939:
1094:
54:
295:
33:
426:
279:
chirality. While controlling the chirality of chemical reaction presents a significant challenge for synthetic chemists, biological processes can be used instead to faithfully produce chiral molecules in cases where direct chemical synthesis is not feasible or efficient. An example of this is the use of
473:
is the causative agent of foal pneumonia (rattles) and mainly infects foals up to three months in age. However, it has a wide host range, sporadically infecting pigs, cattle, and immunocompromised humans, in particular AIDS patients and those undergoing immunosuppressive therapy. Both pathogens rely
1278:
McLeod MP, Warren RL, Hsiao WW, Araki N, Mihre M, Fernandes C, Miyazawa D, Wong W, Lillquist AL, Wang D, Dosanjh M, Hara H, Petrescu A, Morin RD, Yang G, Stott JM, Schein JE, Shin H, Smailus D, Siddiqui AS, Marra MA, Jones SJ, Holt R, Brinkman FS, Miyauchi K, Fukuda M, Davies JE, Mohn WW, Eltis LD
278:
substrates by first oxygenating the aromatic ring to form a diol (two alcohol groups). Then, the ring is cleaved with intra/extradiol mechanisms, opening the ring and exposing the substrate to further metabolism. Since the chemistry is very stereospecific, the diols are created with predictable
1395:
Buckland, Barry C.; Drew, Stephen W.; Connors, Neal C.; Chartrain, Michel M.; Lee, Chanyong; Salmon, Peter M.; Gbewonyo, Kodzo; Zhou, Weichang; Gailliot, Pat; Singhvi, Rahul; Olewinski, Roger C.; Sun, Wen-Jun; Reddy, Jayanthi; Zhang, Jinyou; Jackey, Barbara A.; Taylor, Colleen; Goklen, Kent E.;
369:
to hydrocarbons, which enhances its ability to degrade these pollutants. They have a wide variety of catabolic pathways and many unique enzyme functions. This gives them the ability to degrade many recalcitrant, toxic hydrocarbons. For example, Rhodococci expresses
1197:
342:
of pollutants as it is commonly found in the natural environment, and they possess certain characteristics that allow them to thrive under a variety of conditions, and they have the capability to metabolize many hydrocarbons.
1904:
Muscatello, G.; Leadon, D. P.; Klay, M.; Ocampo-Sosa, A.; Lewis, D. A.; Fogarty, U.; Buckley, T.; Gilkerson, J. R.; Meijer, W. G.; et al. (2007). "Rhodococcus equi infection in foals: the science of 'rattles'".
251:, and their involvement in fossil fuel biodesulfurization. This genetic and catabolic diversity is not only due to the large bacterial chromosome, but also to the presence of three large linear plasmids.
1940:
Salter, S; Cox, M; Turek, E; Calus, S; Cookson, W; Moffatt, M; Turner, P; Parkhill, J; Loman, N; Walker, A (2014). "Reagent contamination can critically impact sequence-based microbiome analyses".
1338:
Treadway, S.L., K.S. Yanagimachi, E. Lankenau, P.A. Lessard, G. Stephanopoulos and A.J. Sinskey (1999). "Isolation and characterization of indene bioconversion genes from
Rhodococcus strain I24".
262:
comes from bioconversion, using biological systems to convert cheap starting material into more valuable compounds, such as its ability to metabolize harmful environmental pollutants, including
501:
has also been identified as a contaminant of DNA extraction kit reagents and ultrapure water systems, which may lead to its erroneous appearance in microbiota or metagenomic datasets.
2252:
1171:
1783:
Parekh, N. R.; Walker, A.; Roberts, S. J.; Welch, S. J. (November 1994). "Rapid degradation of the triazinone herbicide metamitron by a
Rhodococcus sp. isolated from treated soil".
433:
sp. strain Q1 grown on quinoline - the organism can use quinoline as a sole source of carbon, nitrogen, and energy, tolerating concentrations up to 3.88 millimoles per liter.
1497:
Blasco, Rafael (2001). "Rhodococcus sp. RB1 grows in the presence of high nitrate and nitrite concentrations and assimilates nitrate in moderately saline environments".
1381:
1699:
Takei, Takayuki; Yamasaki, Mika; Yoshida, Masahiro (2014-04-01). "Cesium accumulation of
Rhodococcus erythropolis CS98 strain immobilized in hydrogel matrices".
2278:
2213:
1396:
Junker, Beth; Greasham, Randolph L. (January 1999). "Microbial
Conversion of Indene to Indandiol: A Key Intermediate in the Synthesis of CRIXIVAN".
255:
is also an experimentally advantageous system owing to a relatively fast growth rate and simple developmental cycle, but is not well characterized.
1672:
O'Loughlin, E.J.; Kehrmeyer, S.R.; Sims, G.K. (1996). "Isolation, characterization, and substrate utilization of a quinoline degrading bacterium".
228:. While a few species are pathogenic, most are benign, and have been found to thrive in a broad range of environments, including soil, water, and
2239:
1254:
1826:
Boyle, Alfred W.; Silvin, Christopher J.; Hassett, John P.; Nakas, James P.; Tanenbaum, S. W. (1992-06-01). "Bacterial PCB biodegradation".
346:
Rhodococci possess many properties that makes them suitable for bioremediation under a range of environments. Their ability to undergo
1549:
1440:
288:
2321:
1457:
1869:
Goethals, K.; Vereecke, D.; Jaziri, M.; Van, Montagu M.; Holsters, M. (2001). "Leafy gall formation by
Rhodococcus fascians".
2244:
2303:
2152:
2265:
2006:
938:
1093:
53:
652:
2283:
1063:
917:
836:
684:
928:
796:
592:
2354:
2349:
1053:
826:
704:
622:
528:
419:
785:
581:
1083:
1023:
1013:
846:
806:
724:
663:
642:
602:
538:
243:
are important owing to their ability to catabolize a wide range of compounds and produce bioactive steroids,
1073:
993:
963:
734:
632:
558:
139:
1458:"Microaerophilic degradation of hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine (RDX) by three Rhodococcus strains"
1033:
774:
744:
569:
548:
518:
2114:
1043:
906:
896:
856:
754:
674:
612:
350:
allows them to survive in environments containing low oxygen concentrations, and their ability to undergo
122:
1003:
953:
943:
1375:
1108:
1098:
886:
816:
764:
973:
382:
sp. strain Q1, a strain naturally found in soil and paper mill sludge, contains the ability to degrade
1221:
1198:"Harnessing the catabolic diversity of rhodococci for environmental and biotechnological applications"
983:
866:
2326:
2293:
2174:
1941:
1292:
714:
451:
351:
2205:
1566:
1736:"Cloning of DNA from a Rhodococcus strain conferring the ability to decolorize sulfonated azo dyes"
399:
1567:"Metabolic responses of Rhodococcus erythropolis PR4 grown on diesel oil and various hydrocarbons"
1851:
1654:
1597:
1565:
Laczi, Krisztián; Kis, Ágnes; Horváth, Balázs; Maróti, Gergely; Hegedüs, Botond (November 2015).
1522:
1363:
876:
163:
48:
2161:
2092:
2047:
1988:
1922:
1886:
1843:
1808:
1800:
1765:
1757:
1716:
1646:
1638:
1589:
1545:
1514:
1479:
1436:
1413:
1355:
1320:
1250:
1225:
355:
2313:
2082:
2037:
1978:
1914:
1878:
1835:
1792:
1747:
1708:
1681:
1628:
1581:
1506:
1469:
1405:
1347:
1310:
1300:
1217:
1209:
694:
490:, one of the most important foal pathogens, is endemic on many stud farms around the world.
457:
375:
1281:"The complete genome of Rhodococcus sp. RHA1 provides insights into a catabolic powerhouse"
232:
cells. Some species have large genomes, including the 9.7 megabasepair genome (67% G/C) of
1615:
Yano, Kenichi; Wachi, Masaaki; Tsuchida, Sakiko; Kitazume, Tomoya; Iwai, Noritaka (2015).
224:
95:
2071:
sp. nov., with the ability to degrade petroleum oil, isolated from oil-contaminated soil"
1296:
358:, which allows them to generate their own nutrients in environments with low nutrients.
2200:
1796:
1617:"Degradation of benzotrifluoride via the dioxygenase pathway in Rhodococcus sp. 065240"
1315:
1280:
361:
Rhodococci also contain characteristics that enhances their ability to degrade organic
347:
339:
75:
1685:
294:
2343:
1752:
1735:
1658:
1474:
366:
218:
213:
85:
1855:
1601:
1367:
403:
371:
283:
to produce chiral indandiol derivatives which serve as synthetic intermediates for
248:
131:
105:
32:
2166:
1882:
1526:
1712:
1633:
1616:
2270:
2226:
2146:
267:
1961:
Ramaprasad, E. V. V.; Mahidhara, Ganesh; Sasikala, Ch.; Ramana, Ch. V. (2018).
2042:
2021:
2007:"First wood-digesting enzyme found in bacteria could boost biofuel production"
1585:
1213:
466:
462:
425:
410:, allowing for easier removal from the environment. Other pollutants, such as
244:
229:
2137:
1918:
1847:
1804:
1761:
1642:
2187:
1305:
415:
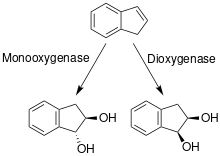
383:
362:
284:
2257:
2096:
2087:
2066:
2051:
1992:
1983:
1967:
sp. nov., a marine electro active actinobacterium isolated from coral reef"
1962:
1926:
1890:
1720:
1650:
1593:
1518:
1483:
1417:
1409:
1359:
1324:
1229:
709:(Gray and Thornton 1928) Goodfellow and Alderson 1979 (Approved Lists 1980)
1812:
1769:
1542:
Microbes in applied research; current advances and challenges; proceedings
1510:
1351:
1139:
digesting enzyme—the first isolated from a bacterium rather than a fungus.
354:
also allows them to survive in oxygenated environments. They also undergo
2131:
1163:
482:
harbors a circular plasmid. Both pathogens are economically significant.
395:
391:
387:
275:
65:
2218:
1839:
411:
407:
263:
2231:
1136:
299:
2108:
2192:
1946:
1260:
1244:
699:(Magnusson 1923) Goodfellow and Alderson 1977 (Approved Lists 1980)
1092:
937:
461:. The former, a plant pathogen, causes leafy gall disease in both
424:
293:
2075:
International
Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology
2030:
International
Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology
1971:
International
Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology
474:
on a conjugative virulence plasmid to cause disease. In case of
2112:
978:(Kruse 1896) Goodfellow and Alderson 1977 (Approved Lists 1980)
2179:
1435:. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 231–256.
338:
has been greatly researched as a potential agent for the
2020:
Takeuchi, M; Hatano, K; Sedlácek, I; Pácová, Z (2002).
1172:
List of
Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature
1734:
Heiss, G. S.; Gowan, B.; Dabbs, E. R. (1992-12-01).
2121:
958:Goodfellow and Alderson 1979 (Approved Lists 1980)
1674:International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation
212:is a genus of aerobic, nonsporulating, nonmotile
968:(Zopf 1891) Tsukamura 1974 (Approved Lists 1980)
145:(Zopf 1891) Tsukamura 1974 (Approved Lists 1980)
1068:(Goodfellow et al. 1995) Goodfellow et al. 2002
1246:Corynebacteria: Genomics and Molecular Biology
647:Rowbotham and Cross 1979 (Approved Lists 1980)
402:. Rhodococci are also capable of accumulating
2065:Chaudhary, Dhiraj Kumar; Kim, Jaisoo (2018).
1196:van der Geize R. & L. Dijkhuizen (2004).
8:
1456:Fuller, M.E.; Perreault, N. (July 8, 2010).
1380:: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (
657:(Serrano et al. 1972) Yassin and Schaal 2005
1621:Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry
2109:
1222:11370/a1dfa0fd-dd65-4c1d-b9b4-bfa98038dcbe
31:
20:
2086:
2041:
2026:sp. nov., isolated from a medieval grave"
1982:
1945:
1751:
1632:
1473:
1314:
1304:
1701:Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering
1273:
1271:
1269:
1191:
1189:
1151:
1125:
486:is a major pathogen of tobacco plants.
365:. Their hydrophobic surface allows for
1574:Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology
1544:. World Scientific. pp. 197–200.
1373:
1157:
1155:
7:
2294:23dcb2c6-536a-44c9-b2cd-5ac0bc474f60
478:, this is a linear plasmid, whereas
422:can also be degraded by Rhodococci.
331:Biodegradation of organic pollutants
1785:The Journal of Applied Bacteriology
291:used in the treatment of HIV/AIDS.
1797:10.1111/j.1365-2672.1994.tb04389.x
14:
512:comprises the following species:
258:Another important application of
1475:10.1111/j.1472-765x.2010.02897.x
429:Scanning electron micrograph of
52:
1462:Letters in Applied Microbiology
374:, which can be used to degrade
1135:was identified as producing a
719:(Tilford 1936) Goodfellow 1984
1:
1883:10.1146/annurev.phyto.39.1.27
1686:10.1016/S0964-8305(96)00032-7
326:-indandiol by Rhodococcus sp.
274:species typically metabolize
1753:10.1016/0378-1097(92)90030-r
1713:10.1016/j.jbiosc.2013.09.013
1634:10.1080/09168451.2014.982502
449:has two pathogenic species:
378:, a recalcitrant pollutant.
216:bacteria closely related to
1965:Rhodococcus electrodiphilus
1340:Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol
348:microaerophilic respiration
2371:
2153:Rhodococcus (Nocardiaceae)
1249:. Caister Academic Press.
1243:Burkovski A., ed. (2008).
406:ions, such as radioactive
2043:10.1099/00207713-52-2-409
1740:FEMS Microbiology Letters
1586:10.1007/s00253-015-6936-z
1540:Mendez-Volas, A. (2012).
1214:10.1016/j.mib.2004.04.001
420:polychlorinated biphenyls
169:
162:
155:
150:
137:
130:
49:Scientific classification
47:
39:
30:
23:
1919:10.2746/042516407x209217
1499:Archives of Microbiology
1431:Alvarez, Héctor (2010).
270:, herbicides, and PCBs.
1306:10.1073/pnas.0607048103
841:Helmke and Weyland 1984
140:Rhodococcus rhodochrous
2088:10.1099/ijsem.0.002750
1984:10.1099/ijsem.0.002895
1871:Annu. Rev. Phytopathol
1433:Biology of Rhodococcus
1410:10.1006/mben.1998.0107
1103:
948:
911:Rehfuss and Urban 2006
871:Chaudhary and Kim 2018
739:Goodfellow et al. 1985
689:Ramaprasad et al. 2018
597:Nimaichand et al. 2013
533:Goodfellow et al. 2004
434:
327:
1511:10.1007/s002030100285
1398:Metabolic Engineering
1352:10.1007/s002530051463
1162:Euzéby JP, Parte AC.
1096:
1058:Matsuyama et al. 2003
941:
653:R. corynebacterioides
428:
297:
1279:(October 17, 2006).
1113:Stoecker et al. 1994
998:Táncsics et al. 2017
801:Mayilraj et al. 2006
769:Takeuchi et al. 2002
494:In molecular biology
1297:2006PNAS..10315582M
1291:(42): 15582–15587.
1048:Kämpfer et al. 2013
944:Rhodococcus rhodnii
901:Nguyen and Kim 2016
759:Nguyen and Kim 2016
679:Kämpfer et al. 2014
617:Kämpfer et al. 2013
575:Hiddema et al. 1985
400:protocatechuic acid
352:aerobic respiration
2024:Rhodococcus jostii
1840:10.1007/BF00129089
1133:Rhodococcus jostii
1104:
1099:Rhodococcus zopfii
1064:R. wratislaviensis
949:
918:R. psychrotolerans
881:Klatte et al. 1995
685:R. electrodiphilus
435:
328:
298:The conversion of
289:protease inhibitor
2337:
2336:
2115:Taxon identifiers
1580:(22): 9745–9759.
1256:978-1-904455-30-1
1114:
1089:
1088:Zhang et al. 2005
1079:
1078:Zhang et al. 2021
1069:
1059:
1049:
1039:
1029:
1019:
1018:Zhang et al. 2021
1009:
999:
989:
979:
969:
959:
934:
929:R. pyridinivorans
924:
923:Silva et al. 2018
912:
902:
892:
882:
872:
862:
852:
842:
832:
831:Zhang et al. 2002
822:
821:Singh et al. 2015
812:
802:
797:R. kroppenstedtii
792:
780:
770:
760:
750:
749:Jones et al. 2004
740:
730:
720:
710:
700:
690:
680:
670:
658:
648:
638:
628:
618:
608:
598:
593:R. canchipurensis
588:
576:
564:
554:
544:
534:
524:
523:Hwang et al. 2015
356:nitrogen fixation
205:
204:
199:
189:
188:Jones et al. 2013
179:
178:Jones et al. 2013
126:
16:Genus of bacteria
2362:
2330:
2329:
2317:
2316:
2307:
2306:
2297:
2296:
2287:
2286:
2274:
2273:
2271:NHMSYS0020930441
2261:
2260:
2258:rhodococcus.html
2248:
2247:
2235:
2234:
2222:
2221:
2209:
2208:
2196:
2195:
2183:
2182:
2170:
2169:
2157:
2156:
2155:
2142:
2141:
2140:
2110:
2101:
2100:
2090:
2081:(5): 1749–1756.
2069:Rhodococcus olei
2062:
2056:
2055:
2045:
2036:(Pt 2): 409–13.
2017:
2011:
2010:
2003:
1997:
1996:
1986:
1977:(8): 2644–2649.
1958:
1952:
1951:
1949:
1937:
1931:
1930:
1901:
1895:
1894:
1866:
1860:
1859:
1834:(2–3): 285–298.
1823:
1817:
1816:
1780:
1774:
1773:
1755:
1746:(2–3): 221–226.
1731:
1725:
1724:
1696:
1690:
1689:
1669:
1663:
1662:
1636:
1612:
1606:
1605:
1571:
1562:
1556:
1555:
1537:
1531:
1530:
1494:
1488:
1487:
1477:
1453:
1447:
1446:
1428:
1422:
1421:
1392:
1386:
1385:
1379:
1371:
1335:
1329:
1328:
1318:
1308:
1275:
1264:
1263:
1240:
1234:
1233:
1193:
1184:
1183:
1181:
1179:
1159:
1140:
1130:
1112:
1087:
1077:
1067:
1057:
1054:R. tukisamuensis
1047:
1037:
1027:
1017:
1008:Lee and Kim 2021
1007:
997:
987:
977:
967:
957:
933:Yoon et al. 2000
932:
922:
910:
900:
890:
880:
870:
860:
850:
840:
837:R. marinonascens
830:
827:R. maanshanensis
820:
810:
800:
790:
779:Yoon et al. 2000
778:
768:
758:
748:
738:
728:
718:
708:
698:
688:
678:
669:Wang et al. 2019
668:
656:
646:
636:
626:
623:R. cercidiphylli
616:
606:
596:
586:
574:
563:Zhao et al. 2012
562:
552:
542:
532:
529:R. aetherivorans
522:
376:benzotrifluoride
197:
187:
177:
121:
57:
56:
35:
21:
2370:
2369:
2365:
2364:
2363:
2361:
2360:
2359:
2355:Bacteria genera
2350:Mycobacteriales
2340:
2339:
2338:
2333:
2325:
2320:
2312:
2310:
2302:
2300:
2292:
2290:
2282:
2277:
2269:
2264:
2256:
2251:
2243:
2238:
2230:
2225:
2217:
2212:
2204:
2199:
2191:
2186:
2178:
2173:
2165:
2160:
2151:
2150:
2145:
2136:
2135:
2130:
2117:
2106:
2104:
2064:
2063:
2059:
2019:
2018:
2014:
2005:
2004:
2000:
1960:
1959:
1955:
1939:
1938:
1934:
1903:
1902:
1898:
1868:
1867:
1863:
1825:
1824:
1820:
1782:
1781:
1777:
1733:
1732:
1728:
1698:
1697:
1693:
1671:
1670:
1666:
1614:
1613:
1609:
1569:
1564:
1563:
1559:
1552:
1539:
1538:
1534:
1496:
1495:
1491:
1455:
1454:
1450:
1443:
1430:
1429:
1425:
1394:
1393:
1389:
1372:
1337:
1336:
1332:
1277:
1276:
1267:
1257:
1242:
1241:
1237:
1195:
1194:
1187:
1177:
1175:
1161:
1160:
1153:
1149:
1144:
1143:
1131:
1127:
1122:
1117:
1028:Lee et al. 2019
791:Liu et al. 2014
786:R. kronopolitis
705:R. erythropolis
607:Lee et al. 2020
587:Lin et al. 2012
582:R. boritolerans
543:Guo et al. 2015
507:
496:
443:
333:
314:-indandiol and
225:Corynebacterium
198:Kim et al. 2022
146:
143:
120:
96:Mycobacteriales
51:
17:
12:
11:
5:
2368:
2366:
2358:
2357:
2352:
2342:
2341:
2335:
2334:
2332:
2331:
2318:
2308:
2298:
2288:
2275:
2262:
2249:
2236:
2223:
2210:
2197:
2184:
2171:
2158:
2143:
2127:
2125:
2119:
2118:
2113:
2103:
2102:
2057:
2012:
1998:
1953:
1947:10.1101/007187
1932:
1913:(5): 470–478.
1896:
1861:
1828:Biodegradation
1818:
1791:(5): 467–475.
1775:
1726:
1707:(4): 497–500.
1691:
1680:(2): 107–118.
1664:
1627:(3): 496–504.
1607:
1557:
1550:
1532:
1505:(6): 435–440.
1489:
1468:(3): 313–318.
1448:
1441:
1423:
1387:
1346:(6): 786–793.
1330:
1265:
1255:
1235:
1208:(3): 255–261.
1185:
1150:
1148:
1145:
1142:
1141:
1124:
1123:
1121:
1118:
1116:
1115:
1091:
1090:
1084:R. yunnanensis
1080:
1070:
1060:
1050:
1040:
1030:
1024:R. subtropicus
1020:
1014:R. spongiicola
1010:
1000:
990:
988:Li et al. 2015
980:
970:
964:R. rhodochrous
960:
936:
935:
925:
913:
903:
893:
891:Li et al. 2020
883:
873:
863:
861:Tsukamura 1983
853:
851:Li et al. 2012
847:R. nanhaiensis
843:
833:
823:
813:
811:Li et al. 2007
807:R. kyotonensis
803:
793:
781:
771:
761:
751:
741:
731:
729:Ma et al. 2017
725:R. gannanensis
721:
711:
701:
691:
681:
671:
664:R. daqingensis
659:
649:
643:R. coprophilus
639:
637:Tsukamura 1983
629:
627:Li et al. 2012
619:
609:
603:R. cavernicola
599:
589:
577:
565:
555:
553:Ko et al. 2015
545:
539:R. agglutinans
535:
525:
514:
506:
503:
495:
492:
442:
436:
340:bioremediation
332:
329:
203:
202:
201:
200:
190:
180:
167:
166:
160:
159:
153:
152:
148:
147:
144:
135:
134:
128:
127:
113:
109:
108:
103:
99:
98:
93:
89:
88:
83:
79:
78:
76:Actinomycetota
73:
69:
68:
63:
59:
58:
45:
44:
37:
36:
28:
27:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2367:
2356:
2353:
2351:
2348:
2347:
2345:
2328:
2323:
2319:
2315:
2309:
2305:
2299:
2295:
2289:
2285:
2280:
2276:
2272:
2267:
2263:
2259:
2254:
2250:
2246:
2241:
2237:
2233:
2228:
2224:
2220:
2215:
2211:
2207:
2202:
2198:
2194:
2189:
2185:
2181:
2176:
2172:
2168:
2163:
2159:
2154:
2148:
2144:
2139:
2133:
2129:
2128:
2126:
2124:
2120:
2116:
2111:
2107:
2098:
2094:
2089:
2084:
2080:
2076:
2072:
2070:
2061:
2058:
2053:
2049:
2044:
2039:
2035:
2031:
2027:
2025:
2016:
2013:
2008:
2002:
1999:
1994:
1990:
1985:
1980:
1976:
1972:
1968:
1966:
1957:
1954:
1948:
1943:
1936:
1933:
1928:
1924:
1920:
1916:
1912:
1908:
1907:Equine Vet. J
1900:
1897:
1892:
1888:
1884:
1880:
1876:
1872:
1865:
1862:
1857:
1853:
1849:
1845:
1841:
1837:
1833:
1829:
1822:
1819:
1814:
1810:
1806:
1802:
1798:
1794:
1790:
1786:
1779:
1776:
1771:
1767:
1763:
1759:
1754:
1749:
1745:
1741:
1737:
1730:
1727:
1722:
1718:
1714:
1710:
1706:
1702:
1695:
1692:
1687:
1683:
1679:
1675:
1668:
1665:
1660:
1656:
1652:
1648:
1644:
1640:
1635:
1630:
1626:
1622:
1618:
1611:
1608:
1603:
1599:
1595:
1591:
1587:
1583:
1579:
1575:
1568:
1561:
1558:
1553:
1551:9789814405034
1547:
1543:
1536:
1533:
1528:
1524:
1520:
1516:
1512:
1508:
1504:
1500:
1493:
1490:
1485:
1481:
1476:
1471:
1467:
1463:
1459:
1452:
1449:
1444:
1442:9783642129377
1438:
1434:
1427:
1424:
1419:
1415:
1411:
1407:
1403:
1399:
1391:
1388:
1383:
1377:
1369:
1365:
1361:
1357:
1353:
1349:
1345:
1341:
1334:
1331:
1326:
1322:
1317:
1312:
1307:
1302:
1298:
1294:
1290:
1286:
1282:
1274:
1272:
1270:
1266:
1261:
1258:
1252:
1248:
1247:
1239:
1236:
1231:
1227:
1223:
1219:
1215:
1211:
1207:
1203:
1199:
1192:
1190:
1186:
1173:
1169:
1167:
1158:
1156:
1152:
1146:
1138:
1134:
1129:
1126:
1119:
1111:
1110:
1106:
1105:
1102:on agar plate
1101:
1100:
1095:
1086:
1085:
1081:
1076:
1075:
1074:R. xishaensis
1071:
1066:
1065:
1061:
1056:
1055:
1051:
1046:
1045:
1041:
1036:
1035:
1031:
1026:
1025:
1021:
1016:
1015:
1011:
1006:
1005:
1001:
996:
995:
994:R. sovatensis
991:
986:
985:
981:
976:
975:
971:
966:
965:
961:
956:
955:
951:
950:
947:on agar plate
946:
945:
940:
931:
930:
926:
920:
919:
914:
909:
908:
907:R. phenolicus
904:
899:
898:
894:
889:
888:
884:
879:
878:
874:
869:
868:
864:
859:
858:
854:
849:
848:
844:
839:
838:
834:
829:
828:
824:
819:
818:
814:
809:
808:
804:
799:
798:
794:
788:
787:
782:
777:
776:
772:
767:
766:
762:
757:
756:
752:
747:
746:
742:
737:
736:
735:R. globerulus
732:
727:
726:
722:
717:
716:
712:
707:
706:
702:
697:
696:
692:
687:
686:
682:
677:
676:
672:
666:
665:
660:
655:
654:
650:
645:
644:
640:
635:
634:
633:R. chubuensis
630:
625:
624:
620:
615:
614:
610:
605:
604:
600:
595:
594:
590:
584:
583:
578:
572:
571:
566:
561:
560:
559:R. artemisiae
556:
551:
550:
546:
541:
540:
536:
531:
530:
526:
521:
520:
516:
515:
513:
511:
504:
502:
500:
493:
491:
489:
485:
481:
477:
472:
468:
464:
460:
459:
454:
453:
448:
441:
437:
432:
427:
423:
421:
417:
413:
409:
405:
401:
397:
393:
390:derivatives,
389:
385:
381:
377:
373:
368:
364:
359:
357:
353:
349:
344:
341:
337:
330:
325:
321:
317:
313:
309:
305:
301:
296:
292:
290:
286:
282:
277:
273:
269:
265:
261:
256:
254:
250:
246:
242:
237:
235:
231:
227:
226:
221:
220:
219:Mycobacterium
215:
214:Gram-positive
211:
210:
195:
194:Spelaeibacter
191:
185:
181:
175:
171:
170:
168:
165:
161:
158:
154:
149:
142:
141:
136:
133:
129:
124:
119:
118:
114:
111:
110:
107:
104:
101:
100:
97:
94:
91:
90:
87:
86:Actinomycetia
84:
81:
80:
77:
74:
71:
70:
67:
64:
61:
60:
55:
50:
46:
42:
38:
34:
29:
26:
22:
19:
2122:
2105:
2078:
2074:
2068:
2060:
2033:
2029:
2023:
2015:
2001:
1974:
1970:
1964:
1956:
1935:
1910:
1906:
1899:
1874:
1870:
1864:
1831:
1827:
1821:
1788:
1784:
1778:
1743:
1739:
1729:
1704:
1700:
1694:
1677:
1673:
1667:
1624:
1620:
1610:
1577:
1573:
1560:
1541:
1535:
1502:
1498:
1492:
1465:
1461:
1451:
1432:
1426:
1404:(1): 63–74.
1401:
1397:
1390:
1376:cite journal
1343:
1339:
1333:
1288:
1284:
1245:
1238:
1205:
1202:Microbiology
1201:
1176:. Retrieved
1165:
1132:
1128:
1107:
1097:
1082:
1072:
1062:
1052:
1042:
1034:R. triatomae
1032:
1022:
1012:
1002:
992:
982:
972:
962:
952:
942:
927:
916:
905:
895:
885:
875:
865:
855:
845:
835:
825:
815:
805:
795:
784:
775:R. koreensis
773:
763:
753:
745:R. gordoniae
743:
733:
723:
713:
703:
693:
683:
673:
662:
651:
641:
631:
621:
611:
601:
591:
580:
570:R. australis
568:
557:
549:R. antrifimi
547:
537:
527:
519:R. aerolatus
517:
509:
508:
498:
497:
487:
483:
479:
475:
470:
456:
450:
446:
444:
439:
430:
379:
372:dioxygenases
360:
345:
335:
334:
323:
319:
315:
311:
307:
303:
280:
271:
259:
257:
252:
249:acrylic acid
240:
238:
233:
223:
217:
208:
207:
206:
193:
183:
174:Prescottella
173:
156:
138:
132:Type species
116:
115:
106:Nocardiaceae
40:
24:
18:
2304:rhodococcus
2227:iNaturalist
2147:Wikispecies
2123:Rhodococcus
1166:Rhodococcus
1044:R. trifolii
1038:Yassin 2005
897:R. pedocola
857:R. obuensis
755:R. humicola
715:R. fascians
675:R. defluvii
613:R. cerastii
510:Rhodococcus
499:Rhodococcus
484:R. fascians
476:R. fascians
452:R. fascians
447:Rhodococcus
440:Rhodococcus
438:Pathogenic
431:Rhodococcus
404:heavy metal
380:Rhodococcus
336:Rhodococcus
281:Rhodococcus
272:Rhodococcus
268:naphthalene
260:Rhodococcus
253:Rhodococcus
241:Rhodococcus
239:Strains of
234:Rhodococcus
209:Rhodococcus
117:Rhodococcus
41:Rhodococcus
25:Rhodococcus
2344:Categories
1147:References
1004:R. spelaei
954:R. rhodnii
467:gymnosperm
463:angiosperm
445:The genus
416:pesticides
386:, various
363:pollutants
245:acrylamide
236:sp. RHA1.
230:eukaryotic
184:Prescottia
157:See text.
1877:: 27–52.
1848:0923-9820
1805:0021-8847
1762:0378-1097
1659:205616972
1643:1347-6947
1109:R. zopfii
887:R. oryzae
877:R. opacus
817:R. lactis
765:R. jostii
384:quinoline
285:indinavir
2201:Fungorum
2132:Wikidata
2097:29620494
2052:11931149
1993:29957174
1927:17910275
1891:11701858
1721:24183457
1651:25412819
1594:26346267
1519:11491084
1484:20666987
1418:10935755
1360:10422226
1325:17030794
1230:15196492
1178:June 25,
974:R. ruber
469:plants.
412:azo dyes
396:benzoate
392:catechol
388:pyridine
367:adhesion
276:aromatic
164:Synonyms
151:Species
102:Family:
72:Phylum:
66:Bacteria
62:Domain:
2219:3224437
2138:Q288311
1942:bioRxiv
1856:7272347
1813:8002472
1770:1490602
1602:9213608
1368:6264248
1316:1622865
1293:Bibcode
984:R. soli
867:R. olei
695:R. equi
505:Species
488:R. equi
480:R. equi
471:R. equi
458:R. equi
408:caesium
264:toluene
112:Genus:
92:Order:
82:Class:
2327:559536
2314:227836
2311:uBio:
2291:NZOR:
2245:957964
2232:541076
2193:1RHDCG
2095:
2050:
1991:
1944:
1925:
1889:
1854:
1846:
1811:
1803:
1768:
1760:
1719:
1657:
1649:
1641:
1600:
1592:
1548:
1527:864067
1525:
1517:
1482:
1439:
1416:
1366:
1358:
1323:
1313:
1253:
1228:
1174:(LPSN)
1137:lignin
398:, and
300:indene
247:, and
2322:WoRMS
2301:PPE:
2206:27375
2180:85900
1852:S2CID
1655:S2CID
1598:S2CID
1570:(PDF)
1523:S2CID
1364:S2CID
1120:Notes
304:trans
2284:1827
2279:NCBI
2253:LPSN
2240:ITIS
2214:GBIF
2188:EPPO
2167:794V
2093:PMID
2048:PMID
1989:PMID
1923:PMID
1887:PMID
1844:ISSN
1809:PMID
1801:ISSN
1766:PMID
1758:ISSN
1717:PMID
1647:PMID
1639:ISSN
1590:PMID
1546:ISBN
1515:PMID
1480:PMID
1437:ISBN
1414:PMID
1382:link
1356:PMID
1321:PMID
1285:PNAS
1251:ISBN
1226:PMID
1180:2022
465:and
455:and
418:and
287:, a
222:and
125:1891
123:Zopf
43:sp.
2266:NBN
2175:EoL
2162:CoL
2083:doi
2038:doi
1979:doi
1915:doi
1879:doi
1836:doi
1793:doi
1748:doi
1709:doi
1705:117
1682:doi
1629:doi
1582:doi
1507:doi
1503:175
1470:doi
1406:doi
1348:doi
1311:PMC
1301:doi
1289:103
1218:hdl
1210:doi
316:cis
302:to
2346::
2324::
2281::
2268::
2255::
2242::
2229::
2216::
2203::
2190::
2177::
2164::
2149::
2134::
2091:.
2079:68
2077:.
2073:.
2046:.
2034:52
2032:.
2028:.
1987:.
1975:68
1973:.
1969:.
1921:.
1911:39
1909:.
1885:.
1875:39
1873:.
1850:.
1842:.
1830:.
1807:.
1799:.
1789:77
1787:.
1764:.
1756:.
1744:78
1742:.
1738:.
1715:.
1703:.
1678:38
1676:.
1653:.
1645:.
1637:.
1625:79
1623:.
1619:.
1596:.
1588:.
1578:99
1576:.
1572:.
1521:.
1513:.
1501:.
1478:.
1466:51
1464:.
1460:.
1412:.
1400:.
1378:}}
1374:{{
1362:.
1354:.
1344:51
1342:.
1319:.
1309:.
1299:.
1287:.
1283:.
1268:^
1259:.
1224:.
1216:.
1204:.
1200:.
1188:^
1170:.
1154:^
921:"
789:"
667:"
585:"
573:"
414:,
394:,
322:,2
318:-1
310:,2
306:-1
266:,
196:"
186:"
176:"
2099:.
2085::
2067:"
2054:.
2040::
2022:"
2009:.
1995:.
1981::
1963:"
1950:.
1929:.
1917::
1893:.
1881::
1858:.
1838::
1832:3
1815:.
1795::
1772:.
1750::
1723:.
1711::
1688:.
1684::
1661:.
1631::
1604:.
1584::
1554:.
1529:.
1509::
1486:.
1472::
1445:.
1420:.
1408::
1402:1
1384:)
1370:.
1350::
1327:.
1303::
1295::
1262:.
1232:.
1220::
1212::
1206:7
1182:.
1168:"
1164:"
915:"
783:"
661:"
579:"
567:"
324:R
320:S
312:R
308:R
192:"
182:"
172:"
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.