397:
urine concentration and urine flow equals the mass of substance excreted during the time that urine has been collected. This mass equals the mass filtered at the glomerulus as nothing is added or removed in the nephron. Dividing this mass by the plasma concentration gives the volume of plasma which the mass must have originally come from, and thus the volume of plasma fluid that has entered Bowman's capsule within the aforementioned period of time. The GFR is typically recorded in units of
171:(GFR) is regarded as the best overall measure of the kidney's ability to carry out these numerous functions. An estimate of the GFR is used clinically to determine the degree of kidney impairment and to track the progression of the disease. The GFR, however, does not reveal the source of the kidney disease. This is accomplished by urinalysis, measurement of urine protein excretion, kidney imaging, and, if necessary, kidney biopsy.
31:
484:, is 100–130 average 125 (mL/min)/(1.73 m) in men and 90–120 (mL/min)/(1.73 m) in women younger than the age of 40. In children, GFR measured by inulin clearance is 110 (mL/min)/(1.73 m) until 2 years of age in both sexes, and then it progressively decreases. After age 40, GFR decreases progressively with age, by 0.4–1.2 mL/min per year.
396:
when any solute is freely filtered and is neither reabsorbed nor secreted by the kidneys. The rate therefore measured is the quantity of the substance in the urine that originated from a calculable volume of blood. Relating this principle to the below equation – for the substance used, the product of
744:
Not all clinicians agree with the above classification, suggesting that it may mislabel patients with mildly reduced kidney function, especially the elderly, as having a disease. A conference was held in 2009 regarding these controversies by Kidney
Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) on CKD:
287:
Blood tests are also used to assess kidney function. These include tests that are intended to directly measure the function of the kidneys, as well as tests that assess the function of the kidneys by looking for evidence of problems associated with abnormal function. One of the measures of kidney
388:
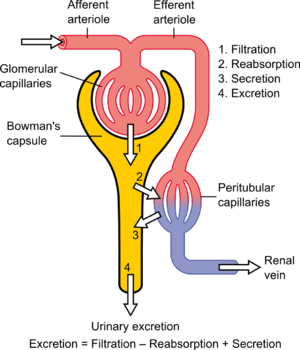
Central to the physiologic maintenance of GFR is the differential basal tone of the afferent and efferent arterioles (see diagram). In other words, the filtration rate is dependent on the difference between the higher blood pressure created by vasoconstriction of the input or afferent arteriole
648:
Risk factors for kidney disease include diabetes, high blood pressure, family history, older age, ethnic group and smoking. For most patients, a GFR over 60 (mL/min)/(1.73 m) is adequate. But significant decline of the GFR from a previous test result can be an early indicator of kidney disease
471:
270:
Part of the assessment of kidney function includes the measurement of urine and its contents. Abnormal kidney function may cause too much or too little urine to be produced. The ability of the kidneys to filter protein is often measured, as
487:
Estimated GFR (eGFR) is now recommended by clinical practice guidelines and regulatory agencies for routine evaluation of GFR whereas measured GFR (mGFR) is recommended as a confirmatory test when more accurate assessment is required.
233:
Clinical assessment can be used to assess the function of the kidneys. This is because a person with abnormally functioning kidneys may have symptoms that develop. For example, a person with chronic kidney disease may develop
34:
Diagram showing a schematic nephron and its blood supply. The basic physiologic mechanisms of handling fluid and electrolytes by the nephron - filtration, secretion, reabsorption, and excretion - are labelled.
476:
There are several different techniques used to calculate or estimate the glomerular filtration rate (GFR or eGFR). The above formula only applies for GFR calculation when it is equal to the
Clearance Rate.
209:
Proper function of the kidney requires that it receives and adequately filters blood. This is performed at the microscopic level by many hundreds of thousands of filtration units called
419:
711:(CKD) is described by six stages; the most severe three are defined by the MDRD-eGFR value, and first three also depend on whether there is other evidence of kidney disease (e.g.,
737:
5) CKD5 kidney failure – GFR less than 15 (mL/min)/(1.73 m) Some people add CKD5D for those stage 5 patients requiring dialysis; many patients in CKD5 are not yet on dialysis.
649:
requiring medical intervention. The sooner kidney dysfunction is diagnosed and treated the greater odds of preserving remaining nephrons, and preventing the need for dialysis.
1027:
238:
due to failure of the kidneys to regulate water balance. They may develop evidence of chronic kidney disease, that can be used to assess its severity, for example
850:(Jun 4, 2013). "Evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease: synopsis of the kidney disease: improving global outcomes 2012 clinical practice guideline".
505:
1171:
942:
Levey AS; Coresh J; Tighiouart H; Greene T; Inker LA (2020). "Measured and estimated glomerular filtration rate: current status and future directions".
358:
may be accurately calculated by comparative measurements of substances in the blood and urine, or estimated by formulas using just a blood test result (
350:
per unit time and is a useful measure for approximating the GFR. Creatinine clearance exceeds GFR due to creatinine secretion, which can be blocked by
508:, may assess kidney function by indicating chronic disease that can impact function, by showing a small or shrivelled kidney.. Other tests, such as
1075:
186:
entering the kidney. This filtrate then flows along the length of the nephron, which is a tubular structure lined by a single layer of specialized
894:
1218:
926:
627:
512:
tests, directly assess the function of the kidney by measuring the perfusion and excretion of radioactive substances through the kidneys.
1100:
755:
1028:"Definition and Classification of CKD: The Debate Should Be About Patient Prognosis – A Position Statement From KDOQI and KDIGO"
288:
function is the glomerular filtration rate (GFR). Other tests that can assess the function of the kidneys include assessment of
1264:
1137:
1562:
1164:
1058:
745:
Definition, Classification and
Prognosis, gathering data on CKD prognosis to refine the definition and staging of CKD.
1540:
1249:
1489:
1344:
1269:
1259:
321:
222:
168:
1416:
1184:
279:
levels, measured either at a single instance or, because of variation throughout the day, as 24-hour urine tests.
1603:
1572:
1499:
1456:
1244:
1157:
800:
557:
466:{\displaystyle GFR={\frac {{\mbox{Urine Concentration}}\times {\mbox{Urine Flow}}}{\mbox{Plasma Concentration}}}}
1461:
1297:
1208:
591:
A urinalysis is helpful even when not showing any pathology, as this finding suggests an extrarenal etiology.
221:. A global assessment of renal function is often ascertained by estimating the rate of filtration, called the
1567:
1302:
708:
643:
374:
370:
1504:
1423:
1079:
785:
600:
393:
389:
versus the lower blood pressure created by lesser vasoconstriction of the output or efferent arteriole.
1111:
1076:"KDIGO Controversies Conference: Definition, Classification and Prognosis in CKD, London, October 2009"
902:
1608:
1529:
1509:
1494:
1149:
805:
760:
529:
133:
76:
1448:
1405:
1389:
1307:
1254:
770:
573:
541:
410:
335:
331:
218:
214:
825:
1466:
1395:
967:
1144:
1105:
1524:
1519:
1433:
1292:
1050:
1008:
959:
922:
875:
867:
795:
501:
481:
113:
60:
863:
1545:
1287:
1213:
1180:
1042:
998:
951:
859:
780:
615:
596:
533:
509:
305:
107:
52:
1223:
765:
525:
497:
210:
1354:
623:
521:
382:
369:) The results of these tests are used to assess the excretory function of the kidneys.
187:
157:
149:
91:
83:
30:
1597:
1536:
1374:
1364:
971:
790:
608:
326:
The glomerular filtration rate (GFR) describes the volume of fluid filtered from the
276:
272:
117:
56:
986:
17:
1400:
1239:
847:
619:
585:
581:
343:
243:
239:
195:
46:
741:
Note: others add a "T" to patients who have had a transplant regardless of stage.
728:
2) CKD2 (mild) – GFR of 60 to 89 (mL/min)/(1.73 m) with evidence of kidney damage
1577:
1442:
1428:
1339:
1334:
720:
712:
592:
524:. Upon presentation of decreased renal function, it is recommended to perform a
378:
301:
289:
129:
72:
1046:
49:, as well as measurements using urine tests, blood tests, and medical imaging.
1380:
1359:
1279:
955:
569:
537:
402:
351:
347:
145:
1125:
871:
1438:
604:
553:
297:
293:
259:
191:
161:
125:
95:
68:
1120:
1054:
1012:
1003:
963:
879:
1078:. Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). 2009. Archived from
577:
565:
561:
549:
178:– the smallest functional unit of the kidney. Each nephron begins with a
42:
1384:
725:
1) CKD1 – GFR above 90 (mL/min)/(1.73 m) with evidence of kidney damage
631:
309:
247:
198:
of water and small molecules from the filtrate into the blood, and the
175:
153:
141:
87:
1115:
406:
327:
235:
121:
64:
1582:
1349:
1193:
719:
0) Normal kidney function – GFR above 90 (mL/min)/(1.73 m) and no
568:. The most important items in a physical examination are signs of
545:
203:
183:
137:
79:
29:
987:"Staging of Chronic Kidney Disease: Time for a Course Correction"
1514:
775:
255:
251:
1153:
607:
may be caused by glomerular disease or by a disease along the
634:. Renal atrophy suggests longstanding chronic renal disease.
626:. Renal enlargement usually indicates diabetic nephropathy,
520:
A decreased renal function can be caused by many types of
1026:
Eckardt KU, Berns JS, Rocco MV, Kasiske BL (June 2009).
174:
Much of renal physiology is studied at the level of the
731:
3) CKD3 (moderate) – GFR of 30 to 59 (mL/min)/(1.73 m)
300:, assessment of acid-base status by the measurement of
456:
449:
439:
422:
1140:
Includes professional references and GFR calculators
734:
4) CKD4 (severe) – GFR of 15 to 29 (mL/min)/(1.73 m)
194:. The major functions of these lining cells are the
1555:
1480:
1415:
1373:
1327:
1320:
1278:
1232:
1201:
1191:
917:Ganong (2016). "Renal Function & Micturition".
112:The functions of the kidney include maintenance of
1138:National Kidney Disease Education Program website.
465:
41:occurs in different ways, using the presence of
496:The kidney function can also be assessed with
1165:
991:Journal of the American Society of Nephrology
841:
839:
540:. The most relevant items in the history are
27:Ways of assessing the function of the kidneys
8:
148:, and other small molecules; regulation of
1324:
1198:
1172:
1158:
1150:
985:Bauer C, Melamed ML, Hostetter TH (2008).
304:levels from a vein, and assessment of the
1002:
448:
438:
435:
421:
377:is based on categories of GFR as well as
864:10.7326/0003-4819-158-11-201306040-00007
651:
1108:for estimating pediatric renal function
817:
250:. If the kidneys are unable to excrete
921:. McGraw-Hill Education. p. 677.
480:The normal range of GFR, adjusted for
338:per unit time. Creatinine clearance (C
919:Review of Medical Physiology, 25th ed
7:
628:focal segmental glomerular sclerosis
254:, a person may develop a widespread
63:; regulating electrolytes including
1035:American Journal of Kidney Diseases
614:The most relevant assessments in a
709:severity of chronic kidney disease
599:usually indicates the presence of
202:of wastes from the blood into the
25:
500:. Some forms of imaging, such as
213:, each of which is composed of a
401:, e.g., milliliters per minute (
55:include maintaining a person's
1126:GFR calculator using Cystatin C
1114:(Cockcroft-Gault Equation)- by
1112:Creatinine clearance calculator
179:
1563:Fractional excretion of sodium
907:– "Glomerular Filtration Rate"
899:Essentials of Human Physiology
199:
1:
638:Chronic kidney disease stages
53:Functions of a healthy kidney
39:Assessment of kidney function
756:Bowman–Heidenhain hypothesis
1541:Effective renal plasma flow
1385:Intracellular fluid/Cytosol
852:Annals of Internal Medicine
182:component that filters the
1625:
1490:Glomerular filtration rate
1482:Assessment and measurement
1345:Atrial natriuretic peptide
1047:10.1053/j.ajkd.2009.04.001
895:"Section 7/7ch04/7ch04p11"
641:
532:, as well as performing a
516:Kidney function in disease
322:Glomerular filtration rate
319:
316:Glomerular filtration rate
223:glomerular filtration rate
169:Glomerular filtration rate
105:
1573:Tubuloglomerular feedback
1500:Augmented renal clearance
1457:Bicarbonate buffer system
1181:Physiology of the kidneys
956:10.1038/s41581-019-0191-y
801:Tubuloglomerular feedback
1462:Respiratory compensation
1219:Clearance of medications
152:; production of various
1568:BUN-to-creatinine ratio
1303:Countercurrent exchange
1004:10.1681/ASN.2008010110
644:Chronic kidney disease
467:
375:chronic kidney disease
35:
1505:Renal clearance ratio
1424:Darrow Yannet diagram
1101:Online GFR Calculator
786:Renal clearance ratio
468:
394:renal clearance ratio
334:capillaries into the
33:
1530:Hemodialysis product
1510:Urea reduction ratio
1495:Creatinine clearance
1335:Antidiuretic hormone
1185:acid–base physiology
806:Urea reduction ratio
530:physical examination
458:Plasma Concentration
420:
392:GFR is equal to the
160:; and activation of
94:; and activation of
18:Creatinine clearance
1406:Transcellular fluid
1390:Extracellular fluid
1308:Filtration fraction
771:Filtration fraction
660:((mL/min)/(1.73 m))
574:lupus erythematosus
560:of kidney disease,
441:Urine Concentration
411:filtration fraction
346:that is cleared of
342:) is the volume of
240:high blood pressure
229:Clinical assessment
1467:Renal compensation
1396:Interstitial fluid
1095:Online calculators
846:Stevens, Paul E.;
601:glomerular disease
463:
460:
453:
443:
354:. Both GFR and C
190:and surrounded by
36:
1591:
1590:
1525:Dialysis adequacy
1520:Standardized Kt/V
1476:
1475:
1434:Davenport diagram
1417:Acid–base balance
1316:
1315:
1293:Renal plasma flow
1121:MDRD GFR Equation
928:978-0-07-184897-8
893:Nosek, Thomas M.
796:Standardized Kt/V
705:
704:
661:
622:and any signs of
618:are renal sizes,
502:kidney ultrasound
482:body surface area
461:
459:
452:
442:
114:acid-base balance
86:; and regulating
61:acid-base balance
59:, maintaining an
16:(Redirected from
1616:
1604:Renal physiology
1546:Extraction ratio
1449:Winters' formula
1325:
1288:Renal blood flow
1214:Pharmacokinetics
1199:
1174:
1167:
1160:
1151:
1145:Lab Tests Online
1106:Schwartz formula
1084:
1083:
1072:
1066:
1065:
1063:
1057:. Archived from
1032:
1023:
1017:
1016:
1006:
982:
976:
975:
939:
933:
932:
914:
908:
906:
901:. Archived from
890:
884:
883:
843:
834:
833:
830:www.uptodate.com
822:
781:Pharmacokinetics
659:
652:
616:renal ultrasound
597:urinary sediment
534:renal ultrasound
510:nuclear medicine
472:
470:
469:
464:
462:
457:
455:
454:
450:
444:
440:
436:
336:Bowman's capsule
306:full blood count
219:Bowman's capsule
211:renal corpuscles
140:; absorption of
120:; regulation of
116:; regulation of
108:Renal physiology
21:
1624:
1623:
1619:
1618:
1617:
1615:
1614:
1613:
1594:
1593:
1592:
1587:
1551:
1472:
1411:
1369:
1321:Other functions
1312:
1298:Ultrafiltration
1274:
1228:
1224:Urine flow rate
1187:
1178:
1134:
1132:Reference links
1097:
1092:
1087:
1074:
1073:
1069:
1061:
1030:
1025:
1024:
1020:
984:
983:
979:
944:Nat Rev Nephrol
941:
940:
936:
929:
916:
915:
911:
892:
891:
887:
858:(11): 825–830.
845:
844:
837:
824:
823:
819:
815:
810:
751:
646:
640:
518:
498:medical imaging
494:
492:Medical imaging
437:
418:
417:
399:volume per time
367:
357:
341:
324:
318:
292:levels such as
285:
268:
231:
110:
104:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1622:
1620:
1612:
1611:
1606:
1596:
1595:
1589:
1588:
1586:
1585:
1580:
1575:
1570:
1565:
1559:
1557:
1553:
1552:
1550:
1549:
1543:
1534:
1533:
1532:
1522:
1517:
1512:
1507:
1502:
1497:
1492:
1486:
1484:
1478:
1477:
1474:
1473:
1471:
1470:
1469:
1464:
1459:
1451:
1446:
1436:
1431:
1426:
1421:
1419:
1413:
1412:
1410:
1409:
1403:
1398:
1392:
1379:
1377:
1371:
1370:
1368:
1367:
1365:Prostaglandins
1362:
1357:
1355:Erythropoietin
1352:
1347:
1342:
1337:
1331:
1329:
1322:
1318:
1317:
1314:
1313:
1311:
1310:
1305:
1300:
1295:
1290:
1284:
1282:
1276:
1275:
1273:
1272:
1267:
1262:
1257:
1252:
1247:
1242:
1236:
1234:
1230:
1229:
1227:
1226:
1221:
1216:
1211:
1205:
1203:
1196:
1189:
1188:
1179:
1177:
1176:
1169:
1162:
1154:
1148:
1147:
1141:
1133:
1130:
1129:
1128:
1123:
1118:
1109:
1103:
1096:
1093:
1091:
1090:External links
1088:
1086:
1085:
1082:on 2010-11-24.
1067:
1064:on 2011-07-25.
1041:(6): 915–920.
1018:
997:(5): 844–846.
977:
934:
927:
909:
905:on 2016-03-24.
885:
835:
816:
814:
811:
809:
808:
803:
798:
793:
788:
783:
778:
773:
768:
763:
758:
752:
750:
747:
739:
738:
735:
732:
729:
726:
723:
703:
702:
699:
695:
694:
691:
687:
686:
683:
679:
678:
675:
671:
670:
667:
663:
662:
656:
642:Main article:
639:
636:
624:hydronephrosis
558:family history
522:kidney disease
517:
514:
493:
490:
474:
473:
447:
434:
431:
428:
425:
409:). Compare to
383:kidney disease
365:
355:
339:
320:Main article:
317:
314:
284:
281:
267:
264:
230:
227:
158:erythropoietin
150:blood pressure
106:Main article:
103:
100:
92:erythropoietin
84:blood pressure
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1621:
1610:
1607:
1605:
1602:
1601:
1599:
1584:
1581:
1579:
1576:
1574:
1571:
1569:
1566:
1564:
1561:
1560:
1558:
1554:
1547:
1544:
1542:
1538:
1537:PAH clearance
1535:
1531:
1528:
1527:
1526:
1523:
1521:
1518:
1516:
1513:
1511:
1508:
1506:
1503:
1501:
1498:
1496:
1493:
1491:
1488:
1487:
1485:
1483:
1479:
1468:
1465:
1463:
1460:
1458:
1455:
1454:
1452:
1450:
1447:
1444:
1440:
1437:
1435:
1432:
1430:
1427:
1425:
1422:
1420:
1418:
1414:
1407:
1404:
1402:
1399:
1397:
1393:
1391:
1388:
1387:
1386:
1382:
1378:
1376:
1375:Fluid balance
1372:
1366:
1363:
1361:
1358:
1356:
1353:
1351:
1348:
1346:
1343:
1341:
1338:
1336:
1333:
1332:
1330:
1326:
1323:
1319:
1309:
1306:
1304:
1301:
1299:
1296:
1294:
1291:
1289:
1286:
1285:
1283:
1281:
1277:
1271:
1268:
1266:
1265:Oligopeptides
1263:
1261:
1258:
1256:
1253:
1251:
1248:
1246:
1243:
1241:
1238:
1237:
1235:
1231:
1225:
1222:
1220:
1217:
1215:
1212:
1210:
1207:
1206:
1204:
1200:
1197:
1195:
1190:
1186:
1182:
1175:
1170:
1168:
1163:
1161:
1156:
1155:
1152:
1146:
1142:
1139:
1136:
1135:
1131:
1127:
1124:
1122:
1119:
1117:
1113:
1110:
1107:
1104:
1102:
1099:
1098:
1094:
1089:
1081:
1077:
1071:
1068:
1060:
1056:
1052:
1048:
1044:
1040:
1036:
1029:
1022:
1019:
1014:
1010:
1005:
1000:
996:
992:
988:
981:
978:
973:
969:
965:
961:
957:
953:
949:
945:
938:
935:
930:
924:
920:
913:
910:
904:
900:
896:
889:
886:
881:
877:
873:
869:
865:
861:
857:
853:
849:
848:Levin, Adeera
842:
840:
836:
831:
827:
821:
818:
812:
807:
804:
802:
799:
797:
794:
792:
791:Renal failure
789:
787:
784:
782:
779:
777:
774:
772:
769:
767:
764:
762:
759:
757:
754:
753:
748:
746:
742:
736:
733:
730:
727:
724:
722:
718:
717:
716:
714:
710:
700:
697:
696:
692:
689:
688:
684:
681:
680:
676:
673:
672:
668:
665:
664:
657:
654:
653:
650:
645:
637:
635:
633:
629:
625:
621:
617:
612:
610:
609:urinary tract
606:
602:
598:
594:
589:
587:
583:
579:
575:
571:
567:
563:
559:
555:
551:
547:
543:
539:
535:
531:
527:
523:
515:
513:
511:
507:
503:
499:
491:
489:
485:
483:
478:
445:
432:
429:
426:
423:
416:
415:
414:
412:
408:
404:
400:
395:
390:
386:
384:
381:and cause of
380:
376:
372:
368:
361:
353:
349:
345:
337:
333:
329:
323:
315:
313:
311:
307:
303:
299:
295:
291:
282:
280:
278:
277:urine protein
274:
273:urine albumin
265:
263:
261:
257:
253:
249:
245:
241:
237:
228:
226:
224:
220:
216:
212:
207:
205:
201:
197:
193:
189:
185:
181:
177:
172:
170:
165:
163:
159:
155:
151:
147:
143:
139:
135:
131:
127:
123:
119:
118:fluid balance
115:
109:
101:
99:
97:
93:
89:
85:
82:; regulating
81:
78:
74:
70:
66:
62:
58:
57:fluid balance
54:
50:
48:
44:
40:
32:
19:
1481:
1240:Solvent drag
1233:Reabsorption
1080:the original
1070:
1059:the original
1038:
1034:
1021:
994:
990:
980:
950:(1): 51–64.
947:
943:
937:
918:
912:
903:the original
898:
888:
855:
851:
829:
820:
743:
740:
706:
647:
620:echogenicity
613:
590:
586:hypertension
582:endocarditis
519:
495:
486:
479:
475:
398:
391:
387:
363:
359:
344:blood plasma
325:
286:
269:
244:osteoporosis
232:
208:
196:reabsorption
173:
166:
130:electrolytes
128:, and other
111:
73:electrolytes
71:, and other
51:
38:
37:
1609:Blood tests
1578:Natriuresis
1443:Delta ratio
1429:Base excess
1340:Aldosterone
721:proteinuria
713:proteinuria
593:Proteinuria
542:medications
379:albuminuria
302:bicarbonate
290:electrolyte
283:Blood tests
266:Urine tests
192:capillaries
146:amino acids
102:Description
1598:Categories
1453:Buffering
1381:Body water
1360:Calcitriol
1280:Filtration
826:"UpToDate"
813:References
658:GFR level
655:CKD stage
570:vasculitis
538:urinalysis
451:Urine Flow
352:cimetidine
348:creatinine
332:glomerular
215:glomerulus
180:filtration
156:, such as
90:, such as
1439:Anion gap
1209:Clearance
1202:Secretion
1192:Creating
972:202573933
872:1539-3704
761:Clearance
605:Hematuria
554:hematuria
446:×
330:(kidney)
298:phosphate
294:potassium
260:confusion
200:secretion
162:vitamin D
134:clearance
126:potassium
96:vitamin D
69:potassium
1328:Hormones
1250:Chloride
1143:eGFR at
1055:19406541
1013:18385419
964:31527790
880:23732715
766:Dialysis
749:See also
701:< 15
698:Stage 5
690:Stage 4
682:Stage 3
674:Stage 2
666:Stage 1
578:diabetes
566:polyuria
562:diabetes
552:, gross
550:nocturia
506:CT scans
154:hormones
88:hormones
77:clearing
43:symptoms
1270:Protein
1260:Glucose
632:myeloma
595:and/or
526:history
371:Staging
310:anaemia
248:anaemia
225:(GFR).
176:nephron
142:glucose
1401:Plasma
1245:Sodium
1116:MDCalc
1053:
1011:
970:
962:
925:
878:
870:
693:15–29
685:30–59
677:60–89
536:and a
236:oedema
217:and a
138:toxins
122:sodium
80:toxins
65:sodium
1583:Urine
1556:Other
1350:Renin
1194:urine
1062:(PDF)
1031:(PDF)
968:S2CID
669:≥ 90
546:edema
328:renal
204:urine
188:cells
184:blood
47:signs
1515:Kt/V
1255:Urea
1183:and
1051:PMID
1009:PMID
960:PMID
923:ISBN
876:PMID
868:ISSN
776:Kt/V
707:The
584:and
564:and
528:and
362:and
360:eGFR
308:for
296:and
256:itch
252:urea
167:The
45:and
1043:doi
999:doi
952:doi
860:doi
856:158
715:):
630:or
504:or
407:min
373:of
275:or
258:or
246:or
136:of
1600::
1383::
1049:.
1039:53
1037:.
1033:.
1007:.
995:19
993:.
989:.
966:.
958:.
948:16
946:.
897:.
874:.
866:.
854:.
838:^
828:.
611:.
603:.
588:.
580:,
576:,
572:,
556:,
548:,
544:,
413:.
403:mL
385:.
366:Cr
364:eC
356:Cr
340:Cr
312:.
262:.
242:,
206:.
164:.
144:,
132:;
124:,
98:.
75:;
67:,
1548:)
1539:(
1445:)
1441:(
1408:)
1394:(
1173:e
1166:t
1159:v
1045::
1015:.
1001::
974:.
954::
931:.
882:.
862::
832:.
433:=
430:R
427:F
424:G
405:/
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.