1044:
claimed that "they (girls) haven't got the imagination that most of the lads have got" and that "I find you can spark the boys a bit easier than you can the girls…Girls have got their own set ideas – it's always '…and we went home for tea'… Whereas you can get the boys to write something really interesting…". In another interview, a teacher perceived gender behavioral differences, remarking "…the girls seem to be typically feminine whilst the boys seem to be typically male…you know, more aggressive... the ideal of what males ought to be", while another categorized boys as more "aggressive, more adventurous than girls". When considering Bem's gender schema theory in relation to these statements, it is not difficult to see how male and female pupils may pick up various behavioral cues from their teachers' gender differentiation and generalizations which then manifest themselves in gendered educational interests and levels of attainment. Clarricoates terms this bias the "hidden curriculum" as it is deviant from the official curriculum which does not discriminate based on gender. She notes that it arises from a teacher's own underlying beliefs about gendered behavior and causes them to act in favor of the boys but to the detriment of the girl pupils. This ultimately leads to the unfolding of a self-fulfilling prophecy in the academic and behavioral performances of the students. Citing
Patricia Pivnick's 1974 dissertation on American primary schools, Clarricoates posits that
943:
lack of women in STEM programs is a reoccurring issue in educational institutions. Furthermore, Bailey and his colleagues studied how the possibility that the gender difference in STEM subjects' anxiety holds a contribution to the underrepresentation of women. The study involved assessing the number of predictions from the “gender stratification model,” which evaluates “cross-national patterns” of gender distinctions in math anxiety and performance. The study tailored itself to the number of outcomes of gender inequality on a national scale that related to math anxiety and performance in education. The analytical data collected from the PISA (Programme for
International Student Assessment) of which 761,655 students from 68 nations participated was measured to further the study. The results of the study showed that countries with more gender-egalitarian, and economically advanced societies have a moderate level of mathematics anxiety. There are comparatively more “mothers in STEM fields” in developed countries; however, according to the study they treasured “mathematical competence” in their sons more than their daughters. The mothers in STEM fields cherished their sons to have more capability in math than their daughters according to the author's study. However, the worldwide average in STEM exams is closer in proximity in terms of performance between girls and boys, according to Baily and his colleagues.
964:
can affect the grade they receive. At schools or colleges, prejudice against male students is common. Usually, teachers happened to have a better perception of girls than boys. Many teachers have a poorer relationship with boys than girls because they relate to girls more deeply than they do with boys. Due to this bias in grading, male students are more likely than female students to obtain worse grades. Some recent studies indicate that discrimination against boys in grading may contribute to some of this gender disparity. Studies have shown that teachers typically have lower expectations of boys' academic performance and behavior in school, even though most teachers aim to be fair and work to provide equitable learning opportunities for all kids. In Ingela Åhslund and Lena Boström's study, they've discovered that girls are seen as autonomous, driven, and high achievers, whereas boys are seen as troublemakers and underachievers. Moreover, Ingela and Lena found out that gender stereotypes cause differing interpretations of the same behavior in boys and girls, with girls being perceived as independent and having stronger communication and organizational skills and boys being seen as unprepared, unmotivated, and infantile, according to studies on gender attribution.
1157:
regarding parental involvement in their child's educational attainment. The data found that females engaged in school discussion with their parents more frequently than male counterparts, however when controlling for test scores, grades, and educational aspirations there was a reduction in magnitude of the gender effect of school discussions, but still maintaining its significance. Its also been found that parents are more involved with school on behalf of their sons, but involvement was not known to be purely academic, or for behavioral/non-academic reasons. There was also no difference found in time limits placed on watching television between males/females after school. However, it was noted that females were more likely than males to have less time spent socializing with friends based on parental involvement, reflecting the concept that parents put forth greater efforts to protect their daughters. Data has also shown that parental attendance at school events is greater for daughters than for sons, and when controlling for academic factors it has been found that over half of the gender differences that had been found were explained by academic factors, meaning that parental involvement in these events were influenced by daughter's academic performance.
910:
students tend to flourish more often in secondary school than boys in developed countries, according to
Sutherland. African and Asian countries have aided and catered to girls by enforcing certain quotas and scholarships to place themselves in higher education to provide opportunities for better education with long-lasting jobs. The outlook and position of women in higher education have improved drastically over the recent years in various countries around the world. In selective countries, the author claimed that women are being misrepresented and unfairly evaluated at the university level of education. Additionally, in some developed countries, women are persistently a “distinct minority” in higher education according to the article. There is a consistent trend in university-level education on how women make up a small proportion of these schools across certain nations. The other frequent struggles that result in these issues stem from women remaining in a small categorical group of not acquiring doctorate degrees and some postgraduate degrees in various countries.
1066:
to as "'fussy', 'bitchy', giggly', 'catty' and 'silly'". According to
Clarricoates' previously stated observations, the terms applied to boys imply positive masculine behavior, meanwhile the categories used for girls are more derogatory. This difference in teachers' reactions to similar behaviors can again be seen as contributing to the development of gender stereotyped behaviors in young pupils. Another element of linguistic sexism that Clarricoates identifies is the difference in the treatment of male and female pupils' use of "improper language" by their teachers; girls tended to be censured more harshly compared to boys, due to unconscious biases about gender appropriate behavior. While girls were deemed as "unladylike" for using "rough" speech, the same speech uttered by their male counterparts was regarded as a part of normal masculine behavior, and they were thus admonished less harshly. This creates a linguistic double standard which can again be seen to contribute to long-term gender disparities in behavior.
939:
database of student success in the STEM field and mentioned and analyzed how girls performed comparably to boys in various countries in the science field. Analytically, girl students emerged as more than capable of performing at prominent levels in STEM at a university level. Furthermore, the analysis acknowledged how girls performed comparably to boys and higher in multiple countries in specific subjects corresponding to math and science. Stoet and Geary mentioned how the relative academic strengths regarding sex differences, and the demand for STEM degrees increased with a rise in gender equality on a national scale in different countries. In addition, mediation analysis showed that “life quality pressures in less gender-equal" nations encourage and advocate for women's involvement in STEM education. Overall, the author mentions that there is intense pressure for less-gender-equal countries to create a surge in the advocation of women's participation in STEM subjects.
1132:
emphasizes the significant roles that white males played in the development of the country. Some curriculum have even been rewritten to highlight the roles played by white males. An example of this would be the way wars are talked about. Curricula on the Civil War, for instance, tend to emphasize the key players as
Ulysses S. Grant, Robert E. Lee, and Abraham Lincoln. Whereas woman or men of color such as Harriet Tubman as a spy for the Union, Harriet Beecher Stowe or Frederick Douglass, are downplayed from their part in the war. Another part is that the topics being taught are masculine or feminine. Shop classes and advanced sciences are seen as more masculine, whereas home economics, art, or humanities are seen as more feminine. The problem comes when students receive different treatment and education because of his or her gender or race. Students may also be socialized for their expected adult roles through the
972:
girls in schools. Boys who fall behind risk dropping out of school, failing to enroll in college or university, or finding themselves unemployed as a result of this disadvantage. In OECD nations, 66% of women and 52% of men, respectively, entered university programs in 2009, and this disparity is widening. In 2015, 43% of women in Europe between the ages of 30-34 completed higher education, as opposed to 34% of men in the same age bracket. There is considerable interest in figuring out the causes of this disparity because it has grown by 4.4 percentage points over the past ten years. Moreover, male students are at a larger risk of experiencing academic, social, and emotional challenges, which can lead to a greater sense of alienation from oneself and society, according to current research on gender disparities in educational settings at all socioeconomic levels.
993:
teachers viewed the tapes, which were also broken down into
African American male and female groups, as well as white male and female teacher-participant groups. Participants were then asked to complete a 32 item behavior rating scale focusing on individual teacher perceptions of students in video tape. Analysis revealed statistical significance in differences related to the gender of the teacher to perception of the African American female student being viewed as most troublesome. However, no statistical significance was found in students ratings in relation to ethnic backgrounds of the teachers, or interaction of ethnicity and gender. Male teachers rated students higher on impulsivity than female teachers in general, however the only statistically significant find was in the rating of African American female students of all participant groups.
1448:
have not yet reached equality in education. Gender gaps are smaller in southern Africa because there are more accessible areas near railroads or on the coast, but the biggest problem for these countries is the way schools are preparing their students. Colleges in Africa have not diversified their systems of education or expanded the level of skills taught in order to prepare them for the demands of labor. Another large problem facing
African women is the vast amount of arranged marriages at a young age. As a direct result of this many young women are forced to drop out of school to care for the needs of their husbands and children. In order to correct many of these issues, governments must address the need for better education and appropriate skills training to help battle the rising unemployment rate.
1385:
the male to female ratio in campuses across the country, where the 2005 averages saw male to female university participants at 43 to 57. Although it is important to note that the rates of both sexes participating in post-secondary studies is increasing, it is equally important to question why female rates are increasing more rapidly than male participation rates. Christofides, Hoy, and Yang study the 15% male to female gap in
Canadian universities with the idea of the University Premium. In 2007, Drolet argues in 2007, that this phenomenon is caused by "A university degree ha a greater payback for women relative to what they could have earned if they only had a high-school diploma because men traditionally have had more options for jobs that pay well even without post-secondary education."
914:
students (424 students) in the physical education sectors. The study required an Item pool test that examined the GPA (Grade Point
Average), Academic Motivation scale (AMS), and the model of personality to collect data. Rogowska's study revealed that gender differences were found in “personality traits and academic motivation scales.” The study also showed how notable gender was and prominent as a “moderator” in the dynamic correlation between conscientiousness and academic achievement. The author noted how gender was integral as a third variable to show the connection between conscientiousness and academic accomplishment. Rogowska's study emerged compelling information regarding the motivation factor of women being more motivated than men based on academic achievement.
968:
test scores, the study found that boys received worse marks than girls. In middle school, the gender bias of teachers toward males accounts for 6% of the math achievement gap between boys and girls. Moreover, she gathered data from schools in a fairly underdeveloped educational region of France. According to the research, inexperienced instructors tend to be more biased toward boys in the classroom. Teachers assigned to underprivileged areas are frequently younger than those working in institutions with greater privileges. Her study established that gender biases among teachers will significantly affect the success gap between boys and girls in different subjects. This explains why boys are falling further behind girls in academic performance.
1062:
situations of disciplinary procedure. One example of this she cites is the gendering of animal and inanimate characters. She states that teachers, together with TV presenters and characters as well as curricular materials all refer to dinosaurs, pandas, squirrels and mathematical characters as "he", conveying to young children that these animals all only come in the male gender. Meanwhile, only motherly figures such as ladybirds, cows and hens are referred to as "she". As a result, school books, media and curriculum content all give students the impression that females do not create history which contributes to the damaging assumption that females cannot transform the world, whereas men can.
1394:
98:
989:
Teachers were found to also have a tendency to praise students matching gender expected norms. Students were praised more often by female mathematics teachers than female literature teachers, but praise was more often given by male literature teachers occurred than by male mathematics teachers. Criticism has also been found to be directed toward male students significantly more often than female students in both literature, and mathematics classes, regardless of teacher's gender. Altermatt suggested however that a greater number of teacher-student interactions may be directed at boys as a result of boy students initiating more interaction.
1074:; qualities which society does not hold in great esteem. However, if she does not conform then she will be admonished more harshly than her equivalent male pupils and also be viewed in a more negative light. She will be regarded as problematic and disruptive to the class, which may ultimately impact her academic performance and career prospects in the future. Furthermore, if she is able to survive the school institution as an assertive and confident individual then she will still face many challenges in the workplace, where these characteristics in women are often perceived as "bossy" or "overbearing".
1161:
spend in education expenditure, compared to boys, is 20% less on girls which is very unequal. The expenditure difference including spending unequally on students' fee, textbooks, school supplies like school bags, uniforms and other education expenditure. And this kind of discrimination is rising in Nepal. Also, parents in Nepal are more willing to spend more money in order to let boys to go to private school for the better education. This phenomenon is more pronounced in Nepal' s rural area, but it happened in urban areas as well.
1100:
1219:
within the school and society are pushing them towards easier, more feminine classes, such as home economics or art. They also might not see many other women going into the STEM field. This then lowers the number of women in STEM, further producing and continuing this cycle. This also has a similar effect on males. Because of interactions from teachers, such as saying boys do not usually cook, males may then be less likely to follow careers such as a chef, an artist, or a writer.
1262:
literacy course. Single-gender classes were most popular, and although no specific studies have shown a statistical advantage to single-gender literacy classes, the overall reaction by boys was positive: "I like that there's no girls and you can't be distracted. You get better marks and you can concentrate more." However, a 2014 meta-analysis based on 84 studies representing the testing of 1.6 million students in Grades K-12 from 21 nations published in the journal of
438:
1088:
family relationship." This caused a significant hindrance in the widespread acceptance of homosexuality and thus, the progression of gender equality in schools. Despite the 2003 repeal of this act, the pupils most at risk of discrimination as a result of gender biases in the "hidden curriculum", are still those who do not conform to gender and heterosexual stereotypes. Indeed, Rodgers cites these teaching approaches as conforming to
1402:
girls should prepare to cater to their husbands while doing things such as cooking, cleaning, and taking care of children. These values also cause bullying in young children to individuals who do not follow the social norms of how girls and boys should act and what interests they should have. On a global scale, many developing countries force females to leave school earlier than men and do not give them the same opportunities.
1253:, Tapscott writes that there are other methods to consider in order to reach boys when it comes to literacy: "Boys tend to be able to read visual images better... study from California State University (Hayword) saw test scores increase by 11 to 16% when teaching methods were changed to incorporate more images". Smith and Wilhelm say that boys typically have a "lower estimation of their reading abilities" than girls do.
1030:
education are some of the most formative for developing ideas about gender identity and can potentially be responsible for reinforcing harmful notions of disparity in the roles of males and females. Jenny
Rodgers identifies that gender stereotypes exist in a number of forms in the primary classroom, including the generalization of attainment levels based upon sex and teacher attitudes towards gender appropriate play.
1249:
retrieval and work-related literacy tasks". It is important, therefore, for the teacher to provide the appropriate activities to highlight boys' strengths in literacy and properly support their weaknesses. Also, boys tend to read less than girls in their free time. This could play a role in the fact that girls typically "comprehend narrative and expository texts better than boys do". In his 2009 book
848:
1083:
society. She notes that gender and heterosexual stereotypes are intrinsically linked, due to expectations of females being sexually attracted to males and vice versa, as part of their gender performance. Thus, one of the major challenges to gender equality is the concealment of sexual diversity under the dominance of heteronormativity. Rodgers identifies that although the
1273:
texts, etc.) that boys are already often reading; provide interest and choice in literacy instruction; expand literacy teaching styles to more hands-on, interactive and problem-solving learning, appealing to a boy's strengths; and to provide a supportive classroom environment, sensitive to the individual learning pace of each boy and providing of a sense of competence.
1411:
whole. Since the government has more money to invest in the education system, more schools were built, and more women gained the opportunity to attend school. Despite this, there is still a huge barrier between discrimination in rural versus urban areas. In rural areas, women have consistently been twice as likely to be illiterate when compared to men. On top of this,
1211:
single out other students. For example, a teacher may call on one or two students more than the others. This causes those who are called on less to be less confident. A gendered example would be a teacher expecting a girl to be good at coloring or a boy to be good at building. These types of interactions restrict a student to the particular role assigned to them.
1196:
1245:
to literacy and the article lists some of the possible areas of literacy education where these difficulties could stem from. These include, but are not limited to, their own gender identity, social and cultural issues, religion, technology, school cultures, teaching styles, curriculum, and the failures of pre-service and in-service teaching courses.
45:
1439:, or the OCR for short, ensures federally funded or assisted organizations follow Title IX by evaluating, investigating, and collecting allegations of sex discrimination. Although Title IX was a great step in the right direction in battling sex discrimination in education in the United States, many people are still discriminated against today.
1356:. The study consisting of 1.5 million 15-year-olds found higher overall female achievement across reading, mathematics, and science literacy and better performance across 70% of participating countries, including many with considerable gaps in economic and political equality, and they fell behind in only 4% of countries. In summary, Stoet and
122:
1244:
Booth, Johns, and Bruce state that at both national and international levels "male students do not do as well as girls in reading and writing and appear more often in special education classes, dropout rates and are less likely to go to university". Boys face a multitude of difficulties when it comes
1206:
Discrimination results for the most part, being in low status, sex-stereotyped occupations, which in part is due to gender differences in majors. They also have to endure the main responsibilities of domestic tasks, even though their labor force participation has increased. Sex discrimination in high
1156:
Child development in educational areas can also be influenced by the treatment a child receives from his/her parents. In a study by Rebecca Carter, of which private and public school 8th graders were looked at using the National Education Longitudinal Study (NELS), a study which provides many details
1131:
may further add to discrimination in the educational system. Hidden curriculum is the idea that race, class, and gender have an influence on the lessons that are taught in schools. Moreover, it is the idea that certain values and norms are instilled through curriculum. For example, U.S. history often
1087:
in the United Kingdom helped to increase opportunities for gender diversity by ensuring that both sexes study the same core subjects, on the other hand, heterosexual stereotyping was exacerbated by the passing of Section 28 of the 1988 Local Government Act, which decreed homosexuality "as a pretended
1043:
and discrimination were widely seen in the classrooms. In an extract from one of the interviews, a teacher claimed that it is "subjects like geography…where the lads do come out…they have got the facts whereas the girls tend to be a bit more woollier in most of the things". Meanwhile, other teachers
900:
Gender based inequalities in education around the world, according to UNESCO, are mainly determined by poverty, geographical isolation, minority status, disability, early marriage, pregnancy and gender-based violence. In the rest of the world, more boys remain out of school than girls, however, women
452:
in the education system affecting both men and women during and after their educational experiences. Men are more likely to be literate on a global average, although higher literacy scores for women are prevalent in many countries. Women are more likely to achieve a tertiary education degree compared
1314:
showed that the achievement gender divide for home-schooled children was less than of public schools. Homeschooled boys (87th percentile) and girls (88th percentile) scored equally well. The income of the parents did not have much impact on the results, however, a major factor in student achievement
1214:
Other consequences come in the form of what is communicated as appropriate behaviors for boys and girls in classes like physical education. While a teacher may not purposely try to communicate these differences, they may tend to make comments based on gender physical ability. For example, a male may
963:
In the past, men tended to get more education than women, however, the gender bias in education gradually turned to men in recent decades. In recent years, teachers have had modest expectations for boys' academic performance. The boys were labeled as reliant, the impression teachers provide students
1410:
China's gender inequality within their education system dates back centuries, but despite some improvement over time has a long way to go. Huge economic and societal development since the 1980s has become a major factor in improving gender equality in not only their education systems but China as a
1401:
Improvements in removing sex discrimination from education have had great advancements in the last many years all over the world, but discrimination does still happen. Sexist values instilled into children's minds insist that boys do well at sports, be physically strong, and be competitive and that
1384:
Since the 1990s, enrollment on university campuses across Canada has risen significantly. Most notable is the soaring rates of female participants, which has surpassed the enrollment and participation rates of their male counterparts. Even in the United States, there is a significant difference in
1240:
show that the gap between eight-grade males and females is more than six times greater than the differences in mathematical reasoning, mathematical reasoning favoring males. These findings have spanned across the globe as the International Association for Evaluation of Educational Achievement (IEA)
1082:
Rodgers identifies that another challenge to gender equality in the elementary school classroom is the dominance of heteronormativity and heterosexual stereotypes. Citing the research of Guasp, she maintains that heteronormative discourse still remains the norm, both in schools and in wider western
1065:
In addition, Clarricoates discusses the linguistic sexism inherent to the adjective choice of teachers when admonishing or rewarding their pupils. She notes that "if boys get out of hand they are regarded as 'boisterous', 'rough', 'assertive', 'rowdy' and 'adventurous'", whereas girls were referred
967:
In a research conducted by Camille Terrier, she discovered that in both arithmetic and French, teachers' gender bias significantly and highly affects how far boys advance relative to girls. Even in subjects like math and science, where their test scores were either equal to or lower than the girls'
942:
Centering the problems of gender education in the STEM field around gender-based bias evaluations of children relating to anxiety and lack of representation of women. Author Drew H. Bailey mentions how regardless of worldwide striving and progress for gender equality across different societies, the
938:
Regarding the issue of gender and education in the STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) field, and how women in STEM have underwhelming sparse numbers in the field which is alarming for policymakers and sociology scientists. The authors Stoet and Geary, utilized an international
922:
A study looking at children born in the 1980s in the United States until their adulthood found that boys with behavioural problems were less likely to complete high school and university than girls with the same behavioural problems. Boys had more exposure to negative experiences and peer pressure,
1261:
One attempted change made to literacy instruction has been the offering of choice in classroom gender populations. In Hamilton, Ontario, Cecil B. Stirling Elementary/Junior School offered students in grades 7 and 8, and their parents, a choice between enrolling in a boys-only, girls-only or co-ed
1248:
It is also important to consider two aspects of boys and literacy education as raised in the Booth article, which draws from the 2002 work of Smith and Wilhelm. The first is achievement; boys typically take longer to learn than girls do, although they excel over girls when it comes to "information
975:
The most likely explanation is that girls put in more effort in school because this difference does not seem to be the result of discrimination and is unlikely to depend on innate differences in ability. Designing measures to close the gender gap in education requires research into why this is the
971:
Due to their poorer grades, boys have a decreased probability of getting admitted into further education, which may ultimately limit their chances of success in the job market. A study conducted by Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development proved that boys are gradually falling behind
1447:
In most Sub-Saharan countries gender gaps increased during the colonial era and after gaining independence most began to decline. Africa had a small initial educational gender gap, but little progress has been made to close it. Sub-Saharan Africa holds twelve out of 17 countries in the world that
1061:
Another element of the "hidden curriculum" Clarricoates identifies is linguistic sexism. She defines this term as the consistent and unconscious use of words and grammatical forms by teachers that denigrate women and emphasize the assumed superiority of men, not only in lesson content but also in
1272:
With boys-only classrooms not always being possible, it then becomes the responsibility of the literacy instructor to broaden the definition of literacy from fiction-rich- literacy programs to expose students to a variety of texts including factual and non-fiction texts (magazines, informational
1210:
Classroom interactions can also have unseen consequences. Because gender is something we learn, day-to-day interactions shape our understandings of how to do gender. Teachers and staff in an elementary may reinforce certain gender roles without thinking. Their communicative interactions may also
1160:
Gender discrimination in education also exist from household discrimination. Parents may spend differently based on gender of their children which is an unequal treatment. Shaleen Khanal studied the expenditure people spent on girls and boys in Nepal. Based on his research, he found that parents
1095:
Another way the educational system discriminates towards females is through course-taking, especially in high school. This is important because course-taking represents a large gender gap in what courses males and females take, which leads to different educational and occupational paths between
1069:
Clarricoates concludes her study by observing that there is a "catch 22" situation for young female pupils. If a girl conforms to institutional ideals by learning her lessons well, speaking appropriately and not bothering the teacher then her success is downplayed in comparison to the equivalent
1048:
It is possible that by using a harsher tone for controlling the behavior of boys than for girls, the teachers actually foster the independent and defiant spirit which is considered 'masculine' in our culture…At the same time, the 'femininity' which the teachers reinforced in girls may foster the
954:
in education is sometimes known as "second sexism". Second sexism has not seen significant backing or research even among those who study discrimination. Second sexism in education, together with obvious sexrole stereotypes, make male students face more punishment in school than female students.
1430:
states that no person should be excluded, denied benefits, or discriminated against based on sex in schools and federally funded activities in the United States. This covers a wide variety of places such as, but not limited to schools, local and state agencies, charters, for-profits, libraries,
1218:
Some gender discrimination, whether intentional or not, also effects the positions students may strive for in the future. Females may not find interest in science, technology, engineering, or math (STEM), because they have not been exposed to those types of classes. This is because interactions
1169:
In a study of 220 universities in the United States, 84% of them offered single-gender scholarships. The study assessed whether these universities were discriminatory if there are 4 or more women-only scholarships compared to men-only, and described 68.5% as discriminatory against men. In many
1024:
learning stages. Research such as May Ling Halim et al.'s 2013 study has shown that children are aware of gender role stereotypes from a young age, with those who are exposed to higher levels of media, as well as gender stereotyped behavior from adults holding the strongest perception of gender
909:
In various developed countries, there has been an increase in education access for women in the last several decades. In developed countries, girls and boys are enrolled in elementary/kindergarten and middle schools at an equal rate in the educational schooling system. In European nations, girl
988:
Gender discrimination in education exists as well from differential treatment students receive by either male or female teachers. In Newfoundland, Jim Duffy et al. found out that teachers may have higher expectations for boys in math and science, and for girls; higher expectations in language.
992:
In a study done by Paulette B. Taylor, video tapes depicting the same inappropriate behavior (pencil tapping, disturbing others, and mild rebukes to the teacher) of 4 different students; An African American male and female, and a white male and female. 87 inservice teachers, and 99 preservice
913:
Other factors based on gender differences in education coherently connect to Aleksandra M. Rogowska and her colleague's study of examining and exploring five traits, academic motivation, personality, and gender in a cross-cultural context. She conducted a study of Polish and Ukrainian college
1029:
identifies that children absorb gender stereotypes by observing the behavior of humans around them and then imitate the actions of those they deem to be of their own gender. Thus, if children attain gender cues from environmental stimuli, it stands to reason that the early years of a child's
935:(STEM). According to the OECD, 71% of men who graduate with a science degree work as professionals in physics, mathematics and engineering, whereas only 43% women work as professionals. "Fewer than 1 in 3 engineering graduates, and fewer than 1 in 5 computer science graduates are female".
1178:
to launch multiple investigations around the country. People pushing to get these removed have mentioned that these scholarships were created in the 1970s when women were under-represented in tertiary education, but it is now men who underperform and that the scholarships should become
1207:
school and college course-taking also results in women not being prepared or qualified to pursue more prestigious, high paying occupations. Sex discrimination in education also results in women being more passive, quiet, and less assertive, due to the effects of the hidden curriculum.
1114:
in education. For example, society suggests that women should be mothers and responsible for the bulk of child rearing. Therefore, women feel compelled to pursue educational pathways that lead to occupations that allow for long leaves of absence, so they can be stay-at-home mothers.
1038:
In her 1978 quantitative study, Katherine Clarricoates conducted field observations and interviews with British primary school teachers from a range of schools located in both rural and urban and wealthy and less wealthy areas. Her study confirms that Rodgers' assertions about
1144:. Girls may be encouraged to learn skills valued in female-dominated fields, while boys might learn leadership skills for male-dominated occupations. For example, as they move into the secondary and post-secondary phases of their education, boys tend to gravitate more toward
1380:
In 2005, USA Today reported that the "college gender gap" was widening, stating that 57% of U.S. college students are female. This gap has been gradually widening, and as of 2014, almost 45% of women had a bachelor's degree, compared to 32% of men with a bachelor's degree.
3552:
Booth D., Bruce F., Elliott-Johns S. (February 2009) Boys' Literacy Attainment: Research and related practice. Report for the 2009 Ontario Education Research Symposium. Centre for Literacy at Nipissing University. Retrieved from Ontario Ministry of Education website:
1235:
assessment, show that girls have met or exceeded the reading performance of boys at all age levels. The literacy gap in fourth grade is equivalent to males being two years behind the average girl in reading and writing. At the middle school level, statistics from the
1123:
in 2013, one out of three girls across the developing world is married before the age of 18. As an accepted practice in many cultures, the investment in a girl's education is given little importance, whereas emphasis is placed on men and boys to be the 'breadwinners.'
1371:
shows that 64.5% of students entering for a four-year bachelor's degree had graduated within six years. Women had a graduation rate that higher than men by 6.9 points. 66.4% of women entering the degree achieved it within 6 years, compared to 60.4% for men. In
1096:
males and females. For example, females tend to take fewer advanced mathematical and scientific courses, thus leading them to be ill-equipped to pursue these careers in higher education. This can further be seen in technology and computer courses.
2069:
Aa, Suzan van der (11 August 2014). "Book review: The second sexism: Discrimination against men and boysBenatarDavidThe second sexism: Discrimination against men and boysChichester: Wiley-Blackwell, 2012, pbk, ISBN 978-0-470-67451-2, 288 pp".
1436:
1431:
museums, and vocational rehabilitation agencies in all 50 states as well as territories of the United States. Despite being initially geared towards protecting women, Title IX covers the discrimination of all people based on sex, including
1215:
be told that he throws like a girl which perpetuates him to become more masculine and use brute force. A female, on the other hand, might be told she is too masculine looking, causing her to become more reserved and less motivated.
1337:
drew from 97 years of 502 effect sizes and 369 samples stemming from the year 1914 to 2011, and found that the magnitude of higher female performance was not affected by year of publication, thereby contradicted recent claims of
3073:
Zuo, Jiping, and Shengming Tang. "Breadwinner Status and Gender Ideologies of Men and Women Regarding Family Roles." Sociological Perspectives, vol. 43, no. 1, 2000, pp. 29–43. JSTOR, JSTOR, www.jstor.org/stable/1389781.
1376:
countries, women are more likely to hold a university degree than men of the same age. The proportion of women aged 25–34 who have a university degree is 20 percentage points higher than men of the same age.
3565:
Martino W. (April 2008) Underachievement: Which Boys are we talking about? What Works? Research into Practice. The Literacy and Numeracy Secretariat. Retrieved from Ontario Ministry of Education website:
453:
to men of the same age. Men tended to receive more education than women in the past, but the gender gap in education has reversed in recent decades in most Western countries and many non-Western countries.
3064:
McCleary-Sills, Jennifer, et al. "Child Marriage: A Critical Barrier to Girls' Schooling and Gender Equality in Education." The Review of Faith & International Affairs, vol. 13, no. 3, 2015, pp. 69–80.
2732:
Taylor, Paulette B.; Gunter, Philip L.; Slate, John R. (February 2001). "Teachers' Perceptions of Inappropriate Student Behavior as a Function of Teachers' and Students' Gender and Ethnic Background".
3086:
Esposito, Jennifer (2011). "Negotiating the gaze and learning the hidden curriculum: a critical race analysis of the embodiment of female students of color at a predominantly white institution".
923:
and had higher rates of grade repetition. Owens, who conducted the study, attributes this to negative stereotypes about boys and says that this may partially explain the gender gap in education.
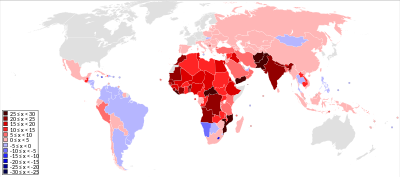
101:
A world map showing countries by gender difference in literacy rate. Blue refers to countries where women's literacy rate is higher; red refers to countries where men's literacy rate is higher.
3630:
Pahlke, Erin; Hyde, Janet Shibley; Allison, Carlie M. (1 July 2014). "The effects of single-sex compared with coeducational schooling on students' performance and attitudes: a meta-analysis".
4267:
1070:
behavior in a male pupil. Indeed, she is regarded as "passive", or a "goody-goody" and as "lesser" than her male pupils. As a result, this reinforcement will foster submissiveness and
465:. The closer to one, the closer to gender equality. When the number is below 1, there are more males than females, and when the number is above 1, there are more females than males.
3474:
Cassese, Erin C.; Bos, Angela L.; Schneider, Monica C. (1 July 2014). "Whose American Government? A Quantitative Analysis of Gender and Authorship in American Politics Texts".
1517:
Pearson, Jennifer. "Gender, Education and." Blackwell Encyclopedia of Sociology. Ritzer, George (ed). Blackwell Publishing, 2007. Blackwell Reference Online. 31 March 2008 <
2697:
Altermatt, Ellen Rydell; Jovanovic, Jasna; Perry, Michelle (1998). "Bias or responsivity? Sex and achievement-level effects on teachers' classroom questioning practices".
2004:"Countries with Higher Levels of Gender Equality Show Larger National Sex Differences in Mathematics Anxiety and Relatively Lower Parental Mathematics Valuation for Girls"
1435:
students. Prior to Title IX being passed many women were denied access to education or participation in extracurricular activities such as sports or male dominant clubs.
1482:
361:
4133:
SteelFisher, Gillian K.; Findling, Mary G.; Bleich, Sara N.; Casey, Logan S.; Blendon, Robert J.; Benson, John M.; Sayde, Justin M.; Miller, Carolyn (29 October 2019).
1789:"Examining Gender Differences, Personality Traits, Academic Performance, and Motivation in Ukrainian and Polish Students of Physical Education: A Cross-Cultural Study"
1477:
1415:, although no longer in effect, made a lasting impact on the discrimination against women by their families as most families hoped to have a son. This so-called "
1353:
865:
1119:
can be another determining factor in ending the formal education and literacy rates of women in various parts of the world. According to research conducted by
3899:
1329:
found females outperformed males in teacher-assigned school marks throughout elementary, junior/middle, high school and at both undergraduate and graduate
3781:
Stoet, Gijsbert; Geary, David C. (1 January 2015). "Sex differences in academic achievement are not related to political, economic, or social equality".
3431:
Cooper, Brenda (1 March 2002). "Boys Don't Cry and female masculinity: reclaiming a life & dismantling the politics of normative heterosexuality".
424:
273:
3682:
3301:
2957:
Pivnick, Patricia (1974). "Sex Role Socialisation: Observations in a First Grade Classroom (It's Hard to Change Your Image Once You're Typecast)".
318:
4296:
Clarricoates, Katherine (1978). "'Dinosaurs in the Classroom'--A Re-examination of Some Aspects of the 'Hidden' Curriculum in Primary Schools".
1393:
1467:
1462:
1016:, are reproduced within schools through formal and informal processes. In Western societies, these processes can be traced all the way back to
4275:
4111:
3115:
2216:
1457:
1368:
1184:
1175:
313:
4317:
Rodgers, Jenny (2014). "Aspirational Practice: Gender Equality The challenge of gender and heterosexual stereotypes in primary Education".
1133:
388:
328:
202:
55:
97:
66:
3997:
153:
1518:
4356:
3593:
1718:
837:
217:
192:
4209:
4060:
2442:
2306:
1360:
said that sex differences in educational achievement are not reliably linked to gender equality. The results do not prove, however,
887:
383:
84:
3274:
1852:
323:
266:
212:
136:
3709:
1361:
290:
261:
238:
187:
1472:
869:
229:
3816:
4351:
3617:
1487:
417:
373:
300:
242:
222:
207:
1092:, and attributes this method to the marginalization of students who do not conform to their stereotypical gender roles.
3413:
Solmon, Melinda A.; Lee, Amelia M. (January 2000). "Research on Social Issues in Elementary School Physical Education".
3352:
1352:
found that girl's overall education achievement is better in 70 percent of all the 47–75 countries that participated in
251:
178:
148:
141:
1053:
This analysis highlights the lifelong hindrances that the "hidden curriculum" of teachers can inflict on both genders.
1334:
1237:
197:
174:
3130:
Kevin Seifert and Rosemary Sutton. (2009) Educational Psychology 2nd Edition. "Chapter 4: Student Diversity." pp. 73
3971:
3131:
951:
278:
163:
3326:
858:
1137:
1084:
295:
256:
113:
4023:
1531:
Davies, Bronwyn (2007). "Gender economies: literacy and the gendered production of neo-liberal subjectivities".
410:
351:
3872:
3842:
3567:
1897:
1419:” has prevailed among most Chinese parents for centuries and continues to make women less important.
1416:
398:
2002:
Stoet, Gijsbert; Bailey, Drew H.; Moore, Alex M.; Geary, David C. (21 April 2016). Windmann, Sabine (ed.).
2662:
Duffy, Jim (2001). "Classroom Interactions: Gender of Teacher, Gender of Student, and Classroom Subject".
1665:
1347:
1339:
1325:
1276:
Other everyday practices that attempt to "close the gender gap" of literacy in the classroom can include:
1264:
2607:
Hyde, Janet S.; Lindberg, Sara M.; Linn, Marcia C.; Ellis, Amy B.; Williams, Caroline C. (25 July 2008).
1690:
3686:
1922:
1640:
1298:
Providing male role models. (High-school Boys Tutoring Younger Boys in Reading, Reading/Speaking Guests)
1089:
1009:
59:
that states a Knowledge (XXG) editor's personal feelings or presents an original argument about a topic.
2366:
1099:
2015:
1848:"Early Childhood Behavior Problems and the Gender Gap in Educational Attainment in the United States"
1026:
31:
3928:
1519:
http://www.blackwellreference.com/subscriber/tocnode?id=g9781405124331_chunk_g978140512433113_ss1-16
462:
378:
4066:
3798:
3663:
3499:
3456:
3395:
3209:"Gender Discrimination in Education Expenditure in Nepal: Evidence from Living Standards Surveys"
3176:
2840:
2757:
2679:
2644:
2542:
2404:
2267:
2138:
2095:
1984:
1597:
1548:
283:
3995:
Droulet, D. (September 2007) Minding the Gender Gap. Retrieved from University Affairs website:
1170:
universities there are scholarships for women only. These have been described as illegal under
17:
4249:
4205:
4172:
4154:
4107:
4056:
4001:
3758:
3735:
3655:
3647:
3589:
3491:
3448:
3230:
3184:
3168:
3111:
2805:
2749:
2714:
2636:
2628:
2589:
2581:
2534:
2526:
2487:
2448:
2438:
2396:
2302:
2259:
2212:
2177:
2130:
2087:
2051:
2033:
1976:
1968:
1879:
1828:
1810:
1769:
1749:
1615:
1589:
1323:
A 2014 meta-analysis of sex differences in scholastic achievement published in the journal of
1128:
1021:
1013:
368:
158:
2788:
Halim, May Ling (2013). "Four-year-olds' Beliefs About How Others Regard Males and Females".
1269:
found no evidence that the view single sex schooling is beneficial over co-gendered schools.
4305:
4241:
4197:
4162:
4146:
4099:
4048:
3950:
3940:
3790:
3750:
3639:
3533:
3483:
3440:
3387:
3220:
3158:
2832:
2797:
2741:
2706:
2671:
2620:
2573:
2518:
2479:
2430:
2386:
2378:
2345:
2294:
2251:
2204:
2169:
2122:
2079:
2041:
2023:
1960:
1949:"The Gender-Equality Paradox in Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics Education"
1869:
1861:
1818:
1800:
1761:
1579:
1540:
1412:
1071:
4191:
2333:
1948:
1726:
437:
3554:
2334:"Teachers' Perceptions of Gender Differences -What about Boys and Girls in the Classroom?"
1241:
found gender to be the most powerful predictor of performance in a study of 14 countries.
977:
333:
1333:
level. The meta-analysis done by researchers Daniel Voyer and Susan D. Voyerwas from the
441:
Since the 20th century, girls have been increasingly likely to attend school and college.
2019:
4167:
2046:
2003:
1874:
1823:
1788:
1357:
1343:
1141:
1116:
393:
4309:
2422:
2239:
1584:
1049:
narcissism and passivity which results in lack of motivation and achievement in girls.
4345:
4070:
3802:
3717:
3503:
3460:
3399:
2844:
2801:
2761:
2683:
2434:
2382:
2271:
2255:
2099:
1552:
1228:
3667:
3248:
2648:
2408:
2142:
1601:
2546:
2126:
1988:
1005:
1568:"The Reversal of the Gender Gap in Education and its Consequences for Family Life"
3794:
3487:
3391:
3147:"Diversity in Experiences of Parental Structure During Childhood and Adolescence"
2561:
2505:
Guiso, Luigi; Monte, Ferdinando; Sapienza, Paola; Zingales, Luigi (30 May 2008).
2196:
2028:
2577:
2208:
1180:
1145:
1104:
1040:
847:
305:
4040:
2836:
2823:
Bem, Sandra (1981). "Gender Schema Theory: A Cognitive Account of Sex Typing".
2745:
2710:
2467:
2286:
4052:
2675:
2483:
2298:
2240:"Lads and Ladettes in School: Gender and a Fear of Failure By Carolyn Jackson"
2157:
1544:
1342:" in school achievement. Another 2015 study by researchers Gijsbert Stoet and
1330:
4253:
4158:
4134:
4091:
4041:"Sexual Orientation and Gender Identity Discrimination as Sex Discrimination"
3651:
3495:
3452:
3234:
3172:
2753:
2718:
2632:
2608:
2585:
2530:
2506:
2491:
2452:
2400:
2263:
2181:
2173:
2134:
2091:
2083:
2037:
1972:
1964:
1865:
1814:
1773:
1765:
1593:
1289:
Allowing time for movement. (Reader's Theaters and plays, "Active" Mnemonics)
4150:
4103:
3975:
3945:
3053:
3001:
Different Families: The Experiences of Children with Lesbian and Gay Parents
2624:
2522:
1787:
Kuśnierz, Cezary; Rogowska, Aleksandra M.; Pavlova, Iuliia (7 August 2020).
1200:
1017:
901:
make up two-thirds of the 750 million adults without basic literacy skills.
4176:
3762:
3659:
3444:
2809:
2640:
2538:
2350:
2055:
1980:
1883:
1847:
1832:
1805:
4229:
4201:
4026:. THE ENCYCLOPEDIA OF WORLD PROBLEMS & HUMAN POTENTIAL. 15 March 2023.
3568:
http://www.edu.gov.on.ca/eng/literacynumeracy/inspire/research/Martino.pdf
3188:
2593:
2156:
Epstein, Debbie; Maw, Janet; Elwood, Jannette; Hey, Valerie (April 1998).
1292:
Allowing opportunities for competition. (Spelling Bees, Jeopardy, Hangman)
980:
used by boys and girls in the classroom must be understood by the school.
4245:
3253:
Save - Leading The Policy Movement For Fairness and Due Process On Campus
3225:
3208:
2367:"Boys lag behind: How teachers' gender biases affect student achievement"
1427:
1171:
1008:
of education view the educational system as an institution of social and
3538:
3521:
2391:
1195:
4336:
3955:
3586:"Reading don't fix no Chevys" : literacy in the lives of young men
3180:
1295:
Choosing books that appeal to boys. ("Boy's Rack" in Classroom Library)
872: in this section. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
3620:, Reporter: Susan Ormiston, Producer: Marijka Hurko, 25 November 2003.
1566:
Van Bavel, Jan; Schwartz, Christine R.; Esteve, Albert (16 May 2018).
976:
case and how it differs with different learning contexts. The diverse
3900:"Women More Likely to Graduate College, but Still Earn Less Than Men"
3754:
3643:
1120:
1111:
1001:
449:
30:"Gender and education" redirects here. For the academic journal, see
3929:"The Determinants of University Participation in Canada (1977–2003)"
3163:
3146:
2338:
International Journal of Learning, Teaching and Educational Research
4047:, Cambridge University Press, pp. 266–333, 30 September 2020,
1567:
1025:
stereotypical roles, regardless of ethnicity. Indeed, Sandra Bem's
4135:"Gender discrimination in the United States: Experiences of women"
3522:""Not just boring stories": Reconsidering the gender gap for boys"
1397:
A broad framework is used to monitor gender equality in education.
1392:
1311:
1280:
Tapping into visual-spatial strengths of boys. (Filmstrips/Comics)
1194:
1098:
436:
96:
1793:
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health
3850:
3608:
Tapscott, D. (2009) Grown Up Digital. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
3378:
Jacobs, J. A. (1996). "Gender Inequality and Higher Education".
2562:"Gender differences in mathematics performance: A meta-analysis"
1432:
1373:
1232:
932:
121:
3736:"Gender Differences in Scholastic Achievement: A Meta-Analysis"
2959:
Thesis of Doctorate of Education at the University of Rochester
1286:
Incorporating technology. (Computer Learning Games, Cyberhunts)
1004:
in education is applied to women in several ways. First, many
3302:"Women's Scholarships And Awards Eliminated To Be Fair To Men"
2986:
Homophobic Bullying in Britain's Schools: The Teachers' Report
2913:
2911:
2909:
2907:
2905:
2880:
2878:
2293:. Thousand Oaks California: SAGE Publications, Inc.: 183–199.
841:
38:
3275:"Do Women STEM College Programs Discriminate Against Males?"
2560:
Hyde, Janet S.; Fennema, Elizabeth; Lamon, Susan J. (1990).
931:
In developed countries, women are often underrepresented in
56:
personal reflection, personal essay, or argumentative essay
4090:
Busch, Elizabeth Kaufer; Thro, William E. (20 May 2018),
3927:
Christofides, Louis N.; Hoy, Michael; Yang, Ling (2009).
984:
Gender differences in education based on teacher's gender
3817:"The Significant Gender Gap in College Graduation Rates"
3024:
3022:
3555:
http://www.edu.gov.on.ca/eng/research/boys_literacy.pdf
1315:
is whether a parent had attained a tertiary education.
62:
3922:
3920:
1012:. The existing patterns of inequality, especially for
4230:"Africa grapples with huge disparities in education"
2423:"OECD Employment Outlook 2012 (Summary in Estonian)"
2609:"Gender Similarities Characterize Math Performance"
2195:Frosh, Stephen; Phoenix, Ann; Pattman, Rob (2002),
1898:"Indicators of Gender Equality in Education – OECD"
933:
science, technologies, engineering, and mathematics
927:
Science, technologies, engineering, and mathematics
3998:"Minding the gender gap | University Affairs"
3710:"New Study Shows Homeschoolers Excel Academically"
2203:, London: Macmillan Education UK, pp. 22–49,
3202:
3200:
3198:
1483:Sex differences in education in the United States
1301:Boys-only reading programs. (Boys-only Book Club)
3776:
3774:
3772:
3681:Connell, Diane; Gunzelmann, Betsy (March 2004).
2332:Åhslund, Ingela; Boström, Lena (26 April 2018).
1478:Gender mainstreaming in teacher education policy
1362:greater intelligence of women in relation to men
3353:"Should female-only scholarships be abolished?"
2468:"Cognitive gender differences are disappearing"
1947:Stoet, Gijsbert; Geary, David C. (April 2018).
1191:Consequences of sex discrimination in education
4268:"Millions of Young Girls Forced Into Marriage"
4223:
4221:
3584:Smith, Michael W.; Jeffrey D. Wilhelm (2002).
2776:Reproduction in education, society and culture
1283:Using hands-on materials. (Websites, handouts)
1152:Differential treatment in parental involvement
27:Educational discrimination on the basis of sex
3088:Journal for Critical Education Policy Studies
418:
8:
2971:
2942:Rosenthal, Robert; Jacobsen, Lenore (1968).
2929:
2917:
2896:
2884:
2869:
2774:Bourdieu, P., & Passeron, J. C. (1990).
2162:International Journal of Inclusive Education
2113:Benatar, David (2003). "The Second Sexism".
1428:Title IX of the Education Amendments of 1972
1187:considered abolishing women's scholarships.
1174:and discriminatory against men, causing the
1110:Cultural norms may also be a factor causing
4024:"Discrimination against women in education"
2790:British Journal of Developmental Psychology
2287:"The Making of Black English Masculinities"
2158:"Guest editorial: Boys' "underachievement""
1750:"Sex Differences in Education: an overview"
3972:"College gender gap widens: 57% are women"
3873:"College gender gap widens: 57% are women"
3526:Journal of Adolescent & Adult Literacy
832:Inequalities in education around the world
714:
593:
472:
425:
411:
104:
4337:Gender Gaps in Math and Science Education
4166:
3954:
3944:
3843:"CO3.1: Educational attainment by gender"
3579:
3577:
3575:
3537:
3515:
3513:
3327:"Women-only scholarships under spotlight"
3224:
3162:
3054:https://doi.org/10.1007/s11125-016-9379-0
2390:
2349:
2045:
2027:
1873:
1822:
1804:
1583:
1513:
1511:
1509:
1507:
1505:
1503:
888:Learn how and when to remove this message
85:Learn how and when to remove this message
1748:Sutherland, Margaret B. (January 1987).
1691:"School enrollment, gender parity index"
1666:"School enrollment, gender parity index"
1641:"School enrollment, gender parity index"
1389:Sex discrimination in education globally
997:Forms of sex discrimination in education
4298:Women's Studies International Quarterly
3970:Marklein, Mary Beth (19 October 2005).
3433:Critical Studies in Media Communication
3145:Wojtkiewicz, Roger A. (February 1992).
3110:. Los Angeles: Sage. pp. 168–173.
3040:
3028:
3013:
2946:. London: Holt, Rinehart & Winston.
2857:
1499:
1227:The latest national test scores in the
457:Gender differences in school enrollment
343:
237:
173:
128:
112:
4193:Title IX, Education Amendments of 1972
4035:
4033:
3476:Journal of Political Science Education
2327:
2325:
2244:British Journal of Educational Studies
1468:Gender gaps in mathematics and reading
1463:Gender disparities in Kenyan education
3729:
3727:
3714:Home School Legal Defense Association
3426:
3424:
3140:
3138:
3101:
3099:
3097:
3081:
3079:
1458:Achievement gaps in the United States
1369:United States Department of Education
1319:Sex differences in tertiary education
1257:Possible solutions and implementation
1176:United States Department of Education
7:
3933:Canadian Journal of Higher Education
3052:Psaki, S. Prospects (2016) 46: 109.
1713:
1711:
959:Grading bias in schools against boys
870:adding citations to reliable sources
4092:"Title IX Implementing Regulations"
2072:International Review of Victimology
1136:laid out by sociologists including
4190:Wilson, Michelle (15 March 2023).
3898:Bidwell, Allie (31 October 2014).
2365:Terrier, Camille (1 August 2020).
838:List of countries by literacy rate
25:
4228:Musau, Zipporah (21 March 2018).
3207:Khanal, Shaleen (15 March 2018).
3106:DeFrancisco, Victoria P. (2014).
2699:Journal of Educational Psychology
1616:"unstats | Millennium Indicators"
1585:10.1146/annurev-soc-073117-041215
3716:. 10 August 2009. Archived from
2802:10.1111/j.2044-835x.2012.02084.x
2466:Feingold, Alan (February 1988).
2435:10.1787/empl_outlook-2012-sum-et
2383:10.1016/j.econedurev.2020.101981
2256:10.1111/j.1467-8527.2007.367_2.x
846:
120:
43:
4274:. 15 March 2013. Archived from
4098:, Routledge, pp. 125–128,
3588:. Portsmouth, N.H.: Heinemann.
2285:Ghaill, Mairtin Mac An (1994).
2238:Mendick, Heather (March 2007).
1725:. 25 April 2013. Archived from
1719:"Education and gender equality"
857:needs additional citations for
18:Gender differences in education
2127:10.5840/soctheorpract200329213
1473:Gender inequality in curricula
1148:than their female classmates.
1078:Dominance of heteronormativity
314:age disparity in relationships
1:
4310:10.1016/s0148-0685(78)91245-9
3520:Taylor, Donna Lester (2004).
2371:Economics of Education Review
1695:World Bank Gender Data Portal
1670:World Bank Gender Data Portal
1645:World Bank Gender Data Portal
1488:Sex differences in psychology
3904:U.S. News & World Report
3795:10.1016/j.intell.2014.11.006
3488:10.1080/15512169.2014.921655
3392:10.1146/annurev.soc.22.1.153
2029:10.1371/journal.pone.0153857
1437:The Office of Credit Ratings
1164:
446:Sex differences in education
2578:10.1037/0033-2909.107.2.139
2507:"Culture, Gender, and Math"
2209:10.1007/978-1-4039-1458-3_2
1335:University of New Brunswick
1238:Educational Testing Service
1179:gender-neutral. In 2008 in
4373:
4196:. SAGE Publications, Inc.
3380:Annual Review of Sociology
2944:Pygmalion in the Classroom
2837:10.1037/0033-295x.88.4.354
2746:10.1177/019874290102600206
2711:10.1037/0022-0663.90.3.516
2115:Social Theory and Practice
1572:Annual Review of Sociology
952:Discrimination against men
947:Second sexism in education
835:
461:This is measured with the
29:
4357:Sex differences in humans
4053:10.1017/9781108694643.007
3415:Elementary School Journal
2484:10.1037/0003-066x.43.2.95
2299:10.4135/9781452243627.n10
1545:10.1080/09540250601087710
1085:1988 Education Reform Act
114:Sex differences in humans
4139:Health Services Research
3821:Women In Academia Report
3213:Asian Development Review
2291:Theorizing Masculinities
2174:10.1080/1360311980020201
2084:10.1177/0269758014533180
1965:10.1177/0956797617741719
1866:10.1177/0038040716650926
1766:10.1080/0305006870230102
1413:China's one-child policy
1134:correspondence principle
4151:10.1111/1475-6773.13217
4104:10.4324/9781315689760-8
3946:10.47678/cjhe.v39i2.483
3734:Voyeur, Daniel (2014).
3108:Gender in Communication
2676:10.1023/A:1014892408105
2625:10.1126/science.1160364
2523:10.1126/science.1154094
2427:OECD Employment Outlook
1846:Owens, Jayanti (2016).
1185:Human Rights Commission
3743:Psychological Bulletin
3632:Psychological Bulletin
3445:10.1080/07393180216552
2566:Psychological Bulletin
2351:10.26803/ijlter.17.4.2
1853:Sociology of Education
1806:10.3390/ijerph17165729
1398:
1326:Psychological Bulletin
1265:Psychological Bulletin
1223:Gender gap in literacy
1203:
1107:
983:
442:
274:Emotional intelligence
137:Sexual differentiation
102:
65:by rewriting it in an
4202:10.4135/9781412961165
2999:Guasp, April (2009).
2984:Guasp, April (2009).
2472:American Psychologist
1953:Psychological Science
1754:Comparative Education
1396:
1306:Homeschooled children
1198:
1102:
1090:hegemonic masculinity
1010:cultural reproduction
814:United Arab Emirates
693:United Arab Emirates
572:United Arab Emirates
440:
100:
4352:Gender and education
4246:10.18356/1a71d0ef-en
3683:"The New Gender Gap"
3226:10.1162/adev_a_00109
3003:. London: Stonewall.
2988:. London: Stonewall.
2825:Psychological Review
2734:Behavioral Disorders
1886:– via Sagepub.
1533:Gender and Education
1346:from the journal of
1165:Women's scholarships
1027:gender schema theory
866:improve this article
721:Gender Parity Index
600:Gender Parity Index
479:Gender Parity Index
262:Emotional expression
32:Gender and Education
3539:10.1598/JAAL.48.4.2
2517:(5880): 1164–1165.
2201:Young Masculinities
2020:2016PLoSO..1153857S
1231:, collected by the
905:Developed countries
463:Gender Parity Index
164:Scientific measures
108:Part of a series on
4045:Feminist Judgments
3720:on 5 January 2013.
3699:, additional text.
1729:on 16 October 2018
1443:Sub-Saharan Africa
1399:
1204:
1112:sex discrimination
1108:
1041:gender stereotypes
1002:Sex discrimination
450:sex discrimination
443:
284:Gender empathy gap
103:
67:encyclopedic style
54:is written like a
4145:(S2): 1442–1453.
4113:978-1-315-68976-0
3879:. 19 October 2005
3823:. 9 November 2022
3618:"Boy's Own Story"
3333:. 31 January 2009
3255:. 3 November 2020
3117:978-1-4522-2009-3
2972:Clarricoates 1978
2930:Clarricoates 1978
2918:Clarricoates 1978
2897:Clarricoates 1978
2885:Clarricoates 1978
2870:Clarricoates 1978
2670:(9/10): 579–593.
2619:(5888): 494–495.
2429:. 6 August 2012.
2218:978-0-333-77923-1
1129:hidden curriculum
1057:Linguistic sexism
1034:Hidden curriculum
1022:elementary school
1014:gender inequality
898:
897:
890:
829:
828:
708:
707:
587:
586:
435:
434:
369:Gender inequality
95:
94:
87:
16:(Redirected from
4364:
4326:
4319:The STeP Journal
4313:
4288:
4287:
4285:
4283:
4264:
4258:
4257:
4225:
4216:
4215:
4187:
4181:
4180:
4170:
4130:
4124:
4123:
4122:
4120:
4087:
4081:
4080:
4079:
4077:
4037:
4028:
4027:
4020:
4014:
4013:
4011:
4009:
4000:. Archived from
3993:
3987:
3986:
3984:
3982:
3967:
3961:
3960:
3958:
3948:
3924:
3915:
3914:
3912:
3910:
3895:
3889:
3888:
3886:
3884:
3869:
3863:
3862:
3860:
3858:
3847:
3839:
3833:
3832:
3830:
3828:
3813:
3807:
3806:
3778:
3767:
3766:
3755:10.1037/a0036620
3749:(4): 1174–1204.
3740:
3731:
3722:
3721:
3706:
3700:
3698:
3696:
3694:
3685:. Archived from
3678:
3672:
3671:
3644:10.1037/a0035740
3638:(4): 1042–1072.
3627:
3621:
3615:
3609:
3606:
3600:
3599:
3581:
3570:
3563:
3557:
3550:
3544:
3543:
3541:
3517:
3508:
3507:
3471:
3465:
3464:
3428:
3419:
3418:
3410:
3404:
3403:
3375:
3369:
3368:
3366:
3364:
3349:
3343:
3342:
3340:
3338:
3323:
3317:
3316:
3314:
3312:
3297:
3291:
3290:
3288:
3286:
3281:. 21 August 2019
3271:
3265:
3264:
3262:
3260:
3245:
3239:
3238:
3228:
3204:
3193:
3192:
3166:
3142:
3133:
3128:
3122:
3121:
3103:
3092:
3091:
3083:
3074:
3071:
3065:
3062:
3056:
3050:
3044:
3038:
3032:
3026:
3017:
3011:
3005:
3004:
2996:
2990:
2989:
2981:
2975:
2969:
2963:
2962:
2954:
2948:
2947:
2939:
2933:
2927:
2921:
2915:
2900:
2894:
2888:
2882:
2873:
2867:
2861:
2855:
2849:
2848:
2820:
2814:
2813:
2785:
2779:
2772:
2766:
2765:
2729:
2723:
2722:
2694:
2688:
2687:
2659:
2653:
2652:
2604:
2598:
2597:
2557:
2551:
2550:
2502:
2496:
2495:
2463:
2457:
2456:
2419:
2413:
2412:
2394:
2362:
2356:
2355:
2353:
2329:
2320:
2319:
2317:
2315:
2282:
2276:
2275:
2235:
2229:
2228:
2227:
2225:
2192:
2186:
2185:
2153:
2147:
2146:
2110:
2104:
2103:
2066:
2060:
2059:
2049:
2031:
1999:
1993:
1992:
1944:
1938:
1937:
1935:
1933:
1919:
1913:
1912:
1910:
1908:
1894:
1888:
1887:
1877:
1843:
1837:
1836:
1826:
1808:
1784:
1778:
1777:
1745:
1739:
1738:
1736:
1734:
1715:
1706:
1705:
1703:
1701:
1687:
1681:
1680:
1678:
1676:
1662:
1656:
1655:
1653:
1651:
1637:
1631:
1630:
1628:
1626:
1612:
1606:
1605:
1587:
1563:
1557:
1556:
1528:
1522:
1515:
1251:Grown Up Digital
1103:School girls in
1072:self-deprecation
893:
886:
882:
879:
873:
850:
842:
715:
594:
473:
427:
420:
413:
399:equality paradox
394:Sociolinguistics
198:Mental disorders
124:
105:
90:
83:
79:
76:
70:
47:
46:
39:
21:
4372:
4371:
4367:
4366:
4365:
4363:
4362:
4361:
4342:
4341:
4333:
4316:
4295:
4292:
4291:
4281:
4279:
4278:on 1 March 2021
4266:
4265:
4261:
4227:
4226:
4219:
4212:
4189:
4188:
4184:
4132:
4131:
4127:
4118:
4116:
4114:
4089:
4088:
4084:
4075:
4073:
4063:
4039:
4038:
4031:
4022:
4021:
4017:
4007:
4005:
3996:
3994:
3990:
3980:
3978:
3969:
3968:
3964:
3926:
3925:
3918:
3908:
3906:
3897:
3896:
3892:
3882:
3880:
3871:
3870:
3866:
3856:
3854:
3845:
3841:
3840:
3836:
3826:
3824:
3815:
3814:
3810:
3780:
3779:
3770:
3738:
3733:
3732:
3725:
3708:
3707:
3703:
3692:
3690:
3680:
3679:
3675:
3629:
3628:
3624:
3616:
3612:
3607:
3603:
3596:
3583:
3582:
3573:
3564:
3560:
3551:
3547:
3519:
3518:
3511:
3473:
3472:
3468:
3430:
3429:
3422:
3412:
3411:
3407:
3377:
3376:
3372:
3362:
3360:
3351:
3350:
3346:
3336:
3334:
3325:
3324:
3320:
3310:
3308:
3300:Elsesser, Kim.
3299:
3298:
3294:
3284:
3282:
3273:
3272:
3268:
3258:
3256:
3247:
3246:
3242:
3206:
3205:
3196:
3164:10.2307/2061363
3144:
3143:
3136:
3129:
3125:
3118:
3105:
3104:
3095:
3085:
3084:
3077:
3072:
3068:
3063:
3059:
3051:
3047:
3039:
3035:
3027:
3020:
3012:
3008:
2998:
2997:
2993:
2983:
2982:
2978:
2970:
2966:
2956:
2955:
2951:
2941:
2940:
2936:
2928:
2924:
2916:
2903:
2895:
2891:
2883:
2876:
2868:
2864:
2856:
2852:
2822:
2821:
2817:
2787:
2786:
2782:
2778:(Vol. 4). Sage.
2773:
2769:
2731:
2730:
2726:
2696:
2695:
2691:
2661:
2660:
2656:
2606:
2605:
2601:
2559:
2558:
2554:
2504:
2503:
2499:
2465:
2464:
2460:
2445:
2421:
2420:
2416:
2364:
2363:
2359:
2331:
2330:
2323:
2313:
2311:
2309:
2284:
2283:
2279:
2237:
2236:
2232:
2223:
2221:
2219:
2194:
2193:
2189:
2155:
2154:
2150:
2112:
2111:
2107:
2068:
2067:
2063:
2014:(4): e0153857.
2001:
2000:
1996:
1946:
1945:
1941:
1931:
1929:
1921:
1920:
1916:
1906:
1904:
1896:
1895:
1891:
1845:
1844:
1840:
1786:
1785:
1781:
1747:
1746:
1742:
1732:
1730:
1717:
1716:
1709:
1699:
1697:
1689:
1688:
1684:
1674:
1672:
1664:
1663:
1659:
1649:
1647:
1639:
1638:
1634:
1624:
1622:
1614:
1613:
1609:
1565:
1564:
1560:
1530:
1529:
1525:
1516:
1501:
1496:
1454:
1445:
1425:
1408:
1391:
1321:
1310:A study by the
1308:
1259:
1225:
1199:School girl in
1193:
1167:
1154:
1117:Child marriages
1080:
1059:
1036:
999:
986:
978:learning styles
961:
949:
929:
920:
907:
894:
883:
877:
874:
863:
851:
840:
834:
713:
592:
471:
459:
431:
218:substance abuse
193:Life expectancy
91:
80:
74:
71:
63:help improve it
60:
48:
44:
35:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
4370:
4368:
4360:
4359:
4354:
4344:
4343:
4340:
4339:
4332:
4331:External links
4329:
4328:
4327:
4314:
4304:(4): 353–364.
4290:
4289:
4259:
4234:Africa Renewal
4217:
4210:
4182:
4125:
4112:
4082:
4061:
4029:
4015:
4004:on 28 May 2012
3988:
3962:
3916:
3890:
3864:
3834:
3808:
3768:
3723:
3701:
3673:
3622:
3610:
3601:
3595:978-0867095098
3594:
3571:
3558:
3545:
3532:(4): 290–298.
3509:
3482:(3): 253–272.
3466:
3420:
3405:
3370:
3359:. 20 July 2008
3344:
3318:
3292:
3266:
3249:"Scholarships"
3240:
3219:(1): 155–174.
3194:
3134:
3123:
3116:
3093:
3075:
3066:
3057:
3045:
3033:
3018:
3006:
2991:
2976:
2974:, p. 363.
2964:
2949:
2934:
2932:, p. 353.
2922:
2920:, p. 360.
2901:
2899:, p. 355.
2889:
2887:, p. 357.
2874:
2862:
2850:
2831:(4): 354–364.
2815:
2796:(1): 128–135.
2780:
2767:
2740:(2): 146–151.
2724:
2705:(3): 516–527.
2689:
2654:
2599:
2572:(2): 139–155.
2552:
2497:
2458:
2443:
2414:
2357:
2321:
2307:
2277:
2230:
2217:
2187:
2148:
2121:(2): 177–210.
2105:
2078:(3): 351–354.
2061:
1994:
1959:(4): 581–593.
1939:
1914:
1889:
1860:(3): 236–258.
1838:
1779:
1740:
1707:
1682:
1657:
1632:
1620:unstats.un.org
1607:
1578:(1): 341–360.
1558:
1523:
1498:
1497:
1495:
1492:
1491:
1490:
1485:
1480:
1475:
1470:
1465:
1460:
1453:
1450:
1444:
1441:
1424:
1421:
1417:son preference
1407:
1404:
1390:
1387:
1367:Data from the
1344:David C. Geary
1320:
1317:
1307:
1304:
1303:
1302:
1299:
1296:
1293:
1290:
1287:
1284:
1281:
1258:
1255:
1224:
1221:
1192:
1189:
1166:
1163:
1153:
1150:
1142:Herbert Gintis
1079:
1076:
1058:
1055:
1051:
1050:
1035:
1032:
998:
995:
985:
982:
960:
957:
948:
945:
928:
925:
919:
916:
906:
903:
896:
895:
854:
852:
845:
833:
830:
827:
826:
823:
822:United States
819:
818:
815:
811:
810:
807:
803:
802:
799:
795:
794:
791:
787:
786:
783:
779:
778:
775:
771:
770:
767:
763:
762:
759:
755:
754:
751:
747:
746:
743:
739:
738:
735:
731:
730:
727:
723:
722:
719:
712:
709:
706:
705:
702:
701:United States
698:
697:
694:
690:
689:
686:
682:
681:
678:
674:
673:
670:
666:
665:
662:
658:
657:
654:
650:
649:
646:
642:
641:
638:
634:
633:
630:
626:
625:
622:
618:
617:
614:
610:
609:
606:
602:
601:
598:
591:
588:
585:
584:
581:
580:United States
577:
576:
573:
569:
568:
565:
561:
560:
557:
553:
552:
549:
545:
544:
541:
537:
536:
533:
529:
528:
525:
521:
520:
517:
513:
512:
509:
505:
504:
501:
497:
496:
493:
489:
488:
485:
481:
480:
477:
470:
467:
458:
455:
448:are a type of
433:
432:
430:
429:
422:
415:
407:
404:
403:
402:
401:
396:
391:
389:Social support
386:
384:Social capital
381:
376:
371:
366:
365:
364:
354:
346:
345:
341:
340:
339:
338:
337:
336:
331:
326:
321:
316:
308:
303:
298:
293:
288:
287:
286:
276:
271:
270:
269:
259:
254:
246:
245:
235:
234:
233:
232:
227:
226:
225:
220:
215:
210:
205:
195:
190:
182:
181:
171:
170:
169:
168:
167:
166:
156:
151:
146:
145:
144:
131:
130:
126:
125:
117:
116:
110:
109:
93:
92:
51:
49:
42:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
4369:
4358:
4355:
4353:
4350:
4349:
4347:
4338:
4335:
4334:
4330:
4324:
4320:
4315:
4311:
4307:
4303:
4299:
4294:
4293:
4277:
4273:
4269:
4263:
4260:
4255:
4251:
4247:
4243:
4239:
4235:
4231:
4224:
4222:
4218:
4213:
4211:9781412961158
4207:
4203:
4199:
4195:
4194:
4186:
4183:
4178:
4174:
4169:
4164:
4160:
4156:
4152:
4148:
4144:
4140:
4136:
4129:
4126:
4115:
4109:
4105:
4101:
4097:
4093:
4086:
4083:
4072:
4068:
4064:
4062:9781108694643
4058:
4054:
4050:
4046:
4042:
4036:
4034:
4030:
4025:
4019:
4016:
4003:
3999:
3992:
3989:
3977:
3973:
3966:
3963:
3957:
3952:
3947:
3942:
3938:
3934:
3930:
3923:
3921:
3917:
3905:
3901:
3894:
3891:
3878:
3874:
3868:
3865:
3853:
3852:
3844:
3838:
3835:
3822:
3818:
3812:
3809:
3804:
3800:
3796:
3792:
3788:
3784:
3777:
3775:
3773:
3769:
3764:
3760:
3756:
3752:
3748:
3744:
3737:
3730:
3728:
3724:
3719:
3715:
3711:
3705:
3702:
3689:on 3 May 2011
3688:
3684:
3677:
3674:
3669:
3665:
3661:
3657:
3653:
3649:
3645:
3641:
3637:
3633:
3626:
3623:
3619:
3614:
3611:
3605:
3602:
3597:
3591:
3587:
3580:
3578:
3576:
3572:
3569:
3562:
3559:
3556:
3549:
3546:
3540:
3535:
3531:
3527:
3523:
3516:
3514:
3510:
3505:
3501:
3497:
3493:
3489:
3485:
3481:
3477:
3470:
3467:
3462:
3458:
3454:
3450:
3446:
3442:
3438:
3434:
3427:
3425:
3421:
3416:
3409:
3406:
3401:
3397:
3393:
3389:
3385:
3381:
3374:
3371:
3358:
3354:
3348:
3345:
3332:
3328:
3322:
3319:
3307:
3303:
3296:
3293:
3280:
3276:
3270:
3267:
3254:
3250:
3244:
3241:
3236:
3232:
3227:
3222:
3218:
3214:
3210:
3203:
3201:
3199:
3195:
3190:
3186:
3182:
3178:
3174:
3170:
3165:
3160:
3156:
3152:
3148:
3141:
3139:
3135:
3132:
3127:
3124:
3119:
3113:
3109:
3102:
3100:
3098:
3094:
3089:
3082:
3080:
3076:
3070:
3067:
3061:
3058:
3055:
3049:
3046:
3043:, p. 60.
3042:
3037:
3034:
3031:, p. 61.
3030:
3025:
3023:
3019:
3016:, p. 59.
3015:
3010:
3007:
3002:
2995:
2992:
2987:
2980:
2977:
2973:
2968:
2965:
2960:
2953:
2950:
2945:
2938:
2935:
2931:
2926:
2923:
2919:
2914:
2912:
2910:
2908:
2906:
2902:
2898:
2893:
2890:
2886:
2881:
2879:
2875:
2871:
2866:
2863:
2859:
2854:
2851:
2846:
2842:
2838:
2834:
2830:
2826:
2819:
2816:
2811:
2807:
2803:
2799:
2795:
2791:
2784:
2781:
2777:
2771:
2768:
2763:
2759:
2755:
2751:
2747:
2743:
2739:
2735:
2728:
2725:
2720:
2716:
2712:
2708:
2704:
2700:
2693:
2690:
2685:
2681:
2677:
2673:
2669:
2665:
2658:
2655:
2650:
2646:
2642:
2638:
2634:
2630:
2626:
2622:
2618:
2614:
2610:
2603:
2600:
2595:
2591:
2587:
2583:
2579:
2575:
2571:
2567:
2563:
2556:
2553:
2548:
2544:
2540:
2536:
2532:
2528:
2524:
2520:
2516:
2512:
2508:
2501:
2498:
2493:
2489:
2485:
2481:
2478:(2): 95–103.
2477:
2473:
2469:
2462:
2459:
2454:
2450:
2446:
2444:9789264166684
2440:
2436:
2432:
2428:
2424:
2418:
2415:
2410:
2406:
2402:
2398:
2393:
2388:
2384:
2380:
2376:
2372:
2368:
2361:
2358:
2352:
2347:
2343:
2339:
2335:
2328:
2326:
2322:
2310:
2308:9780803949041
2304:
2300:
2296:
2292:
2288:
2281:
2278:
2273:
2269:
2265:
2261:
2257:
2253:
2249:
2245:
2241:
2234:
2231:
2220:
2214:
2210:
2206:
2202:
2198:
2191:
2188:
2183:
2179:
2175:
2171:
2167:
2163:
2159:
2152:
2149:
2144:
2140:
2136:
2132:
2128:
2124:
2120:
2116:
2109:
2106:
2101:
2097:
2093:
2089:
2085:
2081:
2077:
2073:
2065:
2062:
2057:
2053:
2048:
2043:
2039:
2035:
2030:
2025:
2021:
2017:
2013:
2009:
2005:
1998:
1995:
1990:
1986:
1982:
1978:
1974:
1970:
1966:
1962:
1958:
1954:
1950:
1943:
1940:
1928:
1924:
1923:"Data – OECD"
1918:
1915:
1903:
1899:
1893:
1890:
1885:
1881:
1876:
1871:
1867:
1863:
1859:
1855:
1854:
1849:
1842:
1839:
1834:
1830:
1825:
1820:
1816:
1812:
1807:
1802:
1798:
1794:
1790:
1783:
1780:
1775:
1771:
1767:
1763:
1759:
1755:
1751:
1744:
1741:
1728:
1724:
1720:
1714:
1712:
1708:
1696:
1692:
1686:
1683:
1671:
1667:
1661:
1658:
1646:
1642:
1636:
1633:
1621:
1617:
1611:
1608:
1603:
1599:
1595:
1591:
1586:
1581:
1577:
1573:
1569:
1562:
1559:
1554:
1550:
1546:
1542:
1538:
1534:
1527:
1524:
1520:
1514:
1512:
1510:
1508:
1506:
1504:
1500:
1493:
1489:
1486:
1484:
1481:
1479:
1476:
1474:
1471:
1469:
1466:
1464:
1461:
1459:
1456:
1455:
1451:
1449:
1442:
1440:
1438:
1434:
1429:
1423:United States
1422:
1420:
1418:
1414:
1405:
1403:
1395:
1388:
1386:
1382:
1378:
1375:
1370:
1365:
1363:
1359:
1355:
1351:
1350:
1345:
1341:
1336:
1332:
1328:
1327:
1318:
1316:
1313:
1305:
1300:
1297:
1294:
1291:
1288:
1285:
1282:
1279:
1278:
1277:
1274:
1270:
1268:
1266:
1256:
1254:
1252:
1246:
1242:
1239:
1234:
1230:
1229:United States
1222:
1220:
1216:
1212:
1208:
1202:
1197:
1190:
1188:
1186:
1182:
1177:
1173:
1162:
1158:
1151:
1149:
1147:
1143:
1139:
1138:Samuel Bowles
1135:
1130:
1125:
1122:
1118:
1113:
1106:
1101:
1097:
1093:
1091:
1086:
1077:
1075:
1073:
1067:
1063:
1056:
1054:
1047:
1046:
1045:
1042:
1033:
1031:
1028:
1023:
1019:
1015:
1011:
1007:
1003:
996:
994:
990:
981:
979:
973:
969:
965:
958:
956:
953:
946:
944:
940:
936:
934:
926:
924:
918:United States
917:
915:
911:
904:
902:
892:
889:
881:
871:
867:
861:
860:
855:This section
853:
849:
844:
843:
839:
831:
824:
821:
820:
816:
813:
812:
808:
805:
804:
800:
797:
796:
792:
789:
788:
784:
781:
780:
776:
773:
772:
768:
765:
764:
760:
757:
756:
752:
749:
748:
744:
741:
740:
736:
733:
732:
728:
725:
724:
720:
717:
716:
710:
703:
700:
699:
695:
692:
691:
687:
684:
683:
679:
676:
675:
671:
668:
667:
663:
660:
659:
655:
652:
651:
647:
644:
643:
639:
636:
635:
631:
628:
627:
623:
620:
619:
615:
612:
611:
607:
604:
603:
599:
596:
595:
589:
582:
579:
578:
574:
571:
570:
566:
563:
562:
558:
555:
554:
550:
547:
546:
542:
539:
538:
534:
531:
530:
526:
523:
522:
518:
515:
514:
510:
507:
506:
502:
499:
498:
494:
491:
490:
486:
483:
482:
478:
475:
474:
468:
466:
464:
456:
454:
451:
447:
439:
428:
423:
421:
416:
414:
409:
408:
406:
405:
400:
397:
395:
392:
390:
387:
385:
382:
380:
377:
375:
372:
370:
367:
363:
360:
359:
358:
355:
353:
350:
349:
348:
347:
342:
335:
332:
330:
327:
325:
322:
320:
317:
315:
312:
311:
309:
307:
304:
302:
299:
297:
294:
292:
289:
285:
282:
281:
280:
277:
275:
272:
268:
265:
264:
263:
260:
258:
255:
253:
250:
249:
248:
247:
244:
240:
236:
231:
228:
224:
221:
219:
216:
214:
213:schizophrenia
211:
209:
206:
204:
201:
200:
199:
196:
194:
191:
189:
186:
185:
184:
183:
180:
176:
172:
165:
162:
161:
160:
157:
155:
152:
150:
147:
143:
140:
139:
138:
135:
134:
133:
132:
127:
123:
119:
118:
115:
111:
107:
106:
99:
89:
86:
78:
68:
64:
58:
57:
52:This article
50:
41:
40:
37:
33:
19:
4322:
4318:
4301:
4297:
4280:. Retrieved
4276:the original
4271:
4262:
4240:(3): 10–11.
4237:
4233:
4192:
4185:
4142:
4138:
4128:
4117:, retrieved
4095:
4085:
4074:, retrieved
4044:
4018:
4006:. Retrieved
4002:the original
3991:
3979:. Retrieved
3965:
3936:
3932:
3907:. Retrieved
3903:
3893:
3881:. Retrieved
3876:
3867:
3855:. Retrieved
3849:
3837:
3825:. Retrieved
3820:
3811:
3786:
3783:Intelligence
3782:
3746:
3742:
3718:the original
3713:
3704:
3691:. Retrieved
3687:the original
3676:
3635:
3631:
3625:
3613:
3604:
3585:
3561:
3548:
3529:
3525:
3479:
3475:
3469:
3439:(1): 44–63.
3436:
3432:
3414:
3408:
3383:
3379:
3373:
3361:. Retrieved
3356:
3347:
3335:. Retrieved
3330:
3321:
3309:. Retrieved
3305:
3295:
3283:. Retrieved
3278:
3269:
3257:. Retrieved
3252:
3243:
3216:
3212:
3157:(1): 59–68.
3154:
3150:
3126:
3107:
3087:
3069:
3060:
3048:
3041:Rodgers 2014
3036:
3029:Rodgers 2014
3014:Rodgers 2014
3009:
3000:
2994:
2985:
2979:
2967:
2958:
2952:
2943:
2937:
2925:
2892:
2865:
2858:Rodgers 2014
2853:
2828:
2824:
2818:
2793:
2789:
2783:
2775:
2770:
2737:
2733:
2727:
2702:
2698:
2692:
2667:
2663:
2657:
2616:
2612:
2602:
2569:
2565:
2555:
2514:
2510:
2500:
2475:
2471:
2461:
2426:
2417:
2392:10419/149202
2374:
2370:
2360:
2344:(4): 28–44.
2341:
2337:
2312:. Retrieved
2290:
2280:
2250:(1): 96–98.
2247:
2243:
2233:
2222:, retrieved
2200:
2190:
2168:(2): 91–94.
2165:
2161:
2151:
2118:
2114:
2108:
2075:
2071:
2064:
2011:
2007:
1997:
1956:
1952:
1942:
1930:. Retrieved
1927:www.oecd.org
1926:
1917:
1905:. Retrieved
1902:www.oecd.org
1901:
1892:
1857:
1851:
1841:
1799:(16): 5729.
1796:
1792:
1782:
1757:
1753:
1743:
1731:. Retrieved
1727:the original
1722:
1698:. Retrieved
1694:
1685:
1673:. Retrieved
1669:
1660:
1648:. Retrieved
1644:
1635:
1623:. Retrieved
1619:
1610:
1575:
1571:
1561:
1536:
1532:
1526:
1446:
1426:
1409:
1400:
1383:
1379:
1366:
1349:Intelligence
1348:
1324:
1322:
1309:
1275:
1271:
1263:
1260:
1250:
1247:
1243:
1226:
1217:
1213:
1209:
1205:
1168:
1159:
1155:
1146:STEM courses
1126:
1109:
1094:
1081:
1068:
1064:
1060:
1052:
1037:
1006:sociologists
1000:
991:
987:
974:
970:
966:
962:
950:
941:
937:
930:
921:
912:
908:
899:
884:
875:
864:Please help
859:verification
856:
782:New Zealand
661:New Zealand
540:New Zealand
460:
445:
444:
356:
291:Intelligence
239:Neuroscience
188:Autoimmunity
81:
75:January 2023
72:
53:
36:
4325:(1): 58–68.
3956:10419/35745
3939:(2): 1–24.
3789:: 137–151.
2197:"Boys talk"
1625:23 February
1539:(1): 1–20.
1181:New Zealand
1105:Afghanistan
362:in the U.S.
306:Neurosexism
230:Stroke care
149:In research
4346:Categories
4008:7 November
3693:31 January
3386:: 153–85.
3151:Demography
2377:: 101981.
2314:18 October
2224:18 October
1932:15 October
1907:15 October
1760:(1): 5–9.
1733:15 October
1494:References
1340:boy crisis
1331:university
836:See also:
726:Australia
605:Australia
484:Australia
374:Leadership
319:attraction
310:Sexuality
301:Narcissism
267:Aggression
243:psychology
208:depression
159:Dimorphism
154:Physiology
4254:2517-9829
4159:0017-9124
4071:243020689
3976:USA Today
3877:USA Today
3803:143234406
3652:1939-1455
3504:143498265
3496:1551-2169
3461:145392513
3453:1529-5036
3400:145628367
3363:16 August
3337:16 August
3311:16 August
3285:16 August
3259:16 August
3235:0116-1105
3173:0070-3370
2845:144018764
2762:143312322
2754:0198-7429
2719:0022-0663
2684:145366257
2664:Sex Roles
2633:0036-8075
2586:1939-1455
2531:0036-8075
2492:1935-990X
2453:1999-1266
2401:0272-7757
2272:144360033
2264:0007-1005
2182:1360-3116
2135:0037-802X
2100:146922475
2092:0269-7580
2038:1932-6203
1973:0956-7976
1815:1660-4601
1774:0305-0068
1594:0360-0572
1553:143595893
1201:Sri Lanka
1018:preschool
878:June 2023
590:Secondary
357:Education
344:Sociology
252:Cognition
142:disorders
4282:16 March
4177:31663120
4119:16 March
4096:Title IX
4076:16 March
3981:16 March
3909:18 April
3763:24773502
3668:15121059
3660:24491022
2810:23331111
2649:28135226
2641:18653867
2539:18511674
2409:46800507
2143:50354829
2056:27100631
2008:PLOS ONE
1981:29442575
1884:30393398
1833:32784806
1602:13717944
1452:See also
1172:Title IX
806:Ukraine
766:Hungary
758:Germany
718:Country
711:Tertiary
685:Ukraine
645:Hungary
637:Germany
597:Country
564:Ukraine
524:Hungary
516:Germany
476:Country
379:Religion
334:jealousy
175:Medicine
4272:Culture
4168:6864374
3857:18 June
3827:18 June
3279:GovTech
3189:1547903
3181:2061363
2613:Science
2594:2138794
2547:2296969
2511:Science
2047:4839696
2016:Bibcode
1989:4874507
1875:6208359
1824:7459791
1700:22 June
1675:22 June
1650:22 June
1433:LGBTQI+
798:Sweden
790:Mexico
750:France
734:Canada
677:Sweden
669:Mexico
629:France
613:Canada
556:Sweden
548:Mexico
508:France
492:Canada
469:Primary
329:fantasy
279:Empathy
223:suicide
129:Biology
61:Please
4252:
4208:
4175:
4165:
4157:
4110:
4069:
4059:
3801:
3761:
3666:
3658:
3650:
3592:
3502:
3494:
3459:
3451:
3398:
3306:Forbes
3233:
3187:
3179:
3171:
3114:
2961:: 159.
2843:
2808:
2760:
2752:
2717:
2682:
2647:
2639:
2631:
2592:
2584:
2545:
2537:
2529:
2490:
2451:
2441:
2407:
2399:
2305:
2270:
2262:
2215:
2180:
2141:
2133:
2098:
2090:
2054:
2044:
2036:
1987:
1979:
1971:
1882:
1872:
1831:
1821:
1813:
1772:
1723:UNESCO
1600:
1592:
1551:
1183:, the
1121:UNICEF
774:Japan
742:China
653:Japan
621:China
532:Japan
500:China
324:desire
296:Memory
257:Coping
203:autism
179:health
4067:S2CID
3883:3 May
3846:(PDF)
3799:S2CID
3739:(PDF)
3664:S2CID
3500:S2CID
3457:S2CID
3396:S2CID
3331:Stuff
3177:JSTOR
2841:S2CID
2758:S2CID
2680:S2CID
2645:S2CID
2543:S2CID
2405:S2CID
2268:S2CID
2139:S2CID
2096:S2CID
1985:S2CID
1598:S2CID
1549:S2CID
1406:China
1358:Geary
1312:HSLDA
825:1.29
809:1.13
801:1.38
793:1.08
785:1.35
777:0.97
769:1.19
761:1.05
753:1.22
745:1.15
737:1.25
729:1.28
704:0.98
696:1.01
688:0.98
680:1.08
664:1.05
648:0.99
640:0.95
616:1.01
608:0.96
575:1.01
567:1.02
559:1.05
551:1.01
527:0.98
519:1.01
511:0.99
503:1.01
495:0.99
352:Crime
4284:2023
4250:ISSN
4206:ISBN
4173:PMID
4155:ISSN
4121:2023
4108:ISBN
4078:2023
4057:ISBN
4010:2011
3983:2015
3911:2016
3885:2010
3859:2023
3851:OECD
3829:2023
3759:PMID
3695:2011
3656:PMID
3648:ISSN
3590:ISBN
3492:ISSN
3449:ISSN
3365:2023
3339:2023
3313:2023
3287:2023
3261:2023
3231:ISSN
3185:PMID
3169:ISSN
3112:ISBN
2806:PMID
2750:ISSN
2715:ISSN
2637:PMID
2629:ISSN
2590:PMID
2582:ISSN
2535:PMID
2527:ISSN
2488:ISSN
2449:ISSN
2439:ISBN
2397:ISSN
2316:2022
2303:ISBN
2260:ISSN
2226:2022
2213:ISBN
2178:ISSN
2131:ISSN
2088:ISSN
2052:PMID
2034:ISSN
1977:PMID
1969:ISSN
1934:2018
1909:2018
1880:PMID
1829:PMID
1811:ISSN
1770:ISSN
1735:2018
1702:2023
1677:2023
1652:2023
1627:2019
1590:ISSN
1521:>
1374:OECD
1354:PISA
1233:NAEP
1140:and
1020:and
817:1.3
672:1.1
241:and
177:and
4306:doi
4242:doi
4198:doi
4163:PMC
4147:doi
4100:doi
4049:doi
3951:hdl
3941:doi
3791:doi
3751:doi
3747:140
3640:doi
3636:140
3534:doi
3484:doi
3441:doi
3388:doi
3357:RNZ
3221:doi
3159:doi
2833:doi
2798:doi
2742:doi
2707:doi
2672:doi
2621:doi
2617:321
2574:doi
2570:107
2519:doi
2515:320
2480:doi
2431:doi
2387:hdl
2379:doi
2346:doi
2295:doi
2252:doi
2205:doi
2170:doi
2123:doi
2080:doi
2042:PMC
2024:doi
1961:doi
1870:PMC
1862:doi
1819:PMC
1801:doi
1762:doi
1580:doi
1541:doi
868:by
4348::
4321:.
4300:.
4270:.
4248:.
4238:31
4236:.
4232:.
4220:^
4204:.
4171:.
4161:.
4153:.
4143:54
4141:.
4137:.
4106:,
4094:,
4065:,
4055:,
4043:,
4032:^
3974:.
3949:.
3937:39
3935:.
3931:.
3919:^
3902:.
3875:.
3848:.
3819:.
3797:.
3787:48
3785:.
3771:^
3757:.
3745:.
3741:.
3726:^
3712:.
3662:.
3654:.
3646:.
3634:.
3574:^
3530:48
3528:.
3524:.
3512:^
3498:.
3490:.
3480:10
3478:.
3455:.
3447:.
3437:19
3435:.
3423:^
3394:.
3384:22
3382:.
3355:.
3329:.
3304:.
3277:.
3251:.
3229:.
3217:35
3215:.
3211:.
3197:^
3183:.
3175:.
3167:.
3155:29
3153:.
3149:.
3137:^
3096:^
3078:^
3021:^
2904:^
2877:^
2839:.
2829:88
2827:.
2804:.
2794:31
2792:.
2756:.
2748:.
2738:26
2736:.
2713:.
2703:90
2701:.
2678:.
2668:45
2666:.
2643:.
2635:.
2627:.
2615:.
2611:.
2588:.
2580:.
2568:.
2564:.
2541:.
2533:.
2525:.
2513:.
2509:.
2486:.
2476:43
2474:.
2470:.
2447:.
2437:.
2425:.
2403:.
2395:.
2385:.
2375:77
2373:.
2369:.
2342:17
2340:.
2336:.
2324:^
2301:.
2289:.
2266:.
2258:.
2248:55
2246:.
2242:.
2211:,
2199:,
2176:.
2164:.
2160:.
2137:.
2129:.
2119:29
2117:.
2094:.
2086:.
2076:20
2074:.
2050:.
2040:.
2032:.
2022:.
2012:11
2010:.
2006:.
1983:.
1975:.
1967:.
1957:29
1955:.
1951:.
1925:.
1900:.
1878:.
1868:.
1858:89
1856:.
1850:.
1827:.
1817:.
1809:.
1797:17
1795:.
1791:.
1768:.
1758:23
1756:.
1752:.
1721:.
1710:^
1693:.
1668:.
1643:.
1618:.
1596:.
1588:.
1576:44
1574:.
1570:.
1547:.
1537:19
1535:.
1502:^
1364:.
1127:A
656:1
632:1
624:1
583:1
543:1
535:1
487:1
4323:1
4312:.
4308::
4302:1
4286:.
4256:.
4244::
4214:.
4200::
4179:.
4149::
4102::
4051::
4012:.
3985:.
3959:.
3953::
3943::
3913:.
3887:.
3861:.
3831:.
3805:.
3793::
3765:.
3753::
3697:.
3670:.
3642::
3598:.
3542:.
3536::
3506:.
3486::
3463:.
3443::
3417:.
3402:.
3390::
3367:.
3341:.
3315:.
3289:.
3263:.
3237:.
3223::
3191:.
3161::
3120:.
3090:.
2872:.
2860:.
2847:.
2835::
2812:.
2800::
2764:.
2744::
2721:.
2709::
2686:.
2674::
2651:.
2623::
2596:.
2576::
2549:.
2521::
2494:.
2482::
2455:.
2433::
2411:.
2389::
2381::
2354:.
2348::
2318:.
2297::
2274:.
2254::
2207::
2184:.
2172::
2166:2
2145:.
2125::
2102:.
2082::
2058:.
2026::
2018::
1991:.
1963::
1936:.
1911:.
1864::
1835:.
1803::
1776:.
1764::
1737:.
1704:.
1679:.
1654:.
1629:.
1604:.
1582::
1555:.
1543::
1338:"
1267:,
891:)
885:(
880:)
876:(
862:.
426:e
419:t
412:v
88:)
82:(
77:)
73:(
69:.
34:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.