17:
90:
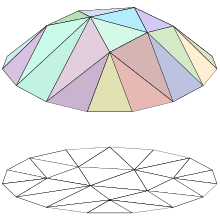
A polyhedral model may be represented in terms of the partition of the plane into polygonal regions, each region being associated with a plane patch which is the image of points of the region under the piecewise-linear function in question.
178:
203:
75:
45:
53:
68:
158:
20:
A piecewise linear function over two dimensions (top) and the polygonal areas on which it is linear (bottom)
25:
40:
that intersects every line parallel to some particular line in a connected set (i.e., a point or a
213:
37:
208:
185:
174:
16:
166:
133:
99:
There are a number of problems in computational geometry which involve polyhedral terrains.
33:
67:
The polyhedral terrain is a generalization of the two-dimensional geometric object, the
170:
138:
121:
52:-axis of the Cartesian coordinate system. Then a polyhedral terrain is the image of a
197:
117:
41:
74:
As the name may suggest, a major application area of polyhedral terrains include
79:
15:
48:, we may assume that the line in question is the
122:"Visibility problems for polyhedral terrains"
8:
137:
108:
153:
151:
149:
7:
171:10.1016/B978-0-444-82537-7.X5000-1
163:Handbook of Computational Geometry
14:
161:; Urrutia, Jorge, eds. (2000).
126:Journal of Symbolic Computation
76:geographic information systems
1:
139:10.1016/S0747-7171(89)80003-3
230:
46:Without loss of generality
54:piecewise-linear function
69:monotone polygonal chain
204:Computational geometry
26:computational geometry
21:
32:in three-dimensional
19:
78:to model real-world
44:) or the empty set.
159:Sack, Jörg-Rüdiger
38:polyhedral surface
30:polyhedral terrain
22:
180:978-0-444-82537-7
221:
188:
184:
155:
144:
143:
141:
113:
229:
228:
224:
223:
222:
220:
219:
218:
194:
193:
192:
191:
181:
157:
156:
147:
116:Cole, Richard;
115:
114:
110:
105:
97:
88:
34:Euclidean space
12:
11:
5:
227:
225:
217:
216:
211:
206:
196:
195:
190:
189:
179:
145:
107:
106:
104:
101:
96:
93:
87:
86:Representation
84:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
226:
215:
212:
210:
207:
205:
202:
201:
199:
187:
182:
176:
172:
168:
164:
160:
154:
152:
150:
146:
140:
135:
131:
127:
123:
119:
118:Sharir, Micha
112:
109:
102:
100:
94:
92:
85:
83:
81:
77:
72:
70:
65:
63:
59:
55:
51:
47:
43:
39:
35:
31:
27:
18:
162:
132:(1): 11–30.
129:
125:
111:
98:
89:
73:
66:
61:
57:
49:
42:line segment
29:
23:
64:variables.
198:Categories
103:References
214:Polyhedra
209:Surfaces
120:(1989).
95:Problems
80:terrains
186:p. 352
177:
36:is a
175:ISBN
60:and
28:, a
167:doi
134:doi
56:in
24:In
200::
173:.
165:.
148:^
128:.
124:.
82:.
71:.
183:.
169::
142:.
136::
130:7
62:y
58:x
50:z
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.