51:
278:: suppose that there are two alleles, T and C. The number of individuals in the case group having allele T is represented by 'A' and the number of individuals in the control group having allele T is represented by 'B'. Similarly, the number of individuals in the case group having allele C is represented by 'X' and the number of individuals in the control group having allele C is represented by 'Y'. In this case the odds ratio for allele T is A:B (meaning 'A to B', in standard odds terminology) divided by X:Y, which in mathematical notation is simply (A/B)/(X/Y).
435:
224:
4807:
4490:
4422:
3880:
3830:
3738:
3420:
3272:
252:
140:
411:
337:
345:
572:. Some have found that the accuracy of prognosis improves, while others report only minor benefits from this use. Generally, a problem with this direct approach is the small magnitudes of the effects observed. A small effect ultimately translates into a poor separation of cases and controls and thus only a small improvement of prognosis accuracy. An alternative application is therefore the potential for GWA studies to elucidate
328:) might contribute to complex diseases. Due to the potentially exponential number of interactions, detecting statistically significant interactions in GWAS data is both computationally and statistically challenging. This task has been tackled in existing publications that use algorithms inspired from data mining. Moreover, the researchers try to integrate GWA data with other biological data such as
819:, but a modified manuscript was later published. Now, many GWAS control for genotyping array. If there are substantial differences between groups on the type of genotyping array, as with any confounder, GWA studies could result in a false positive. Another consequence is that such studies are unable to detect the contribution of very rare mutations not included in the array or able to be imputed.
876:
357:
methods that impute genotypic data to a set of reference panel of haplotypes, which typically have been densely genotyped using whole-genome sequencing. These methods take advantage of sharing of haplotypes between individuals over short stretches of sequence to impute alleles. Existing software packages for genotype imputation include IMPUTE2, Minimac, Beagle and MaCH.
810:
In addition to easily correctible problems such as these, some more subtle but important issues have surfaced. A high-profile GWA study that investigated individuals with very long life spans to identify SNPs associated with longevity is an example of this. The publication came under scrutiny because
604:
gene, encoding interferon lambda 3, are associated with significant differences in response to the treatment. A later report demonstrated that the same genetic variants are also associated with the natural clearance of the genotype 1 hepatitis C virus. These major findings facilitated the development
263:
setup, which compares two large groups of individuals, one healthy control group and one case group affected by a disease. All individuals in each group are typically genotyped at common known SNPs. The exact number of SNPs depends on the genotyping technology, but are typically one million or more.
757:
GWA studies act as an important tool in plant breeding. With large genotyping and phenotyping data, GWAS are powerful in analyzing complex inheritance modes of traits that are important yield components such as number of grains per spike, weight of each grain and plant structure. In a study on GWAS
364:
the results. Sex, age, and ancestry are common examples of confounding variables. Moreover, it is also known that many genetic variations are associated with the geographical and historical populations in which the mutations first arose. Because of this association, studies must take account of the
859:
to provide coverage of the entire genome by genotyping a subset of variants. Because of this, the reported associated variants are unlikely to be the actual causal variants. Associated regions can contain hundreds of variants spanning large regions and encompassing many different genes, making the
863:
Fine-mapping requires all variants in the associated region to have been genotyped or imputed (dense coverage), very stringent quality control resulting in high-quality genotypes, and large sample sizes sufficient in separating out highly correlated signals. There are several different methods to
538:
A central point of debate on GWA studies has been that most of the SNP variations found by GWA studies are associated with only a small increased risk of the disease, and have only a small predictive value. The median odds ratio is 1.33 per risk-SNP, with only a few showing odds ratios above 3.0.
356:
of genotypes at SNPs not on the genotype chip used in the study. This process greatly increases the number of SNPs that can be tested for association, increases the power of the study, and facilitates meta-analysis of GWAS across distinct cohorts. Genotype imputation is carried out by statistical
78:
for a particular trait or disease. These participants may be people with a disease (cases) and similar people without the disease (controls), or they may be people with different phenotypes for a particular trait, for example blood pressure. This approach is known as phenotype-first, in which the
822:
Additionally, GWA studies identify candidate risk variants for the population from which their analysis is performed, and with most GWA studies historically stemming from
European databases, there is a lack of translation of the identified risk variants to other non-European populations. For
495:
Since these first landmark GWA studies, there have been two general trends. One has been towards larger and larger sample sizes. In 2018, several genome-wide association studies are reaching a total sample size of over 1 million participants, including 1.1 million in a genome-wide study of
1910:
Carré C, Carluer JB, Chaux C, Estoup-Streiff C, Roche N, Hosy E, Mas A, Krouk G (March, 2024). "Next-Gen GWAS: full 2D epistatic interaction maps retrieve part of missing heritability and improve phenotypic prediction". Genome biology. doi:10.1186/s13059-024-03202-0. PMID 38523316. S2CID
713:. While the evidence supporting the genetic basis of schizophrenia is not controversial, one study found that 25 candidate schizophrenia genes discovered from GWAS had little association with schizophrenia, demonstrating that GWAS alone may be insufficient to identify candidate genes.
195:
is found more often than expected in individuals with the phenotype of interest (e.g. with the disease being studied). Early calculations on statistical power indicated that this approach could be better than linkage studies at detecting weak genetic effects.
289:. Finding odds ratios that are significantly different from 1 is the objective of the GWA study because this shows that a SNP is associated with disease. Because so many variants are tested, it is standard practice to require the p-value to be lower than
787:
The first GWA study in chickens was done by Abasht and Lamont in 2007. This GWA was used to study the fatness trait in F2 population found previously. Significantly related SNPs were found are on 10 chromosomes (1, 2, 3, 4, 7, 8, 10, 12, 15 and 27).
332:
to extract more informative results. Despite the previously perceived challenge posed by the vast number of SNP combinations, a recent study has successfully unveiled complete epistatic maps at a gene-level resolution in plants/Arabidopsis thaliana
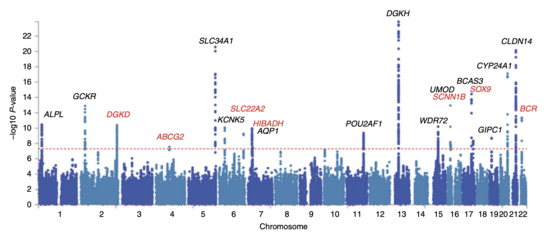
3433:
Ge D, Fellay J, Thompson AJ, Simon JS, Shianna KV, Urban TJ, Heinzen EL, Qiu P, Bertelsen AH, Muir AJ, Sulkowski M, McHutchison JG, Goldstein DB (September 2009). "Genetic variation in IL28B predicts hepatitis C treatment-induced viral clearance".
864:
perform fine-mapping, and all methods produce a posterior probability that a variant in that locus is causal. Because the requirements are often difficult to satisfy, there are still limited examples of these methods being more generally applied.
401:
to be significant in the face of hundreds of thousands to millions of tested SNPs. GWA studies typically perform the first analysis in a discovery cohort, followed by validation of the most significant SNPs in an independent validation cohort.
3800:
Dubé JB, Johansen CT, Hegele RA (June 2011). "Sortilin: an unusual suspect in cholesterol metabolism: from GWAS identification to in vivo biochemical analyses, sortilin has been identified as a novel mediator of human lipoprotein metabolism".
384:
as a function of genomic location. Thus the SNPs with the most significant association stand out on the plot, usually as stacks of points because of haploblock structure. Importantly, the P-value threshold for significance is corrected for
770:
have posed serious threats to plant health and biodiversity. Under this consideration, identification of wild types that have the natural resistance to certain pathogens could be of vital importance. Furthermore, we need to predict which
625:. As a result, major GWA studies by 2011 typically included extensive eQTL analysis. One of the strongest eQTL effects observed for a GWA-identified risk SNP is the SORT1 locus. Functional follow up studies of this locus using
801:
are common problems. On the statistical issue of multiple testing, it has been noted that "the GWA approach can be problematic because the massive number of statistical tests performed presents an unprecedented potential for
455:, which was an unexpected finding in the research of ARMD. The findings from these first GWA studies have subsequently prompted further functional research towards therapeutical manipulation of the complement system in ARMD.
758:
in spring wheat, GWAS have revealed a strong correlation of grain production with booting data, biomass and number of grains per spike. GWA study is also a success in study genetic architecture of complex traits in rice.
323:
such as SNPTEST and PLINK, which also include support for many of these alternative statistics. GWAS focuses on the effect of individual SNPs. However, it is also possible that complex interactions among two or more SNPs
3485:
Thomas DL, Thio CL, Martin MP, Qi Y, Ge D, O'Huigin C, Kidd J, Kidd K, Khakoo SI, Alexander G, Goedert JJ, Kirk GD, Donfield SM, Rosen HR, Tobler LH, Busch MP, McHutchison JG, Goldstein DB, Carrington M (October 2009).
175:, which can be anything from disease risk to physical properties such as height. Around the year 2000, prior to the introduction of GWA studies, the primary method of investigation was through inheritance studies of
272:. The odds ratio is the ratio of two odds, which in the context of GWA studies are the odds of case for individuals having a specific allele and the odds of case for individuals who do not have that same allele.
559:
and diagnostics development, including better integration of genetic studies into the drug-development process and a focus on the role of genetic variation in maintaining health as a blueprint for designing new
796:
GWA studies have several issues and limitations that can be taken care of through proper quality control and study setup. Lack of well defined case and control groups, insufficient sample size, control for
3592:
Folkersen L, van't Hooft F, Chernogubova E, Agardh HE, Hansson GK, Hedin U, Liska J, Syvänen AC, Paulsson-Berne G, Paulssson-Berne G, Franco-Cereceda A, Hamsten A, Gabrielsen A, Eriksson P (August 2010).
255:
Illustration of a simulated genotype by phenotype regression for a single SNP. Each dot represents an individual. A GWAS of a continuous trait essentially consists of repeating this analysis at each SNP.
127:, these associations are very weak, but while each individual association may not explain much of the risk, they provide insight into critical genes and pathways and can be important when considered
123:
compared to healthy controls. As of 2017, over 3,000 human GWA studies have examined over 1,800 diseases and traits, and thousands of SNP associations have been found. Except in the case of rare
3991:
4503:
Sebastiani P, Solovieff N, Dewan AT, Walsh KM, Puca A, Hartley SW, Melista E, Andersen S, Dworkis DA, Wilk JB, Myers RH, Steinberg MH, Montano M, Baldwin CT, Hoh J, Perls TT (18 January 2012).
430:
level is given by the left Y-axis. The dot representing the rs73015013 SNP (in the top-middle) has a high Y-axis location because this SNP explains some of the variation in LDL-cholesterol.
860:
biological interpretation of GWAS loci more difficult. Fine-mapping is a process to refine these lists of associated variants to a credible set most likely to include the causal variant.
442:
Attempts have been made at creating comprehensive catalogues of SNPs that have been identified from GWA studies. As of 2009, SNPs associated with diseases are numbered in the thousands.
211:
identified by HapMap project also allowed the focus on the subset of SNPs that would describe most of the variation. Also the development of the methods to genotype all these SNPs using
2587:
Haines JL, Hauser MA, Schmidt S, Scott WK, Olson LM, Gallins P, Spencer KL, Kwan SY, Noureddine M, Gilbert JR, Schnetz-Boutaud N, Agarwal A, Postel EA, Pericak-Vance MA (April 2005).
464:(WTCCC) study, the largest GWA study ever conducted at the time of its publication in 2007. The WTCCC included 14,000 cases of seven common diseases (~2,000 individuals for each of
203:, which are repositories of human genetic material that greatly reduced the cost and difficulty of collecting sufficient numbers of biological specimens for study. Another was the
281:
When the allele frequency in the case group is much higher than in the control group, the odds ratio is higher than 1, and vice versa for lower allele frequency. Additionally, a
4461:
Sebastiani P, Solovieff N, Puca A, Hartley SW, Melista E, Andersen S, Dworkis DA, Wilk JB, Myers RH, Steinberg MH, Montano M, Baldwin CT, Perls TT (July 2011). "Retraction".
828:
547:
twins. For example, it is known that 40% of variance in depression can be explained by hereditary differences, but GWA studies only account for a minority of this variance.
115:
The first successful GWAS published in 2002 studied myocardial infarction. This study design was then implemented in the landmark GWA 2005 study investigating patients with
4329:
Abasht B, Lamont SJ (October 2007). "Genome-wide association analysis reveals cryptic alleles as an important factor in heterosis for fatness in chicken F2 population".
3005:"Genome-wide association identifies nine common variants associated with fasting proinsulin levels and provides new insights into the pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes"
451:(ARMD) with 50 healthy controls. It identified two SNPs with significantly altered allele frequency between the two groups. These SNPs were located in the gene encoding
3730:
4364:
Sebastiani P, Solovieff N, Puca A, Hartley SW, Melista E, Andersen S, Dworkis DA, Wilk JB, Myers RH, Steinberg MH, Montano M, Baldwin CT, Perls TT (July 2010).
183:. However, for common and complex diseases the results of genetic linkage studies proved hard to reproduce. A suggested alternative to linkage studies was the
4974:
102:
GWA studies investigate the entire genome, in contrast to methods that specifically test a small number of pre-specified genetic regions. Hence, GWAS is a
2646:"Design and development of TT30, a novel C3d-targeted C3/C5 convertase inhibitor for treatment of human complement alternative pathway-mediated diseases"
827:
have been conducted primarily in
Caucasian populations, which does not give adequate insight in other ethnic populations, including African Americans or
621:(eQTL) studies. The reason is that GWAS studies identify risk-SNPs, but not risk-genes, and specification of genes is one step closer towards actionable
3999:
4901:
1067:
2277:"A novel computational biostatistics approach implies impaired dephosphorylation of growth factor receptors as associated with severity of autism"
1550:
Schena M, Shalon D, Davis RW, Brown PO (October 1995). "Quantitative monitoring of gene expression patterns with a complementary DNA microarray".
4412:
2173:
Novembre J, Johnson T, Bryc K, Kutalik Z, Boyko AR, Auton A, Indap A, King KS, Bergmann S, Nelson MR, Stephens M, Bustamante CD (November 2008).
3843:
Bauer RC, Stylianou IM, Rader DJ (April 2011). "Functional validation of new pathways in lipoprotein metabolism identified by human genetics".
460:
112:. GWA studies identify SNPs and other variants in DNA associated with a disease, but they cannot on their own specify which genes are causal.
1887:
1296:
775:
are associated with the resistance. GWA studies is a powerful tool to detect the relationships of certain variants and the resistance to the
843:-based GWA studies. High-throughput sequencing does have potential to side-step some of the shortcomings of non-sequencing GWA. Cross-trait
815:
in the case and control group, which caused several SNPs to be falsely highlighted as associated with longevity. The study was subsequently
2827:"Polygenic prediction of educational attainment within and between families from genome-wide association analyses in 3 million individuals"
2776:
Lee JJ, Wedow R, Okbay A, Kong E, Maghzian O, Zacher M, Nguyen-Viet TA, Bowers P, Sidorenko J, Karlsson Linnér R, et al. (July 2018).
894:
3595:"Association of genetic risk variants with expression of proximal genes identifies novel susceptibility genes for cardiovascular disease"
4820:
Border R, Athanasiadis G, Buil A, Schork AJ, Cai N, Young AI, Werge T, Flint J, Kendler KS, Sankararaman S, Dahl AW, Zaitlen NA (2022).
268:
is significantly altered between the case and the control group. In such setups, the fundamental unit for reporting effect sizes is the
2428:"Fine mapping of five loci associated with low-density lipoprotein cholesterol detects variants that double the explained heritability"
99:
with the disease. The associated SNPs are then considered to mark a region of the human genome that may influence the risk of disease.
816:
618:
308:
4943:
4732:
949:
4172:"GWAS for plant growth stages and yield components in spring wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) harvested in three regions of Kazakhstan"
2778:"Gene discovery and polygenic prediction from a genome-wide association study of educational attainment in 1.1 million individuals"
909:
1482:
The
International HapMap Project, Gibbs RA, Belmont JW, Hardenbol P, Willis TD, Yu F, Yang H, Ch'Ang LY, Huang W (December 2003).
422:
levels. This type of plot is similar to the
Manhattan plot in the lead section, but for a more limited section of the genome. The
447:
116:
2077:"A unified approach to genotype imputation and haplotype-phase inference for large data sets of trios and unrelated individuals"
706:
329:
47:(SNPs) and traits like major human diseases, but can equally be applied to any other genetic variants and any other organisms.
5038:
4967:
740:
planning. Utilizing GWA studies to determine adaptive genes could help elucidate the relationship between neutral and adaptive
320:
43:
in different individuals to see if any variant is associated with a trait. GWA studies typically focus on associations between
4436:
4113:"Conservation genetics as a management tool: The five best-supported paradigms to assist the management of threatened species"
5179:
5174:
5141:
4668:"Power of linkage versus association analysis of quantitative traits, by use of variance-components models, for sibship data"
3942:
Ganapathiraju MK, Thahir M, Handen A, Sarkar SN, Sweet RA, Nimgaonkar VL, Loscher CE, Bauer EM, Chaparala S (27 April 2016).
192:
156:
84:
59:
44:
40:
438:
Relationship between the minor allele frequency and the effect size of genome wide significant variants in a GWAS of height.
50:
1926:"Next-Gen GWAS: full 2D epistatic interaction maps retrieve part of missing heritability and improve phenotypic prediction"
5164:
944:
593:
589:
4914:
3093:
Liu JZ, Erlich Y, Pickrell JK (March 2017). "Case-control association mapping by proxy using family history of disease".
5131:
613:
The goal of elucidating pathophysiology has also led to increased interest in the association between risk-SNPs and the
204:
4924:
2693:
360:
In addition to the calculation of association, it is common to take into account any variables that could potentially
3685:"A genome-wide association study in Europeans and South Asians identifies five new loci for coronary artery disease"
705:
Research using a High-Precision
Protein Interaction Prediction (HiPPIP) computational model that discovered 504 new
303:. A common alternative to case-control GWA studies is the analysis of quantitative phenotypic data, e.g. height or
4960:
504:
containing 1.3 million individuals. The reason is the drive towards reliably detecting risk-SNPs that have smaller
199:
In addition to the conceptual framework several additional factors enabled the GWA studies. One was the advent of
5169:
798:
366:
1083:"Functional SNPs in the lymphotoxin-alpha gene that are associated with susceptibility to myocardial infarction"
605:
of personalized medicine and allowed physicians to customize medical decisions based on the patient's genotype.
568:. Several studies have looked into the use of risk-SNP markers as a means of directly improving the accuracy of
508:
and lower allele frequency. Another trend has been towards the use of more narrowly defined phenotypes, such as
492:) and 3,000 shared controls. This study was successful in uncovering many genes associated with these diseases.
434:
155:
differ in millions of different ways. There are small variations in the individual nucleotides of the genomes (
4064:"No Evidence That Schizophrenia Candidate Genes Are More Associated With Schizophrenia Than Noncandidate Genes"
2479:"Potential etiologic and functional implications of genome-wide association loci for human diseases and traits"
1870:
Ayati M, Koyutürk M (1 January 2015). "Assessing the
Collective Disease Association of Multiple Genomic Loci".
807:
473:
469:
390:
3636:"Abdominal aortic aneurysm is associated with a variant in low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1"
5095:
5028:
4170:
Turuspekov Y, Baibulatova A, Yermekbayev K, Tokhetova L, Chudinov V, Sereda G, et al. (November 2017).
2886:"Genome-wide analysis of insomnia in 1,331,010 individuals identifies new risk loci and functional pathways"
634:
240:
80:
1483:
4806:
4489:
4421:
3879:
3829:
3737:
3419:
3271:
924:
919:
856:
824:
638:
497:
465:
223:
4774:"Evidence-based psychiatric genetics, AKA the false dichotomy between common and rare variant hypotheses"
2644:
Fridkis-Hareli M, Storek M, Mazsaroff I, Risitano AM, Lundberg AS, Horvath CJ, Holers VM (October 2011).
2275:
Wittkowski KM, Sonakya V, Bigio B, Tonn MK, Shic F, Ascano M, Nasca C, Gold-Von Simson G (January 2014).
5064:
3724:
626:
539:
These magnitudes are considered small because they do not explain much of the heritable variation. This
353:
168:
4223:"Genome-wide association mapping reveals a rich genetic architecture of complex traits in Oryza sativa"
3751:
Johnson T, Gaunt TR, Newhouse SJ, Padmanabhan S, Tomaszewski M, Kumari M, et al. (December 2011).
2922:
728:
genes to help evaluate ability of species to adapt to changing environmental conditions as the global
5136:
5126:
5074:
4833:
4516:
4234:
4124:
3499:
3443:
3392:
3234:
2897:
2600:
2490:
2186:
1872:
Proceedings of the 6th ACM Conference on
Bioinformatics, Computational Biology and Health Informatics
1621:
1559:
1498:
1399:
1228:
1141:
954:
939:
737:
658:
477:
386:
312:
304:
164:
70:, so the peaks indicate genetic variants that are found more often in individuals with kidney stones.
67:
5069:
5043:
5018:
5002:
2950:
Kathiresan S, Willer CJ, Peloso GM, Demissie S, Musunuru K, Schadt EE, et al. (January 2009).
1770:
Llinares-López F, Grimm DG, Bodenham DA, Gieraths U, Sugiyama M, Rowan B, Borgwardt K (June 2015).
1390:
Risch N, Merikangas K (September 1996). "The future of genetic studies of complex human diseases".
1288:
934:
889:
721:
690:
654:
561:
452:
427:
236:
184:
160:
63:
36:
1610:"Genome-wide association study of 14,000 cases of seven common diseases and 3,000 shared controls"
1312:
4769:
4742:
4599:
3868:
3712:
3467:
3260:
3118:
2884:
Jansen PR, Watanabe K, Stringer S, Skene N, Bryois J, Hammerschlag AR, et al. (March 2019).
2758:
2626:
2008:
1924:
Carré C, Carluer JB, Chaux C, Estoup-Streiff C, Roche N, Hosy E, Mas A, Krouk G (25 March 2024).
1893:
1721:
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, Thomas L, Ferreira MA, Bender D, et al. (September 2007).
1583:
1532:
1423:
1110:
844:
260:
2426:
Sanna S, Li B, Mulas A, Sidore C, Kang HM, Jackson AU, et al. (July 2011). Gibson G (ed.).
1821:"MOBAS: identification of disease-associated protein subnetworks using modularity-based scoring"
584:
One such success is related to identifying the genetic variant associated with response to anti-
481:
336:
251:
4280:"Genome-Wide Association Studies In Plant Pathosystems: Toward an Ecological Genomics Approach"
4023:"F200. Elucidating The Role of Cilia in Neuropsychiatric Diseases Through Interactome Analysis"
2477:
Hindorff LA, Sethupathy P, Junkins HA, Ramos EM, Mehta JP, Collins FS, Manolio TA (June 2009).
555:
A challenge for future successful GWA study is to apply the findings in a way that accelerates
5023:
4983:
4867:
4849:
4795:
4728:
4697:
4648:
4591:
4583:
4544:
4478:
4404:
4385:
4346:
4311:
4260:
4203:
4152:
4093:
3973:
3924:
3860:
3818:
3782:
3704:
3665:
3634:
Bown MJ, Jones GT, Harrison SC, Wright BJ, Bumpstead S, Baas AF, et al. (November 2011).
3616:
3574:
3525:
3459:
3408:
3365:
3336:"Association between a literature-based genetic risk score and cardiovascular events in women"
3316:
3285:
Muehlschlegel JD, Liu KY, Perry TE, Fox AA, Collard CD, Shernan SK, Body SC (September 2010).
3252:
3203:
3159:
3110:
3075:
3034:
2981:
2927:
2866:
2807:
2750:
2675:
2618:
2569:
2518:
2459:
2408:
2377:"An expanded set of genome-wide association studies of brain imaging phenotypes in UK Biobank"
2357:
2306:
2257:
2212:
2155:
2106:
2057:
2000:
1965:
1947:
1883:
1852:
1801:
1752:
1703:
1647:
1575:
1524:
1464:
1415:
1372:
1292:
1256:
1167:
1102:
1045:
1005:
904:
741:
622:
565:
139:
207:, which, from 2003 identified a majority of the common SNPs interrogated in a GWA study. The
5079:
5048:
4947:
4857:
4841:
4785:
4720:
4687:
4679:
4638:
4630:
4575:
4534:
4524:
4470:
4396:
4377:
4338:
4301:
4291:
4250:
4242:
4193:
4183:
4142:
4132:
4083:
4075:
4062:
Johnson EC, Border R, Melroy-Greif WE, de Leeuw CA, Ehringer MA, Keller MC (November 2017).
4042:
4034:
3963:
3955:
3914:
3906:
3852:
3810:
3772:
3764:
3696:
3655:
3647:
3606:
3564:
3556:
3515:
3507:
3451:
3400:
3355:
3347:
3334:
Paynter NP, Chasman DI, Paré G, Buring JE, Cook NR, Miletich JP, Ridker PM (February 2010).
3306:
3298:
3242:
3193:
3149:
3102:
3065:
3024:
3016:
2971:
2963:
2917:
2907:
2856:
2846:
2838:
2797:
2789:
2740:
2732:
2665:
2657:
2608:
2559:
2549:
2508:
2498:
2449:
2439:
2398:
2388:
2347:
2337:
2296:
2288:
2247:
2239:
2202:
2194:
2145:
2137:
2096:
2088:
2047:
2039:
1992:
1983:
Marchini J, Howie B (July 2010). "Genotype imputation for genome-wide association studies".
1955:
1937:
1875:
1842:
1832:
1791:
1783:
1772:"Genome-wide detection of intervals of genetic heterogeneity associated with complex traits"
1742:
1734:
1693:
1685:
1637:
1629:
1567:
1514:
1506:
1454:
1407:
1362:
1354:
1280:
1246:
1236:
1157:
1149:
1094:
1037:
995:
832:
556:
485:
286:
265:
232:
180:
120:
4892:
1672:
Clarke GM, Anderson CA, Pettersson FH, Cardon LR, Morris AP, Zondervan KT (February 2011).
410:
5110:
5033:
4928:
4754:
1459:
1442:
962:
tool designed to help interpret the results generated from a genome wide association study
929:
614:
601:
573:
419:
176:
128:
124:
4822:"Cross-trait assortative mating is widespread and inflates genetic correlation estimates"
3000:
1281:
1028:
Pearson TA, Manolio TA (March 2008). "How to interpret a genome-wide association study".
4837:
4520:
4238:
4221:
Zhao K, Tung CW, Eizenga GC, Wright MH, Ali ML, Price AH, et al. (September 2011).
4128:
3503:
3447:
3396:
3238:
2604:
2494:
2190:
2126:"MaCH: using sequence and genotype data to estimate haplotypes and unobserved genotypes"
1960:
1925:
1625:
1563:
1502:
1403:
1232:
1145:
1081:
Ozaki K, Ohnishi Y, Iida A, Sekine A, Yamada R, Tsunoda T, et al. (December 2002).
4862:
4821:
4692:
4667:
4643:
4618:
4539:
4504:
4306:
4279:
4255:
4222:
4198:
4171:
4147:
4112:
4088:
4063:
4047:
4022:
3968:
3943:
3919:
3894:
3777:
3752:
3660:
3635:
3569:
3544:
3520:
3487:
3360:
3335:
3311:
3287:"Chromosome 9p21 variant predicts mortality after coronary artery bypass graft surgery"
3286:
3029:
3004:
2976:
2951:
2861:
2826:
2825:
Okbay A, Wu Y, Wang N, Jayashankar H, Bennett M, Nehzati SM, et al. (April 2022).
2802:
2745:
2720:
2670:
2645:
2564:
2537:
2513:
2478:
2454:
2427:
2403:
2376:
2352:
2325:
2301:
2276:
2207:
2174:
2150:
2125:
2101:
2076:
2052:
2027:
1847:
1820:
1796:
1771:
1747:
1722:
1698:
1673:
1642:
1609:
1367:
1342:
1251:
1216:
1162:
1129:
881:
803:
776:
767:
729:
630:
377:
239:
with the trait in question. The numbers in this example are taken from a 2007 study of
108:
74:
When applied to human data, GWA studies compare the DNA of participants having varying
55:
3302:
3070:
3053:
1723:"PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses"
5158:
4603:
4342:
2375:
Smith SM, Douaud G, Chen W, Hanayik T, Alfaro-Almagro F, Sharp K, Elliott LT (2021).
1128:
Klein RJ, Zeiss C, Chew EY, Tsai JY, Sackler RS, Haynes C, et al. (April 2005).
710:
678:
650:
3872:
3716:
3611:
3594:
2696:(Press release). Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium. 6 June 2007. Archived from
2630:
2589:"Complement factor H variant increases the risk of age-related macular degeneration"
1787:
1114:
344:
79:
participants are classified first by their clinical manifestation(s), as opposed to
4563:
4474:
4400:
4079:
3471:
3264:
3122:
2762:
2012:
1897:
1587:
1536:
1427:
899:
540:
509:
489:
415:
365:
geographic and ethnic background of participants by controlling for what is called
152:
3404:
1411:
1186:"GWAS Catalog: The NHGRI-EBI Catalog of published genome-wide association studies"
227:
Example calculation illustrating the methodology of a case-control GWA study. The
4529:
4111:
Willi Y, Kristensen TN, Sgrò CM, Weeks AR, Ørsted M, Hoffmann AA (January 2022).
3856:
2661:
2444:
2342:
1571:
1241:
681:
modulation and cardiac development. It was also identified new genes involved in
91:. If there is significant statistical evidence that one type of the variant (one
4617:
Rosenberg NA, Huang L, Jewett EM, Szpiech ZA, Jankovic I, Boehnke M (May 2010).
4038:
3560:
682:
585:
544:
505:
361:
4117:
Proceedings of the
National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
3768:
3651:
2842:
2483:
Proceedings of the
National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
2393:
2092:
1942:
875:
380:. In the context of GWA studies, this plot shows the negative logarithm of the
4579:
4188:
3910:
2912:
2885:
2793:
1837:
871:
836:
733:
725:
513:
285:
for the significance of the odds ratio is typically calculated using a simple
269:
4853:
4587:
2697:
1951:
1041:
520:, and their analyses may be of value to functional research into biomarkers.
5105:
4921:
4845:
4724:
4381:
4365:
4296:
4137:
3959:
2613:
2588:
2503:
1879:
1443:"The uneasy ethical and legal underpinnings of large-scale genomic biobanks"
1153:
959:
840:
812:
597:
569:
423:
325:
316:
212:
208:
172:
88:
75:
4871:
4799:
4701:
4652:
4595:
4548:
4482:
4408:
4389:
4350:
4315:
4264:
4207:
4156:
4097:
3977:
3928:
3864:
3822:
3814:
3786:
3708:
3669:
3620:
3578:
3529:
3488:"Genetic variation in IL28B and spontaneous clearance of hepatitis C virus"
3463:
3412:
3369:
3320:
3256:
3207:
3163:
3114:
3079:
3038:
3003:, Prokopenko I, Barker A, Ahlqvist E, Rybin D, et al. (October 2011).
2985:
2931:
2870:
2811:
2754:
2679:
2622:
2573:
2554:
2522:
2463:
2412:
2361:
2310:
2261:
2216:
2159:
2110:
2061:
2004:
1969:
1856:
1805:
1756:
1707:
1689:
1651:
1528:
1468:
1376:
1260:
1171:
1106:
1049:
1009:
653:
accomplished in 2018 revealed the discovery of 70 new loci associated with
369:. If they did not do so, the studies could produce false positive results.
3351:
2043:
1579:
1419:
1343:"Genomewide scans of complex human diseases: true linkage is hard to find"
1082:
1000:
983:
3383:
Couzin-Frankel J (June 2010). "Major heart disease genes prove elusive".
2851:
1519:
914:
501:
200:
95:) is more frequent in people with the disease, the variant is said to be
20:
3511:
3455:
3154:
3137:
2292:
2198:
1633:
1510:
143:
GWA studies typically identify common variants with small effect sizes (
4997:
4893:
Statistical
Methods for the Analysis of Genome-Wide Association Studies
4790:
4773:
4246:
3944:"Schizophrenia interactome with 504 novel protein-protein interactions"
2252:
2141:
381:
373:
319:
penetrance patterns can be used. Calculations are typically done using
282:
58:
depicting several strongly associated risk loci. Each dot represents a
3020:
1185:
1130:"Complement factor H polymorphism in age-related macular degeneration"
984:"Genomewide association studies and assessment of the risk of disease"
779:, which is beneficial for developing new pathogen-resisted cultivars.
2721:"Validating, augmenting and refining genome-wide association signals"
2243:
1341:
Altmüller J, Palmer LJ, Fischer G, Scherb H, Wjst M (November 2001).
772:
670:
228:
188:
92:
4952:
4937:
4888:
Genotype-phenotype interaction software tools and databases on omicX
4634:
3895:"Multi-ethnic genome-wide association study for atrial fibrillation"
3684:
3247:
3222:
3198:
3181:
3106:
2736:
2230:
Charney E (January 2017). "Genes, behavior, and behavior genetics".
1996:
500:
follow by another in 2022 with 3 million individuals and a study of
376:
have been calculated for all SNPs, a common approach is to create a
4683:
3700:
3138:"The pursuit of genome-wide association studies: where are we now?"
2967:
2902:
2694:"Largest ever study of genetics of common diseases published today"
1738:
1358:
1098:
458:
Another landmark publication in the history of GWA studies was the
171:. Any of these may cause alterations in an individual's traits, or
4909:— a central database of summary-level genetic association findings
3054:"C-reactive protein and coronary disease: is there a causal link?"
686:
674:
445:
The first GWA study, conducted in 2005, compared 96 patients with
389:
issues. The exact threshold varies by study, but the conventional
343:
243:(CAD) that showed that the individuals with the G-allele of SNP1 (
4897:
4887:
4562:
Tam V, Patel N, Turcotte M, Bossé Y, Paré G, Meyre D (May 2019).
3992:"New Schizophrenia Study Focuses on Protein-Protein Interactions"
2952:"Common variants at 30 loci contribute to polygenic dyslipidemia"
1063:
835:. More recently, the rapidly decreasing price of complete genome
3683:
Coronary Artery Disease (C4D) Genetics Consortium (March 2011).
2124:
Li Y, Willer CJ, Ding J, Scheet P, Abecasis GR (December 2010).
694:
666:
662:
4956:
1608:
Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium, Burton PR (June 2007).
4906:
736:
risk for species and could therefore be an important tool for
62:, with the X-axis showing genomic location and Y-axis showing
4946:
Impact of functional information on understanding variation.
4564:"Benefits and limitations of genome-wide association studies"
2538:"An open access database of genome-wide association results"
2324:
Barsh GS, Copenhaver GP, Gibson G, Williams SM (July 2012).
1674:"Basic statistical analysis in genetic case-control studies"
657:. It has been identified different variants associated with
527:
of people with a disease. This type of study has been named
523:
A variation of GWAS uses participants that are first-degree
340:
Full 2D epistatic interaction maps point to epistatic signal
231:
count of each measured SNP is evaluated—in this case with a
179:
in families. This approach had proven highly useful towards
83:. Each person gives a sample of DNA, from which millions of
3753:"Blood pressure loci identified with a gene-centric array"
2777:
677:, which are involved in cardiac conduction regulation, in
543:
variation is estimated from heritability studies based on
414:
Regional association plot, showing individual SNPs in the
3543:
Lu YF, Goldstein DB, Angrist M, Cavalleri G (July 2014).
1819:
Ayati M, Erten S, Chance MR, Koyutürk M (December 2015).
588:
virus treatment. For genotype 1 hepatitis C treated with
348:
Zoom in a full epistatic map for an Arabidopsis phenotype
4619:"Genome-wide association studies in diverse populations"
3182:"Personal genomes: The case of the missing heritability"
4505:"Genetic signatures of exceptional longevity in humans"
4366:"Genetic signatures of exceptional longevity in humans"
1825:
EURASIP Journal on Bioinformatics & Systems Biology
847:
can inflate estimates of genetic phenotype similarity.
66:. This example is taken from a GWA study investigating
4715:
Borecki IB (2006). "Linkage and Association Studies".
1316:
264:
For each of these SNPs it is then investigated if the
4666:
Sham PC, Cherny SS, Purcell S, Hewitt JK (May 2000).
1874:. BCB '15. New York, NY, USA: ACM. pp. 376–385.
1215:
Bush WS, Moore JH (2012). Lewitter F, Kann M (eds.).
5119:
5088:
5057:
5011:
4990:
4922:
Consortia of genome-wide association studies (GWAS)
4437:"Serious flaws revealed in "longevity genes" study"
3545:"Personalized medicine and human genetic diversity"
2945:
2943:
2941:
2232:Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews. Cognitive Science
16:Study of genetic variants in different individuals
4021:Ganapathiraju M, Chaparala S, Lo C (April 2018).
2026:Howie B, Marchini J, Stephens M (November 2011).
637:, which have important clinical implications for
600:, a GWA study has shown that SNPs near the human
352:A key step in the majority of GWA studies is the
3136:Ku CS, Loy EY, Pawitan Y, Chia KS (April 2010).
2326:"Guidelines for genome-wide association studies"
311:. Likewise, alternative statistics designed for
119:, and found two SNPs with significantly altered
3175:
3173:
2028:"Genotype imputation with thousands of genomes"
1667:
1665:
1663:
1661:
1336:
1334:
259:The most common approach of GWA studies is the
1210:
1208:
1206:
1023:
1021:
1019:
977:
975:
839:have also provided a realistic alternative to
4968:
4915:"How to read a genome-wide association study"
1217:"Chapter 11: Genome-wide association studies"
159:) as well as many larger variations, such as
8:
2719:Ioannidis JP, Thomas G, Daly MJ (May 2009).
1447:Annual Review of Genomics and Human Genetics
855:Genotyping arrays designed for GWAS rely on
806:results". This is why all modern GWAS use a
247:) were overrepresented amongst CAD-patients.
4940:— whole genome association analysis toolset
3729:: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (
3549:Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine
3223:"Genomics: Hepatitis C virus gets personal"
2923:1871.1/08af5d9e-8621-41f1-97c5-e77a1063495f
831:. Alternative strategies suggested involve
4975:
4961:
4953:
2075:Browning BL, Browning SR (February 2009).
1287:(4th ed.). Garland Science. pp.
1274:
1272:
1270:
724:level GWA studies may be used to identify
4861:
4789:
4691:
4642:
4538:
4528:
4305:
4295:
4254:
4197:
4187:
4146:
4136:
4087:
4046:
3967:
3918:
3776:
3659:
3610:
3568:
3519:
3359:
3310:
3246:
3197:
3153:
3069:
3028:
2975:
2921:
2911:
2901:
2860:
2850:
2801:
2744:
2669:
2612:
2563:
2553:
2536:Johnson AD, O'Donnell CJ (January 2009).
2512:
2502:
2453:
2443:
2402:
2392:
2351:
2341:
2300:
2251:
2206:
2149:
2100:
2051:
1959:
1941:
1846:
1836:
1795:
1746:
1697:
1641:
1518:
1458:
1366:
1250:
1240:
1161:
999:
4902:National Human Genome Research Institute
3221:Iadonato SP, Katze MG (September 2009).
1603:
1601:
1599:
1597:
1068:National Human Genome Research Institute
945:Common disease-common variant hypothesis
823:instance, GWA studies for diseases like
753:Plant growth stages and yield components
516:or similar biomarkers. These are called
433:
426:is visualized with colour scale and the
409:
335:
250:
222:
138:
49:
971:
709:(PPIs) associated with genes linked to
301:Variations on the case-control approach
4750:
4740:
3722:
2175:"Genes mirror geography within Europe"
529:genome-wide association study by proxy
461:Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium
109:gene-specific candidate-driven studies
1919:
1917:
1460:10.1146/annurev.genom.7.080505.115721
1313:"Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man"
1190:European Molecular Biology Laboratory
811:of a discrepancy between the type of
633:have shed light on the metabolism of
7:
3893:Roselli C, Chafin M, Weng L (2018).
3599:Circulation: Cardiovascular Genetics
3052:Danesh J, Pepys MB (November 2009).
895:Transcriptome-wide association study
609:eQTL, LDL and cardiovascular disease
988:The New England Journal of Medicine
689:) or associated with alteration of
330:protein-protein interaction network
297:to consider a variant significant.
187:study. This study type asks if the
4672:American Journal of Human Genetics
3757:American Journal of Human Genetics
3640:American Journal of Human Genetics
2081:American Journal of Human Genetics
1727:American Journal of Human Genetics
1484:"The International HapMap Project"
1347:American Journal of Human Genetics
619:expression quantitative trait loci
551:Clinical applications and examples
14:
3303:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.924233
3071:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.907212
1064:"Genome-Wide Association Studies"
950:Microbiome-wide association study
4898:Whole genome association studies
4805:
4772:, Derks EM, Wray NR (May 2012).
4488:
4420:
4343:10.1111/j.1365-2052.2007.01642.x
3878:
3828:
3736:
3418:
3270:
874:
448:age-related macular degeneration
418:region and their association to
117:age-related macular degeneration
5039:Single-nucleotide polymorphisms
4931:— by Bennett SN, Caporaso, NE,
3612:10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.110.948935
617:of nearby genes, the so-called
215:was an important prerequisite.
45:single-nucleotide polymorphisms
5142:Human Genome Diversity Project
4719:. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
4475:10.1126/science.333.6041.404-a
4401:10.1126/science.333.6041.404-a
4080:10.1016/j.biopsych.2017.06.033
1:
5101:Genome-wide association study
4717:Encyclopedia of Life Sciences
3845:Current Opinion in Lipidology
3405:10.1126/science.328.5983.1220
1788:10.1093/bioinformatics/btv263
1412:10.1126/science.273.5281.1516
594:Pegylated interferon-alpha-2b
590:Pegylated interferon-alpha-2a
25:genome-wide association study
5132:International HapMap Project
4530:10.1371/journal.pone.0029848
3998:. 3 May 2016. Archived from
3857:10.1097/MOL.0b013e32834469b3
2662:10.1182/blood-2011-06-359646
2445:10.1371/journal.pgen.1002198
2343:10.1371/journal.pgen.1002812
1572:10.1126/science.270.5235.467
1242:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002822
910:Gene–environment interaction
732:. This could help determine
707:protein-protein interactions
205:International HapMap Project
4435:MacArthur D (8 July 2010).
3561:10.1101/cshperspect.a008581
1279:Strachan T, Read A (2011).
808:very low p-value threshold.
5196:
4913:Barrett J (18 July 2010).
4284:Frontiers in Plant Science
4278:Bartoli C, Roux F (2017).
3769:10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.10.013
3652:10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.10.002
2843:10.1038/s41588-022-01016-z
2394:10.1038/s41593-021-00826-4
2093:10.1016/j.ajhg.2009.01.005
1943:10.1186/s13059-024-03202-0
1221:PLOS Computational Biology
4580:10.1038/s41576-019-0127-1
4189:10.1186/s12870-017-1131-2
4039:10.1093/schbul/sby017.731
3911:10.1038/s41588-018-0133-9
3180:Maher B (November 2008).
3142:Journal of Human Genetics
2913:10.1038/s41588-018-0333-3
2794:10.1038/s41588-018-0147-3
1838:10.1186/s13637-015-0025-6
799:population stratification
748:Agricultural applications
717:Conservation applications
367:population stratification
106:approach, in contrast to
4927:26 February 2018 at the
2281:Translational Psychiatry
1283:Human Molecular Genetics
1042:10.1001/jama.299.11.1335
982:Manolio TA (July 2010).
635:low-density lipoproteins
391:genome-wide significance
39:of a genome-wide set of
5096:Whole genome sequencing
5029:Human genetic variation
4944:ENCODE threads explorer
4846:10.1126/science.abo2059
4725:10.1038/npg.els.0005483
4623:Nature Reviews Genetics
4568:Nature Reviews Genetics
4382:10.1126/science.1190532
4297:10.3389/fpls.2017.00763
4138:10.1073/pnas.2105076119
3960:10.1038/npjschz.2016.12
2725:Nature Reviews Genetics
2614:10.1126/science.1110359
2504:10.1073/pnas.0903103106
1985:Nature Reviews Genetics
1880:10.1145/2808719.2808758
1154:10.1126/science.1109557
518:intermediate phenotypes
321:bioinformatics software
307:concentrations or even
241:coronary artery disease
4027:Schizophrenia Bulletin
3815:10.1002/bies.201100003
2555:10.1186/1471-2350-10-6
1690:10.1038/nprot.2010.182
925:Molecular epidemiology
920:Linkage disequilibrium
857:linkage disequilibrium
730:climate becomes warmer
661:coding-genes, such as
639:cardiovascular disease
498:educational attainment
466:coronary heart disease
439:
431:
372:After odds ratios and
349:
341:
256:
248:
235:—to identify variants
169:copy number variations
148:
71:
5180:Personalized medicine
5175:Human genome projects
5065:Personalized medicine
4395:(Retracted, see
4227:Nature Communications
4068:Biological Psychiatry
3352:10.1001/jama.2010.119
2044:10.1534/g3.111.001198
1001:10.1056/NEJMra0905980
627:small interfering RNA
580:Hepatitis C treatment
437:
413:
347:
339:
254:
226:
181:single gene disorders
142:
54:An illustration of a
53:
5165:Genetic epidemiology
5137:1000 Genomes Project
5127:Human Genome Project
5075:Genetic epidemiology
4778:Molecular Psychiatry
2542:BMC Medical Genetics
2130:Genetic Epidemiology
955:Conservation biology
940:Genetic epidemiology
659:transcription factor
478:rheumatoid arthritis
424:haploblock structure
209:haploblock structure
104:non-candidate-driven
68:kidney stone disease
5089:Analysis techniques
5070:Predictive medicine
5044:Identity by descent
5019:Biological specimen
5003:Biological database
4917:. Genomes Unzipped.
4838:2022Sci...378..754B
4521:2012PLoSO...729848S
4239:2011NatCo...2..467Z
4129:2022PNAS..11905076W
4033:(suppl_1): S298-9.
3512:10.1038/nature08463
3504:2009Natur.461..798T
3456:10.1038/nature08309
3448:2009Natur.461..399G
3397:2010Sci...328.1220C
3297:(11 Suppl): S60–5.
3239:2009Natur.461..357I
3155:10.1038/jhg.2010.19
2605:2005Sci...308..419H
2495:2009PNAS..106.9362H
2293:10.1038/tp.2013.124
2199:10.1038/nature07331
2191:2008Natur.456...98N
1634:10.1038/nature05911
1626:2007Natur.447..661B
1564:1995Sci...270..467S
1511:10.1038/nature02168
1503:2003Natur.426..789G
1404:1996Sci...273.1516R
1233:2012PLSCB...8E2822B
1146:2005Sci...308..385K
935:Population genetics
890:Association mapping
825:Alzheimer's disease
691:cardiac muscle cell
655:atrial fibrillation
645:Atrial fibrillation
631:gene knock-out mice
453:complement factor H
185:genetic association
37:observational study
4791:10.1038/mp.2011.65
4247:10.1038/ncomms1467
4123:(1): e2105076119.
4002:on 11 January 2020
2142:10.1002/gepi.20533
1441:Greely HT (2007).
1319:on 5 December 2011
845:assortative mating
766:The emergences of
440:
432:
350:
342:
257:
249:
149:
72:
5150:
5149:
5024:De-identification
4984:Personal genomics
4832:(6621): 754–761.
4176:BMC Plant Biology
3948:npj Schizophrenia
3498:(7265): 798–801.
3442:(7262): 399–401.
3021:10.2337/db11-0415
1889:978-1-4503-3853-0
1298:978-0-8153-4149-9
905:Genetic diversity
742:genetic diversity
213:genotyping arrays
64:association level
5187:
5170:Genetics studies
5080:Pharmacogenomics
5049:Genetic disorder
4977:
4970:
4963:
4954:
4948:Nature (journal)
4918:
4876:
4875:
4865:
4817:
4811:
4810:
4809:
4803:
4793:
4765:
4759:
4758:
4752:
4748:
4746:
4738:
4712:
4706:
4705:
4695:
4663:
4657:
4656:
4646:
4614:
4608:
4607:
4559:
4553:
4552:
4542:
4532:
4500:
4494:
4493:
4492:
4486:
4458:
4452:
4451:
4449:
4447:
4432:
4426:
4425:
4424:
4418:
4414:Retraction Watch
4393:
4361:
4355:
4354:
4326:
4320:
4319:
4309:
4299:
4275:
4269:
4268:
4258:
4218:
4212:
4211:
4201:
4191:
4182:(Suppl 1): 190.
4167:
4161:
4160:
4150:
4140:
4108:
4102:
4101:
4091:
4059:
4053:
4052:
4050:
4018:
4012:
4011:
4009:
4007:
3996:psychcentral.com
3988:
3982:
3981:
3971:
3939:
3933:
3932:
3922:
3905:(9): 1225–1233.
3890:
3884:
3883:
3882:
3876:
3840:
3834:
3833:
3832:
3826:
3797:
3791:
3790:
3780:
3748:
3742:
3741:
3740:
3734:
3728:
3720:
3680:
3674:
3673:
3663:
3631:
3625:
3624:
3614:
3589:
3583:
3582:
3572:
3540:
3534:
3533:
3523:
3482:
3476:
3475:
3430:
3424:
3423:
3422:
3416:
3391:(5983): 1220–1.
3380:
3374:
3373:
3363:
3331:
3325:
3324:
3314:
3282:
3276:
3275:
3274:
3268:
3250:
3218:
3212:
3211:
3201:
3177:
3168:
3167:
3157:
3133:
3127:
3126:
3090:
3084:
3083:
3073:
3049:
3043:
3042:
3032:
2999:Strawbridge RJ,
2996:
2990:
2989:
2979:
2947:
2936:
2935:
2925:
2915:
2905:
2881:
2875:
2874:
2864:
2854:
2822:
2816:
2815:
2805:
2788:(8): 1112–1121.
2773:
2767:
2766:
2748:
2716:
2710:
2709:
2707:
2705:
2690:
2684:
2683:
2673:
2641:
2635:
2634:
2616:
2599:(5720): 419–21.
2584:
2578:
2577:
2567:
2557:
2533:
2527:
2526:
2516:
2506:
2474:
2468:
2467:
2457:
2447:
2423:
2417:
2416:
2406:
2396:
2372:
2366:
2365:
2355:
2345:
2321:
2315:
2314:
2304:
2272:
2266:
2265:
2255:
2244:10.1002/wcs.1405
2227:
2221:
2220:
2210:
2185:(7218): 98–101.
2170:
2164:
2163:
2153:
2121:
2115:
2114:
2104:
2072:
2066:
2065:
2055:
2023:
2017:
2016:
1980:
1974:
1973:
1963:
1945:
1921:
1912:
1908:
1902:
1901:
1867:
1861:
1860:
1850:
1840:
1816:
1810:
1809:
1799:
1767:
1761:
1760:
1750:
1718:
1712:
1711:
1701:
1678:Nature Protocols
1669:
1656:
1655:
1645:
1620:(7145): 661–78.
1605:
1592:
1591:
1558:(5235): 467–70.
1547:
1541:
1540:
1522:
1497:(6968): 789–96.
1488:
1479:
1473:
1472:
1462:
1438:
1432:
1431:
1398:(5281): 1516–7.
1387:
1381:
1380:
1370:
1338:
1329:
1328:
1326:
1324:
1315:. Archived from
1309:
1303:
1302:
1286:
1276:
1265:
1264:
1254:
1244:
1227:(12): e1002822.
1212:
1201:
1200:
1198:
1196:
1182:
1176:
1175:
1165:
1125:
1119:
1118:
1078:
1072:
1071:
1060:
1054:
1053:
1025:
1014:
1013:
1003:
979:
884:
879:
878:
841:genotyping array
833:linkage analysis
813:genotyping array
486:bipolar disorder
400:
398:
387:multiple testing
296:
294:
287:chi-squared test
266:allele frequency
233:chi-squared test
125:genetic diseases
121:allele frequency
85:genetic variants
41:genetic variants
5195:
5194:
5190:
5189:
5188:
5186:
5185:
5184:
5155:
5154:
5151:
5146:
5115:
5111:Genetic testing
5084:
5053:
5034:Genetic linkage
5007:
4991:Data collection
4986:
4981:
4929:Wayback Machine
4912:
4884:
4879:
4819:
4818:
4814:
4804:
4767:
4766:
4762:
4749:
4739:
4735:
4714:
4713:
4709:
4665:
4664:
4660:
4635:10.1038/nrg2760
4616:
4615:
4611:
4561:
4560:
4556:
4502:
4501:
4497:
4487:
4460:
4459:
4455:
4445:
4443:
4434:
4433:
4429:
4419:
4394:
4363:
4362:
4358:
4331:Animal Genetics
4328:
4327:
4323:
4277:
4276:
4272:
4220:
4219:
4215:
4169:
4168:
4164:
4110:
4109:
4105:
4074:(10): 702–708.
4061:
4060:
4056:
4020:
4019:
4015:
4005:
4003:
3990:
3989:
3985:
3941:
3940:
3936:
3899:Nature Genetics
3892:
3891:
3887:
3877:
3842:
3841:
3837:
3827:
3799:
3798:
3794:
3750:
3749:
3745:
3735:
3721:
3689:Nature Genetics
3682:
3681:
3677:
3633:
3632:
3628:
3591:
3590:
3586:
3542:
3541:
3537:
3484:
3483:
3479:
3432:
3431:
3427:
3417:
3382:
3381:
3377:
3333:
3332:
3328:
3284:
3283:
3279:
3269:
3248:10.1038/461357a
3233:(7262): 357–8.
3220:
3219:
3215:
3199:10.1038/456018a
3192:(7218): 18–21.
3179:
3178:
3171:
3135:
3134:
3130:
3107:10.1038/ng.3766
3095:Nature Genetics
3092:
3091:
3087:
3051:
3050:
3046:
3015:(10): 2624–34.
2998:
2997:
2993:
2956:Nature Genetics
2949:
2948:
2939:
2890:Nature Genetics
2883:
2882:
2878:
2831:Nature Genetics
2824:
2823:
2819:
2782:Nature Genetics
2775:
2774:
2770:
2737:10.1038/nrg2544
2718:
2717:
2713:
2703:
2701:
2692:
2691:
2687:
2656:(17): 4705–13.
2643:
2642:
2638:
2586:
2585:
2581:
2535:
2534:
2530:
2476:
2475:
2471:
2438:(7): e1002198.
2425:
2424:
2420:
2374:
2373:
2369:
2336:(7): e1002812.
2323:
2322:
2318:
2274:
2273:
2269:
2229:
2228:
2224:
2172:
2171:
2167:
2123:
2122:
2118:
2074:
2073:
2069:
2025:
2024:
2020:
1997:10.1038/nrg2796
1982:
1981:
1977:
1923:
1922:
1915:
1909:
1905:
1890:
1869:
1868:
1864:
1818:
1817:
1813:
1769:
1768:
1764:
1720:
1719:
1715:
1671:
1670:
1659:
1607:
1606:
1595:
1549:
1548:
1544:
1486:
1481:
1480:
1476:
1440:
1439:
1435:
1389:
1388:
1384:
1340:
1339:
1332:
1322:
1320:
1311:
1310:
1306:
1299:
1278:
1277:
1268:
1214:
1213:
1204:
1194:
1192:
1184:
1183:
1179:
1140:(5720): 385–9.
1127:
1126:
1122:
1087:Nature Genetics
1080:
1079:
1075:
1062:
1061:
1057:
1036:(11): 1335–44.
1027:
1026:
1017:
981:
980:
973:
969:
930:Polygenic score
880:
873:
870:
853:
794:
785:
768:plant pathogens
764:
762:Plant pathogens
755:
750:
719:
703:
693:communication (
649:For example, a
647:
615:gene expression
611:
582:
574:pathophysiology
553:
482:Crohn's disease
474:type 2 diabetes
470:type 1 diabetes
420:LDL-cholesterol
408:
396:
394:
309:gene expression
292:
290:
221:
193:genetic variant
177:genetic linkage
137:
87:are read using
17:
12:
11:
5:
5193:
5191:
5183:
5182:
5177:
5172:
5167:
5157:
5156:
5148:
5147:
5145:
5144:
5139:
5134:
5129:
5123:
5121:
5120:Major projects
5117:
5116:
5114:
5113:
5108:
5103:
5098:
5092:
5090:
5086:
5085:
5083:
5082:
5077:
5072:
5067:
5061:
5059:
5055:
5054:
5052:
5051:
5046:
5041:
5036:
5031:
5026:
5021:
5015:
5013:
5012:Field concepts
5009:
5008:
5006:
5005:
5000:
4994:
4992:
4988:
4987:
4982:
4980:
4979:
4972:
4965:
4957:
4951:
4950:
4941:
4935:
4919:
4910:
4904:
4895:
4890:
4883:
4882:External links
4880:
4878:
4877:
4812:
4760:
4733:
4707:
4684:10.1086/302891
4678:(5): 1616–30.
4658:
4609:
4574:(8): 467–484.
4554:
4495:
4453:
4427:
4356:
4337:(5): 491–498.
4321:
4270:
4213:
4162:
4103:
4054:
4013:
3983:
3934:
3885:
3835:
3792:
3763:(6): 688–700.
3743:
3701:10.1038/ng.782
3675:
3626:
3584:
3555:(9): a008581.
3535:
3477:
3425:
3375:
3326:
3277:
3213:
3169:
3148:(4): 195–206.
3128:
3101:(3): 325–331.
3085:
3064:(21): 2036–9.
3044:
2991:
2968:10.1038/ng.291
2937:
2903:10.1101/214973
2896:(3): 394–403.
2876:
2837:(4): 437–449.
2817:
2768:
2711:
2700:on 4 June 2008
2685:
2636:
2579:
2528:
2489:(23): 9362–7.
2469:
2418:
2387:(5): 737–745.
2367:
2316:
2267:
2238:(1–2): e1405.
2222:
2165:
2116:
2067:
2018:
1991:(7): 499–511.
1975:
1930:Genome Biology
1913:
1903:
1888:
1862:
1811:
1782:(12): i240-9.
1776:Bioinformatics
1762:
1739:10.1086/519795
1713:
1657:
1593:
1542:
1474:
1433:
1382:
1359:10.1086/324069
1330:
1304:
1297:
1266:
1202:
1177:
1120:
1099:10.1038/ng1047
1073:
1055:
1015:
970:
968:
965:
964:
963:
957:
952:
947:
942:
937:
932:
927:
922:
917:
912:
907:
902:
897:
892:
886:
885:
882:Biology portal
869:
866:
852:
849:
804:false-positive
793:
790:
784:
781:
777:plant pathogen
763:
760:
754:
751:
749:
746:
718:
715:
702:
699:
646:
643:
610:
607:
596:combined with
581:
578:
552:
549:
407:
404:
378:Manhattan plot
220:
217:
136:
133:
81:genotype-first
56:Manhattan plot
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
5192:
5181:
5178:
5176:
5173:
5171:
5168:
5166:
5163:
5162:
5160:
5153:
5143:
5140:
5138:
5135:
5133:
5130:
5128:
5125:
5124:
5122:
5118:
5112:
5109:
5107:
5104:
5102:
5099:
5097:
5094:
5093:
5091:
5087:
5081:
5078:
5076:
5073:
5071:
5068:
5066:
5063:
5062:
5060:
5056:
5050:
5047:
5045:
5042:
5040:
5037:
5035:
5032:
5030:
5027:
5025:
5022:
5020:
5017:
5016:
5014:
5010:
5004:
5001:
4999:
4996:
4995:
4993:
4989:
4985:
4978:
4973:
4971:
4966:
4964:
4959:
4958:
4955:
4949:
4945:
4942:
4939:
4936:
4934:
4930:
4926:
4923:
4920:
4916:
4911:
4908:
4905:
4903:
4899:
4896:
4894:
4891:
4889:
4886:
4885:
4881:
4873:
4869:
4864:
4859:
4855:
4851:
4847:
4843:
4839:
4835:
4831:
4827:
4823:
4816:
4813:
4808:
4801:
4797:
4792:
4787:
4784:(5): 474–85.
4783:
4779:
4775:
4771:
4768:Visscher PM,
4764:
4761:
4756:
4744:
4736:
4734:9780470015902
4730:
4726:
4722:
4718:
4711:
4708:
4703:
4699:
4694:
4689:
4685:
4681:
4677:
4673:
4669:
4662:
4659:
4654:
4650:
4645:
4640:
4636:
4632:
4629:(5): 356–66.
4628:
4624:
4620:
4613:
4610:
4605:
4601:
4597:
4593:
4589:
4585:
4581:
4577:
4573:
4569:
4565:
4558:
4555:
4550:
4546:
4541:
4536:
4531:
4526:
4522:
4518:
4515:(1): e29848.
4514:
4510:
4506:
4499:
4496:
4491:
4484:
4480:
4476:
4472:
4469:(6041): 404.
4468:
4464:
4457:
4454:
4442:
4438:
4431:
4428:
4423:
4416:
4415:
4410:
4406:
4402:
4398:
4391:
4387:
4383:
4379:
4375:
4371:
4367:
4360:
4357:
4352:
4348:
4344:
4340:
4336:
4332:
4325:
4322:
4317:
4313:
4308:
4303:
4298:
4293:
4289:
4285:
4281:
4274:
4271:
4266:
4262:
4257:
4252:
4248:
4244:
4240:
4236:
4232:
4228:
4224:
4217:
4214:
4209:
4205:
4200:
4195:
4190:
4185:
4181:
4177:
4173:
4166:
4163:
4158:
4154:
4149:
4144:
4139:
4134:
4130:
4126:
4122:
4118:
4114:
4107:
4104:
4099:
4095:
4090:
4085:
4081:
4077:
4073:
4069:
4065:
4058:
4055:
4049:
4044:
4040:
4036:
4032:
4028:
4024:
4017:
4014:
4001:
3997:
3993:
3987:
3984:
3979:
3975:
3970:
3965:
3961:
3957:
3953:
3949:
3945:
3938:
3935:
3930:
3926:
3921:
3916:
3912:
3908:
3904:
3900:
3896:
3889:
3886:
3881:
3874:
3870:
3866:
3862:
3858:
3854:
3850:
3846:
3839:
3836:
3831:
3824:
3820:
3816:
3812:
3808:
3804:
3796:
3793:
3788:
3784:
3779:
3774:
3770:
3766:
3762:
3758:
3754:
3747:
3744:
3739:
3732:
3726:
3718:
3714:
3710:
3706:
3702:
3698:
3695:(4): 339–44.
3694:
3690:
3686:
3679:
3676:
3671:
3667:
3662:
3657:
3653:
3649:
3646:(5): 619–27.
3645:
3641:
3637:
3630:
3627:
3622:
3618:
3613:
3608:
3605:(4): 365–73.
3604:
3600:
3596:
3588:
3585:
3580:
3576:
3571:
3566:
3562:
3558:
3554:
3550:
3546:
3539:
3536:
3531:
3527:
3522:
3517:
3513:
3509:
3505:
3501:
3497:
3493:
3489:
3481:
3478:
3473:
3469:
3465:
3461:
3457:
3453:
3449:
3445:
3441:
3437:
3429:
3426:
3421:
3414:
3410:
3406:
3402:
3398:
3394:
3390:
3386:
3379:
3376:
3371:
3367:
3362:
3357:
3353:
3349:
3345:
3341:
3337:
3330:
3327:
3322:
3318:
3313:
3308:
3304:
3300:
3296:
3292:
3288:
3281:
3278:
3273:
3266:
3262:
3258:
3254:
3249:
3244:
3240:
3236:
3232:
3228:
3224:
3217:
3214:
3209:
3205:
3200:
3195:
3191:
3187:
3183:
3176:
3174:
3170:
3165:
3161:
3156:
3151:
3147:
3143:
3139:
3132:
3129:
3124:
3120:
3116:
3112:
3108:
3104:
3100:
3096:
3089:
3086:
3081:
3077:
3072:
3067:
3063:
3059:
3055:
3048:
3045:
3040:
3036:
3031:
3026:
3022:
3018:
3014:
3010:
3006:
3002:
2995:
2992:
2987:
2983:
2978:
2973:
2969:
2965:
2961:
2957:
2953:
2946:
2944:
2942:
2938:
2933:
2929:
2924:
2919:
2914:
2909:
2904:
2899:
2895:
2891:
2887:
2880:
2877:
2872:
2868:
2863:
2858:
2853:
2852:11368/3026010
2848:
2844:
2840:
2836:
2832:
2828:
2821:
2818:
2813:
2809:
2804:
2799:
2795:
2791:
2787:
2783:
2779:
2772:
2769:
2764:
2760:
2756:
2752:
2747:
2742:
2738:
2734:
2731:(5): 318–29.
2730:
2726:
2722:
2715:
2712:
2699:
2695:
2689:
2686:
2681:
2677:
2672:
2667:
2663:
2659:
2655:
2651:
2647:
2640:
2637:
2632:
2628:
2624:
2620:
2615:
2610:
2606:
2602:
2598:
2594:
2590:
2583:
2580:
2575:
2571:
2566:
2561:
2556:
2551:
2547:
2543:
2539:
2532:
2529:
2524:
2520:
2515:
2510:
2505:
2500:
2496:
2492:
2488:
2484:
2480:
2473:
2470:
2465:
2461:
2456:
2451:
2446:
2441:
2437:
2433:
2432:PLOS Genetics
2429:
2422:
2419:
2414:
2410:
2405:
2400:
2395:
2390:
2386:
2382:
2378:
2371:
2368:
2363:
2359:
2354:
2349:
2344:
2339:
2335:
2331:
2330:PLOS Genetics
2327:
2320:
2317:
2312:
2308:
2303:
2298:
2294:
2290:
2286:
2282:
2278:
2271:
2268:
2263:
2259:
2254:
2249:
2245:
2241:
2237:
2233:
2226:
2223:
2218:
2214:
2209:
2204:
2200:
2196:
2192:
2188:
2184:
2180:
2176:
2169:
2166:
2161:
2157:
2152:
2147:
2143:
2139:
2136:(8): 816–34.
2135:
2131:
2127:
2120:
2117:
2112:
2108:
2103:
2098:
2094:
2090:
2087:(2): 210–23.
2086:
2082:
2078:
2071:
2068:
2063:
2059:
2054:
2049:
2045:
2041:
2038:(6): 457–70.
2037:
2033:
2029:
2022:
2019:
2014:
2010:
2006:
2002:
1998:
1994:
1990:
1986:
1979:
1976:
1971:
1967:
1962:
1957:
1953:
1949:
1944:
1939:
1935:
1931:
1927:
1920:
1918:
1914:
1907:
1904:
1899:
1895:
1891:
1885:
1881:
1877:
1873:
1866:
1863:
1858:
1854:
1849:
1844:
1839:
1834:
1830:
1826:
1822:
1815:
1812:
1807:
1803:
1798:
1793:
1789:
1785:
1781:
1777:
1773:
1766:
1763:
1758:
1754:
1749:
1744:
1740:
1736:
1733:(3): 559–75.
1732:
1728:
1724:
1717:
1714:
1709:
1705:
1700:
1695:
1691:
1687:
1684:(2): 121–33.
1683:
1679:
1675:
1668:
1666:
1664:
1662:
1658:
1653:
1649:
1644:
1639:
1635:
1631:
1627:
1623:
1619:
1615:
1611:
1604:
1602:
1600:
1598:
1594:
1589:
1585:
1581:
1577:
1573:
1569:
1565:
1561:
1557:
1553:
1546:
1543:
1538:
1534:
1530:
1526:
1521:
1520:2027.42/62838
1516:
1512:
1508:
1504:
1500:
1496:
1492:
1485:
1478:
1475:
1470:
1466:
1461:
1456:
1452:
1448:
1444:
1437:
1434:
1429:
1425:
1421:
1417:
1413:
1409:
1405:
1401:
1397:
1393:
1386:
1383:
1378:
1374:
1369:
1364:
1360:
1356:
1353:(5): 936–50.
1352:
1348:
1344:
1337:
1335:
1331:
1318:
1314:
1308:
1305:
1300:
1294:
1290:
1285:
1284:
1275:
1273:
1271:
1267:
1262:
1258:
1253:
1248:
1243:
1238:
1234:
1230:
1226:
1222:
1218:
1211:
1209:
1207:
1203:
1191:
1187:
1181:
1178:
1173:
1169:
1164:
1159:
1155:
1151:
1147:
1143:
1139:
1135:
1131:
1124:
1121:
1116:
1112:
1108:
1104:
1100:
1096:
1092:
1088:
1084:
1077:
1074:
1069:
1065:
1059:
1056:
1051:
1047:
1043:
1039:
1035:
1031:
1024:
1022:
1020:
1016:
1011:
1007:
1002:
997:
994:(2): 166–76.
993:
989:
985:
978:
976:
972:
966:
961:
958:
956:
953:
951:
948:
946:
943:
941:
938:
936:
933:
931:
928:
926:
923:
921:
918:
916:
913:
911:
908:
906:
903:
901:
898:
896:
893:
891:
888:
887:
883:
877:
872:
867:
865:
861:
858:
850:
848:
846:
842:
838:
834:
830:
826:
820:
818:
814:
809:
805:
800:
791:
789:
782:
780:
778:
774:
769:
761:
759:
752:
747:
745:
743:
739:
735:
731:
727:
723:
716:
714:
712:
711:schizophrenia
708:
701:Schizophrenia
700:
698:
696:
692:
688:
684:
680:
679:ionic channel
676:
672:
668:
664:
660:
656:
652:
651:meta-analysis
644:
642:
640:
636:
632:
628:
624:
620:
616:
608:
606:
603:
599:
595:
591:
587:
579:
577:
575:
571:
567:
563:
558:
550:
548:
546:
542:
536:
534:
530:
526:
521:
519:
515:
511:
507:
503:
499:
493:
491:
487:
483:
479:
475:
471:
467:
463:
462:
456:
454:
450:
449:
443:
436:
429:
425:
421:
417:
412:
405:
403:
393:threshold is
392:
388:
383:
379:
375:
370:
368:
363:
358:
355:
346:
338:
334:
331:
327:
322:
318:
314:
310:
306:
302:
298:
288:
284:
279:
277:
273:
271:
267:
262:
253:
246:
242:
238:
234:
230:
225:
218:
216:
214:
210:
206:
202:
197:
194:
190:
186:
182:
178:
174:
170:
166:
162:
158:
154:
153:human genomes
146:
141:
134:
132:
130:
126:
122:
118:
113:
111:
110:
105:
100:
98:
94:
90:
86:
82:
77:
69:
65:
61:
57:
52:
48:
46:
42:
38:
34:
30:
26:
22:
5152:
5100:
5058:Applications
4932:
4907:GWAS Central
4829:
4825:
4815:
4781:
4777:
4763:
4716:
4710:
4675:
4671:
4661:
4626:
4622:
4612:
4571:
4567:
4557:
4512:
4508:
4498:
4466:
4462:
4456:
4444:. Retrieved
4440:
4430:
4413:
4411:,
4373:
4369:
4359:
4334:
4330:
4324:
4287:
4283:
4273:
4230:
4226:
4216:
4179:
4175:
4165:
4120:
4116:
4106:
4071:
4067:
4057:
4030:
4026:
4016:
4004:. Retrieved
4000:the original
3995:
3986:
3951:
3947:
3937:
3902:
3898:
3888:
3851:(2): 123–8.
3848:
3844:
3838:
3809:(6): 430–7.
3806:
3802:
3795:
3760:
3756:
3746:
3725:cite journal
3692:
3688:
3678:
3643:
3639:
3629:
3602:
3598:
3587:
3552:
3548:
3538:
3495:
3491:
3480:
3439:
3435:
3428:
3388:
3384:
3378:
3346:(7): 631–7.
3343:
3339:
3329:
3294:
3290:
3280:
3230:
3226:
3216:
3189:
3185:
3145:
3141:
3131:
3098:
3094:
3088:
3061:
3057:
3047:
3012:
3008:
2994:
2962:(1): 56–65.
2959:
2955:
2893:
2889:
2879:
2834:
2830:
2820:
2785:
2781:
2771:
2728:
2724:
2714:
2702:. Retrieved
2698:the original
2688:
2653:
2649:
2639:
2596:
2592:
2582:
2545:
2541:
2531:
2486:
2482:
2472:
2435:
2431:
2421:
2384:
2381:Nat Neurosci
2380:
2370:
2333:
2329:
2319:
2284:
2280:
2270:
2235:
2231:
2225:
2182:
2178:
2168:
2133:
2129:
2119:
2084:
2080:
2070:
2035:
2031:
2021:
1988:
1984:
1978:
1933:
1929:
1906:
1871:
1865:
1828:
1824:
1814:
1779:
1775:
1765:
1730:
1726:
1716:
1681:
1677:
1617:
1613:
1555:
1551:
1545:
1494:
1490:
1477:
1450:
1446:
1436:
1395:
1391:
1385:
1350:
1346:
1321:. Retrieved
1317:the original
1307:
1282:
1224:
1220:
1193:. Retrieved
1189:
1180:
1137:
1133:
1123:
1093:(4): 650–4.
1090:
1086:
1076:
1058:
1033:
1029:
991:
987:
900:Epidemiology
862:
854:
851:Fine-mapping
821:
795:
786:
765:
756:
738:conservation
720:
704:
648:
623:drug targets
612:
583:
554:
537:
532:
528:
524:
522:
517:
510:blood lipids
506:effect sizes
494:
490:hypertension
459:
457:
446:
444:
441:
416:LDL receptor
371:
359:
351:
300:
299:
280:
275:
274:
261:case-control
258:
244:
198:
150:
144:
129:in aggregate
114:
107:
103:
101:
96:
73:
32:
28:
24:
18:
4751:|work=
3291:Circulation
3058:Circulation
2287:(1): e354.
2253:10161/13337
829:East Asians
792:Limitations
734:extirpation
683:tachycardia
586:hepatitis C
566:diagnostics
545:monozygotic
428:association
145:lower right
5159:Categories
4770:Goddard ME
4446:7 December
4233:(1): 467.
1453:: 343–64.
1323:6 December
967:References
837:sequencing
722:Population
514:proinsulin
354:imputation
270:odds ratio
237:associated
165:insertions
135:Background
97:associated
89:SNP arrays
76:phenotypes
5106:SNP array
4900:— by the
4854:0036-8075
4753:ignored (
4743:cite book
4604:148570302
4588:1471-0056
3954:: 16012.
3803:BioEssays
1952:1474-760X
1936:(1): 76.
960:WGAViewer
817:retracted
598:ribavirin
570:prognosis
541:heritable
525:relatives
326:epistasis
317:recessive
313:dominance
305:biomarker
245:rs1333049
173:phenotype
161:deletions
35:), is an
29:GWA study
4925:Archived
4872:36395242
4800:21670730
4702:10762547
4653:20395969
4596:31068683
4549:22279548
4509:PLOS ONE
4483:21778381
4409:21778381
4390:20595579
4376:(5987).
4351:17894563
4316:28588588
4265:21915109
4208:29143598
4157:34930821
4098:28823710
4006:22 April
3978:27336055
3929:29892015
3873:24020035
3865:21311327
3823:21462369
3787:22100073
3717:39712343
3709:21378988
3670:22055160
3621:20562444
3579:25059740
3530:19759533
3464:19684573
3413:20522751
3370:20159871
3321:20837927
3257:19759611
3208:18987709
3164:20300123
3115:28092683
3080:19901186
3039:21873549
3009:Diabetes
3001:Dupuis J
2986:19060906
2932:30804565
2871:35361970
2812:30038396
2755:19373277
2680:21860027
2631:32716116
2623:15761120
2574:19161620
2523:19474294
2464:21829380
2413:33875891
2362:22792080
2311:24473445
2262:27906529
2217:18758442
2160:21058334
2111:19200528
2062:22384356
2005:20517342
1970:38523316
1961:10962106
1857:28194175
1831:(1): 7.
1806:26072488
1757:17701901
1708:21293453
1652:17554300
1529:14685227
1469:17550341
1377:11565063
1261:23300413
1195:18 April
1172:15761122
1115:21414260
1107:12426569
1050:18349094
1010:20647212
915:Genomics
868:See also
726:adaptive
502:insomnia
374:P-values
362:confound
201:biobanks
151:Any two
21:genomics
4998:Biobank
4863:9901291
4834:Bibcode
4826:Science
4693:1378020
4644:3079573
4540:3261167
4517:Bibcode
4463:Science
4370:Science
4307:5441063
4290:: 763.
4256:3195253
4235:Bibcode
4199:5688510
4148:8740573
4125:Bibcode
4089:5643230
4048:5887623
3969:4898894
3920:6136836
3778:3234370
3661:3213391
3570:4143101
3521:3172006
3500:Bibcode
3472:1707096
3444:Bibcode
3393:Bibcode
3385:Science
3361:2845522
3312:2943860
3265:7602652
3235:Bibcode
3123:5598845
3030:3178302
2977:2881676
2898:bioRxiv
2862:9005349
2803:6393768
2763:6463743
2746:7877552
2704:19 June
2671:3208285
2601:Bibcode
2593:Science
2565:2639349
2514:2687147
2491:Bibcode
2455:3145627
2404:7610742
2353:3390399
2302:3905234
2208:2735096
2187:Bibcode
2151:3175618
2102:2668004
2053:3276165
2013:1465707
1898:5942777
1848:5270451
1797:4559912
1748:1950838
1699:3154648
1643:2719288
1622:Bibcode
1588:6720459
1580:7569999
1560:Bibcode
1552:Science
1537:4387110
1499:Bibcode
1428:5228523
1420:8801636
1400:Bibcode
1392:Science
1368:1274370
1252:3531285
1229:Bibcode
1163:1512523
1142:Bibcode
1134:Science
783:Chicken
773:alleles
406:Results
382:P-value
283:P-value
276:Example
219:Methods
4933:et al.
4870:
4860:
4852:
4798:
4731:
4700:
4690:
4651:
4641:
4602:
4594:
4586:
4547:
4537:
4481:
4407:
4403:,
4388:
4349:
4314:
4304:
4263:
4253:
4206:
4196:
4155:
4145:
4096:
4086:
4045:
3976:
3966:
3927:
3917:
3871:
3863:
3821:
3785:
3775:
3715:
3707:
3668:
3658:
3619:
3577:
3567:
3528:
3518:
3492:Nature
3470:
3462:
3436:Nature
3411:
3368:
3358:
3319:
3309:
3263:
3255:
3227:Nature
3206:
3186:Nature
3162:
3121:
3113:
3078:
3037:
3027:
2984:
2974:
2930:
2900:
2869:
2859:
2810:
2800:
2761:
2753:
2743:
2678:
2668:
2629:
2621:
2572:
2562:
2521:
2511:
2462:
2452:
2411:
2401:
2360:
2350:
2309:
2299:
2260:
2215:
2205:
2179:Nature
2158:
2148:
2109:
2099:
2060:
2050:
2011:
2003:
1968:
1958:
1950:
1911:146570
1896:
1886:
1855:
1845:
1804:
1794:
1755:
1745:
1706:
1696:
1650:
1640:
1614:Nature
1586:
1578:
1535:
1527:
1491:Nature
1467:
1426:
1418:
1375:
1365:
1295:
1291:–495.
1259:
1249:
1170:
1160:
1113:
1105:
1048:
1008:
671:NKX2-5
488:, and
229:allele
189:allele
93:allele
4938:PLINK
4600:S2CID
4441:Wired
3869:S2CID
3713:S2CID
3468:S2CID
3261:S2CID
3119:S2CID
2759:S2CID
2650:Blood
2627:S2CID
2548:: 6.
2009:S2CID
1894:S2CID
1584:S2CID
1533:S2CID
1487:(PDF)
1424:S2CID
1111:S2CID
687:CASQ2
675:PITX2
602:IL28B
562:drugs
191:of a
31:, or
4868:PMID
4850:ISSN
4796:PMID
4755:help
4729:ISBN
4698:PMID
4649:PMID
4592:PMID
4584:ISSN
4545:PMID
4479:PMID
4448:2011
4405:PMID
4386:PMID
4374:2010
4347:PMID
4312:PMID
4261:PMID
4204:PMID
4153:PMID
4094:PMID
4008:2023
3974:PMID
3925:PMID
3861:PMID
3819:PMID
3783:PMID
3731:link
3705:PMID
3666:PMID
3617:PMID
3575:PMID
3526:PMID
3460:PMID
3409:PMID
3366:PMID
3340:JAMA
3317:PMID
3253:PMID
3204:PMID
3160:PMID
3111:PMID
3076:PMID
3035:PMID
2982:PMID
2928:PMID
2867:PMID
2808:PMID
2751:PMID
2706:2008
2676:PMID
2619:PMID
2570:PMID
2519:PMID
2460:PMID
2409:PMID
2358:PMID
2307:PMID
2258:PMID
2213:PMID
2156:PMID
2107:PMID
2058:PMID
2001:PMID
1966:PMID
1948:ISSN
1884:ISBN
1853:PMID
1829:2015
1802:PMID
1753:PMID
1704:PMID
1648:PMID
1576:PMID
1525:PMID
1465:PMID
1416:PMID
1373:PMID
1325:2011
1293:ISBN
1257:PMID
1197:2017
1168:PMID
1103:PMID
1046:PMID
1030:JAMA
1006:PMID
695:PKP2
667:TBX5
665:and
663:TBX3
629:and
564:and
557:drug
533:GWAX
167:and
157:SNPs
33:GWAS
23:, a
4858:PMC
4842:doi
4830:378
4786:doi
4721:doi
4688:PMC
4680:doi
4639:PMC
4631:doi
4576:doi
4535:PMC
4525:doi
4471:doi
4467:333
4397:doi
4378:doi
4339:doi
4302:PMC
4292:doi
4251:PMC
4243:doi
4194:PMC
4184:doi
4143:PMC
4133:doi
4121:119
4084:PMC
4076:doi
4043:PMC
4035:doi
3964:PMC
3956:doi
3915:PMC
3907:doi
3853:doi
3811:doi
3773:PMC
3765:doi
3697:doi
3656:PMC
3648:doi
3607:doi
3565:PMC
3557:doi
3516:PMC
3508:doi
3496:461
3452:doi
3440:461
3401:doi
3389:328
3356:PMC
3348:doi
3344:303
3307:PMC
3299:doi
3295:122
3243:doi
3231:461
3194:doi
3190:456
3150:doi
3103:doi
3066:doi
3062:120
3025:PMC
3017:doi
2972:PMC
2964:doi
2918:hdl
2908:doi
2857:PMC
2847:hdl
2839:doi
2798:PMC
2790:doi
2741:PMC
2733:doi
2666:PMC
2658:doi
2654:118
2609:doi
2597:308
2560:PMC
2550:doi
2509:PMC
2499:doi
2487:106
2450:PMC
2440:doi
2399:PMC
2389:doi
2348:PMC
2338:doi
2297:PMC
2289:doi
2248:hdl
2240:doi
2203:PMC
2195:doi
2183:456
2146:PMC
2138:doi
2097:PMC
2089:doi
2048:PMC
2040:doi
1993:doi
1956:PMC
1938:doi
1876:doi
1843:PMC
1833:doi
1792:PMC
1784:doi
1743:PMC
1735:doi
1694:PMC
1686:doi
1638:PMC
1630:doi
1618:447
1568:doi
1556:270
1515:hdl
1507:doi
1495:426
1455:doi
1408:doi
1396:273
1363:PMC
1355:doi
1289:467
1247:PMC
1237:doi
1158:PMC
1150:doi
1138:308
1095:doi
1038:doi
1034:299
996:doi
992:363
697:).
592:or
535:).
315:or
60:SNP
19:In
5161::
4866:.
4856:.
4848:.
4840:.
4828:.
4824:.
4794:.
4782:17
4780:.
4776:.
4747::
4745:}}
4741:{{
4727:.
4696:.
4686:.
4676:66
4674:.
4670:.
4647:.
4637:.
4627:11
4625:.
4621:.
4598:.
4590:.
4582:.
4572:20
4570:.
4566:.
4543:.
4533:.
4523:.
4511:.
4507:.
4477:.
4465:.
4439:.
4384:.
4372:.
4368:.
4345:.
4335:38
4333:.
4310:.
4300:.
4286:.
4282:.
4259:.
4249:.
4241:.
4229:.
4225:.
4202:.
4192:.
4180:17
4178:.
4174:.
4151:.
4141:.
4131:.
4119:.
4115:.
4092:.
4082:.
4072:82
4070:.
4066:.
4041:.
4031:44
4029:.
4025:.
3994:.
3972:.
3962:.
3950:.
3946:.
3923:.
3913:.
3903:50
3901:.
3897:.
3867:.
3859:.
3849:22
3847:.
3817:.
3807:33
3805:.
3781:.
3771:.
3761:89
3759:.
3755:.
3727:}}
3723:{{
3711:.
3703:.
3693:43
3691:.
3687:.
3664:.
3654:.
3644:89
3642:.
3638:.
3615:.
3601:.
3597:.
3573:.
3563:.
3551:.
3547:.
3524:.
3514:.
3506:.
3494:.
3490:.
3466:.
3458:.
3450:.
3438:.
3407:.
3399:.
3387:.
3364:.
3354:.
3342:.
3338:.
3315:.
3305:.
3293:.
3289:.
3259:.
3251:.
3241:.
3229:.
3225:.
3202:.
3188:.
3184:.
3172:^
3158:.
3146:55
3144:.
3140:.
3117:.
3109:.
3099:49
3097:.
3074:.
3060:.
3056:.
3033:.
3023:.
3013:60
3011:.
3007:.
2980:.
2970:.
2960:41
2958:.
2954:.
2940:^
2926:.
2916:.
2906:.
2894:51
2892:.
2888:.
2865:.
2855:.
2845:.
2835:54
2833:.
2829:.
2806:.
2796:.
2786:50
2784:.
2780:.
2757:.
2749:.
2739:.
2729:10
2727:.
2723:.
2674:.
2664:.
2652:.
2648:.
2625:.
2617:.
2607:.
2595:.
2591:.
2568:.
2558:.
2546:10
2544:.
2540:.
2517:.
2507:.
2497:.
2485:.
2481:.
2458:.
2448:.
2434:.
2430:.
2407:.
2397:.
2385:24
2383:.
2379:.
2356:.
2346:.
2332:.
2328:.
2305:.
2295:.
2283:.
2279:.
2256:.
2246:.
2234:.
2211:.
2201:.
2193:.
2181:.
2177:.
2154:.
2144:.
2134:34
2132:.
2128:.
2105:.
2095:.
2085:84
2083:.
2079:.
2056:.
2046:.
2034:.
2032:G3
2030:.
2007:.
1999:.
1989:11
1987:.
1964:.
1954:.
1946:.
1934:25
1932:.
1928:.
1916:^
1892:.
1882:.
1851:.
1841:.
1827:.
1823:.
1800:.
1790:.
1780:31
1778:.
1774:.
1751:.
1741:.
1731:81
1729:.
1725:.
1702:.
1692:.
1680:.
1676:.
1660:^
1646:.
1636:.
1628:.
1616:.
1612:.
1596:^
1582:.
1574:.
1566:.
1554:.
1531:.
1523:.
1513:.
1505:.
1493:.
1489:.
1463:.
1449:.
1445:.
1422:.
1414:.
1406:.
1394:.
1371:.
1361:.
1351:69
1349:.
1345:.
1333:^
1269:^
1255:.
1245:.
1235:.
1223:.
1219:.
1205:^
1188:.
1166:.
1156:.
1148:.
1136:.
1132:.
1109:.
1101:.
1091:32
1089:.
1085:.
1066:.
1044:.
1032:.
1018:^
1004:.
990:.
986:.
974:^
744:.
673:o
669:,
641:.
576:.
512:,
484:,
480:,
476:,
472:,
468:,
399:10
295:10
163:,
147:).
131:.
4976:e
4969:t
4962:v
4874:.
4844::
4836::
4802:.
4788::
4757:)
4737:.
4723::
4704:.
4682::
4655:.
4633::
4606:.
4578::
4551:.
4527::
4519::
4513:7
4485:.
4473::
4450:.
4417:)
4399::
4392:.
4380::
4353:.
4341::
4318:.
4294::
4288:8
4267:.
4245::
4237::
4231:2
4210:.
4186::
4159:.
4135::
4127::
4100:.
4078::
4051:.
4037::
4010:.
3980:.
3958::
3952:2
3931:.
3909::
3875:.
3855::
3825:.
3813::
3789:.
3767::
3733:)
3719:.
3699::
3672:.
3650::
3623:.
3609::
3603:3
3581:.
3559::
3553:4
3532:.
3510::
3502::
3474:.
3454::
3446::
3415:.
3403::
3395::
3372:.
3350::
3323:.
3301::
3267:.
3245::
3237::
3210:.
3196::
3166:.
3152::
3125:.
3105::
3082:.
3068::
3041:.
3019::
2988:.
2966::
2934:.
2920::
2910::
2873:.
2849::
2841::
2814:.
2792::
2765:.
2735::
2708:.
2682:.
2660::
2633:.
2611::
2603::
2576:.
2552::
2525:.
2501::
2493::
2466:.
2442::
2436:7
2415:.
2391::
2364:.
2340::
2334:8
2313:.
2291::
2285:4
2264:.
2250::
2242::
2236:8
2219:.
2197::
2189::
2162:.
2140::
2113:.
2091::
2064:.
2042::
2036:1
2015:.
1995::
1972:.
1940::
1900:.
1878::
1859:.
1835::
1808:.
1786::
1759:.
1737::
1710:.
1688::
1682:6
1654:.
1632::
1624::
1590:.
1570::
1562::
1539:.
1517::
1509::
1501::
1471:.
1457::
1451:8
1430:.
1410::
1402::
1379:.
1357::
1327:.
1301:.
1263:.
1239::
1231::
1225:8
1199:.
1174:.
1152::
1144::
1117:.
1097::
1070:.
1052:.
1040::
1012:.
998::
685:(
531:(
397:×
395:5
324:(
293:×
291:5
27:(
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.