133:
316:). SLBP binding is required for efficient processing, export, and translation of histone mRNAs, allowing it to function as a highly sensitive biochemical "switch". During S-phase, accumulation of SLBP acts together with NPAT to drastically increase the efficiency of histone production. However, once S-phase ends, both SLBP and bound RNA are rapidly degraded. This immediately halts histone production and prevents a toxic buildup of free histones.
238:
325:
36:
333:
nucleosome octamers, resulting in the release of H3-H4 and H2A-H2B subunits. Reassembly of nucleosomes behind the replication fork is mediated by chromatin assembly factors (CAFs) that are loosely associated with replication proteins. Though not fully understood, the reassembly does not appear to utilize the
337:
scheme seen in DNA replication. Labeling experiments indicate that nucleosome duplication is predominantly conservative. The paternal H3-H4 core nucleosome remains completely segregated from newly synthesized H3-H4, resulting in the formation of nucleosomes that either contain exclusively old H3-H4
280:
Complete replication fork assembly and activation only occurs on a small subset of replication origins. All eukaryotes possess many more replication origins than strictly needed during one cycle of DNA replication. Redundant origins may increase the flexibility of DNA replication, allowing cells to
357:
However, for small domains approaching the size of individual genes, old nucleosomes are spread too thinly for accurate propagation of histone modifications. In these regions, chromatin structure is probably controlled by incorporation of histone variants during nucleosome reassembly. The close
375:
detects stalled replication forks by integrating signals from RPA, ATR Interacting
Protein (ATRIP), and RAD17. Upon activation, the replication checkpoint upregulates nucleotide biosynthesis and blocks replication initiation from unfired origins. Both of these processes contribute to rescue of
332:
Free histones produced by the cell during S-phase are rapidly incorporated into new nucleosomes. This process is closely tied to the replication fork, occurring immediately in “front” and “behind” the replication complex. Translocation of MCM helicase along the leading strand disrupts parental
301:, a nuclear coactivator of histone transcription. NPAT is activated by phosphorylation and recruits the Tip60 chromatin remodeling complex to the promoters of histone genes. Tip60 activity removes inhibitory chromatin structures and drives a three to ten-fold increase in transcription rate.
193:(R), which commits cells to the remainder of the cell-cycle if there is adequate nutrients and growth signaling. This transition is essentially irreversible; after passing the restriction point, the cell will progress through S-phase even if environmental conditions become unfavorable.
424:
cells dramatically prolongs S-phase and causes permanent arrest in G2-phase. This unique arrest phenotype is not associated with activation of canonical DNA damage pathways, indicating that nucleosome assembly and histone supply may be scrutinized by a novel S-phase checkpoint.
346:
Immediately after division, each daughter chromatid only possesses half the epigenetic modifications present in the paternal chromatid. The cell must use this partial set of instructions to re-establish functional chromatin domains before entering mitosis.
260:
Activation of the pre-RC is a closely regulated and highly sequential process. After Cdc7 and S-phase CDKs phosphorylate their respective substrates, a second set of replicative factors associate with the pre-RC. Stable association encourages
366:
During S-phase, the cell continuously scrutinizes its genome for abnormalities. Detection of DNA damage induces activation of three canonical S-phase "checkpoint pathways" that delay or arrest further cell cycle progression:
354:) and several other histone-modifying complexes can "copy" modifications present on old histones onto new histones. This process amplifies epigenetic marks and counters the dilutive effect of nucleosome duplication.
383:
blocks mitosis until the entire genome has been successfully duplicated. This pathway induces arrest by inhibiting the Cyclin-B-CDK1 complex, which gradually accumulates throughout the cell cycle to promote mitotic
403:
kinases. In addition to facilitating DNA repair, active ATR and ATM stalls cell cycle progression by promoting degradation of CDC25A, a phosphatase that removes inhibitory phosphate residues from CDKs.
223:
transcription factor, which in turn initiates expression of S-phase genes. Several E2F target genes promote further release of E2F, creating a positive feedback loop similar to the one found in yeast.
420:
In addition to these canonical checkpoints, recent evidence suggests that abnormalities in histone supply and nucleosome assembly can also alter S-phase progression. Depletion of free histones in
196:
Accordingly, entry into S-phase is controlled by molecular pathways that facilitate a rapid, unidirectional shift in cell state. In yeast, for instance, cell growth induces accumulation of Cln3
253:
distributed throughout the genome. During S-phase, the cell converts pre-RCs into active replication forks to initiate DNA replication. This process depends on the kinase activity of
358:
correlation seen between H3.3/H2A.Z and transcriptionally active regions lends support to this proposed mechanism. Unfortunately, a causal relationship has yet to be proven.
175:. Since accurate duplication of the genome is critical to successful cell division, the processes that occur during S-phase are tightly regulated and widely conserved.
350:
For large genomic regions, inheritance of old H3-H4 nucleosomes is sufficient for accurate re-establishment of chromatin domains. Polycomb
Repressive Complex 2 (
1210:
338:
or exclusively new H3-H4. “Old” and “new” histones are assigned to each daughter strand semi-randomly, resulting in equal division of regulatory modifications.
803:"Stem-loop binding protein, the protein that binds the 3' end of histone mRNA, is cell cycle regulated by both translational and posttranslational mechanisms"
700:"Transcriptional activation of histone genes requires NPAT-dependent recruitment of TRRAP-Tip60 complex to histone promoters during the G1/S phase transition"
254:
219:
signals received throughout G1-phase cause gradual accumulation of cyclin D, which complexes with CDK4/6. Active cyclin D-CDK4/6 complex induces release of
1502:
1396:
1442:
304:
In addition to increasing transcription of histone genes, S-phase entry also regulates histone production at the RNA level. Instead of
481:
274:
132:
1203:
119:
57:
1196:
334:
1512:
100:
72:
1653:
1356:
277:
sliding clamps. Loading of these factors completes the active replication fork and initiates synthesis of new DNA.
265:
to unwind a small stretch of parental DNA into two strands of ssDNA, which in turn recruits replication protein A (
262:
204:
CDK2. The Cln3-CDK2 complex promotes transcription of S-phase genes by inactivating the transcriptional repressor
46:
1351:
1346:
1341:
1336:
1331:
1326:
1321:
1316:
1311:
405:
79:
53:
1303:
246:
201:
297:
proteins occurs alongside DNA replication. During early S-phase, the cyclin E-Cdk2 complex phosphorylates
86:
1635:
1386:
269:), an ssDNA binding protein. RPA recruitment primes the replication fork for loading of replicative DNA
266:
250:
1089:"DNA repair by nonhomologous end joining and homologous recombination during cell cycle in human cells"
443:
937:
212:, this pathway creates a positive feedback loop that fully commits cells to S-phase gene expression.
68:
1708:
434:
1648:
1453:
1069:
439:
1643:
1174:
1118:
1061:
1011:
963:
883:
832:
783:
729:
675:
623:
569:
487:
477:
449:
190:
1164:
1154:
1108:
1100:
1053:
1001:
953:
945:
873:
863:
822:
814:
773:
765:
719:
711:
665:
657:
613:
559:
551:
412:
double-strand breaks, is most active in S phase, declines in G2/M and is nearly absent in
305:
232:
184:
156:
941:
1169:
1142:
1113:
1088:
958:
925:
878:
851:
778:
753:
724:
699:
670:
645:
564:
539:
270:
237:
324:
17:
1702:
1582:
827:
818:
802:
93:
1073:
1604:
1625:
1594:
1044:
Bartek J, Lukas C, Lukas J (October 2004). "Checking on DNA damage in S phase".
661:
298:
35:
1546:
1430:
1219:
769:
509:
409:
400:
396:
392:
290:
148:
868:
801:
Whitfield ML, Zheng LX, Baldwin A, Ohta T, Hurt MM, Marzluff WF (June 2000).
491:
328:
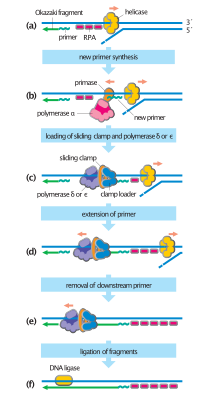
Conservative reassembly of core H3/H4 nucleosome behind the replication fork.
1669:
1619:
1609:
1292:
1288:
1278:
1274:
1270:
1260:
1256:
1246:
1242:
852:"How the cell cycle impacts chromatin architecture and influences cell fate"
309:
257:
and various S-phase CDKs, both of which are upregulated upon S-phase entry.
1178:
1122:
1065:
1015:
1006:
989:
967:
949:
887:
836:
787:
733:
679:
627:
618:
601:
573:
1674:
1614:
1599:
1568:
1554:
1284:
1266:
1252:
1238:
1104:
715:
413:
168:
160:
1159:
1683:
1590:
1222:
294:
216:
1188:
1522:
1438:
1424:
1420:
1416:
1408:
1366:
1361:
1230:
990:"Split decision: what happens to nucleosomes during DNA replication?"
281:
control the rate of DNA synthesis and respond to replication stress.
197:
1143:"Histone supply regulates S phase timing and cell cycle progression"
1057:
555:
208:. Since upregulation of S-phase genes drive further suppression of
1497:
1492:
1381:
1376:
1371:
236:
215:
A remarkably similar regulatory scheme exists in mammalian cells.
131:
1526:
1517:
1487:
1466:
1404:
351:
313:
209:
205:
27:
DNA replication phase of the cell cycle, between G1 and G2 phase
1192:
1507:
1471:
1461:
1434:
1412:
220:
152:
29:
1087:
Mao Z, Bozzella M, Seluanov A, Gorbunova V (September 2008).
540:"Control of cell cycle transcription during G1 and S phases"
698:
DeRan M, Pulvino M, Greene E, Su C, Zhao J (January 2008).
293:
to function properly, synthesis of canonical (non-variant)
312:
motif that selective binds to Stem Loop
Binding Protein (
245:
Throughout M phase and G1 phase, cells assemble inactive
136:
Asymmetry in the synthesis of leading and lagging strands
308:, canonical histone transcripts possess a conserved 3`
376:
stalled forks by increasing the availability of dNTPs.
1662:
1634:
1581:
1545:
1536:
1480:
1452:
1395:
1302:
1229:
1141:Günesdogan U, Jäckle H, Herzig A (September 2014).
538:Bertoli C, Skotheim JM, de Bruin RA (August 2013).
60:. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
602:"DNA replication and progression through S phase"
1204:
8:
474:The cell cycle : principles of control
189:Entry into S-phase is controlled by the G1
1542:
1211:
1197:
1189:
924:Ramachandran S, Henikoff S (August 2015).
650:Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology
1503:Cellular apoptosis susceptibility protein
1168:
1158:
1112:
1005:
957:
877:
867:
826:
777:
723:
669:
617:
563:
120:Learn how and when to remove this message
850:Ma Y, Kanakousaki K, Buttitta L (2015).
752:Marzluff WF, Koreski KP (October 2017).
323:
511:The Restriction Point of the Cell Cycle
461:
1046:Nature Reviews. Molecular Cell Biology
1039:
1037:
1035:
1033:
1031:
1029:
1027:
1025:
919:
917:
644:Leonard AC, Méchali M (October 2013).
544:Nature Reviews. Molecular Cell Biology
1136:
1134:
1132:
983:
981:
979:
977:
915:
913:
911:
909:
907:
905:
903:
901:
899:
897:
7:
747:
745:
743:
693:
691:
689:
639:
637:
595:
593:
591:
589:
587:
585:
583:
533:
531:
529:
527:
525:
523:
521:
503:
501:
467:
465:
342:Reestablishment of chromatin domains
289:Since new DNA must be packaged into
58:adding citations to reliable sources
994:The Journal of Biological Chemistry
508:Pardee AB, Blagosklonny MV (2013).
754:"Birth and Death of Histone mRNAs"
25:
600:Takeda DY, Dutta A (April 2005).
819:10.1128/MCB.20.12.4188-4198.2000
34:
45:needs additional citations for
807:Molecular and Cellular Biology
704:Molecular and Cellular Biology
446:(oncology/pathology prognosis)
1:
395:(DSBs) through activation of
988:Annunziato AT (April 2005).
1513:Maturation promoting factor
662:10.1101/cshperspect.a010116
476:. Oxford University Press.
200:, which complexes with the
1725:
1654:Postreplication checkpoint
408:, an accurate process for
230:
182:
926:"Replicating Nucleosomes"
770:10.1016/j.tig.2017.07.014
646:"DNA replication origins"
247:pre-replication complexes
869:10.3389/fgene.2015.00019
406:Homologous recombination
389:intra-S Phase Checkpoint
202:cyclin dependent kinase
1636:Cell cycle checkpoints
1007:10.1074/jbc.R400039200
950:10.1126/sciadv.1500587
619:10.1038/sj.onc.1208616
373:Replication Checkpoint
362:DNA damage checkpoints
329:
320:Nucleosome replication
242:
241:Steps in DNA synthesis
147:) is the phase of the
137:
18:Synthesis (cell cycle)
1663:Other cellular phases
1387:CDK-activating kinase
856:Frontiers in Genetics
327:
240:
135:
1105:10.4161/cc.7.18.6679
716:10.1128/MCB.00607-07
514:. Landes Bioscience.
393:Double Strand Breaks
306:polyadenylated tails
159:, occurring between
54:improve this article
1160:10.7554/eLife.02443
942:2015SciA....1E0587R
435:S phase index (SPI)
251:replication origins
1649:Spindle checkpoint
1454:P53 p63 p73 family
758:Trends in Genetics
330:
243:
138:
1696:
1695:
1692:
1691:
1644:Restriction point
450:Restriction point
335:semi-conservative
285:Histone synthesis
191:restriction point
130:
129:
122:
104:
16:(Redirected from
1716:
1543:
1213:
1206:
1199:
1190:
1183:
1182:
1172:
1162:
1138:
1127:
1126:
1116:
1084:
1078:
1077:
1041:
1020:
1019:
1009:
985:
972:
971:
961:
930:Science Advances
921:
892:
891:
881:
871:
847:
841:
840:
830:
798:
792:
791:
781:
749:
738:
737:
727:
695:
684:
683:
673:
641:
632:
631:
621:
597:
578:
577:
567:
535:
516:
515:
505:
496:
495:
472:David M (2007).
469:
444:S-phase fraction
125:
118:
114:
111:
105:
103:
62:
38:
30:
21:
1724:
1723:
1719:
1718:
1717:
1715:
1714:
1713:
1699:
1698:
1697:
1688:
1678:
1658:
1630:
1577:
1572:
1558:
1538:
1532:
1476:
1448:
1391:
1298:
1225:
1217:
1187:
1186:
1140:
1139:
1130:
1086:
1085:
1081:
1058:10.1038/nrm1493
1052:(10): 792–804.
1043:
1042:
1023:
1000:(13): 12065–8.
987:
986:
975:
936:(7): e1500587.
923:
922:
895:
849:
848:
844:
813:(12): 4188–98.
800:
799:
795:
764:(10): 745–759.
751:
750:
741:
697:
696:
687:
656:(10): a010116.
643:
642:
635:
612:(17): 2827–43.
599:
598:
581:
556:10.1038/nrm3629
537:
536:
519:
507:
506:
499:
484:
471:
470:
463:
458:
431:
364:
344:
322:
287:
235:
233:DNA replication
229:
227:DNA replication
187:
185:G1/S transition
181:
172:
164:
145:Synthesis phase
126:
115:
109:
106:
63:
61:
51:
39:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1722:
1720:
1712:
1711:
1701:
1700:
1694:
1693:
1690:
1689:
1687:
1686:
1681:
1676:
1672:
1666:
1664:
1660:
1659:
1657:
1656:
1651:
1646:
1640:
1638:
1632:
1631:
1629:
1628:
1623:
1617:
1612:
1607:
1602:
1597:
1587:
1585:
1579:
1578:
1576:
1575:
1570:
1566:
1561:
1556:
1551:
1549:
1540:
1534:
1533:
1531:
1530:
1520:
1515:
1510:
1505:
1500:
1495:
1490:
1484:
1482:
1478:
1477:
1475:
1474:
1469:
1464:
1458:
1456:
1450:
1449:
1447:
1446:
1428:
1401:
1399:
1393:
1392:
1390:
1389:
1384:
1379:
1374:
1369:
1364:
1359:
1354:
1349:
1344:
1339:
1334:
1329:
1324:
1319:
1314:
1308:
1306:
1300:
1299:
1297:
1296:
1282:
1264:
1250:
1235:
1233:
1227:
1226:
1218:
1216:
1215:
1208:
1201:
1193:
1185:
1184:
1128:
1099:(18): 2902–6.
1079:
1021:
973:
893:
842:
793:
739:
685:
633:
579:
517:
497:
483:978-0199206100
482:
460:
459:
457:
454:
453:
452:
447:
437:
430:
427:
418:
417:
385:
381:S-M Checkpoint
377:
363:
360:
343:
340:
321:
318:
286:
283:
231:Main article:
228:
225:
183:Main article:
180:
177:
170:
162:
128:
127:
42:
40:
33:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1721:
1710:
1707:
1706:
1704:
1685:
1682:
1680:
1673:
1671:
1668:
1667:
1665:
1661:
1655:
1652:
1650:
1647:
1645:
1642:
1641:
1639:
1637:
1633:
1627:
1624:
1621:
1618:
1616:
1613:
1611:
1608:
1606:
1603:
1601:
1598:
1596:
1592:
1589:
1588:
1586:
1584:
1580:
1574:
1567:
1565:
1562:
1560:
1553:
1552:
1550:
1548:
1544:
1541:
1535:
1528:
1524:
1521:
1519:
1516:
1514:
1511:
1509:
1506:
1504:
1501:
1499:
1496:
1494:
1491:
1489:
1486:
1485:
1483:
1479:
1473:
1470:
1468:
1465:
1463:
1460:
1459:
1457:
1455:
1451:
1444:
1440:
1436:
1432:
1429:
1426:
1422:
1418:
1414:
1410:
1406:
1403:
1402:
1400:
1398:
1397:CDK inhibitor
1394:
1388:
1385:
1383:
1380:
1378:
1375:
1373:
1370:
1368:
1365:
1363:
1360:
1358:
1355:
1353:
1350:
1348:
1345:
1343:
1340:
1338:
1335:
1333:
1330:
1328:
1325:
1323:
1320:
1318:
1315:
1313:
1310:
1309:
1307:
1305:
1301:
1294:
1290:
1286:
1283:
1280:
1276:
1272:
1268:
1265:
1262:
1258:
1254:
1251:
1248:
1244:
1240:
1237:
1236:
1234:
1232:
1228:
1224:
1221:
1214:
1209:
1207:
1202:
1200:
1195:
1194:
1191:
1180:
1176:
1171:
1166:
1161:
1156:
1152:
1148:
1144:
1137:
1135:
1133:
1129:
1124:
1120:
1115:
1110:
1106:
1102:
1098:
1094:
1090:
1083:
1080:
1075:
1071:
1067:
1063:
1059:
1055:
1051:
1047:
1040:
1038:
1036:
1034:
1032:
1030:
1028:
1026:
1022:
1017:
1013:
1008:
1003:
999:
995:
991:
984:
982:
980:
978:
974:
969:
965:
960:
955:
951:
947:
943:
939:
935:
931:
927:
920:
918:
916:
914:
912:
910:
908:
906:
904:
902:
900:
898:
894:
889:
885:
880:
875:
870:
865:
861:
857:
853:
846:
843:
838:
834:
829:
824:
820:
816:
812:
808:
804:
797:
794:
789:
785:
780:
775:
771:
767:
763:
759:
755:
748:
746:
744:
740:
735:
731:
726:
721:
717:
713:
710:(1): 435–47.
709:
705:
701:
694:
692:
690:
686:
681:
677:
672:
667:
663:
659:
655:
651:
647:
640:
638:
634:
629:
625:
620:
615:
611:
607:
603:
596:
594:
592:
590:
588:
586:
584:
580:
575:
571:
566:
561:
557:
553:
550:(8): 518–28.
549:
545:
541:
534:
532:
530:
528:
526:
524:
522:
518:
513:
512:
504:
502:
498:
493:
489:
485:
479:
475:
468:
466:
462:
455:
451:
448:
445:
441:
438:
436:
433:
432:
428:
426:
423:
415:
411:
410:repairing DNA
407:
402:
398:
394:
390:
386:
382:
378:
374:
370:
369:
368:
361:
359:
355:
353:
348:
341:
339:
336:
326:
319:
317:
315:
311:
307:
302:
300:
296:
292:
284:
282:
278:
276:
272:
268:
264:
258:
256:
252:
248:
239:
234:
226:
224:
222:
218:
213:
211:
207:
203:
199:
194:
192:
186:
178:
176:
174:
166:
158:
154:
150:
146:
142:
134:
124:
121:
113:
110:December 2010
102:
99:
95:
92:
88:
85:
81:
78:
74:
71: –
70:
66:
65:Find sources:
59:
55:
49:
48:
43:This article
41:
37:
32:
31:
19:
1605:Prometaphase
1563:
1150:
1146:
1096:
1092:
1082:
1049:
1045:
997:
993:
933:
929:
859:
855:
845:
810:
806:
796:
761:
757:
707:
703:
653:
649:
609:
605:
547:
543:
510:
473:
421:
419:
388:
380:
372:
365:
356:
349:
345:
331:
303:
288:
279:
263:MCM helicase
259:
249:(pre-RC) on
244:
214:
195:
188:
144:
140:
139:
116:
107:
97:
90:
83:
76:
64:
52:Please help
47:verification
44:
1626:Cytokinesis
1595:Preprophase
1539:checkpoints
291:nucleosomes
271:polymerases
1709:Cell cycle
1547:Interphase
1537:Phases and
1220:Cell cycle
1153:: e02443.
1093:Cell Cycle
456:References
440:S-fraction
422:Drosophila
179:Regulation
157:replicated
149:cell cycle
80:newspapers
1670:Apoptosis
1620:Telophase
1610:Metaphase
1405:INK4a/ARF
492:813540567
310:stem loop
217:Mitogenic
151:in which
69:"S phase"
1703:Category
1615:Anaphase
1600:Prophase
1223:proteins
1179:25205668
1123:18769152
1074:33560392
1066:15459660
1016:15664979
968:26269799
888:25691891
837:10825184
788:28867047
734:17967892
680:23838439
628:15838518
606:Oncogene
574:23877564
429:See also
414:G1 phase
391:detects
1684:Meiosis
1591:Mitosis
1583:M phase
1564:S phase
1431:cip/kip
1170:4157229
1114:2754209
959:4530793
938:Bibcode
879:4315090
779:5645032
725:2223310
671:3783049
565:4569015
295:histone
141:S phase
94:scholar
1523:Cullin
1409:p14arf
1231:Cyclin
1177:
1167:
1121:
1111:
1072:
1064:
1014:
966:
956:
886:
876:
862:: 19.
835:
825:
786:
776:
732:
722:
678:
668:
626:
572:
562:
490:
480:
384:entry.
198:cyclin
96:
89:
82:
75:
67:
1679:phase
1573:phase
1559:phase
1498:Cdc42
1493:Cdc25
1481:Other
1263:, B3)
1147:eLife
1070:S2CID
828:85788
173:phase
165:phase
101:JSTOR
87:books
1527:CUL7
1488:Cdc2
1175:PMID
1119:PMID
1062:PMID
1012:PMID
964:PMID
884:PMID
833:PMID
784:PMID
730:PMID
676:PMID
624:PMID
570:PMID
488:OCLC
478:ISBN
399:and
387:The
379:The
371:The
352:PRC2
314:SLBP
299:NPAT
275:PCNA
273:and
255:Cdc7
210:Whi5
206:Whi5
167:and
73:news
1518:Wee
1508:E2F
1472:p73
1467:p63
1462:p53
1443:p57
1439:p27
1435:p21
1425:p19
1421:p18
1417:p15
1413:p16
1367:11B
1362:11A
1304:CDK
1165:PMC
1155:doi
1109:PMC
1101:doi
1054:doi
1002:doi
998:280
954:PMC
946:doi
874:PMC
864:doi
823:PMC
815:doi
774:PMC
766:doi
720:PMC
712:doi
666:PMC
658:doi
614:doi
560:PMC
552:doi
442:or
401:ATM
397:ATR
267:RPA
221:E2F
155:is
153:DNA
56:by
1705::
1441:,
1437:,
1423:,
1419:,
1415:,
1382:14
1377:13
1372:12
1357:10
1293:E2
1291:,
1289:E1
1279:D3
1277:,
1275:D2
1273:,
1271:D1
1261:B2
1259:,
1257:B1
1247:A2
1245:,
1243:A1
1173:.
1163:.
1149:.
1145:.
1131:^
1117:.
1107:.
1095:.
1091:.
1068:.
1060:.
1048:.
1024:^
1010:.
996:.
992:.
976:^
962:.
952:.
944:.
932:.
928:.
896:^
882:.
872:.
858:.
854:.
831:.
821:.
811:20
809:.
805:.
782:.
772:.
762:33
760:.
756:.
742:^
728:.
718:.
708:28
706:.
702:.
688:^
674:.
664:.
652:.
648:.
636:^
622:.
610:24
608:.
604:.
582:^
568:.
558:.
548:14
546:.
542:.
520:^
500:^
486:.
464:^
1677:0
1675:G
1622:)
1593:(
1571:2
1569:G
1557:1
1555:G
1529:)
1525:(
1445:)
1433:(
1427:)
1411:/
1407:(
1352:9
1347:8
1342:7
1337:6
1332:5
1327:4
1322:3
1317:2
1312:1
1295:)
1287:(
1285:E
1281:)
1269:(
1267:D
1255:(
1253:B
1249:)
1241:(
1239:A
1212:e
1205:t
1198:v
1181:.
1157::
1151:3
1125:.
1103::
1097:7
1076:.
1056::
1050:5
1018:.
1004::
970:.
948::
940::
934:1
890:.
866::
860:6
839:.
817::
790:.
768::
736:.
714::
682:.
660::
654:5
630:.
616::
576:.
554::
494:.
416:.
171:2
169:G
163:1
161:G
143:(
123:)
117:(
112:)
108:(
98:·
91:·
84:·
77:·
50:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.