1248:, and then coordinated an attack into the heart of Germany both overland and by river. The Roman fleet and legions met on the Elbe, whereupon Tiberius departed from the Elbe to march back westward at the end of the summer without stationing occupying forces at this eastern position. This accomplished a demonstration to his troops, to Rome, and to the German peoples that his army could move largely unopposed through Germany, but like Drusus, he did nothing to hold territory. Tiberius' forces were attacked by German troops on the way west back to the Rhine, but successfully defended themselves.
1212:. The next year, conflicts between the Rome and the Cherusci flared up. While the elite members of one faction sought stronger ties with Roman leaders, the Cherusci as a whole would continue to resist for the next twenty years. Although Ahenobarbus had marched to the Elbe and directed the construction of infrastructure in the region east of the Rhine, he did not do well against the Cherusci warrior bands, who he tried to handle like Tiberius had the Sicambri. Augustus recalled Ahenobarbus to Rome in 2 BC and replaced him with a more seasoned military commander,
1392:
the road southwest around the hill's northeastern point). Roman forces continued along the sloshy sandbank at the base of the hill until the front of the column was attacked. They heard loud shouting and spears began falling on them from the woody slope to their left. Spears then began falling from the woods to their right and the front fell into disorder from panic. The surrounded soldiers were unable to defend themselves because they were marching in close formation and the terrain was too muddy for them to move effectively.
1396:
soldiers at the front further into the enemy, and thousands of German warriors began to pour out of the woods to attack up close. The soldiers at the middle and rear of the column began to flee in all directions, but most of them were caught in the bog or killed. Varus realized the severity of his situation and killed himself with his sword. A few Romans survived and made their way back to the winter quarters at Xanten by staying hidden and carefully travelling through the forests.
1040:
1170:
1252:
1413:
2286:
1375:
anyway, and the small revolt would only be a small detour – about two days away. Varus departed to deal with the revolt believing that
Arminius would ride ahead to garner the support of his tribesmen for the Roman cause. In reality, Arminius was actually preparing an ambush. Varus took no extra precautions on the march to quell the uprising, as he was expecting no trouble.
50:
1050:, an experienced general and stepson of Augustus, was made governor of Gaul in 13 BC. The following year saw an uprising in Gaul – a response to the Roman census and taxation policy set in place by Augustus. For most of the following year he conducted reconnaissance and dealt with supply and communications. He also had several forts built along the Rhine, including
1324:
1148:, "conquering with difficulty the territory traversed and defeating the forces that attacked him only after considerable bloodshed." Afterwards, he once again attacked the Cherusci, and followed the retreating Cherusci across the Weser River, and advanced as far as the Elbe, "pillaging everything in his way", as Cassius Dio puts it.
1388:. Scouts were local Germans as they would have had knowledge of the terrain, and so would had to have been a part of Arminius' ploy. Indeed, they reported that the path ahead was safe. Historians Wells and Abdale say that the scouts likely alerted the Germans to the advancing column, giving them time to get into position.
1278:, who was around twenty-two at the time. Membership in this clan gave him special favor with Rome. Tiberius lent support to this ruling clan to gain control over the Cherusci, and he granted the tribe a free status among the German peoples. To keep an eye on the Cherusci, Tiberius had a winter base built on the Lippe.
1122:, and pushed as far east as the Weser. This was the furthest east into northern Europe that a Roman general had ever traveled, a feat which won him much renown. Between depleted supplies and the coming winter, he decided to march back to friendly territory. On the return trip, Drusus' legions were nearly destroyed at
1499:. Roman writers, including Tacitus and Cassius Dio, mention that Augustus left a statement ordering the end of imperial expansion. It's not known if Augustus actually made such an order, or if Tiberius found it necessary to stop Roman expansion as the costs were too great, both financially and militarily.
1460:
According to Seager and Wells, Velleius' account is almost certainly an exaggeration. Seager says that
Tiberius successfully applied tactics that he had developed in Illyricum, but that his attacks were "no more than punitive raids". Tiberius did not get far in his conquest of Germany, because he was
1421:
It had become clear that German lands had not been pacified. After word reached Rome of Varus' defeat, Augustus had
Tiberius sent back to the Rhine to stabilize the frontier in AD 10. Tiberius increased the defensive capabilities of the Rhine fortifications and redistributed forces across the region.
1374:
Not much is known of the campaign of AD 9 until the return trip, when Varus left with his legions from their camp on the Weser. On their way back to Castra Vetera, Varus received reports from
Arminius that there was a small uprising west of the Roman camp. The Romans were on the way back to the Rhine
1358:
Varus imposed civic changes on the
Germans, including a tax – what Augustus expected any governor of a subdued province to do. However, the Germanic tribes began rallying around a new leader, Arminius of the Cherusci. Arminius, who Rome considered an ally, and who had fought in the Roman army before.
983:
After Gaul had been pacified, improvements were made to the infrastructure, including those to the Roman road network in 20 BC by
Aggripa. Rome increased its military presence along the Rhine and several forts were constructed there between 19 and 17 BC. Augustus thought that the future prosperity of
1545:
Between AD 14 and 16, Germanicus led Roman armies across the Rhine into
Germany against the forces of Arminius and his allies. Germanicus made great use of the navy, which he needed for logistics given the lack of roads in Germany at the time. The war culminated in AD 16 with the decisive victories
1472:
for the campaigns of AD 11 and 12. The two generals crossed the Rhine and made various excursions into enemy territory, moving with the same caution as
Tiberius had the year before. The campaigns were conducted against the Bructeri and the Marsi to avenge the defeat of Varus, but had no significant
1189:
After Drusus' death, Tiberius was given command of the Rhine's forces and waged two campaigns within
Germania over the course of 8 and 7 BC. He marched his army between the Rhine and the Elbe, and met little resistance except from the Sicambri. Tiberius came close to exterminating the Sicambri, and
1563:
Tiberius decided to suspend all military activities beyond the Rhine, leaving the German tribes to dispute over their territories and fight amongst each other. He was content favoring alliances with certain tribes over the others in order to maintain their conflicts against each other. He achieved
1391:
The Roman column followed the road going north until it began to wrap around a hill. The hill was to the west of the road and was wooded. There was boggy terrain all around the hill, woodland to the east, and a swamp to the north (out of sight of the Roman column until they reached the bend taking
1308:
Part of the Roman strategy was to resettle troublesome tribal peoples, to move them to locations where Rome could keep better tabs on them and away from their regular allies. Tiberius resettled the
Sicambri, who had caused particular problems for Drusus, in a new site west of the Rhine, where they
1273:
The elite of the Cherusci tribe came to be special friends of Rome after Tiberius's campaigns of AD 5. In the preceding years, a power struggle had resulted in the alliance of one party with Rome. In this tribe was a ruling lineage that played a critical role in forging this friendship between the
1160:
When Augustus learned Drusus was sick, he sent Tiberius to quickly go to him. Ovid states Tiberius was at the city of Pavia at the time, and when he had learned of his brother's condition, he rode to be at his dying brother's side. He arrived in time, but it wasn't long before Drusus drew his last
1395:
Within ten minutes, word reached the middle of the column where Varus was. Communication was hampered by the column being packed densely in the narrow road. Not knowing the full extent of the attack, Varus ordered his forces to advance forward to reinforce his forces at the front. This pushed the
1554:
in which the Germanic coalition under Arminius was destroyed. Arminius himself barely managed to survive the conflict. Rome handed annexed lands over to friendly chieftains and withdrew from most of Germany, as they felt the military effort required to continue was too great in comparison to any
1564:
less of his objectives in direct involvement than he had with diplomatic relations. In general, it was too risky to go beyond the Rhine, and it was too costly in economic and military resources than Rome could recover even if they had conquered all the lands between the Rhine and the Elbe.
1011:
they captured. This defeat convinced Augustus to reorganize and improve the military presence in Gaul in order to prepare the region for campaigns across the Rhine. An attack soon after by Lollius and Augustus caused the invaders to retreat back to Germania and sue for peace with Rome.
979:
from Germania to supply the insurrection. At the time, Rome's military presence in the Rhineland was small and its only military operations there were punitive expeditions against incursions. It was seen as more important to secure Gaul and wipe out any signs of resistance there.
1152:
states that Drusus extended Rome's dominion to new lands that had only been discovered recently. On his way back to the Rhine, Drusus fell from his horse and was badly wounded. His injury became seriously infected, and after thirty days, Drusus died from the disease, most likely
916:
Drusus led three more campaigns against the Germanic tribes in the years 11–9 BC. For the campaign of 10 BC, he was celebrated for being the Roman who traveled farthest east in northern Europe. Succeeding generals would continue attacking across the Rhine until AD 16, notably
1383:
Arminius' revolt came during the Pannonian revolt, at a time when the majority of Rome's legions were tied down in Illyricum. Varus only had three legions, which were isolated in the heart of Germany. Scouts were sent ahead of Roman forces as the column approached
1205:
was appointed as the commander in Germany by Augustus in 6 BC, and three years later, in 3 BC, he reached and crossed the Elbe with his army. Under his command causeways were constructed across the bogs somewhere in the region between the Ems and the Rhine, called
943:("Varian Disaster"), the name used by Roman historians to describe the Battle of the Teutoburg Forest, and to prove that Roman military might could still overcome German lands. The last general to lead Roman forces in the region during this time was
1439:
penetrated into the heart of the country, opened up military roads, devastated fields, burned houses, routed those who came against him, and, without loss to the troops with which he had crossed, he returned, covered with glory, to winter quarters.
1077:
Drusus first saw action following an incursion by the Sicambri and the Usipetes into Gaul, which he repelled before launching a retaliatory attack across the Rhine. This marked the beginning of Rome's 28 years of campaigns across the lower Rhine.
1198:
writing in the 6th century AD asserts that all Germans living between the Elbe and the Rhine had submitted to Roman power. However, the military situation in Germany was very different from what was suggested by imperial propaganda.
1350:
had been pacified, and Rome had begun integrating the region into the empire, there was a risk of rebellion during the military subjugation of a province. Following Tiberius's departure to Illyricum, Augustus appointed
363:
1416:
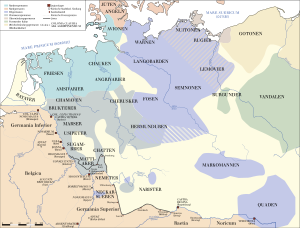
Campaigns of Tiberius and Germanicus in the years AD 10–12. In pink the anti-Roman Germanic coalition led by Arminius. In dark green, territories still directly held by the Romans, in yellow the Roman client
1023:) in Gaul, to supply a means of coining money to pay the soldiers, organized a census for collecting taxes from Gaul, and coordinated the establishment of military bases on the west bank of the Rhine.
1081:
He crossed the Rhine with his army and invaded the land of the Usipetes. He then marched north against the Sicambri and pillaged their lands. Travelling down the Rhine and landing in what is now the
243:
1133:
be closed, a sign the empire was at peace. However, peace did not last, for in the spring of 10 BC, he once again campaigned across the Rhine and spent the majority of the year attacking the
2599:
1232:
Again in AD 4, Augustus sent Tiberius to the Rhine frontier as the commander in Germany. He campaigned in northern Germany for the next two years. During the first year, he conquered the
233:
1219:
Between 2 BC and AD 4, Vinicius commanded the 5 legions stationed in Germany. At around the time of his appointment, many of the Germanic tribes arose in what the historian
2609:
1477:, prevented the Germanic coalition, led by Arminius, from crossing the Rhine to invade Gaul and Italy. In the winter of AD 12, Tiberius and Germanicus returned to Rome.
1502:
About one-third of Rome's total military forces, eight legions, were stationed in the Rhine following their redeployment by Tiberius. Four were in lower Germany under
1431:
penetrat interius, aperit limites, vastat agros, urit domos, fundit obvios maximaque cum gloria, incolumi omnium, quos transduxerat, numero in hiberna revertitur.
1137:. In his third campaign, he conquered the Chatti and other German tribes, and then returned to Rome, as he had done before at the end of the campaign season.
1140:
In 9 BC, he began his fourth campaign, this time as consul. Despite bad omens, Drusus again attacked the Chatti and advanced as far as the territory of the
2306:
1503:
1202:
1178:
156:
1461:
moving slowly as to not risk wasting lives. His advance was cautious and deliberate: he ravaged crops, burned dwellings, and dispersed the population.
2664:
226:
1422:
He began to improve discipline and led small attacks across the Rhine. Velleius reports Tiberius as having enormous success. He says Tiberius:
2604:
1491:
Augustus appointed Germanicus commander of the forces in the Rhine the following year. In August AD 14, Augustus died and on 17 September the
2581:
2563:
2541:
2519:
2501:
2483:
2465:
2447:
2413:
2395:
2377:
2639:
1244:, and subdued the Cherusci. Soon thereafter, he declared the Cherusci "friends of the Roman people." In AD 5, he campaigned against the
2644:
219:
1104:
The following spring, Drusus began his second campaign across the Rhine. He first subdued the Usipetes, and then marched east to the
2301:
719:
1555:
potential gain. Tacitus says the purpose of the campaigns was to avenge the defeat of Varus, rather than to expand Rome's borders.
2654:
657:
620:
2649:
2634:
749:
1551:
1213:
926:
553:
350:
335:
161:
921:
in AD 9. During the return trip from his campaign, Varus' army was ambushed and almost destroyed by a Germanic force led by
823:
2106:
1355:
to the German command, as he was an experienced officer, but not the great military leader a serious threat would warrant.
1130:
394:
1223:
calls the "vast war". However, no account of this war exists. Vinicius must have performed well, for he was awarded the
838:
558:
404:
1015:
From 16 to 13 BC, Augustus was active in Gaul. In preparation for the coming campaigns, Augustus established a mint at
833:
798:
426:
421:
1465:
reports that Tiberius' orders were given in writing and that he was to be consulted directly on any doubtful points.
984:
the Empire depended on the expansion of its borders, and Germania had become the next target for imperial expansion.
2350:
1318:
1294:
724:
692:
682:
2614:
1575:
in 47, which was stopped in its tracks after initial successes against the Frisians and Chaucis. It is not until
1352:
918:
697:
672:
548:
462:
330:
184:
166:
781:
521:
2619:
1519:
968:
848:
734:
702:
615:
610:
585:
298:
2340:
1190:
had those who survived transported to the Roman side of the Rhine, where they could be watched more closely.
1572:
729:
630:
595:
580:
502:
278:
2629:
1335:
1281:
It was Roman opinion that by AD 6 the German tribes had largely been pacified, if not conquered. Only the
933:, had previously fought in the Roman army, and was considered by Rome to be an ally. Roman expansion into
575:
487:
457:
382:
340:
2624:
1225:
793:
714:
667:
652:
640:
605:
533:
528:
472:
1289:, remained to be subdued. Rome planned a massive pincer attack against them involving 12 legions from
1547:
1047:
906:
774:
769:
600:
543:
514:
497:
492:
482:
452:
345:
146:
106:
17:
1220:
1191:
1039:
818:
570:
370:
303:
283:
268:
1094:
828:
813:
677:
590:
538:
477:
2574:
Conflict in Ancient Greece and Rome: The Definitive Political, Social, and Military Encyclopedia
1583:, following the campaigns carried out by his generals between 83 and 85 (in what was called the
1305:
arrived the attack was called off and concluded peace with Maroboduus, recognizing him as king.
635:
2659:
2577:
2559:
2551:
2537:
2515:
2497:
2479:
2461:
2443:
2409:
2391:
2373:
1596:
1592:
1535:
1531:
1515:
1473:
effect. However, the campaign, combined with Rome's alliance to the Marcommanic federation of
1302:
1169:
843:
803:
788:
744:
687:
662:
625:
438:
409:
273:
211:
1114:). Then, he passed through the territory of the Cherusci, whose territory stretched from the
2291:
One or more of the preceding sentences incorporates text from a publication now in the
1620:
1539:
1527:
1331:
1266:
1123:
357:
325:
263:
170:
99:
1615:
in 15 BC. The Roman Empire would launch no other major incursion into Germania Magna until
1616:
1511:
1507:
1327:
1000:
875:
870:
868:. Tensions between the Germanic tribes and the Romans began as early as 17/16 BC with the
808:
754:
739:
399:
310:
134:
1251:
999:
crossed the river and attacked a Roman cavalry unit. Unexpectedly, they came across the
2530:
2436:
2431:
1588:
1584:
1412:
1347:
1008:
1004:
987:
After capturing and executing Roman soldiers east of the Rhine in 17/16 BC, the tribes
951:, who in AD 16 had launched the final major military expedition by Rome into Germania.
939:
934:
879:
467:
2593:
2297:
2292:
1067:
895:
41:
1567:
It is possible that a new attempt to invade Germania took place during the reign of
937:
stopped as a result, and all campaigns immediately after were in retaliation of the
1523:
1492:
1098:
1051:
865:
761:
256:
129:
27:
Series of military conflicts between Germanic tribes and the Romans (12 BC – 16 AD)
1579:
that new territories were acquired, between the high valleys of the Rhine and the
1129:
He was made consul for the following year, and it was voted that the doors to the
2129:
1896:
1608:
1364:
1257:
1233:
1195:
1145:
1115:
1111:
1082:
1059:
290:
1486:
1469:
1360:
1286:
1282:
1237:
1055:
972:
944:
179:
2388:
The Julio-Claudian Succession: Reality and Perception of the "Augustan Model"
2310:. Vol. 22 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 812–813.
1462:
1385:
1368:
975:. During the Gallic uprisings, weapons were smuggled into Gaul across the
1587:). In 85, lands on the western side of the Rhine were organized into the
1576:
1568:
1496:
1290:
1275:
1241:
1174:
1154:
1086:
1016:
996:
992:
988:
964:
960:
948:
930:
922:
898:
891:
887:
883:
445:
190:
151:
75:
2556:
The Cambridge Ancient History: X, The Augustan Empire, 43 B.C. – A.D. 69
913:
in 13 BC and launched a retaliatory campaign across the Rhine in 12 BC.
49:
2231:
1612:
1604:
1298:
1323:
1600:
1580:
1474:
1245:
1134:
1126:
by Cherusci warriors taking advantage of the terrain to harass them.
1090:
1089:, who thereafter served in his army as allies. Then, he attacked the
1071:
2572:
Phang, Sara E.; Spence, Iain; Kelly, Douglas; Londey, Peter (2016),
1411:
1322:
1262:
1250:
1141:
1063:
1038:
976:
910:
111:
2554:, in Bowman, Alan K.; Champlin, Edward; Lintott, Andrew (eds.),
1149:
1119:
1020:
902:
1274:
Cherusci and Rome. Belonging to this elite clan, was the young
1101:. Around winter, he recrossed the Rhine, and returned to Rome.
901:
responded by rapidly developing military infrastructure across
864:
were a series of conflicts between the Germanic tribes and the
215:
1522:
at or near Cologne). Another four were in upper Germany under
1424:
2558:, vol. 10 (2nd ed.), Cambridge University Press,
2532:
Moment of Battle: The Twenty Clashes that Changed the World
1359:
He accompanied Varus, who was in Germania with the Legions
2320:
1265:
was erected in 9 BC as part of a funerary monument to
2424:
Reallexikon der Germanischen Altertumskunde (RGA) 11
2529:
2435:
1603:had been established to the south in what is now
1794:
1792:
1790:
2370:Four Days in September: The Battle of Teutoburg
1194:portrays Germany as essentially conquered, and
1165:Campaigns of Tiberius, Ahenobarbus and Vinicius
34:
1346:Although it was assumed that the province of
227:
8:
2600:Roman campaigns in Germania (12 BC – AD 16)
2215:
2213:
2200:
2198:
2086:
2084:
2082:
2069:
2067:
2065:
1984:
1936:
1912:
1863:
1861:
1852:
1811:
1809:
1807:
1798:
1207:
1105:
862:Roman campaigns in Germania (12 BC – AD 16)
377:Roman campaigns in Germania during the 230s
319:Roman campaigns in Germania (12 BC – AD 16)
245:Warfare between Romans and Germanic peoples
1680:
1678:
234:
220:
212:
31:
2528:Lacey, James; Murray, Williamson (2013),
1653:
1651:
1649:
1647:
2610:Battles involving early Germanic peoples
1468:Tiberius was joined by his adoptive son
1168:
433:Gothic invasion of the Balkans (267–268)
389:Gothic invasion of the Balkans (250–251)
2247:
1631:
1487:Germanicus § Commander of Germania
2177:
2165:
2153:
2117:
2090:
2008:
1769:
1732:
1708:
1696:
1669:
1638:
2357:, Latin text with English translation
2271:
2259:
2219:
2204:
2189:
2141:
2073:
2056:
2044:
2032:
2020:
1996:
1972:
1960:
1948:
1924:
1879:
1867:
1815:
1781:
1757:
1720:
1684:
1657:
1451:
7:
1840:
1371:to finish the conquest of Germania.
416:Gothic invasion of the Balkans (254)
35:Early imperial campaigns in Germania
18:Early Imperial campaigns in Germania
2422:Kehne, Peter (1998), "Germanicus",
25:
929:; Arminius was the leader of the
909:, began building forts along the
720:Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain
2284:
48:
2665:Wars involving the Roman Empire
1309:could be watched more closely.
1043:Campaigns of Drusus in Germania
1007:, whom they defeated and whose
947:, the adoptive son of Emperor
927:Battle of the Teutoburg Forest
154:(8–7 BC, AD 4–5, and AD 11–12)
90:
1:
2605:Campaigns of the Roman Empire
1829:Compendium of Roman History 2
1447:—Velleius Paterculus 2.120.2
2512:The Battle That Stopped Rome
2458:Claude, l'empereur inattendu
2372:, Pen & Sword Military,
2496:, Oxford University Press,
1893:Compendium of Roman History
1495:met to confirm Tiberius as
1203:Lucius Domitius Ahenobarbus
1179:Lucius Domitius Ahenobarbus
882:was defeated by the tribes
2681:
2640:10s BC in the Roman Empire
1484:
1319:Battle of Teutoburg Forest
1316:
971:to quell the uprisings in
725:Treason of the Long Knives
2645:0s BC in the Roman Empire
2478:, John Wiley & Sons,
2386:Gibson, Alisdair (2013),
2368:Abdale, Jason R. (2016),
1571:, with the expedition of
1353:Publius Quinctilius Varus
919:Publius Quinctilius Varus
364:participating Roman units
253:
197:
140:
123:
58:
47:
39:
2510:Wells, Peter S. (2003),
2456:Renucci, Pierre (2012),
2404:Jones, Brian W. (1992),
1619:(r. 161–180) during the
1599:, while the province of
1428:
187:(AD 11–12, and AD 14–16)
54:Map of Germania in AD 50
2655:10s in the Roman Empire
2438:Tiberius the Politician
2307:Encyclopædia Britannica
1985:Lacey & Murray 2013
1937:Lacey & Murray 2013
1913:Lacey & Murray 2013
1853:Lacey & Murray 2013
1799:Lacey & Murray 2013
1481:Campaigns of Germanicus
1229:on his return to Rome.
2650:0s in the Roman Empire
2635:1st-century BC battles
2474:Seager, Robin (2008),
1437:
1418:
1338:
1336:North Rhine-Westphalia
1301:, but when word of an
1270:
1208:
1186:
1106:
1044:
141:Commanders and leaders
2492:Syme, Ronald (1939),
2460:(in French), Perrin,
2351:Velleius Paterculus,
2347:, English translation
1891:Velleius Paterculus,
1827:Velleius Paterculus,
1415:
1408:Campaigns of Tiberius
1326:
1303:uprising in Illyricum
1254:
1226:ornamenta triumphalia
1172:
1042:
1027:Campaigns before the
715:Groans of the Britons
198:Casualties and losses
2494:The Roman Revolution
2406:The Emperor Domitian
1548:Battle of Idistaviso
1400:Campaigns after the
1095:northwestern Germany
1048:Nero Claudius Drusus
907:Nero Claudius Drusus
782:Gothic War (535–554)
522:Gothic War (376–382)
509:Gothic War (367–369)
446:Roman–Alemannic Wars
2550:Rüger, C. (2004) ,
1379:Victory of Arminius
1221:Velleius Paterculus
1192:Velleius Paterculus
1085:, he conquered the
1035:Campaigns of Drusus
395:Nicopolis ad Istrum
104:Establishment of a
42:Roman–Germanic Wars
2250:, pp. 189–192
2222:, pp. 206–207
2059:, pp. 174–175
1419:
1339:
1328:Statue of Arminius
1271:
1187:
1144:, in the words of
1045:
658:Nervasos Mountains
2583:978-1-61069-020-1
2565:978-0-521-26430-3
2543:978-0-345-52697-7
2521:978-0-393-32643-7
2503:978-0-19-881001-8
2485:978-0-470-77541-7
2467:978-2-262-03779-6
2449:978-0-415-21753-8
2415:978-0-415-10195-0
2397:978-90-04-23191-7
2379:978-1-4738-6085-8
2362:Secondary sources
2321:Phang et al. 2016
2274:, pp. 527–28
1597:Germania Superior
1593:Germania Inferior
1458:
1457:
1313:Campaign of Varus
857:
856:
259:(113 BC – 101 BC)
210:
209:
119:
118:
16:(Redirected from
2672:
2615:10s BC conflicts
2586:
2568:
2546:
2536:, Bantam Books,
2535:
2524:
2506:
2488:
2470:
2452:
2441:
2427:
2418:
2400:
2382:
2324:
2318:
2312:
2311:
2290:
2288:
2287:
2281:
2275:
2269:
2263:
2257:
2251:
2245:
2239:
2229:
2223:
2217:
2208:
2202:
2193:
2187:
2181:
2180:, pp. 50–53
2175:
2169:
2168:, pp. 80–82
2163:
2157:
2151:
2145:
2139:
2133:
2127:
2121:
2115:
2109:
2100:
2094:
2088:
2077:
2071:
2060:
2054:
2048:
2042:
2036:
2030:
2024:
2018:
2012:
2011:, pp. 162–3
2006:
2000:
1994:
1988:
1982:
1976:
1970:
1964:
1958:
1952:
1951:, pp. 205–8
1946:
1940:
1939:, pp. 69–70
1934:
1928:
1922:
1916:
1910:
1904:
1889:
1883:
1882:, pp. 158–9
1877:
1871:
1865:
1856:
1855:, pp. 68–69
1850:
1844:
1838:
1832:
1825:
1819:
1813:
1802:
1796:
1785:
1779:
1773:
1767:
1761:
1760:, pp. 156–7
1755:
1749:
1742:
1736:
1730:
1724:
1723:, pp. 155–6
1718:
1712:
1706:
1700:
1694:
1688:
1682:
1673:
1667:
1661:
1655:
1642:
1636:
1621:Marcomannic Wars
1552:Angrivarian Wall
1425:
1332:Teutoburg Forest
1267:Drusus the Elder
1211:
1109:
1066:, Germany), and
824:Naples (542–543)
709:Anglo-Saxon Wars
549:Adrianople Siege
358:Marcomannic Wars
351:Angrivarian Wall
336:Teutoburg Forest
248:
246:
236:
229:
222:
213:
175:
100:Germania Antiqua
60:
59:
52:
32:
21:
2680:
2679:
2675:
2674:
2673:
2671:
2670:
2669:
2620:0s BC conflicts
2590:
2589:
2584:
2571:
2566:
2549:
2544:
2527:
2522:
2509:
2504:
2491:
2486:
2473:
2468:
2455:
2450:
2432:Levick, Barbara
2430:
2421:
2416:
2403:
2398:
2385:
2380:
2367:
2364:
2337:
2335:Primary sources
2332:
2327:
2319:
2315:
2300:, ed. (1911). "
2296:
2285:
2283:
2282:
2278:
2270:
2266:
2258:
2254:
2246:
2242:
2230:
2226:
2218:
2211:
2203:
2196:
2188:
2184:
2176:
2172:
2164:
2160:
2152:
2148:
2140:
2136:
2128:
2124:
2120:, pp. 36–7
2116:
2112:
2101:
2097:
2089:
2080:
2072:
2063:
2055:
2051:
2043:
2039:
2031:
2027:
2019:
2015:
2007:
2003:
1995:
1991:
1983:
1979:
1971:
1967:
1963:, pp. 25–6
1959:
1955:
1947:
1943:
1935:
1931:
1923:
1919:
1911:
1907:
1890:
1886:
1878:
1874:
1866:
1859:
1851:
1847:
1839:
1835:
1826:
1822:
1814:
1805:
1797:
1788:
1780:
1776:
1772:, pp. 76–7
1768:
1764:
1756:
1752:
1743:
1739:
1735:, pp. 75–6
1731:
1727:
1719:
1715:
1711:, pp. 74–5
1707:
1703:
1695:
1691:
1683:
1676:
1668:
1664:
1656:
1645:
1637:
1633:
1629:
1617:Marcus Aurelius
1589:Roman provinces
1561:
1514:at Xanten; the
1489:
1483:
1442:
1434:
1410:
1405:
1381:
1344:
1321:
1315:
1214:Marcus Vinicius
1167:
1131:Temple of Janus
1097:in what is now
1093:, who lived in
1037:
1032:
957:
905:. His general,
871:Clades Lolliana
858:
853:
565:Visigothic Wars
311:Clades Lolliana
293:(58 BC – 57 BC)
249:
244:
242:
240:
183:
178:
171:
165:
160:
155:
150:
135:Germanic tribes
95:
78:
53:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
2678:
2676:
2668:
2667:
2662:
2657:
2652:
2647:
2642:
2637:
2632:
2627:
2622:
2617:
2612:
2607:
2602:
2592:
2591:
2588:
2587:
2582:
2569:
2564:
2547:
2542:
2525:
2520:
2507:
2502:
2489:
2484:
2471:
2466:
2453:
2448:
2428:
2419:
2414:
2401:
2396:
2383:
2378:
2363:
2360:
2359:
2358:
2348:
2336:
2333:
2331:
2328:
2326:
2325:
2313:
2298:Chisholm, Hugh
2276:
2264:
2252:
2240:
2224:
2209:
2194:
2182:
2170:
2158:
2146:
2144:, pp. 203
2134:
2122:
2110:
2095:
2078:
2061:
2049:
2037:
2025:
2013:
2001:
1989:
1977:
1965:
1953:
1941:
1929:
1917:
1905:
1884:
1872:
1857:
1845:
1833:
1820:
1803:
1786:
1784:, pp. 157
1774:
1762:
1750:
1737:
1725:
1713:
1701:
1689:
1674:
1662:
1643:
1630:
1628:
1625:
1585:Agri Decumates
1560:
1557:
1485:Main article:
1482:
1479:
1456:
1455:
1454:, p. 202
1448:
1444:
1443:
1435:
1409:
1406:
1404:
1402:Clades Variana
1398:
1380:
1377:
1348:Germania Magna
1343:
1340:
1317:Main article:
1314:
1311:
1166:
1163:
1036:
1033:
1031:
1029:Clades Variana
1025:
1005:Marcus Lollius
956:
953:
940:Clades Variana
935:Germania Magna
880:Marcus Lollius
855:
854:
852:
851:
849:Mons Lactarius
846:
841:
836:
834:Rome (549–550)
831:
826:
821:
816:
811:
806:
801:
799:Rome (537–538)
796:
791:
778:
777:
772:
758:
757:
752:
747:
742:
740:Mons Badonicus
737:
735:Mercredesburne
732:
727:
722:
717:
706:
705:
700:
695:
690:
685:
680:
675:
670:
665:
660:
655:
644:
643:
638:
633:
628:
623:
618:
613:
608:
603:
598:
593:
588:
583:
578:
573:
562:
561:
556:
554:Constantinople
551:
546:
541:
536:
531:
518:
517:
506:
505:
500:
495:
490:
485:
480:
475:
470:
465:
460:
455:
442:
441:
430:
429:
424:
413:
412:
407:
402:
397:
386:
385:
374:
373:
354:
353:
348:
343:
338:
333:
328:
307:
306:
301:
287:
286:
281:
276:
271:
266:
254:
251:
250:
241:
239:
238:
231:
224:
216:
208:
207:
204:
200:
199:
195:
194:
188:
143:
142:
138:
137:
132:
126:
125:
121:
120:
117:
116:
115:
114:
102:
94:
93:
86:
84:
80:
79:
74:
72:
68:
67:
64:
56:
55:
45:
44:
37:
36:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2677:
2666:
2663:
2661:
2658:
2656:
2653:
2651:
2648:
2646:
2643:
2641:
2638:
2636:
2633:
2631:
2630:10s conflicts
2628:
2626:
2623:
2621:
2618:
2616:
2613:
2611:
2608:
2606:
2603:
2601:
2598:
2597:
2595:
2585:
2579:
2575:
2570:
2567:
2561:
2557:
2553:
2548:
2545:
2539:
2534:
2533:
2526:
2523:
2517:
2513:
2508:
2505:
2499:
2495:
2490:
2487:
2481:
2477:
2472:
2469:
2463:
2459:
2454:
2451:
2445:
2442:, Routledge,
2440:
2439:
2433:
2429:
2425:
2420:
2417:
2411:
2408:, Routledge,
2407:
2402:
2399:
2393:
2389:
2384:
2381:
2375:
2371:
2366:
2365:
2361:
2356:
2354:
2353:Roman History
2349:
2346:
2344:
2343:Roman History
2341:Cassius Dio,
2339:
2338:
2334:
2329:
2323:, p. 940
2322:
2317:
2314:
2309:
2308:
2303:
2299:
2294:
2293:public domain
2280:
2277:
2273:
2268:
2265:
2262:, p. 130
2261:
2256:
2253:
2249:
2244:
2241:
2237:
2233:
2228:
2225:
2221:
2216:
2214:
2210:
2207:, p. 204
2206:
2201:
2199:
2195:
2192:, p. 203
2191:
2186:
2183:
2179:
2174:
2171:
2167:
2162:
2159:
2155:
2150:
2147:
2143:
2138:
2135:
2131:
2126:
2123:
2119:
2114:
2111:
2108:
2105:
2099:
2096:
2092:
2087:
2085:
2083:
2079:
2076:, p. 202
2075:
2070:
2068:
2066:
2062:
2058:
2053:
2050:
2047:, p. 171
2046:
2041:
2038:
2035:, p. 170
2034:
2029:
2026:
2023:, p. 166
2022:
2017:
2014:
2010:
2005:
2002:
1999:, p. 169
1998:
1993:
1990:
1986:
1981:
1978:
1974:
1969:
1966:
1962:
1957:
1954:
1950:
1945:
1942:
1938:
1933:
1930:
1927:, p. 160
1926:
1921:
1918:
1914:
1909:
1906:
1902:
1901:Roman History
1898:
1894:
1888:
1885:
1881:
1876:
1873:
1870:, p. 159
1869:
1864:
1862:
1858:
1854:
1849:
1846:
1843:, p. 401
1842:
1837:
1834:
1830:
1824:
1821:
1818:, p. 158
1817:
1812:
1810:
1808:
1804:
1800:
1795:
1793:
1791:
1787:
1783:
1778:
1775:
1771:
1766:
1763:
1759:
1754:
1751:
1747:
1746:Roman History
1744:Cassius Dio,
1741:
1738:
1734:
1729:
1726:
1722:
1717:
1714:
1710:
1705:
1702:
1698:
1693:
1690:
1687:, p. 155
1686:
1681:
1679:
1675:
1671:
1666:
1663:
1659:
1654:
1652:
1650:
1648:
1644:
1640:
1635:
1632:
1626:
1624:
1622:
1618:
1614:
1610:
1606:
1602:
1598:
1594:
1590:
1586:
1582:
1578:
1574:
1570:
1565:
1558:
1556:
1553:
1549:
1543:
1541:
1537:
1533:
1529:
1525:
1521:
1517:
1513:
1509:
1505:
1504:Aulus Caecina
1500:
1498:
1494:
1488:
1480:
1478:
1476:
1471:
1466:
1464:
1453:
1449:
1446:
1445:
1441:
1436:
1433:
1432:
1427:
1426:
1423:
1414:
1407:
1403:
1399:
1397:
1393:
1389:
1387:
1378:
1376:
1372:
1370:
1366:
1362:
1356:
1354:
1349:
1341:
1337:
1333:
1329:
1325:
1320:
1312:
1310:
1306:
1304:
1300:
1296:
1292:
1288:
1285:, under king
1284:
1279:
1277:
1268:
1264:
1260:
1259:
1253:
1249:
1247:
1243:
1239:
1235:
1230:
1228:
1227:
1222:
1217:
1215:
1210:
1204:
1200:
1197:
1193:
1184:
1180:
1176:
1173:Invasions of
1171:
1164:
1162:
1158:
1156:
1151:
1147:
1143:
1138:
1136:
1132:
1127:
1125:
1121:
1117:
1113:
1108:
1102:
1100:
1096:
1092:
1088:
1084:
1079:
1075:
1073:
1069:
1068:Castra Vetera
1065:
1061:
1057:
1053:
1049:
1041:
1034:
1030:
1026:
1024:
1022:
1018:
1013:
1010:
1006:
1002:
998:
994:
990:
985:
981:
978:
974:
970:
966:
962:
954:
952:
950:
946:
942:
941:
936:
932:
928:
924:
920:
914:
912:
908:
904:
900:
897:
896:Roman Emperor
893:
889:
885:
881:
877:
873:
872:
867:
863:
850:
847:
845:
842:
840:
837:
835:
832:
830:
827:
825:
822:
820:
817:
815:
812:
810:
807:
805:
802:
800:
797:
795:
792:
790:
787:
786:
785:
784:
783:
776:
773:
771:
768:
767:
766:
765:
763:
756:
753:
751:
748:
746:
743:
741:
738:
736:
733:
731:
730:Wippedesfleot
728:
726:
723:
721:
718:
716:
713:
712:
711:
710:
704:
701:
699:
696:
694:
691:
689:
686:
684:
681:
679:
676:
674:
671:
669:
666:
664:
661:
659:
656:
654:
651:
650:
649:
648:
647:Vandalic Wars
642:
639:
637:
634:
632:
629:
627:
624:
622:
619:
617:
614:
612:
609:
607:
604:
602:
599:
597:
594:
592:
589:
587:
584:
582:
579:
577:
574:
572:
569:
568:
567:
566:
560:
557:
555:
552:
550:
547:
545:
542:
540:
537:
535:
532:
530:
527:
526:
525:
524:
523:
516:
513:
512:
511:
510:
504:
503:Campi Cannini
501:
499:
496:
494:
491:
489:
486:
484:
481:
479:
476:
474:
471:
469:
466:
464:
461:
459:
456:
454:
451:
450:
449:
448:
447:
440:
437:
436:
435:
434:
428:
425:
423:
420:
419:
418:
417:
411:
408:
406:
405:Philippopolis
403:
401:
398:
396:
393:
392:
391:
390:
384:
381:
380:
379:
378:
372:
369:
368:
367:
365:
361:
359:
352:
349:
347:
344:
342:
339:
337:
334:
332:
329:
327:
324:
323:
322:
321:
320:
315:
314:
312:
305:
302:
300:
297:
296:
295:
294:
292:
285:
282:
280:
279:Aquae Sextiae
277:
275:
272:
270:
267:
265:
262:
261:
260:
258:
252:
247:
237:
232:
230:
225:
223:
218:
217:
214:
205:
202:
201:
196:
192:
189:
186:
181:
176:
174:
168:
163:
158:
153:
148:
145:
144:
139:
136:
133:
131:
128:
127:
122:
113:
109:
108:
103:
101:
97:
96:
92:
88:
87:
85:
82:
81:
77:
73:
70:
69:
66:12 BC – AD 16
65:
62:
61:
57:
51:
46:
43:
38:
33:
30:
19:
2625:0s conflicts
2576:, ABC-CLIO,
2573:
2555:
2531:
2511:
2493:
2475:
2457:
2437:
2423:
2405:
2387:
2369:
2352:
2342:
2330:Bibliography
2316:
2305:
2279:
2267:
2255:
2248:Renucci 2012
2243:
2235:
2227:
2185:
2173:
2161:
2156:, p. 37
2149:
2137:
2125:
2113:
2103:
2098:
2093:, p. 36
2052:
2040:
2028:
2016:
2004:
1992:
1987:, p. 71
1980:
1975:, p. 26
1968:
1956:
1944:
1932:
1920:
1915:, p. 69
1908:
1900:
1892:
1887:
1875:
1848:
1836:
1828:
1823:
1801:, p. 68
1777:
1765:
1753:
1745:
1740:
1728:
1716:
1704:
1699:, p. 74
1692:
1672:, p. 73
1665:
1660:, p. 77
1641:, p. 72
1634:
1566:
1562:
1544:
1524:Gaius Silius
1501:
1490:
1467:
1459:
1438:
1430:
1429:
1420:
1401:
1394:
1390:
1382:
1373:
1357:
1345:
1307:
1280:
1272:
1256:
1231:
1224:
1218:
1209:pontes longi
1201:
1188:
1182:
1159:
1139:
1128:
1103:
1099:Lower Saxony
1080:
1076:
1074:, Germany).
1052:Argentoratum
1046:
1028:
1014:
986:
982:
958:
938:
915:
874:, where the
869:
866:Roman Empire
861:
859:
839:Sena Gallica
794:Naples (536)
780:
779:
762:Vandalic War
760:
759:
750:Woden's Burg
708:
707:
668:Hippo Regius
646:
645:
564:
563:
559:Thessalonica
520:
519:
508:
507:
493:Argentoratum
488:Durocortorum
458:Lake Benacus
444:
443:
432:
431:
422:Thessalonica
415:
414:
388:
387:
376:
375:
356:
355:
341:Pontes Longi
318:
317:
316:
309:
308:
289:
288:
257:Cimbrian War
255:
172:
130:Roman Empire
124:Belligerents
105:
40:Part of the
29:
2178:Levick 1999
2166:Gibson 2013
2154:Seager 2008
2130:Cassius Dio
2118:Seager 2008
2102:Suetonius,
2091:Seager 2008
2009:Abdale 2016
1903:55, 28, 6–7
1897:Cassius Dio
1895:2, 109, 5;
1770:Abdale 2016
1733:Abdale 2016
1709:Abdale 2016
1697:Abdale 2016
1670:Abdale 2016
1639:Abdale 2016
1609:Switzerland
1258:Drususstein
1234:Canninefati
1196:Cassiodorus
1146:Cassius Dio
1112:Weser River
1083:Netherlands
1060:Moguntiacum
1058:, France),
641:4th Arelate
626:3rd Arelate
606:2nd Arelate
601:1st Arelate
529:Marcianople
427:Thermopylae
331:Lupia River
291:Gallic Wars
164:(2 BC–AD 4)
157:Ahenobarbus
2594:Categories
2514:, Norton,
2272:Rüger 2004
2260:Jones 1992
2220:Wells 2003
2205:Wells 2003
2190:Wells 2003
2142:Wells 2003
2074:Wells 2003
2057:Wells 2003
2045:Wells 2003
2033:Wells 2003
2021:Wells 2003
1997:Wells 2003
1973:Wells 2003
1961:Wells 2003
1949:Wells 2003
1925:Wells 2003
1880:Wells 2003
1868:Wells 2003
1816:Wells 2003
1782:Wells 2003
1758:Wells 2003
1721:Wells 2003
1685:Wells 2003
1658:Wells 2003
1627:References
1470:Germanicus
1452:Wells 2003
1287:Maroboduus
1283:Marcomanni
1185:3 BCE–6 CE
1001:5th Legion
959:In 27 BC,
955:Background
945:Germanicus
876:5th Legion
829:Rome (546)
775:Tricamarum
770:Ad Decimum
693:Garigliano
683:Agrigentum
678:Rome (455)
591:Rome (410)
544:Adrianople
534:Ad Salices
515:Noviodunum
498:Solicinium
483:Vindonissa
453:Mediolanum
346:Idistaviso
182:(AD 14–16)
180:Germanicus
2552:"Germany"
2426:: 438–448
2390:, Brill,
2236:Annals 11
2132:, LVI, 25
1841:Syme 1939
1559:Aftermath
1463:Suetonius
1386:Kalkriese
1295:Illyricum
1056:Strasburg
967:and sent
819:Mucellium
764:(533–534)
698:Cartagena
571:Pollentia
463:Placentia
371:Carnuntum
360:(166–180)
284:Vercellae
269:Burdigala
193:(AD 9–16)
149:(12–9 BC)
91:aftermath
2660:Augustus
2476:Tiberius
2434:(1999),
2104:Tiberius
1577:Domitian
1569:Claudius
1497:princeps
1291:Germania
1276:Arminius
1242:Bructeri
1238:Attuarii
1175:Tiberius
1161:breath.
1155:gangrene
1107:Visurgis
1087:Frisians
1017:Lugdunum
997:Tencteri
993:Usipetes
989:Sicambri
965:princeps
961:Augustus
949:Tiberius
931:Cherusci
923:Arminius
899:Augustus
892:Tencteri
888:Usipetes
884:Sicambri
814:Faventia
789:Panormus
703:Cape Bon
673:Carthage
616:Toulouse
611:Narbonne
596:Massilia
586:Faesulae
581:Florence
539:Dibaltum
478:Lingones
383:Harzhorn
191:Arminius
162:Vinicius
159:(3–2 BC)
152:Tiberius
76:Germania
71:Location
2355:Book II
2345:Book 55
2295::
2238:, 18–20
2232:Tacitus
1613:Austria
1605:Bavaria
1573:Corbulo
1342:Prelude
1299:Rhaetia
1118:to the
969:Agrippa
963:became
925:at the
844:Taginae
804:Treviso
688:Corsica
663:Tarraco
631:Orleans
621:Châlons
439:Naissus
410:Abritus
313:(16 BC)
274:Arausio
206:Unknown
203:Unknown
173:†
110:on the
98:End of
2580:
2562:
2540:
2518:
2500:
2482:
2464:
2446:
2412:
2394:
2376:
2302:Raetia
2289:
1601:Raetia
1581:Danube
1538:, and
1493:senate
1475:Marbod
1417:states
1367:, and
1297:, and
1246:Chauci
1240:, the
1236:, the
1135:Chatti
1124:Arbalo
1091:Chauci
1072:Xanten
1003:under
995:, and
973:Gallia
890:, and
878:under
809:Verona
745:Dyrham
576:Verona
326:Arbalo
299:Vosges
264:Noreia
185:Flavus
177:(AD 9)
169:
147:Drusus
83:Result
1831:, 104
1748:55, 1
1526:(the
1506:(the
1365:XVIII
1334:, in
1263:Mainz
1183:circa
1142:Suebi
1064:Mainz
1009:eagle
977:Rhine
911:Rhine
755:Raith
653:Rhine
636:Déols
473:Pavia
400:Beroe
304:Sabis
167:Varus
112:Rhine
107:limes
2578:ISBN
2560:ISBN
2538:ISBN
2516:ISBN
2498:ISBN
2480:ISBN
2462:ISBN
2444:ISBN
2410:ISBN
2392:ISBN
2374:ISBN
2107:18.2
1611:and
1595:and
1550:and
1540:14th
1536:16th
1532:13th
1520:20th
1518:and
1512:21st
1510:and
1361:XVII
1255:The
1177:and
1150:Ovid
1120:Elbe
1021:Lyon
903:Gaul
860:The
468:Fano
89:See
63:Date
2304:".
1591:of
1546:of
1542:).
1528:2nd
1516:1st
1508:5th
1369:XIX
1330:at
1261:in
1181:in
1116:Ems
2596::
2234:,
2212:^
2197:^
2081:^
2064:^
1899:,
1860:^
1806:^
1789:^
1677:^
1646:^
1623:.
1607:,
1534:,
1530:,
1363:,
1293:,
1269:.
1216:.
1157:.
991:,
894:.
886:,
366:)
1450:—
1110:(
1070:(
1062:(
1054:(
1019:(
362:(
235:e
228:t
221:v
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.