31:
165:
One limitation of current technology is that the size for DNA precise insertion is not large enough to meet the demand for genome research. RNA-guided DNA transposition is an emerging area to solve this problem. More efficient methods are expected to be developed and applied in the genome engineering
214:
In-frame insertions occur when the reading frame is not altered as a result of the insertion; the number of inserted nucleotides is divisible by three. The reading frame remains intact after the insertion and translation will most likely run to completion if the inserted nucleotides do not code for
69:
slipping. Insertions can be anywhere in size from one base pair incorrectly inserted into a DNA sequence to a section of one chromosome inserted into another. The mechanism of the smallest single base insertion mutations is believed to be through base-pair separation between the template and primer
210:
during translation, thus not resulting in any protein product. If translated, the truncated proteins frequently are unable to function properly or at all and can result in any number of genetic disorders depending on the gene in which the insertion occurs.
487:
215:
a stop codon. However, because of the inserted nucleotides, the finished protein will contain, depending on the size of the insertion, multiple new amino acids that may affect the function of the protein.
443:
Sun, Chao; Lei, Yuan; Li, Boshu; Gao, Qiang; Li, Yunjia; Cao, Wen; Yang, Chao; Li, Hongchao; Wang, Zhiwei; Li, Yan; Wang, Yanpeng; Liu, Jun; Zhao, Kevin
Tianmeng; Gao, Caixia (2023).
198:. Frameshift mutations will alter all the amino acids encoded by the gene following the mutation. Usually, insertions and the subsequent frameshift mutation will cause the active
146:, different systems have already been developed to achieve specific functions. For example, one strategy is double-strand nucleases cutting system, using the normal
128:
206:, resulting in an end to translation and the production of a truncated protein. Transcripts carrying the frameshift mutation may also be degraded through
603:
377:
342:
97:
299:
635:
534:
113:
194:
of a gene, results if the number of inserted nucleotides is not divisible by three, i.e., the number of nucleotides per
70:
strands followed by non-neighbor base stacking, which can occur locally within the DNA polymerase active site. On a
794:
744:
62:
264:
Banavali, Nilesh K. (2013). "Partial Base
Flipping is Sufficient for Strand Slippage near DNA Duplex Termini".
789:
229:
207:
628:
199:
749:
713:
676:
93:
79:
124:
107:
162:
system, which uses Cas9 nickase and the prime editing guide RNA (pegRNA) carrying the target genes.
723:
663:
244:
187:
132:
557:
515:
468:
425:
307:
369:
363:
360:"5 Molecular Genetics and Mental Illness: The Search for Disease Mechanisms: Types of Mutations"
78:
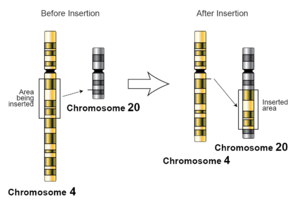
refers to the insertion of a larger sequence into a chromosome. This can happen due to unequal
815:
708:
703:
621:
599:
507:
460:
417:
373:
359:
338:
330:
281:
154:(sgRNA) and then achieving the gene insertion through end-joining or dividing cells with the
779:
728:
549:
499:
452:
409:
273:
143:
136:
718:
398:"Genome editing with CRISPR–Cas nucleases, base editors, transposases and prime editors"
695:
66:
135:
are the three main methods used in the former research to achieve gene insertion. And
116:
are classified as insertion mutations and sometimes as a separate class of mutations.
809:
519:
472:
445:"Precise integration of large DNA sequences in plant genomes using PrimeRoot editors"
444:
429:
191:
159:
397:
671:
561:
30:
17:
535:"Using a VOM Model for Reconstructing Potential Coding Regions in EST Sequences"
565:
456:
365:
Genetics of Mental
Disorders: A Guide for Students, Clinicians, and Researchers
553:
413:
203:
179:
155:
71:
51:
503:
319:] Understanding Evolution For Teachers Home. Retrieved on September 19, 2009
151:
54:
511:
464:
421:
285:
784:
774:
769:
644:
239:
234:
39:
83:
277:
139:
have already become one of the most used methods to present research.
488:"CRISPR technology: A decade of genome editing is only the beginning"
224:
195:
306:. University of California Museum of Paleontology. Archived from
183:
175:
147:
617:
358:
Faraone, Stephen V.; Tsuang, Ming T.; Tsuang, Debby W. (1999).
58:
174:
Insertions can be particularly hazardous if they occur in an
396:
Anzalone, Andrew V.; Koblan, Luke W.; Liu, David R. (2020).
613:
129:
Transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALEN)
110:
encoded by the ends of the recombining gene segments.
762:
737:
694:
687:
651:
304:
Evolution 101: Understanding
Evolution For Teachers
300:"Mechanisms: Genetic Variation: Types of Mutations"
34:
An illustration of an insertion at chromosome level
92:is the addition of non-coded nucleotides during
629:
8:
691:
636:
622:
614:
486:Wang, Joy Y.; Doudna, Jennifer A. (2023).
763:Mutation with respect to overall fitness
266:Journal of the American Chemical Society
29:
256:
202:of the gene to encounter a premature
98:terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase
7:
533:Shmilovici, A.; Ben-Gal, I. (2007).
391:
389:
542:Journal of Computational Statistics
61:sequence. This can often happen in
688:Mutation with respect to structure
25:
50:) is the addition of one or more
337:. Garland Science. p. 510.
598:(5th ed.). W. H. Freeman.
596:Genetics: A Conceptual Approach
158:system. Another example is the
190:, an alteration in the normal
1:
331:"16 Mutations and DNA Repair"
594:Pierce, Benjamin A. (2013).
832:
745:Chromosomal translocations
457:10.1038/s41587-023-01769-w
368:. Guilford Press. p.
329:Brown, Terence A. (2007).
240:Gain-of-Function Mutations
235:Loss-of-Function Mutations
554:10.1007/s00180-007-0021-8
414:10.1038/s41587-020-0561-9
125:Zinc finger nuclease(ZFN)
785:Nearly neutral mutation
504:10.1126/science.add8643
230:Insertional mutagenesis
208:Nonsense-mediated decay
795:Nonsynonymous mutation
750:Chromosomal inversions
652:Mechanisms of mutation
104:P nucleotide insertion
35:
775:Advantageous mutation
714:Conservative mutation
114:Trinucleotide repeats
108:palindromic sequences
33:
770:Deleterious mutation
738:Large-scale mutation
449:Nature Biotechnology
402:Nature Biotechnology
150:protein with single
106:is the insertion of
790:Synonymous mutation
724:Frameshift mutation
245:Deletion (genetics)
188:frameshift mutation
182:coding region of a
133:CRISPR gene editing
65:regions due to the
498:(6629): eadd8643.
48:insertion mutation
36:
18:Insertion mutation
803:
802:
758:
757:
709:Missense mutation
704:Nonsense mutation
605:978-1-4641-5084-5
379:978-1-57230-479-6
344:978-0-8153-4138-3
278:10.1021/ja401573j
272:(22): 8274–8282.
90:N region addition
16:(Redirected from
823:
780:Neutral mutation
729:Dynamic mutation
692:
638:
631:
624:
615:
609:
580:
579:
577:
576:
570:
564:. Archived from
539:
530:
524:
523:
483:
477:
476:
440:
434:
433:
393:
384:
383:
355:
349:
348:
326:
320:
318:
316:
315:
296:
290:
289:
261:
144:CRISPR/Cas tools
137:CRISPR/Cas tools
46:(also called an
27:Type of mutation
21:
831:
830:
826:
825:
824:
822:
821:
820:
806:
805:
804:
799:
754:
733:
719:Silent mutation
683:
647:
642:
612:
606:
593:
589:
587:Further reading
584:
583:
574:
572:
568:
537:
532:
531:
527:
485:
484:
480:
442:
441:
437:
395:
394:
387:
380:
357:
356:
352:
345:
328:
327:
323:
313:
311:
298:
297:
293:
263:
262:
258:
253:
221:
172:
122:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
829:
827:
819:
818:
808:
807:
801:
800:
798:
797:
792:
787:
782:
777:
772:
766:
764:
760:
759:
756:
755:
753:
752:
747:
741:
739:
735:
734:
732:
731:
726:
721:
716:
711:
706:
700:
698:
696:Point mutation
689:
685:
684:
682:
681:
680:
679:
674:
666:
661:
655:
653:
649:
648:
643:
641:
640:
633:
626:
618:
611:
610:
604:
590:
588:
585:
582:
581:
525:
478:
435:
408:(7): 824–844.
385:
378:
350:
343:
321:
291:
255:
254:
252:
249:
248:
247:
242:
237:
232:
227:
220:
217:
171:
168:
121:
118:
67:DNA polymerase
63:microsatellite
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
828:
817:
814:
813:
811:
796:
793:
791:
788:
786:
783:
781:
778:
776:
773:
771:
768:
767:
765:
761:
751:
748:
746:
743:
742:
740:
736:
730:
727:
725:
722:
720:
717:
715:
712:
710:
707:
705:
702:
701:
699:
697:
693:
690:
686:
678:
675:
673:
670:
669:
668:Substitution
667:
665:
662:
660:
657:
656:
654:
650:
646:
639:
634:
632:
627:
625:
620:
619:
616:
607:
601:
597:
592:
591:
586:
571:on 2020-05-31
567:
563:
559:
555:
551:
547:
543:
536:
529:
526:
521:
517:
513:
509:
505:
501:
497:
493:
489:
482:
479:
474:
470:
466:
462:
458:
454:
450:
446:
439:
436:
431:
427:
423:
419:
415:
411:
407:
403:
399:
392:
390:
386:
381:
375:
371:
367:
366:
361:
354:
351:
346:
340:
336:
332:
325:
322:
310:on 2009-04-14
309:
305:
301:
295:
292:
287:
283:
279:
275:
271:
267:
260:
257:
250:
246:
243:
241:
238:
236:
233:
231:
228:
226:
223:
222:
218:
216:
212:
209:
205:
201:
197:
193:
192:reading frame
189:
185:
181:
177:
169:
167:
163:
161:
160:prime editing
157:
153:
149:
145:
140:
138:
134:
130:
126:
119:
117:
115:
111:
109:
105:
101:
99:
95:
94:recombination
91:
87:
85:
81:
77:
73:
68:
64:
60:
56:
53:
49:
45:
41:
32:
19:
672:Transversion
658:
595:
573:. Retrieved
566:the original
548:(1): 49–69.
545:
541:
528:
495:
491:
481:
448:
438:
405:
401:
364:
353:
334:
324:
312:. Retrieved
308:the original
303:
294:
269:
265:
259:
213:
173:
164:
141:
123:
112:
103:
102:
89:
88:
75:
47:
43:
37:
200:translation
677:Transition
575:2014-01-10
314:2009-09-19
251:References
204:stop codon
180:amino acid
156:DNA repair
74:level, an
72:chromosome
55:base pairs
52:nucleotide
659:Insertion
520:255966509
473:258311438
430:256820370
335:Genomes 3
152:guide RNA
142:Based on
80:crossover
76:insertion
44:insertion
816:Mutation
810:Category
664:Deletion
645:Mutation
512:36656942
465:37095350
451:: 1–12.
422:32572269
286:23692220
219:See also
40:genetics
562:2737235
492:Science
170:Effects
120:Methods
84:meiosis
82:during
57:into a
602:
560:
518:
510:
471:
463:
428:
420:
376:
341:
284:
178:, the
166:area.
131:, and
569:(PDF)
558:S2CID
538:(PDF)
516:S2CID
469:S2CID
426:S2CID
225:Indel
196:codon
186:. A
42:, an
600:ISBN
508:PMID
461:PMID
418:PMID
374:ISBN
339:ISBN
282:PMID
184:gene
176:exon
148:Cas9
550:doi
500:doi
496:379
453:doi
410:doi
370:145
274:doi
270:135
96:by
59:DNA
38:In
812::
556:.
546:22
544:.
540:.
514:.
506:.
494:.
490:.
467:.
459:.
447:.
424:.
416:.
406:38
404:.
400:.
388:^
372:.
362:.
333:.
302:.
280:.
268:.
127:,
100:.
86:.
637:e
630:t
623:v
608:.
578:.
552::
522:.
502::
475:.
455::
432:.
412::
382:.
347:.
317:.
288:.
276::
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.