17:
253:(UDSS) – is a data-driven urban water management system that uses sensors attached to water appliances in urban residences to collect data about water usage. The system was developed with a European Commission investment of 2.46 Million Euros to improve the water consumption behavior of households. Information about appliances and facilities such as dishwashers, showers, washing machines, taps – is wirelessly recorded and sent to the UDSS App on the user's mobile device. The UDSS is then able to analyze and show homeowners which appliances are using the most water, and which behavior or habits should be avoided in order to reduce the water usage.
75:, based on the premise that by managing the urban water cycle as a whole; a more efficient use of resources can be achieved providing not only economic benefits but also improved social and environmental outcomes. One approach is to establish an inner, urban, water cycle loop through the implementation of reuse strategies. Developing this urban water cycle loop requires an understanding both of the natural, pre-development, water balance and the post-development water balance. Accounting for flows in the pre- and post-development systems is an important step toward limiting urban impacts on the natural water cycle.
170:), IUWM requires the management of the urban water cycle in coordination with the hydrological water cycle which are significantly altered by urban landscapes and its correlation to increasing demand. Under natural conditions the water inputs at any point in the system are precipitation and overland flows; while the outputs are via surface flows, evapo-transpiration and
274:
of urban water systems. Climate change is likely to affect all urban centers, either with increasingly heavy storms or with prolonged droughts, or perhaps both. To address the challenges facing IUWM it is crucial to develop good approaches, so that policy development and planning are directed towards
261:
One of the most significant challenges for IUWM could be securing a consensus on the definition of IUWM and the implementation of stated objectives at operational stages of projects. In the developing world there is still a significant fraction of the population that has no access to proper water
201:
The UNEP 3 Step
Strategic Approach developed in 2005 is based on the application of the "Cleaner Production approach" that has been successful in the industrial sector. The three steps are: Prevention, Treatment for reuse, and Planned discharge with stimulation of self-purification
240:
process, whereby the needs of all parties were included into the final management plan. A partnership was created between New York City, the agricultural community, and the federal government. The case has become a model for successful IUWM.
174:. The large volumes of piped water introduced with the change to an urban setting and the introduction of vast impervious areas strongly impact the water balance, increasing in-flows and dramatically altering the out-flow components.
78:
IUWM within an urban water system can also be conducted by performance assessment of any new intervention strategies by developing a holistic approach which encompasses various system elements and criteria including
304:
191:
for
Integrated water resources management in more detail for urban areas. One of the objectives of Agenda 21 is to develop environmentally sound management of water resources for urban use.
16:
589:
195:
289:
543:"Sustainable Water Management in the City of the Future: Report providing an inventory of conventional and of innovative approaches for Urban water Management"
567:
299:
205:
UNESCO's
Institute for Water Education seeks to build on the progress made by the Bellagio Statement and UNEP's 3-step approach by developing the
542:
338:
229:
505:
366:
198:
in 2000 include principals such as: Human dignity, quality of life, environmental security, an open stakeholder process, and many others.
714:
709:
399:
223:
568:"New York: New York City and Seven Upstate New York Counties - Effective Watershed Management Earns Filtration Waiver for New York"
270:
continue to cause pollution and depletion of water sources. In the developed world, pollution of water sources is threatening the
588:
Eggimann, Sven; Mutzner, Lena; Wani, Omar; Mariane Yvonne, Schneider; Spuhler, Dorothee; Beutler, Philipp; Maurer, Max (2017).
135:
Increase economic efficiency of services to sustain operations and investments for water, wastewater, and stormwater management
400:"Advantages of integrated and sustainability based assessment for metabolism based strategic planning of urban water systems"
498:
294:
668:
64:
210:
250:
63:
within the scope of the entire river basin. IUWM is commonly seen as a strategy for achieving the goals of
284:
237:
99:
type flows in urban water system can also be useful for analysing processes in urban water cycle of IUWM.
678:. Computing and Control for the Water Industry (CCWI2015) Sharing the best practice in water management.
455:
188:
546:
213:, new methods of planning urban water systems, and modifications to planning and strategy development.
604:
410:
171:
130:
232:
that provides 1.4 billion US gallons (5,300,000 m) of water per day, including to all of
638:
275:
addressing these global change pressures, and to achieving truly sustainable urban water systems.
620:
436:
374:
344:
334:
267:
116:
68:
683:
612:
478:
470:
426:
418:
154:
60:
147:
608:
414:
669:"A Benchmarking Model for Household Water Consumption Based on Adaptive Logic Networks"
309:
271:
194:
The
Bellagio Statement formulated by the Environmental Sanitation Working Group of the
166:
According to
Australia's Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (
123:
80:
44:
703:
233:
126:
474:
422:
263:
162:
Support capacity development of personnel and institutions that are engaged in IUWM
139:
112:
84:
48:
159:
Establish and implement policies and strategies to facilitate the above activities
688:
456:"Modelling metabolism based performance of an urban water system using WaterMet2"
20:
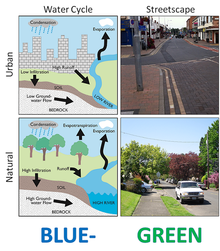
Comparing the natural and urban water cycle and streetscapes in conventional and
590:"The potential of knowing more – a review of data-driven urban water management"
509:
92:
88:
72:
40:
639:"Integrated Support System for Efficient Water Usage and Resources Management"
96:
56:
52:
36:
32:
348:
616:
369:. Australia's Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (
184:
21:
624:
440:
483:
431:
329:
Jonathan
Parkinson; J. A. Goldenfum; Carlos E. M. Tucci, eds. (2010).
187:(UN Department for Sustainable Development, 1992) has worked out the
667:
Chen, Xiaomin; Yang, Shuang-Hua; Yang, Lili; Chen, Xi (2015-01-01).
367:"Advancing IUWM through an understanding of the urban water balance"
83:
type ones in which integration of water system components including
370:
167:
15:
143:
262:
supply and sanitation. At the same time, population growth,
153:
Engage communities to reflect their needs and knowledge for
305:
209:
approach to IUWM. Components include: the addition of a
646:
331:
Integrated urban water management : humid tropics
545:. SWITCH authors. 2006. pp. 3–17. Archived from
196:Water Supply and Sanitation Collaborative Council
107:Activities under the IUWM include the following:
290:Integrated urban water management in Tegucigalpa
95:subsystems would be advantageous. Simulation of
8:
508:(UNEP). 2009. pp. 1–2. Archived from
687:
482:
430:
236:. The IUWM process included an extensive
537:
535:
533:
531:
529:
360:
358:
321:
300:Water management in Greater Mexico City
47:management plan. It builds on existing
597:Environmental Science & Technology
463:Resources, Conservation and Recycling
67:. IUWM seeks to change the impact of
7:
506:United Nations Environment Programme
393:
391:
333:. Boca Raton: CRC Press. p. 2.
499:"Integrated urban water management"
31:(IUWM) is the practice of managing
59:settlement by incorporating urban
14:
454:Behzadian, k; Kapelan, Z (2015).
398:Behzadian, K; Kapelan, Z (2015).
224:New York City water supply system
29:Integrated urban water management
407:Science of the Total Environment
475:10.1016/j.resconrec.2015.03.015
423:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.04.097
230:Catskill/ Delaware water system
245:Urban decision support systems
1:
295:International trade and water
689:10.1016/j.proeng.2015.08.998
65:Water Sensitive Urban Design
731:
715:Sustainable urban planning
710:Water resources management
228:An example of IUWM is the
221:
570:. EPA. 2009. pp. 1–2
211:sustainability assessment
55:considerations within an
617:10.1021/acs.est.6b04267
251:Decision Support System
285:One Water (Management)
238:stakeholder engagement
25:
365:Barton, A.B. (2009).
19:
676:Procedia Engineering
409:. 527–528: 220–231.
172:groundwater recharge
138:Utilize alternative
131:wastewater treatment
609:2017EnST...51.2538E
415:2015ScTEn.527..220B
43:as components of a
26:
373:). Archived from
340:978-0-203-88117-0
268:industrialization
189:Dublin Principles
150:and treated water
69:urban development
722:
694:
693:
691:
673:
664:
658:
657:
655:
654:
645:. Archived from
635:
629:
628:
603:(5): 2538–2553.
594:
585:
579:
578:
576:
575:
564:
558:
557:
555:
554:
539:
524:
523:
521:
520:
514:
503:
495:
489:
488:
486:
460:
451:
445:
444:
434:
404:
395:
386:
385:
383:
382:
362:
353:
352:
326:
155:water management
61:water management
730:
729:
725:
724:
723:
721:
720:
719:
700:
699:
698:
697:
671:
666:
665:
661:
652:
650:
637:
636:
632:
592:
587:
586:
582:
573:
571:
566:
565:
561:
552:
550:
541:
540:
527:
518:
516:
512:
501:
497:
496:
492:
458:
453:
452:
448:
402:
397:
396:
389:
380:
378:
364:
363:
356:
341:
328:
327:
323:
318:
281:
259:
247:
226:
220:
180:
105:
71:on the natural
12:
11:
5:
728:
726:
718:
717:
712:
702:
701:
696:
695:
659:
630:
580:
559:
525:
490:
446:
387:
354:
339:
320:
319:
317:
314:
313:
312:
310:Water security
307:
302:
297:
292:
287:
280:
277:
272:sustainability
258:
255:
246:
243:
222:Main article:
219:
216:
215:
214:
203:
199:
192:
179:
176:
164:
163:
160:
157:
151:
136:
133:
124:drinking water
120:
104:
101:
81:sustainability
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
727:
716:
713:
711:
708:
707:
705:
690:
685:
682:: 1391–1398.
681:
677:
670:
663:
660:
649:on 2017-01-12
648:
644:
640:
634:
631:
626:
622:
618:
614:
610:
606:
602:
598:
591:
584:
581:
569:
563:
560:
549:on 2009-04-03
548:
544:
538:
536:
534:
532:
530:
526:
515:on 2011-07-18
511:
507:
500:
494:
491:
485:
480:
476:
472:
468:
464:
457:
450:
447:
442:
438:
433:
428:
424:
420:
416:
412:
408:
401:
394:
392:
388:
377:on 2008-03-24
376:
372:
368:
361:
359:
355:
350:
346:
342:
336:
332:
325:
322:
315:
311:
308:
306:
303:
301:
298:
296:
293:
291:
288:
286:
283:
282:
278:
276:
273:
269:
265:
256:
254:
252:
244:
242:
239:
235:
234:New York City
231:
225:
217:
212:
208:
204:
200:
197:
193:
190:
186:
182:
181:
177:
175:
173:
169:
161:
158:
156:
152:
149:
145:
141:
140:water sources
137:
134:
132:
128:
125:
121:
118:
114:
110:
109:
108:
102:
100:
98:
94:
90:
86:
82:
76:
74:
70:
66:
62:
58:
54:
50:
46:
42:
38:
34:
30:
24:-Green Cities
23:
18:
679:
675:
662:
651:. Retrieved
647:the original
643:issewatus.eu
642:
633:
600:
596:
583:
572:. Retrieved
562:
551:. Retrieved
547:the original
517:. Retrieved
510:the original
493:
466:
462:
449:
406:
379:. Retrieved
375:the original
330:
324:
264:urbanization
260:
248:
227:
206:
165:
142:, including
113:water supply
106:
85:water supply
77:
49:water supply
28:
27:
484:10871/17108
432:10871/17351
117:consumption
93:storm water
89:waste water
73:water cycle
41:storm water
704:Categories
653:2017-01-10
574:2009-09-15
553:2009-09-14
519:2009-09-14
381:2009-09-14
316:References
257:Challenges
178:Approaches
119:efficiency
103:Components
97:metabolism
53:sanitation
45:basin-wide
37:wastewater
33:freshwater
469:: 84–99.
349:671648461
202:capacity.
185:Agenda 21
148:reclaimed
144:rainwater
625:28125222
441:25965035
279:See also
218:Examples
122:Upgrade
111:Improve
605:Bibcode
411:Bibcode
127:quality
623:
439:
347:
337:
249:Urban
207:SWITCH
146:, and
39:, and
672:(PDF)
593:(PDF)
513:(PDF)
502:(PDF)
459:(PDF)
403:(PDF)
371:CSIRO
168:CSIRO
57:urban
621:PMID
437:PMID
345:OCLC
335:ISBN
266:and
183:The
129:and
115:and
91:and
51:and
22:Blue
684:doi
680:119
613:doi
479:hdl
471:doi
427:hdl
419:doi
706::
674:.
641:.
619:.
611:.
601:51
599:.
595:.
528:^
504:.
477:.
467:99
465:.
461:.
435:.
425:.
417:.
405:.
390:^
357:^
343:.
87:,
35:,
692:.
686::
656:.
627:.
615::
607::
577:.
556:.
522:.
487:.
481::
473::
443:.
429::
421::
413::
384:.
351:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.