176:
29:
242:
of the Golomb graph is 10/3. The fact that this number is at least this large follows from the fact that the graph has 10 vertices, at most three of which can be in any independent set. The fact that the number is at most this large follows from the fact that one can find 10 three-vertex independent
243:
sets, such that each vertex is in exactly three of these sets. This fractional chromatic number is less than the number 7/2 for the Moser spindle and less than the fractional chromatic number of the unit distance graph of the plane, which is bounded between 3.6190 and 4.3599.
183:
The method of construction of the Golomb graph as a unit distance graph, by drawing an outer regular polygon connected to an inner twisted polygon or star polygon, has also been used for unit distance representations of the
228:
274:
107:
264:
192:. As with the Moser spindle, the coordinates of the unit-distance embedding of the Golomb graph can be represented in the
156:
239:
434:
189:
439:
333:
128:
46:
144:
132:
97:
56:
198:
385:
359:
66:
407:
290:
270:
136:
39:
266:
The
Mathematical Coloring Book: Mathematics of Coloring and the Colorful Life of its Creators
369:
350:
Cranston, Daniel W.; Rabern, Landon (2017), "The fractional chromatic number of the plane",
302:
260:
124:
92:
76:
381:
316:
377:
312:
193:
160:
185:
148:
175:
428:
152:
389:
164:
140:
116:
410:
329:
307:
373:
28:
415:
293:(2012), "All generalized Petersen graphs are unit-distance graphs",
364:
174:
167:
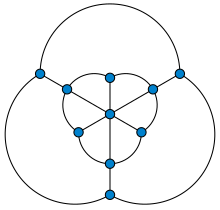
has differently-colored endpoints requires at least four colors.
179:
4-coloring of the Golomb graph, drawn as a unit distance graph
201:
16:
Undirected unit-distance graph requiring four colors
85:
75:
65:
55:
45:
35:
21:
222:
8:
334:"Moser Spindles, Golomb Graphs and Root 33"
295:Journal of the Korean Mathematical Society
363:
306:
210:
203:
202:
200:
252:
18:
7:
155:, it provides a lower bound for the
269:, New York: Springer, p. 19,
14:
147:that requires four colors in any
139:, who constructed it (with a non-
27:
289:Žitnik, Arjana; Horvat, Boris;
338:Wolfram Demonstrations Project
217:
207:
108:Table of graphs and parameters
1:
159:: coloring the points of the
223:{\displaystyle \mathbb {Q} }
240:fractional chromatic number
190:generalized Petersen graphs
456:
308:10.4134/JKMS.2012.49.3.475
374:10.1007/s00493-016-3380-3
151:. Thus, like the simpler
106:
26:
157:Hadwiger–Nelson problem
224:
180:
332:(December 21, 2017),
225:
178:
199:
135:. It is named after
234:Fractional coloring
145:unit distance graph
408:Weisstein, Eric W.
220:
181:
163:so that each unit
435:Individual graphs
276:978-0-387-74640-1
261:Soifer, Alexander
215:
137:Solomon W. Golomb
113:
112:
40:Solomon W. Golomb
447:
421:
420:
393:
392:
367:
347:
341:
340:
326:
320:
319:
310:
286:
280:
279:
257:
229:
227:
226:
221:
216:
211:
206:
143:embedding) as a
125:polyhedral graph
77:Chromatic number
31:
19:
455:
454:
450:
449:
448:
446:
445:
444:
425:
424:
406:
405:
402:
397:
396:
349:
348:
344:
328:
327:
323:
291:Pisanski, Tomaž
288:
287:
283:
277:
259:
258:
254:
249:
236:
197:
196:
194:quadratic field
173:
161:Euclidean plane
102:
17:
12:
11:
5:
453:
451:
443:
442:
437:
427:
426:
423:
422:
411:"Golomb Graph"
401:
400:External links
398:
395:
394:
358:(5): 837–861,
342:
321:
301:(3): 475–491,
281:
275:
251:
250:
248:
245:
235:
232:
219:
214:
209:
205:
186:Petersen graph
172:
169:
149:graph coloring
111:
110:
104:
103:
101:
100:
95:
89:
87:
83:
82:
79:
73:
72:
69:
63:
62:
59:
53:
52:
49:
43:
42:
37:
33:
32:
24:
23:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
452:
441:
440:Planar graphs
438:
436:
433:
432:
430:
418:
417:
412:
409:
404:
403:
399:
391:
387:
383:
379:
375:
371:
366:
361:
357:
353:
352:Combinatorica
346:
343:
339:
335:
331:
325:
322:
318:
314:
309:
304:
300:
296:
292:
285:
282:
278:
272:
268:
267:
262:
256:
253:
246:
244:
241:
233:
231:
212:
195:
191:
187:
177:
170:
168:
166:
162:
158:
154:
153:Moser spindle
150:
146:
142:
138:
134:
130:
126:
122:
118:
109:
105:
99:
98:unit distance
96:
94:
91:
90:
88:
84:
80:
78:
74:
70:
68:
67:Automorphisms
64:
60:
58:
54:
50:
48:
44:
41:
38:
34:
30:
25:
20:
414:
355:
351:
345:
337:
330:Pegg, Ed Jr.
324:
298:
294:
284:
265:
255:
237:
182:
171:Construction
165:line segment
121:Golomb graph
120:
117:graph theory
114:
22:Golomb graph
36:Named after
429:Categories
365:1501.01647
247:References
93:polyhedral
86:Properties
416:MathWorld
263:(2008),
129:vertices
127:with 10
47:Vertices
390:4687673
382:3737371
317:2953031
188:and of
131:and 18
388:
380:
315:
273:
141:planar
119:, the
386:S2CID
360:arXiv
133:edges
123:is a
57:Edges
271:ISBN
238:The
370:doi
303:doi
115:In
431::
413:.
384:,
378:MR
376:,
368:,
356:37
354:,
336:,
313:MR
311:,
299:49
297:,
230:.
213:33
61:18
51:10
419:.
372::
362::
305::
218:]
208:[
204:Q
81:4
71:6
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.