140:
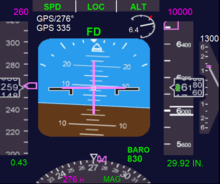
the right and the pitch bar will deflect upwards. The pilot will then pull back on the control column while banking to the right. Once the aircraft reaches the proper bank angle, the FD vertical bar will center and remain centered until it is time to roll back to wings level (when the heading approaches 090°). When the aircraft approaches FL200 the FD horizontal bar will deflect downwards thus commanding the pilot to lower the nose in order to level off at FL200.
91:
332:
83:
75:
139:
FL150 at 260 kn (480 km/h) indicated airspeed, the FD bars are thus centered. Then the flight director is set to heading 090° and a new flight level FL200. The aircraft must thus turn to the right and climb. This is done by banking to the right while climbing. The roll bar will deflect to
130:
sources. The flight data computer integrates all of the data such as speed, position, closure, drift, track, desired course, and altitude into a command signal. The command signal is displayed on the attitude indicator in the form of command bars, which show the pitch and roll inputs necessary to
98:
Flight director (FD) modes integrated with autopilot systems perform calculations for more advanced automation, like "selected course (intercepting), changing altitudes, and tracking navigation sources with cross winds." FD computes and displays the proper pitch and bank angles required for the
134:
The pilot simply keeps the aircraft symbol on the attitude indicator aligned with the command bars, or allow the autopilot to make the actual control movements to fly the selected track and altitude. A simple example: The aircraft flies level on 045° heading at
151:(AP), where the FD commands the AP to put the aircraft in the attitude necessary to follow a trajectory. In some aircraft, the autopilot cannot function without the flight director engaged.
106:(ADC) and a flight data computer. The ADC supplies altitude, airspeed and temperature data, heading data from magnetic sources such as flux valves, heading selected on the
268:
397:
207:
373:
123:
171:
107:
297:
86:
Command bars in yellow and the aircraft symbol in orange, indicating a level bank angle and pitch up input is required.
366:
119:
115:
402:
144:
114:(PFD)/multi-function display (MFD)/ electronic horizontal situation indicator (EHSI)), navigation data from
78:
Command bars in yellow are aligned with the aircraft symbol in orange, indicating straight and level flight.
58:
the attitude required to execute the desired flight path. Flight directors are mostly commonly used during
359:
111:
159:
181:
176:
47:
392:
103:
43:
343:
90:
186:
94:
Some aircraft use crossed bars, leading the pilot to the desired attitude and flight path.
17:
239:
154:
The exact form of the flight director's display varies with the instrument type, either
59:
386:
136:
304:
82:
74:
155:
148:
63:
331:
249:. Federal Aviation Administration, U.S. Department of Transportation. 2009
339:
55:
31:
51:
89:
81:
73:
143:
A flight director can be used with or without automation of the
127:
147:. The FD is commonly used in direct connection with the
347:
102:The flight director usually receives input from an
62:and landing. They can be used with or without
367:
8:
99:aircraft to follow a selected flight path.
374:
360:
240:"Advanced Avionics Handbook, FAA-H-8083-6"
199:
172:Acronyms and abbreviations in avionics
234:
232:
7:
328:
326:
346:. You can help Knowledge (XXG) by
25:
330:
398:Navigational flight instruments
131:achieve the selected targets.
108:Horizontal Situation Indicator
1:
303:. p. 6-2. Archived from
269:"Advanced Avionics Handbook"
208:"Advanced Avionics Handbook"
419:
325:
18:Flight director (aviation)
120:VHF omnidirectional range
116:Flight Management System
46:that is overlaid on the
145:flight control surfaces
342:-related article is a
112:Primary flight display
95:
87:
79:
93:
85:
77:
162:(so-called "cue").
182:Flight instruments
177:Attitude indicator
96:
88:
80:
48:attitude indicator
355:
354:
104:Air Data Computer
44:flight instrument
27:Flight instrument
16:(Redirected from
410:
376:
369:
362:
334:
327:
320:
319:
317:
315:
309:
302:
298:"GFC-700 Manual"
294:
288:
287:
285:
283:
273:
265:
259:
258:
256:
254:
244:
236:
227:
226:
224:
222:
212:
204:
21:
418:
417:
413:
412:
411:
409:
408:
407:
383:
382:
381:
380:
324:
323:
313:
311:
307:
300:
296:
295:
291:
281:
279:
271:
267:
266:
262:
252:
250:
242:
238:
237:
230:
220:
218:
210:
206:
205:
201:
196:
187:Head-up display
168:
72:
50:that shows the
36:flight director
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
416:
414:
406:
405:
403:Aviation stubs
400:
395:
385:
384:
379:
378:
371:
364:
356:
353:
352:
335:
322:
321:
310:on 6 July 2017
289:
278:. pp. 4–5
260:
228:
198:
197:
195:
192:
191:
190:
184:
179:
174:
167:
164:
71:
68:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
415:
404:
401:
399:
396:
394:
391:
390:
388:
377:
372:
370:
365:
363:
358:
357:
351:
349:
345:
341:
336:
333:
329:
306:
299:
293:
290:
277:
270:
264:
261:
248:
241:
235:
233:
229:
217:. p. 4-4
216:
209:
203:
200:
193:
188:
185:
183:
180:
178:
175:
173:
170:
169:
165:
163:
161:
157:
152:
150:
146:
141:
138:
132:
129:
125:
121:
117:
113:
109:
105:
100:
92:
84:
76:
69:
67:
65:
61:
57:
53:
49:
45:
41:
37:
33:
19:
348:expanding it
337:
312:. Retrieved
305:the original
292:
280:. Retrieved
275:
263:
253:18 September
251:. Retrieved
247:Sheppard Air
246:
219:. Retrieved
214:
202:
160:command bars
153:
142:
137:flight level
133:
101:
97:
39:
35:
29:
314:28 November
282:28 November
221:28 November
70:Description
387:Categories
194:References
110:(HSI) (or
156:crosshair
149:autopilot
66:systems.
64:autopilot
393:Avionics
340:aviation
166:See also
60:approach
56:aircraft
32:aviation
276:FAA.gov
215:FAA.gov
122:(VOR)/
118:(FMS),
42:) is a
126:, and
54:of an
338:This
308:(PDF)
301:(PDF)
272:(PDF)
243:(PDF)
211:(PDF)
189:(HUD)
124:(DME)
52:pilot
344:stub
316:2020
284:2020
255:2023
223:2020
128:RNAV
34:, a
158:or
30:In
389::
274:.
245:.
231:^
213:.
40:FD
375:e
368:t
361:v
350:.
318:.
286:.
257:.
225:.
38:(
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.