111:
126:
239:: any increase in load capacitance increases C, heat-induced resistance the R factor, and supply threshold voltage increases will affect whether more than one time constants are required to reach the threshold. If the output of a logic gate is connected to a long trace or used to drive many other gates (high
235:(often expressed as a percentage of the high-voltage supply rail), naturally increases proportionately. Increases in output load capacitance, often from placing increased fan-out loads on a wire, will also increase propagation delay. All of these factors influence each other through an
201:
allows them to process data at a faster rate and improve overall performance. The determination of the propagation delay of a combined circuit requires identifying the longest path of propagation delays from input to output and by adding each propagation delay along this path.
180:
this refers to the time required for the output to reach 50% of its final output level from when the input changes to 50% of its final input level. This may depend on the direction of the level change, in which case separate fall and rise delays
246:
Wires have an approximate propagation delay of 1 ns for every 6 inches (15 cm) of length. Logic gates can have propagation delays ranging from more than 10 ns down to the picosecond range, depending on the technology being used.
59:, propagation delay is the amount of time it takes for the head of the signal to travel from the sender to the receiver. It can be computed as the ratio between the link length and the propagation speed over the specific medium.
263:
field, the propagation delay is the length of time it takes for a signal to travel to its destination. For example, in the case of an electric signal, it is the time taken for the signal to travel through a wire. See also
231:, as resistance of conductive materials tends to increase with temperature. Marginal increases in supply voltage can increase propagation delay since the upper switching threshold voltage, V
346:
321:
451:
414:
176:
becomes stable and valid to change, to the time that the output of that logic gate is stable and valid to change. Often on manufacturers'
98:
generally ranges from .59c to .77c. This delay is the major obstacle in the development of high-speed computers and is called the
446:
441:
375:
221:
406:
Mcgraw Hill - Complete
Digital Design A Comprehensive Guide To Digital Electronics And Computer System Architecture
436:
354:
99:
115:
75:
291:
228:
210:
110:
281:
165:
301:
125:
410:
286:
269:
236:
56:
36:
265:
260:
198:
161:
224:
utilizes propagation delays to compare designs implementing the same logical statement.
17:
296:
214:
87:
430:
205:
The difference in propagation delays of logic elements is the major contributor to
35:
is the time duration taken for a signal to reach its destination. It can relate to
404:
157:
91:
40:
173:
134:
130:
177:
119:
256:
44:
240:
206:
347:"Propagation Delay and Its Relationship to Maximum Cable Length"
27:
Time for a signal or other quantity to reach its destination
398:
396:
172:, is the length of time which starts when the input to a
322:"What is propagation delay? (Ethernet Physical Layer)"
243:) the propagation delay increases substantially.
8:
409:. McGraw-Hill Professional. p. 430.
124:
109:
313:
7:
197:are given. Reducing gate delays in
25:
227:Propagation delay increases with
133:has an overall gate delay of 3
62:Propagation delay is equal to
1:
452:Timing in electronic circuits
376:"Logic Signal Voltage Levels"
78:. In wireless communication,
168:, the propagation delay, or
222:principle of logical effort
468:
18:Signal propagation delay
100:interconnect bottleneck
259:, particularly in the
153:
122:
76:wave propagation speed
292:Latency (engineering)
229:operating temperature
211:asynchronous circuits
128:
113:
447:Electronics concepts
403:Balch, Mark (2003).
145:to the carry output
70:is the distance and
442:Digital electronics
351:Networking Glossary
282:Contamination delay
166:digital electronics
380:All About Circuits
302:Transmission delay
154:
123:
114:Propagation delay
416:978-0-07-140927-8
287:Delay calculation
270:radio propagation
57:computer networks
33:Propagation delay
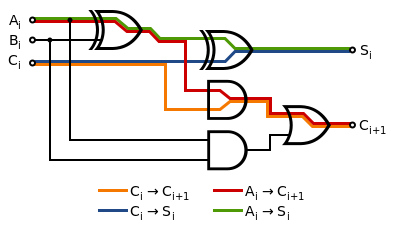
16:(Redirected from
459:
437:Digital circuits
421:
420:
400:
391:
390:
388:
386:
372:
366:
365:
363:
362:
353:. Archived from
343:
337:
336:
334:
333:
318:
237:RC time constant
199:digital circuits
162:digital circuits
137:from the inputs
21:
467:
466:
462:
461:
460:
458:
457:
456:
427:
426:
425:
424:
417:
402:
401:
394:
384:
382:
374:
373:
369:
360:
358:
345:
344:
340:
331:
329:
320:
319:
315:
310:
278:
266:velocity factor
261:electromagnetic
253:
234:
215:race conditions
213:as a result of
196:
192:
188:
184:
151:
108:
102:in IC systems.
53:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
465:
463:
455:
454:
449:
444:
439:
429:
428:
423:
422:
415:
392:
367:
338:
312:
311:
309:
306:
305:
304:
299:
297:Time of flight
294:
289:
284:
277:
274:
252:
249:
232:
194:
190:
186:
182:
149:
116:timing diagram
107:
104:
88:speed of light
52:
49:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
464:
453:
450:
448:
445:
443:
440:
438:
435:
434:
432:
418:
412:
408:
407:
399:
397:
393:
381:
377:
371:
368:
357:on 2011-02-20
356:
352:
348:
342:
339:
327:
323:
317:
314:
307:
303:
300:
298:
295:
293:
290:
288:
285:
283:
280:
279:
275:
273:
271:
267:
262:
258:
250:
248:
244:
242:
238:
230:
225:
223:
218:
216:
212:
208:
203:
200:
179:
175:
171:
167:
163:
159:
152:shown in red.
148:
144:
140:
136:
132:
127:
121:
117:
112:
105:
103:
101:
97:
93:
89:
85:
81:
77:
73:
69:
65:
60:
58:
50:
48:
46:
42:
38:
34:
30:
19:
405:
383:. Retrieved
379:
370:
359:. Retrieved
355:the original
350:
341:
330:. Retrieved
328:. 2010-10-21
326:Ethernet FAQ
325:
316:
254:
245:
226:
219:
204:
169:
155:
146:
142:
138:
95:
94:, the speed
83:
79:
71:
67:
63:
61:
54:
32:
31:
29:
158:electronics
135:logic gates
106:Electronics
92:copper wire
86:, i.e. the
41:electronics
431:Categories
361:2010-11-09
332:2010-11-09
308:References
178:datasheets
174:logic gate
170:gate delay
131:full adder
51:Networking
37:networking
276:See also
207:glitches
120:NOT gate
257:physics
251:Physics
74:is the
45:physics
413:
385:1 June
241:fanout
66:where
193:and t
185:and t
118:of a
90:. In
64:d / s
411:ISBN
387:2016
268:and
220:The
189:or t
164:and
141:and
255:In
209:in
187:PLH
183:PHL
156:In
150:out
55:In
43:or
433::
395:^
378:.
349:.
324:.
272:.
233:IH
217:.
160:,
129:A
47:.
39:,
419:.
389:.
364:.
335:.
195:r
191:f
181:t
147:C
143:B
139:A
96:s
84:c
82:=
80:s
72:s
68:d
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.