589:
6783:
1265:
895:
1436:, a name suggested by Sidney van den Bergh after he discovered that the stars in these nebulae had a non-uniform distribution. These young stellar groupings contain main sequence stars that are not sufficiently massive to disperse the interstellar clouds in which they formed. This allows the properties of the surrounding dark cloud to be examined by astronomers. Because R associations are more plentiful than OB associations, they can be used to trace out the structure of the galactic spiral arms. An example of an R association is
1026:
549:: Spectroscopic observations of external galaxies make it possible to characterize the bulk motions of the stars they contain. While these stellar populations in external galaxies are generally not resolved to the level where one can track the motion of individual stars (except for the very nearest galaxies) measurements of the kinematics of the integrated stellar population along the line of sight provides information including the mean velocity and the
705:, or proportion of elements with atomic numbers higher than helium. Among nearby stars, it has been found that population I stars with higher metallicity are generally located in the stellar disk while older population II stars are in random orbits with little net rotation. The latter have elliptical orbits that are inclined to the plane of the Milky Way. Comparison of the kinematics of nearby stars has also led to the identification of
739:
6757:
6534:
1459:
713:
gravitational potential of all the other stars and other mass within the galaxy plays a dominant role in determining the stellar motion. Stellar kinematics can provide insights into the location of where the star formed within the galaxy. Measurements of an individual star's kinematics can identify stars that are peculiar outliers such as a high-velocity star moving much faster than its nearby neighbors.
539:
center. These stars have little to no average rotation. Many stars in this group belong to globular clusters which formed long ago and thus have a distinct formation history, which can be inferred from their kinematics and poor metallicities. The halo may be further subdivided into an inner and outer halo, with the inner halo having a net prograde motion with respect to the Milky Way and the outer a net
6807:
1300:
152:
6831:
6795:
955:. Further measurements placed its origin within the Milky Way. Due to uncertainty about the distribution of mass within the Milky Way, determining whether a HVS is unbound is difficult. A further five known high-velocity stars may be unbound from the Milky Way, and 16 HVSs are thought to be bound. The nearest currently known HVS (HVS2) is about 19
6819:
6545:
681:, serving as crucial indicators for understanding the mass distribution within the Milky Way. GAIA DR3 improved the quality of previously published data by providing detailed astrophysical parameters. While the complete GAIA DR4 is yet to be unveiled, the latest release offers enhanced insights into white dwarfs,
1291:. The OB, T, and R associations form a continuum of young stellar groupings. But it is currently uncertain whether they are an evolutionary sequence, or represent some other factor at work. Some groups also display properties of both OB and T associations, so the categorization is not always clear-cut.
286:
in which the stars are bound. This means that if accurate stellar kinematics measurements are made for a star or group of stars orbiting in a certain region of a galaxy, the gravitational potential and mass distribution can be inferred given that the gravitational potential in which the star is bound
806:
Multiple mechanisms may accelerate the same runaway star. For example, a massive star that was originally ejected due to gravitational interactions with its stellar neighbors may itself go supernova, producing a remnant with a velocity modulated by the supernova kick. If this supernova occurs in the
1207:
containing dozens to thousands of members with similar ages and compositions. These clusters dissociate with time. Groups of young stars that escape a cluster, or are no longer bound to each other, form stellar associations. As these stars age and disperse, their association is no longer readily
1056:
Supernova-induced HVSs may also be possible, although they are presumably rare. In this scenario, a HVS is ejected from a close binary system as a result of the companion star undergoing a supernova explosion. Ejection velocities up to 770 km/s, as measured from the galactic rest frame, are
920:
of the galaxy. In the Milky Way, stars usually have velocities on the order of 100 km/s, whereas hypervelocity stars typically have velocities on the order of 1000 km/s. Most of these fast-moving stars are thought to be produced near the center of the Milky Way, where there is a larger
859:
Halo stars are very old stars that do not follow circular orbits around the center of the Milky Way within its disk. Instead, the halo stars travel in elliptical orbits, often inclined to the disk, which take them well above and below the plane of the Milky Way. Although their orbital velocities
269:
information about stars, and the galaxies in which they reside. Stellar kinematics data combined with astrophysical modeling produces important information about the galactic system as a whole. Measured stellar velocities in the innermost regions of galaxies including the Milky Way have provided
538:
and no net circular velocity. The
Galactic stellar halo consists of stars with orbits that extend to the outer regions of the galaxy. Some of these stars will continually orbit far from the galactic center, while others are on trajectories which bring them to various distances from the galactic
729:
relative to the surrounding interstellar medium. The three types of high-velocity stars are: runaway stars, halo stars and hypervelocity stars. High-velocity stars were studied by Jan Oort, who used their kinematic data to predict that high-velocity stars have very little tangential velocity.
1241:, whose stars share a common origin and are still moving together through space, but have become gravitationally unbound. Associations are primarily identified by their common movement vectors and ages. Identification by chemical composition is also used to factor in association memberships.
742:
Four runaway stars moving through regions of dense interstellar gas and creating bright bow waves and trailing tails of glowing gas. The stars in these NASA Hubble Space
Telescope images are among 14 young runaway stars spotted by the Advanced Camera for Surveys between October 2005 and July
321:: Using stellar kinematics, astronomers construct models which seek to explain the overall galactic structure in terms of distinct kinematic populations of stars. This is possible because these distinct populations are often located in specific regions of galaxies. For example, within the
712:
There are many additional ways to classify stars based on their measured velocity components, and this provides detailed information about the nature of the star's formation time, its present location, and the general structure of the galaxy. As a star moves in a galaxy, the smoothed out
1097:
One theory regarding the ignition of Type Ia supernovae invokes the onset of a merger between two white dwarfs in a binary star system, triggering the explosion of the more massive white dwarf. If the less massive white dwarf is not destroyed during the explosion, it will no longer be
1420:. T associations are often found in the vicinity of the molecular cloud from which they formed. Some, but not all, include O–B class stars. Group members have the same age and origin, the same chemical composition, and the same amplitude and direction in their vector of velocity.
115:
provides important information about the formation and evolutionary history of our Galaxy. Kinematic measurements can also identify exotic phenomena such as hypervelocity stars escaping from the Milky Way, which are interpreted as the result of gravitational encounters of
302:
of stars within the Milky way disc one can show that there is differential rotation. When combining these measurements of stars' proper motions and their radial velocities, along with careful modeling, it is possible to obtain a picture of the rotation of the Milky Way
782:
A collision or close encounter between stellar systems, including galaxies, may result in the disruption of both systems, with some of the stars being accelerated to high velocities, or even ejected. A large-scale example is the gravitational interaction between the
337:. These kinematic groups are closely related to the stellar populations in the Milky Way, forming a strong correlation between the motion and chemical composition, thus indicating different formation mechanisms. For the Milky Way, the speed of disk stars is
1337:
after roughly one million years. As a result, OB associations are generally only a few million years in age or less. The O-B stars in the association will have burned all their fuel within ten million years. (Compare this to the current age of the
1098:
gravitationally bound to its destroyed companion, causing it to leave the system as a hypervelocity star with its pre-explosion orbital velocity of 1000–2500 km/s. In 2018, three such stars were discovered using data from the Gaia satellite.
46:
2400:
Hodgkin, S. T.; Harrison, D. L.; Breedt, E.; Wevers, T.; Rixon, G.; Delgado, A.; Yoldas, A.; Kostrzewa-Rutkowska, Z.; Wyrzykowski, Ł; Leeuwen, M. van; Blagorodnova, N.; Campbell, H.; Eappachen, D.; Fraser, M.; Ihanec, N. (2021-08-01).
135:. Stellar-dynamical models of systems such as galaxies or star clusters are often compared with or tested against stellar-kinematic data to study their evolutionary history and mass distributions, and to detect the presence of
553:
which can then be used to infer the distribution of mass within the galaxy. Measurement of the mean velocity as a function of position gives information on the galaxy's rotation, with distinct regions of the galaxy that are
3125:
Brown, Warren R.; Geller, Margaret J.; Kenyon, Scott J.; Kurtz, Michael J.; Bromley, Benjamin C. (2007). "Hypervelocity Stars. III. The Space
Density and Ejection History of Main-Sequence Stars from the Galactic Center".
2342:
Fouesneau, M.; Frémat, Y.; Andrae, R.; Korn, A. J.; Soubiran, C.; Kordopatis, G.; Vallenari, A.; Heiter, U.; Creevey, O. L.; Sarro, L. M.; Laverny, P. de; Lanzafame, A. C.; Lobel, A.; Sordo, R.; Rybizki, J. (2023-06-01).
604:
data, contributing to a more nuanced understanding of the Milky Way's structure. Notably, it facilitated the determination of proper motions for numerous celestial objects, including the absolute proper motions of 75
774:
can result in large accelerations of one or more of the involved stars. In some cases, stars may even be ejected. This can occur in seemingly stable star systems of only three stars, as described in studies of the
536:
466:
1542:(ARG), confirmed with Gaia. Moving groups can sometimes be further subdivided in smaller distinct groups. The Great Austral Young Association (GAYA) complex was found to be subdivided into the moving groups
1329:. Once the surrounding dust and gas is blown away, the remaining stars become unbound and begin to drift apart. It is believed that the majority of all stars in the Milky Way were formed in OB associations.
392:
256:
with statistical uncertainty (+0.69−0.75, +0.47−0.47, +0.37−0.36) km/s and systematic uncertainty (1, 2, 0.5) km/s. (Note that V is 7 km/s larger than estimated in 1998 by Dehnen et al.)
1082:
explosions, and their extreme speeds are very likely the result of an asymmetric supernova explosion or the loss of their near partner during the supernova explosions that forms them. The neutron star
5025:
1067:
Some HVSs may have originated from a disrupted dwarf galaxy. When it made its closest approach to the center of the Milky Way, some of its stars broke free and were thrown into space, due to the
1325:. In addition, these associations also contain hundreds or thousands of low- and intermediate-mass stars. Association members are believed to form within the same small volume inside a giant
3041:
Brown, Warren R.; Anderson, Jay; Gnedin, Oleg Y.; Bond, Howard E.; et al. (July 19, 2010). "A Galactic Origin For HE 0437–5439, The
Hypervelocity Star Near The Large Magellanic Cloud".
1223:). As the stars in a moving group formed in proximity and at nearly the same time from the same gas cloud, although later disrupted by tidal forces, they share similar characteristics.
725:
star is a star moving faster than 65 km/s to 100 km/s relative to the average motion of the other stars in the star's neighborhood. The velocity is also sometimes defined as
600:
Data
Release 2 (GAIA DR2) marked a significant advancement in stellar kinematics, offering a rich dataset of precise measurements. This release included detailed stellar kinematic and
1530:
The list of young moving groups is constantly evolving. The Banyan Σ tool currently lists 29 nearby young moving groups Recent additions to nearby moving groups are the
1766:
1453:
983:(DR2) show that most high-velocity late-type stars have a high probability of being bound to the Milky Way. However, distant hypervelocity star candidates are more promising.
1283:
Viktor
Ambartsumian first categorized stellar associations into two groups, OB and T, based on the properties of their stars. A third category, R, was later suggested by
701:
Stars within galaxies may be classified based on their kinematics. For example, the stars in the Milky Way can be subdivided into two general populations, based on their
1987:
1926:
656:
287:
produces its orbit and serves as the impetus for its stellar motion. Examples of using kinematics combined with modeling to construct an astrophysical system include:
1195:, the remains of a star forming region, or collections of overlapping star formation bursts at differing time periods in adjacent regions. Most stars are born within
5016:
1049:(in the sense of entering orbit around it), while the other escapes with high velocity, becoming a HVS. Such maneuvers are analogous to the capture and ejection of
633:
1191:
A set of stars with similar space motion and ages is known as a kinematic group. These are stars that could share a common origin, such as the evaporation of an
6385:
4766:
675:
1885:
Johnson, Dean R. H.; Soderblom, David R. (1987). "Calculating galactic space velocities and their uncertainties, with an application to the Ursa Major group".
867:, is an example of the high-velocity stars that lie near the Sun: Its observed radial velocity is −245 km/s, and the components of its space velocity are
2506:
576:, we can determine the mass distribution of the Milky Way or other galaxies. This is accomplished by combining kinematic measurements with dynamical modeling.
1821:
588:
3614:
3391:
916:
in stellar catalogues) have substantially higher velocities than the rest of the stellar population of a galaxy. Some of these stars may even exceed the
229:
at the mean velocity of those nearby stars with low velocity dispersion. The Sun's motion with respect to the LSR is called the "peculiar solar motion".
4070:
2932:
Brown, Warren R.; Geller, Margaret J.; Kenyon, Scott J.; Kurtz, Michael J. (2005). "Discovery of an
Unbound Hypervelocity Star in the Milky Way Halo".
2830:
Tauris, T.M.; Takens, R.J. (1998). "Runaway velocities of stellar components originating from disrupted binaries via asymmetric supernova explosions".
2616:
Oh, Seungkyung; Kroupa, Pavel; Pflamm-Altenburg, Jan (2015). "Dependency of
Dynamical Ejections of O Stars on the Masses of Very Young Star Clusters".
3230:
de la Fuente Marcos, R.; de la Fuente Marcos, C. (8 July 2019). "Flying far and fast: the distribution of distant hypervelocity star candidates from
6582:
1078:
are inferred to be traveling with similar speeds. This could be related to HVSs and the HVS ejection mechanism. Neutron stars are the remnants of
4933:
Edelmann, H.; Napiwotzki, R.; Heber, U.; Christlieb, N.; et al. (2005). "HE 0437-5439: An
Unbound Hypervelocity Main-Sequence B-Type Star".
2988:
Edelmann, H.; Napiwotzki, R.; Heber, U.; Christlieb, N.; et al. (2005). "HE 0437-5439: An
Unbound Hypervelocity Main-Sequence B-Type Star".
3963:
de Zeeuw, P. T.; Hoogerwerf, R.; de Bruijne, J. H. J.; Brown, A. G. A.; et al. (1999). "A HIPPARCOS Census of the Nearby OB Associations".
826:
moves through the Milky Way at about 20 km/s faster than the local average). Tracing their motions back, their paths intersect near to the
6866:
6782:
205:
must be found by taking a series of positional determinations against more distant objects. Once the distance to a star is determined through
6417:
4517:
4505:
471:
401:
240:
are usually designated U, V, and W, given in km/s, with U positive in the direction of the Galactic Center, V positive in the direction of
4989:
1264:
1064:
stars with masses a few times that of the Sun. HVSs with smaller masses are also expected and G/K-dwarf HVS candidates have been found.
863:
Typical examples are the halo stars passing through the disk of the Milky Way at steep angles. One of the nearest 45 stars, called
92:
4785:
1354:
6643:
6392:
5711:
3556:"Three Hypervelocity White Dwarfs in Gaia DR2: Evidence for Dynamically Driven Double-degenerate Double-detonation Type Ia Supernovae"
3446:
2600:
2575:
340:
962:
As of 1 September 2017, there have been roughly 20 observed hypervelocity stars. Though most of these were observed in the
3043:
2803:
Blaauw, A. (1961). "On the origin of the O- and B-type stars with high velocities (the run-away stars), and some related problems".
2182:
6104:
3525:
1791:
1469:
If the remnants of a stellar association drift through the Milky Way as a somewhat coherent assemblage, then they are termed a
225:(LSR). The latter is typically taken as a position at the Sun's present location that is following a circular orbit around the
6018:
4206:
Gagné, Jonathan; Mamajek, Eric E.; Malo, Lison; Riedel, Adric; Rodriguez, David; Lafrenière, David; et al. (2018-03-21).
6397:
6034:
5053:
5003:
3651:
López-Santiago, J.; Montes, D.; Crespo-Chacón, I.; Fernández-Figueroa, M. J. (June 2006). "The Nearest Young Moving Groups".
1720:
540:
4770:
6861:
6648:
6444:
6311:
5013:
4591:
1725:
1551:
6773:
2857:
6575:
6427:
6378:
6353:
5646:
1661:
1057:
possible for late-type B-stars. This mechanism can explain the origin of HVSs which are ejected from the galactic disk.
973:
It is believed that about 1,000 HVSs exist in the Milky Way. Considering that there are around 100 billion stars in the
5731:
6856:
6655:
6623:
6368:
6348:
1646:
1405:
860:
relative to the Milky Way may be no faster than disk stars, their different paths result in high relative velocities.
4529:
Allers, K.N.; Liu, Michael C. (2013-07-09). "A near-infrared spectroscopic study of young field ultra-cool dwarfs".
921:
population of these objects than further out. One of the fastest known stars in our Galaxy is the O-class sub-dwarf
6851:
6432:
6363:
6333:
4668:
Wylie-de Boer, Elizabeth; et al. (February 2010). "Evidence of Tidal Debris from ω Cen in the Kapteyn Group".
3236:
2542:
1715:
1651:
842:
237:
894:
6439:
6316:
6293:
5875:
5324:
5319:
5314:
5309:
5304:
5299:
1829:
1666:
1559:
Young moving groups have well known ages and can help with the characterization of objects with hard-to-estimate
1397:
1277:
1091:
997:, traveling 1,755 km/s (3,930,000 mph), faster than any other star detected so far. The star is in the
3179:
Boubert, Douglas; Guillochon, James; Hawkins, Keith; Ginsburg, Idan; Evans, N. Wyn; Strader, Jay (6 June 2018).
5582:
5456:
5091:
3622:
3096:
274:
at their center. In farther out regions of galaxies such as within the galactic halo, velocity measurements of
6109:
5778:
4208:"The BANYAN Σ multivariate Bayesian algorithm to identify members of young associations with 150 pc"
3293:
1413:
1179:
1172:
1165:
1152:
1145:
1138:
4100:
3939:
3324:
1256:(or constellations) in which they are located; the association type, and, sometimes, a numerical identifier.
1211:
Astronomers are able to determine if stars are members of a kinematic group because they share the same age,
572:: Through measurement of the kinematics of tracer objects such as globular clusters and the orbits of nearby
155:
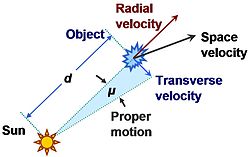
Relation between proper motion and velocity components of an object. At emission, the object was at distance
6568:
6358:
5908:
5818:
5760:
5686:
5257:
5183:
1705:
1641:
1596:
1497:
1482:
1462:
1038:
1014:
678:
283:
271:
140:
69:
5133:
3417:
2402:
2344:
1417:
1025:
6519:
6499:
6271:
6266:
6059:
6008:
5813:
5803:
5476:
5274:
5242:
5116:
3289:
1560:
1369:
1318:
1311:
1132:
1111:
948:
788:
468:. For bulge population stars, the velocities are randomly oriented with a larger relative RMS velocity of
222:
1409:
677:. Furthermore, Gaia's comprehensive dataset enabled the measurement of absolute proper motions in nearby
6760:
6633:
6373:
6343:
6338:
6328:
6256:
6044:
5210:
1710:
1700:
1695:
1519:
lies in its outer fringes, without being part of the group. Hence, although members are concentrated at
822:, all of which are moving away from each other at velocities of over 100 km/s (for comparison, the
178:= the component of velocity transverse to line of sight from the Sun. (The diagram illustrates an angle
5491:
1556:. The three Associations are not very distinct from each other, and have similar kinematic properties.
709:. These are most likely groups of stars that share a common point of origin in giant molecular clouds.
5008:
4620:"New Members of the TW Hydrae Association, β Pictoris Moving Group, and Tucana/Horologium Association"
807:
very nearby vicinity of other stars, it is possible that it may produce more runaways in the process.
52:, showing position every 5 years in the period 1985–2005. Barnard's Star is the star with the highest
6737:
6514:
6412:
6402:
6251:
6219:
6013:
5808:
5793:
5106:
4952:
4905:
4858:
4817:
4734:
4687:
4634:
4548:
4482:
4364:
4305:
4229:
4161:
4130:
4092:
4035:
3982:
3908:
3862:
3828:
3782:
3727:
3670:
3577:
3496:
3255:
3202:
3145:
3062:
3007:
2951:
2895:
2839:
2812:
2767:
2700:
2635:
2518:
2474:
2424:
2366:
2306:
2217:
2145:
2086:
2055:
2006:
1945:
1894:
1859:
1761:
1504:
1284:
998:
563:
282:. Both of these cases derive from the key fact that stellar kinematics can be related to the overall
5353:
4274:
Gagné, Jonathan; Mamajek, Eric E.; Malo, Lison; Riedel, Adric; Rodriguez, David; Lafrenière, David;
6835:
6691:
6114:
5974:
5957:
5628:
5530:
1771:
1690:
1656:
1568:
1531:
1524:
1249:
1232:
1050:
967:
963:
760:
752:
706:
682:
550:
245:
99:. Measurement of the kinematics of stars in different subcomponents of the Milky Way including the
1437:
990:
was reported to be a confirmed hypervelocity star ejected from the stellar disk of the Milky Way.
936:
131:, which involves the theoretical study or modeling of the motions of stars under the influence of
6823:
6811:
6509:
6470:
6422:
6407:
6321:
6261:
6184:
6094:
6064:
5998:
5920:
5611:
5247:
5046:
4968:
4942:
4921:
4895:
4874:
4848:
4703:
4677:
4650:
4572:
4538:
4472:
4449:
4421:
4390:
4354:
4323:
4295:
4255:
4219:
4082:
4051:
4025:
3998:
3972:
3798:
3772:
3745:
3717:
3686:
3660:
3595:
3567:
3486:
3360:
3329:
3271:
3245:
3192:
3161:
3135:
3078:
3052:
3023:
2997:
2967:
2941:
2911:
2757:
2726:
2690:
2659:
2625:
2534:
2414:
2356:
2324:
2296:
2241:
2207:
2135:
2104:
2024:
1996:
1963:
1935:
987:
944:
931:
first predicted the existence of HVSs in 1988. This was later confirmed in 2005 by Warren Brown,
776:
686:
308:
4156:
Eggen, O.J. (1965). "Moving groups of stars". In Blaauw, Adriaan & Schmidt, Maarten (eds.).
3851:"R associations. I – UBV photometry and MK spectroscopy of stars in southern reflection nebulae"
4998:
4619:
638:
6460:
5945:
5885:
5858:
5838:
5638:
5422:
5410:
5237:
5217:
5171:
5153:
5121:
4986:
4564:
4513:
4501:
4441:
4382:
4247:
3325:"A Black Hole Threw a Star Out of the Milky Way Galaxy – So long, S5-HVS1, we hardly knew you"
2785:
2718:
2651:
2596:
2571:
2440:
2382:
2233:
2178:
2044:"Observational evidence confirming Lindblad's hypothesis of a rotation of the galactic system"
1743:
1539:
1535:
1512:
1288:
1273:
978:
900:
864:
831:
597:
334:
299:
108:
49:
39:
4886:
Brown; Geller; Kenyon; Kurtz (2006). "A Successful Targeted Search for Hypervelocity Stars".
4179:
2198:
Carollo, Daniela; et al. (2007). "Two Stellar Components in the Halo of the Milky Way".
6799:
6670:
6628:
6288:
6241:
6191:
6179:
6157:
6152:
6079:
6039:
5986:
5768:
5691:
5666:
5560:
5481:
5205:
5166:
4960:
4913:
4866:
4825:
4789:
4742:
4695:
4642:
4556:
4431:
4372:
4313:
4237:
4138:
4096:
4043:
3990:
3916:
3870:
3790:
3735:
3678:
3585:
3504:
3370:
3263:
3259:
3210:
3153:
3070:
3015:
2959:
2903:
2843:
2775:
2708:
2643:
2526:
2482:
2432:
2428:
2374:
2370:
2314:
2225:
2153:
2094:
2014:
1953:
1902:
1867:
1863:
1614:
1492:
in the 1960s. A list of the nearest young moving groups has been compiled by López-Santiago
1373:
940:
898:
Positions and trajectories of 20 high-velocity stars as reconstructed from data acquired by
726:
606:
601:
573:
395:
275:
128:
1009:
10 AU) from Earth. It may have been ejected from the Milky Way after interacting with
6475:
6278:
6147:
5991:
5962:
5903:
5898:
5773:
5501:
5466:
5400:
5346:
5341:
5286:
5096:
5020:
4993:
4839:
Hoogerwerf, R.; de Bruijne, J.H.J.; de Zeeuw, P.T. (2000). "The Origin of Runaway Stars".
3763:
Johnston, Kathryn V. (1996). "Fossil Signatures of Ancient Accretion Events in the Halo".
1828:. Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation. 2005-08-18. Archived from
1674:
1580:
1326:
1216:
1200:
1196:
932:
925:, which is moving away from the Milky Way with a total velocity of around 1200 km/s.
917:
612:
592:
Expected motion of 40,000 stars in the next 400 thousand years, as determined by Gaia EDR3
226:
194:
31:
2884:"Hyper-velocity and tidal stars from binaries disrupted by a massive Galactic black hole"
2285:"Evidence for an Intermediate-Mass Milky Way from Gaia DR2 Halo Globular Cluster Motions"
1252:
in 1947. The conventional name for an association uses the names or abbreviations of the
325:, there are three primary components, each with its own distinct stellar kinematics: the
4956:
4909:
4862:
4821:
4738:
4691:
4638:
4552:
4486:
4368:
4309:
4233:
4165:
4134:
4039:
3986:
3912:
3866:
3832:
3786:
3731:
3674:
3581:
3500:
3206:
3149:
3066:
3011:
2955:
2899:
2816:
2771:
2704:
2639:
2522:
2478:
2310:
2221:
2149:
2090:
2059:
2010:
1949:
1898:
1871:
802:
system can accelerate both the supernova remnant and remaining stars to high velocities.
6787:
6686:
6537:
6303:
6142:
5969:
5940:
5915:
5848:
5537:
5405:
5291:
5193:
5083:
5073:
5014:
https://myspaceastronomy.com/magnetar-the-most-magnetic-stars-in-the-universe-my-space/
4500:. Monograph Publications (online). Volume 5. Astronomical Society of the Pacific.
4275:
3392:"Bizarre Star Found Hurtling Out of Our Galaxy Centre Is Fastest of Its Kind Ever Seen"
3320:
1756:
1087:
1068:
1010:
771:
738:
660:
330:
312:
198:
121:
4699:
3074:
6845:
6742:
6727:
6489:
6283:
6246:
6214:
6089:
5798:
5621:
5592:
5570:
5188:
5161:
5138:
5039:
4707:
4560:
4453:
4394:
4327:
4259:
4055:
3740:
3705:
3690:
3451:
3275:
2730:
2713:
2678:
2663:
2647:
2538:
2158:
2123:
2108:
2019:
1982:
1967:
1958:
1921:
1679:
1389:
1253:
1220:
1204:
1083:
1061:
1002:
977:, this is a minuscule fraction (~0.000001%). Results from the second data release of
928:
854:
799:
756:
326:
295:
202:
53:
35:
4972:
4925:
4654:
4576:
4002:
3819:
Israelian, Garik (1997). "Obituary: Victor Amazaspovich Ambartsumian, 1912 –1996".
3802:
3749:
3599:
3165:
3082:
3027:
2971:
2328:
2043:
2028:
1799:
1458:
1086:, which was measured to move at a record speed of over 1,500 km/s (0.5% of the
6701:
6638:
6618:
6613:
6549:
6224:
6174:
6169:
6069:
5952:
5935:
5893:
5853:
5788:
5671:
5616:
5597:
5577:
5555:
5547:
5390:
5383:
5222:
5143:
5126:
4878:
4158:
Observational Aspects of Galactic Structure: Lecture notes reported by participants
2915:
2563:
2245:
1618:
1584:
1385:
1238:
1192:
1128:
1075:
827:
266:
112:
4806:"The Space Motions of AE Aurigae and mu Columbae with Respect to the Orion Nebula"
3267:
2436:
2378:
1376:. These associations can be quite sparse, spanning 1,500 light-years in diameter.
17:
1029:
Runaway star speeding from 30 Doradus. Image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope.
6722:
6665:
6660:
6594:
6465:
6164:
6137:
6129:
6119:
6099:
6074:
6003:
5925:
5681:
5656:
5651:
5565:
5525:
5486:
5451:
5434:
5429:
5101:
3294:"Researchers confirm massive hyper-runaway star ejected from the Milky Way Disk"
1621:
that has now been torn apart and stretched out along its orbit by tidal forces.
1567:. Members of nearby young moving groups are also candidates for directly imaged
1564:
1520:
1349:
satellite provided measurements that located a dozen OB associations within 650
1330:
1314:
1212:
1034:
819:
702:
304:
279:
206:
136:
117:
5028:, David Montes, Departamento de Astrofísica, Universidad Complutense de Madrid.
4436:
4410:"The nearby, young, Argus association: Membership, age, and dusty debris disks"
4409:
4377:
4342:
4318:
4279:
4242:
4207:
3590:
3555:
2319:
2284:
2099:
2074:
6732:
6049:
5746:
5719:
5696:
5676:
5661:
5513:
5417:
5395:
5373:
5368:
5232:
4747:
4722:
3442:
1738:
1501:
1489:
1358:
1303:
1046:
834:
is believed to be the remnant of the supernova that launched the other stars.
815:
811:
104:
73:
4568:
4445:
4386:
4278:; Roy-Loubier, Olivier; Pueyo, Laurent; Robin, Annie C.; Doyon, René (2018).
4251:
2789:
2722:
2655:
2444:
2386:
6236:
6084:
5868:
5833:
5828:
5823:
5783:
5736:
5726:
5520:
5496:
5471:
5378:
5329:
5262:
5252:
5227:
5200:
5176:
5111:
3540:
3509:
3474:
3375:
3352:
3215:
3180:
1751:
1576:
1572:
1346:
1334:
1079:
1042:
974:
952:
841:, where photodigital techniques reveal the presence of a typical supersonic
795:
784:
559:
322:
241:
233:
100:
88:
61:
3353:"Discovery of a nearby 1700 km/s star ejected from the Milky Way by Sgr A*"
2780:
2745:
2237:
1299:
1114:) (a.k.a. The Outcast Star) – the first hypervelocity star to be discovered
747:
A runaway star is one that is moving through space with an abnormally high
151:
2259:
1392:. These sparse populations of up to a thousand T Tauri stars are known as
278:
clusters orbiting in these halo regions of galaxies provides evidence for
6229:
5930:
5604:
5363:
5336:
4947:
4900:
4853:
4121:
Herbst, W. (1975). "R-associations III. Local optical spiral structure".
4087:
4030:
3977:
3777:
3722:
3665:
3298:
3002:
2946:
2140:
2001:
1635:
838:
748:
722:
555:
210:
84:
4343:"Volans-Carina: A new 90 Myr old stellar association at 85 pc"
4341:
Gagné, Jonathan; Faherty, Jacqueline K.; Mamajek, Eric E. (2018-10-01).
2229:
45:
6504:
5979:
5741:
5508:
5461:
5444:
5439:
5358:
4467:
Torres, C.A.O.; Quast, G.R.; Melo, C.H.F.; Sterzik, M.F. (2008-08-25).
3706:"Late-type members of young stellar kinematic groups – I. Single stars"
3447:"Our Local Supermassive Black Hole Shot A Star Right Out Of THe Galaxy"
2530:
1684:
1478:
1245:
994:
966:, the possibility remains that there are HVSs only observable from the
132:
3945:. GAIA: Composition, Formation and Evolution of the Galaxy. 2000-04-06
531:{\displaystyle \mathrm {V_{RMS}} =150~\mathrm {km} ~\mathrm {s} ^{-1}}
193:
The component of stellar motion toward or away from the Sun, known as
6608:
6494:
6482:
5701:
5587:
5009:
Entry in the Encyclopedia of Astrobiology, Astronomy, and Spaceflight
4999:
Entry in the Encyclopedia of Astrobiology, Astronomy, and Spaceflight
2907:
1610:
1441:
1429:
1401:
1350:
1203:. The stars formed within such a cloud compose gravitationally bound
1121:
956:
922:
763:, of which the star was formerly a member, before it was hurled out.
690:
461:{\displaystyle \mathrm {V_{RMS}} =50~\mathrm {km} ~\mathrm {s} ^{-1}}
96:
30:"Space velocity (astronomy)" redirects here. Not to be confused with
2883:
1033:
HVSs are believed to predominantly originate by close encounters of
6544:
4964:
4917:
4870:
4830:
4805:
4646:
4426:
4359:
4300:
4224:
4142:
4047:
3994:
3921:
3896:
3875:
3850:
3794:
3682:
3572:
3365:
3250:
3197:
3157:
3019:
2963:
2762:
2630:
2487:
2462:
2419:
2361:
2301:
1906:
6560:
4682:
4543:
4496:
Handbook of Star Forming Regions: Volume II, The Southern Sky
4477:
3491:
3140:
3057:
2744:
Boubert, D.; Erkal, D.; Evans, N. W.; Izzard, R. G. (2017-04-10).
2695:
2212:
1940:
1508:
1457:
1298:
1263:
1158:
1024:
893:
737:
127:
Stellar kinematics is related to but distinct from the subject of
44:
947:
were known, one of which is believed to have originated from the
6591:
5863:
5843:
5062:
4071:"New proper motions of pre-main-sequence stars in Taurus-Auriga"
4016:
Maíz-Apellániz, Jesús (2001). "The Origin of the Local Bubble".
2075:"Galactic Rotation and the Oort Constants in the Solar Vicinity"
1850:
Fich, Michel; Tremaine, Scott (1991). "The mass of the Galaxy".
1606:
387:{\displaystyle \mathrm {V} =220~\mathrm {km} ~\mathrm {s} ^{-1}}
77:
6564:
5035:
3418:"Fastest star ever found is being flicked out of the Milky Way"
6209:
4069:
Frink, S.; Roeser, S.; Neuhaeuser, R.; Sterzik, M. K. (1999).
1516:
1362:
1339:
1269:
823:
218:
2403:"Gaia Early Data Release 3 - Gaia photometric science alerts"
1045:. One of the two partners is gravitationally captured by the
248:. The peculiar motion of the Sun with respect to the LSR is
3475:"Maximum speed of hypervelocity stars ejected from binaries"
810:
An example of a related set of runaway stars is the case of
4494:
1523:
near 60°N, some outliers are as far away across the sky as
1404:
from the Sun. Other examples of T associations include the
1310:
Young associations will contain 10 to 100 massive stars of
993:
In July 2019, astronomers reported finding an A-type star,
2805:
Bulletin of the Astronomical Institutes of the Netherlands
2677:
Gvaramadze, Vasilii V.; Gualandris, Alessia (2010-09-30).
2570:. United States: Cambridge University Press. p. 111.
2048:
Bulletin of the Astronomical Institutes of the Netherlands
83:
Stellar kinematics encompasses the measurement of stellar
1481:
moving group at two billion years, or young, such as the
766:
Mechanisms that may give rise to a runaway star include:
213:, the space velocity can be computed. This is the star's
143:
through their gravitational influence on stellar orbits.
5031:
2746:"Hypervelocity runaways from the Large Magellanic Cloud"
1920:
Schönrich, Ralph; Binney, James; Dehnen, Walter (2010).
197:, can be measured from the spectrum shift caused by the
2679:"Very massive runaway stars from three-body encounters"
2467:
Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific
1400:(Tau–Aur T association), located at a distance of 140
904:, overlaid on top of an artistic view of the Milky Way
6771:
4160:. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. p. 111.
2345:"Gaia Data Release 3 – Apsis. II. Stellar parameters"
1767:
List of nearby stellar associations and moving groups
1454:
List of nearby stellar associations and moving groups
663:
641:
615:
474:
404:
343:
4721:
McDonald, A. R. E.; Hearnshaw, J. B. (August 1983).
3351:
Koposov, Sergey E.; et al. (11 November 2019).
2463:"The Kinematics and Evolution of Population I Stars"
1384:
Young stellar groups can contain a number of infant
1005:
in the southern sky and is about 29,000 ly (1.8
6715:
6679:
6601:
6453:
6302:
6200:
6128:
6027:
5884:
5759:
5637:
5546:
5273:
5152:
5082:
759:of a runaway star often points exactly away from a
95:as well as the internal kinematics of more distant
4493:
1244:Stellar associations were first discovered by the
1094:, is thought to have been produced the first way.
669:
650:
627:
530:
460:
386:
307:. The local character of galactic rotation in the
4727:Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society
4201:
4199:
3710:Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society
3479:Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society
3357:Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society
3185:Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society
2858:"Two Exiled Stars Are Leaving Our Galaxy Forever"
2750:Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society
2683:Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society
2128:Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society
1988:Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society
1927:Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society
1922:"Local kinematics and the local standard of rest"
1428:Associations of stars that illuminate reflection
1208:apparent and they become moving groups of stars.
3120:
3118:
5004:Two Exiled Stars Are Leaving Our Galaxy Forever
3181:"Revisiting hypervelocity stars after Gaia DR2"
2505:Elmegreen, B.; Nikolaevich Efremov, Y. (1998).
2595:. Princeton University Press. pp. 16–17.
2177:. Princeton University Press. pp. 16–19.
1983:"Local stellar kinematics from HIPPARCOS data"
1388:that are still in the process of entering the
1353:of the Sun. The nearest OB association is the
770:Gravitational interactions between stars in a
182:swept out in unit time at tangential velocity
122:supermassive black hole at the Galactic Center
6576:
5047:
4592:"Stellar streams are revealing their secrets"
3821:Bulletin of the American Astronomical Society
3526:"Milky Way's fastest stars may be immigrants"
2456:
2454:
8:
3097:"The Milky Way's fastest stars are runaways"
1368:OB associations have also been found in the
4618:Song, Inseok; et al. (December 2003).
4613:
4611:
4609:
3646:
3644:
3642:
3640:
3615:"Nearest Bright 'Hypervelocity Star' Found"
2591:Binney, James; Merrifield, Michael (1998).
1852:Annual Review of Astronomy and Astrophysics
1465:, the closest stellar moving group to Earth
6583:
6569:
6561:
5279:
5054:
5040:
5032:
2124:"Refining the Oort and Galactic constants"
1826:Australia Telescope Outreach and Education
252:(U, V, W) = (11.1, 12.24, 7.25) km/s,
4946:
4899:
4852:
4829:
4788:. University of Tennessee. Archived from
4746:
4681:
4542:
4476:
4435:
4425:
4376:
4358:
4317:
4299:
4241:
4223:
4086:
4029:
3976:
3920:
3890:
3888:
3886:
3874:
3814:
3812:
3776:
3739:
3721:
3704:Montes, D.; et al. (November 2001).
3664:
3589:
3571:
3508:
3490:
3374:
3364:
3249:
3214:
3196:
3139:
3056:
3001:
2945:
2779:
2761:
2712:
2694:
2629:
2500:
2498:
2486:
2418:
2360:
2318:
2300:
2211:
2157:
2139:
2098:
2018:
2000:
1981:Dehnen, Walter; Binney, James J. (1998).
1957:
1939:
662:
640:
614:
519:
514:
502:
480:
475:
473:
449:
444:
432:
410:
405:
403:
375:
370:
358:
344:
342:
244:, and W positive in the direction of the
6706:
4769:. University of Virginia. Archived from
2283:Watkins, Laura; et al. (May 2018).
1488:Moving groups were studied intensely by
1477:. Moving groups can be old, such as the
587:
232:The components of space velocity in the
159:from the Sun, and moved at angular rate
150:
6778:
4786:"The Space Velocity and its Components"
3934:
3932:
2983:
2981:
2927:
2925:
2173:Binney, James; Tremaine, Scott (2008).
1782:
1500:which includes all of the stars in the
4590:Schilling, Govert (January 12, 2022).
3844:
3842:
1629:Some nearby kinematic groups include:
1515:. This is sufficiently close that the
1237:A stellar association is a very loose
609:situated at distances extending up to
319:Structural components of the Milky Way
4987:ESO press release about runaway stars
3541:"Chandra discovers cosmic cannonball"
398:) velocity relative to this speed of
7:
4723:"The Wolf 630 moving group of stars"
3621:. University of Utah. Archived from
3416:Irving, Michael (13 November 2019).
1333:are short-lived, and will expire as
837:Another example is the X-ray object
721:Depending on the definition, a high-
265:Stellar kinematics yields important
2260:"Gaia DR2 contents – Gaia – Cosmos"
2122:Olling, RP; Merrifield, MR (1998).
1872:10.1146/annurev.aa.29.090191.002205
1534:Association (VCA), discovered with
1106:As of 2014, twenty HVS were known.
908:Hypervelocity stars (designated as
6644:List of most massive star clusters
3554:Shen, Ken J.; et al. (2018).
3539:Watzke, Megan (28 November 2007).
1117:HVS 2 – (SDSS J093320.86+441705.4
515:
506:
503:
487:
484:
481:
477:
445:
436:
433:
417:
414:
411:
407:
371:
362:
359:
345:
25:
4469:Young, nearby, loose associations
4280:"Figures 4 & 5 of Gagné
3044:The Astrophysical Journal Letters
1792:"Barnard's Star (V2500 Ophiuchi)"
1790:Kaler, James B. (November 2005).
1287:for associations that illuminate
270:evidence that many galaxies host
6829:
6817:
6805:
6793:
6781:
6756:
6755:
6543:
6533:
6532:
3741:10.1046/j.1365-8711.2001.04781.x
3390:Starr, Michelle (31 July 2019).
2714:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.17446.x
2507:"The Formation of Star Clusters"
2159:10.1046/j.1365-8711.1998.01577.x
2073:Li, C; Zhao, G; Yang, C (2019).
2020:10.1046/j.1365-8711.1998.01600.x
1959:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.16253.x
1798:. James B. Kaler. Archived from
1687:supercluster (Argus Association)
1485:at only 120 million years.
1406:R Corona Australis T association
830:about 2 million years ago.
689:, and the merger history of the
292:Rotation of the Milky Way's disc
4804:Blaauw A.; Morgan W.W. (1954).
3895:Herbst, W.; Racine, R. (1976).
3524:Maggie McKee (4 October 2008).
5026:Young stellar kinematic groups
1721:Pisces-Eridanus stellar stream
1355:Scorpius–Centaurus association
1342:at about five billion years.)
27:Study of the movement of stars
1:
6867:Stellar astrophysics concepts
6649:List of largest star clusters
6445:Timeline of stellar astronomy
1822:"Stellar Motions (Extension)"
1726:Tucana-Horologium association
1396:. The nearest example is the
1276:view of a stellar nursery in
1021:Origin of hypervelocity stars
1017:at the center of the galaxy.
261:Use of kinematic measurements
4765:Majewski, Steven R. (2006).
4408:Zuckerman, B. (2018-12-31).
4184:www.exoplanetes.umontreal.ca
2407:Astronomy & Astrophysics
2349:Astronomy & Astrophysics
1662:Corona Australis association
1161:– (SDSS J113312.12+010824.9)
751:relative to the surrounding
562:in relation to the galaxy's
72:study or measurement of the
6656:Hypercompact stellar system
6624:Hypercompact stellar system
6105:Hertzsprung–Russell diagram
4700:10.1088/0004-6256/139/2/636
3897:"R associations. V. MON R2"
3268:10.1051/0004-6361/201935008
3075:10.1088/2041-8205/719/1/L23
2566:; Gallagher, J. S. (2007).
2437:10.1051/0004-6361/202140735
2379:10.1051/0004-6361/202243919
1647:Alpha Persei moving cluster
1398:Taurus-Auriga T association
581:Recent advancements due to
6883:
6019:Kelvin–Helmholtz mechanism
4561:10.1088/0004-637X/772/2/79
4492:Reipurth, Bo, ed. (2008).
4075:Astronomy and Astrophysics
3613:Zheng Zheng (7 May 2014).
3473:Tauris, Thomas M. (2015).
3237:Astronomy and Astrophysics
2832:Astronomy and Astrophysics
2648:10.1088/0004-637X/805/2/92
1716:Zeta Herculis moving group
1652:Beta Pictoris moving group
1594:
1451:
1230:
852:
238:Galactic coordinate system
29:
6751:
6528:
5282:
5069:
4935:The Astrophysical Journal
4888:The Astrophysical Journal
4841:The Astrophysical Journal
4810:The Astrophysical Journal
4627:The Astrophysical Journal
4531:The Astrophysical Journal
4414:The Astrophysical Journal
4347:The Astrophysical Journal
4288:The Astrophysical Journal
4212:The Astrophysical Journal
4018:The Astrophysical Journal
3765:The Astrophysical Journal
3653:The Astrophysical Journal
3560:The Astrophysical Journal
3128:The Astrophysical Journal
2990:The Astrophysical Journal
2934:The Astrophysical Journal
2618:The Astrophysical Journal
2461:Johnson, Hugh M. (1957).
2289:The Astrophysical Journal
2079:The Astrophysical Journal
1671:Hercules-Lyra association
1667:Eta Chamaeleontis cluster
1092:Chandra X-ray Observatory
679:dwarf spheroidal galaxies
651:{\displaystyle G\approx }
6398:With multiple exoplanets
4670:The Astronomical Journal
4437:10.3847/1538-4357/aaee66
4378:10.3847/1538-4357/aadaed
4319:10.3847/1538-4357/aaae09
4243:10.3847/1538-4357/aaae09
3965:The Astronomical Journal
3591:10.3847/1538-4357/aad55b
2568:Galaxies in the Universe
2320:10.3847/1538-4357/ab089f
2100:10.3847/1538-4357/ab0104
1414:Chamaeleon T association
1306:, a large OB association
1180:SDSS J120337.85+180250.4
1173:SDSS J102137.08-005234.8
1166:SDSS J094214.04+200322.1
1153:SDSS J110557.45+093439.5
1146:SDSS J091759.42+672238.7
1139:SDSS J091301.00+305120.0
1112:SDSS J090744.99+024506.8
779:in gravitational theory.
574:satellite dwarf galaxies
272:supermassive black holes
141:supermassive black holes
5184:Asymptotic giant branch
4748:10.1093/mnras/204.3.841
4097:1997A&A...325..613F
3260:2019A&A...627A.104D
2844:1998A&A...330.1047T
2429:2021A&A...652A..76H
2371:2023A&A...674A..28F
1864:1991ARA&A..29..409F
1706:Ursa Major Moving Group
1642:AB Doradus moving group
1597:List of stellar streams
1498:Ursa Major Moving Group
1463:Ursa Major Moving Group
1039:supermassive black hole
1015:supermassive black hole
697:Stellar kinematic types
311:is encapsulated in the
6520:Tidal disruption event
6009:Circumstellar envelope
5243:Luminous blue variable
4276:Faherty, Jacqueline K.
3290:University of Michigan
1625:Known kinematic groups
1466:
1370:Large Magellanic Cloud
1307:
1280:
1133:Large Magellanic Cloud
1131:) – possibly from the
1030:
949:Large Magellanic Cloud
905:
789:Large Magellanic Cloud
744:
671:
652:
635:and a bright limit of
629:
593:
532:
462:
388:
223:local standard of rest
190:
57:
6761:Category:Star systems
6634:Dark globular cluster
6045:Effective temperature
4594:. Sky & Telescope
3510:10.1093/mnrasl/slu189
3376:10.1093/mnras/stz3081
3216:10.1093/mnras/sty1601
2882:Hills, J. G. (1988).
1711:Wolf 630 moving group
1701:TW Hydrae association
1605:is an association of
1461:
1452:Further information:
1418:Velorum T association
1302:
1267:
1071:effect of the boost.
1041:in the center of the
1028:
897:
741:
687:gravitational lensing
672:
653:
630:
591:
533:
463:
389:
201:. The transverse, or
154:
48:
6862:Stellar associations
6515:Planet-hosting stars
6393:With resolved images
6364:Historical brightest
6294:Photometric-standard
6220:Solar radio emission
6014:Eddington luminosity
5794:Triple-alpha process
5732:Thorne–Żytkow object
5107:Young stellar object
4123:Astronomical Journal
3901:Astronomical Journal
3855:Astronomical Journal
3445:(13 November 2019).
3323:(14 November 2019).
3101:Science and Children
2781:10.1093/mnras/stx848
1887:Astronomical Journal
1762:Open cluster remnant
1569:protoplanetary disks
1357:, located about 400
1285:Sidney van den Bergh
1227:Stellar associations
1102:Partial list of HVSs
1051:interstellar objects
707:stellar associations
661:
639:
628:{\displaystyle G=21}
613:
472:
402:
341:
6692:Stellar association
6339:Highest temperature
6110:Color–color diagram
5975:Protoplanetary disk
5779:Proton–proton chain
5457:Chemically peculiar
4957:2005ApJ...634L.181E
4910:2006ApJ...640L..35B
4863:2000ApJ...544L.133H
4822:1954ApJ...119..625B
4739:1983MNRAS.204..841M
4692:2010AJ....139..636W
4639:2003ApJ...599..342S
4553:2013ApJ...772...79A
4487:2008hsf2.book..757T
4369:2018ApJ...865..136G
4310:2018ApJ...856...23G
4234:2018ApJ...856...23G
4166:1965gast.book..111E
4135:1975AJ.....80..503H
4040:2001ApJ...560L..83M
3987:1999AJ....117..354D
3913:1976AJ.....81..840H
3867:1975AJ.....80..212H
3849:Herbst, W. (1976).
3833:1997BAAS...29.1466I
3787:1996ApJ...465..278J
3732:2001MNRAS.328...45M
3675:2006ApJ...643.1160L
3582:2018ApJ...865...15S
3501:2015MNRAS.448L...6T
3207:2018MNRAS.479.2789B
3150:2007ApJ...671.1708B
3067:2010ApJ...719L..23B
3012:2005ApJ...634L.181E
2956:2005ApJ...622L..33B
2900:1988Natur.331..687H
2817:1961BAN....15..265B
2772:2017MNRAS.469.2151B
2705:2011MNRAS.410..304G
2640:2015ApJ...805...92O
2523:1998AmSci..86..264E
2479:1957PASP...69...54J
2311:2019ApJ...873..118W
2230:10.1038/nature06460
2222:2007Natur.450.1020C
2206:(7172): 1020–1025.
2150:1998MNRAS.297..943O
2091:2019ApJ...872..205L
2060:1927BAN.....3..275O
2011:1998MNRAS.298..387D
1950:2010MNRAS.403.1829S
1899:1987AJ.....93..864J
1802:on 5 September 2006
1772:Stellar association
1657:Castor moving group
1634:Local Association (
1575:or directly imaged
1525:Triangulum Australe
1502:Plough / Big Dipper
1496:The closest is the
1483:AB Dor Moving Group
1440:, located 830 ± 50
1410:Lupus T association
1321:, and are known as
1250:Viktor Ambartsumian
1233:Stellar association
968:Southern Hemisphere
964:Northern Hemisphere
890:Hypervelocity stars
843:bow shock hyperbola
761:stellar association
753:interstellar medium
717:High-velocity stars
683:hypervelocity stars
551:velocity dispersion
246:North Galactic Pole
163:radian/s, that is,
6857:Galactic astronomy
6707:Hypervelocity star
6344:Lowest temperature
6095:Photometric system
6065:Absolute magnitude
5999:Circumstellar dust
5612:Stellar black hole
5248:Stellar population
5134:Herbig–Haro object
5019:2023-03-06 at the
4992:2008-05-16 at the
4214:. BANYAN XI.
3625:on 1 November 2014
3330:The New York Times
2593:Galactic Astronomy
2531:10.1511/1998.3.264
2511:American Scientist
2264:www.cosmos.esa.int
1696:MBM 12 association
1467:
1308:
1289:reflection nebulae
1281:
1215:, and kinematics (
1031:
906:
777:three-body problem
745:
667:
648:
625:
594:
570:Mass distributions
528:
458:
384:
309:solar neighborhood
191:
66:stellar kinematics
58:
18:High-velocity star
6852:Stellar astronomy
6769:
6768:
6558:
6557:
6461:Substellar object
6440:Planetary nebulae
5859:Luminous red nova
5769:Deuterium burning
5755:
5754:
5238:Instability strip
5218:Wolf-Rayet nebula
5172:Horizontal branch
5117:Pre-main-sequence
4767:"Stellar Motions"
4518:978-1-58381-671-4
4507:978-1-58381-678-3
3940:"OB Associations"
3292:(13 March 2019).
3244:: A104 (17 pp.).
2894:(6158): 687–689.
2175:Galactic Dynamics
2042:Oort, JH (1927).
1553:Tucana-Horologium
1540:Argus Association
1201:stellar nurseries
1090:) in 2007 by the
943:. As of 2008, 10
670:{\displaystyle 3}
607:globular clusters
564:systemic velocity
547:External galaxies
541:retrograde motion
512:
501:
442:
431:
368:
357:
300:radial velocities
242:galactic rotation
40:peculiar velocity
16:(Redirected from
6874:
6834:
6833:
6832:
6822:
6821:
6820:
6810:
6809:
6808:
6798:
6797:
6796:
6786:
6785:
6777:
6759:
6758:
6671:Planetary system
6629:Globular cluster
6585:
6578:
6571:
6562:
6550:Stars portal
6548:
6547:
6536:
6535:
6192:Planetary system
6115:Strömgren sphere
5987:Asteroseismology
5708:Black hole star
5280:
5206:Planetary nebula
5167:Red-giant branch
5056:
5049:
5042:
5033:
4976:
4950:
4948:astro-ph/0511321
4941:(2): L181–L184.
4929:
4903:
4901:astro-ph/0601580
4882:
4856:
4854:astro-ph/0007436
4835:
4833:
4800:
4798:
4797:
4781:
4779:
4778:
4753:
4752:
4750:
4718:
4712:
4711:
4685:
4665:
4659:
4658:
4624:
4615:
4604:
4603:
4601:
4599:
4587:
4581:
4580:
4546:
4526:
4520:
4511:
4499:
4490: in
4489:
4480:
4464:
4458:
4457:
4439:
4429:
4405:
4399:
4398:
4380:
4362:
4338:
4332:
4331:
4321:
4303:
4270:
4264:
4263:
4245:
4227:
4203:
4194:
4193:
4191:
4190:
4176:
4170:
4169:
4153:
4147:
4146:
4118:
4112:
4111:
4109:
4108:
4099:. Archived from
4090:
4088:astro-ph/9704281
4066:
4060:
4059:
4033:
4031:astro-ph/0108472
4013:
4007:
4006:
3980:
3978:astro-ph/9809227
3960:
3954:
3953:
3951:
3950:
3944:
3936:
3927:
3926:
3924:
3892:
3881:
3880:
3878:
3846:
3837:
3836:
3827:(4): 1466–1467.
3816:
3807:
3806:
3780:
3778:astro-ph/9602060
3760:
3754:
3753:
3743:
3725:
3723:astro-ph/0106537
3701:
3695:
3694:
3668:
3666:astro-ph/0601573
3659:(2): 1160–1165.
3648:
3635:
3634:
3632:
3630:
3610:
3604:
3603:
3593:
3575:
3551:
3545:
3544:
3536:
3530:
3529:
3528:. New Scientist.
3521:
3515:
3514:
3512:
3494:
3470:
3464:
3463:
3461:
3459:
3439:
3433:
3432:
3430:
3428:
3413:
3407:
3406:
3404:
3402:
3396:ScienceAlert.com
3387:
3381:
3380:
3378:
3368:
3348:
3342:
3341:
3339:
3337:
3317:
3311:
3310:
3308:
3306:
3286:
3280:
3279:
3253:
3227:
3221:
3220:
3218:
3200:
3191:(2): 2789–2795.
3176:
3170:
3169:
3143:
3134:(2): 1708–1716.
3122:
3113:
3112:
3110:
3108:
3103:: 14. 1 Sep 2017
3093:
3087:
3086:
3060:
3038:
3032:
3031:
3005:
3003:astro-ph/0511321
2996:(2): L181–L184.
2985:
2976:
2975:
2949:
2947:astro-ph/0501177
2929:
2920:
2919:
2908:10.1038/331687a0
2879:
2873:
2872:
2870:
2869:
2854:
2848:
2847:
2827:
2821:
2820:
2800:
2794:
2793:
2783:
2765:
2756:(2): 2151–2162.
2741:
2735:
2734:
2716:
2698:
2674:
2668:
2667:
2633:
2613:
2607:
2606:
2588:
2582:
2581:
2560:
2554:
2553:
2551:
2550:
2541:. Archived from
2502:
2493:
2492:
2490:
2458:
2449:
2448:
2422:
2397:
2391:
2390:
2364:
2339:
2333:
2332:
2322:
2304:
2280:
2274:
2273:
2271:
2270:
2256:
2250:
2249:
2215:
2195:
2189:
2188:
2170:
2164:
2163:
2161:
2143:
2141:astro-ph/9802034
2119:
2113:
2112:
2102:
2070:
2064:
2063:
2039:
2033:
2032:
2022:
2004:
2002:astro-ph/9710077
1978:
1972:
1971:
1961:
1943:
1934:(4): 1829–1833.
1917:
1911:
1910:
1882:
1876:
1875:
1847:
1841:
1840:
1838:
1837:
1818:
1812:
1811:
1809:
1807:
1787:
1615:globular cluster
1613:that was once a
1374:Andromeda Galaxy
1197:molecular clouds
1187:Kinematic groups
1008:
951:rather than the
886:
884:
879:
877:
873:
871:
676:
674:
673:
668:
657:
655:
654:
649:
634:
632:
631:
626:
602:stellar parallax
537:
535:
534:
529:
527:
526:
518:
510:
509:
499:
492:
491:
490:
467:
465:
464:
459:
457:
456:
448:
440:
439:
429:
422:
421:
420:
396:Root mean square
393:
391:
390:
385:
383:
382:
374:
366:
365:
355:
348:
217:relative to the
129:stellar dynamics
21:
6882:
6881:
6877:
6876:
6875:
6873:
6872:
6871:
6842:
6841:
6840:
6830:
6828:
6818:
6816:
6806:
6804:
6794:
6792:
6780:
6772:
6770:
6765:
6747:
6716:Visual grouping
6711:
6675:
6597:
6589:
6559:
6554:
6542:
6524:
6449:
6418:Milky Way novae
6354:Smallest volume
6298:
6279:Radial velocity
6202:
6196:
6148:Common envelope
6124:
6023:
5992:Helioseismology
5963:Bipolar outflow
5904:Microturbulence
5899:Convection zone
5880:
5774:Lithium burning
5761:Nucleosynthesis
5751:
5633:
5542:
5269:
5148:
5097:Molecular cloud
5078:
5065:
5060:
5021:Wayback Machine
4994:Wayback Machine
4983:
4932:
4885:
4838:
4803:
4795:
4793:
4784:
4776:
4774:
4764:
4761:
4759:Further reading
4756:
4720:
4719:
4715:
4667:
4666:
4662:
4622:
4617:
4616:
4607:
4597:
4595:
4589:
4588:
4584:
4528:
4527:
4523:
4508:
4491:
4466:
4465:
4461:
4407:
4406:
4402:
4340:
4339:
4335:
4273:
4271:
4267:
4205:
4204:
4197:
4188:
4186:
4180:"BANYAN Σ"
4178:
4177:
4173:
4155:
4154:
4150:
4120:
4119:
4115:
4106:
4104:
4068:
4067:
4063:
4015:
4014:
4010:
3962:
3961:
3957:
3948:
3946:
3942:
3938:
3937:
3930:
3894:
3893:
3884:
3848:
3847:
3840:
3818:
3817:
3810:
3762:
3761:
3757:
3703:
3702:
3698:
3650:
3649:
3638:
3628:
3626:
3612:
3611:
3607:
3553:
3552:
3548:
3538:
3537:
3533:
3523:
3522:
3518:
3472:
3471:
3467:
3457:
3455:
3441:
3440:
3436:
3426:
3424:
3415:
3414:
3410:
3400:
3398:
3389:
3388:
3384:
3350:
3349:
3345:
3335:
3333:
3321:Overbye, Dennis
3319:
3318:
3314:
3304:
3302:
3288:
3287:
3283:
3229:
3228:
3224:
3178:
3177:
3173:
3124:
3123:
3116:
3106:
3104:
3095:
3094:
3090:
3040:
3039:
3035:
2987:
2986:
2979:
2931:
2930:
2923:
2881:
2880:
2876:
2867:
2865:
2856:
2855:
2851:
2829:
2828:
2824:
2802:
2801:
2797:
2743:
2742:
2738:
2676:
2675:
2671:
2615:
2614:
2610:
2603:
2590:
2589:
2585:
2578:
2562:
2561:
2557:
2548:
2546:
2504:
2503:
2496:
2460:
2459:
2452:
2399:
2398:
2394:
2341:
2340:
2336:
2282:
2281:
2277:
2268:
2266:
2258:
2257:
2253:
2197:
2196:
2192:
2185:
2172:
2171:
2167:
2121:
2120:
2116:
2072:
2071:
2067:
2041:
2040:
2036:
1980:
1979:
1975:
1919:
1918:
1914:
1884:
1883:
1879:
1849:
1848:
1844:
1835:
1833:
1820:
1819:
1815:
1805:
1803:
1789:
1788:
1784:
1780:
1735:
1730:
1675:Hercules stream
1627:
1599:
1593:
1591:Stellar streams
1581:Beta Pictoris b
1513:η Ursae Majoris
1475:kinematic group
1456:
1450:
1426:
1382:
1327:molecular cloud
1323:OB associations
1297:
1295:OB associations
1262:
1235:
1229:
1217:radial velocity
1189:
1104:
1060:Known HVSs are
1023:
1006:
986:In March 2019,
933:Margaret Geller
918:escape velocity
892:
882:
881:
875:
874:
869:
868:
857:
851:
798:explosion in a
736:
719:
699:
685:, cosmological
659:
658:
637:
636:
611:
610:
586:
513:
476:
470:
469:
443:
406:
400:
399:
369:
339:
338:
263:
227:Galactic Center
195:radial velocity
187:
176:
168:
149:
80:through space.
43:
32:radial velocity
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
6880:
6878:
6870:
6869:
6864:
6859:
6854:
6844:
6843:
6839:
6838:
6826:
6814:
6802:
6790:
6767:
6766:
6764:
6763:
6752:
6749:
6748:
6746:
6745:
6740:
6735:
6730:
6725:
6719:
6717:
6713:
6712:
6710:
6709:
6704:
6699:
6694:
6689:
6687:Stellar stream
6683:
6681:
6677:
6676:
6674:
6673:
6668:
6663:
6658:
6653:
6652:
6651:
6646:
6641:
6636:
6631:
6626:
6616:
6611:
6605:
6603:
6599:
6598:
6590:
6588:
6587:
6580:
6573:
6565:
6556:
6555:
6553:
6552:
6540:
6529:
6526:
6525:
6523:
6522:
6517:
6512:
6507:
6502:
6497:
6492:
6487:
6486:
6485:
6480:
6479:
6478:
6473:
6457:
6455:
6451:
6450:
6448:
6447:
6442:
6437:
6436:
6435:
6430:
6420:
6415:
6410:
6405:
6400:
6395:
6390:
6389:
6388:
6383:
6382:
6381:
6371:
6366:
6361:
6356:
6351:
6349:Largest volume
6346:
6341:
6336:
6326:
6325:
6324:
6319:
6308:
6306:
6300:
6299:
6297:
6296:
6291:
6286:
6281:
6276:
6275:
6274:
6269:
6264:
6254:
6249:
6244:
6239:
6234:
6233:
6232:
6227:
6222:
6217:
6206:
6204:
6198:
6197:
6195:
6194:
6189:
6188:
6187:
6182:
6177:
6167:
6162:
6161:
6160:
6155:
6150:
6145:
6134:
6132:
6126:
6125:
6123:
6122:
6117:
6112:
6107:
6102:
6097:
6092:
6087:
6082:
6077:
6072:
6067:
6062:
6060:Magnetic field
6057:
6052:
6047:
6042:
6037:
6031:
6029:
6025:
6024:
6022:
6021:
6016:
6011:
6006:
6001:
5996:
5995:
5994:
5984:
5983:
5982:
5977:
5970:Accretion disk
5967:
5966:
5965:
5960:
5950:
5949:
5948:
5946:Alfvén surface
5943:
5941:Stellar corona
5938:
5933:
5928:
5918:
5916:Radiation zone
5913:
5912:
5911:
5906:
5896:
5890:
5888:
5882:
5881:
5879:
5878:
5873:
5872:
5871:
5866:
5861:
5856:
5851:
5841:
5836:
5831:
5826:
5821:
5816:
5811:
5806:
5801:
5796:
5791:
5786:
5781:
5776:
5771:
5765:
5763:
5757:
5756:
5753:
5752:
5750:
5749:
5744:
5739:
5734:
5729:
5724:
5723:
5722:
5717:
5714:
5706:
5705:
5704:
5699:
5694:
5689:
5684:
5679:
5674:
5669:
5664:
5654:
5649:
5643:
5641:
5635:
5634:
5632:
5631:
5626:
5625:
5624:
5614:
5609:
5608:
5607:
5602:
5601:
5600:
5595:
5585:
5575:
5574:
5573:
5563:
5558:
5552:
5550:
5544:
5543:
5541:
5540:
5538:Blue straggler
5535:
5534:
5533:
5523:
5518:
5517:
5516:
5506:
5505:
5504:
5499:
5494:
5489:
5484:
5479:
5474:
5469:
5464:
5454:
5449:
5448:
5447:
5442:
5437:
5427:
5426:
5425:
5415:
5414:
5413:
5408:
5403:
5393:
5388:
5387:
5386:
5381:
5376:
5366:
5361:
5356:
5351:
5350:
5349:
5344:
5334:
5333:
5332:
5327:
5322:
5317:
5312:
5307:
5302:
5296:Main sequence
5294:
5289:
5283:
5277:
5275:Classification
5271:
5270:
5268:
5267:
5266:
5265:
5260:
5250:
5245:
5240:
5235:
5230:
5225:
5220:
5215:
5214:
5213:
5211:Protoplanetary
5203:
5198:
5197:
5196:
5191:
5181:
5180:
5179:
5169:
5164:
5158:
5156:
5150:
5149:
5147:
5146:
5141:
5136:
5131:
5130:
5129:
5124:
5119:
5114:
5104:
5099:
5094:
5088:
5086:
5080:
5079:
5077:
5076:
5070:
5067:
5066:
5061:
5059:
5058:
5051:
5044:
5036:
5030:
5029:
5023:
5011:
5006:
5001:
4996:
4982:
4981:External links
4979:
4978:
4977:
4965:10.1086/498940
4930:
4918:10.1086/503279
4894:(1): L35–L38.
4883:
4871:10.1086/317315
4836:
4831:10.1086/145866
4801:
4782:
4760:
4757:
4755:
4754:
4733:(3): 841–852.
4713:
4676:(2): 636–645.
4660:
4647:10.1086/379194
4633:(1): 342–350.
4605:
4582:
4521:
4506:
4459:
4400:
4333:
4265:
4195:
4171:
4148:
4143:10.1086/111771
4113:
4061:
4048:10.1086/324016
4024:(1): L83–L86.
4008:
3995:10.1086/300682
3971:(1): 354–399.
3955:
3928:
3922:10.1086/111963
3882:
3876:10.1086/111734
3838:
3808:
3795:10.1086/177418
3755:
3696:
3683:10.1086/503183
3636:
3605:
3546:
3531:
3516:
3465:
3434:
3408:
3382:
3343:
3312:
3281:
3222:
3171:
3158:10.1086/523642
3114:
3088:
3033:
3020:10.1086/498940
2977:
2964:10.1086/429378
2940:(1): L33–L36.
2921:
2874:
2864:. Jan 27, 2006
2849:
2822:
2795:
2736:
2689:(1): 304–312.
2669:
2608:
2602:978-0691004020
2601:
2583:
2577:978-0521671866
2576:
2555:
2494:
2488:10.1086/127012
2450:
2392:
2334:
2275:
2251:
2190:
2183:
2165:
2134:(3): 943–952.
2114:
2065:
2034:
1995:(2): 387–394.
1973:
1912:
1907:10.1086/114370
1893:(2): 864–867.
1877:
1858:(1): 409–445.
1842:
1813:
1781:
1779:
1776:
1775:
1774:
1769:
1764:
1759:
1757:n-body problem
1754:
1749:
1741:
1734:
1731:
1729:
1728:
1723:
1718:
1713:
1708:
1703:
1698:
1693:
1688:
1682:
1677:
1672:
1669:
1664:
1659:
1654:
1649:
1644:
1639:
1631:
1626:
1623:
1603:stellar stream
1592:
1589:
1449:
1446:
1444:from the Sun.
1434:R associations
1425:
1424:R associations
1422:
1394:T associations
1381:
1380:T associations
1378:
1312:spectral class
1296:
1293:
1261:
1258:
1231:Main article:
1228:
1225:
1188:
1185:
1184:
1183:
1176:
1169:
1162:
1156:
1149:
1142:
1135:
1125:
1115:
1103:
1100:
1088:speed of light
1069:slingshot-like
1022:
1019:
1011:Sagittarius A*
959:from the Sun.
891:
888:
865:Kapteyn's Star
850:
847:
832:Barnard's Loop
804:
803:
792:
780:
772:stellar system
735:
732:
718:
715:
698:
695:
666:
647:
644:
624:
621:
618:
585:
579:
578:
577:
567:
544:
525:
522:
517:
508:
505:
498:
495:
489:
486:
483:
479:
455:
452:
447:
438:
435:
428:
425:
419:
416:
413:
409:
381:
378:
373:
364:
361:
354:
351:
347:
316:
313:Oort constants
296:proper motions
262:
259:
254:
253:
209:means such as
199:Doppler effect
185:
174:
166:
148:
147:Space velocity
145:
76:or motions of
50:Barnard's Star
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
6879:
6868:
6865:
6863:
6860:
6858:
6855:
6853:
6850:
6849:
6847:
6837:
6827:
6825:
6815:
6813:
6803:
6801:
6791:
6789:
6784:
6779:
6775:
6762:
6754:
6753:
6750:
6744:
6743:Constellation
6741:
6739:
6736:
6734:
6731:
6729:
6728:Multiple star
6726:
6724:
6721:
6720:
6718:
6714:
6708:
6705:
6703:
6700:
6698:
6695:
6693:
6690:
6688:
6685:
6684:
6682:
6678:
6672:
6669:
6667:
6664:
6662:
6659:
6657:
6654:
6650:
6647:
6645:
6642:
6640:
6637:
6635:
6632:
6630:
6627:
6625:
6622:
6621:
6620:
6617:
6615:
6612:
6610:
6607:
6606:
6604:
6600:
6596:
6593:
6586:
6581:
6579:
6574:
6572:
6567:
6566:
6563:
6551:
6546:
6541:
6539:
6531:
6530:
6527:
6521:
6518:
6516:
6513:
6511:
6510:Intergalactic
6508:
6506:
6503:
6501:
6498:
6496:
6493:
6491:
6490:Galactic year
6488:
6484:
6481:
6477:
6474:
6472:
6469:
6468:
6467:
6464:
6463:
6462:
6459:
6458:
6456:
6452:
6446:
6443:
6441:
6438:
6434:
6431:
6429:
6426:
6425:
6424:
6421:
6419:
6416:
6414:
6411:
6409:
6406:
6404:
6401:
6399:
6396:
6394:
6391:
6387:
6384:
6380:
6377:
6376:
6375:
6372:
6370:
6369:Most luminous
6367:
6365:
6362:
6360:
6357:
6355:
6352:
6350:
6347:
6345:
6342:
6340:
6337:
6335:
6332:
6331:
6330:
6327:
6323:
6320:
6318:
6315:
6314:
6313:
6310:
6309:
6307:
6305:
6301:
6295:
6292:
6290:
6287:
6285:
6284:Proper motion
6282:
6280:
6277:
6273:
6270:
6268:
6265:
6263:
6260:
6259:
6258:
6255:
6253:
6250:
6248:
6247:Constellation
6245:
6243:
6240:
6238:
6235:
6231:
6228:
6226:
6223:
6221:
6218:
6216:
6215:Solar eclipse
6213:
6212:
6211:
6208:
6207:
6205:
6201:Earth-centric
6199:
6193:
6190:
6186:
6183:
6181:
6178:
6176:
6173:
6172:
6171:
6168:
6166:
6163:
6159:
6156:
6154:
6151:
6149:
6146:
6144:
6141:
6140:
6139:
6136:
6135:
6133:
6131:
6127:
6121:
6118:
6116:
6113:
6111:
6108:
6106:
6103:
6101:
6098:
6096:
6093:
6091:
6088:
6086:
6083:
6081:
6078:
6076:
6073:
6071:
6068:
6066:
6063:
6061:
6058:
6056:
6053:
6051:
6048:
6046:
6043:
6041:
6038:
6036:
6033:
6032:
6030:
6026:
6020:
6017:
6015:
6012:
6010:
6007:
6005:
6002:
6000:
5997:
5993:
5990:
5989:
5988:
5985:
5981:
5978:
5976:
5973:
5972:
5971:
5968:
5964:
5961:
5959:
5956:
5955:
5954:
5951:
5947:
5944:
5942:
5939:
5937:
5934:
5932:
5929:
5927:
5924:
5923:
5922:
5919:
5917:
5914:
5910:
5907:
5905:
5902:
5901:
5900:
5897:
5895:
5892:
5891:
5889:
5887:
5883:
5877:
5874:
5870:
5867:
5865:
5862:
5860:
5857:
5855:
5852:
5850:
5847:
5846:
5845:
5842:
5840:
5837:
5835:
5832:
5830:
5827:
5825:
5822:
5820:
5817:
5815:
5812:
5810:
5807:
5805:
5802:
5800:
5799:Alpha process
5797:
5795:
5792:
5790:
5787:
5785:
5782:
5780:
5777:
5775:
5772:
5770:
5767:
5766:
5764:
5762:
5758:
5748:
5745:
5743:
5740:
5738:
5735:
5733:
5730:
5728:
5725:
5721:
5718:
5715:
5713:
5710:
5709:
5707:
5703:
5700:
5698:
5695:
5693:
5690:
5688:
5685:
5683:
5680:
5678:
5675:
5673:
5670:
5668:
5665:
5663:
5660:
5659:
5658:
5655:
5653:
5650:
5648:
5645:
5644:
5642:
5640:
5636:
5630:
5627:
5623:
5620:
5619:
5618:
5615:
5613:
5610:
5606:
5603:
5599:
5596:
5594:
5591:
5590:
5589:
5586:
5584:
5581:
5580:
5579:
5576:
5572:
5571:Helium planet
5569:
5568:
5567:
5564:
5562:
5561:Parker's star
5559:
5557:
5554:
5553:
5551:
5549:
5545:
5539:
5536:
5532:
5529:
5528:
5527:
5524:
5522:
5519:
5515:
5512:
5511:
5510:
5507:
5503:
5500:
5498:
5495:
5493:
5492:Lambda Boötis
5490:
5488:
5485:
5483:
5480:
5478:
5475:
5473:
5470:
5468:
5465:
5463:
5460:
5459:
5458:
5455:
5453:
5450:
5446:
5443:
5441:
5438:
5436:
5433:
5432:
5431:
5428:
5424:
5421:
5420:
5419:
5416:
5412:
5409:
5407:
5404:
5402:
5399:
5398:
5397:
5394:
5392:
5389:
5385:
5382:
5380:
5377:
5375:
5372:
5371:
5370:
5367:
5365:
5362:
5360:
5357:
5355:
5352:
5348:
5345:
5343:
5340:
5339:
5338:
5335:
5331:
5328:
5326:
5323:
5321:
5318:
5316:
5313:
5311:
5308:
5306:
5303:
5301:
5298:
5297:
5295:
5293:
5290:
5288:
5285:
5284:
5281:
5278:
5276:
5272:
5264:
5261:
5259:
5258:Superluminous
5256:
5255:
5254:
5251:
5249:
5246:
5244:
5241:
5239:
5236:
5234:
5231:
5229:
5226:
5224:
5221:
5219:
5216:
5212:
5209:
5208:
5207:
5204:
5202:
5199:
5195:
5192:
5190:
5187:
5186:
5185:
5182:
5178:
5175:
5174:
5173:
5170:
5168:
5165:
5163:
5162:Main sequence
5160:
5159:
5157:
5155:
5151:
5145:
5142:
5140:
5139:Hayashi track
5137:
5135:
5132:
5128:
5125:
5123:
5120:
5118:
5115:
5113:
5110:
5109:
5108:
5105:
5103:
5100:
5098:
5095:
5093:
5090:
5089:
5087:
5085:
5081:
5075:
5072:
5071:
5068:
5064:
5057:
5052:
5050:
5045:
5043:
5038:
5037:
5034:
5027:
5024:
5022:
5018:
5015:
5012:
5010:
5007:
5005:
5002:
5000:
4997:
4995:
4991:
4988:
4985:
4984:
4980:
4974:
4970:
4966:
4962:
4958:
4954:
4949:
4944:
4940:
4936:
4931:
4927:
4923:
4919:
4915:
4911:
4907:
4902:
4897:
4893:
4889:
4884:
4880:
4876:
4872:
4868:
4864:
4860:
4855:
4850:
4846:
4842:
4837:
4832:
4827:
4823:
4819:
4815:
4811:
4807:
4802:
4792:on 2008-02-16
4791:
4787:
4783:
4773:on 2012-01-25
4772:
4768:
4763:
4762:
4758:
4749:
4744:
4740:
4736:
4732:
4728:
4724:
4717:
4714:
4709:
4705:
4701:
4697:
4693:
4689:
4684:
4679:
4675:
4671:
4664:
4661:
4656:
4652:
4648:
4644:
4640:
4636:
4632:
4628:
4621:
4614:
4612:
4610:
4606:
4593:
4586:
4583:
4578:
4574:
4570:
4566:
4562:
4558:
4554:
4550:
4545:
4540:
4536:
4532:
4525:
4522:
4519:
4515:
4509:
4503:
4498:
4497:
4488:
4484:
4479:
4474:
4470:
4463:
4460:
4455:
4451:
4447:
4443:
4438:
4433:
4428:
4423:
4419:
4415:
4411:
4404:
4401:
4396:
4392:
4388:
4384:
4379:
4374:
4370:
4366:
4361:
4356:
4352:
4348:
4344:
4337:
4334:
4329:
4325:
4320:
4315:
4311:
4307:
4302:
4297:
4293:
4289:
4285:
4283:
4277:
4269:
4266:
4261:
4257:
4253:
4249:
4244:
4239:
4235:
4231:
4226:
4221:
4217:
4213:
4209:
4202:
4200:
4196:
4185:
4181:
4175:
4172:
4167:
4163:
4159:
4152:
4149:
4144:
4140:
4136:
4132:
4128:
4124:
4117:
4114:
4103:on 2010-08-07
4102:
4098:
4094:
4089:
4084:
4080:
4076:
4072:
4065:
4062:
4057:
4053:
4049:
4045:
4041:
4037:
4032:
4027:
4023:
4019:
4012:
4009:
4004:
4000:
3996:
3992:
3988:
3984:
3979:
3974:
3970:
3966:
3959:
3956:
3941:
3935:
3933:
3929:
3923:
3918:
3914:
3910:
3906:
3902:
3898:
3891:
3889:
3887:
3883:
3877:
3872:
3868:
3864:
3860:
3856:
3852:
3845:
3843:
3839:
3834:
3830:
3826:
3822:
3815:
3813:
3809:
3804:
3800:
3796:
3792:
3788:
3784:
3779:
3774:
3770:
3766:
3759:
3756:
3751:
3747:
3742:
3737:
3733:
3729:
3724:
3719:
3715:
3711:
3707:
3700:
3697:
3692:
3688:
3684:
3680:
3676:
3672:
3667:
3662:
3658:
3654:
3647:
3645:
3643:
3641:
3637:
3624:
3620:
3616:
3609:
3606:
3601:
3597:
3592:
3587:
3583:
3579:
3574:
3569:
3565:
3561:
3557:
3550:
3547:
3542:
3535:
3532:
3527:
3520:
3517:
3511:
3506:
3502:
3498:
3493:
3488:
3485:(1): L6–L10.
3484:
3480:
3476:
3469:
3466:
3454:
3453:
3452:Bad Astronomy
3448:
3444:
3438:
3435:
3423:
3419:
3412:
3409:
3397:
3393:
3386:
3383:
3377:
3372:
3367:
3362:
3358:
3354:
3347:
3344:
3332:
3331:
3326:
3322:
3316:
3313:
3301:
3300:
3295:
3291:
3285:
3282:
3277:
3273:
3269:
3265:
3261:
3257:
3252:
3247:
3243:
3239:
3238:
3233:
3226:
3223:
3217:
3212:
3208:
3204:
3199:
3194:
3190:
3186:
3182:
3175:
3172:
3167:
3163:
3159:
3155:
3151:
3147:
3142:
3137:
3133:
3129:
3121:
3119:
3115:
3102:
3098:
3092:
3089:
3084:
3080:
3076:
3072:
3068:
3064:
3059:
3054:
3050:
3046:
3045:
3037:
3034:
3029:
3025:
3021:
3017:
3013:
3009:
3004:
2999:
2995:
2991:
2984:
2982:
2978:
2973:
2969:
2965:
2961:
2957:
2953:
2948:
2943:
2939:
2935:
2928:
2926:
2922:
2917:
2913:
2909:
2905:
2901:
2897:
2893:
2889:
2885:
2878:
2875:
2863:
2859:
2853:
2850:
2845:
2841:
2838:: 1047–1059.
2837:
2833:
2826:
2823:
2818:
2814:
2810:
2806:
2799:
2796:
2791:
2787:
2782:
2777:
2773:
2769:
2764:
2759:
2755:
2751:
2747:
2740:
2737:
2732:
2728:
2724:
2720:
2715:
2710:
2706:
2702:
2697:
2692:
2688:
2684:
2680:
2673:
2670:
2665:
2661:
2657:
2653:
2649:
2645:
2641:
2637:
2632:
2627:
2623:
2619:
2612:
2609:
2604:
2598:
2594:
2587:
2584:
2579:
2573:
2569:
2565:
2564:Sparke, L. S.
2559:
2556:
2545:on 2016-07-01
2544:
2540:
2536:
2532:
2528:
2524:
2520:
2516:
2512:
2508:
2501:
2499:
2495:
2489:
2484:
2480:
2476:
2472:
2468:
2464:
2457:
2455:
2451:
2446:
2442:
2438:
2434:
2430:
2426:
2421:
2416:
2412:
2408:
2404:
2396:
2393:
2388:
2384:
2380:
2376:
2372:
2368:
2363:
2358:
2354:
2350:
2346:
2338:
2335:
2330:
2326:
2321:
2316:
2312:
2308:
2303:
2298:
2294:
2290:
2286:
2279:
2276:
2265:
2261:
2255:
2252:
2247:
2243:
2239:
2235:
2231:
2227:
2223:
2219:
2214:
2209:
2205:
2201:
2194:
2191:
2186:
2184:9780691130279
2180:
2176:
2169:
2166:
2160:
2155:
2151:
2147:
2142:
2137:
2133:
2129:
2125:
2118:
2115:
2110:
2106:
2101:
2096:
2092:
2088:
2084:
2080:
2076:
2069:
2066:
2061:
2057:
2053:
2049:
2045:
2038:
2035:
2030:
2026:
2021:
2016:
2012:
2008:
2003:
1998:
1994:
1990:
1989:
1984:
1977:
1974:
1969:
1965:
1960:
1955:
1951:
1947:
1942:
1937:
1933:
1929:
1928:
1923:
1916:
1913:
1908:
1904:
1900:
1896:
1892:
1888:
1881:
1878:
1873:
1869:
1865:
1861:
1857:
1853:
1846:
1843:
1832:on 2013-06-06
1831:
1827:
1823:
1817:
1814:
1801:
1797:
1793:
1786:
1783:
1777:
1773:
1770:
1768:
1765:
1763:
1760:
1758:
1755:
1753:
1750:
1748:
1746:
1742:
1740:
1737:
1736:
1732:
1727:
1724:
1722:
1719:
1717:
1714:
1712:
1709:
1707:
1704:
1702:
1699:
1697:
1694:
1692:
1691:Kapteyn group
1689:
1686:
1683:
1681:
1680:Hyades Stream
1678:
1676:
1673:
1670:
1668:
1665:
1663:
1660:
1658:
1655:
1653:
1650:
1648:
1645:
1643:
1640:
1638:moving group)
1637:
1633:
1632:
1630:
1624:
1622:
1620:
1616:
1612:
1608:
1604:
1598:
1590:
1588:
1586:
1582:
1578:
1574:
1570:
1566:
1562:
1557:
1555:
1554:
1549:
1545:
1541:
1537:
1533:
1532:Volans-Carina
1528:
1526:
1522:
1518:
1514:
1510:
1506:
1503:
1499:
1495:
1491:
1486:
1484:
1480:
1476:
1472:
1464:
1460:
1455:
1448:Moving groups
1447:
1445:
1443:
1439:
1435:
1431:
1423:
1421:
1419:
1415:
1411:
1407:
1403:
1399:
1395:
1391:
1390:main sequence
1387:
1386:T Tauri stars
1379:
1377:
1375:
1371:
1366:
1364:
1360:
1356:
1352:
1348:
1343:
1341:
1336:
1332:
1331:O-class stars
1328:
1324:
1320:
1316:
1313:
1305:
1301:
1294:
1292:
1290:
1286:
1279:
1275:
1271:
1266:
1259:
1257:
1255:
1254:constellation
1251:
1247:
1242:
1240:
1234:
1226:
1224:
1222:
1221:proper motion
1218:
1214:
1209:
1206:
1205:open clusters
1202:
1198:
1194:
1186:
1181:
1177:
1174:
1170:
1167:
1163:
1160:
1157:
1154:
1150:
1147:
1143:
1140:
1136:
1134:
1130:
1126:
1123:
1120:
1116:
1113:
1109:
1108:
1107:
1101:
1099:
1095:
1093:
1089:
1085:
1084:RX J0822-4300
1081:
1077:
1076:neutron stars
1072:
1070:
1065:
1063:
1062:main-sequence
1058:
1054:
1052:
1048:
1044:
1040:
1036:
1027:
1020:
1018:
1016:
1012:
1004:
1003:constellation
1000:
996:
991:
989:
984:
982:
981:
976:
971:
969:
965:
960:
958:
954:
950:
946:
942:
941:Michael Kurtz
938:
934:
930:
929:Jack G. Hills
926:
924:
919:
915:
911:
903:
902:
896:
889:
887:
866:
861:
856:
855:Galactic halo
848:
846:
844:
840:
835:
833:
829:
825:
821:
817:
813:
808:
801:
800:multiple star
797:
793:
790:
786:
781:
778:
773:
769:
768:
767:
764:
762:
758:
757:proper motion
754:
750:
740:
734:Runaway stars
733:
731:
728:
724:
716:
714:
710:
708:
704:
696:
694:
692:
688:
684:
680:
664:
645:
642:
622:
619:
616:
608:
603:
599:
596:In 2018, the
590:
584:
580:
575:
571:
568:
565:
561:
557:
552:
548:
545:
542:
523:
520:
496:
493:
453:
450:
426:
423:
397:
379:
376:
352:
349:
336:
332:
328:
324:
320:
317:
314:
310:
306:
301:
297:
293:
290:
289:
288:
285:
281:
277:
273:
268:
267:astrophysical
260:
258:
251:
250:
249:
247:
243:
239:
235:
230:
228:
224:
220:
216:
215:actual motion
212:
208:
204:
203:proper motion
200:
196:
188:
181:
177:
170:
162:
158:
153:
146:
144:
142:
138:
134:
130:
125:
123:
119:
114:
110:
106:
102:
98:
94:
90:
86:
81:
79:
75:
71:
70:observational
67:
63:
55:
54:proper motion
51:
47:
41:
37:
36:proper motion
33:
19:
6836:Solar System
6702:Runaway star
6697:Moving group
6696:
6639:Open cluster
6619:Star cluster
6614:Dwarf galaxy
6413:White dwarfs
6403:Brown dwarfs
6386:Most distant
6334:Most massive
6312:Proper names
6272:Photographic
6225:Solar System
6203:observations
6130:Star systems
6054:
5953:Stellar wind
5936:Chromosphere
5909:Oscillations
5789:Helium flash
5639:Hypothetical
5617:X-ray binary
5556:Compact star
5391:Bright giant
5144:Henyey track
5122:Herbig Ae/Be
4938:
4934:
4891:
4887:
4844:
4840:
4813:
4809:
4794:. Retrieved
4790:the original
4775:. Retrieved
4771:the original
4730:
4726:
4716:
4673:
4669:
4663:
4630:
4626:
4598:December 13,
4596:. Retrieved
4585:
4534:
4530:
4524:
4495:
4468:
4462:
4417:
4413:
4403:
4350:
4346:
4336:
4291:
4287:
4281:
4268:
4215:
4211:
4187:. Retrieved
4183:
4174:
4157:
4151:
4126:
4122:
4116:
4105:. Retrieved
4101:the original
4078:
4074:
4064:
4021:
4017:
4011:
3968:
3964:
3958:
3947:. Retrieved
3904:
3900:
3858:
3854:
3824:
3820:
3768:
3764:
3758:
3716:(1): 45–63.
3713:
3709:
3699:
3656:
3652:
3627:. Retrieved
3623:the original
3618:
3608:
3566:(1): 15–28.
3563:
3559:
3549:
3534:
3519:
3482:
3478:
3468:
3456:. Retrieved
3450:
3437:
3425:. Retrieved
3422:NewAtlas.com
3421:
3411:
3399:. Retrieved
3395:
3385:
3356:
3346:
3334:. Retrieved
3328:
3315:
3303:. Retrieved
3297:
3284:
3241:
3235:
3231:
3225:
3188:
3184:
3174:
3131:
3127:
3105:. Retrieved
3100:
3091:
3048:
3042:
3036:
2993:
2989:
2937:
2933:
2891:
2887:
2877:
2866:. Retrieved
2861:
2852:
2835:
2831:
2825:
2808:
2804:
2798:
2753:
2749:
2739:
2686:
2682:
2672:
2621:
2617:
2611:
2592:
2586:
2567:
2558:
2547:. Retrieved
2543:the original
2514:
2510:
2470:
2466:
2410:
2406:
2395:
2352:
2348:
2337:
2292:
2288:
2278:
2267:. Retrieved
2263:
2254:
2203:
2199:
2193:
2174:
2168:
2131:
2127:
2117:
2082:
2078:
2068:
2051:
2047:
2037:
1992:
1986:
1976:
1931:
1925:
1915:
1890:
1886:
1880:
1855:
1851:
1845:
1834:. Retrieved
1830:the original
1825:
1816:
1804:. Retrieved
1800:the original
1795:
1785:
1747:(spacecraft)
1744:
1628:
1619:dwarf galaxy
1602:
1600:
1565:brown dwarfs
1558:
1552:
1547:
1543:
1529:
1521:declinations
1493:
1487:
1474:
1471:moving group
1470:
1468:
1438:Monoceros R2
1433:
1427:
1393:
1383:
1367:
1344:
1322:
1309:
1282:
1243:
1239:star cluster
1236:
1210:
1193:open cluster
1190:
1129:HE 0437-5439
1118:
1105:
1096:
1073:
1066:
1059:
1055:
1035:binary stars
1032:
992:
985:
979:
972:
961:
945:unbound HVSs
937:Scott Kenyon
927:
913:
909:
907:
899:
878:= −288 km/s,
862:
858:
836:
828:Orion Nebula
809:
805:
765:
746:
720:
711:
700:
595:
582:
569:
546:
394:and an RMS (
335:bulge or bar
318:
291:
264:
255:
231:
214:
192:
183:
179:
172:
164:
160:
156:
126:
118:binary stars
113:stellar halo
82:
65:
59:
6824:Outer space
6812:Spaceflight
6723:Double star
6666:Binary star
6661:Star system
6466:Brown dwarf
6242:Circumpolar
6120:Kraft break
6100:Color index
6075:Metallicity
6035:Designation
6004:Cosmic dust
5926:Photosphere
5692:Dark-energy
5667:Electroweak
5652:Black dwarf
5583:Radio-quiet
5566:White dwarf
5452:White dwarf
5102:Bok globule
4847:(2): L133.
4081:: 613–622.
3861:: 212–226.
3619:News Center
3543:. Newswise.
3477:. Letters.
3458:19 November
3443:Plait, Phil
3427:18 November
3401:18 November
3336:18 November
3234:DR2 data".
2862:Space Daily
2473:(406): 54.
2054:: 275–282.
1609:orbiting a
1507:except for
1432:are called
1359:light-years
1248:astronomer
1213:metallicity
1053:by a star.
1001:(or Crane)
988:LAMOST-HVS1
885:= −52 km/s.
872:= +19 km/s,
820:Mu Columbae
703:metallicity
560:blueshifted
294:: From the
280:dark matter
207:astrometric
137:dark matter
6846:Categories
6733:Star cloud
6428:Candidates
6423:Supernovae
6408:Red dwarfs
6267:Extinction
6055:Kinematics
6050:Luminosity
6028:Properties
5921:Atmosphere
5819:Si burning
5809:Ne burning
5747:White hole
5720:Quasi-star
5647:Blue dwarf
5502:Technetium
5418:Hypergiant
5396:Supergiant
4796:2008-02-25
4777:2008-02-25
4427:1811.01508
4360:1808.04420
4353:(2): 136.
4301:1801.09051
4225:1801.09051
4189:2019-11-15
4107:2009-10-12
3949:2013-11-14
3573:1804.11163
3366:1907.11725
3251:1906.05227
3198:1804.10179
3051:(1): L23.
2868:2009-09-24
2763:1704.01373
2631:1503.08827
2549:2006-08-23
2517:(3): 264.
2420:2106.01394
2362:2206.05992
2302:1804.11348
2295:(2): 118.
2269:2024-03-08
2085:(2): 205.
1836:2008-11-19
1778:References
1739:Astrometry
1595:See also:
1579:, such as
1577:exoplanets
1571:, such as
1563:, such as
1538:, and the
1490:Olin Eggen
1335:supernovae
1304:Carina OB1
1178:HVS 10 – (
1047:black hole
853:See also:
849:Halo stars
816:53 Arietis
812:AE Aurigae
727:supersonic
556:redshifted
111:, and the
105:thick disk
93:satellites
85:velocities
74:kinematics
6800:Astronomy
6359:Brightest
6257:Magnitude
6237:Pole star
6158:Symbiotic
6153:Eclipsing
6085:Starlight
5886:Structure
5876:Supernova
5869:Micronova
5864:Recurrent
5849:Symbiotic
5834:p-process
5829:r-process
5824:s-process
5814:O burning
5804:C burning
5784:CNO cycle
5727:Gravastar
5263:Hypernova
5253:Supernova
5228:Dredge-up
5201:Blue loop
5194:super-AGB
5177:Red clump
5154:Evolution
5112:Protostar
5092:Accretion
5084:Formation
4708:119217292
4683:0910.3735
4569:0004-637X
4544:1305.4418
4537:(2): 79.
4512:printed:
4478:0808.3362
4454:119452542
4446:1538-4357
4420:(1): 27.
4395:119402144
4387:0004-637X
4328:119185386
4294:(1): 23.
4260:119185386
4252:0004-637X
4218:(1): 23.
4056:119338135
3691:119520529
3492:1412.0657
3276:186207054
3141:0709.1471
3058:1007.3493
2790:0035-8711
2731:123481910
2723:0035-8711
2696:1007.5057
2664:119255350
2656:0004-637X
2624:(2): 92.
2539:262334560
2445:0004-6361
2387:0004-6361
2213:0706.3005
2109:127759240
1968:118697588
1941:0912.3693
1752:Hipparcos
1573:TW Hydrae
1527:at 70°S.
1361:from the
1347:Hipparcos
1278:Monoceros
1268:Infrared
1199:known as
1171:HVS 9 – (
1164:HVS 8 – (
1151:HVS 6 – (
1144:HVS 5 – (
1137:HVS 4 – (
1127:HVS 3 – (
1110:HVS 1 – (
1080:supernova
1043:Milky Way
1037:with the
975:Milky Way
953:Milky Way
796:supernova
785:Milky Way
646:≈
521:−
451:−
377:−
323:Milky Way
284:potential
234:Milky Way
120:with the
101:thin disk
89:Milky Way
62:astronomy
6738:Asterism
6538:Category
6433:Remnants
6329:Extremes
6289:Parallax
6262:Apparent
6252:Asterism
6230:Sunlight
6180:Globular
6165:Multiple
6090:Variable
6080:Rotation
6040:Dynamics
5931:Starspot
5605:Magnetar
5548:Remnants
5364:Subgiant
5337:Subdwarf
5189:post-AGB
5017:Archived
4990:Archived
4973:15189914
4926:17220212
4655:51833191
4577:59289573
4284:. 2018a"
4003:16098861
3803:16091481
3750:55727428
3600:53416740
3305:13 March
3299:Phys.org
3166:15074398
3083:55832434
3028:15189914
2972:14322324
2329:85463973
2238:18075581
2029:15936627
1733:See also
1636:Pleiades
1585:GU Psc b
1505:asterism
1416:and the
1372:and the
1246:Armenian
839:Vela X-1
787:and the
749:velocity
723:velocity
276:globular
211:parallax
97:galaxies
91:and its
6788:Physics
6774:Portals
6680:Unbound
6595:systems
6592:Stellar
6505:Gravity
6454:Related
6374:Nearest
6322:Chinese
6170:Cluster
6143:Contact
5980:Proplyd
5854:Remnant
5742:Blitzar
5716:Hawking
5672:Strange
5622:Burster
5578:Neutron
5531:Extreme
5482:He-weak
5127:T Tauri
4953:Bibcode
4906:Bibcode
4879:6725343
4859:Bibcode
4818:Bibcode
4816:: 625.
4735:Bibcode
4688:Bibcode
4635:Bibcode
4549:Bibcode
4483:Bibcode
4365:Bibcode
4306:Bibcode
4230:Bibcode
4162:Bibcode
4131:Bibcode
4129:: 503.
4093:Bibcode
4036:Bibcode
3983:Bibcode
3909:Bibcode
3907:: 840.
3863:Bibcode
3829:Bibcode
3783:Bibcode
3771:: 278.
3728:Bibcode
3671:Bibcode
3629:27 June
3578:Bibcode
3497:Bibcode
3256:Bibcode
3203:Bibcode
3146:Bibcode
3063:Bibcode
3008:Bibcode
2952:Bibcode
2916:4250308
2896:Bibcode
2840:Bibcode
2813:Bibcode
2811:: 265.
2768:Bibcode
2701:Bibcode
2636:Bibcode
2519:Bibcode
2475:Bibcode
2425:Bibcode
2413:: A76.
2367:Bibcode
2355:: A28.
2307:Bibcode
2246:4387133
2218:Bibcode
2146:Bibcode
2087:Bibcode
2056:Bibcode
2007:Bibcode
1946:Bibcode
1895:Bibcode
1860:Bibcode
1806:12 July
1685:IC 2391
1548:Columba
1479:HR 1614
1442:parsecs
1430:nebulae
1402:parsecs
1351:parsecs
995:S5-HVS1
221:or the
133:gravity
87:in the
68:is the
6609:Galaxy
6495:Galaxy
6483:Planet
6471:Desert
6379:bright
6317:Arabic
6138:Binary
5958:Bubble
5682:Planck
5657:Exotic
5593:Binary
5588:Pulsar
5526:Helium
5487:Barium
5430:Carbon
5423:Yellow
5411:Yellow
5384:Yellow
5223:PG1159
4971:
4924:
4877:
4706:
4653:
4575:
4567:
4516:
4504:
4452:
4444:
4393:
4385:
4326:
4258:
4250:
4054:
4001:
3801:
3748:
3689:
3598:
3274:
3164:
3107:11 Feb
3081:
3026:
2970:
2914:
2888:Nature
2788:
2729:
2721:
2662:
2654:
2599:
2574:
2537:
2443:
2385:
2327:
2244:
2236:
2200:Nature
2181:
2107:
2027:
1966:
1611:galaxy
1550:, and
1544:Carina
1494:et al.
1412:, the
1408:, the
1122:US 708
1013:, the
939:, and
923:US 708
755:. The
691:Galaxy
511:
500:
441:
430:
367:
356:
107:, the
103:, the
6602:Bound
6500:Guest
6304:Lists
6185:Super
5839:Fusor
5712:Black
5697:Quark
5677:Preon
5662:Boson
5598:X-ray
5514:Shell
5467:Ap/Bp
5369:Giant
5287:Early
5233:OH/IR
5063:Stars
4969:S2CID
4943:arXiv
4922:S2CID
4896:arXiv
4875:S2CID
4849:arXiv
4704:S2CID
4678:arXiv
4651:S2CID
4623:(PDF)
4573:S2CID
4539:arXiv
4473:arXiv
4450:S2CID
4422:arXiv
4391:S2CID
4355:arXiv
4324:S2CID
4296:arXiv
4282:et al
4256:S2CID
4220:arXiv
4083:arXiv
4052:S2CID
4026:arXiv
3999:S2CID
3973:arXiv
3943:(PDF)
3799:S2CID
3773:arXiv
3746:S2CID
3718:arXiv
3687:S2CID
3661:arXiv
3596:S2CID
3568:arXiv
3487:arXiv
3361:arXiv
3272:S2CID
3246:arXiv
3193:arXiv
3162:S2CID
3136:arXiv
3079:S2CID
3053:arXiv
3024:S2CID
2998:arXiv
2968:S2CID
2942:arXiv
2912:S2CID
2758:arXiv
2727:S2CID
2691:arXiv
2660:S2CID
2626:arXiv
2535:S2CID
2415:arXiv
2357:arXiv
2325:S2CID
2297:arXiv
2242:S2CID
2208:arXiv
2136:arXiv
2105:S2CID
2025:S2CID
1997:arXiv
1964:S2CID
1936:arXiv
1796:Stars
1607:stars
1509:Dubhe
1274:VISTA
1260:Types
1159:HVS 7
1074:Some
743:2006.
171:with
165:μ = v
109:bulge
78:stars
38:, or
6175:Open
6070:Mass
5894:Core
5844:Nova
5737:Iron
5687:Dark
5497:Lead
5477:HgMn
5472:CEMP
5401:Blue
5374:Blue
5292:Late
5074:List
4600:2022
4565:ISSN
4514:ISBN
4502:ISBN
4442:ISSN
4383:ISSN
4272:See
4248:ISSN
3631:2014
3460:2019
3429:2019
3403:2019
3338:2019
3307:2019
3232:Gaia
3109:2018
2786:ISSN
2719:ISSN
2652:ISSN
2597:ISBN
2572:ISBN
2441:ISSN
2383:ISSN
2234:PMID
2179:ISBN
1808:2018
1745:Gaia
1561:ages
1536:Gaia
1511:and
1345:The
1317:and
1219:and
999:Grus
980:Gaia
901:Gaia
880:and
818:and
598:Gaia
583:Gaia
333:and
331:halo
327:disc
305:disc
298:and
6476:Sub
6210:Sun
5629:SGR
5406:Red
5379:Red
4961:doi
4939:634
4914:doi
4892:640
4867:doi
4845:544
4826:doi
4814:119
4743:doi
4731:204
4696:doi
4674:139
4643:doi
4631:599
4557:doi
4535:772
4432:doi
4418:870
4373:doi
4351:865
4314:doi
4292:856
4238:doi
4216:856
4139:doi
4079:325
4044:doi
4022:560
3991:doi
3969:117
3917:doi
3871:doi
3791:doi
3769:465
3736:doi
3714:328
3679:doi
3657:643
3586:doi
3564:865
3505:doi
3483:448
3371:doi
3264:doi
3242:627
3211:doi
3189:479
3154:doi
3132:671
3071:doi
3049:719
3016:doi
2994:634
2960:doi
2938:622
2904:doi
2892:331
2836:330
2776:doi
2754:469
2709:doi
2687:410
2644:doi
2622:805
2527:doi
2483:doi
2433:doi
2411:652
2375:doi
2353:674
2315:doi
2293:873
2226:doi
2204:450
2154:doi
2132:297
2095:doi
2083:872
2015:doi
1993:298
1954:doi
1932:403
1903:doi
1868:doi
1617:or
1583:or
1517:Sun
1473:or
1363:Sun
1340:Sun
1272:'s
1270:ESO
957:kpc
912:or
910:HVS
824:Sun
497:150
353:220
236:'s
219:Sun
169:/ d
139:or
60:In
6848::
5509:Be
5462:Am
5445:CH
5440:CN
5359:OB
5354:WR
4967:.
4959:.
4951:.
4937:.
4920:.
4912:.
4904:.
4890:.
4873:.
4865:.
4857:.
4843:.
4824:.
4812:.
4808:.
4741:.
4729:.
4725:.
4702:.
4694:.
4686:.
4672:.
4649:.
4641:.
4629:.
4625:.
4608:^
4571:.
4563:.
4555:.
4547:.
4533:.
4481:.
4471:.
4448:.
4440:.
4430:.
4416:.
4412:.
4389:.
4381:.
4371:.
4363:.
4349:.
4345:.
4322:.
4312:.
4304:.
4290:.
4286:.
4254:.
4246:.
4236:.
4228:.
4210:.
4198:^
4182:.
4137:.
4127:80
4125:.
4091:.
4077:.
4073:.
4050:.
4042:.
4034:.
4020:.
3997:.
3989:.
3981:.
3967:.
3931:^
3915:.
3905:81
3903:.
3899:.
3885:^
3869:.
3859:80
3857:.
3853:.
3841:^
3825:29
3823:.
3811:^
3797:.
3789:.
3781:.
3767:.
3744:.
3734:.
3726:.
3712:.
3708:.
3685:.
3677:.
3669:.
3655:.
3639:^
3617:.
3594:.
3584:.
3576:.
3562:.
3558:.
3503:.
3495:.
3481:.
3449:.
3420:.
3394:.
3369:.
3359:.
3355:.
3327:.
3296:.
3270:.
3262:.
3254:.
3240:.
3209:.
3201:.
3187:.
3183:.
3160:.
3152:.
3144:.
3130:.
3117:^
3099:.
3077:.
3069:.
3061:.
3047:.
3022:.
3014:.
3006:.
2992:.
2980:^
2966:.
2958:.
2950:.
2936:.
2924:^
2910:.
2902:.
2890:.
2886:.
2860:.
2834:.
2809:15
2807:.
2784:.
2774:.
2766:.
2752:.
2748:.
2725:.
2717:.
2707:.
2699:.
2685:.
2681:.
2658:.
2650:.
2642:.
2634:.
2620:.
2533:.
2525:.
2515:86
2513:.
2509:.
2497:^
2481:.
2471:69
2469:.
2465:.
2453:^
2439:.
2431:.
2423:.
2409:.
2405:.
2381:.
2373:.
2365:.
2351:.
2347:.
2323:.
2313:.
2305:.
2291:.
2287:.
2262:.
2240:.
2232:.
2224:.
2216:.
2202:.
2152:.
2144:.
2130:.
2126:.
2103:.
2093:.
2081:.
2077:.
2050:.
2046:.
2023:.
2013:.
2005:.
1991:.
1985:.
1962:.
1952:.
1944:.
1930:.
1924:.
1901:.
1891:93
1889:.
1866:.
1856:29
1854:.
1824:.
1794:.
1601:A
1587:.
1546:,
1365:.
1119:or
970:.
935:,
914:HV
845:.
814:,
794:A
693:.
623:21
558:/
427:50
329:,
189:.)
124:.
64:,
34:,
6776::
6584:e
6577:t
6570:v
5702:Q
5521:B
5435:S
5347:B
5342:O
5330:M
5325:K
5320:G
5315:F
5310:A
5305:B
5300:O
5055:e
5048:t
5041:v
4975:.
4963::
4955::
4945::
4928:.
4916::
4908::
4898::
4881:.
4869::
4861::
4851::
4834:.
4828::
4820::
4799:.
4780:.
4751:.
4745::
4737::
4710:.
4698::
4690::
4680::
4657:.
4645::
4637::
4602:.
4579:.
4559::
4551::
4541::
4510:,
4485::
4475::
4456:.
4434::
4424::
4397:.
4375::
4367::
4357::
4330:.
4316::
4308::
4298::
4262:.
4240::
4232::
4222::
4192:.
4168:.
4164::
4145:.
4141::
4133::
4110:.
4095::
4085::
4058:.
4046::
4038::
4028::
4005:.
3993::
3985::
3975::
3952:.
3925:.
3919::
3911::
3879:.
3873::
3865::
3835:.
3831::
3805:.
3793::
3785::
3775::
3752:.
3738::
3730::
3720::
3693:.
3681::
3673::
3663::
3633:.
3602:.
3588::
3580::
3570::
3513:.
3507::
3499::
3489::
3462:.
3431:.
3405:.
3379:.
3373::
3363::
3340:.
3309:.
3278:.
3266::
3258::
3248::
3219:.
3213::
3205::
3195::
3168:.
3156::
3148::
3138::
3111:.
3085:.
3073::
3065::
3055::
3030:.
3018::
3010::
3000::
2974:.
2962::
2954::
2944::
2918:.
2906::
2898::
2871:.
2846:.
2842::
2819:.
2815::
2792:.
2778::
2770::
2760::
2733:.
2711::
2703::
2693::
2666:.
2646::
2638::
2628::
2605:.
2580:.
2552:.
2529::
2521::
2491:.
2485::
2477::
2447:.
2435::
2427::
2417::
2389:.
2377::
2369::
2359::
2331:.
2317::
2309::
2299::
2272:.
2248:.
2228::
2220::
2210::
2187:.
2162:.
2156::
2148::
2138::
2111:.
2097::
2089::
2062:.
2058::
2052:3
2031:.
2017::
2009::
1999::
1970:.
1956::
1948::
1938::
1909:.
1905::
1897::
1874:.
1870::
1862::
1839:.
1810:.
1319:B
1315:O
1182:)
1175:)
1168:)
1155:)
1148:)
1141:)
1124:)
1007:×
883:w
876:v
870:u
791:.
665:3
643:G
620:=
617:G
566:.
543:.
524:1
516:s
507:m
504:k
494:=
488:S
485:M
482:R
478:V
454:1
446:s
437:m
434:k
424:=
418:S
415:M
412:R
408:V
380:1
372:s
363:m
360:k
350:=
346:V
315:.
186:t
184:v
180:μ
175:t
173:v
167:t
161:μ
157:d
56:.
42:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.