95:
184:
187:(RCF-1) Trigonal form of recombinant oxidized long chain flavodoxin in Anabaena/Nostoc sp. The active site is characterized by a FMN (flavin mono-nucleotide) cofactor highlighted in magenta. SO4 residue highlighted in yellow. As with most flavodoxins, the residues near the binding site are large and hydrophobic.
81:
became limited. Ferredoxin is iron-dependant as well as oxidant-sensitive. Under these limited iron conditions, ferredoxin was no longer preferred. Flavodoxin on the other hand is the opposite of these traits, as it is oxidant-resistant and has iron-free isofunctional counterparts. Therefore, for
130:
of flavin mononucleotide as well as assist in the formation of folded intermediates. However, it is still not certain what the loops true function is. In addition, the flavin mononucleotide is non-covalently bound to the flavodoxin protein and works to shuttle
149:
the most prevalent human gastric pathogen, requires flavodoxins in its essential POR (pyruvate oxidoreductase enzyme complex) used in pyruvate decarboxylation. Most flavodoxins have a large hydrophobic residue such as tryptophan near the
174:
residue near the binding site, aid in lowering SQ reactivity. The hydroquinone form is forced into a planar conformation, destabilizing it. Electron transfer occurs at the dimethylbenzene ring of the FMN.
170:
Flavodoxins require a highly negative redox potential to be active. The semiquinone conformation is stabilized by a hydrogen bond to the N-5 position of the flavin. This bond, as well as a common
118:= 15-22 kDa), flavodoxins exist in "long" and "short" chain classifications. Short chain flavodoxins contain between 140 and 180 amino acid residues, while long chain flavodoxins include a 20
508:"The importance of flavodoxin for environmental stress tolerance in photosynthetic microorganisms and transgenic plants. Mechanism, evolution and biotechnological potential"
795:
758:
869:
763:
768:
690:"Gas exchange in the filamentous cyanobacterium Nostoc punctiforme strain ATCC 29133 and Its hydrogenase-deficient mutant strain NHM5"
77:, another redox protein, was the only protein able to be used in this manner. However, when oxygen became present in the environment,
158:
has an alanine residue instead, allowing for a pocket of solute to form. Current research is being done to identify non toxic,
854:
555:
Cremades N, Bueno M, Toja M, Sancho J (April 2005). "Towards a new therapeutic target: Helicobacter pylori flavodoxin".
82:
some time flavodoxin was the primary redox protein. Now however, when ferredoxin and flavodoxin are present in the same
788:
834:
829:
752:
864:
849:
844:
208:
to deliver electrons to nitrogenase, as well as reducing N2 and NADP+, nitrogen fixation and H2 formation.
824:
781:
388:
Prakash D, Iyer PR, Suharti S, Walters KA, Santiago-Martinez MG, Golbeck JH, et al. (December 2019).
894:
819:
151:
67:
27:
701:
405:
144:
874:
670:
537:
485:
264:
71:
920:
915:
889:
884:
727:
662:
627:
572:
529:
477:
433:
365:
316:
256:
192:
30:
as prosthetic group. The structure of flavodoxin is characterized by a five-stranded parallel
717:
709:
654:
617:
607:
564:
519:
467:
423:
413:
355:
347:
306:
298:
246:
238:
127:
705:
409:
251:
226:
645:
Simondsen RP, Tollin G (December 1980). "Structure-function relations in flavodoxins".
622:
591:
428:
389:
360:
336:"Crystal structure of oxidized flavodoxin, an essential protein in Helicobacter pylori"
335:
311:
286:
748:
722:
689:
909:
879:
759:"Flavodoxin Folding and Stability Research at Wageningen University, the Netherlands"
205:
59:
43:
35:
713:
674:
541:
94:
839:
808:
489:
268:
183:
111:
524:
507:
86:, ferredoxin is still used but under low iron conditions, flavodoxin is induced.
107:
66:, flavodoxins were discovered over 50 years ago. These proteins evolved from an
39:
398:
Proceedings of the
National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
568:
242:
201:
171:
123:
119:
74:
63:
31:
418:
731:
631:
576:
533:
481:
437:
369:
320:
260:
666:
287:"The long goodbye: the rise and fall of flavodoxin during plant evolution"
773:
612:
506:
Lodeyro AF, Ceccoli RD, Pierella
Karlusich JJ, Carrillo N (August 2012).
302:
132:
23:
804:
658:
472:
455:
334:
Freigang J, Diederichs K, Schäfer KP, Welte W, Paul R (February 2002).
162:
specific flavodoxin inhibitors for the purpose of treating infection.
351:
83:
182:
103:
93:
47:
390:"Structure and function of an unusual flavodoxin from the domain
78:
777:
126:. These residues form a loop which may be used to increase the
285:
Pierella
Karlusich JJ, Lodeyro AF, Carrillo N (October 2014).
227:"Flavodoxins: sequence, folding, binding, function and beyond"
456:"Folding of proteins with a flavodoxin-like architecture"
592:"Flavodoxins as Novel Therapeutic Targets against
688:Lindberg P, Lindblad P, Cournac L (April 2004).
764:"The crossovers of flavodoxin" at virginia.edu
789:
8:
600:International Journal of Molecular Sciences
22:(Fld) are small, soluble electron-transfer
796:
782:
774:
454:Houwman JA, van Mierlo CP (October 2017).
751:at the U.S. National Library of Medicine
721:
621:
611:
523:
471:
427:
417:
359:
310:
250:
217:
694:Applied and Environmental Microbiology
449:
447:
383:
381:
379:
7:
501:
499:
280:
278:
231:Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences
870:Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase
647:Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry
590:Salillas S, Sancho J (March 2020).
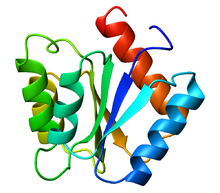
98:3-D structure of flavodoxin protein
14:
102:Three forms of flavodoxin exist:
714:10.1128/AEM.70.4.2137-2145.2004
114:(HQ). While relatively small (M
38:. They have been isolated from
855:Dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase
291:Journal of Experimental Botany
1:
525:10.1016/j.febslet.2012.07.026
596:and Other Gastric Pathogens"
179:Flavodoxins in Cyanobacteria
937:
835:Butyryl CoA dehydrogenase
830:Apoptosis-inducing factor
815:
769:Diagram at ohio-state.edu
569:10.1016/j.bpc.2004.12.045
243:10.1007/s00018-005-5514-4
191:In cyanobacteria such as
753:Medical Subject Headings
122:insertion into the last
865:Methemoglobin reductase
850:Cytokinin dehydrogenase
845:Cytochrome b5 reductase
419:10.1073/pnas.1908578116
225:Sancho J (April 2006).
204:-specific, and used in
26:. Flavodoxins contains
825:Acyl CoA dehydrogenase
188:
99:
46:, and some eukaryotic
895:Thioredoxin reductase
820:Acetolactate synthase
557:Biophysical Chemistry
186:
97:
68:anaerobic environment
34:, surrounded by five
28:flavin mononucleotide
613:10.3390/ijms21051881
139:Medical applications
72:selective pressures.
58:Originally found in
706:2004ApEnM..70.2137L
594:Helicobacter pylori
410:2019PNAS..11625917P
404:(51): 25917–25922.
200:., flavodoxins are
875:NADH dehydrogenase
659:10.1007/BF00224568
473:10.1111/febs.14077
303:10.1093/jxb/eru273
189:
145:Heliobacter pylori
100:
903:
902:
890:Sarcosine oxidase
885:Nitrate reductase
518:(18): 2917–2924.
466:(19): 3145–3167.
297:(18): 5161–5178.
928:
798:
791:
784:
775:
736:
735:
725:
700:(4): 2137–2145.
685:
679:
678:
642:
636:
635:
625:
615:
587:
581:
580:
563:(2–3): 267–276.
552:
546:
545:
527:
503:
494:
493:
475:
460:The FEBS Journal
451:
442:
441:
431:
421:
385:
374:
373:
363:
352:10.1110/ps.28602
331:
325:
324:
314:
282:
273:
272:
254:
237:(7–8): 855–864.
222:
128:binding affinity
936:
935:
931:
930:
929:
927:
926:
925:
906:
905:
904:
899:
811:
802:
745:
740:
739:
687:
686:
682:
644:
643:
639:
589:
588:
584:
554:
553:
549:
505:
504:
497:
453:
452:
445:
387:
386:
377:
340:Protein Science
333:
332:
328:
284:
283:
276:
224:
223:
219:
214:
181:
168:
141:
117:
92:
56:
17:
12:
11:
5:
934:
932:
924:
923:
918:
908:
907:
901:
900:
898:
897:
892:
887:
882:
877:
872:
867:
862:
857:
852:
847:
842:
837:
832:
827:
822:
816:
813:
812:
803:
801:
800:
793:
786:
778:
772:
771:
766:
761:
756:
744:
743:External links
741:
738:
737:
680:
653:(1–2): 13–24.
637:
582:
547:
495:
443:
375:
346:(2): 253–261.
326:
274:
216:
215:
213:
210:
180:
177:
167:
164:
140:
137:
115:
91:
88:
55:
52:
16:Protein family
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
933:
922:
919:
917:
914:
913:
911:
896:
893:
891:
888:
886:
883:
881:
880:NADPH oxidase
878:
876:
873:
871:
868:
866:
863:
861:
858:
856:
853:
851:
848:
846:
843:
841:
838:
836:
833:
831:
828:
826:
823:
821:
818:
817:
814:
810:
809:flavoproteins
806:
799:
794:
792:
787:
785:
780:
779:
776:
770:
767:
765:
762:
760:
757:
754:
750:
747:
746:
742:
733:
729:
724:
719:
715:
711:
707:
703:
699:
695:
691:
684:
681:
676:
672:
668:
664:
660:
656:
652:
648:
641:
638:
633:
629:
624:
619:
614:
609:
605:
601:
597:
595:
586:
583:
578:
574:
570:
566:
562:
558:
551:
548:
543:
539:
535:
531:
526:
521:
517:
513:
509:
502:
500:
496:
491:
487:
483:
479:
474:
469:
465:
461:
457:
450:
448:
444:
439:
435:
430:
425:
420:
415:
411:
407:
403:
399:
395:
393:
384:
382:
380:
376:
371:
367:
362:
357:
353:
349:
345:
341:
337:
330:
327:
322:
318:
313:
308:
304:
300:
296:
292:
288:
281:
279:
275:
270:
266:
262:
258:
253:
248:
244:
240:
236:
232:
228:
221:
218:
211:
209:
207:
206:photosystem 1
203:
199:
198:
195:
185:
178:
176:
173:
165:
163:
161:
157:
153:
148:
146:
138:
136:
134:
129:
125:
121:
113:
109:
105:
96:
89:
87:
85:
80:
76:
73:
69:
65:
61:
60:cyanobacteria
53:
51:
49:
45:
44:cyanobacteria
41:
37:
36:alpha helices
33:
29:
25:
21:
859:
840:Cryptochrome
697:
693:
683:
650:
646:
640:
603:
599:
593:
585:
560:
556:
550:
515:
512:FEBS Letters
511:
463:
459:
401:
397:
391:
343:
339:
329:
294:
290:
234:
230:
220:
196:
193:
190:
169:
159:
155:
143:
142:
112:hydroquinone
101:
57:
19:
18:
606:(5): 1881.
124:beta-strand
110:, (SQ) and
108:semiquinone
40:prokaryotes
20:Flavodoxins
910:Categories
860:Flavodoxin
749:Flavodoxin
212:References
202:heterocyst
172:tryptophan
120:amino acid
75:Ferredoxin
64:clostridia
54:Background
32:beta sheet
166:Mechanism
133:electrons
90:Structure
70:, due to
921:Bacteria
916:Proteins
732:15066806
675:24764348
632:32164177
577:15752617
542:19298219
534:22819831
482:28380286
438:31801875
370:11790835
321:25009172
261:16465441
252:11136378
104:Oxidized
24:proteins
805:Protein
702:Bibcode
667:6782445
623:7084853
490:3933842
429:6926009
406:Bibcode
392:Archaea
361:2373437
312:4400536
269:6090402
106:, (OX)
755:(MeSH)
730:
723:383079
720:
673:
665:
630:
620:
575:
540:
532:
488:
480:
436:
426:
368:
358:
319:
309:
267:
259:
249:
194:Nostoc
154:, but
84:genome
671:S2CID
538:S2CID
486:S2CID
265:S2CID
147:(Hp),
48:algae
728:PMID
663:PMID
628:PMID
573:PMID
530:PMID
478:PMID
434:PMID
366:PMID
317:PMID
257:PMID
79:iron
62:and
718:PMC
710:doi
655:doi
618:PMC
608:doi
565:doi
561:115
520:doi
516:586
468:doi
464:284
424:PMC
414:doi
402:116
356:PMC
348:doi
307:PMC
299:doi
247:PMC
239:doi
152:FMN
912::
807::
726:.
716:.
708:.
698:70
696:.
692:.
669:.
661:.
651:33
649:.
626:.
616:.
604:21
602:.
598:.
571:.
559:.
536:.
528:.
514:.
510:.
498:^
484:.
476:.
462:.
458:.
446:^
432:.
422:.
412:.
400:.
396:.
378:^
364:.
354:.
344:11
342:.
338:.
315:.
305:.
295:65
293:.
289:.
277:^
263:.
255:.
245:.
235:63
233:.
229:.
197:sp
160:Hp
156:Hp
135:.
50:.
42:,
797:e
790:t
783:v
734:.
712::
704::
677:.
657::
634:.
610::
579:.
567::
544:.
522::
492:.
470::
440:.
416::
408::
394:"
372:.
350::
323:.
301::
271:.
241::
116:w
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.