127:
161:. Another suggestion is that the Karakoram fault is offset at least 500 km as measured by the offset of late Paleozoic granites in the Kunlun batholith. Most researchers tend to agree with the lower slip estimates. A major obstacle in measuring the total offset along the fault is in deciding what is actually a part of the fault and which faults are separate. Currently some researchers believe that the Karakoram fault merges and terminates into the Indus-Yalu suture zone at Mount Kailas. Other researchers also add the Gurla Mandhata detachment, in the South-Eastern segment, to the fault.
31:
196:
northern approximately 1 km wide area of the fault, and contains listric normal faults. The Gurla
Mandhata fault system is thought to be encompassed within the Karakoram fault system at its southern tip, which cause the southern tip of the fault to be approximately 36 km wide. Exhumation along the Gurla Mandhata detachment, which is a low-angle normal-fault system, suggest that the faults have allowed for between 36 and 66 kilometers of slip.
177:
provinces. In this north-western segment, the
Karakoram Fault currently has predominantly normal fault motion, and right-lateral strike-slip offset. The slip in this section of the Karakoram fault is measured to be approximately 150 km, as measured by the offset of the Aghil formation. The Aghil
148:
had been offset 1000 km dextrally along the
Karakoram Fault based on mapping in the central Karakoram, in nearby Ladakh-Zanskar, and in south Tibet. Some researchers suggest that this might be incorrect due to associating granite that was never part of the same batholith. Others researchers work
195:
and the South Kailas Thrust, and that the strain in this region is almost entirely accommodated for by a north-south shortening in the
Himalaya, just south of the Indus Suture Zone. The Neogene Gar Basin in western Tibet also accommodates slip along the Karakoram fault. The basin lies within the
190:
Most people agree that the South-Eastern portion of the fault merges into and parallels the Indus Suture Zone in South West Tibet. The southern segment of the
Karakoram Fault shows that only 120 km of dextral motion is evident from offset of geologic features, such as the
114:. Around 10-11 million years ago the Karakoram fault had become trans-tensional and extended southwest into Tibet. The southwest extension is marked by the Karakoram fault crossing the active South Kailas Thrust in the vicinity of present-day
584:
Searle, M. P.; R. F. Weinberg; W. J. Dunlap (1998). "Transpressional tectonics along the
Karakoram fault zone, northern Ladakh: Constraints on Tibetan extrusion, in continental transpressional and transtensional tectonics".
748:
Searle, M. P.; A. J. Rex; R. Tirrul; D. C. Rex; A. Barnicoat; B.F. Windley (1989). "Metamorphic, magmatic, and tectonic evolution of the central
Karakoram in the Biafo-Baltoro-Hushe regions of northern Pakistan".
375:
Sobel, E. R.; L. M. Schoenbohm; J. Chen; R. Thiede; D. F. Stockli; M. Sudo; M. R. Strecker (2011). "Late
Miocene-Pliocene deceleration of dextral slip between Pamir and Tarim: Implications for Pamir orogensis".
462:
Murphy, Mike A.; A. Yin; P. Kapp; T. M. Harrison; C. E. Manning (2002). "Isotopic characteristics of the Gurla
Mandhata metamorphic core complex: Implications for the architecture of the Himalayan orogen".
623:
Sanchez, Veronica; M. Murphy; W. R. Dupré; Lin Ding; Ran Zhang (2010). "Structural evolution of the
Neogene Gar Basin, Western Tibet: Implications for releasing bend development and drainage patters".
662:
707:
169:
The north-western segment of the Karakoram Fault is far less disputed than other areas. It terminates in the extensions of the Miuji Basin, in the Pamir Mountains, along the border between
182:
formation. Before entering the Pamir region the Karakoram fault is believed to split into two distinct faults. These faults are the main Karakoram fault itself, and the Achiehkopai fault.
918:
Lacassin, Robin; Frank Valli; Nicholas Arnaud; P.Hervé Leloup; Jean Louis Paquette; Li Haibing; Paul Tapponnier; Marie-Luce Chevalier; Stephane Guillot; Gweltaz Maheo; Zhiqin Xu (2004).
422:
Searle, M. P. (February 1996). "Geological evidence against large scale pre-holocene offsets along the Karakoram fault: Implications for the limited extrusion of the Tibetan Plateau".
919:
86:
seaway which once separated the two modern continents of Asia and India. The Karakoram fault itself does not trace a plate boundary, except for where it possibly ends in the
883:
Searle, M. P. (1986). "Structural evolution and sequence of thrusting in the High Himalayan Tibetan Tethys and Indus suture zones of Zanskar and Ladakh, western Himalaya".
534:
Valli, Franck; Nicholas Arnaud; Phillipe Hervé Leloup; Edward R. Sobel; Gweltaz Mahe'o; Robin Lacassin; Stephane Guillot; Haibing Li; Paul Tapponnier; Zhiqin Xu (2007).
269:
110:
starting approximately 20 million years ago. Approximately 14 million years ago the fault changed to a predominately normal fault. This conclusion is based on
1009:
Murphy, M.; A. Yin (2003). "Structural evolution and sequence of thrusting in the Tethyan fold-thrust belt and Indus-Yalu suture zone, southwest Tibet".
332:
Murphy, M. A.; P. Copeland (2005). "Transtentional deformation in the central Himalay and its role in accommodating growth of the Himalayan orogeny".
974:
Pecher, A. (1991). "The contact between the Higher Himalaya crystallines and the Tibetan sedimentary series: Miocene large-scale dextral shearing".
663:"Geologic offsets across the northern Karakorum fault: Implications for its role and terrane correlations in the western Himalayan-Tibetan orogeny"
535:
74:
is around 44±5 mm per year in the western Himalaya-Pamir region and approximately 50±2 mm per year in the eastern Himalayan region.
766:
782:
Searle, M. P.; R.R. Parrish; R. Tirrul; D.C. Rex (1990). "Age of crystallization and cooling of the K2 gneiss in the Baltoro Karakoram".
950:
126:
1058:
1063:
34:
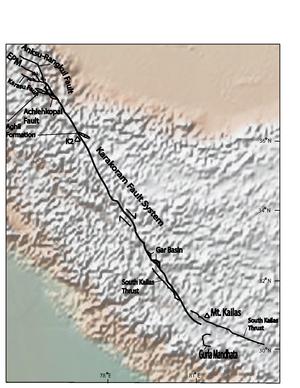
Topographical map of India and Himalaya region with Karakoram fault superimposed on top of it. Karakoram overlay modified from
149:
have shown 600 km of right lateral slip since 23 million years ago, and possibly starting 34 million years ago, based on
708:"Formation and evolution of strike-slip faults, rifts, and basins during the India-Asia collision: An experimental approach"
308:
130:
Karakoram fault information modified from and superimposed on top of topographic map of region. EPM= East Pamir Mountains
536:"Twenty million years of continuous deformation along the Karakoram fault, Western Tibet: A Thermochronological analysis"
54:
and Asia. The slip along the fault accommodates radial expansion of the Himalayan arc, northward indentation of the
1068:
87:
1030:
158:
296:
205:
179:
1018:
983:
934:
892:
849:
791:
722:
677:
632:
550:
503:
431:
385:
341:
284:
270:"Southward propagation of the Karakoram fault system, southwest Tibet: Timing and magnitude of slip"
150:
153:. Slip in this model has been transferred into the Indus-Yalu suture zone, as well as large scale
865:
807:
602:
566:
357:
235:
111:
43:
1034:
762:
300:
30:
1026:
991:
942:
938:
900:
857:
840:
Searle, M. P.; R. Tirrul (1991). "Structural and thermal evolution of the Karakoram crust".
799:
754:
730:
685:
681:
640:
594:
558:
511:
472:
439:
393:
389:
349:
292:
210:
231:
95:
59:
55:
1022:
987:
896:
853:
795:
726:
636:
554:
507:
435:
345:
288:
516:
491:
71:
63:
946:
17:
1052:
904:
869:
811:
606:
570:
361:
115:
920:"Large-scale geometry, offset and kinematic evolution of the Karakoram fault, Tibet"
219:
91:
83:
67:
598:
241:
215:
192:
157:. Research in the early 1990s suggested that this slip was transferred into the
689:
397:
170:
135:
107:
1038:
861:
803:
304:
734:
154:
145:
82:
The creation of the Karakoram fault started with the closing of the ancient
562:
353:
174:
47:
758:
268:
Murphy, M.; A. Yin; P. Kipp; T. M. Harrison; D. Lin; J. H. Guo (2000).
142:
995:
476:
443:
644:
225:
139:
51:
29:
701:
699:
1031:
10.1130/0016-7606(2003)115<0021:SEASOT>2.0.CO;2
27:
Fault system in the Himalayan region across India and Asia
297:
10.1130/0091-7613(2000)28<451:SPOTKF>2.0.CO;2
618:
616:
457:
455:
453:
263:
261:
259:
257:
90:. The original thrusting occurred by linking existing
753:. GSA Special Papers. Vol. 232. pp. 47–73.
529:
527:
656:
654:
587:Geological Society of America Special Publication
222:is causing rapid uplifting of lower crustal rocks
827:Geology and Tectonics of the Karakoram Mountains
417:
415:
413:
411:
409:
407:
98:starting between 17 and 20 million years ago.
8:
715:Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth
228:- similar small scale erosion to the Indus
515:
66:suggest that the convergence between the
125:
106:The Karakoram fault was a right lateral
58:, and eastward lateral extrusion of the
253:
1011:Geological Society of America Bulletin
625:Geological Society of America Bulletin
7:
829:. New York: John Wiley. p. 358.
927:Earth and Planetary Science Letters
706:Peltzer, G.; P. Tapponnier (1988).
670:Earth and Planetary Science Letters
378:Earth and Planetary Science Letters
751:Tectonics of the western Himalayas
517:10.1111/j.1365-246X.1990.tb06579.x
25:
496:Geophysical Journal International
234:to the North (also discussed in
1:
947:10.1016/S0012-821X(04)00006-8
599:10.1144/gsl.sp.1998.135.01.20
905:10.1016/0191-8141(86)90037-4
842:Geological Society of London
784:Geological Society of London
134:It is suggested that a late
1085:
690:10.1016/j.epsl.2008.12.039
398:10.1016/j.epsl.2011.02.012
88:Indus-Yarlung Suture Zone
862:10.1144/gsjgs.148.1.0065
804:10.1144/gsjgs.147.4.0603
661:Robinson, A. C. (2009).
159:South Tibetan Detachment
1059:Geology of the Himalaya
939:2004E&PSL.219..255L
735:10.1029/JB093iB12p15085
682:2009E&PSL.279..123R
492:"Current Plate Motions"
390:2011E&PSL.304..369S
206:Geology of the Himalaya
180:fossiliferous carbonate
1064:Seismic faults of Asia
825:Searle, M. P. (1991).
131:
35:
18:Karakoram Fault System
186:South-Eastern segment
165:North-Western segment
129:
33:
721:(15b): 15085–15117.
563:10.1029/2005TC001913
354:10.1029/2004TC001659
1023:2003GSAB..115...21M
988:1991Tecto..10..587P
897:1986JSG.....8..923S
854:1991JGSoc.148...65S
796:1990JGSoc.147..603S
727:1988JGR....9315085P
637:2010GSAB..122..926S
555:2007Tecto..26.4004V
508:1990GeoJI.101..425D
490:Demets, C. (1990).
436:1996Tecto..15..171S
346:2005Tecto..24.4012M
289:2000Geo....28..451M
94:in what is now the
885:Structural Geology
759:10.1130/SPE232-p47
236:Geography of Tibet
132:
44:oblique-slip fault
36:
996:10.1029/90TC02655
768:978-0-8137-2232-0
477:10.1130/G23774A.1
444:10.1029/95TC01693
218:- the erosion at
16:(Redirected from
1076:
1069:Geology of India
1043:
1042:
1006:
1000:
999:
971:
965:
964:
962:
961:
955:
949:. Archived from
933:(3–4): 255–269.
924:
915:
909:
908:
880:
874:
873:
837:
831:
830:
822:
816:
815:
779:
773:
772:
745:
739:
738:
712:
703:
694:
693:
676:(1–2): 123–130.
667:
658:
649:
648:
645:10.1130/B26566.1
631:(5–6): 926–945.
620:
611:
610:
581:
575:
574:
540:
531:
522:
521:
519:
487:
481:
480:
471:(114): 428–447.
459:
448:
447:
419:
402:
401:
384:(3–4): 369–378.
372:
366:
365:
329:
323:
322:
320:
319:
313:
307:. Archived from
274:
265:
211:Geology of Nepal
21:
1084:
1083:
1079:
1078:
1077:
1075:
1074:
1073:
1049:
1048:
1047:
1046:
1008:
1007:
1003:
973:
972:
968:
959:
957:
953:
922:
917:
916:
912:
882:
881:
877:
839:
838:
834:
824:
823:
819:
781:
780:
776:
769:
747:
746:
742:
710:
705:
704:
697:
665:
660:
659:
652:
622:
621:
614:
583:
582:
578:
538:
533:
532:
525:
489:
488:
484:
461:
460:
451:
421:
420:
405:
374:
373:
369:
331:
330:
326:
317:
315:
311:
272:
267:
266:
255:
250:
232:Tibetan Plateau
202:
188:
178:formation is a
167:
124:
104:
96:Pamir Mountains
80:
60:Tibetan plateau
56:Pamir Mountains
40:Karakoram fault
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1082:
1080:
1072:
1071:
1066:
1061:
1051:
1050:
1045:
1044:
1001:
982:(3): 587–598.
966:
910:
891:(8): 923–936.
875:
832:
817:
790:(4): 603–606.
774:
767:
740:
695:
650:
612:
576:
523:
502:(1): 425–478.
482:
449:
430:(1): 171–186.
403:
367:
324:
283:(5): 451–454.
252:
251:
249:
246:
245:
244:
239:
229:
223:
213:
208:
201:
198:
187:
184:
166:
163:
123:
120:
103:
100:
79:
76:
72:Eurasian Plate
50:region across
46:system in the
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1081:
1070:
1067:
1065:
1062:
1060:
1057:
1056:
1054:
1040:
1036:
1032:
1028:
1024:
1020:
1016:
1012:
1005:
1002:
997:
993:
989:
985:
981:
977:
970:
967:
956:on 2013-12-03
952:
948:
944:
940:
936:
932:
928:
921:
914:
911:
906:
902:
898:
894:
890:
886:
879:
876:
871:
867:
863:
859:
855:
851:
847:
843:
836:
833:
828:
821:
818:
813:
809:
805:
801:
797:
793:
789:
785:
778:
775:
770:
764:
760:
756:
752:
744:
741:
736:
732:
728:
724:
720:
716:
709:
702:
700:
696:
691:
687:
683:
679:
675:
671:
664:
657:
655:
651:
646:
642:
638:
634:
630:
626:
619:
617:
613:
608:
604:
600:
596:
592:
588:
580:
577:
572:
568:
564:
560:
556:
552:
548:
544:
537:
530:
528:
524:
518:
513:
509:
505:
501:
497:
493:
486:
483:
478:
474:
470:
466:
458:
456:
454:
450:
445:
441:
437:
433:
429:
425:
418:
416:
414:
412:
410:
408:
404:
399:
395:
391:
387:
383:
379:
371:
368:
363:
359:
355:
351:
347:
343:
339:
335:
328:
325:
314:on 2013-12-02
310:
306:
302:
298:
294:
290:
286:
282:
278:
271:
264:
262:
260:
258:
254:
247:
243:
240:
237:
233:
230:
227:
224:
221:
217:
214:
212:
209:
207:
204:
203:
199:
197:
194:
185:
183:
181:
176:
172:
164:
162:
160:
156:
152:
147:
144:
141:
137:
128:
121:
119:
117:
113:
109:
101:
99:
97:
93:
92:thrust faults
89:
85:
77:
75:
73:
69:
65:
64:plate motions
61:
57:
53:
49:
45:
41:
32:
19:
1017:(1): 21–34.
1014:
1010:
1004:
979:
975:
969:
958:. Retrieved
951:the original
930:
926:
913:
888:
884:
878:
848:(1): 65–82.
845:
841:
835:
826:
820:
787:
783:
777:
750:
743:
718:
714:
673:
669:
628:
624:
590:
586:
579:
546:
542:
499:
495:
485:
468:
464:
427:
423:
381:
377:
370:
337:
333:
327:
316:. Retrieved
309:the original
280:
276:
226:Sutlej River
220:Nanga Parbat
189:
168:
133:
116:Mount Kailas
112:argon dating
105:
84:Tethys Ocean
81:
68:Indian Plate
39:
37:
593:: 307–326.
549:(4): 1–26.
242:Paleotethys
216:Indus River
193:Indus River
151:U-Pb dating
1053:Categories
960:2013-11-21
340:(4): n/a.
318:2013-11-21
248:References
171:Tajikistan
136:Cretaceous
108:slip fault
62:. Current
1039:0016-7606
976:Tectonics
870:128818804
812:129956294
607:130363239
571:135348627
543:Tectonics
424:Tectonics
362:106406740
334:Tectonics
305:0091-7613
155:boudinage
146:batholith
102:Evolution
48:Himalayan
200:See also
175:Xinjiang
70:and the
1019:Bibcode
984:Bibcode
935:Bibcode
893:Bibcode
850:Bibcode
844:. 148.
792:Bibcode
786:. 147.
723:Bibcode
678:Bibcode
633:Bibcode
551:Bibcode
504:Bibcode
465:Geology
432:Bibcode
386:Bibcode
342:Bibcode
285:Bibcode
277:Geology
143:granite
1037:
868:
810:
765:
605:
569:
360:
303:
140:Eocene
122:Length
78:Origin
42:is an
954:(PDF)
923:(PDF)
866:S2CID
808:S2CID
711:(PDF)
666:(PDF)
603:S2CID
567:S2CID
539:(PDF)
358:S2CID
312:(PDF)
273:(PDF)
52:India
1035:ISSN
763:ISBN
301:ISSN
173:and
38:The
1027:doi
1015:115
992:doi
943:doi
931:219
901:doi
858:doi
846:148
800:doi
788:147
755:doi
731:doi
686:doi
674:279
641:doi
629:122
595:doi
591:135
559:doi
512:doi
500:101
473:doi
440:doi
394:doi
382:304
350:doi
293:doi
1055::
1033:.
1025:.
1013:.
990:.
980:10
978:.
941:.
929:.
925:.
899:.
887:.
864:.
856:.
806:.
798:.
761:.
729:.
719:93
717:.
713:.
698:^
684:.
672:.
668:.
653:^
639:.
627:.
615:^
601:.
589:.
565:.
557:.
547:26
545:.
541:.
526:^
510:.
498:.
494:.
469:35
467:.
452:^
438:.
428:15
426:.
406:^
392:.
380:.
356:.
348:.
338:24
336:.
299:.
291:.
281:28
279:.
275:.
256:^
118:.
1041:.
1029::
1021::
998:.
994::
986::
963:.
945::
937::
907:.
903::
895::
889:8
872:.
860::
852::
814:.
802::
794::
771:.
757::
737:.
733::
725::
692:.
688::
680::
647:.
643::
635::
609:.
597::
573:.
561::
553::
520:.
514::
506::
479:.
475::
446:.
442::
434::
400:.
396::
388::
364:.
352::
344::
321:.
295::
287::
238:)
138:-
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.