354:
58:
739:
847:) cannot be controlled with a tourniquet; however there is an FDA approved device known as an Abdominal Aortic and Junctional Tourniquet (AAJT) designed for proximal aortic control, although very few studies examining its use have been published. For bleeding at junctional sites, a dressing with a blood clotting agent (
392:
Blood loss can be estimated based on heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate, and mental status. Blood is circulated throughout the body and all major organ systems through a closed loop system. When there is damage to the blood vessel or the blood is thinner than the physiologic consistency,
397:
responds in two large ways as an attempt to compensate for the opening in the system. These two actions are easily monitored by checking the heart rate and blood pressure. Blood pressure will initially decrease due to the loss of blood. This is where the ANS comes in and attempts to compensate by
1278:
1375:
Brannstrom A., Rocksen D., Hartman J., et al
Abdominal aortic and junctional tourniquet release after 240 minutes is survivable and associated with small intestine and liver ischemia after porcine class II hemorrhage. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg.. 2018;85(4):717-724.
1072:
Teixeira, Pedro G. R.; Inaba, Kenji; Hadjizacharia, Pantelis; Brown, Carlos; Salim, Ali; Rhee, Peter; Browder, Timothy; Noguchi, Thomas T.; Demetriades, Demetrios (December 2007). "Preventable or
Potentially Preventable Mortality at a Mature Trauma Center".
1356:
Kheirabadi BS, Terrazas IB, Miranda N, Voelker AN, Grimm R, Kragh JF Jr,Dubick MA. Physiological
Consequences of Abdominal Aortic and Junc-tional Tourniquet (AAJT) application to control hemorrhage in a swinemodel.Shock (Augusta, Ga). 2016;46(3 Suppl
402:. The heart will start to pump faster causing the heart rate to increase, as an attempt to get blood delivered to vital organ systems faster. When the heart beats faster than the healthy and normal range, this is called
398:
contracting the muscles that surround these vessels. As a result, a person who is bleeding internally may initially have a normal blood pressure. When the blood pressure falls below the normal range, this is called
788:
after trauma should be diagnosed, resuscitated, and stabilized in the
Emergency Department in less than 10 minutes before undergoing surgery to reduce the risk of death from internal bleeding. A patient with
1347:
Rall JM, Ross JD, Clemens MS, Cox JM, Buckley TA, Morrison JJ. Hemo-dynamic effects of the
Abdominal Aortic and Junctional Tourniquet in ahemorrhagic swine model.JSurgRes. 2017;212:159–166.
714:. As soon as the clinician recognizes that the patient may have a severe, continuing hemorrhage requiring more than 4 units in 1 hour or 10 units in 6 hours, they should initiate a
365:
Internal bleeding could be a result of complications following surgery or other medical procedures. Some medications may also increase a person's risk for bleeding, such as
630:
It is important to examine the person for visible signs that may suggest the presence of internal bleeding and/or the source of the bleed. Some of these signs may include:
134:
Signs and symptoms of internal bleeding may vary based on location, presence of injury or trauma, and severity of bleeding. Common symptoms of blood loss may include:
1366:
Taylor DM, Coleman M, Parker PJ. The evaluation of an abdominal aortictourniquet for the control of pelvic and lower limb hemorrhage.Mil Med.2013;178(11):1196–1201.
1540:
1338:
Croushorn J, Thomas G, McCord SR. Abdominal aortic tourniquet controlsjunctional hemorrhage from a gunshot wound of the axilla.J Spec Oper Med.2013;13(3):1–4.
189:
A patient may lose more than 30% of their blood volume before there are changes in their vital signs or level of consciousness. This is called hemorrhagic or
951:
126:
if proper medical treatment is not received quickly. Internal bleeding is a medical emergency and should be treated immediately by medical professionals.
676:. If the patient has unstable vital signs, they may not undergo diagnostic imaging and instead may receive immediate medical or surgical treatment.
406:. If the bleeding is not controlled or stopped, a patient will experience tachycardia and hypotension, which altogether is a state of shock, called
106:
but the extent of severity depends on bleeding rate and location of the bleeding (e.g. head, torso, extremities). Severe internal bleeding into the
1329:
Croushorn J. Abdominal Aortic and
Junctional Tourniquet controls hemor-rhage from a gunshot wound of the left groin.JSpecOperMed.2014;14(2):6–8.
768:
Unlike with external bleeding, most internal bleeding cannot be controlled by applying pressure to the site of injury. Internal bleeding in the
1314:
1056:
876:
1870:
1248:
935:
1191:
1394:
1875:
1431:
1926:
186:
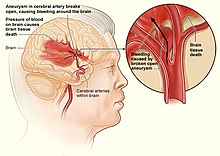
Of note, it is possible to have internal bleeding without any of the above symptoms, and pain may or may not be present.
1967:
1567:
1535:
715:
414:
922:
1890:
1608:
810:
762:
758:
205:
Internal bleeding can be caused by a broad number of things. We can break these up into three large categories:
1504:
1496:
394:
329:
1735:
1730:
707:
619:
567:
529:
492:
374:
70:
809:
has also been used for non-traumatic causes of internal bleeding, including bleeding during childbirth and
706:. In order to replace blood loss quickly and with large amounts of IV fluids or blood, patients may need a
276:
is another cause of vascular injury that can result in internal bleeding. It can occur after a high speed
1931:
1740:
1577:
1572:
212:
Genetic and acquired conditions, along with various medications, that result in an increased bleeding risk
784:) cannot be controlled with direct pressure (compression). A patient with acute internal bleeding in the
1919:
1705:
1665:
1509:
1479:
781:
341:
246:
is the most common cause of vascular injury and can result in internal bleeding. It can occur after a
1880:
1519:
1424:
650:
1715:
1685:
848:
687:
Internal bleeding is a medical emergency and should be treated immediately by medical professionals
321:
281:
194:
228:. Death from trauma accounts for 1.5 million of the 1.9 million deaths per year due to bleeding.
1850:
1829:
1788:
1655:
1027:
607:
370:
255:
243:
232:
102:
that collects inside the body, and is not usually visible from the outside. It can be a serious
293:
A number of pathological conditions and diseases can lead to internal bleeding. These include:
1962:
1957:
1695:
1650:
1310:
1244:
1187:
1156:
1090:
1052:
1019:
931:
711:
703:
407:
310:
259:
190:
119:
103:
79:
75:
31:
417:(ATLS) by the American College of Surgeons separates hemorrhagic shock into four categories.
1845:
1809:
1377:
1220:
1179:
1148:
1117:
1108:
Duncan, Nicholas S.; Moran, Chris (2010). "(i) Initial resuscitation of the trauma victim".
1082:
1011:
790:
773:
710:. Patients with severe bleeding need to receive large quantities of replacement blood via a
589:
509:
358:
247:
1417:
1395:"Stop the Bleed - SAVE A LIFE: What Everyone Should Know to Stop Bleeding After an Injury"
777:
754:
839:
Internal bleeding where the torso meets the extremities ("junctional sites" such as the
1902:
1897:
1720:
1587:
1136:
719:
603:
298:
263:
83:
1209:"STEMI - the importance of balance between antithrombotic treatment and bleeding risk"
1951:
1936:
1819:
1783:
1778:
1640:
1582:
1474:
1183:
1031:
817:
366:
306:
730:
in varying ratios based on the cause of the bleeding (traumatic vs. non-traumatic).
1914:
1814:
1773:
1763:
1758:
1680:
1464:
1459:
833:
723:
337:
277:
273:
236:
99:
17:
353:
258:
occurs in blood vessels close to the heart, it can quickly lead to hemorrhagic or
57:
1279:"Initial management of moderate to severe hemorrhage in the adult trauma patient"
1225:
1208:
1121:
602:
Assessing circulation occurs after assessing the patient's airway and breathing (
1885:
1824:
1670:
1592:
1381:
1086:
699:
684:
Management of internal bleeding depends on the cause and severity of the bleed.
669:
403:
399:
386:
1152:
1793:
1675:
1514:
1454:
825:
821:
750:
746:
640:
251:
820:
in the arms or legs may be partially controlled with direct pressure using a
1645:
662:
611:
325:
302:
1160:
1094:
1023:
738:
30:
This article is about the medical condition. For the death metal band, see
1015:
1909:
727:
225:
197:
that occurs when there is not enough blood to reach organs in the body.
829:
794:
673:
532:< 90 mmHg or change in blood pressure > 20-30% from presentation
393:
blood can exit the vessel which disrupts this close-looped system. The
111:
1629:
1469:
1440:
1309:(10th ed.). American College of Surgeons. 2018. pp. 43–52.
1207:
Pospíšil, Jan; Hromádka, Milan; Bernat, Ivo; Rokyta, Richard (2013).
840:
798:
785:
769:
317:
115:
844:
806:
802:
737:
634:
615:
333:
267:
123:
107:
745:
It is crucial to stop the internal bleeding immediately (achieve
1768:
209:
Trauma, or direct injury to blood vessels within the body cavity
1413:
1139:(2004). "Differential Diagnosis of Gastrointestinal Bleeding".
1049:
International Trauma Life
Support for Emergency Care Providers
749:) after identifying its cause. The longer it takes to achieve
1075:
The
Journal of Trauma: Injury, Infection, and Critical Care
854:
A campaign is to improve the care of the bleeding known as
702:), intravenous fluids can be used until they can receive a
1307:
ATLS- Advanced Trauma Life
Support - Student Course Manual
1409:
585:
Significantly altered mental status (confused, lethargic)
1002:
Cannon, Jeremy (January 25, 2018). "Hemorrhagic Shock".
665:
may be performed to look for bleeding in the abdomen.
1241:
Current
Diagnosis & Treatment: Emergency Medicine
1051:. Pearson Education Limited. 2018. pp. 172–173.
928:
Current Diagnosis & Treatment: Emergency Medicine
1863:
1838:
1802:
1751:
1628:
1621:
1601:
1560:
1553:
1528:
1495:
1488:
1447:
1141:
Techniques in Vascular and Interventional Radiology
316:Other diseases linked to internal bleeding include
69:
47:
42:
921:
606:). If internal bleeding is suspected, a patient's
672:, they may undergo diagnostic imaging such as a
361:(Brinton's disease) can cause internal bleeding
1174:Bray, M. (2009). "Hemorrhagic Fever Viruses".
594:Significantly decreased or absent urine output
1541:Focused assessment with sonography for trauma
1425:
8:
718:. The massive transfusion protocol replaces
224:The most common cause of death in trauma is
163:Visible signs of internal bleeding include:
1272:
1270:
1268:
1266:
1264:
1262:
1260:
1625:
1557:
1492:
1432:
1418:
1410:
828:placement, the patient may need immediate
419:
56:
39:
1224:
543:Altered mental status (anxious, confused)
297:Blood vessel rupture as a result of high
352:
867:
930:(7e ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill.
753:in people with traumatic causes (e.g.
1301:
1299:
997:
995:
993:
991:
698:If a patient has low blood pressure (
7:
1043:
1041:
989:
987:
985:
983:
981:
979:
977:
975:
973:
971:
915:
913:
911:
909:
907:
905:
903:
901:
899:
661:If internal bleeding is suspected a
421:Classification of Hemorrhagic Shock
1871:Acute respiratory distress syndrome
1004:The New England Journal of Medicine
878:Field Guide to Wilderness Medicine
801:after trauma may require use of a
765:), the higher the death rate is.
25:
1081:(6): 1338–46, discussion 1346–7.
805:device to slow the bleeding. The
757:) and non-traumatic causes (e.g.
1876:Chronic traumatic encephalopathy
1184:10.1016/B978-012373944-5.00303-5
27:Leakage of blood within the body
884:(12 ed.). pp. 129–131
858:campaign is also taking place.
588:Cool, clammy skin with delayed
508:Cool, clammy skin with delayed
231:There are two types of trauma:
1927:Post-traumatic stress disorder
491:Normal or minimally decreased
440:Respiratory rate (per minute)
395:autonomic nervous system (ANS)
65:Internal bleeding in the brain
1:
459:Normal or minimally elevated
1568:Advanced trauma life support
1536:Diagnostic peritoneal lavage
1226:10.1016/j.crvasa.2013.02.004
1176:Encyclopedia of Microbiology
1122:10.1016/j.mporth.2009.12.003
716:massive transfusion protocol
415:Advanced trauma life support
98:) is a loss of blood from a
1382:10.1097/TA.0000000000002013
1243:. McGraw-Hill. 2011-05-23.
1087:10.1097/TA.0b013e31815078ae
1984:
1153:10.1053/j.tvir.2004.12.001
668:If the patient has stable
29:
1609:Resuscitative thoracotomy
1497:Clinical prediction rules
816:Internal bleeding from a
811:gastrointestinal bleeding
793:internal bleeding in the
763:abdominal aortic aneurysm
759:gastrointestinal bleeding
144:Urinating less than usual
64:
55:
1505:Abbreviated Injury Scale
646:abnormal skin sensation
431:Heart rate (per minute)
330:viral hemorrhagic fevers
1736:Penetrating head injury
1731:Intracranial hemorrhage
1110:Orthopaedics and Trauma
708:central venous catheter
620:doppler ultrasonography
568:Systolic blood pressure
530:Systolic blood pressure
493:systolic blood pressure
375:coronary artery disease
1932:Subcutaneous emphysema
1891:Volkmann's contracture
1741:Traumatic brain injury
1578:Early appropriate care
1573:Damage control surgery
1277:Colwell, Christopher.
923:"Vascular Emergencies"
742:
546:Decreased urine output
437:Pulse pressure (mmHg)
362:
118:, or thighs can cause
1706:Thoracic aorta injury
1666:Diaphragmatic rupture
1510:Injury Severity Score
1480:Trauma triad of death
1016:10.1056/NEJMra1705649
920:Fritz, Davis (2011).
851:) should be applied.
832:to find the bleeding
782:retroperitoneal space
741:
734:Stopping the bleeding
428:Estimated blood loss
356:
328:deficiency, and rare
193:, which is a type of
153:Pale and/or cold skin
1881:Compartment syndrome
1520:Revised Trauma Score
1178:. pp. 339–353.
776:(including both the
651:compartment syndrome
626:Physical examination
610:is assessed through
519:Class III hemorrhage
373:in the treatment of
159:Generalized weakness
96:internal haemorrhage
1968:Medical emergencies
1716:Blunt kidney trauma
1686:Pulmonary contusion
849:hemostatic dressing
554:Class IV hemorrhage
481:Class II hemorrhage
422:
322:hematologic disease
282:automobile accident
51:Internal hemorrhage
18:Internal hemorrhage
1830:Spinal cord injury
1789:Penetrating trauma
1656:Soft tissue injury
1137:Laberge, Jeanne M.
743:
608:circulatory system
449:Class I hemorrhage
420:
371:antiplatelet drugs
363:
357:This stomach with
256:penetrating trauma
244:Penetrating trauma
233:penetrating trauma
167:Blood in the urine
130:Signs and symptoms
1945:
1944:
1859:
1858:
1701:Internal bleeding
1696:Cardiac tamponade
1651:Joint dislocation
1617:
1616:
1549:
1548:
1393:Pons, MD, Peter.
712:blood transfusion
704:blood transfusion
694:Fluid replacement
643:blood collection
600:
599:
408:hemorrhagic shock
311:ectopic pregnancy
260:hypovolemic shock
191:hypovolemic shock
182:Throwing up blood
173:Bright red stools
170:Dark black stools
120:hemorrhagic shock
104:medical emergency
92:Internal bleeding
89:
88:
80:hypovolemic shock
76:Hemorrhagic shock
43:Internal bleeding
37:Medical condition
32:Internal Bleeding
16:(Redirected from
1975:
1851:Pediatric trauma
1846:Geriatric trauma
1810:Abdominal trauma
1626:
1558:
1493:
1434:
1427:
1420:
1411:
1399:
1398:
1390:
1384:
1373:
1367:
1364:
1358:
1354:
1348:
1345:
1339:
1336:
1330:
1327:
1321:
1320:
1316:978-78-0-9968267
1303:
1294:
1293:
1291:
1289:
1274:
1255:
1254:
1237:
1231:
1230:
1228:
1219:(2): e135–e146.
1204:
1198:
1197:
1171:
1165:
1164:
1135:Lee, Edward W.;
1132:
1126:
1125:
1105:
1099:
1098:
1069:
1063:
1062:
1058:978-1292-17084-8
1045:
1036:
1035:
999:
966:
965:
963:
962:
948:
942:
941:
925:
917:
894:
893:
891:
889:
883:
875:Auerback, Paul.
872:
774:abdominal cavity
590:capillary refill
510:capillary refill
473:Slightly anxious
423:
359:Linitis plastica
60:
40:
21:
1983:
1982:
1978:
1977:
1976:
1974:
1973:
1972:
1948:
1947:
1946:
1941:
1855:
1834:
1798:
1747:
1622:Pathophysiology
1613:
1597:
1545:
1524:
1484:
1443:
1438:
1408:
1403:
1402:
1392:
1391:
1387:
1374:
1370:
1365:
1361:
1355:
1351:
1346:
1342:
1337:
1333:
1328:
1324:
1317:
1305:
1304:
1297:
1287:
1285:
1276:
1275:
1258:
1251:
1239:
1238:
1234:
1206:
1205:
1201:
1194:
1173:
1172:
1168:
1134:
1133:
1129:
1107:
1106:
1102:
1071:
1070:
1066:
1059:
1047:
1046:
1039:
1001:
1000:
969:
960:
958:
956:www.dynamed.com
950:
949:
945:
938:
919:
918:
897:
887:
885:
881:
874:
873:
869:
864:
778:intraperitoneal
755:pelvic fracture
736:
720:red blood cells
696:
682:
659:
628:
434:Blood pressure
413:
390:
383:
351:
291:
222:
203:
150:Fast heart rate
138:Lightheadedness
132:
38:
35:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1981:
1979:
1971:
1970:
1965:
1960:
1950:
1949:
1943:
1942:
1940:
1939:
1934:
1929:
1924:
1923:
1922:
1917:
1907:
1906:
1905:
1903:Rhabdomyolysis
1898:Crush syndrome
1895:
1894:
1893:
1883:
1878:
1873:
1867:
1865:
1861:
1860:
1857:
1856:
1854:
1853:
1848:
1842:
1840:
1836:
1835:
1833:
1832:
1827:
1822:
1817:
1812:
1806:
1804:
1800:
1799:
1797:
1796:
1791:
1786:
1781:
1776:
1771:
1766:
1761:
1755:
1753:
1749:
1748:
1746:
1745:
1744:
1743:
1738:
1733:
1725:
1724:
1723:
1721:Splenic injury
1718:
1710:
1709:
1708:
1703:
1698:
1690:
1689:
1688:
1683:
1678:
1673:
1668:
1660:
1659:
1658:
1653:
1648:
1643:
1634:
1632:
1623:
1619:
1618:
1615:
1614:
1612:
1611:
1605:
1603:
1599:
1598:
1596:
1595:
1590:
1588:Trauma surgery
1585:
1580:
1575:
1570:
1564:
1562:
1555:
1551:
1550:
1547:
1546:
1544:
1543:
1538:
1532:
1530:
1529:Investigations
1526:
1525:
1523:
1522:
1517:
1512:
1507:
1501:
1499:
1490:
1486:
1485:
1483:
1482:
1477:
1472:
1467:
1462:
1457:
1451:
1449:
1445:
1444:
1439:
1437:
1436:
1429:
1422:
1414:
1407:
1406:External links
1404:
1401:
1400:
1385:
1368:
1359:
1349:
1340:
1331:
1322:
1315:
1295:
1256:
1250:978-0071701075
1249:
1232:
1199:
1192:
1166:
1147:(3): 112–122.
1127:
1100:
1064:
1057:
1037:
1010:(4): 370–379.
967:
943:
937:978-0071701075
936:
895:
866:
865:
863:
860:
856:Stop The Bleed
735:
732:
695:
692:
681:
678:
658:
655:
654:
653:
647:
644:
641:
637:
627:
624:
604:ABC (medicine)
598:
597:
596:
595:
592:
586:
581:
578:
571:
565:
559:
556:
550:
549:
548:
547:
544:
539:
536:
533:
527:
524:
521:
515:
514:
513:
512:
506:
505:Mildly anxious
501:
498:
495:
489:
486:
483:
477:
476:
475:
474:
469:
466:
463:
460:
457:
451:
445:
444:
441:
438:
435:
432:
429:
426:
389:
384:
382:
379:
350:
347:
346:
345:
332:, such as the
314:
299:blood pressure
290:
287:
286:
285:
271:
264:exsanguination
221:
218:
217:
216:
213:
210:
202:
199:
184:
183:
180:
177:
174:
171:
168:
161:
160:
157:
154:
151:
148:
145:
142:
139:
131:
128:
87:
86:
84:exsanguination
73:
67:
66:
62:
61:
53:
52:
49:
45:
44:
36:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1980:
1969:
1966:
1964:
1961:
1959:
1956:
1955:
1953:
1938:
1937:Wound healing
1935:
1933:
1930:
1928:
1925:
1921:
1918:
1916:
1913:
1912:
1911:
1908:
1904:
1901:
1900:
1899:
1896:
1892:
1889:
1888:
1887:
1884:
1882:
1879:
1877:
1874:
1872:
1869:
1868:
1866:
1864:Complications
1862:
1852:
1849:
1847:
1844:
1843:
1841:
1837:
1831:
1828:
1826:
1823:
1821:
1820:Facial trauma
1818:
1816:
1813:
1811:
1808:
1807:
1805:
1801:
1795:
1792:
1790:
1787:
1785:
1784:Gunshot wound
1782:
1780:
1779:Electrocution
1777:
1775:
1772:
1770:
1767:
1765:
1762:
1760:
1757:
1756:
1754:
1750:
1742:
1739:
1737:
1734:
1732:
1729:
1728:
1726:
1722:
1719:
1717:
1714:
1713:
1711:
1707:
1704:
1702:
1699:
1697:
1694:
1693:
1691:
1687:
1684:
1682:
1679:
1677:
1674:
1672:
1669:
1667:
1664:
1663:
1661:
1657:
1654:
1652:
1649:
1647:
1644:
1642:
1641:Bone fracture
1639:
1638:
1636:
1635:
1633:
1631:
1627:
1624:
1620:
1610:
1607:
1606:
1604:
1600:
1594:
1591:
1589:
1586:
1584:
1583:Trauma center
1581:
1579:
1576:
1574:
1571:
1569:
1566:
1565:
1563:
1559:
1556:
1552:
1542:
1539:
1537:
1534:
1533:
1531:
1527:
1521:
1518:
1516:
1513:
1511:
1508:
1506:
1503:
1502:
1500:
1498:
1494:
1491:
1487:
1481:
1478:
1476:
1475:Resuscitation
1473:
1471:
1468:
1466:
1463:
1461:
1458:
1456:
1453:
1452:
1450:
1446:
1442:
1435:
1430:
1428:
1423:
1421:
1416:
1415:
1412:
1405:
1396:
1389:
1386:
1383:
1379:
1372:
1369:
1363:
1360:
1353:
1350:
1344:
1341:
1335:
1332:
1326:
1323:
1318:
1312:
1308:
1302:
1300:
1296:
1284:
1280:
1273:
1271:
1269:
1267:
1265:
1263:
1261:
1257:
1252:
1246:
1242:
1236:
1233:
1227:
1222:
1218:
1214:
1210:
1203:
1200:
1195:
1193:9780123739445
1189:
1185:
1181:
1177:
1170:
1167:
1162:
1158:
1154:
1150:
1146:
1142:
1138:
1131:
1128:
1123:
1119:
1115:
1111:
1104:
1101:
1096:
1092:
1088:
1084:
1080:
1076:
1068:
1065:
1060:
1054:
1050:
1044:
1042:
1038:
1033:
1029:
1025:
1021:
1017:
1013:
1009:
1005:
998:
996:
994:
992:
990:
988:
986:
984:
982:
980:
978:
976:
974:
972:
968:
957:
953:
947:
944:
939:
933:
929:
924:
916:
914:
912:
910:
908:
906:
904:
902:
900:
896:
880:
879:
871:
868:
861:
859:
857:
852:
850:
846:
842:
837:
835:
831:
827:
823:
819:
818:bone fracture
814:
812:
808:
804:
800:
796:
792:
787:
783:
779:
775:
771:
766:
764:
760:
756:
752:
748:
740:
733:
731:
729:
725:
721:
717:
713:
709:
705:
701:
693:
691:
689:
688:
679:
677:
675:
671:
666:
664:
656:
652:
648:
645:
642:
638:
636:
633:
632:
631:
625:
623:
621:
617:
613:
609:
605:
593:
591:
587:
584:
583:
582:
579:
576:
572:
570:< 90 mmHg
569:
566:
563:
560:
557:
555:
552:
551:
545:
542:
541:
540:
537:
534:
531:
528:
525:
522:
520:
517:
516:
511:
507:
504:
503:
502:
499:
496:
494:
490:
487:
484:
482:
479:
478:
472:
471:
470:
467:
464:
461:
458:
455:
452:
450:
447:
446:
442:
439:
436:
433:
430:
427:
425:
424:
418:
416:
411:
409:
405:
401:
396:
388:
385:
380:
378:
376:
372:
368:
367:anticoagulant
360:
355:
348:
343:
339:
335:
331:
327:
323:
319:
315:
312:
308:
307:peptic ulcers
304:
300:
296:
295:
294:
289:Non-traumatic
288:
283:
279:
275:
272:
269:
265:
261:
257:
253:
249:
245:
242:
241:
240:
238:
234:
229:
227:
219:
214:
211:
208:
207:
206:
200:
198:
196:
192:
187:
181:
178:
175:
172:
169:
166:
165:
164:
158:
155:
152:
149:
146:
143:
140:
137:
136:
135:
129:
127:
125:
121:
117:
113:
109:
105:
101:
97:
94:(also called
93:
85:
81:
77:
74:
72:
71:Complications
68:
63:
59:
54:
50:
46:
41:
33:
19:
1815:Chest injury
1774:Crush injury
1764:Blunt trauma
1759:Blast injury
1700:
1681:Pneumothorax
1465:Traumatology
1460:Major trauma
1388:
1371:
1362:
1352:
1343:
1334:
1325:
1306:
1286:. Retrieved
1282:
1240:
1235:
1216:
1212:
1202:
1175:
1169:
1144:
1140:
1130:
1113:
1109:
1103:
1078:
1074:
1067:
1048:
1007:
1003:
959:. Retrieved
955:
946:
927:
886:. Retrieved
877:
870:
855:
853:
838:
834:blood vessel
815:
767:
744:
697:
686:
685:
683:
667:
660:
629:
601:
574:
561:
553:
518:
480:
453:
448:
412:
391:
364:
292:
278:deceleration
274:Blunt trauma
237:blunt trauma
230:
223:
204:
188:
185:
176:Bloody noses
162:
133:
100:blood vessel
95:
91:
90:
1886:Contracture
1839:Demographic
1825:Head injury
1671:Flail chest
1593:Trauma team
1357:1):160–166.
1213:Cor et Vasa
761:, ruptured
700:hypotension
670:vital signs
404:tachycardia
400:hypotension
387:Vital signs
48:Other names
1952:Categories
1794:Stab wound
1676:Hemothorax
1602:Procedures
1561:Principles
1554:Management
1515:NACA score
1489:Assessment
1455:Polytrauma
1448:Principles
961:2023-10-08
862:References
826:tourniquet
822:tourniquet
751:hemostasis
747:hemostasis
573:Narrowed (
526:120 - 140
488:100 - 120
252:stab wound
250:injury or
1752:Mechanism
1646:Degloving
1032:205117992
952:"DynaMed"
728:platelets
680:Treatment
663:FAST exam
649:signs of
639:bruising
612:palpation
577:25 mmHg)
558:> 40%
535:Narrowed
523:30 - 40%
497:Narrowed
485:15 - 30%
381:Diagnosis
369:drugs or
326:Vitamin K
303:aneurysms
248:ballistic
220:Traumatic
147:Confusion
1963:Injuries
1958:Bleeding
1910:Embolism
1283:UpToDate
1161:16015555
1095:18212658
1024:29365303
888:13 March
824:. After
538:30 - 40
500:20 - 30
344:viruses.
226:bleeding
179:Bruising
1692:Cardio
1288:5 March
1116:: 1–8.
830:surgery
795:abdomen
674:CT scan
657:Imaging
635:a wound
580:>35
468:Normal
465:Normal
462:Normal
342:Marburg
141:Fatigue
112:abdomen
1803:Region
1727:Neuro
1630:Injury
1470:Triage
1441:Trauma
1313:
1247:
1190:
1159:
1093:
1055:
1030:
1022:
934:
841:axilla
799:pelvis
786:thorax
770:thorax
726:, and
724:plasma
616:pulses
443:Other
338:Dengue
318:cancer
280:in an
266:, and
201:Causes
156:Thirst
116:pelvis
1662:Resp
1028:S2CID
882:(PDF)
845:groin
807:REBOA
803:REBOA
791:acute
349:Other
334:Ebola
309:, or
268:death
254:. If
215:Other
195:shock
124:death
108:chest
1769:Burn
1637:MSK
1311:ISBN
1290:2019
1245:ISBN
1188:ISBN
1157:PMID
1091:PMID
1053:ISBN
1020:PMID
932:ISBN
890:2019
780:and
772:and
618:and
575:<
564:140
562:>
456:15%
454:<
235:and
1920:fat
1915:air
1712:GI
1378:doi
1221:doi
1180:doi
1149:doi
1118:doi
1083:doi
1012:doi
1008:378
843:or
797:or
690:.
614:of
340:or
122:or
1954::
1298:^
1281:.
1259:^
1217:55
1215:.
1211:.
1186:.
1155:.
1143:.
1114:24
1112:.
1089:.
1079:63
1077:.
1040:^
1026:.
1018:.
1006:.
970:^
954:.
926:.
898:^
836:.
813:.
722:,
622:.
410:.
377:.
336:,
324:,
320:,
305:,
301:,
262:,
239:.
114:,
110:,
82:,
78:,
1433:e
1426:t
1419:v
1397:.
1380::
1319:.
1292:.
1253:.
1229:.
1223::
1196:.
1182::
1163:.
1151::
1145:7
1124:.
1120::
1097:.
1085::
1061:.
1034:.
1014::
964:.
940:.
892:.
313:.
284:.
270:.
34:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.