67:
234:
252:
114:
859:
43:
330:
The most common problem with syndactyly correction is creeping of the skin towards the fingertip over time. This is likely due to tension at the site of the repair between the digits. Additional surgery may be required to correct this. One critique of using skin grafts is that the grafts darken in
321:
Because the circumference of the conjoined fingers is smaller than the circumference of the two separated fingers, there is not enough skin to cover both digits once they are separated at the time of surgery. Therefore, the surgeon must bring new skin into the area at the time of surgery. This is
312:
Syndactyly of the border digits (thumb/index finger or ring/small fingers) is treated at early age to prevent the larger digit from curving towards the smaller digit with growth. Typically, syndactyly of these digits is treated at six months of age. The treatment of syndactyly of the other digits
331:
the years after surgery and become more noticeable. Also, if the skin grafts are harvested from the groin area, the skin may grow hair. Finally, the fingers may deviate after surgery. This is most commonly seen in complex syndactyly (when there has been a bone joining of the fingers).
890:
322:
most commonly done with a skin graft (from groin or anterior elbow). Skin can also be used from the back of the hand by mobilizing it (called a "graftless" syndactyly correction), which requires planning over a period of months prior to surgery.
883:
758:
743:
158:
Fenestrated syndactyly, also known as acrosyndactyly or terminal syndactyly, means the skin is joined for most of the digit but in a proximal area there are gaps in the syndactyly with normal skin. This type of syndactyly is found in
876:
313:
is elective and is more commonly performed when the digits have grown, at 18 months of age. Special situations, such as complex syndactyly and involvement of border digits, may warrant surgical intervention earlier than 6 months.
174:, also known as SHH, which dissolves the tissue between the fingers and toes, and the webbing disappears. In some fetuses, this process does not occur completely between all fingers or toes and some residual webbing remains.
166:
Simple syndactyly can be full or partial, and is present at birth (congenital). In early human fetal development, webbing (syndactyly) of the toes and fingers is normal. At about 6 weeks of gestation,
1572:
1470:
963:
868:
547:"Localization of the syndactyly type II (synpolydactyly) locus to 2q31 region and identification of tight linkage to HOXD8 intragenic marker"
1411:
773:
299:
1365:
1084:
277:
1200:
903:
1370:
1089:
919:
907:
273:
118:
1401:
1455:
1375:
1310:
953:
793:
262:
1347:
981:
958:
281:
266:
160:
88:
863:
147:
In incomplete syndactyly, the skin is only joined part of the distance to the tip of the involved digits.
1250:
915:
1465:
339:
The earliest appreciation of syndactyly as a birth anomaly or burn-trauma can be traced back to the
66:
1283:
899:
762:
1145:
628:
Dao, Khiem D.; Shin, Alexander Y.; Billings, Annette; Oberg, Kerby C.; Wood, Virchel E. (2004).
1480:
1460:
833:
804:
706:
657:
649:
610:
569:
527:
478:
429:
421:
55:
1527:
1522:
1443:
1435:
1355:
1319:
1127:
1079:
1036:
696:
688:
641:
600:
561:
517:
509:
468:
460:
413:
351:
183:
60:
1543:
1278:
1108:
1074:
1027:
80:
546:
197:: 2q34-q36; webbing occurs between middle and ring fingers and/or second and third toes.
144:
In complete syndactyly, the skin is joined all the way to the tip of the involved digits.
1406:
1337:
1301:
1273:
1195:
1099:
973:
844:
701:
676:
522:
497:
473:
448:
348:
233:
203:: 2q31; also involves long and ring fingers, but has a sixth finger merged in between.
171:
152:
767:
417:
1566:
1416:
1360:
1327:
1210:
1031:
645:
1498:
1391:
1233:
1205:
991:
986:
464:
390:
798:
1421:
1188:
1179:
1064:
996:
828:
369:
251:
809:
1396:
1332:
1245:
1239:
1215:
1150:
1119:
1069:
1041:
605:
588:
344:
340:
226:
222:
113:
653:
425:
1503:
1448:
1255:
1140:
1133:
1114:
1046:
1010:
839:
752:
629:
187:
167:
17:
710:
661:
614:
565:
531:
482:
433:
182:
Five types of syndactyly have been identified in humans. The corresponding
858:
573:
945:
941:
923:
692:
133:
129:
In simple syndactyly, adjacent fingers or toes are joined by soft tissue.
735:
1513:
1171:
363:
42:
747:
498:"Localization of a Gene for Syndactyly Type 1 to Chromosome 2q34-q36"
84:
132:
In complex syndactyly, the bones of adjacent digits are fused. The
513:
366:, the arrangement of fingers and toes in different kinds of animals
237:
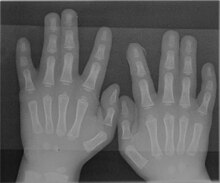
Radiograph of Type 1 syndactyly of the hands (no bony involvement)
232:
112:
1056:
787:
784:
781:
778:
872:
1489:
1019:
932:
245:
87:, but is an unusual condition in humans. The term is from
677:"Syndactyly: phenotypes, genetics and current classification"
155:) and typically involves more digits than simple syndactyly.
634:
The
Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
27:
Condition of fingers or toes being fused together at birth
630:"Surgical treatment of congenital syndactyly of the hand"
347:(d. 1013 CE), known in the West as Abulcasis. The French
209:: 6q21-q23; small finger is merged into the ring finger.
151:
Complex syndactyly occurs as part of a syndrome (such as
50:
Partial simple syndactyly in the second and third toes
725:
354:
also described syndactyly in the sixteenth century.
1536:
1512:
1488:
1479:
1434:
1384:
1346:
1318:
1309:
1300:
1266:
1226:
1170:
1163:
1098:
1055:
1018:
1009:
972:
940:
931:
914:
819:
729:
372:, the common name for syndactyly affecting the feet
54:
35:
453:Proceedings (Baylor University. Medical Center)
83:are fused together. It occurs normally in some
1573:Congenital disorders of musculoskeletal system
496:Bosse K, Betz RC, Lee YA, et al. (2000).
884:
186:associated with these types and their common
8:
587:Sato D, Liang D, Wu L, et al. (2007).
280:. Unsourced material may be challenged and
1485:
1315:
1306:
1167:
1015:
937:
928:
891:
877:
869:
726:
215:: 7q36; involves all fingers and/or toes.
140:Syndactyly can be complete or incomplete.
65:
41:
32:
700:
604:
589:"A syndactyly type IV locus maps to 7q36"
521:
472:
300:Learn how and when to remove this message
404:Maisels, D.O. (1962). "Acrosyndactyly".
221:: 2q31-q32; similar to type I, but the
545:Sarfarazi, Akarsu; et al. (1995).
382:
125:Syndactyly can be simple or complex.
7:
1412:Greig cephalopolysyndactyly syndrome
278:adding citations to reliable sources
170:takes place due to a protein named
79:is a condition wherein two or more
902:malformations and deformations of
681:European Journal of Human Genetics
406:British Journal of Plastic Surgery
25:
675:Malik, Sajid (15 February 2012).
121:with syndactyly of several digits
857:
646:10.5435/00124635-200401000-00006
250:
1085:Congenital patellar dislocation
964:Wallis–Zieff–Goldblatt syndrome
465:10.1080/08998280.2005.11928029
1:
418:10.1016/s0007-1226(62)80021-6
98: 'together' and
391:"Diprotodontia Introduction"
136:exhibits complex syndactyly.
1371:Oto-palato-digital syndrome
1366:Hallermann–Streiff syndrome
1090:Congenital knee dislocation
908:musculoskeletal abnormality
190:expression are as follows:
119:Greig cephalopolysyndactyly
1589:
1402:Craniodiaphyseal dysplasia
447:Flatt A (1 January 2005).
117:The hand of a person with
1376:Treacher Collins syndrome
1227:reduction deficits / limb
606:10.1007/s10038-007-0150-5
593:Journal of Human Genetics
49:
40:
1201:Cenani–Lenz syndactylism
954:Cleidocranial dysostosis
1348:Craniofacial dysostosis
904:musculoskeletal system
238:
161:amniotic band syndrome
122:
1456:Klippel–Feil syndrome
866:at Wikimedia Commons
236:
116:
1466:Spina bifida occulta
982:Madelung's deformity
959:Sprengel's deformity
693:10.1038/ejhg.2012.14
566:10.1093/hmg/4.8.1453
274:improve this section
1284:RAPADILINO syndrome
1146:Rocker bottom foot
820:External resources
239:
229:may also be fused.
123:
1560:
1559:
1556:
1555:
1552:
1551:
1481:Thoracic skeleton
1461:Spondylolisthesis
1430:
1429:
1296:
1295:
1292:
1291:
1159:
1158:
1005:
1004:
862:Media related to
854:
853:
502:Am. J. Hum. Genet
310:
309:
302:
74:
73:
30:Medical condition
16:(Redirected from
1580:
1528:Pectus carinatum
1523:Pectus excavatum
1486:
1444:Spinal curvature
1436:Vertebral column
1356:Crouzon syndrome
1320:Craniosynostosis
1316:
1307:
1172:fingers and toes
1168:
1080:Discoid meniscus
1037:Upington disease
1016:
938:
929:
893:
886:
879:
870:
861:
727:
715:
714:
704:
672:
666:
665:
625:
619:
618:
608:
584:
578:
577:
551:
542:
536:
535:
525:
493:
487:
486:
476:
449:"Webbed fingers"
444:
438:
437:
401:
395:
394:
387:
305:
298:
294:
291:
285:
254:
246:
105: 'finger'.
70:
69:
61:Medical genetics
45:
33:
21:
1588:
1587:
1583:
1582:
1581:
1579:
1578:
1577:
1563:
1562:
1561:
1548:
1544:Poland syndrome
1532:
1508:
1475:
1426:
1380:
1342:
1288:
1279:Larsen syndrome
1267:multiple joints
1262:
1222:
1155:
1094:
1075:Genu recurvatum
1051:
1028:Hip dislocation
1001:
968:
918:
910:
897:
855:
850:
849:
815:
814:
738:
724:
719:
718:
674:
673:
669:
627:
626:
622:
586:
585:
581:
554:Hum. Mol. Genet
549:
544:
543:
539:
495:
494:
490:
446:
445:
441:
403:
402:
398:
389:
388:
384:
379:
360:
343:Muslim surgeon
337:
328:
319:
306:
295:
289:
286:
271:
255:
244:
180:
111:
64:
31:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1586:
1584:
1576:
1575:
1565:
1564:
1558:
1557:
1554:
1553:
1550:
1549:
1547:
1546:
1540:
1538:
1534:
1533:
1531:
1530:
1525:
1519:
1517:
1510:
1509:
1507:
1506:
1501:
1495:
1493:
1483:
1477:
1476:
1474:
1473:
1468:
1463:
1458:
1453:
1452:
1451:
1440:
1438:
1432:
1431:
1428:
1427:
1425:
1424:
1419:
1414:
1409:
1407:Dolichocephaly
1404:
1399:
1394:
1388:
1386:
1382:
1381:
1379:
1378:
1373:
1368:
1363:
1358:
1352:
1350:
1344:
1343:
1341:
1340:
1338:Trigonocephaly
1335:
1330:
1324:
1322:
1313:
1311:Skull and face
1304:
1298:
1297:
1294:
1293:
1290:
1289:
1287:
1286:
1281:
1276:
1274:Arthrogryposis
1270:
1268:
1264:
1263:
1261:
1260:
1259:
1258:
1253:
1248:
1236:
1230:
1228:
1224:
1223:
1221:
1220:
1219:
1218:
1208:
1203:
1198:
1196:Arachnodactyly
1193:
1192:
1191:
1176:
1174:
1165:
1161:
1160:
1157:
1156:
1154:
1153:
1148:
1143:
1138:
1137:
1136:
1124:
1123:
1122:
1117:
1104:
1102:
1100:foot deformity
1096:
1095:
1093:
1092:
1087:
1082:
1077:
1072:
1067:
1061:
1059:
1053:
1052:
1050:
1049:
1044:
1039:
1034:
1024:
1022:
1013:
1007:
1006:
1003:
1002:
1000:
999:
994:
989:
984:
978:
976:
974:hand deformity
970:
969:
967:
966:
961:
956:
950:
948:
935:
926:
912:
911:
898:
896:
895:
888:
881:
873:
852:
851:
848:
847:
836:
824:
823:
821:
817:
816:
813:
812:
801:
790:
770:
755:
739:
734:
733:
731:
730:Classification
723:
722:External links
720:
717:
716:
687:(8): 817–824.
667:
620:
579:
537:
514:10.1086/303028
488:
439:
396:
381:
380:
378:
375:
374:
373:
367:
359:
356:
349:barber surgeon
336:
333:
327:
324:
318:
315:
308:
307:
258:
256:
249:
243:
240:
231:
230:
216:
210:
204:
198:
179:
176:
172:sonic hedgehog
153:Apert syndrome
149:
148:
145:
138:
137:
130:
110:
109:Classification
107:
72:
71:
58:
52:
51:
47:
46:
38:
37:
29:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1585:
1574:
1571:
1570:
1568:
1545:
1542:
1541:
1539:
1535:
1529:
1526:
1524:
1521:
1520:
1518:
1515:
1511:
1505:
1502:
1500:
1497:
1496:
1494:
1491:
1487:
1484:
1482:
1478:
1472:
1471:Sacralization
1469:
1467:
1464:
1462:
1459:
1457:
1454:
1450:
1447:
1446:
1445:
1442:
1441:
1439:
1437:
1433:
1423:
1420:
1418:
1417:Plagiocephaly
1415:
1413:
1410:
1408:
1405:
1403:
1400:
1398:
1395:
1393:
1390:
1389:
1387:
1383:
1377:
1374:
1372:
1369:
1367:
1364:
1362:
1361:Hypertelorism
1359:
1357:
1354:
1353:
1351:
1349:
1345:
1339:
1336:
1334:
1331:
1329:
1328:Scaphocephaly
1326:
1325:
1323:
1321:
1317:
1314:
1312:
1308:
1305:
1303:
1299:
1285:
1282:
1280:
1277:
1275:
1272:
1271:
1269:
1265:
1257:
1254:
1252:
1249:
1247:
1244:
1243:
1242:
1241:
1237:
1235:
1232:
1231:
1229:
1225:
1217:
1214:
1213:
1212:
1211:Brachydactyly
1209:
1207:
1204:
1202:
1199:
1197:
1194:
1190:
1187:
1186:
1185:
1181:
1178:
1177:
1175:
1173:
1169:
1166:
1164:Either / both
1162:
1152:
1149:
1147:
1144:
1142:
1139:
1135:
1132:
1131:
1130:
1129:
1125:
1121:
1118:
1116:
1113:
1112:
1111:
1110:
1106:
1105:
1103:
1101:
1097:
1091:
1088:
1086:
1083:
1081:
1078:
1076:
1073:
1071:
1068:
1066:
1063:
1062:
1060:
1058:
1054:
1048:
1045:
1043:
1040:
1038:
1035:
1033:
1032:Hip dysplasia
1029:
1026:
1025:
1023:
1021:
1017:
1014:
1012:
1008:
998:
995:
993:
990:
988:
985:
983:
980:
979:
977:
975:
971:
965:
962:
960:
957:
955:
952:
951:
949:
947:
943:
939:
936:
934:
930:
927:
925:
921:
917:
913:
909:
905:
901:
894:
889:
887:
882:
880:
875:
874:
871:
867:
865:
860:
846:
842:
841:
837:
835:
831:
830:
826:
825:
822:
818:
811:
807:
806:
802:
800:
796:
795:
791:
789:
786:
783:
780:
776:
775:
771:
769:
765:
764:
760:
756:
754:
750:
749:
745:
741:
740:
737:
732:
728:
721:
712:
708:
703:
698:
694:
690:
686:
682:
678:
671:
668:
663:
659:
655:
651:
647:
643:
639:
635:
631:
624:
621:
616:
612:
607:
602:
598:
594:
590:
583:
580:
575:
571:
567:
563:
560:(8): 1453–8.
559:
555:
548:
541:
538:
533:
529:
524:
519:
515:
511:
507:
503:
499:
492:
489:
484:
480:
475:
470:
466:
462:
458:
454:
450:
443:
440:
435:
431:
427:
423:
419:
415:
411:
407:
400:
397:
392:
386:
383:
376:
371:
368:
365:
362:
361:
357:
355:
353:
352:Ambroise Paré
350:
346:
342:
334:
332:
326:Complications
325:
323:
316:
314:
304:
301:
293:
290:February 2020
283:
279:
275:
269:
268:
264:
259:This section
257:
253:
248:
247:
241:
235:
228:
224:
220:
217:
214:
211:
208:
205:
202:
199:
196:
193:
192:
191:
189:
185:
177:
175:
173:
169:
164:
162:
156:
154:
146:
143:
142:
141:
135:
131:
128:
127:
126:
120:
115:
108:
106:
104:
100:
97:
93:
90:
89:Ancient Greek
86:
82:
78:
68:
62:
59:
57:
53:
48:
44:
39:
34:
19:
1392:Macrocephaly
1238:
1234:Acheiropodia
1206:Ectrodactyly
1183:
1126:
1107:
992:Oligodactyly
987:Clinodactyly
916:Appendicular
856:
845:orthoped/563
838:
827:
803:
792:
772:
757:
742:
684:
680:
670:
640:(1): 39–48.
637:
633:
623:
599:(6): 561–4.
596:
592:
582:
557:
553:
540:
508:(2): 492–7.
505:
501:
491:
459:(1): 26–37.
456:
452:
442:
409:
405:
399:
385:
338:
329:
320:
311:
296:
287:
272:Please help
260:
218:
212:
206:
200:
194:
188:phenotypical
181:
165:
157:
150:
139:
124:
102:
99:
95:
92:
76:
75:
18:Syndactylism
1422:Saddle nose
1189:Webbed toes
1180:Polydactyly
1065:Genu valgum
997:Polydactyly
829:MedlinePlus
412:: 166–172.
370:Webbed toes
227:metatarsals
223:metacarpals
1397:Platybasia
1333:Oxycephaly
1246:Phocomelia
1240:Ectromelia
1216:Stub thumb
1184:Syndactyly
1151:Hammer toe
1120:Pigeon toe
1070:Genu varum
1042:Coxa valga
900:Congenital
864:Syndactyly
805:DiseasesDB
377:References
345:Al-Zahrawi
341:Andalusian
317:Techniques
242:Management
103:(daktulos)
77:Syndactyly
36:Syndactyly
1449:Scoliosis
1256:Hemimelia
1141:Pes cavus
1134:Flat feet
1115:Club foot
1047:Coxa vara
840:eMedicine
654:1067-151X
426:0007-1226
261:does not
168:apoptosis
56:Specialty
1567:Category
1499:Cervical
946:shoulder
942:clavicle
924:dysmelia
711:22333904
662:14753796
615:17476456
532:10877983
483:16200145
434:14468563
358:See also
207:type III
178:Genetics
134:kangaroo
101:δάκτυλος
1514:sternum
799:D013576
702:3400728
574:7581388
523:1287194
474:1200697
364:Dactyly
335:History
282:removed
267:sources
213:type IV
201:type II
85:mammals
1537:other:
1251:Amelia
1128:valgus
834:003289
788:186300
785:186200
782:186100
779:185900
709:
699:
660:
652:
613:
572:
530:
520:
481:
471:
432:
424:
219:type V
195:type I
81:digits
63:
1504:Bifid
1385:other
1302:Axial
1109:varus
810:29330
768:755.1
550:(PDF)
96:(syn)
91:
1490:ribs
1057:knee
933:Arms
920:limb
794:MeSH
774:OMIM
763:9-CM
707:PMID
658:PMID
650:ISSN
611:PMID
570:PMID
528:PMID
479:PMID
430:PMID
422:ISSN
265:any
263:cite
225:and
184:loci
1020:hip
1011:Leg
759:ICD
753:Q70
744:ICD
697:PMC
689:doi
642:doi
601:doi
562:doi
518:PMC
510:doi
469:PMC
461:doi
414:doi
276:by
94:σύν
1569::
1182:/
1030:/
944:/
922:/
906:/
843::
832::
808::
797::
777::
766::
751::
748:10
705:.
695:.
685:20
683:.
679:.
656:.
648:.
638:12
636:.
632:.
609:.
597:52
595:.
591:.
568:.
556:.
552:.
526:.
516:.
506:67
504:.
500:.
477:.
467:.
457:18
455:.
451:.
428:.
420:.
410:15
408:.
163:.
1516::
1492::
892:e
885:t
878:v
761:-
746:-
736:D
713:.
691::
664:.
644::
617:.
603::
576:.
564::
558:4
534:.
512::
485:.
463::
436:.
416::
393:.
303:)
297:(
292:)
288:(
284:.
270:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.