206:
31:
587:
Era, animals could move without oceanic impediment from
Siberia over the North Pole to Antarctica over the South Pole. In the Mesozoic Era, rifting and subsequent opening of the Atlantic split Pangaea. As a consequence, the Variscan Belt around the then periphery of Baltica ended up many hundreds of
566:
of southern Europe, which had rifted off
Gondwana after Avalonia later in the Ordovician, was pushed into Avalonia, creating a second range, the North American/European Variscan, to the east of the Caledonide/Appalachian. The collision of Gondwana proper with Laurussia followed in the early
570:
By the end of the
Carboniferous, Gondwana had united with Laurussia on its western end through northern South America and northwestern Africa. Siberia was approaching from the northeast, separated from Laurussia only by shallow waters. Collision with Siberia produced the
1101:
Stampfli, GM; Borel, GD (2004). "The TRANSMED Transects in Space and Time: Constraints on the
Paleotectonic Evolution of the Mediterranean Domain". In Cavazza W; Roure F; Spakman W; Stampfli GM; Ziegler P (eds.).
190:
underwent a further meaning shift since the 1960s. Geologists generally began to use it to characterize late
Paleozoic fold-belts and orogenic phases having an age of approximately 380 to 280 Ma.
304:
remain as testimony. In southern Iberia it is marked by a classic strike-slip suture zone between very distinct suspect terranes, and clear evidence can be seen of ductile shearing between high-grade
778:
Crespo-Blanc, Ana; Orozco, Miguel (1991-10-01). "The boundary between the Ossa-Morena and
Southportuguese Zones (Southern Iberian Massif): Major suture in the European Hercynian Chain".
179:
but is somewhat less used than the latter. In the United States, it is used only for
European orogenies; the contemporaneous and genetically linked mountain-building phases in the
149:
direction reflected the direction of ancient fold belts cropping out throughout
Germany and adjacent countries and the meaning shifted from direction to the fold belt proper.
197:
for fold belts of even younger age, deviating from the meaning as a term for the North
American and European orogeny related to the Gondwana-Laurasia collision.
727:
Martínez Catalán, José R. (2012-07-01). "The
Central Iberian arc, an orocline centered in the Iberian Massif and some implications for the Variscan belt".
327:
is the eastern end of the unmodified Variscan belt of crustal deformation in Europe. Further Variscan developments to the southeast are partly hidden and
1062:
von Raumer, J.; Stampfli, G.M.; Bussy, F. (2003). "Gondwana-derived microcontinents - the constituents of the Variscan and Alpine collisional orogens".
1111:
1008:
959:
Matte, P. (2001). "The Variscan collage and orogeny (480 ±290 Ma) and the tectonic definition of the Armorica microplate: a review".
670:
1191:
1162:
713:
575:
in the latest Paleozoic and completed the formation of Pangaea. Eastern Laurussia was still divided from Gondwana by the
438:
collisions, making the exact reconstruction of the plate tectonic processes difficult. Plate convergence that caused the
684:
539:
to the south of Avalonia pushed the latter into north Laurentia and thrust up the northern Appalachian Mountains in the
910:
831:
1181:
402:
in northwestern Africa show close relations to the Appalachian Mountains and used to form the eastern part of the
1196:
1186:
391:
547:
between Avalonia and Baltica was entirely closed. Thus Avalonia formed the southern coast of the new continent
559:
continent in present-day North America, the British Isles, northern Germany, Scandinavia and western Russia).
1127:
1079:
922:
839:
328:
707:
379:
205:
180:
58:
1071:
1034:
968:
872:
787:
736:
108:
1084:
1155:
470:
465:
Period, a land mass, which has been named Gondwana (present day South America, Africa, Antarctica,
403:
371:
35:
1019:
1050:
984:
811:
760:
536:
524:
497:, located as if on the vertices of a triangle. To the south of them was a large archipelago, the
439:
375:
434:
The Variscan orogeny involved a complicated heterogeneous assembly of different microplates and
1107:
1004:
803:
752:
563:
556:
466:
352:
242:
363:, Greek and Turkish mountain chains are the southeastern termination of the Variscan proper.
1089:
1042:
976:
880:
795:
744:
661:. Website of University of California Museum of Paleontology. Accessed on December 29, 2007.
305:
213:
The North American and European Variscan Belt includes the mountains of Portugal and Spain (
134:
130:
857:
1166:
1159:
914:
835:
540:
419:
395:
367:
324:
238:
214:
1075:
1038:
972:
876:
791:
740:
435:
572:
516:
415:
407:
332:
301:
258:
70:
1093:
1175:
1054:
996:
988:
980:
815:
764:
656:
544:
520:
451:
234:
153:
39:
567:
Carboniferous, when the Variscan belt was already in place and actively developing.
297:
293:
277:
152:
One of the pioneers in research on the Variscan fold belt was the German geologist
104:
17:
926:
843:
685:"Geology of petroleum and coal deposits in the North China Basin, Eastern China"
647:. In German: 1.170 for "variszische Orogenese", 154 for "herzynische Orogenese".
576:
387:
383:
317:
285:
250:
1020:"The organisation of pre-Variscan basement areas at the north-Gondwanan margin"
884:
856:
Burkhard, M.; Caritg, S.; Helg, U.; Robert-Charrue, C.; Soulaimani, A. (2006).
748:
548:
505:
478:
462:
399:
356:
348:
340:
62:
807:
756:
692:
552:
528:
486:
474:
423:
360:
313:
209:
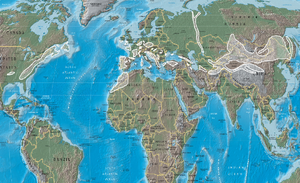
Distribution of orogenies with similar ages to the Variscan orogeny (shaded)
112:
55:
904:
828:
30:
1046:
156:, establishing a still valid division of the European Variscides in 1927.
584:
580:
512:
501:
447:
443:
411:
273:
254:
246:
226:
218:
116:
95:
66:
799:
498:
494:
490:
482:
455:
454:
Periods. Both orogenies resulted in the assembly of a super-continent,
414:
times. 'Variscan' mountains in a broad chronological sense include the
344:
309:
266:
222:
172:
100:
74:
1148:
1138:
1133:
938:
532:
519:
times, Baltica and Laurentia drifted towards each other, closing the
289:
262:
120:
908:. Paleogeographic reconstructions for the Devonian and Carboniferous
123:
in Germany, which is in the Variscan belt, has the same etymology.)
485:
on one side of the globe. Off to the west were three other masses:
42:
period. Present day coastlines are indicated in grey for reference.
27:
Collision of tectonic plates resulting in the creation of mountains
1143:
458:, which was essentially complete by the end of the Carboniferous.
312:
and extending into the northernmost part the autonomous region of
281:
230:
90:
1104:
The TRANSMED Atlas: the Mediterranean Region from Crust to Mantle
336:
164:
1018:
von Raumer, J.; Stampfli, G.M.; Borel, G.D.; Bussy, F. (2002).
621:
Kossmat, F. (1927). "Gliederung des varistischen Gebirgsbaus".
1003:(2 ed.). Shell Internationale Petroleum Maatschappij BV.
308:
and lower grade sedimentary rocks in a wide belt north of the
374:
in the United States and Canada, responsible for forming the
167:
Mountains in Germany, saw a similar shift in meaning. Today,
562:
In late Devonian and in the Carboniferous the archipelago
446:
continued to form the Variscan orogeny in the succeeding
54:, was a geologic mountain-building event caused by Late
382:. North American areas with Variscan foldbelts include
527:
and formed the Caledonide mountains of North America,
639:Google search on December 29, 2007: ca. 44.500 for
323:In the Czech Republic and southwestern Poland the
939:Paleogeographic configuration Lower Carboniferous
543:of the Caledonian orogeny. Contemporaneously the
673:. Historical Geology, University of North Texas.
504:, rifted off the north Gondwana margin in early
477:and Australia), straddled the space between the
137:directions observed by geologists in the field,
838:. Institute of Geology and Paleontology of the
115:, a rare green mineral first discovered in the
1001:Geological Atlas of Western and Central Europe
8:
945:by C.Scotese. Accessed on December 29, 2007.
366:The Variscan was contemporaneous with the
1083:
245:. Its effects are present in France from
858:"Tectonics of the anti-Atlas of Morocco"
204:
29:
1027:International Journal of Earth Sciences
729:International Journal of Earth Sciences
609:
597:
133:. Both words were descriptive terms of
829:Tectonic Map of the western Tethysides
705:
129:, on the other hand, derives from the
605:
7:
919:Tethyan Plate Tectonic Working Group
99:, the home of a Germanic tribe, the
38:mountain belts in the middle of the
1158:, Colorado Plateau Geosystems Inc:
523:between them. They collided in the
292:and other regions on both sides of
276:in Italy and in Germany where the
25:
1160:Europe in the Late Carboniferous
981:10.1046/j.1365-3121.2001.00327.x
929:. Accessed on December 29, 2007.
846:. Accessed on December 29, 2007.
193:Some publications use the term
145:for northwest to southeast. The
272:The Variscan Belt reappears in
221:), southwestern Ireland (i.e.
107:, professor of geology at the
1:
1094:10.1016/S0040-1951(03)00015-5
588:miles from the Appalachians.
111:, coined the term in 1880. (
339:a Variscan core is built by
141:for southwest to northeast,
426:and other Asian foldbelts.
163:, for the direction of the
1213:
885:10.1016/j.crte.2005.11.012
712:: CS1 maint: postscript (
406:before the opening of the
34:Location of the Hercynian-
1192:Natural history of Europe
865:Comptes Rendus Geoscience
749:10.1007/s00531-011-0715-6
658:Tectonics of the Devonian
392:Newfoundland and Labrador
531:, the British Isles and
89:comes from the Medieval
1139:Early Carboniferous Map
671:"The Hercynian Orogeny"
1144:Late Carboniferous Map
1128:Christopher R. Scotese
923:University of Lausanne
840:University of Lausanne
623:Abh. Sächs. Geol. L.-A
210:
183:have different names.
93:name for the district
43:
1047:10.1007/s005310100200
780:Geologische Rundschau
380:Appalachian Mountains
208:
181:Appalachian Mountains
159:The other direction,
59:continental collision
33:
1130:, Paleomap Project:
109:University of Vienna
1106:. Springer Verlag.
1076:2003Tectp.365....7V
1039:2002IJEaS..91...35V
973:2001TeNov..13..122M
877:2006CRGeo.338...11B
792:1991GeoRu..80..691C
741:2012IJEaS.101.1299M
683:Lee, K. Y. (1989).
471:Indian subcontinent
404:Appalachian orogeny
372:Alleghenian orogeny
171:is often used as a
1165:2015-09-22 at the
1134:Early Devonian Map
913:2011-06-08 at the
834:2008-04-23 at the
800:10.1007/BF01803695
689:USGS Bulletin 1871
537:Seafloor spreading
525:Caledonian orogeny
511:By the end of the
440:Caledonian orogeny
211:
186:The regional term
44:
1182:Hercynian orogeny
1113:978-3-540-22181-4
1010:978-90-6644-125-5
645:Hercynian orogeny
557:Old Red Sandstone
306:metamorphic rocks
243:Vale of Glamorgan
52:Hercynian orogeny
18:Hercynian orogeny
16:(Redirected from
1204:
1197:Geology of Devon
1187:Paleozoic Europe
1117:
1097:
1087:
1058:
1024:
1014:
992:
946:
943:Paleomap Project
936:
930:
902:
896:
895:
893:
891:
862:
853:
847:
826:
820:
819:
775:
769:
768:
735:(5): 1299–1314.
724:
718:
717:
711:
703:
702:. Table 1, p. 3.
701:
700:
691:. Archived from
680:
674:
668:
662:
654:
648:
641:Variscan orogeny
637:
631:
630:
629:. Leipzig: 1–39.
618:
612:
602:
131:Hercynian Forest
65:(Laurussia) and
48:Variscan orogeny
21:
1212:
1211:
1207:
1206:
1205:
1203:
1202:
1201:
1172:
1171:
1167:Wayback Machine
1124:
1114:
1100:
1085:10.1.1.430.1420
1061:
1022:
1017:
1011:
995:
958:
955:
953:Further reading
950:
949:
937:
933:
915:Wayback Machine
903:
899:
889:
887:
860:
855:
854:
850:
836:Wayback Machine
827:
823:
777:
776:
772:
726:
725:
721:
704:
698:
696:
682:
681:
677:
669:
665:
655:
651:
638:
634:
620:
619:
615:
603:
599:
594:
432:
396:Moroccan Meseta
325:Bohemian Massif
239:Gower Peninsula
203:
83:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1210:
1208:
1200:
1199:
1194:
1189:
1184:
1174:
1173:
1170:
1169:
1153:
1152:
1151:
1146:
1141:
1136:
1123:
1122:External links
1120:
1119:
1118:
1112:
1098:
1064:Tectonophysics
1059:
1015:
1009:
993:
967:(2): 122–128.
954:
951:
948:
947:
931:
897:
848:
821:
786:(3): 691–702.
770:
719:
675:
663:
649:
632:
613:
596:
595:
593:
590:
583:Period of the
579:Ocean. In the
573:Ural Mountains
517:Early Devonian
436:heterochronous
431:
428:
408:Atlantic Ocean
333:Alpine orogeny
302:Harz Mountains
259:Massif Central
202:
199:
82:
79:
71:supercontinent
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1209:
1198:
1195:
1193:
1190:
1188:
1185:
1183:
1180:
1179:
1177:
1168:
1164:
1161:
1157:
1156:Ronald Blakey
1154:
1150:
1147:
1145:
1142:
1140:
1137:
1135:
1132:
1131:
1129:
1126:
1125:
1121:
1115:
1109:
1105:
1099:
1095:
1091:
1086:
1081:
1077:
1073:
1070:(1–4): 7–22.
1069:
1065:
1060:
1056:
1052:
1048:
1044:
1040:
1036:
1032:
1028:
1021:
1016:
1012:
1006:
1002:
998:
997:Ziegler, P.A.
994:
990:
986:
982:
978:
974:
970:
966:
962:
957:
956:
952:
944:
940:
935:
932:
928:
924:
920:
916:
912:
909:
907:
901:
898:
886:
882:
878:
874:
870:
866:
859:
852:
849:
845:
841:
837:
833:
830:
825:
822:
817:
813:
809:
805:
801:
797:
793:
789:
785:
781:
774:
771:
766:
762:
758:
754:
750:
746:
742:
738:
734:
730:
723:
720:
715:
709:
695:on 2019-09-13
694:
690:
686:
679:
676:
672:
667:
664:
660:
659:
653:
650:
646:
643:, ca. 15.000
642:
636:
633:
628:
624:
617:
614:
611:
607:
601:
598:
591:
589:
586:
582:
578:
574:
568:
565:
560:
558:
554:
550:
546:
545:Tornquist Sea
542:
541:acadian phase
538:
534:
530:
526:
522:
521:Iapetus Ocean
518:
514:
509:
507:
503:
500:
496:
492:
488:
484:
480:
476:
472:
468:
464:
459:
457:
453:
452:Carboniferous
449:
445:
441:
437:
429:
427:
425:
421:
417:
413:
409:
405:
401:
397:
393:
389:
385:
381:
377:
373:
369:
364:
362:
358:
354:
350:
346:
342:
338:
334:
330:
326:
321:
319:
316:and southern
315:
311:
307:
303:
299:
296:Valley), the
295:
291:
287:
283:
279:
275:
270:
268:
264:
260:
256:
252:
248:
244:
240:
236:
235:Pembrokeshire
232:
228:
224:
220:
216:
207:
200:
198:
196:
191:
189:
184:
182:
178:
174:
170:
166:
162:
157:
155:
154:Franz Kossmat
150:
148:
144:
140:
136:
132:
128:
124:
122:
118:
114:
110:
106:
102:
98:
97:
92:
88:
80:
78:
76:
72:
68:
64:
60:
57:
53:
49:
41:
40:Carboniferous
37:
32:
19:
1149:Triassic Map
1103:
1067:
1063:
1033:(1): 35–52.
1030:
1026:
1000:
964:
960:
942:
934:
918:
905:
900:
888:. Retrieved
871:(1): 11–24.
868:
864:
851:
824:
783:
779:
773:
732:
728:
722:
708:cite journal
697:. Retrieved
693:the original
688:
678:
666:
657:
652:
644:
640:
635:
626:
622:
616:
610:Ziegler 1990
600:
569:
561:
510:
460:
433:
365:
322:
298:Black Forest
294:Middle Rhine
278:Rhine Massif
271:
249:, below the
212:
201:Distribution
194:
192:
187:
185:
176:
168:
160:
158:
151:
146:
142:
138:
126:
125:
119:district of
105:Eduard Suess
94:
86:
84:
81:Nomenclature
69:to form the
51:
47:
45:
927:Switzerland
906:Paleotethys
844:Switzerland
577:Paleotethys
388:Nova Scotia
384:New England
329:overprinted
318:Extremadura
280:(Ardennes,
251:Paris Basin
36:Alleghenian
1176:Categories
961:Terra Nova
890:1 November
699:2017-09-17
606:Matte 2001
592:References
549:Euramerica
506:Ordovician
479:South Pole
463:Ordovician
400:Anti-Atlas
357:Aar Massif
349:Belledonne
341:Mercantour
63:Euramerica
1080:CiteSeerX
1055:131617311
989:129727506
816:128688878
808:1432-1149
765:195334509
757:1437-3262
604:Based on
553:Laurussia
529:Greenland
487:Laurentia
475:Zealandia
430:Formation
424:Tian Shan
353:Montblanc
335:. In the
314:Andalusia
169:Hercynian
161:Hercynian
143:hercynian
127:Hercynian
113:Variscite
85:The name
56:Paleozoic
1163:Archived
999:(1990).
911:Archived
832:Archived
585:Mesozoic
581:Triassic
564:Armorica
513:Silurian
502:Avalonia
481:and the
448:Devonian
444:Silurian
412:Jurassic
398:and the
376:Ouachita
286:Hunsrück
274:Sardinia
255:Ardennes
247:Brittany
241:and the
227:Cornwall
219:Pyrenees
195:Variscan
188:Variscan
177:Variscan
147:variscan
139:variscan
117:Vogtland
96:Variscia
87:Variscan
67:Gondwana
61:between
1072:Bibcode
1035:Bibcode
969:Bibcode
921:of the
873:Bibcode
788:Bibcode
737:Bibcode
515:and in
499:terrane
495:Baltica
491:Siberia
483:Equator
461:In the
456:Pangaea
442:in the
368:Acadian
361:Dinaric
345:Pelvoux
331:by the
310:Algarve
267:Corsica
253:to the
223:Munster
215:Galicia
173:synonym
101:Varisci
75:Pangaea
1110:
1082:
1053:
1007:
987:
814:
806:
763:
755:
555:, the
533:Norway
469:, the
467:Arabia
422:, the
418:, the
394:. The
290:Taunus
263:Vosges
261:, the
257:, the
237:, the
217:, and
135:strike
121:Saxony
1051:S2CID
1023:(PDF)
985:S2CID
861:(PDF)
812:S2CID
761:S2CID
420:Pamir
416:Urals
282:Eifel
231:Devon
91:Latin
50:, or
1108:ISBN
1005:ISBN
892:2015
804:ISSN
753:ISSN
714:link
608:and
493:and
450:and
390:and
378:and
370:and
355:and
337:Alps
300:and
265:and
175:for
165:Harz
46:The
1090:doi
1068:365
1043:doi
977:doi
881:doi
869:338
796:doi
745:doi
733:101
410:in
225:),
73:of
1178::
1088:.
1078:.
1066:.
1049:.
1041:.
1031:91
1029:.
1025:.
983:.
975:.
965:13
963:.
941:.
925:,
917:.
879:.
867:.
863:.
842:,
810:.
802:.
794:.
784:80
782:.
759:.
751:.
743:.
731:.
710:}}
706:{{
687:.
625:.
535:.
508:.
489:,
473:,
386:,
359:.
351:,
347:,
343:,
320:.
288:,
284:,
269:.
233:,
229:,
103:;
77:.
1116:.
1096:.
1092::
1074::
1057:.
1045::
1037::
1013:.
991:.
979::
971::
894:.
883::
875::
818:.
798::
790::
767:.
747::
739::
716:)
627:1
551:(
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.