866:
3864:
3863:
3862:
3861:
3856:
3846:
3841:
3836:
3831:
3826:
3820:
3818:
3812:
3811:
3809:
3808:
3803:
3802:
3801:
3796:
3795:
3794:
3789:
3774:
3773:
3772:
3767:
3762:
3757:
3746:
3744:
3735:
3729:
3728:
3726:
3725:
3720:
3715:
3714:
3713:
3703:
3698:
3697:
3696:
3686:
3685:
3684:
3679:
3674:
3664:
3659:
3654:
3653:
3652:
3647:
3642:
3626:
3625:
3624:
3619:
3614:
3604:
3603:
3602:
3597:
3587:
3586:
3585:
3575:
3574:
3573:
3563:
3558:
3553:
3547:
3545:
3535:
3534:
3529:
3522:
3521:
3518:
3517:
3514:
3513:
3511:
3510:
3505:
3500:
3495:
3489:
3487:
3481:
3480:
3478:
3477:
3472:
3467:
3461:
3459:
3455:
3454:
3452:
3451:
3446:
3441:
3436:
3431:
3426:
3421:
3415:
3413:
3407:
3406:
3404:
3403:
3401:Standard error
3398:
3393:
3388:
3387:
3386:
3381:
3370:
3368:
3362:
3361:
3359:
3358:
3353:
3348:
3343:
3338:
3333:
3331:Optimal design
3328:
3323:
3317:
3315:
3305:
3304:
3299:
3292:
3291:
3288:
3287:
3284:
3283:
3281:
3280:
3275:
3270:
3265:
3260:
3255:
3250:
3245:
3240:
3235:
3230:
3225:
3220:
3215:
3210:
3204:
3202:
3196:
3195:
3193:
3192:
3187:
3186:
3185:
3180:
3170:
3165:
3159:
3157:
3151:
3150:
3148:
3147:
3142:
3137:
3131:
3129:
3128:Summary tables
3125:
3124:
3122:
3121:
3115:
3113:
3107:
3106:
3103:
3102:
3100:
3099:
3098:
3097:
3092:
3087:
3077:
3071:
3069:
3063:
3062:
3060:
3059:
3054:
3049:
3044:
3039:
3034:
3029:
3023:
3021:
3015:
3014:
3012:
3011:
3006:
3001:
3000:
2999:
2994:
2989:
2984:
2979:
2974:
2969:
2964:
2962:Contraharmonic
2959:
2954:
2943:
2941:
2932:
2922:
2921:
2916:
2909:
2908:
2906:
2905:
2900:
2894:
2891:
2890:
2885:
2883:
2882:
2875:
2868:
2860:
2854:
2853:
2848:
2843:
2833:
2832:External links
2830:
2829:
2828:
2822:
2801:
2795:
2770:
2737:
2733:
2720:
2702:
2699:
2696:
2695:
2673:
2658:
2621:
2614:
2585:
2572:
2523:
2482:
2467:
2460:
2439:
2418:(3): 276–284.
2396:
2383:
2364:(5): 688–701.
2348:
2335:
2306:(3): 413–419.
2290:
2271:(3): 328–338.
2255:
2228:(4): 216–224.
2212:
2203:
2167:
2138:(4): 297–300.
2115:
2096:
2037:
2015:
1999:
1979:
1972:. Boston, MA:
1960:
1927:
1888:(1): 196–220.
1868:
1850:
1849:
1847:
1844:
1841:
1840:
1814:
1813:
1811:
1808:
1804:
1803:
1798:
1792:
1786:
1780:
1772:
1769:
1748:
1745:
1744:
1743:
1735:
1719:
1718:
1699:antidepressant
1675:
1668:Stratification
1665:
1659:
1655:placebo effect
1648:
1641:Cohort studies
1638:
1594:
1591:
1583:
1582:
1579:
1576:
1573:
1561:
1558:
1557:
1556:
1549:
1538:
1484:
1481:
1431:Medieval Latin
1422:
1419:
1406:
1403:
1400:
1397:
1389:
1386:
1383:
1380:
1320:
1319:
1310:
1308:
1293:
1285:
1282:
1279:
1276:
1273:
1265:
1262:
1259:
1251:
1248:
1245:
1237:
1234:
1231:
1228:
1225:
1220:
1218:
1216:
1213:
1205:
1202:
1199:
1196:
1193:
1185:
1182:
1179:
1171:
1168:
1165:
1157:
1154:
1151:
1148:
1145:
1141:
1138:
1135:
1127:
1124:
1121:
1113:
1105:
1102:
1099:
1096:
1093:
1092:
1067:
1064:
1061:
1058:
1055:
1003:
1002:
993:
991:
980:
977:
974:
971:
968:
965:
962:
959:
956:
953:
950:
947:
942:
938:
934:
931:
928:
925:
922:
914:
911:
908:
905:
876:
873:
870:
867:
859:
856:
853:
850:
821:
820:
811:
809:
798:
795:
792:
789:
786:
783:
780:
777:
774:
771:
768:
760:
757:
754:
751:
685:
682:
669:
666:
663:
660:
657:
654:
651:
648:
645:
642:
639:
631:
628:
625:
622:
602:
599:
596:
593:
590:
587:
559:
556:
553:
550:
547:
522:
519:
516:
513:
510:
507:
504:
501:
498:
495:
492:
484:
481:
478:
475:
421:
418:
415:
412:
409:
406:
377:
376:
367:
365:
354:
351:
348:
345:
342:
339:
336:
333:
330:
327:
324:
316:
313:
310:
307:
258:
255:
252:
249:
241:
238:
235:
232:
196:. We say that
157:
154:
144:
143:Simple Example
141:
92:
91:
74:September 2019
53:
51:
44:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
5692:
5681:
5678:
5676:
5673:
5671:
5668:
5666:
5663:
5662:
5660:
5645:
5642:
5640:
5637:
5635:
5630:
5625:
5623:
5620:
5618:
5615:
5614:
5611:
5605:
5602:
5600:
5597:
5595:
5594:
5590:
5589:
5586:
5583:
5581:
5580:
5575:
5572:
5570:
5567:
5565:
5562:
5560:
5557:
5554:
5551:
5549:
5548:
5544:
5543:
5540:
5537:
5535:
5532:
5530:
5527:
5525:
5524:
5520:
5519:
5516:
5513:
5511:
5508:
5506:
5503:
5501:
5500:
5496:
5495:
5493:
5491:
5484:
5480:
5474:
5471:
5469:
5468:Compare means
5466:
5465:
5462:
5460:
5456:
5452:
5450:
5448:
5444:
5440:
5438:
5435:
5433:
5432:
5428:
5427:
5424:
5421:
5418:
5416:
5413:
5411:
5410:
5409:Random effect
5406:
5405:
5402:
5399:
5397:
5394:
5392:
5389:
5388:
5386:
5384:
5379:
5375:
5369:
5366:
5364:
5361:
5359:
5358:
5354:
5352:
5351:Orthogonality
5349:
5347:
5344:
5342:
5339:
5337:
5334:
5332:
5329:
5327:
5326:
5322:
5321:
5319:
5317:
5312:
5308:
5302:
5299:
5297:
5294:
5292:
5289:
5287:
5286:Randomization
5284:
5282:
5279:
5277:
5273:
5272:
5268:
5267:
5264:
5261:
5259:
5256:
5254:
5251:
5247:
5244:
5242:
5239:
5237:
5234:
5232:
5229:
5228:
5226:
5224:
5218:
5214:
5207:
5202:
5200:
5195:
5193:
5188:
5187:
5184:
5172:
5171:
5162:
5160:
5159:
5150:
5148:
5147:
5142:
5136:
5134:
5133:
5124:
5123:
5120:
5106:
5103:
5101:
5100:Geostatistics
5098:
5096:
5093:
5091:
5088:
5086:
5083:
5082:
5080:
5078:
5074:
5068:
5067:Psychometrics
5065:
5063:
5060:
5058:
5055:
5053:
5050:
5048:
5045:
5043:
5040:
5038:
5035:
5033:
5030:
5028:
5025:
5023:
5020:
5019:
5017:
5015:
5011:
5005:
5002:
5000:
4997:
4995:
4991:
4988:
4986:
4983:
4981:
4978:
4976:
4973:
4972:
4970:
4968:
4964:
4958:
4955:
4953:
4950:
4948:
4944:
4941:
4939:
4936:
4935:
4933:
4931:
4930:Biostatistics
4927:
4923:
4919:
4914:
4910:
4892:
4891:Log-rank test
4889:
4888:
4886:
4882:
4876:
4873:
4872:
4870:
4868:
4864:
4858:
4855:
4853:
4850:
4848:
4845:
4843:
4840:
4839:
4837:
4835:
4831:
4828:
4826:
4822:
4812:
4809:
4807:
4804:
4802:
4799:
4797:
4794:
4792:
4789:
4788:
4786:
4784:
4780:
4774:
4771:
4769:
4766:
4764:
4762:(Box–Jenkins)
4758:
4756:
4753:
4751:
4748:
4744:
4741:
4740:
4739:
4736:
4735:
4733:
4731:
4727:
4721:
4718:
4716:
4715:Durbin–Watson
4713:
4711:
4705:
4703:
4700:
4698:
4697:Dickey–Fuller
4695:
4694:
4692:
4688:
4682:
4679:
4677:
4674:
4672:
4671:Cointegration
4669:
4667:
4664:
4662:
4659:
4657:
4654:
4652:
4649:
4647:
4646:Decomposition
4644:
4643:
4641:
4637:
4634:
4632:
4628:
4618:
4615:
4614:
4613:
4610:
4609:
4608:
4605:
4601:
4598:
4597:
4596:
4593:
4591:
4588:
4586:
4583:
4581:
4578:
4576:
4573:
4571:
4568:
4566:
4563:
4561:
4558:
4557:
4555:
4553:
4549:
4543:
4540:
4538:
4535:
4533:
4530:
4528:
4525:
4523:
4520:
4518:
4517:Cohen's kappa
4515:
4514:
4512:
4510:
4506:
4502:
4498:
4494:
4490:
4486:
4481:
4477:
4463:
4460:
4458:
4455:
4453:
4450:
4448:
4445:
4444:
4442:
4440:
4436:
4430:
4426:
4422:
4416:
4414:
4411:
4410:
4408:
4406:
4402:
4396:
4393:
4391:
4388:
4386:
4383:
4381:
4378:
4376:
4373:
4371:
4370:Nonparametric
4368:
4366:
4363:
4362:
4360:
4356:
4350:
4347:
4345:
4342:
4340:
4337:
4335:
4332:
4331:
4329:
4327:
4323:
4317:
4314:
4312:
4309:
4307:
4304:
4302:
4299:
4297:
4294:
4293:
4291:
4289:
4285:
4279:
4276:
4274:
4271:
4269:
4266:
4264:
4261:
4260:
4258:
4256:
4252:
4248:
4241:
4238:
4236:
4233:
4232:
4228:
4224:
4208:
4205:
4204:
4203:
4200:
4198:
4195:
4193:
4190:
4186:
4183:
4181:
4178:
4177:
4176:
4173:
4172:
4170:
4168:
4164:
4154:
4151:
4147:
4141:
4139:
4133:
4131:
4125:
4124:
4123:
4120:
4119:Nonparametric
4117:
4115:
4109:
4105:
4102:
4101:
4100:
4094:
4090:
4089:Sample median
4087:
4086:
4085:
4082:
4081:
4079:
4077:
4073:
4065:
4062:
4060:
4057:
4055:
4052:
4051:
4050:
4047:
4045:
4042:
4040:
4034:
4032:
4029:
4027:
4024:
4022:
4019:
4017:
4014:
4012:
4010:
4006:
4004:
4001:
4000:
3998:
3996:
3992:
3986:
3984:
3980:
3978:
3976:
3971:
3969:
3964:
3960:
3959:
3956:
3953:
3951:
3947:
3937:
3934:
3932:
3929:
3927:
3924:
3923:
3921:
3919:
3915:
3909:
3906:
3902:
3899:
3898:
3897:
3894:
3890:
3887:
3886:
3885:
3882:
3880:
3877:
3876:
3874:
3872:
3868:
3860:
3857:
3855:
3852:
3851:
3850:
3847:
3845:
3842:
3840:
3837:
3835:
3832:
3830:
3827:
3825:
3822:
3821:
3819:
3817:
3813:
3807:
3804:
3800:
3797:
3793:
3790:
3788:
3785:
3784:
3783:
3780:
3779:
3778:
3775:
3771:
3768:
3766:
3763:
3761:
3758:
3756:
3753:
3752:
3751:
3748:
3747:
3745:
3743:
3739:
3736:
3734:
3730:
3724:
3721:
3719:
3716:
3712:
3709:
3708:
3707:
3704:
3702:
3699:
3695:
3694:loss function
3692:
3691:
3690:
3687:
3683:
3680:
3678:
3675:
3673:
3670:
3669:
3668:
3665:
3663:
3660:
3658:
3655:
3651:
3648:
3646:
3643:
3641:
3635:
3632:
3631:
3630:
3627:
3623:
3620:
3618:
3615:
3613:
3610:
3609:
3608:
3605:
3601:
3598:
3596:
3593:
3592:
3591:
3588:
3584:
3581:
3580:
3579:
3576:
3572:
3569:
3568:
3567:
3564:
3562:
3559:
3557:
3554:
3552:
3549:
3548:
3546:
3544:
3540:
3536:
3532:
3527:
3523:
3509:
3506:
3504:
3501:
3499:
3496:
3494:
3491:
3490:
3488:
3486:
3482:
3476:
3473:
3471:
3468:
3466:
3463:
3462:
3460:
3456:
3450:
3447:
3445:
3442:
3440:
3437:
3435:
3432:
3430:
3427:
3425:
3422:
3420:
3417:
3416:
3414:
3412:
3408:
3402:
3399:
3397:
3396:Questionnaire
3394:
3392:
3389:
3385:
3382:
3380:
3377:
3376:
3375:
3372:
3371:
3369:
3367:
3363:
3357:
3354:
3352:
3349:
3347:
3344:
3342:
3339:
3337:
3334:
3332:
3329:
3327:
3324:
3322:
3319:
3318:
3316:
3314:
3310:
3306:
3302:
3297:
3293:
3279:
3276:
3274:
3271:
3269:
3266:
3264:
3261:
3259:
3256:
3254:
3251:
3249:
3246:
3244:
3241:
3239:
3236:
3234:
3231:
3229:
3226:
3224:
3223:Control chart
3221:
3219:
3216:
3214:
3211:
3209:
3206:
3205:
3203:
3201:
3197:
3191:
3188:
3184:
3181:
3179:
3176:
3175:
3174:
3171:
3169:
3166:
3164:
3161:
3160:
3158:
3156:
3152:
3146:
3143:
3141:
3138:
3136:
3133:
3132:
3130:
3126:
3120:
3117:
3116:
3114:
3112:
3108:
3096:
3093:
3091:
3088:
3086:
3083:
3082:
3081:
3078:
3076:
3073:
3072:
3070:
3068:
3064:
3058:
3055:
3053:
3050:
3048:
3045:
3043:
3040:
3038:
3035:
3033:
3030:
3028:
3025:
3024:
3022:
3020:
3016:
3010:
3007:
3005:
3002:
2998:
2995:
2993:
2990:
2988:
2985:
2983:
2980:
2978:
2975:
2973:
2970:
2968:
2965:
2963:
2960:
2958:
2955:
2953:
2950:
2949:
2948:
2945:
2944:
2942:
2940:
2936:
2933:
2931:
2927:
2923:
2919:
2914:
2910:
2904:
2901:
2899:
2896:
2895:
2892:
2888:
2881:
2876:
2874:
2869:
2867:
2862:
2861:
2858:
2852:
2849:
2847:
2844:
2842:
2839:
2838:
2831:
2825:
2823:9780521551281
2819:
2815:
2810:
2809:
2802:
2798:
2796:9780521551281
2792:
2788:
2784:
2779:
2778:
2771:
2767:
2761:
2753:
2735:
2731:
2721:
2717:
2710:
2705:
2704:
2700:
2692:. p. 28.
2691:
2687:
2686:
2677:
2674:
2669:
2662:
2659:
2654:
2650:
2646:
2642:
2639:(12): 915–9.
2638:
2634:
2633:
2625:
2622:
2617:
2611:
2607:
2602:
2601:
2595:
2589:
2586:
2582:
2576:
2573:
2568:
2564:
2559:
2554:
2550:
2546:
2543:(8): 505–07.
2542:
2538:
2534:
2527:
2524:
2519:
2515:
2510:
2505:
2501:
2497:
2493:
2486:
2483:
2478:
2471:
2468:
2463:
2457:
2453:
2446:
2444:
2440:
2435:
2431:
2426:
2421:
2417:
2413:
2412:
2407:
2400:
2397:
2393:
2387:
2384:
2379:
2375:
2371:
2367:
2363:
2359:
2352:
2349:
2345:
2339:
2336:
2331:
2327:
2323:
2319:
2314:
2309:
2305:
2301:
2294:
2291:
2286:
2282:
2278:
2274:
2270:
2266:
2259:
2256:
2251:
2247:
2243:
2239:
2235:
2231:
2227:
2223:
2216:
2213:
2207:
2204:
2198:
2193:
2189:
2185:
2181:
2174:
2172:
2168:
2163:
2159:
2155:
2151:
2146:
2141:
2137:
2133:
2126:
2119:
2116:
2111:
2107:
2100:
2097:
2092:
2088:
2083:
2078:
2074:
2070:
2066:
2062:
2058:
2054:
2053:
2048:
2041:
2038:
2033:
2026:
2019:
2016:
2012:
2006:
2004:
2000:
1996:
1990:
1988:
1986:
1984:
1980:
1975:
1971:
1964:
1961:
1955:
1950:
1946:
1942:
1938:
1931:
1928:
1923:
1919:
1914:
1909:
1905:
1901:
1896:
1891:
1887:
1883:
1879:
1872:
1869:
1865:
1861:
1855:
1852:
1845:
1837:
1833:
1829:
1825:
1819:
1816:
1809:
1807:
1802:
1799:
1796:
1793:
1790:
1787:
1784:
1781:
1778:
1775:
1774:
1770:
1768:
1765:
1764:control group
1760:
1758:
1754:
1746:
1740:
1736:
1732:
1728:
1724:
1723:
1722:
1716:
1712:
1708:
1704:
1700:
1696:
1692:
1688:
1684:
1680:
1676:
1673:
1669:
1666:
1663:
1660:
1656:
1652:
1649:
1646:
1642:
1639:
1636:
1631:
1626:
1623:
1622:
1621:
1618:
1614:
1612:
1607:
1603:
1601:
1592:
1590:
1588:
1580:
1577:
1574:
1571:
1570:
1569:
1567:
1566:Down Syndrome
1559:
1554:
1550:
1547:
1543:
1539:
1536:
1532:
1528:
1527:
1526:
1522:
1520:
1516:
1512:
1507:
1505:
1501:
1497:
1494:
1490:
1482:
1480:
1477:
1475:
1471:
1467:
1463:
1458:
1453:
1451:
1447:
1443:
1439:
1435:
1432:
1428:
1420:
1418:
1398:
1387:
1384:
1378:
1370:
1365:
1363:
1359:
1355:
1351:
1347:
1343:
1339:
1335:
1331:
1326:
1318:
1311:
1309:
1283:
1280:
1274:
1263:
1260:
1257:
1249:
1246:
1243:
1235:
1232:
1226:
1223:
1219:
1203:
1200:
1194:
1183:
1180:
1177:
1169:
1166:
1163:
1155:
1152:
1146:
1139:
1125:
1122:
1111:
1103:
1100:
1094:
1083:
1082:
1079:
1065:
1059:
1053:
1045:
1040:
1038:
1034:
1030:
1026:
1022:
1018:
1014:
1010:
1001:
994:
992:
975:
969:
963:
960:
957:
954:
951:
945:
940:
936:
932:
923:
912:
909:
903:
896:
895:
892:
890:
868:
857:
854:
848:
840:
836:
832:
828:
819:
812:
810:
793:
790:
787:
781:
778:
769:
758:
755:
749:
742:
741:
738:
737:We have that
731:
727:
725:
721:
717:
713:
709:
705:
701:
697:
691:
683:
681:
664:
661:
658:
652:
649:
640:
629:
626:
620:
597:
594:
591:
585:
577:
573:
554:
551:
548:
517:
514:
511:
505:
502:
493:
482:
479:
473:
464:
462:
459:
455:
451:
447:
443:
439:
435:
416:
413:
410:
404:
396:
392:
388:
384:
375:
368:
366:
349:
346:
343:
337:
334:
325:
314:
311:
305:
298:
297:
294:
292:
288:
284:
280:
276:
272:
250:
239:
236:
230:
221:
219:
215:
211:
207:
203:
199:
195:
191:
187:
183:
179:
175:
171:
167:
163:
155:
153:
149:
142:
140:
138:
133:
131:
127:
123:
119:
115:
111:
107:
98:
88:
85:
77:
67:
63:
57:
54:This article
52:
43:
42:
37:
33:
19:
5591:
5577:
5559:Latin square
5545:
5521:
5497:
5458:
5454:
5447:multivariate
5446:
5442:
5429:
5407:
5355:
5345:
5323:
5269:
5168:
5156:
5137:
5130:
5042:Econometrics
4992: /
4975:Chemometrics
4952:Epidemiology
4945: /
4918:Applications
4760:ARIMA model
4707:Q-statistic
4656:Stationarity
4552:Multivariate
4495: /
4491: /
4489:Multivariate
4487: /
4427: /
4423: /
4272:
4197:Bayes factor
4096:Signed rank
4008:
3982:
3974:
3962:
3657:Completeness
3493:Cohort study
3391:Opinion poll
3326:Missing data
3313:Study design
3268:Scatter plot
3190:Scatter plot
3183:Spearman's ρ
3145:Grouped data
2807:
2781:. New York:
2776:
2751:
2715:
2682:
2676:
2667:
2661:
2636:
2630:
2624:
2599:
2588:
2580:
2575:
2540:
2536:
2526:
2502:(1): 49–54.
2499:
2495:
2485:
2476:
2470:
2451:
2415:
2409:
2399:
2391:
2386:
2361:
2357:
2351:
2346:B 2 107-180.
2343:
2338:
2303:
2299:
2293:
2268:
2264:
2258:
2225:
2221:
2215:
2206:
2187:
2183:
2135:
2131:
2118:
2112:: 1941–1979.
2109:
2105:
2099:
2056:
2050:
2040:
2031:
2018:
2010:
1997:pp. 391–401.
1994:
1969:
1963:
1947:(1): 29–46.
1944:
1940:
1930:
1885:
1881:
1871:
1863:
1854:
1835:
1831:
1827:
1823:
1818:
1805:
1761:
1750:
1720:
1714:
1710:
1694:
1690:
1658:differently.
1629:
1619:
1615:
1604:
1596:
1584:
1563:
1552:
1541:
1535:experimental
1530:
1523:
1511:epidemiology
1508:
1486:
1478:
1462:epidemiology
1454:
1446:partitioning
1436:
1426:
1424:
1368:
1366:
1362:bad controls
1349:
1345:
1341:
1337:
1333:
1329:
1327:
1323:
1312:
1043:
1041:
1036:
1032:
1028:
1024:
1020:
1016:
1012:
1008:
1006:
995:
888:
838:
834:
830:
826:
824:
813:
736:
723:
719:
715:
714:and Y since
711:
707:
703:
699:
695:
693:
575:
465:
457:
449:
445:
441:
437:
436:upon seeing
394:
390:
386:
382:
380:
369:
290:
286:
282:
278:
274:
270:
222:
217:
213:
209:
205:
201:
197:
193:
189:
181:
177:
169:
161:
159:
150:
146:
134:
116:, causing a
109:
103:
80:
71:
55:
5534:Box–Behnken
5415:Mixed model
5346:Confounding
5341:Interaction
5331:Effect size
5301:Sample size
5170:WikiProject
5085:Cartography
5047:Jurimetrics
4999:Reliability
4730:Time domain
4709:(Ljung–Box)
4631:Time-series
4509:Categorical
4493:Time-series
4485:Categorical
4420:(Bernoulli)
4255:Correlation
4235:Correlation
4031:Jarque–Bera
4003:Chi-squared
3765:M-estimator
3718:Asymptotics
3662:Sufficiency
3429:Interaction
3341:Replication
3321:Effect size
3278:Violin plot
3258:Radar chart
3238:Forest plot
3228:Correlogram
3178:Kendall's τ
2785:. pp.
1672:risk ratios
1611:replication
1606:Peer review
1504:experiments
1468:(1935) and
1427:confounding
5659:Categories
5490:randomized
5488:Completely
5459:covariance
5221:Scientific
5037:Demography
4755:ARMA model
4560:Regression
4137:(Friedman)
4098:(Wilcoxon)
4036:Normality
4026:Lilliefors
3973:Student's
3849:Resampling
3723:Robustness
3711:divergence
3701:Efficiency
3639:(monotone)
3634:Likelihood
3551:Population
3384:Stratified
3336:Population
3155:Dependence
3111:Count data
3042:Percentile
3019:Dispersion
2952:Arithmetic
2887:Statistics
1846:References
1679:covariates
1356:bias" or "
688:See also:
461:randomized
156:Definition
110:confounder
5499:Factorial
5383:inference
5363:Covariate
5325:Treatment
5311:Treatment
4418:Logistic
4185:posterior
4111:Rank sum
3859:Jackknife
3854:Bootstrap
3672:Bootstrap
3607:Parameter
3556:Statistic
3351:Statistic
3263:Run chart
3248:Pie chart
3243:Histogram
3233:Fan chart
3208:Bar chart
3090:L-moments
2977:Geometric
2760:cite book
2308:CiteSeerX
2265:Am Sociol
2250:198174446
2190:(1): 31.
1895:1304.0564
1747:Artifacts
1500:pesticide
1388:∣
1254:give drug
1244:∣
1240:recovered
1174:give drug
1164:∣
1160:recovered
1130:give drug
1112:∣
1108:recovered
1063:→
1057:←
955:∣
937:∑
913:∣
858:∣
791:∣
779:≠
759:∣
662:∣
630:∣
595:∣
515:∣
483:∣
414:∣
347:∣
315:∣
240:∣
208:whenever
130:notations
36:Confusion
5622:Category
5617:Glossary
5423:Bayesian
5401:Bayesian
5357:Blocking
5336:Contrast
5316:blocking
5276:Bayesian
5263:Blinding
5253:validity
5250:external
5246:Internal
5132:Category
4825:Survival
4702:Johansen
4425:Binomial
4380:Isotonic
3967:(normal)
3612:location
3419:Blocking
3374:Sampling
3253:Q–Q plot
3218:Box plot
3200:Graphics
3095:Skewness
3085:Kurtosis
3057:Variance
2987:Heronian
2982:Harmonic
2653:11565527
2596:(1987).
2434:11479193
2378:52832751
2242:12415925
2154:20696848
2091:25124526
2059:: 6085.
1922:25544784
1771:See also
1715:stronger
1711:opposite
1695:polarity
1691:strength
1685:such as
1560:Examples
1442:blocking
1354:collider
397:, where
164:be some
5515:Taguchi
5483:Designs
5241:Control
5158:Commons
5105:Kriging
4990:Process
4947:studies
4806:Wavelet
4639:General
3806:Plug-in
3600:L space
3379:Cluster
3080:Moments
2898:Outline
2583:, Wiley
2567:2673334
2558:1009818
2518:9925122
2330:3771081
2285:2089381
2162:9068532
2082:5381407
2061:Bibcode
2052:Sci Rep
1913:4276366
1444:(i.e.,
1421:History
684:Control
456:, with
432:is the
128:. Some
60:Please
5555:(GRBD)
5455:Ancova
5443:Manova
5378:Models
5223:method
5027:Census
4617:Normal
4565:Manova
4385:Robust
4135:2-way
4127:1-way
3965:-test
3636:
3213:Biplot
3004:Median
2997:Lehmer
2939:Center
2820:
2793:
2651:
2612:
2565:
2555:
2516:
2458:
2432:
2376:
2328:
2310:
2283:
2248:
2240:
2160:
2152:
2089:
2079:
1920:
1910:
1734:group.
1635:Alaska
1496:health
1466:Neyman
1438:Fisher
1288:female
1268:female
168:, and
122:causal
5547:Block
4651:Trend
4180:prior
4122:anova
4011:-test
3985:-test
3977:-test
3884:Power
3829:Pivot
3622:shape
3617:scale
3067:Shape
3047:Range
2992:Heinz
2967:Cubic
2903:Index
2814:17–39
2712:(PDF)
2374:S2CID
2281:JSTOR
2246:S2CID
2158:S2CID
2128:(PDF)
2028:(PDF)
1890:arXiv
1834:, or
1810:Notes
1729:of a
1493:human
1483:Types
1474:Pearl
1470:Rubin
570:(see
172:some
5381:and
5314:and
5248:and
4884:Test
4084:Sign
3936:Wald
3009:Mode
2947:Mean
2818:ISBN
2791:ISBN
2787:3–16
2766:link
2649:PMID
2610:ISBN
2563:PMID
2514:PMID
2456:ISBN
2430:PMID
2326:PMID
2238:PMID
2150:PMID
2087:PMID
1918:PMID
1707:SSRI
1705:and
1630:i.e.
1457:Kish
1340:and
1208:male
1188:male
1035:and
1027:and
829:and
722:and
448:and
389:and
289:and
223:Let
216:and
200:and
192:and
108:, a
4064:BIC
4059:AIC
2641:doi
2637:345
2553:PMC
2545:doi
2504:doi
2420:doi
2416:154
2366:doi
2318:doi
2273:doi
2230:doi
2192:doi
2140:doi
2077:PMC
2069:doi
1949:doi
1908:PMC
1900:doi
1703:TCA
1693:or
1681:is
1602:).
1585:In
1529:An
1011:on
180:on
104:In
64:to
5661::
5274::
2816:.
2789:.
2762:}}
2758:{{
2714:.
2647:.
2635:.
2608:.
2604:.
2561:.
2551:.
2541:46
2539:.
2535:.
2512:.
2500:69
2498:.
2494:.
2442:^
2428:.
2414:.
2408:.
2372:.
2362:66
2360:.
2324:.
2316:.
2304:15
2302:.
2279:.
2269:26
2267:.
2244:.
2236:.
2226:47
2224:.
2188:14
2186:.
2182:.
2170:^
2156:.
2148:.
2136:65
2134:.
2130:.
2108:.
2085:.
2075:.
2067:.
2055:.
2049:.
2030:.
2002:^
1982:^
1945:14
1943:.
1939:.
1916:.
1906:.
1898:.
1886:41
1884:.
1880:.
1830:,
1826:,
1551:A
1540:A
1521:.
1392:do
1364:.
1116:do
917:do
862:do
763:do
726::
680:.
634:do
542:do
487:do
463:.
440:=
393:=
385:=
319:do
285:.
281:=
273:=
244:do
220:.
139:.
5461:)
5457:(
5449:)
5445:(
5205:e
5198:t
5191:v
4009:G
3983:F
3975:t
3963:Z
3682:V
3677:U
2879:e
2872:t
2865:v
2826:.
2799:.
2768:)
2736:k
2732:2
2718:.
2655:.
2643::
2618:.
2569:.
2547::
2520:.
2506::
2464:.
2436:.
2422::
2380:.
2368::
2332:.
2320::
2287:.
2275::
2252:.
2232::
2200:.
2194::
2164:.
2142::
2110:9
2093:.
2071::
2063::
2057:4
2034:.
1976:.
1957:.
1951::
1924:.
1902::
1892::
1838:.
1647:.
1405:)
1402:)
1399:x
1396:(
1385:y
1382:(
1379:P
1369:Z
1350:Z
1346:Z
1342:Y
1338:X
1334:Z
1330:Z
1317:)
1315:4
1313:(
1292:)
1284:=
1281:Z
1278:(
1275:P
1272:)
1264:=
1261:Z
1258:,
1250:=
1247:X
1236:=
1233:Y
1230:(
1227:P
1224:+
1212:)
1204:=
1201:Z
1198:(
1195:P
1192:)
1184:=
1181:Z
1178:,
1170:=
1167:X
1156:=
1153:Y
1150:(
1147:P
1140:=
1137:)
1134:)
1126:=
1123:x
1120:(
1104:=
1101:Y
1098:(
1095:P
1066:Y
1060:Z
1054:X
1044:Z
1037:Y
1033:X
1029:Y
1025:X
1021:Z
1017:Z
1013:Y
1009:X
1000:)
998:3
996:(
979:)
976:z
973:(
970:P
967:)
964:z
961:,
958:x
952:y
949:(
946:P
941:z
933:=
930:)
927:)
924:x
921:(
910:y
907:(
904:P
889:Z
875:)
872:)
869:x
866:(
855:y
852:(
849:P
839:Z
835:X
831:Z
827:X
818:)
816:2
814:(
797:)
794:x
788:y
785:(
782:P
776:)
773:)
770:x
767:(
756:y
753:(
750:P
724:Y
720:X
716:Z
712:X
708:Z
704:Y
700:Z
696:X
668:)
665:x
659:y
656:(
653:P
650:=
647:)
644:)
641:x
638:(
627:y
624:(
621:P
601:)
598:x
592:y
589:(
586:P
576:Y
558:)
555:x
552:=
549:X
546:(
521:)
518:x
512:y
509:(
506:P
503:=
500:)
497:)
494:x
491:(
480:y
477:(
474:P
458:x
450:Y
446:X
442:x
438:X
420:)
417:x
411:y
408:(
405:P
395:y
391:Y
387:x
383:X
374:)
372:1
370:(
353:)
350:x
344:y
341:(
338:P
335:=
332:)
329:)
326:x
323:(
312:y
309:(
306:P
291:Y
287:X
283:x
279:X
275:y
271:Y
257:)
254:)
251:x
248:(
237:y
234:(
231:P
218:Y
214:X
210:Z
206:Z
202:Y
198:X
194:Y
190:X
182:Y
178:X
170:Y
162:X
87:)
81:(
76:)
72:(
58:.
38:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.