20:
531:
74:
internal gear. When two external gears mesh together they rotate in the opposite directions. An internal gear can only mesh with an external gear and the gears rotate in the same direction. Due to the close positioning of shafts, internal gear assemblies are more compact than external gear assemblies.
70:(cutting the tooth narrower closer to its base) is sometimes used to avoid interference but is usually not suitable because the decreased thickness leaves the tooth weaker at its base. In this situation, corrected gears are used. In corrected gears the cutter rack is shifted upwards or downwards.
73:
Spur gears can be classified into two main categories: External and
Internal. Gears with teeth on the outside of the cylinder are known as "external gears". Gears with teeth on the internal side of the cylinder are known as "internal gears". An external gear can mesh with an external gear or an
65:
profile or cycloidal profile. When two gears are in mesh it is possible that an involute portion of one will contact a non-involute portion of the other gear. This phenomenon is known as "interference" and occurs when the number of teeth on the smaller of the two meshing gears is less than a
54:. Spur gears mesh together correctly only if fitted to parallel shafts. No axial thrust is created by the tooth loads. Spur gears are excellent at moderate speeds but tend to be noisy at high speeds.
42:. Looking down the length of the shaft, a tooth's cross section is usually not triangular. Instead of being straight (as in a triangle) the sides of the cross section have a curved form (usually
38:. They consist of a cylinder or disk with teeth projecting radially. Viewing the gear at 90 degrees from the shaft length (side on) the tooth faces are straight and aligned parallel to the
572:
61:, 20° being the current industry standard and 14½° being the former (often found in older equipment). Spur gear teeth are manufactured as either
166:
389:
369:
228:
39:
565:
510:
67:
596:
364:
558:
124:
432:
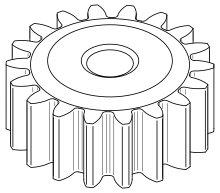
158:
92:
Normal spur gears (over 17 teeth) have a pitch circle diameter (PCD) equal to MOD × number of teeth.
538:
276:
271:
221:
500:
490:
317:
286:
266:
162:
542:
327:
150:
384:
281:
261:
151:
591:
394:
214:
58:
95:
Corrected spur gears (under 17 teeth) have a PCD equal to MOD × number of teeth + MOD.
585:
374:
343:
43:
196:
348:
47:
19:
495:
455:
475:
422:
379:
312:
307:
256:
51:
505:
485:
480:
447:
437:
427:
62:
417:
530:
18:
182:
322:
237:
83:
35:
210:
206:
546:
468:
446:
410:
403:
357:
336:
295:
244:
84:Gear § Standard pitches and the module system
566:
222:
157:. New York: Industrial Press. 2012. pp.
8:
88:In the case of Module (MOD) 4.0 spur gears:
573:
559:
407:
229:
215:
207:
99:There are two types of corrected gears:
197:"Metrics in Engineering - Metric Gears"
116:
57:Spur gear can be classified into two
7:
527:
525:
545:. You can help Knowledge (XXG) by
390:Continuously variable transmission
14:
529:
1:
267:Epicyclic (planetary) gearing
106:S gearing (x1 + x2 ≠ zero)
103:S0 gearing (x1 + x2 = zero)
613:
524:
81:
511:Spur gear corrected tooth
34:are the simplest type of
50:) to achieve a constant
541:-related article is a
24:
22:
16:Simplest type of gear
433:Shaft-driven bicycle
153:Machinery's Handbook
272:Sun and planet gear
501:Gear manufacturing
337:Geartooth profiles
131:. 16 November 2000
66:required minimum.
46:and less commonly
32:straight-cut gears
25:
554:
553:
519:
518:
464:
463:
287:Non-circular gear
252:Spur gear systems
168:978-0-8311-2900-2
129:howstuffworks.com
604:
575:
568:
561:
533:
526:
408:
231:
224:
217:
208:
201:
200:
193:
187:
186:
179:
173:
172:
156:
147:
141:
140:
138:
136:
125:"How Gears Work"
121:
40:axis of rotation
612:
611:
607:
606:
605:
603:
602:
601:
582:
581:
580:
579:
522:
520:
515:
460:
442:
399:
385:Bicycle gearing
353:
332:
291:
282:Cycloidal drive
262:Rack and pinion
240:
235:
205:
204:
195:
194:
190:
183:"McMaster-Carr"
181:
180:
176:
169:
149:
148:
144:
134:
132:
123:
122:
118:
113:
86:
80:
59:pressure angles
17:
12:
11:
5:
610:
608:
600:
599:
597:Industry stubs
594:
584:
583:
578:
577:
570:
563:
555:
552:
551:
534:
517:
516:
514:
513:
508:
503:
498:
493:
488:
483:
478:
472:
470:
466:
465:
462:
461:
459:
458:
452:
450:
444:
443:
441:
440:
435:
430:
425:
420:
414:
412:
405:
401:
400:
398:
397:
392:
387:
382:
377:
372:
367:
361:
359:
355:
354:
352:
351:
346:
340:
338:
334:
333:
331:
330:
325:
320:
315:
310:
305:
299:
297:
293:
292:
290:
289:
284:
279:
277:Harmonic drive
274:
269:
264:
259:
254:
248:
246:
242:
241:
236:
234:
233:
226:
219:
211:
203:
202:
188:
174:
167:
142:
115:
114:
112:
109:
108:
107:
104:
97:
96:
93:
82:Main article:
79:
76:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
609:
598:
595:
593:
590:
589:
587:
576:
571:
569:
564:
562:
557:
556:
550:
548:
544:
540:
535:
532:
528:
523:
512:
509:
507:
504:
502:
499:
497:
494:
492:
489:
487:
484:
482:
479:
477:
474:
473:
471:
467:
457:
454:
453:
451:
449:
445:
439:
436:
434:
431:
429:
426:
424:
421:
419:
416:
415:
413:
409:
406:
402:
396:
393:
391:
388:
386:
383:
381:
378:
376:
373:
371:
368:
366:
363:
362:
360:
356:
350:
347:
345:
342:
341:
339:
335:
329:
326:
324:
321:
319:
316:
314:
311:
309:
306:
304:
301:
300:
298:
294:
288:
285:
283:
280:
278:
275:
273:
270:
268:
265:
263:
260:
258:
255:
253:
250:
249:
247:
243:
239:
232:
227:
225:
220:
218:
213:
212:
209:
198:
192:
189:
184:
178:
175:
170:
164:
160:
155:
154:
146:
143:
130:
126:
120:
117:
110:
105:
102:
101:
100:
94:
91:
90:
89:
85:
77:
75:
71:
69:
64:
60:
55:
53:
49:
45:
41:
37:
33:
29:
21:
547:expanding it
536:
521:
370:Differential
365:Transmission
318:Spiral bevel
302:
251:
191:
177:
152:
145:
135:20 September
133:. Retrieved
128:
119:
98:
87:
72:
68:Undercutting
56:
31:
27:
26:
496:Chain drive
456:Wheel train
328:Herringbone
78:PCD and MOD
52:drive ratio
586:Categories
491:Belt drive
476:Ball screw
423:Derailleur
257:Worm drive
111:References
28:Spur gears
506:Freewheel
486:Jackscrew
481:Leadscrew
358:Mechanics
48:cycloidal
23:Spur gear
539:industry
469:See also
448:Horology
438:Sprocket
428:Hub gear
411:Bicycles
404:Examples
375:Coupling
344:Involute
63:involute
44:involute
349:Cycloid
323:Helical
245:Systems
418:Cogset
395:Offset
296:Shapes
165:
592:Gears
537:This
380:Train
313:Crown
308:Bevel
238:Gears
543:stub
303:Spur
163:ISBN
159:2125
137:2018
36:gear
30:or
588::
161:.
127:.
574:e
567:t
560:v
549:.
230:e
223:t
216:v
199:.
185:.
171:.
139:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.