124:
331:
22:
136:
304:) was established with Hjorth and Schram among the board of directors. Amidst considerable resistance from landowners, trouble with unstable labour and excessive expenditures, the economic resources necessary to complete the line were provided, and the Copenhagen-Roskilde line was opened, as the first in Denmark, on 26 June 1847. English engineer
454:, the state decided on a somewhat different approach to build the railways. Here the state financed and owned the lines and infrastructure right from the start, whilst trusting the daily administration of lines and trains to the private company of "Det danske Jernbanedriftsselskab" (lit.:
398:), until it was taken over by the state in 1880. This ownership change was not without issues, and in several cases DSJ refused to build additional lines or make necessary upgrades, without financial guaranties. The last lines to be built by DSJ was "Nordvestbanen" (lit.:
466:. Other lines criss-crossing Jutland north-south and east-west - including the island of Funen -, soon followed. The last railways to be laid, before major changes were made, connected the north–south mainline on the east coast known as "Den Østjydske Længdebane" (lit.:
147:
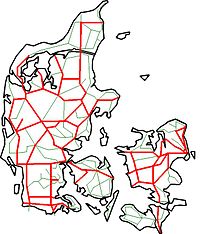
A large part of the main railway lines in
Denmark has been steadily privatized and outsourced from state owned (red) to privately owned (green) over the years, in particular in the 1990s. During this process, many lines have been
342:
in 1849, there was political will to improve trade routes to
England and provide better connections between Copenhagen and the rest of the country. The primary means for this was to extend the Copenhagen-Roskilde line to
261:
in 1864. The railway line was not the first in what constituted
Denmark at the time (as Holstein was part of the German Confederation), but it was nonetheless the first to be built under the Danish monarchy.
635:
489:) owned by the state and the company of "De Sjællandske Statsbaner" on private hands. In 1885 these two companies merged to form the state owned company of "De Danske Statsbaner" (it.:
289:
had been established. In 1843, after substantial financial recalculations, they applied for a concession to construct a railway from
Copenhagen via Roskilde to a coastal town on West
39:
761:
593:
628:
233:, but to preempt these efforts, the Danish government set up the first Danish railway commission in 1835 to establish the layout of a railway line through the Duchy of
898:
711:
378:) was granted concession to build the line, which opened on 6 October 1854. The railway was very successful, carrying English transit goods until 1857, when the
957:
347:, on the west coast of Zealand. During the 1850s, sufficient funding to extend the line to Korsør was secured, and the new segment was opened on 26 April 1856.
527:
818:
621:
972:
883:
86:
813:
793:
676:
366:
to limit German influence on trade. However, these plans were hampered by the war and the new political system. In 1852, the construction company
58:
788:
868:
863:
838:
65:
962:
893:
751:
741:
726:
721:
686:
681:
671:
656:
485:
By 1880, all major railway lines and companies in
Denmark proper, had been bought up by the company of "De Jydsk-Fynske Statsbaner" (lit.:
193:, was established in 1885. Until recently, DSB administered most aspects of rail operations in Denmark proper, but the politically decided
691:
888:
878:
858:
848:
833:
828:
778:
746:
731:
706:
967:
873:
798:
768:
72:
736:
565:
105:
926:
823:
325:
54:
931:
783:
293:. This was granted about a year later, albeit not with the same level of governmental economic support as the Kiel-Altona line.
936:
853:
773:
43:
916:
696:
843:
803:
756:
701:
666:
661:
921:
808:
581:
531:
309:
270:
79:
32:
507:
502:
246:
305:
301:
285:
would be profitable. However, there was no further interest in this project until 1841, when cooperation with
367:
339:
254:
183:
351:
286:
603:
258:
179:
431:
213:
In the 1830s, England and North
Germany planned to construct a railway line between the cities of
375:
394:
was constructed by the privately owned company of "Det Sjællandske
Jernbaneselskab" DSJ (lit.:
229:. The Copenhagen government frowned on this, as they wanted to retain waterway traffic through
561:
290:
190:
470:) and the north-south mainline on the west coast known as "Den Vestjydske Længdebane" (lit.:
123:
238:
171:
379:
266:
316:, England, built the initial batch of locomotives, the first of which was named 'Odin'.
205:, is currently among the largest of these, operating c. 17% of the Danish rail network.
359:
250:
613:
330:
253:
with
Denmark, with the King of Denmark being Duke of Holstein, and as a result of the
951:
194:
585:
427:
371:
198:
21:
458:). In 1862, the first line in Jutland was inaugurated, connecting the towns of
475:
423:
411:
363:
313:
278:
230:
226:
197:
efforts during the 1990s, has resulted in several local lines and tasks being
159:
355:
222:
407:
344:
218:
403:
282:
234:
175:
163:
178:
was completed three years earlier, but the region was later lost to the
135:
479:
463:
447:
435:
419:
391:
214:
201:
to a number of privately owned companies. The multinational company of
459:
202:
451:
329:
249:
on 18 September 1844. However, the Duchy of
Holstein was only in
602:
Winchester, Clarence, ed. (1936), "Denmark's modern transport",
242:
167:
617:
354:, plans had been made in Schleswig to construct a railway from
15:
610:
illustrated description of
Denmark's railways in the 1930s
158:
began in 1847 with the opening of a railway line between
438:, was sold almost as soon as it opened for traffic.
907:
649:
46:. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
334:Railway line in Denmark at the turn of the 1900s
434:. The last parts of the line on the island of
277:, in which they argued that a railway between
629:
8:
636:
622:
614:
106:Learn how and when to remove this message
519:
275:Jærnbane mellem Kjøbenhavn og Roeskilde
189:The Danish national railway operator,
55:"History of rail transport in Denmark"
487:the Jutlandic – Fuenic State Railways
456:The Danish Railway Operations Company
7:
958:History of rail transport by country
237:. Consequently, the railway between
156:history of rail transport in Denmark
44:adding citations to reliable sources
644:History of rail transport in Europe
474:). The line connected the towns of
14:
472:The West Jutlandic Longitude Line
468:The East Jutlandic Longitude Line
326:Narrow gauge railways in Denmark
134:
122:
20:
973:History of transport in Denmark
298:Det Sjællandske Jernbaneselskab
31:needs additional citations for
338:Following ratification of the
221:to ease transport between the
1:
396:The Zealandic Railway Company
271:Johan Christian Gustav Schram
605:Railway Wonders of the World
560:. Forlaget Kunst og Kultur.
530:. Arriva plc. Archived from
257:, Holstein was ceded to the
141:Major railway lines in 2018.
129:Major railway lines in 1932.
963:Economic history of Denmark
558:Danmarks Jernbaner i 150 år
390:The first railway lines on
989:
594:DSB: History and nostalgia
323:
310:Sharp Brothers and Company
302:Railway Company of Zealand
968:Rail transport in Denmark
508:Rail transport in Denmark
503:History of rail transport
491:the Danish State Railways
414:, and "Sydbanen" (lit.:
320:Expanding the main lines
418:) connecting Roskilde,
368:Peto, Brassey and Betts
255:Second War of Schleswig
184:Second War of Schleswig
692:Bosnia and Herzegovina
582:Danish railway history
352:First War of Schleswig
335:
493:) also known as DSB.
333:
608:, pp. 1369–1374
534:on 14 September 2008
478:and the new port of
273:published the paper
265:In 1840, technician
259:German Confederation
180:German Confederation
40:improve this article
908:States with limited
340:Danish Constitution
245:was opened by King
556:Koed, Jan (1997):
400:The Northwest Line
376:Samuel Morton Peto
336:
308:led construction.
287:Industriforeningen
945:
944:
442:Jutland and Funen
116:
115:
108:
90:
980:
650:Sovereign states
638:
631:
624:
615:
609:
571:
544:
543:
541:
539:
528:"Arriva Denmark"
524:
432:Nykøbing Falster
370:(represented in
138:
126:
111:
104:
100:
97:
91:
89:
48:
24:
16:
988:
987:
983:
982:
981:
979:
978:
977:
948:
947:
946:
941:
927:Northern Cyprus
909:
903:
824:North Macedonia
645:
642:
601:
578:
569:
553:
548:
547:
537:
535:
526:
525:
521:
516:
499:
444:
388:
382:was abolished.
328:
322:
306:William Radford
296:On 2 July 1844
269:and accountant
211:
152:
151:
150:
149:
144:
143:
142:
139:
131:
130:
127:
112:
101:
95:
92:
49:
47:
37:
25:
12:
11:
5:
986:
984:
976:
975:
970:
965:
960:
950:
949:
943:
942:
940:
939:
934:
929:
924:
919:
913:
911:
905:
904:
902:
901:
899:United Kingdom
896:
891:
886:
881:
876:
871:
866:
861:
856:
851:
846:
841:
836:
831:
826:
821:
816:
811:
806:
801:
796:
791:
786:
781:
776:
771:
766:
764:
759:
754:
749:
744:
739:
734:
729:
724:
719:
714:
712:Czech Republic
709:
704:
699:
694:
689:
684:
679:
674:
669:
664:
659:
653:
651:
647:
646:
643:
641:
640:
633:
626:
618:
612:
611:
599:
591:
577:
576:External links
574:
573:
572:
552:
549:
546:
545:
518:
517:
515:
512:
511:
510:
505:
498:
495:
482:specifically.
443:
440:
416:The South Line
387:
384:
321:
318:
251:personal union
247:Christian VIII
210:
207:
146:
145:
140:
133:
132:
128:
121:
120:
119:
118:
117:
114:
113:
28:
26:
19:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
985:
974:
971:
969:
966:
964:
961:
959:
956:
955:
953:
938:
935:
933:
932:South Ossetia
930:
928:
925:
923:
920:
918:
915:
914:
912:
906:
900:
897:
895:
892:
890:
887:
885:
882:
880:
877:
875:
872:
870:
867:
865:
862:
860:
857:
855:
852:
850:
847:
845:
842:
840:
837:
835:
832:
830:
827:
825:
822:
820:
817:
815:
812:
810:
807:
805:
802:
800:
797:
795:
792:
790:
787:
785:
784:Liechtenstein
782:
780:
777:
775:
772:
770:
767:
765:
763:
760:
758:
755:
753:
750:
748:
745:
743:
740:
738:
735:
733:
730:
728:
725:
723:
720:
718:
715:
713:
710:
708:
705:
703:
700:
698:
695:
693:
690:
688:
685:
683:
680:
678:
675:
673:
670:
668:
665:
663:
660:
658:
655:
654:
652:
648:
639:
634:
632:
627:
625:
620:
619:
616:
607:
606:
600:
598:
595:
592:
590:
587:
583:
580:
579:
575:
567:
566:87-7600-199-7
563:
559:
555:
554:
550:
533:
529:
523:
520:
513:
509:
506:
504:
501:
500:
496:
494:
492:
488:
483:
481:
477:
473:
469:
465:
461:
457:
453:
449:
441:
439:
437:
433:
429:
425:
421:
417:
413:
409:
405:
402:) connecting
401:
397:
393:
385:
383:
381:
377:
373:
369:
365:
361:
357:
353:
348:
346:
341:
332:
327:
319:
317:
315:
311:
307:
303:
299:
294:
292:
288:
284:
280:
276:
272:
268:
263:
260:
256:
252:
248:
244:
240:
236:
232:
228:
224:
220:
216:
208:
206:
204:
200:
196:
195:privatization
192:
187:
185:
181:
177:
173:
169:
165:
161:
157:
137:
125:
110:
107:
99:
88:
85:
81:
78:
74:
71:
67:
64:
60:
57: –
56:
52:
51:Find sources:
45:
41:
35:
34:
29:This article
27:
23:
18:
17:
937:Transnistria
716:
604:
596:
588:
557:
536:. Retrieved
532:the original
522:
490:
486:
484:
471:
467:
455:
445:
415:
399:
395:
389:
380:Øresund toll
349:
337:
297:
295:
274:
267:Søren Hjorth
264:
212:
188:
155:
153:
102:
96:October 2014
93:
83:
76:
69:
62:
50:
38:Please help
33:verification
30:
910:recognition
884:Switzerland
819:Netherlands
597:(in Danish)
589:(in Danish)
586:Banedanmark
570:(in Danish)
428:Vordingborg
372:Scandinavia
350:Before the
209:Early steps
952:Categories
854:San Marino
814:Montenegro
794:Luxembourg
774:Kazakhstan
677:Azerbaijan
514:References
476:Lunderskov
412:Kalundborg
324:See also:
314:Manchester
279:Copenhagen
227:Baltic Sea
199:outsourced
160:Copenhagen
148:abandoned.
66:newspapers
789:Lithuania
538:4 October
356:Flensburg
223:North Sea
917:Abkhazia
869:Slovenia
864:Slovakia
839:Portugal
697:Bulgaria
497:See also
404:Roskilde
283:Roskilde
235:Holstein
225:and the
176:Holstein
174:line in
164:Roskilde
894:Ukraine
844:Romania
804:Moldova
762:Ireland
757:Iceland
752:Hungary
742:Germany
737:Georgia
727:Finland
722:Estonia
717:Denmark
702:Croatia
687:Belgium
682:Belarus
672:Austria
667:Armenia
662:Andorra
657:Albania
551:Sources
480:Esbjerg
464:Randers
450:and on
448:Jutland
436:Falster
424:Næstved
392:Zealand
386:Zealand
364:Tönning
291:Zealand
231:Øresund
215:Hamburg
182:in the
80:scholar
922:Kosovo
889:Turkey
879:Sweden
859:Serbia
849:Russia
834:Poland
829:Norway
809:Monaco
779:Latvia
747:Greece
732:France
707:Cyprus
564:
460:Aarhus
408:Holbæk
358:, via
345:Korsør
239:Altona
219:Lübeck
203:Arriva
172:Altona
166:. The
82:
75:
68:
61:
53:
874:Spain
799:Malta
769:Italy
584:from
452:Funen
362:, to
360:Husum
312:, in
300:(The
87:JSTOR
73:books
562:ISBN
540:2014
462:and
430:and
420:Køge
410:and
281:and
243:Kiel
241:and
217:and
168:Kiel
162:and
154:The
59:news
446:In
374:by
191:DSB
42:by
954::
568:.
426:,
422:,
406:,
186:.
637:e
630:t
623:v
542:.
170:-
109:)
103:(
98:)
94:(
84:·
77:·
70:·
63:·
36:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.