109:
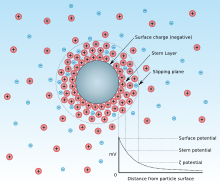
surface charge of adsorbent is described by the ion that lies on the surface of the particle (adsorbent) structure like image. At a lower pH, hydrogen ions (protons, H) would be more adsorbed than other cations (adsorbate) so that the other cations would be less adsorbed than in the case of the negatively charged particle. On the other hand, if the surface is positively charged and pH is increased, anions will be less adsorbed as pH increases. From the view of the adsorbent, if the pH of the solution is below the pzc value, the surface charge of the adsorbent would become positive so that the anions can be adsorbed. Conversely, if the pH is above the pzc value, the surface charge would be negative so that the cations can be adsorbed.
20:
362:
including wood ash, sawdust, etc. are used as an adsorbent by eliminating harmful heavy metals like arsenic, cobalt, mercury ion and so forth in contaminated neutral drainage (CND), which is a passive reactor that could possible metal adsorption with low-cost materials. Therefore, the pzc values of the organic substrates were evaluated to optimize the selection of materials in CND. Another example is that the emission of
204:, with identical or (confusingly) near-identical meaning: zero point of charge (zpc), point of zero net charge (pznc), point of zero net proton charge (pznpc), pristine point of zero charge (ppzc), point of zero salt effect (pzse), zero point of titration (zpt) of colloidal dispersion, and isoelectric point of the solid (ieps) and point of zero surface tension (pzst or pzs).
321:
The structure of electrolyte at the electrode surface can also depend on the surface charge, with a change around the pzc potential. For example, on a platinum electrode, water molecules have been reported to be weakly hydrogen-bonded with "oxygen-up" orientation on negatively charged surfaces, and
361:
is involved in many techniques that can eliminate pollutants and governs the concentration of chemicals in soils and/or atmosphere. When studying pollutant degradation or a sorption process, it is important to examine the pzc value related to adsorption. For example, natural and organic substrates
108:
is equal to zero. This concept has been introduced by an increase of interest in the pH of the solution during adsorption experiments. The reason is that the adsorption of some substances is very dependent on pH. The pzc value is determined by the characteristics of an adsorbent. For example, the
821:
Osawa, Masatoshi; Tsushima, Minoru; Mogami, Hirokazu; Samjeské, Gabor; Yamakata, Akira (2008). "Structure of Water at the
Electrified Platinum−Water Interface: A Study by Surface-Enhanced Infrared Absorption Spectroscopy".
124:
ions present in the solution above the crystals. Then, the pzc value of the AgI surface will be described by a function of the concentration of I in the solution (or by the negative decimal logarithm of this concentration,
370:
capacity. Different soil pH leads to the different surface charges of minerals so the emission of nitrous acid would be varied, further impacting on the biological cycle involved in the nitrous acid species.
317:
is the potential of the same electrode when the surface charge is zero, in the absence of specific adsorption other than that of the solvent, against the reference electrode as used above, in volts
647:
Bakatula, Elisee Nsimba; Richard, Dominique; Neculita, Carmen
Mihaela; Zagury, Gerald J. (2018). "Determination of point of zero charge of natural organic materials".
475:
Bakatula, Elisee Nsimba; Richard, Dominique; Neculita, Carmen
Mihaela; Zagury, Gerald J. (2018). "Determination of point of zero charge of natural organic materials".
811:
R. J. Stol & P. L. de Bruyn; "Thermodynamic stabilization of colloids"; Journal of
Colloid and Interface Science; 1980; 75 (1): pp. 185–198.
727:
389:
192:), the pzc is established as the common intersection point (cip) of the lines. Therefore, pzc is also sometimes referred to as cip.
177:
of the particles and the pH of the suspension. Several titrations are required to distinguish pzc from iep, using different
96:
characteristics exist along with the pzc value, including zero point of charge (zpc), point of zero net charge (pznc), etc.
157:
in suspension in water. In the presence of specific adsorption, pzc and isoelectric point generally have different values.
60:
at the point of zero charge. Generally, the pzc in electrochemistry is the value of the negative decimal logarithm of the
860:
246:
604:
Nasiruddin Khan, M.; Sarwar, Anila (2007). "Determination of points of zero charge of natural and treated adsorbents".
19:
855:
174:
200:
Besides pzc, iep, and cip, there are also numerous other terms used in the literature, usually expressed as
23:
178:
69:
539:"Soil surface acidity plays a determining role in the atmospheric-terrestrial exchange of nitrous acid"
412:
760:
656:
613:
550:
484:
424:
61:
239:
235:
221:
57:
688:
516:
776:
733:
723:
680:
672:
629:
586:
568:
508:
500:
440:
385:
142:
81:
64:
of the potential-determining ion in the bulk fluid. The pzc is of fundamental importance in
831:
768:
715:
664:
621:
576:
558:
492:
432:
46:'s surface) is equal to zero. This concept has been introduced in the studies dealing with
217:
65:
39:
460:
802:
Jean-Pierre
Jolivet, "Metal Oxide Chemistry and Synthesis", John Wiley & Sons, 2000.
764:
660:
617:
554:
488:
428:
581:
538:
334:
330:
189:
185:
16:
The pH value at which the surface of a colloidal solid carries no net electrical charge
793:
Marek
Kosmulski, "Chemical Properties of Material Surfaces", Marcel Dekker Inc., 2001.
322:
strongly hydrogen-bonded with nearly flat orientation at positively charged surfaces.
92:
and several titration methods have been developed. Related values associated with the
849:
308:
is the potential of the same electrode against a defined reference electrode in volts
117:
113:
692:
520:
363:
338:
50:
296:
is the electrode potential difference with respect to the point of zero charge,
250:
182:
84:
of minerals. Therefore, the pzc value has been examined in many application of
668:
625:
496:
358:
342:
201:
146:
105:
85:
76:
potentially harmful ions. It also has countless applications in technology of
73:
43:
780:
737:
676:
633:
572:
504:
444:
104:
The point of zero charge is the pH value for which the net surface charge of
563:
346:
213:
166:
89:
684:
590:
512:
719:
326:
170:
77:
47:
835:
772:
436:
188:). Once satisfactory curves are obtained (acid/base amount—pH, and pH—
706:
Kosmulski, Marek (2001). "Chemical
Properties of Material Surfaces".
121:
88:
to the environmental science. The pzc value is typically obtained by
367:
227:
154:
18:
537:
Donaldson, Melissa A.; Bish, David L.; Raff, Jonathan D. (2014).
258:
potential difference with respect to the potential of zero charge
216:-electrolyte interface is generally charged. If the electrode is
93:
245:
The potential of zero charge is used for determination of the
26:
around a negatively charged particle in suspension in water.
35:
153:. This is often the case for pure ("pristine surface")
751:
Sposito, Garrison (1998). "On Points of Zero Charge".
337:), minimum stability (exhibits maximum coagulation or
112:
For example, the electrical charge on the surface of
72:, it determines how easily a substrate is able to
333:(that is, the particles remain stationary in an
543:Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
242:) at which one of the charges defined is zero.
53:to explain why pH is affecting the phenomenon.
349:of the dispersion, and other peculiarities.
56:A related concept in electrochemistry is the
8:
649:Environmental Science and Pollution Research
477:Environmental Science and Pollution Research
456:
454:
165:The pzc is typically obtained by acid-base
382:Surface Charging and Points of Zero Charge
580:
562:
353:Application in environmental geochemistry
220:, then its surface charge depends on the
151:potential determining H/OH at the surface
116:(AgI) crystals can be determined by the
401:
357:In the field of environmental science,
100:Term definition of point of zero charge
753:Environmental Science & Technology
417:Environmental Science & Technology
384:. CRC Press; 1st edition (Hardcover).
532:
530:
470:
468:
407:
405:
232:potential at the point of zero charge
7:
415:(1998). "On Points of Zero Charge".
161:Method of experimental determination
137:Relation of pzc to isoelectric point
366:, which controls the atmosphere's
14:
208:Application in electrochemistry
68:. For example, in the field of
42:of the particle surface (i.e.
34:is generally described as the
1:
345:of the solid phase, maximum
247:absolute electrode potential
141:The pzc is the same as the
877:
606:Surface Review and Letters
32:point of zero charge (pzc)
669:10.1007/s11356-017-1115-7
626:10.1142/S0218625X07009517
497:10.1007/s11356-017-1115-7
236:potential of an electrode
212:In electrochemistry, the
175:electrophoretic mobility
564:10.1073/pnas.1418545112
256:IUPAC also defines the
181:(including varying the
179:supporting electrolytes
149:of other ions than the
24:Electrical double layer
27:
720:10.1201/9780585418049
380:Kosmulski M. (2009).
196:Related abbreviations
173:while monitoring the
171:colloidal dispersions
145:(iep) if there is no
70:environmental science
22:
861:Colloidal chemistry
765:1998EnST...32.2815S
661:2018ESPR...25.7823B
618:2007SRL....14..461N
555:2014PNAS..11118472D
549:(52): 18472–18477.
489:2018ESPR...25.7823B
429:1998EnST...32.2815S
240:reference electrode
238:(against a defined
222:electrode potential
58:electrode potential
856:Physical chemistry
708:Surfactant Science
28:
836:10.1021/jp710386g
830:(11): 4248–4256.
773:10.1021/es9802347
759:(19): 2815–2819.
729:978-0-8247-0560-2
437:10.1021/es9802347
423:(19): 2815–2819.
413:Sposito, Garrison
390:978-1-4200-5188-9
143:isoelectric point
40:electrical charge
38:at which the net
868:
840:
839:
824:J. Phys. Chem. C
818:
812:
809:
803:
800:
794:
791:
785:
784:
748:
742:
741:
703:
697:
696:
655:(8): 7823–7833.
644:
638:
637:
601:
595:
594:
584:
566:
534:
525:
524:
483:(8): 7823–7833.
472:
463:
458:
449:
448:
409:
327:colloidal system
282:
152:
876:
875:
871:
870:
869:
867:
866:
865:
846:
845:
844:
843:
820:
819:
815:
810:
806:
801:
797:
792:
788:
750:
749:
745:
730:
705:
704:
700:
646:
645:
641:
603:
602:
598:
536:
535:
528:
474:
473:
466:
461:IUPAC Gold Book
459:
452:
411:
410:
403:
398:
377:
375:Further reading
355:
341:rate), maximum
316:
302:
295:
281:
270:
264:
210:
198:
163:
150:
139:
128:
102:
66:surface science
17:
12:
11:
5:
874:
872:
864:
863:
858:
848:
847:
842:
841:
813:
804:
795:
786:
743:
728:
698:
639:
612:(3): 461–469.
596:
526:
464:
450:
400:
399:
397:
394:
393:
392:
376:
373:
354:
351:
335:electric field
331:zeta potential
329:exhibits zero
319:
318:
314:
309:
303:
300:
293:
284:
283:
279:
268:
209:
206:
197:
194:
190:zeta potential
186:ionic strength
162:
159:
138:
135:
126:
101:
98:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
873:
862:
859:
857:
854:
853:
851:
837:
833:
829:
825:
817:
814:
808:
805:
799:
796:
790:
787:
782:
778:
774:
770:
766:
762:
758:
754:
747:
744:
739:
735:
731:
725:
721:
717:
713:
709:
702:
699:
694:
690:
686:
682:
678:
674:
670:
666:
662:
658:
654:
650:
643:
640:
635:
631:
627:
623:
619:
615:
611:
607:
600:
597:
592:
588:
583:
578:
574:
570:
565:
560:
556:
552:
548:
544:
540:
533:
531:
527:
522:
518:
514:
510:
506:
502:
498:
494:
490:
486:
482:
478:
471:
469:
465:
462:
457:
455:
451:
446:
442:
438:
434:
430:
426:
422:
418:
414:
408:
406:
402:
395:
391:
387:
383:
379:
378:
374:
372:
369:
365:
360:
352:
350:
348:
344:
340:
336:
332:
328:
323:
313:
310:
307:
304:
299:
292:
289:
288:
287:
278:
274:
267:
263:
262:
261:
259:
254:
252:
248:
243:
241:
237:
233:
229:
225:
223:
219:
215:
207:
205:
203:
195:
193:
191:
187:
184:
180:
176:
172:
168:
160:
158:
156:
148:
144:
136:
134:
132:
123:
119:
118:concentration
115:
114:silver iodide
110:
107:
99:
97:
95:
91:
87:
83:
79:
75:
71:
67:
63:
59:
54:
52:
49:
45:
41:
37:
33:
25:
21:
827:
823:
816:
807:
798:
789:
756:
752:
746:
711:
707:
701:
652:
648:
642:
609:
605:
599:
546:
542:
480:
476:
420:
416:
381:
364:nitrous acid
356:
339:flocculation
325:At pzc, the
324:
320:
311:
305:
297:
290:
285:
276:
272:
265:
257:
255:
244:
231:
230:defines the
226:
211:
199:
164:
140:
130:
111:
103:
55:
51:flocculation
31:
29:
251:electrolyte
249:in a given
218:polarizable
202:initialisms
183:electrolyte
850:Categories
396:References
359:adsorption
343:solubility
167:titrations
147:adsorption
90:titrations
86:adsorption
781:0013-936X
738:2155-6512
677:0944-1344
634:0218-625X
573:0027-8424
505:1614-7499
445:0013-936X
368:oxidative
347:viscosity
214:electrode
106:adsorbent
82:flotation
48:colloidal
44:adsorbent
712:20011074
685:29294236
591:25512517
513:29294236
80:, e.g.,
78:colloids
62:activity
761:Bibcode
693:3946219
657:Bibcode
614:Bibcode
582:4284574
551:Bibcode
521:3946219
485:Bibcode
425:Bibcode
286:where:
234:as the
779:
736:
726:
691:
683:
675:
632:
589:
579:
571:
519:
511:
503:
443:
388:
155:oxides
122:iodide
74:adsorb
689:S2CID
517:S2CID
228:IUPAC
777:ISSN
734:ISSN
724:ISBN
681:PMID
673:ISSN
630:ISSN
587:PMID
569:ISSN
509:PMID
501:ISSN
441:ISSN
386:ISBN
260:as:
133:I).
125:-log
94:soil
30:The
832:doi
828:112
769:doi
716:doi
665:doi
622:doi
577:PMC
559:doi
547:111
493:doi
433:doi
315:σ=0
301:σ=0
294:pzc
280:σ=0
269:pzc
169:of
120:of
852::
826:.
775:.
767:.
757:32
755:.
732:.
722:.
714:.
710:.
687:.
679:.
671:.
663:.
653:25
651:.
628:.
620:.
610:14
608:.
585:.
575:.
567:.
557:.
545:.
541:.
529:^
515:.
507:.
499:.
491:.
481:25
479:.
467:^
453:^
439:.
431:.
421:32
419:.
404:^
275:−
271:=
253:.
224:.
129:=
127:10
36:pH
838:.
834::
783:.
771::
763::
740:.
718::
695:.
667::
659::
636:.
624::
616::
593:.
561::
553::
523:.
495::
487::
447:.
435::
427::
312:E
306:E
298:E
291:E
277:E
273:E
266:E
131:p
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.