111:
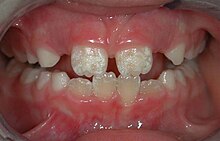
of fluoride exposure. There are different classifications to diagnose the severity based on the appearances. The clinical manifestation of mild dental fluorosis is mostly characterised a snow flaking appearance that lack a clear border, opaque, white spots, narrow white lines following the perikymata or patches as the opacities may coalesce with an intact, hard and smooth enamel surface on most of the teeth. With increasing severity, the subsurface enamel, all along the tooth becomes more porous. Enamel may appear yellow/brown with discolouration and/or many pitted white-brown lesions similar to cavities. They are often described as "mottled teeth". Fluorosis does not cause discolouration to the enamel directly, as upon eruption into the mouth, affected permanent teeth are not discoloured yet. In dental enamel, fluorosis causes subsurface porosity or
87:, and, in some cases, physical damage to the teeth. The severity of the condition is dependent on the dose, duration, and age of the individual during the exposure. The "very mild" (and most common) form of fluorosis, is characterized by small, opaque, "paper white" areas scattered irregularly over the tooth, covering less than 25% of the tooth surface. In the "mild" form of the disease, these mottled patches can involve up to half of the surface area of the teeth. When fluorosis is moderate, all of the surfaces of the teeth are mottled and teeth may be ground down and brown stains frequently "disfigure" the teeth. Severe fluorosis is characterized by brown discoloration and discrete or confluent pitting; brown stains are widespread and teeth often present a corroded-looking appearance.
319:
most crucial course is during the first 2 years of the child's life. From roughly 7 years old thereafter, most children's permanent teeth would have undergone complete development (except their wisdom teeth), and therefore their susceptibility to fluorosis is greatly reduced, or even insignificant, despite the amount of intake of fluoride. The severity of dental fluorosis depends on the amount of fluoride exposure, the age of the child, individual response, weight, degree of physical activity, nutrition, and bone growth. Individual susceptibility to fluorosis is also influenced by genetic factors.
723:, a prominent American dentist of the time. After examining specimens of affected enamel, in 1916 Black described the condition as "n endemic imperfection of the enamel of the teeth, heretofore unknown in the literature of dentistry." They made the interesting observation that although the mottled enamel was hypomineralized, and therefore should be more susceptible to decay, this was not the case. Gradually, they became aware of existing and further reports of a similar condition worldwide.
183:
40:
349:
the enamel formation, and not caused by the general effects of fluoride on the calcium metabolism, or by the poisoning effects that suppress the fluoride metabolism. However, despite decades of research and studies, there have yet to be any studies that substantiate the believed mechanism whereby dental fluorosis is a result of alteration in the mineralisation that takes place when fluoride interacts with mineralising tissues.
103:
191:
123:
327:. The last of these sources is directly or indirectly responsible for 40% of all fluorosis, but the resulting effect due to water fluoridation is largely and typically aesthetic. Severe cases can be caused by exposure to water that is naturally fluoridated to levels above the recommended levels, or by exposure to other fluoride sources such as
314:
Dental fluorosis is caused by a higher than normal amount of fluoride ingestion whilst teeth are forming. Primary dentine fluorosis and enamel fluorosis can only happen during tooth formation, so fluoride exposure occurs in childhood. Enamel fluorosis has a white opaque appearance which is due to the
305:
Proposed by
Thylstrup and Fejerskov in 1978, the TF index represents a logical extension of Dean's index, incorporating modern understanding of the underlying pathology of fluorosis. It scores the spectrum of fluorotic changes in enamel from 0 to 9, allowing more precise definition of mild and severe
685:
or using water that is either free of fluoride or low in fluoride to prepare powdered or liquid concentrate formula. They go on to say that the way to get the benefits of fluoride but minimize the risk of fluorosis for a child is to get the right amount of fluoride, not too much and not too little.
348:
Teeth are the most studied body tissues to examine the impact of fluoride to human health. There are a few possible mechanisms that have been proposed. It is generally believed that the hypomineralization of affected enamel is mainly due to in-situ toxic effects of the fluoride on the ameloblasts in
318:
The most superficial concern in dental fluorosis is aesthetic changes in the permanent dentition (the adult teeth). The period when these teeth are at highest risk of developing fluorosis is between when the child is born up to 6 years old, though there has been some research which proposes that the
110:
The adequate diagnosis of fluorosis can be diagnosed by visual clinical examination. This requires inspection of dry and clean tooth surfaces under a good lighting. There are individual variations in clinical fluorosis manifestation which are highly dependent on the duration, timing, and dosage
680:
published information stating that water fluoridation is safe, effective and healthy; that enamel fluorosis, usually mild and difficult for anyone except a dental health care professional to see, can result from ingesting more than optimal amounts of fluoride in early childhood; that it is safe to
672:
Fluoride consumption can exceed the tolerable upper limit when someone drinks a lot of fluoride-containing water in combination with other fluoride sources, such as swallowing fluoridated toothpaste, consuming food with a high fluoride content, or consuming fluoride supplements. The use of fluoride
259:
Small, opaque, paper white areas scattered irregularly over the tooth but not involving as much as approximately 25% of the tooth surface. Frequently included in this classification are teeth showing no more than about 1 – 2mm of white opacity at the tip of the summit of the cusps, of the bicuspids
731:
helped to identify a causal link between high concentrations of fluoride in the drinking water and mottled enamel. He also produced a classification system for dental fluorosis that is still used in modern times, Dean's Index. As research continued, the protective effect of fluoride against dental
322:
Many well-known sources of fluoride may contribute to overexposure including dentifrice/fluoridated mouthrinse (which young children may swallow), excessive ingestion of fluoride toothpaste, bottled waters which are not tested for their fluoride content, inappropriate use of fluoride supplements,
198:
The two main classification systems are described below. Others include the tooth surface fluorosis index (Horowitz et al. 1984), which combines Deans index and the TF index; and the fluorosis risk index (Pendrys 1990), which is intended to define the time at which fluoride exposure occurs, and
334:
Dental fluorosis has been growing in the United States concurrent with fluoridation of municipal water supplies, although disproportionately by race. A 2010 CDC report acknowledges an overall incidence of dental fluorosis of 22% from 1986-87 increased to 41% in the early 21st century, with an
510:
in a 1999-2002 study of
American children and adolescents than was found in a similar survey from 1986-1987 (from 22.8% in 1986-1987 to 32% in 1999-2002). In addition, the survey provides further evidence that African Americans suffer from higher rates of fluorosis than Caucasian Americans.
439:
in the USA between 1986 and 1987 and by the Center of
Disease Control between 1999 and 2004 are the only national sources of data concerning the prevalence of dental fluorosis. Before the 1999-2004 study was published, CDC published an interim report covering data from 1999 to 2002.
247:
The enamel discloses slight aberrations from the translucency of normal enamel, ranging from a few white flecks to occasional white spots. This classification is utilised in those instances where a definite diagnosis is not warranted and a classification of 'normal' not justified
360:
via a decrease in the availability of free calcium ions in the mineralization environment. This results in the formation of enamel with less mineralization. This hypomineralized enamel has altered optical properties and appears opaque and lusterless relative to normal enamel.
293:
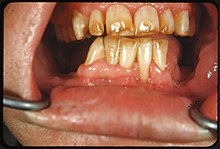
All enamel surfaces are affected and hypoplasia is so marked that the general form of the tooth may be affected. The major diagnostic sign of this classification is discrete or confluent pitting. Brown stains are widespread and teeth often present a corroded-like appearance.
726:
In 1931, 3 different groups of scientists around the world published their discoveries that this condition was caused by fluoride in drinking water during childhood. The condition then started to become termed "dental fluorosis". Through epidemiological studies in the US,
668:
If the water supply is fluoridated at the level of 1 ppm, one must consume one litre of water in order to take in 1 mg of fluoride. It is thus improbable a person will receive more than the tolerable upper limit from consuming optimally fluoridated water alone.
368:, however, hypoplasia does not occur as a result of fluorosis. The pits, bands, and loss of areas of enamel seen in severe fluorosis are the result of damage to the severely hypomineralized, brittle and fragile enamel which occurs after they erupt into the mouth.
339:
figures documented another 31% overall increase among
American teens since the previous decade, with a total adolescent population impact of 61% afflicted. More than one in five American teens (23%) have moderate to severe dental fluorosis on at least two teeth.
514:
The condition is more prevalent in rural areas where drinking water is derived from shallow wells or hand pumps. It is also more likely to occur in areas where the drinking water has a fluoride content greater than 1 ppm (part per million).
2085:
2070:
694:
Dental fluorosis can be prevented by lowering the amount of fluoride intake to below the tolerable upper limit. This can be achieved by consuming de-fluorinated water and improving the general nutritional status of the people.
710:
In 1901 Eager published the first description of the "mottled enamel" of immigrants from a small village near Naples, Italy. He writes that the condition is called "Denti di Chiaie" (Chiaie teeth), named after
1326:
Buzalaf MAR, Levy SM (2011): Fluoride intake of children: considerations for dental caries and dental fluorosis in
Fluoride and the Environment. Editor: MAR Buzalaf, Karger, Basel. Pages 1-19
719:, set up practice in Colorado Springs in 1901 and discovered a high proportion of the residents had stained teeth, locally termed the "Colorado brown stain". He took this information to
1487:
436:
707:
describes what is thought to be dental fluorosis. However, it was not until the early 20th century that dental fluorosis became increasingly recognized and scientifically studied.
211:. The index underwent two changes, appearing in its final form in 1942. An individual's fluorosis score is based on the most severe form of fluorosis found on two or more teeth.
173:: Mechanical trauma to the primary tooth may cause disturbance to the maturation phase of enamel formation, which may result in enamel opacities on the permanent successors.
3298:
1114:
Skaare AB, Maseng Aas AL, Wang NJ (April 2013). "Enamel defects in permanent incisors after trauma to primary predecessors: inter-observer agreement based on photographs".
3480:
336:
94:(tooth decay caused by bacteria), although there may be cosmetic concern. In moderate to severe fluorosis, teeth are weakened and suffer permanent physical damage.
2527:
394:
Dental fluorosis may or may not be of cosmetic concern. In some cases, there may be varying degrees of negative psychosocial effects. The treatment options are:
3485:
236:
The enamel represents the usual translucent semivitriform (glass-like) type of structure. The surface is smooth, glossy and usually of pale creamy white color
115:, which extend toward the dentinal-enamel junction as the condition progresses and the affected teeth become more susceptible to staining. Due to diffusion of
431:
Fluorosis is common in the United States, with 41% of adolescents having definite fluorosis, and another 20% "questionably" having fluorosis according to the
673:
supplements as a prevention for tooth decay is rare in areas with water fluoridation, but was recommended by many dentists in the UK until the early 1990s.
1807:"Table 23, Surveillance for Dental Caries, Dental Sealants, Tooth Retention, Edentulism, and Enamel Fluorosis --- United States, 1988--1994 and 1999--2002"
4142:
356:) are enzymatically broken down and the rate at which the subsequent breakdown products are removed. Fluoride may also indirectly alter the action of
2139:
4112:
3310:
3261:
4137:
1748:
1557:"Surveillance for Dental Caries, Dental Sealants, Tooth Retention, Edentulism, and Enamel Fluorosis — United States, 1988–1994 and 1999–2002"
1252:
1187:
894:
818:
782:
2011:
1498:
681:
use fluoridated water to mix infant formula; and that the probability of babies developing fluorosis can be reduced by using ready-to-feed
282:
All enamel surfaces of the teeth are affected and surfaces subject to attrition show wear. Brown stain is frequently a disfiguring feature
3795:
3638:
2912:
2396:
4039:
1046:
186:
Severe fluorosis: brown discolored and mottled enamel of an individual from a region with high levels of naturally occurring fluoride
2672:
1533:
1212:
1918:
Velu H, Balozet L (1931). "Reproduction experimentale chez Ie mouton de la dystrophie dentaire des animaux des zones phosphates".
352:
In the extra-cellular environment of maturing enamel, an excess of fluoride ions alters the rate at which enamel matrix proteins (
4014:
3951:
3946:
3828:
3256:
3236:
2148:
1618:"Dental Fluorosis over Time: A comparison of National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data from 2001-2002 and 2011-2012"
3860:
3497:
2951:
1760:
3845:
3680:
1432:"Comment-Response Summary Report for the Peer Review of the Fluoride: Dose-Response Analysis for Non-Cancer Effects Document"
1518:
1336:
3685:
3209:
2818:
2522:
2507:
2445:
2391:
2314:
2132:
1845:
3737:
3700:
3430:
2711:
2623:
686:"Your dentist, pediatrician or family physician can help you determine how to optimize your child's fluoride intake."
677:
3747:
3695:
3502:
3435:
3204:
2704:
2699:
2650:
1431:
3752:
3470:
3374:
2845:
2309:
432:
271:
The white opaque areas in the enamel of the teeth are more extensive but do involve as much as 50% of the tooth.
4059:
3838:
3823:
3519:
3475:
3420:
3293:
3251:
3019:
2865:
2100:
1787:
69:
3892:
3224:
943:
3956:
3757:
3722:
3548:
3415:
3219:
2999:
2840:
2786:
2716:
2638:
2618:
2605:
2582:
2125:
152:
4102:
4069:
3742:
3732:
3727:
3669:
3596:
3552:
3448:
3443:
3229:
3059:
3054:
3029:
2875:
2806:
2633:
2542:
2460:
2187:
1829:
138:
131:
2726:
2450:
3911:
3813:
3425:
3303:
3283:
3165:
3124:
2987:
2975:
2924:
2587:
720:
112:
2660:
4009:
3648:
3633:
3199:
3132:
2738:
2470:
1973:
405:
126:
Enamel hypoplasia caused by untreated celiac disease: this condition is often confused with fluorosis
712:
4064:
3800:
3780:
3770:
3643:
3576:
3458:
3453:
3379:
3278:
2931:
2855:
2694:
2643:
2592:
2572:
2485:
2475:
2401:
2376:
2234:
2089:
1354:
973:
728:
182:
116:
84:
2341:
47:
Mild fluorosis: in its usual mildest form, fluorosis appears as opaque white patches on the enamel
4107:
3961:
3765:
3581:
3529:
3490:
3187:
3103:
3034:
2743:
2567:
2547:
2500:
2386:
2331:
2294:
2284:
2269:
2199:
2034:
1288:"Timing of fluoride intake in relation to development of fluorosis on maxillary central incisors"
1065:"Distinguishing between enamel fluorosis and other enamel defects in permanent teeth of children"
741:
416:
324:
4054:
4029:
3690:
1827:
Frequently Asked
Questions (FAQ), American Dental Association Website accessed February 4, 2012
1806:
4147:
3805:
3394:
3359:
3192:
3088:
2946:
2870:
2577:
2517:
2480:
2455:
2304:
2182:
2177:
2026:
1989:
1900:
1752:
1715:
1680:
1639:
1598:
1568:
1529:
1475:
1410:
1369:
1353:
Abanto
Alvarez J, Rezende KM, Marocho SM, Alves FB, Celiberti P, Ciamponi AL (February 2009).
1309:
1268:
1248:
1235:
Denbesten P, Li W (2011). "Chronic fluoride toxicity: dental fluorosis". In
Buzalaf MA (ed.).
1208:
1183:
1177:
1131:
1096:
1023:
988:
972:
Abanto
Alvarez J, Rezende KM, Marocho SM, Alves FB, Celiberti P, Ciamponi AL (February 2009).
890:
884:
865:
814:
778:
772:
746:
420:
412:
365:
156:
52:
808:
3775:
3410:
3400:
3364:
3273:
3024:
2963:
2897:
2835:
2733:
2628:
2465:
1981:
1946:
1890:
1707:
1670:
1629:
1465:
1400:
1299:
1258:
1240:
1123:
1086:
1076:
1015:
855:
847:
208:
119:(e.g., iron and copper), stains develop into the increasingly and abnormally porous enamel.
102:
3931:
3717:
3512:
3405:
3241:
3160:
3140:
3064:
3049:
2919:
2823:
2791:
2762:
2684:
2610:
2406:
2289:
2279:
2224:
2209:
1833:
1050:
1043:
716:
399:
378:
in a three step process. Dental fluorosis can be prevented at a population level through
145:
1556:
507:
1977:
1879:"Public Health Reports, November 1, 1901: Denti di Chiaie (Chiaie teeth), by J.M. Eager"
946:. Oral Health Services Research Centre, University College Cork, Ireland. Archived from
39:
4097:
4049:
4019:
3887:
3818:
3785:
3507:
3246:
2980:
2860:
2655:
2440:
2253:
1895:
1878:
1634:
1617:
1263:
1091:
1064:
1019:
860:
835:
682:
379:
371:
2094:
4131:
3999:
3877:
3705:
3524:
3288:
3268:
3177:
3044:
3004:
2801:
2562:
2537:
2512:
2490:
2274:
2264:
2229:
1304:
1287:
1127:
170:
91:
1737:
1587:
914:
3850:
3626:
3621:
3606:
3586:
3556:
3389:
3098:
3039:
2970:
2892:
2882:
2850:
2813:
2774:
2766:
2381:
2336:
2321:
2219:
2214:
2117:
1937:
Churchill HV (1931). "Occurrence of fluorides in some water of the United States".
851:
375:
73:
2105:
1286:
Hong L, Levy SM, Broffitt B, Warren JJ, Kanellis MJ, Wefel JS, Dawson CV (2006).
4044:
4034:
4024:
3941:
3936:
3867:
2941:
2902:
2721:
2597:
2557:
2425:
2346:
2326:
1985:
1658:
834:
Wong MC, Glenny AM, Tsang BW, Lo EC, Worthington HV, Marinho VC (January 2010).
164:
1711:
190:
4004:
3790:
3616:
3384:
3214:
3155:
3093:
3083:
3076:
3071:
3009:
2992:
2936:
2907:
2828:
2689:
2667:
2552:
2532:
2079:
1964:
Smith MC, Lantz EM, Smith HV (September 1931). "The Cause of
Mottled Enamel".
353:
167:: Fluorosis-resembling enamel defects are often misdiagnosed as dental caries.
1738:"Prevalence and Severity of Dental Fluorosis in the United States, 1999–2004"
1684:
1588:"Prevalence and severity of dental fluorosis in the United States, 1999-2004"
3872:
3855:
3591:
3369:
3172:
2796:
2679:
2299:
2194:
2172:
328:
57:
2030:
1993:
1756:
1719:
1643:
1602:
1572:
1479:
1470:
1453:
1414:
1405:
1388:
1373:
1313:
1272:
1135:
1100:
1027:
992:
869:
508:
9 percentage point increase in the prevalence of confirmed dental fluorosis
335:
increase in moderate to severe dental fluorosis from 1% to 4%. The 2011-12
122:
3882:
3833:
3601:
3354:
3335:
3315:
3136:
3014:
2958:
2204:
1904:
1698:
Aoba, T; Fejerskov, O (2016). "Dental Fluorosis: Chemistry and Biology".
383:
357:
77:
2062:
1950:
323:
ingestion of foods especially imported from other countries, and public
3968:
3926:
3611:
3571:
3465:
3339:
3128:
2495:
1081:
1675:
1488:"NHMRC Public Statement: The Efficacy and Safety of Fluoridation 2007"
1244:
3710:
3182:
2770:
2365:
2074:
1239:. Monographs in Oral Science, Vol. 22. Vol. 22. pp. 81–96.
106:
Amelogenesis imperfecta: this condition can be mistaken for fluorosis
83:
It appears as a range of visual changes in enamel causing degrees of
1517:
Fawell J, Bailey K, Chilton J, Dahi E, Fewtrell L, Magara Y (2006).
715:, an Italian professor. In the United States of America, a dentist,
408:(outer affected layer of enamel is abraded in an acidic environment)
1736:
Beltrán-Aguilar, Eugenio D.; Barker, Laurie; Dye, Bruce A. (2010).
1616:
Wiener, R. C; Shen, C; Findley, P; Tan, X; Sambamoorthi, U (2018).
947:
704:
189:
181:
121:
101:
161:
Enamel defects caused by infection of a primary tooth predecessor
1454:"A systematic review of the efficacy and safety of fluoridation"
4086:
3985:
3909:
3667:
3546:
3332:
3122:
2760:
2423:
2363:
2251:
2159:
2121:
1866:
Eager JM (November 1, 1901). "Denti di Chiaie (Chiaie teeth)".
1826:
1389:"Fluoride use in caries prevention in the primary care setting"
1207:. Washington, D.C. : National Academy Press. p. 171.
2161:
16:
Tooth enamel discoloration due to excessive fluoride ingestion
1561:
Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. Surveillance Summaries
836:"Topical fluoride as a cause of dental fluorosis in children"
774:
McDonald and Avery's Dentistry for the Child and Adolescent
813:(4th ed.). Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 52–54.
1846:"Fluorosis: Causes, Diagnosis, Management and Prevention"
777:(10th ed.). Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 132.
1355:"Dental fluorosis: exposure, prevention and management"
974:"Dental fluorosis: exposure, prevention and management"
1179:
Dental Caries: The Disease and Its Clinical Management
437:
National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research
207:
Dean's fluorosis index was first published in 1934 by
144:
Enamel defects caused by an undiagnosed and untreated
1519:"Environmental occurrence, geochemistry and exposure"
807:
Neville BW, Chi AC, Damm DD, Allen CM (13 May 2015).
497:
Total confirmed and questionable fluorosis prevalence
364:
Traditionally severe fluorosis has been described as
199:
relates fluorosis risk with tooth development stage.
194:
Severe fluorosis: the enamel is pitted and discolored
2052:
1586:
Beltrán-Aguilar, E. D; Barker, L; Dye, B. A (2010).
937:
935:
2056:
1555:Beltrán-Aguilar ED, et al. (August 26, 2005).
51:
29:
24:
3561:Jaw joints, chewing muscles and bite abnormalities
1809:. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2005
1659:"How 'Clean' Must a Cavity Be before Restoration?"
919:The History of Fluorine, Fluoride and Fluoridation
90:People with fluorosis are relatively resistant to
1171:
1169:
1167:
1165:
1795:. American Dental Association. 2005. p. 29.
1163:
1161:
1159:
1157:
1155:
1153:
1151:
1149:
1147:
1145:
1063:Sabokseir A, Golkari A, Sheiham A (2016-02-25).
967:
965:
3916:Teeth, jaws, tongue and associated soft tissues
1700:Critical Reviews in Oral Biology & Medicine
2528:Hereditary benign intraepithelial dyskeratosis
3486:Neuralgia-inducing cavitational osteonecrosis
2133:
2005:
2003:
1362:Medicina Oral, Patologia Oral y Cirugia Bucal
1008:Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry
981:Medicina Oral, Patologia Oral y Cirugia Bucal
802:
800:
798:
796:
794:
506:The U.S. Centers for Disease Control found a
315:surface of the enamel being hypomineralised.
8:
1861:
1859:
1528:. World Health Organization. pp. 5–27.
908:
906:
1495:National Health and Medial Research Council
1182:. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 299–327.
942:Whelton H, Browne D, Felicia P, Whelton J.
840:The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews
4083:
3982:
3906:
3664:
3543:
3329:
3119:
2757:
2420:
2360:
2248:
2156:
2140:
2126:
2118:
2053:
1731:
1729:
766:
764:
762:
382:, the downward adjustment of the level of
38:
21:
1894:
1674:
1633:
1469:
1404:
1303:
1292:Community Dentistry and Oral Epidemiology
1262:
1090:
1080:
915:"HT Dean´s epidemiology of Mottled Teeth"
859:
444:CDC findings on children and adolescents
141:(although this is usually more localized)
1044:Dental Enamel Defects and Celiac Disease
883:Bergc JH, Slayton RL (26 October 2015).
517:
442:
213:
4113:Oral manifestations of systemic disease
3262:Acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis
1782:
1780:
1387:Clark MB, Slayton RL (September 2014).
944:"E-training for Dean's Index Version 2"
758:
519:Dietary reference intakes for fluoride
68:is a common disorder, characterized by
3299:As a manifestation of systemic disease
1426:
1424:
1006:Ritter AV (2005). "Dental fluorosis".
889:. John Wiley & Sons. p. 113.
435:. As of 2005 surveys conducted by the
331:or pollution from high fluoride coal.
2019:The National Medical Journal of India
1749:National Center for Health Statistics
1230:
1228:
1226:
1224:
1176:Fejerskov O, Kidd E (16 March 2009).
1039:
1037:
7:
3145:Gums and tooth-supporting structures
489:Total confirmed fluorosis prevalence
3796:Papillary cystadenoma lymphomatosum
3639:Temporomandibular joint dysfunction
1205:Health effects of ingested fluoride
2913:Maxillary lateral incisor agenesis
2397:Inflammatory papillary hyperplasia
1053:National Institute of Health (NIH)
1020:10.1111/j.1708-8240.2005.tb00139.x
14:
4143:Toxic effects of dietary elements
1237:Fluoride and the Oral Environment
225:Criteria – description of enamel
76:caused by ingestion of excessive
4015:Cutaneous sinus of dental origin
3952:Obesity hypoventilation syndrome
3947:Central hypoventilation syndrome
3829:Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma
3257:Necrotizing periodontal diseases
3237:Hereditary gingival fibromatosis
2149:Oral and maxillofacial pathology
1305:10.1111/j.1600-0528.2006.00281.x
1128:10.1111/j.1600-9657.2012.01153.x
810:Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology
533:Tolerable upper intake (mg/day)
3861:Chronic sclerosing sialadenitis
3498:Osteoporotic bone marrow defect
2952:Keratocystic odontogenic tumour
1766:from the original on 2016-06-16
1439:Environmental Protection Agency
451:
448:
3846:Sclerosing polycystic adenosis
3681:Benign lymphoepithelial lesion
852:10.1002/14651858.CD007693.pub2
1:
4138:Developmental tooth disorders
4040:Melkersson–Rosenthal syndrome
3989:Soft tissues around the mouth
3686:Ectopic salivary gland tissue
134:for this condition includes:
85:intrinsic tooth discoloration
3210:Gingival cyst of the newborn
2819:Failure of eruption of teeth
2523:Hand, foot and mouth disease
2508:Focal epithelial hyperplasia
2446:Angina bullosa haemorrhagica
2392:Palatal cysts of the newborn
2315:Transient lingual papillitis
481:Moderate to severe fluorosis
3738:Salivary gland diverticulum
3701:Necrotizing sialometaplasia
2712:Smokeless tobacco keratosis
2624:Basaloid squamous carcinoma
1986:10.1126/science.74.1914.244
886:Early Childhood Oral Health
678:American Dental Association
4164:
3748:Salivary gland hyperplasia
3696:HIV salivary gland disease
3205:Gingival cyst of the adult
2651:Oral florid papillomatosis
1759:. NCHS data brief, no 53.
1712:10.1177/154411130201300206
1526:Fluoride in Drinking-water
771:Dean JA (10 August 2015).
653:Females 19 years and over
4093:
4082:
3995:
3987:Orofacial soft tissues –
3981:
3922:
3905:
3753:Salivary gland hypoplasia
3676:
3663:
3567:
3542:
3481:Bisphosphonate-associated
3375:Idiopathic osteosclerosis
3350:
3328:
3151:
3118:
2846:Dentinogenesis imperfecta
2782:
2756:
2436:
2419:
2372:
2359:
2310:Median rhomboid glossitis
2260:
2247:
2168:
2155:
1832:January 12, 2016, at the
1622:Journal of Dental Hygiene
530:Adequate intake (mg/day)
527:Reference weight kg (lb)
433:Center of Disease Control
80:during enamel formation.
46:
37:
4060:Orofacial granulomatosis
3839:Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
3824:Adenoid cystic carcinoma
3758:Salivary gland neoplasms
3549:Temporomandibular joints
3520:Periapical periodontitis
3252:Linear gingival erythema
3020:Regional odontodysplasia
2866:Enamel hypocalcification
1458:Evidence-Based Dentistry
732:decay was demonstrated.
639:Males 19 years and over
3957:Obstructive sleep apnea
3723:Salivary duct stricture
3503:Paget's disease of bone
3000:Pulp canal obliteration
2841:Dentin hypersensitivity
2787:Amelogenesis imperfecta
2639:Squamous cell carcinoma
2619:Adenosquamous carcinoma
2606:Squamous cell papilloma
2583:Melanocytic oral lesion
153:amelogenesis imperfecta
4103:Hemifacial hypertrophy
4070:Pyostomatitis vegetans
3743:Salivary gland fistula
3733:Salivary gland atresia
3728:Salivary gland aplasia
3582:Mandibular dislocation
3553:muscles of mastication
3431:Calcifying odontogenic
3060:Vertical root fracture
3055:Cracked tooth syndrome
3030:Shovel-shaped incisors
2925:Wisdom tooth impaction
2807:Early childhood caries
2673:Benign mucous membrane
2634:Spindle cell carcinoma
2543:Intraoral dental sinus
2461:Burning mouth syndrome
1497:. 2007. Archived from
1471:10.1038/sj.ebd.6400578
1406:10.1542/peds.2014-1699
1049:March 5, 2016, at the
457:Questionable fluorosis
195:
187:
132:differential diagnosis
127:
107:
3912:Stomatognathic system
3814:Acinic cell carcinoma
3436:Glandular odontogenic
2588:Molluscum contagiosum
1883:Public Health Reports
1868:Public Health Reports
1657:Kidd, E.A.M. (2004).
1441:. 2010. 820-R-10-016.
721:Greene Vardiman Black
676:In November 2006 the
202:
193:
185:
125:
105:
4055:Oral Crohn's disease
4010:Basal cell carcinoma
3649:Condylar hyperplasia
3634:Maxillary hypoplasia
3200:Gingival enlargement
3133:periodontal ligament
2739:Verruciform xanthoma
2471:Condyloma acuminatum
1920:Bull Acad Vet France
594:Children 9–13 years
552:Infants 7–12 months
406:Enamel microabrasion
4065:Perioral dermatitis
3801:Pleomorphic adenoma
3781:Monomorphic adenoma
3771:Canalicular adenoma
3644:Condylar hypoplasia
3577:Condylar resorption
3421:Lateral periodontal
3380:Mandibular fracture
3279:Periodontal abscess
2876:Turner's hypoplasia
2644:Verrucous carcinoma
2593:Morsicatio buccarum
2573:Lupus erythematosus
2486:Erythema multiforme
2402:Stomatitis nicotina
1978:1931Sci....74..244C
1951:10.1021/ie50261a007
1116:Dental Traumatology
729:Henry Trendley Dean
580:Children 4–8 years
566:Children 1–3 years
538:Infants 0–6 months
520:
465:Very mild fluorosis
445:
386:in drinking water.
215:
151:Some mild forms of
139:Turner's hypoplasia
113:hypomineralizations
4108:Facial hemiatrophy
3962:Periodic breathing
3893:Sjögren's syndrome
3766:Basal cell adenoma
3530:Torus mandibularis
3508:Periapical abscess
3491:Osteoradionecrosis
3416:Buccal bifurcation
3395:Intraosseous cysts
3284:Periodontal trauma
3188:Pyogenic granuloma
3035:Supernumerary root
2988:Pulp calcification
2976:Premature eruption
2947:Odontogenic tumors
2744:White sponge nevus
2717:Submucous fibrosis
2661:Smoker's melanosis
2548:Irritation fibroma
2387:High-arched palate
2295:Foliate papillitis
2285:Cunnilingus tongue
2270:Black hairy tongue
2200:Congenital lip pit
2012:"Dental fluorosis"
2010:Teotia SP (1999).
1889:(3): 284–5. 1976.
1852:. August 15, 2017.
1789:Fluoridation Facts
1337:"Dental Fluorosis"
1203:Wagner BM (1993).
1082:10.7717/peerj.1745
742:Skeletal fluorosis
703:In ancient times,
625:Girls 14–18 years
518:
443:
415:, Micro-abrasion,
413:Composite fillings
325:water fluoridation
260:or second molars.
214:
196:
188:
128:
108:
70:hypomineralization
4125:
4124:
4121:
4120:
4078:
4077:
3977:
3976:
3901:
3900:
3806:Sebaceous adenoma
3659:
3658:
3538:
3537:
3449:Median mandibular
3444:Nasopalatine duct
3360:Alveolar osteitis
3324:
3323:
3311:Perio-endo lesion
3193:Congenital epulis
3114:
3113:
2871:Enamel hypoplasia
2752:
2751:
2727:Riga–Fede disease
2578:Melanocytic nevus
2518:Hairy leukoplakia
2481:Epulis fissuratum
2415:
2414:
2355:
2354:
2305:Geographic tongue
2243:
2242:
2115:
2114:
1676:10.1159/000077770
1452:Yeung CA (2008).
1254:978-3-8055-9659-6
1245:10.1159/000327028
1189:978-1-4443-0928-7
896:978-1-118-79210-0
820:978-1-4557-7052-6
784:978-0-323-28746-3
747:Fluoride toxicity
666:
665:
608:Boys 14–18 years
504:
503:
366:enamel hypoplasia
298:
297:
157:enamel hypoplasia
63:
62:
19:Medical condition
4155:
4084:
3983:
3907:
3776:Ductal papilloma
3665:
3544:
3441:Non-odontogenic:
3426:Globulomaxillary
3365:Buccal exostosis
3330:
3274:Peri-implantitis
3120:
2836:Dentin dysplasia
2758:
2734:Verruca vulgaris
2629:Mucosal melanoma
2476:Darier's disease
2451:Behçet's disease
2421:
2377:Bednar's aphthae
2361:
2249:
2235:Trumpeter's wart
2157:
2142:
2135:
2128:
2119:
2054:
2042:
2041:
2039:
2033:. Archived from
2016:
2007:
1998:
1997:
1961:
1955:
1954:
1934:
1928:
1927:
1915:
1909:
1908:
1898:
1875:
1874:(44): 2576–2577.
1863:
1854:
1853:
1842:
1836:
1824:
1818:
1817:
1815:
1814:
1803:
1797:
1796:
1794:
1784:
1775:
1774:
1772:
1771:
1765:
1742:
1733:
1724:
1723:
1695:
1689:
1688:
1678:
1654:
1648:
1647:
1637:
1613:
1607:
1606:
1592:
1583:
1577:
1576:
1552:
1546:
1545:
1543:
1542:
1523:
1514:
1508:
1505:
1503:
1492:
1483:
1473:
1449:
1443:
1442:
1436:
1428:
1419:
1418:
1408:
1384:
1378:
1377:
1359:
1350:
1344:
1343:
1341:
1333:
1327:
1324:
1318:
1317:
1307:
1283:
1277:
1276:
1266:
1232:
1219:
1218:
1200:
1194:
1193:
1173:
1140:
1139:
1111:
1105:
1104:
1094:
1084:
1060:
1054:
1041:
1032:
1031:
1003:
997:
996:
978:
969:
960:
959:
957:
955:
939:
930:
929:
927:
925:
910:
901:
900:
880:
874:
873:
863:
831:
825:
824:
804:
789:
788:
768:
521:
446:
404:Moderate cases:
374:is converted to
216:
209:H. Trendley Dean
66:Dental fluorosis
42:
25:Dental fluorosis
22:
4163:
4162:
4158:
4157:
4156:
4154:
4153:
4152:
4128:
4127:
4126:
4117:
4089:
4074:
4030:Ludwig's angina
3991:
3973:
3932:Mouth breathing
3918:
3897:
3718:Pneumoparotitis
3691:Frey's syndrome
3672:
3670:Salivary glands
3655:
3563:
3534:
3513:Phoenix abscess
3346:
3342:hard tissues –
3320:
3242:Hypercementosis
3161:Cementoblastoma
3147:
3110:
2824:Dens evaginatus
2778:
2748:
2700:Denture-related
2685:Plasmoacanthoma
2611:Keratoacanthoma
2432:
2430:Lining of mouth
2411:
2407:Torus palatinus
2368:
2351:
2332:Lingual thyroid
2290:Fissured tongue
2280:Crenated tongue
2256:
2239:
2225:Nasolabial cyst
2210:Herpes labialis
2164:
2151:
2146:
2116:
2111:
2110:
2065:
2051:
2046:
2045:
2037:
2014:
2009:
2008:
2001:
1963:
1962:
1958:
1936:
1935:
1931:
1917:
1916:
1912:
1877:
1865:
1864:
1857:
1844:
1843:
1839:
1834:Wayback Machine
1825:
1821:
1812:
1810:
1805:
1804:
1800:
1792:
1786:
1785:
1778:
1769:
1767:
1763:
1745:NCHS Data Brief
1740:
1735:
1734:
1727:
1697:
1696:
1692:
1663:Caries Research
1656:
1655:
1651:
1615:
1614:
1610:
1595:NCHS Data Brief
1590:
1585:
1584:
1580:
1554:
1553:
1549:
1540:
1538:
1536:
1521:
1516:
1515:
1511:
1501:
1490:
1486:
1451:
1450:
1446:
1434:
1430:
1429:
1422:
1386:
1385:
1381:
1357:
1352:
1351:
1347:
1339:
1335:
1334:
1330:
1325:
1321:
1285:
1284:
1280:
1255:
1234:
1233:
1222:
1215:
1202:
1201:
1197:
1190:
1175:
1174:
1143:
1113:
1112:
1108:
1062:
1061:
1057:
1051:Wayback Machine
1042:
1035:
1005:
1004:
1000:
976:
971:
970:
963:
953:
951:
941:
940:
933:
923:
921:
912:
911:
904:
897:
882:
881:
877:
846:(1): CD007693.
833:
832:
828:
821:
806:
805:
792:
785:
770:
769:
760:
755:
738:
717:Frederick McKay
701:
692:
429:
400:Tooth bleaching
392:
346:
312:
303:
205:
180:
100:
20:
17:
12:
11:
5:
4161:
4159:
4151:
4150:
4145:
4140:
4130:
4129:
4123:
4122:
4119:
4118:
4116:
4115:
4110:
4105:
4100:
4098:Eagle syndrome
4094:
4091:
4090:
4087:
4080:
4079:
4076:
4075:
4073:
4072:
4067:
4062:
4057:
4052:
4047:
4042:
4037:
4032:
4027:
4022:
4020:Cystic hygroma
4017:
4012:
4007:
4002:
3996:
3993:
3992:
3986:
3979:
3978:
3975:
3974:
3972:
3971:
3966:
3965:
3964:
3959:
3954:
3949:
3944:
3934:
3929:
3923:
3920:
3919:
3910:
3903:
3902:
3899:
3898:
3896:
3895:
3890:
3888:Sialolithiasis
3885:
3880:
3875:
3870:
3865:
3864:
3863:
3858:
3848:
3843:
3842:
3841:
3836:
3831:
3826:
3821:
3819:Adenocarcinoma
3816:
3808:
3803:
3798:
3793:
3788:
3786:Myoepithelioma
3783:
3778:
3773:
3768:
3755:
3750:
3745:
3740:
3735:
3730:
3725:
3720:
3715:
3714:
3713:
3703:
3698:
3693:
3688:
3683:
3677:
3674:
3673:
3668:
3661:
3660:
3657:
3656:
3654:
3653:
3652:
3651:
3646:
3636:
3631:
3630:
3629:
3624:
3619:
3614:
3609:
3604:
3599:
3594:
3584:
3579:
3574:
3568:
3565:
3564:
3547:
3540:
3539:
3536:
3535:
3533:
3532:
3527:
3522:
3517:
3516:
3515:
3505:
3500:
3495:
3494:
3493:
3488:
3483:
3473:
3468:
3463:
3462:
3461:
3459:Traumatic bone
3456:
3454:Median palatal
3451:
3446:
3438:
3433:
3428:
3423:
3418:
3413:
3408:
3392:
3387:
3382:
3377:
3372:
3367:
3362:
3357:
3351:
3348:
3347:
3333:
3326:
3325:
3322:
3321:
3319:
3318:
3313:
3308:
3307:
3306:
3301:
3296:
3286:
3281:
3276:
3271:
3266:
3265:
3264:
3254:
3249:
3247:Hypocementosis
3244:
3239:
3234:
3233:
3232:
3227:
3222:
3212:
3207:
3202:
3197:
3196:
3195:
3190:
3180:
3175:
3170:
3169:
3168:
3158:
3152:
3149:
3148:
3123:
3116:
3115:
3112:
3111:
3109:
3108:
3107:
3106:
3101:
3096:
3091:
3081:
3080:
3079:
3069:
3068:
3067:
3062:
3057:
3052:
3042:
3037:
3032:
3027:
3022:
3017:
3012:
3007:
3002:
2997:
2996:
2995:
2985:
2984:
2983:
2981:Neonatal teeth
2973:
2968:
2967:
2966:
2956:
2955:
2954:
2944:
2939:
2934:
2929:
2928:
2927:
2917:
2916:
2915:
2905:
2900:
2895:
2890:
2885:
2880:
2879:
2878:
2868:
2863:
2861:Ectopic enamel
2858:
2853:
2848:
2843:
2838:
2833:
2832:
2831:
2821:
2816:
2811:
2810:
2809:
2799:
2794:
2789:
2783:
2780:
2779:
2761:
2754:
2753:
2750:
2749:
2747:
2746:
2741:
2736:
2731:
2730:
2729:
2719:
2714:
2709:
2708:
2707:
2702:
2697:
2687:
2682:
2677:
2676:
2675:
2665:
2664:
2663:
2656:Oral melanosis
2653:
2648:
2647:
2646:
2641:
2636:
2631:
2626:
2621:
2613:
2608:
2595:
2590:
2585:
2580:
2575:
2570:
2565:
2560:
2555:
2550:
2545:
2540:
2535:
2530:
2525:
2520:
2515:
2510:
2505:
2504:
2503:
2493:
2488:
2483:
2478:
2473:
2468:
2463:
2458:
2456:Bohn's nodules
2453:
2448:
2443:
2441:Amalgam tattoo
2437:
2434:
2433:
2424:
2417:
2416:
2413:
2412:
2410:
2409:
2404:
2399:
2394:
2389:
2384:
2379:
2373:
2370:
2369:
2364:
2357:
2356:
2353:
2352:
2350:
2349:
2344:
2339:
2334:
2329:
2324:
2319:
2318:
2317:
2312:
2307:
2297:
2292:
2287:
2282:
2277:
2272:
2267:
2261:
2258:
2257:
2252:
2245:
2244:
2241:
2240:
2238:
2237:
2232:
2227:
2222:
2217:
2212:
2207:
2202:
2197:
2192:
2191:
2190:
2185:
2180:
2169:
2166:
2165:
2160:
2153:
2152:
2147:
2145:
2144:
2137:
2130:
2122:
2113:
2112:
2109:
2108:
2097:
2082:
2066:
2061:
2060:
2058:
2057:Classification
2050:
2049:External links
2047:
2044:
2043:
2040:on 2016-03-04.
1999:
1956:
1945:(9): 996–998.
1929:
1910:
1855:
1837:
1819:
1798:
1776:
1725:
1690:
1669:(3): 305–313.
1649:
1608:
1578:
1547:
1534:
1509:
1507:
1506:
1504:on 2014-02-13.
1444:
1420:
1379:
1345:
1328:
1319:
1298:(4): 299–309.
1278:
1253:
1220:
1213:
1195:
1188:
1141:
1106:
1055:
1033:
998:
961:
950:on 4 June 2016
931:
902:
895:
875:
826:
819:
790:
783:
757:
756:
754:
751:
750:
749:
744:
737:
734:
713:Stefano Chiaie
700:
697:
691:
688:
683:infant formula
664:
663:
660:
657:
654:
650:
649:
646:
643:
640:
636:
635:
632:
629:
626:
622:
621:
618:
615:
609:
605:
604:
601:
598:
595:
591:
590:
587:
584:
581:
577:
576:
573:
570:
567:
563:
562:
559:
556:
553:
549:
548:
545:
542:
539:
535:
534:
531:
528:
525:
502:
501:
498:
494:
493:
490:
486:
485:
482:
478:
477:
474:
473:Mild fluorosis
470:
469:
466:
462:
461:
458:
454:
453:
450:
428:
425:
424:
423:
411:Severe cases:
409:
402:
391:
388:
380:defluoridation
372:Hydroxyapatite
345:
342:
311:
308:
302:
299:
296:
295:
291:
288:
284:
283:
280:
277:
273:
272:
269:
266:
262:
261:
257:
254:
250:
249:
245:
242:
238:
237:
234:
231:
227:
226:
223:
220:
219:Classification
204:
201:
179:
178:Classification
176:
175:
174:
168:
162:
159:
149:
146:celiac disease
142:
117:exogenous ions
99:
96:
61:
60:
55:
49:
48:
44:
43:
35:
34:
33:Mottled enamel
31:
27:
26:
18:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
4160:
4149:
4146:
4144:
4141:
4139:
4136:
4135:
4133:
4114:
4111:
4109:
4106:
4104:
4101:
4099:
4096:
4095:
4092:
4085:
4081:
4071:
4068:
4066:
4063:
4061:
4058:
4056:
4053:
4051:
4048:
4046:
4043:
4041:
4038:
4036:
4033:
4031:
4028:
4026:
4023:
4021:
4018:
4016:
4013:
4011:
4008:
4006:
4003:
4001:
4000:Actinomycosis
3998:
3997:
3994:
3990:
3984:
3980:
3970:
3967:
3963:
3960:
3958:
3955:
3953:
3950:
3948:
3945:
3943:
3940:
3939:
3938:
3935:
3933:
3930:
3928:
3925:
3924:
3921:
3917:
3913:
3908:
3904:
3894:
3891:
3889:
3886:
3884:
3881:
3879:
3878:Sialodochitis
3876:
3874:
3871:
3869:
3866:
3862:
3859:
3857:
3854:
3853:
3852:
3849:
3847:
3844:
3840:
3837:
3835:
3832:
3830:
3827:
3825:
3822:
3820:
3817:
3815:
3812:
3809:
3807:
3804:
3802:
3799:
3797:
3794:
3792:
3789:
3787:
3784:
3782:
3779:
3777:
3774:
3772:
3769:
3767:
3764:
3761:
3760:
3759:
3756:
3754:
3751:
3749:
3746:
3744:
3741:
3739:
3736:
3734:
3731:
3729:
3726:
3724:
3721:
3719:
3716:
3712:
3709:
3708:
3707:
3704:
3702:
3699:
3697:
3694:
3692:
3689:
3687:
3684:
3682:
3679:
3678:
3675:
3671:
3666:
3662:
3650:
3647:
3645:
3642:
3641:
3640:
3637:
3635:
3632:
3628:
3625:
3623:
3620:
3618:
3615:
3613:
3610:
3608:
3605:
3603:
3600:
3598:
3595:
3593:
3590:
3589:
3588:
3585:
3583:
3580:
3578:
3575:
3573:
3570:
3569:
3566:
3562:
3558:
3557:malocclusions
3554:
3550:
3545:
3541:
3531:
3528:
3526:
3525:Stafne defect
3523:
3521:
3518:
3514:
3511:
3510:
3509:
3506:
3504:
3501:
3499:
3496:
3492:
3489:
3487:
3484:
3482:
3479:
3478:
3477:
3476:Osteonecrosis
3474:
3472:
3471:Osteomyelitis
3469:
3467:
3464:
3460:
3457:
3455:
3452:
3450:
3447:
3445:
3442:
3439:
3437:
3434:
3432:
3429:
3427:
3424:
3422:
3419:
3417:
3414:
3412:
3409:
3407:
3404:
3402:
3398:
3397:
3396:
3393:
3391:
3388:
3386:
3383:
3381:
3378:
3376:
3373:
3371:
3368:
3366:
3363:
3361:
3358:
3356:
3353:
3352:
3349:
3345:
3344:Bones of jaws
3341:
3337:
3331:
3327:
3317:
3314:
3312:
3309:
3305:
3302:
3300:
3297:
3295:
3292:
3291:
3290:
3289:Periodontitis
3287:
3285:
3282:
3280:
3277:
3275:
3272:
3270:
3269:Pericoronitis
3267:
3263:
3260:
3259:
3258:
3255:
3253:
3250:
3248:
3245:
3243:
3240:
3238:
3235:
3231:
3228:
3226:
3225:Granulomatous
3223:
3221:
3218:
3217:
3216:
3213:
3211:
3208:
3206:
3203:
3201:
3198:
3194:
3191:
3189:
3186:
3185:
3184:
3181:
3179:
3178:Eruption cyst
3176:
3174:
3171:
3167:
3164:
3163:
3162:
3159:
3157:
3154:
3153:
3150:
3146:
3142:
3138:
3134:
3130:
3126:
3121:
3117:
3105:
3102:
3100:
3097:
3095:
3092:
3090:
3087:
3086:
3085:
3082:
3078:
3075:
3074:
3073:
3070:
3066:
3063:
3061:
3058:
3056:
3053:
3051:
3048:
3047:
3046:
3043:
3041:
3038:
3036:
3033:
3031:
3028:
3026:
3023:
3021:
3018:
3016:
3013:
3011:
3008:
3006:
3005:Pulp necrosis
3003:
3001:
2998:
2994:
2991:
2990:
2989:
2986:
2982:
2979:
2978:
2977:
2974:
2972:
2969:
2965:
2964:Dens in dente
2962:
2961:
2960:
2957:
2953:
2950:
2949:
2948:
2945:
2943:
2940:
2938:
2935:
2933:
2930:
2926:
2923:
2922:
2921:
2918:
2914:
2911:
2910:
2909:
2906:
2904:
2901:
2899:
2896:
2894:
2891:
2889:
2886:
2884:
2881:
2877:
2874:
2873:
2872:
2869:
2867:
2864:
2862:
2859:
2857:
2856:Discoloration
2854:
2852:
2849:
2847:
2844:
2842:
2839:
2837:
2834:
2830:
2827:
2826:
2825:
2822:
2820:
2817:
2815:
2812:
2808:
2805:
2804:
2803:
2800:
2798:
2795:
2793:
2790:
2788:
2785:
2784:
2781:
2776:
2772:
2768:
2764:
2759:
2755:
2745:
2742:
2740:
2737:
2735:
2732:
2728:
2725:
2724:
2723:
2720:
2718:
2715:
2713:
2710:
2706:
2703:
2701:
2698:
2696:
2693:
2692:
2691:
2688:
2686:
2683:
2681:
2678:
2674:
2671:
2670:
2669:
2666:
2662:
2659:
2658:
2657:
2654:
2652:
2649:
2645:
2642:
2640:
2637:
2635:
2632:
2630:
2627:
2625:
2622:
2620:
2617:
2614:
2612:
2609:
2607:
2604:
2601:
2600:
2599:
2596:
2594:
2591:
2589:
2586:
2584:
2581:
2579:
2576:
2574:
2571:
2569:
2566:
2564:
2563:Lichen planus
2561:
2559:
2556:
2554:
2551:
2549:
2546:
2544:
2541:
2539:
2538:Herpes zoster
2536:
2534:
2531:
2529:
2526:
2524:
2521:
2519:
2516:
2514:
2513:Fordyce spots
2511:
2509:
2506:
2502:
2499:
2498:
2497:
2494:
2492:
2491:Erythroplakia
2489:
2487:
2484:
2482:
2479:
2477:
2474:
2472:
2469:
2467:
2464:
2462:
2459:
2457:
2454:
2452:
2449:
2447:
2444:
2442:
2439:
2438:
2435:
2431:
2427:
2422:
2418:
2408:
2405:
2403:
2400:
2398:
2395:
2393:
2390:
2388:
2385:
2383:
2380:
2378:
2375:
2374:
2371:
2367:
2362:
2358:
2348:
2345:
2343:
2340:
2338:
2335:
2333:
2330:
2328:
2325:
2323:
2320:
2316:
2313:
2311:
2308:
2306:
2303:
2302:
2301:
2298:
2296:
2293:
2291:
2288:
2286:
2283:
2281:
2278:
2276:
2275:Caviar tongue
2273:
2271:
2268:
2266:
2265:Ankyloglossia
2263:
2262:
2259:
2255:
2250:
2246:
2236:
2233:
2231:
2230:Sun poisoning
2228:
2226:
2223:
2221:
2218:
2216:
2213:
2211:
2208:
2206:
2203:
2201:
2198:
2196:
2193:
2189:
2186:
2184:
2181:
2179:
2176:
2175:
2174:
2171:
2170:
2167:
2163:
2158:
2154:
2150:
2143:
2138:
2136:
2131:
2129:
2124:
2123:
2120:
2107:
2103:
2102:
2098:
2096:
2092:
2091:
2087:
2083:
2081:
2077:
2076:
2072:
2068:
2067:
2064:
2059:
2055:
2048:
2036:
2032:
2028:
2024:
2020:
2013:
2006:
2004:
2000:
1995:
1991:
1987:
1983:
1979:
1975:
1972:(1914): 244.
1971:
1967:
1960:
1957:
1952:
1948:
1944:
1940:
1933:
1930:
1925:
1921:
1914:
1911:
1906:
1902:
1897:
1892:
1888:
1884:
1880:
1876:Reprinted in
1873:
1869:
1862:
1860:
1856:
1851:
1847:
1841:
1838:
1835:
1831:
1828:
1823:
1820:
1808:
1802:
1799:
1791:
1790:
1783:
1781:
1777:
1762:
1758:
1754:
1750:
1746:
1739:
1732:
1730:
1726:
1721:
1717:
1713:
1709:
1706:(2): 155–70.
1705:
1701:
1694:
1691:
1686:
1682:
1677:
1672:
1668:
1664:
1660:
1653:
1650:
1645:
1641:
1636:
1631:
1627:
1623:
1619:
1612:
1609:
1604:
1600:
1596:
1589:
1582:
1579:
1574:
1570:
1566:
1562:
1558:
1551:
1548:
1537:
1535:92-4-156319-2
1531:
1527:
1520:
1513:
1510:
1500:
1496:
1489:
1485:
1484:
1481:
1477:
1472:
1467:
1463:
1459:
1455:
1448:
1445:
1440:
1433:
1427:
1425:
1421:
1416:
1412:
1407:
1402:
1399:(3): 626–33.
1398:
1394:
1390:
1383:
1380:
1375:
1371:
1368:(2): E103–7.
1367:
1363:
1356:
1349:
1346:
1338:
1332:
1329:
1323:
1320:
1315:
1311:
1306:
1301:
1297:
1293:
1289:
1282:
1279:
1274:
1270:
1265:
1260:
1256:
1250:
1246:
1242:
1238:
1231:
1229:
1227:
1225:
1221:
1216:
1214:9786610211333
1210:
1206:
1199:
1196:
1191:
1185:
1181:
1180:
1172:
1170:
1168:
1166:
1164:
1162:
1160:
1158:
1156:
1154:
1152:
1150:
1148:
1146:
1142:
1137:
1133:
1129:
1125:
1121:
1117:
1110:
1107:
1102:
1098:
1093:
1088:
1083:
1078:
1074:
1070:
1066:
1059:
1056:
1052:
1048:
1045:
1040:
1038:
1034:
1029:
1025:
1021:
1017:
1013:
1009:
1002:
999:
994:
990:
987:(2): E103–7.
986:
982:
975:
968:
966:
962:
949:
945:
938:
936:
932:
920:
916:
909:
907:
903:
898:
892:
888:
887:
879:
876:
871:
867:
862:
857:
853:
849:
845:
841:
837:
830:
827:
822:
816:
812:
811:
803:
801:
799:
797:
795:
791:
786:
780:
776:
775:
767:
765:
763:
759:
752:
748:
745:
743:
740:
739:
735:
733:
730:
724:
722:
718:
714:
708:
706:
698:
696:
689:
687:
684:
679:
674:
670:
661:
658:
655:
652:
651:
647:
644:
641:
638:
637:
633:
630:
627:
624:
623:
619:
616:
614:
610:
607:
606:
602:
599:
596:
593:
592:
588:
585:
582:
579:
578:
574:
571:
568:
565:
564:
560:
557:
554:
551:
550:
546:
543:
540:
537:
536:
532:
529:
526:
523:
522:
516:
512:
509:
499:
496:
495:
491:
488:
487:
483:
480:
479:
475:
472:
471:
467:
464:
463:
459:
456:
455:
447:
441:
438:
434:
426:
422:
418:
414:
410:
407:
403:
401:
397:
396:
395:
389:
387:
385:
381:
377:
373:
369:
367:
362:
359:
355:
350:
343:
341:
338:
332:
330:
326:
320:
316:
309:
307:
300:
292:
289:
286:
285:
281:
278:
275:
274:
270:
267:
264:
263:
258:
255:
252:
251:
246:
243:
240:
239:
235:
232:
229:
228:
224:
221:
218:
217:
212:
210:
200:
192:
184:
177:
172:
171:Dental trauma
169:
166:
165:Dental caries
163:
160:
158:
154:
150:
147:
143:
140:
137:
136:
135:
133:
124:
120:
118:
114:
104:
97:
95:
93:
92:dental caries
88:
86:
81:
79:
75:
71:
67:
59:
56:
54:
50:
45:
41:
36:
32:
28:
23:
3988:
3915:
3851:Sialadenitis
3810:
3762:
3627:Scissor bite
3622:Retrognathia
3607:Overeruption
3587:Malocclusion
3560:
3440:
3399:
3390:Micrognathia
3343:
3334:Periapical,
3220:Desquamative
3144:
3125:Periodontium
3099:Acid erosion
3040:Taurodontism
2971:Open contact
2887:
2883:Enamel pearl
2851:Dilaceration
2814:Concrescence
2615:
2602:
2429:
2382:Cleft palate
2342:Microglossia
2337:Macroglossia
2322:Glossoptosis
2220:Microcheilia
2215:Macrocheilia
2099:
2084:
2069:
2035:the original
2022:
2018:
1969:
1965:
1959:
1942:
1939:Ind Eng Chem
1938:
1932:
1923:
1919:
1913:
1886:
1882:
1871:
1867:
1849:
1840:
1822:
1811:. Retrieved
1801:
1788:
1768:. Retrieved
1744:
1703:
1699:
1693:
1666:
1662:
1652:
1628:(1): 23–29.
1625:
1621:
1611:
1594:
1581:
1564:
1560:
1550:
1539:. Retrieved
1525:
1512:
1499:the original
1494:
1464:(2): 39–43.
1461:
1457:
1447:
1438:
1396:
1392:
1382:
1365:
1361:
1348:
1331:
1322:
1295:
1291:
1281:
1236:
1204:
1198:
1178:
1122:(2): 79–83.
1119:
1115:
1109:
1072:
1068:
1058:
1014:(5): 326–7.
1011:
1007:
1001:
984:
980:
952:. Retrieved
948:the original
922:. Retrieved
918:
885:
878:
843:
839:
829:
809:
773:
725:
709:
702:
693:
675:
671:
667:
612:
513:
505:
449:Deans Index
430:
427:Epidemiology
398:Mild cases:
393:
376:fluorapatite
370:
363:
351:
347:
333:
321:
317:
313:
304:
241:Questionable
206:
203:Dean's index
197:
129:
109:
89:
82:
74:tooth enamel
65:
64:
4045:Microstomia
4035:Macrostomia
4025:Gnathophyma
3942:Catathrenia
3937:Sleep apnea
3868:Sialectasis
3411:Dentigerous
3401:Odontogenic
3230:Plasma cell
3166:Gigantiform
2942:Microdontia
2932:Macrodontia
2903:Hyperdontia
2598:Oral cancer
2558:Leukoplakia
2466:Candidiasis
2426:Oral mucosa
2347:Rhabdomyoma
2327:Hypoglossia
2188:Plasma cell
2025:(3): 96–8.
1597:(53): 1–8.
1567:(3): 1–44.
954:12 November
924:12 November
30:Other names
4132:Categories
4005:Angioedema
3811:Malignant:
3791:Oncocytoma
3617:Prognathia
3406:periapical
3385:Microgenia
3336:mandibular
3294:Aggressive
3215:Gingivitis
3156:Cementicle
3094:Abfraction
3084:Tooth wear
3077:Edentulism
3072:Tooth loss
3025:Resorption
3010:Pulp polyp
2993:Pulp stone
2937:Meth mouth
2908:Hypodontia
2898:Gemination
2829:Talon cusp
2722:Ulceration
2690:Stomatitis
2668:Pemphigoid
2616:Malignant:
2568:Linea alba
2553:Leukoedema
2533:Herpangina
2501:Giant-cell
1813:2006-10-29
1770:2011-04-26
1541:2009-01-24
1393:Pediatrics
913:Meiers P.
753:References
690:Prevention
524:Age group
390:Management
354:amelogenin
3873:Sialocele
3856:Parotitis
3597:Open bite
3592:Crossbite
3370:Cherubism
3340:maxillary
3173:Cementoma
3104:Attrition
2920:Impaction
2888:Fluorosis
2797:Anodontia
2792:Ankylosis
2680:Pemphigus
2300:Glossitis
2195:Cleft lip
2173:Cheilitis
1685:0008-6568
1075:: e1745.
656:61 (133)
642:76 (166)
628:57 (125)
344:Mechanism
329:brick tea
253:Very Mild
98:Diagnosis
58:Dentistry
53:Specialty
4148:Fluorine
3883:Sialosis
3834:Lymphoma
3706:Mucocele
3602:Overbite
3355:Agnathia
3316:Teething
3141:alveolus
3137:cementum
3089:Abrasion
3065:Occlusal
3050:Avulsion
3015:Pulpitis
2959:Odontoma
2705:Herpetic
2695:Aphthous
2205:Eclabium
2031:10492579
1994:17755565
1830:Archived
1761:Archived
1757:21211168
1720:12097358
1644:29500282
1603:21211168
1573:16121123
1480:18584000
1415:25157014
1374:19179949
1314:16856950
1273:21701193
1136:22676308
1101:26966672
1047:Archived
1028:16225799
993:19179949
870:20091645
736:See also
597:40 (88)
583:22 (48)
569:13 (29)
384:fluoride
358:protease
301:TF index
276:Moderate
78:fluoride
3969:Snoring
3927:Bruxism
3763:Benign:
3612:Overjet
3572:Bruxism
3466:Osteoma
3304:Chronic
3129:gingiva
2603:Benign:
2496:Fibroma
2183:Angular
2178:Actinic
2106:D009050
1974:Bibcode
1966:Science
1896:1438998
1850:AIMU.us
1751:: 1–8.
1635:5929463
1264:3433161
1092:4782718
861:8078481
699:History
555:9 (20)
541:7 (16)
500:43.15%
492:31.65%
468:21.68%
417:Veneers
306:cases.
3711:Ranula
3183:Epulis
3045:Trauma
2893:Fusion
2802:Caries
2775:enamel
2771:dentin
2366:Palate
2254:Tongue
2029:
1992:
1926:: 373.
1905:818673
1903:
1893:
1755:
1747:(53).
1718:
1683:
1642:
1632:
1601:
1571:
1532:
1478:
1413:
1372:
1312:
1271:
1261:
1251:
1211:
1186:
1134:
1099:
1089:
1026:
991:
893:
868:
858:
817:
781:
613:(142)
484:3.26%
476:6.59%
460:11.5%
421:Crowns
337:NHANES
310:Causes
287:Severe
230:Normal
4088:Other
2763:Teeth
2095:520.3
2080:K00.3
2038:(PDF)
2015:(PDF)
1793:(PDF)
1764:(PDF)
1741:(PDF)
1591:(PDF)
1522:(PDF)
1502:(PDF)
1491:(PDF)
1435:(PDF)
1358:(PDF)
1340:(PDF)
1069:PeerJ
977:(PDF)
705:Galen
544:0.01
452:2002
4050:Noma
3555:and
3338:and
3143:) –
2767:pulp
2162:Lips
2101:MeSH
2090:9-CM
2027:PMID
1990:PMID
1901:PMID
1753:PMID
1716:PMID
1681:ISSN
1640:PMID
1599:PMID
1569:PMID
1530:ISBN
1476:PMID
1411:PMID
1370:PMID
1310:PMID
1269:PMID
1249:ISBN
1209:ISBN
1184:ISBN
1132:PMID
1097:PMID
1024:PMID
989:PMID
956:2015
926:2015
891:ISBN
866:PMID
844:2010
815:ISBN
779:ISBN
659:3.0
645:4.0
631:3.0
617:3.0
600:2.0
589:2.2
586:1.0
575:1.3
572:0.7
561:0.9
558:0.5
547:0.7
265:Mild
222:Code
155:and
130:The
2086:ICD
2071:ICD
1982:doi
1947:doi
1891:PMC
1708:doi
1671:doi
1630:PMC
1466:doi
1401:doi
1397:134
1300:doi
1259:PMC
1241:doi
1124:doi
1087:PMC
1077:doi
1016:doi
856:PMC
848:doi
662:10
648:10
634:10
620:10
611:64
603:10
72:of
4134::
3914:–
3559:–
3551:,
3139:,
3135:,
3131:,
2773:,
2769:,
2428:–
2104::
2093::
2078::
2075:10
2023:12
2021:.
2017:.
2002:^
1988:.
1980:.
1970:74
1968:.
1943:23
1941:.
1922:.
1899:.
1887:91
1885:.
1881:.
1872:16
1870:.
1858:^
1848:.
1779:^
1743:.
1728:^
1714:.
1704:13
1702:.
1679:.
1667:38
1665:.
1661:.
1638:.
1626:92
1624:.
1620:.
1593:.
1565:54
1563:.
1559:.
1524:.
1493:.
1474:.
1460:.
1456:.
1437:.
1423:^
1409:.
1395:.
1391:.
1366:14
1364:.
1360:.
1308:.
1296:34
1294:.
1290:.
1267:.
1257:.
1247:.
1223:^
1144:^
1130:.
1120:29
1118:.
1095:.
1085:.
1071:.
1067:.
1036:^
1022:.
1012:17
1010:.
985:14
983:.
979:.
964:^
934:^
917:.
905:^
864:.
854:.
842:.
838:.
793:^
761:^
419:,
3403::
3127:(
2777:)
2765:(
2141:e
2134:t
2127:v
2088:-
2073:-
2063:D
1996:.
1984::
1976::
1953:.
1949::
1924:4
1907:.
1816:.
1773:.
1722:.
1710::
1687:.
1673::
1646:.
1605:.
1575:.
1544:.
1482:.
1468::
1462:9
1417:.
1403::
1376:.
1342:.
1316:.
1302::
1275:.
1243::
1217:.
1192:.
1138:.
1126::
1103:.
1079::
1073:4
1030:.
1018::
995:.
958:.
928:.
899:.
872:.
850::
823:.
787:.
290:5
279:4
268:3
256:2
244:1
233:0
148:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.