143:(as opposed to a charge composed exclusively of the same refrigerant inside the system, known as a parallel charge), set so that the vapor pressure vs temperature curve of the bulb charge "crosses" the vapor pressure vs temperature curve of the system's refrigerant at a certain temperature value (that is, a bulb charge set so that, below a certain refrigerant temperature, the vapor pressure of the bulb charge suddenly becomes higher than that of the system's refrigerant, forcing the metering pin to stay into an open position), help to reduce the superheat hunt phenomenon by preventing the valve orifice from completely closing during system operation. The same result can be attained through different kinds of bleed passages that generate a minimum refrigerant flow at all times. The cost, however, is determining a certain flow of refrigerant that will not reach the suction line in a fully evaporated state while the heat load is particularly low, and that the compressor must be designed to handle. By carefully selecting the amount of a liquid sensing bulb charge, a so-called MOP (maximum operating pressure) effect can be also attained; above a precise refrigerant temperature, the sensing bulb charge will be entirely evaporated, making the valve begin restricting flow irrespective of the sensed superheat, rather than increasing it in order to bring evaporator superheat down to the target value. Therefore, the evaporator pressure will be kept from increasing above the MOP value. This feature helps to control the compressor's maximum operating torque to a value that is acceptable for the application, such as a small displacement car engine.
135:
increases. As the suction line temperature decreases, so does the pressure in the bulb and therefore on the spring, causing the valve to close. An air conditioning system with a TX valve is often more efficient than those with designs that do not use one. Also, TX valve air conditioning systems do not require an accumulator (a refrigerant tank placed downstream of the evaporator's outlet), since the valves reduce the liquid refrigerant flow when the evaporator's thermal load decreases, so that all the refrigerant completely evaporates inside the evaporator (in normal operating conditions such as a proper evaporator temperature and airflow). However, a liquid refrigerant receiver tank needs to be placed in the liquid line before the TX valve so that, in low evaporator thermal load conditions, any excess liquid refrigerant can be stored inside it, preventing any liquid from backflowing inside the condenser coil from the liquid line.
169:
on all applications; however, an externally equalized TXV cannot be replaced with an internally equalized TXV. For automotive applications, a type of externally equalized thermal expansion valve, known as the block type valve, is often used. In this type, either a sensing bulb is located within the suction line connection within the valve body and is in constant contact with the refrigerant that flows out of the evaporator's outlet, or a heat transfer means is provided so that the refrigerant is able to exchange heat with the sensing charge contained in a chamber located above the diaphragm as it flows to the suction line.
173:
control range and flexibility that bulb/diaphragm types cannot provide, they add complexity and points of failure to a system as they require additional temperature and pressure sensors and an electronic control circuit. Most electronic valves use a stepper motor hermetically sealed inside the valve to actuate a needle valve with a screw mechanism, on some units only the stepper rotor is within the hermetic body and is magnetically driven through the sealed valve body by stator coils on the outside of the device.
122:
29:
20:
110:
the other hand, excessive superheat indicates that there is insufficient refrigerant flowing through the evaporator coil, and thus a significant portion toward the end is not providing cooling. Therefore, by regulating the superheat to a small value, typically only a few °C, the heat transfer of the evaporator will be near optimal, without excess liquid refrigerant being returned to the compressor.
1708:
98:
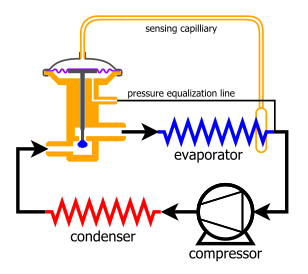
cools the high-pressure and high-temperature gas allowing it to condense to a high-pressure liquid by transferring heat to a lower temperature medium, usually ambient air. In order to produce a cooling effect from the higher pressure liquid, the flow of refrigerant entering the evaporator is restricted by the expansion valve, reducing the pressure and allowing
105:
A TXV type expansion device has a sensing bulb that is filled with a liquid whose thermodynamic properties are similar to those of the refrigerant. This bulb is thermally connected to the output of the evaporator so that the temperature of the refrigerant that leaves the evaporator can be sensed. The
65:
systems that controls the amount of refrigerant released into the evaporator and is intended to regulate the superheat of the refrigerant that flows out of the evaporator to a steady value. Although often described as a "thermostatic" valve, an expansion valve is not able to regulate the evaporator's
155:
There are two main types of thermal expansion valves: internally or externally equalized. The difference between externally and internally equalized valves is how the evaporator pressure affects the position of the needle. In internally equalized valves, the evaporator pressure against the diaphragm
32:
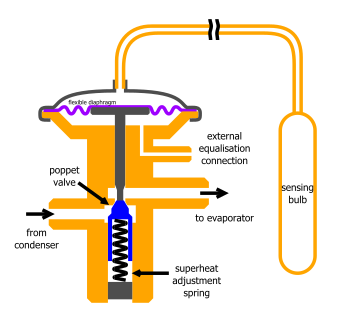
The sensing bulb is positioned near the end of the evaporator and ensures enough refrigerant flows to chill the whole evaporator, but not so much that liquid reaches the sensing position. The equalisation connection is needed when the pressure at the sensing position differs from the pressure at the
168:
Internally equalized valves can be used on single circuit evaporator coils having low-pressure drop. If a refrigerant distributor is used for multiple parallel evaporators (rather than a valve on each evaporator) then an externally equalized valve must be used. Externally equalized TXVs can be used
113:
In order to provide an appropriate superheat, a spring force is often applied in the direction that would close the valve, meaning that the valve will close when the bulb is at a lower temperature than the refrigerant is evaporating at. Spring-type valves may be fixed, or adjustable, although other
109:
The superheat is the excess temperature of the vapor above its boiling point at the evaporating pressure. No superheat indicates that the refrigerant is not being fully vaporized within the evaporator and liquid may end up recirculated to the compressor which is inefficient and can cause damage. On
138:
At heat loads which are very low compared to the valve's power rating, the orifice can become oversized for the heat load, and the valve can begin to repeatedly open and close, in an attempt to control the superheat to the set value, making the superheat oscillate. Cross charges, that is, sensing
97:
The cycle starts when refrigerant enters the compressor in a low-pressure, moderate-temperature, gaseous form. The refrigerant is compressed by the compressor to a high-pressure and high-temperature gaseous state. The high-pressure and high-temperature gas then enters the condenser. The condenser
146:
A low refrigerant charge condition is often accompanied when the compressor is operational by a loud whooshing sound heard from the thermal expansion valve and the evaporator, which is caused by the lack of a liquid head right before the valve's moving orifice, resulting in the orifice trying to
172:
Although the bulb/diaphragm type is used in most systems that control the refrigerant superheat, electronic expansion valves are becoming more common in larger systems or systems with multiple evaporators to allow them to be adjusted independently. Although electronic valves can provide greater
134:
Flow control, or metering, of the refrigerant is accomplished by use of a temperature sensing bulb, filled with a gas or liquid charge similar to the one inside the system, that causes the orifice in the valve to open against the spring pressure in the valve body as the temperature on the bulb
69:
Thermal expansion valves are often referred to generically as "metering devices", although this may also refer to any other device that releases liquid refrigerant into the low-pressure section but does not react to temperature, such as a capillary tube or a pressure-controlled valve.
23:
Basic construction of a TEV. The flexible diaphragm actuates the poppet valve; an increasing pressure in the sensing bulb will press down on the poppet and open the valve further. There is also an adjustable spring providing a closing force on the valve which controls the
117:
Some thermal expansion valves are also specifically designed to ensure that a certain minimum flow of refrigerant can always flow through the system, while others can also be designed to control the evaporator's pressure so that it never rises above a maximum
164:
of the evaporator. Externally equalized thermostatic expansion valves compensate for any pressure drop through the evaporator. For internally equalised valves a pressure drop in the evaporator will have the effect of increasing the superheat.
1595:
66:
temperature to a precise value. The evaporator's temperature will vary only with the evaporating pressure, which will have to be regulated through other means (such as by adjusting the compressor's capacity).
106:
gas pressure in the sensing bulb provides the force to open the TXV, and as the temperature drops this force will decrease, therefore dynamically adjusting the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator.
160:
of the evaporator (typically via an internal connection to the outlet of the valve), whereas in externally equalized valves, the evaporator pressure against the diaphragm is the pressure at the
228:
1545:
1575:
1590:
1083:
332:
1585:
1517:
125:
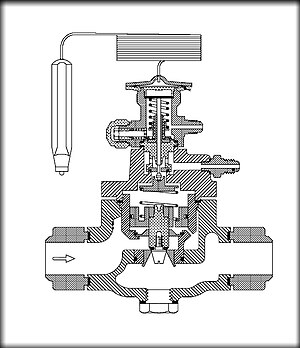
A pilot-operated thermostatic expansion valve, the upper valve is an externally balanced TEV, flow through this valve opens the larger lower valve.
1390:
1550:
1512:
82:; this is the cycle that makes air conditioning, or air cooling, possible. A basic refrigeration cycle consists of four major elements: a
239:
1373:
1415:
1128:
664:
393:
212:
114:
methods to ensure a superheat also exist, such as the sensing bulb having a different vapor composition to the rest of the system.
484:
1565:
1379:
759:
58:
323:
296:
1527:
1471:
1466:
1043:
571:
1698:
1088:
639:
560:
519:
1733:
1431:
1233:
744:
679:
597:
509:
373:
1580:
1461:
1168:
933:
777:
1633:
1492:
1456:
1258:
888:
843:
771:
623:
566:
1680:
1502:
1198:
798:
577:
468:
453:
1675:
1600:
1522:
1451:
1395:
1327:
1138:
1048:
1013:
489:
1665:
1627:
1507:
1218:
649:
1685:
1363:
1322:
1038:
709:
529:
201:
Whitman, William C.; Johnson, Bill; Johnson, William M.; Tomczyk, John; Whitman, Bill (October 2004).
1487:
1477:
1421:
1358:
1253:
833:
782:
348:
94:. As a refrigerant passes through a circuit containing these four elements, air conditioning occurs.
189:
121:
1353:
1343:
1317:
1103:
765:
674:
644:
544:
514:
408:
368:
139:
bulb charges composed of a mixture of different refrigerants or also non-refrigerant gases such as
1616:
1560:
1497:
1274:
1153:
1148:
938:
749:
734:
316:
28:
19:
1188:
1143:
898:
893:
823:
719:
555:
358:
208:
202:
102:
expansion back into the vapor phase to take place, which absorbs heat and results in cooling.
301:
1655:
1410:
1405:
988:
694:
592:
587:
582:
499:
62:
1728:
1650:
1622:
1264:
1178:
1173:
1118:
1108:
1098:
1028:
968:
883:
868:
689:
684:
659:
654:
524:
448:
264:
1400:
1297:
1073:
1053:
1018:
953:
873:
714:
704:
613:
463:
433:
388:
383:
87:
83:
1722:
1712:
1482:
1333:
1228:
1193:
963:
958:
913:
908:
754:
729:
724:
699:
669:
539:
438:
418:
398:
309:
1660:
1338:
1238:
1213:
1208:
1203:
1133:
1068:
948:
918:
858:
853:
828:
739:
618:
534:
458:
443:
428:
1670:
1312:
1269:
1243:
1183:
1163:
1158:
1033:
993:
978:
923:
848:
818:
813:
629:
494:
413:
99:
1426:
1348:
1279:
1248:
1123:
1093:
1023:
973:
943:
928:
903:
808:
608:
504:
423:
363:
91:
1707:
1385:
1063:
1058:
1008:
983:
838:
634:
79:
1368:
1302:
803:
603:
403:
378:
353:
140:
878:
550:
1555:
1307:
1113:
863:
1570:
1003:
190:
https://www.tranebelgium.com/files/book-doc/22/fr/22.v67u8zhe.pdf
1078:
998:
305:
147:
meter a vapor or a vapor/liquid mixture instead of a liquid.
16:
Component of air conditioning and refrigeration systems
1696:
1643:
1609:
1536:
1440:
1288:
791:
477:
339:
78:A thermal expansion valve is a key element to a
274:. Parker Hannifin Corporation, Sporlan Division
204:Refrigeration & Air Conditioning Technology
238:. Emerson Climate Technologies. Archived from
317:
8:
1084:High efficiency glandless circulating pump
333:Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning
324:
310:
302:
1518:Mold growth, assessment, and remediation
120:
27:
18:
1703:
182:
1391:Programmable communicating thermostat
7:
1513:Mechanical, electrical, and plumbing
1374:Minimum efficiency reporting value
229:"Flow Control-Contractor Tip Card"
14:
1416:Standard temperature and pressure
1129:Packaged terminal air conditioner
665:Passive daytime radiative cooling
394:Heat pump and refrigeration cycle
1706:
485:Absorption-compression heat pump
1380:Normal temperature and pressure
760:Vapor-compression refrigeration
265:"Thermostatic Expansion Valves"
59:vapor-compression refrigeration
1:
1528:Testing, adjusting, balancing
1472:Building information modeling
1467:Building services engineering
1044:Ground-coupled heat exchanger
572:Demand controlled ventilation
520:Building insulation materials
1089:High-pressure cut-off switch
640:Ice storage air conditioning
561:Dedicated outdoor air system
43:thermostatic expansion valve
1432:Thermostatic radiator valve
1234:Thermostatic radiator valve
745:Underfloor air distribution
680:Radiant heating and cooling
598:Energy recovery ventilation
510:Automobile air conditioning
374:Domestic energy consumption
207:. Thomson Delmar Learning.
90:, a metering device and an
1750:
1581:Institute of Refrigeration
1462:Architectural technologist
934:Electrostatic precipitator
1634:Volatile organic compound
1493:Environmental engineering
1457:Architectural engineering
1259:Ultra-low particulate air
844:Automatic balancing valve
772:Variable refrigerant flow
624:Heat recovery ventilation
567:Deep water source cooling
1681:Template:Home automation
1503:Kitchen exhaust cleaning
1199:Solar-assisted heat pump
799:Air conditioner inverter
578:Displacement ventilation
469:Vapour pressure of water
454:Thermal destratification
1676:World Refrigeration Day
1523:Refrigerant reclamation
1452:Architectural acoustics
1396:Programmable thermostat
1328:Clean air delivery rate
1224:Thermal expansion valve
1139:Pressurisation ductwork
1049:Ground source heat pump
490:Absorption refrigerator
156:is the pressure at the
39:thermal expansion valve
1666:Glossary of HVAC terms
1628:Sick building syndrome
1508:Mechanical engineering
1219:Smoke exhaust ductwork
650:Mixed-mode ventilation
236:www.emersonclimate.com
126:
45:(often abbreviated as
34:
25:
1686:Template:Solar energy
1364:Intelligent buildings
1323:Carbon dioxide sensor
710:Room air distribution
530:Central solar heating
124:
31:
22:
1488:Duct leakage testing
1478:Deep energy retrofit
1422:Thermographic camera
1359:Infrared thermometer
834:Air source heat pump
783:Water heat recycling
349:Air changes per hour
297:How does a TEV work?
57:) is a component in
1354:HVAC control system
1344:Home energy monitor
1318:Building automation
1104:Inverter compressor
766:Variable air volume
675:Passive ventilation
645:Kitchen ventilation
545:Constant air volume
515:Autonomous building
74:Theory of operation
1734:Cooling technology
1617:Indoor air quality
1561:ASTM International
1498:Hydronic balancing
1275:Wood-burning stove
1154:Radiator reflector
939:Evaporative cooler
750:Underfloor heating
735:Thermal insulation
127:
35:
26:
1694:
1693:
1610:Health and safety
1189:Scroll compressor
1144:Process duct work
899:Convection heater
894:Condensing boiler
824:Air-mixing plenum
720:Solar combisystem
556:Cross ventilation
359:Building envelope
272:sporlanonline.com
1741:
1711:
1710:
1702:
1656:Building science
1411:Smart thermostat
1406:Room temperature
989:Fireplace insert
695:Radon mitigation
593:Electric heating
588:District heating
583:District cooling
500:Air conditioning
326:
319:
312:
303:
284:
283:
281:
279:
269:
261:
255:
254:
252:
250:
244:
233:
225:
219:
218:
198:
192:
187:
63:air conditioning
1749:
1748:
1744:
1743:
1742:
1740:
1739:
1738:
1719:
1718:
1717:
1705:
1697:
1695:
1690:
1651:ASHRAE Handbook
1639:
1623:Passive smoking
1605:
1538:
1532:
1444:
1442:
1436:
1290:
1284:
1265:Whole-house fan
1179:Run-around coil
1174:Reversing valve
1119:Mechanical room
1109:Kerosene heater
1099:Infrared heater
1029:Gasoline heater
969:Fan filter unit
884:Condensate pump
869:Centrifugal fan
787:
690:Radiant heating
685:Radiant cooling
660:Passive cooling
655:Microgeneration
525:Central heating
473:
449:Thermal comfort
341:
335:
330:
293:
291:Further reading
288:
287:
277:
275:
267:
263:
262:
258:
248:
246:
245:on 27 June 2013
242:
231:
227:
226:
222:
215:
200:
199:
195:
188:
184:
179:
153:
132:
76:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1747:
1745:
1737:
1736:
1731:
1721:
1720:
1716:
1715:
1692:
1691:
1689:
1688:
1683:
1678:
1673:
1668:
1663:
1658:
1653:
1647:
1645:
1641:
1640:
1638:
1637:
1631:
1625:
1620:
1613:
1611:
1607:
1606:
1604:
1603:
1598:
1593:
1588:
1583:
1578:
1573:
1568:
1563:
1558:
1553:
1548:
1542:
1540:
1534:
1533:
1531:
1530:
1525:
1520:
1515:
1510:
1505:
1500:
1495:
1490:
1485:
1480:
1475:
1469:
1464:
1459:
1454:
1448:
1446:
1438:
1437:
1435:
1434:
1429:
1424:
1419:
1413:
1408:
1403:
1401:Psychrometrics
1398:
1393:
1388:
1383:
1377:
1371:
1366:
1361:
1356:
1351:
1346:
1341:
1336:
1331:
1325:
1320:
1315:
1310:
1305:
1300:
1298:Air flow meter
1294:
1292:
1286:
1285:
1283:
1282:
1277:
1272:
1267:
1262:
1256:
1251:
1246:
1241:
1236:
1231:
1226:
1221:
1216:
1211:
1206:
1201:
1196:
1191:
1186:
1181:
1176:
1171:
1166:
1161:
1156:
1151:
1146:
1141:
1136:
1131:
1126:
1121:
1116:
1111:
1106:
1101:
1096:
1091:
1086:
1081:
1076:
1074:Heating system
1071:
1066:
1061:
1056:
1054:Heat exchanger
1051:
1046:
1041:
1036:
1031:
1026:
1021:
1019:Gas compressor
1016:
1011:
1006:
1001:
996:
991:
986:
981:
976:
971:
966:
961:
956:
954:Expansion tank
951:
946:
941:
936:
931:
926:
921:
916:
911:
906:
901:
896:
891:
886:
881:
876:
874:Ceramic heater
871:
866:
861:
856:
851:
846:
841:
836:
831:
826:
821:
816:
811:
806:
801:
795:
793:
789:
788:
786:
785:
780:
775:
769:
763:
757:
752:
747:
742:
737:
732:
727:
722:
717:
715:Solar air heat
712:
707:
705:Renewable heat
702:
697:
692:
687:
682:
677:
672:
667:
662:
657:
652:
647:
642:
637:
632:
627:
621:
616:
614:Forced-air gas
611:
606:
601:
595:
590:
585:
580:
575:
569:
564:
558:
553:
548:
542:
537:
532:
527:
522:
517:
512:
507:
502:
497:
492:
487:
481:
479:
475:
474:
472:
471:
466:
464:Thermodynamics
461:
456:
451:
446:
441:
436:
434:Psychrometrics
431:
426:
421:
416:
411:
406:
401:
396:
391:
389:Gas compressor
386:
384:Fluid dynamics
381:
376:
371:
366:
361:
356:
351:
345:
343:
337:
336:
331:
329:
328:
321:
314:
306:
300:
299:
292:
289:
286:
285:
256:
220:
213:
193:
181:
180:
178:
175:
152:
149:
131:
128:
75:
72:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1746:
1735:
1732:
1730:
1727:
1726:
1724:
1714:
1709:
1704:
1700:
1687:
1684:
1682:
1679:
1677:
1674:
1672:
1669:
1667:
1664:
1662:
1659:
1657:
1654:
1652:
1649:
1648:
1646:
1642:
1635:
1632:
1629:
1626:
1624:
1621:
1618:
1615:
1614:
1612:
1608:
1602:
1599:
1597:
1594:
1592:
1589:
1587:
1584:
1582:
1579:
1577:
1574:
1572:
1569:
1567:
1564:
1562:
1559:
1557:
1554:
1552:
1549:
1547:
1544:
1543:
1541:
1539:organizations
1535:
1529:
1526:
1524:
1521:
1519:
1516:
1514:
1511:
1509:
1506:
1504:
1501:
1499:
1496:
1494:
1491:
1489:
1486:
1484:
1483:Duct cleaning
1481:
1479:
1476:
1473:
1470:
1468:
1465:
1463:
1460:
1458:
1455:
1453:
1450:
1449:
1447:
1439:
1433:
1430:
1428:
1425:
1423:
1420:
1417:
1414:
1412:
1409:
1407:
1404:
1402:
1399:
1397:
1394:
1392:
1389:
1387:
1384:
1381:
1378:
1375:
1372:
1370:
1367:
1365:
1362:
1360:
1357:
1355:
1352:
1350:
1347:
1345:
1342:
1340:
1337:
1335:
1334:Control valve
1332:
1329:
1326:
1324:
1321:
1319:
1316:
1314:
1311:
1309:
1306:
1304:
1301:
1299:
1296:
1295:
1293:
1287:
1281:
1278:
1276:
1273:
1271:
1268:
1266:
1263:
1260:
1257:
1255:
1254:Turning vanes
1252:
1250:
1247:
1245:
1242:
1240:
1237:
1235:
1232:
1230:
1229:Thermal wheel
1227:
1225:
1222:
1220:
1217:
1215:
1212:
1210:
1207:
1205:
1202:
1200:
1197:
1195:
1194:Solar chimney
1192:
1190:
1187:
1185:
1182:
1180:
1177:
1175:
1172:
1170:
1167:
1165:
1162:
1160:
1157:
1155:
1152:
1150:
1147:
1145:
1142:
1140:
1137:
1135:
1132:
1130:
1127:
1125:
1122:
1120:
1117:
1115:
1112:
1110:
1107:
1105:
1102:
1100:
1097:
1095:
1092:
1090:
1087:
1085:
1082:
1080:
1077:
1075:
1072:
1070:
1067:
1065:
1062:
1060:
1057:
1055:
1052:
1050:
1047:
1045:
1042:
1040:
1037:
1035:
1032:
1030:
1027:
1025:
1022:
1020:
1017:
1015:
1012:
1010:
1007:
1005:
1002:
1000:
997:
995:
992:
990:
987:
985:
982:
980:
977:
975:
972:
970:
967:
965:
964:Fan coil unit
962:
960:
957:
955:
952:
950:
947:
945:
942:
940:
937:
935:
932:
930:
927:
925:
922:
920:
917:
915:
912:
910:
909:Cooling tower
907:
905:
902:
900:
897:
895:
892:
890:
887:
885:
882:
880:
877:
875:
872:
870:
867:
865:
862:
860:
857:
855:
852:
850:
847:
845:
842:
840:
837:
835:
832:
830:
827:
825:
822:
820:
817:
815:
812:
810:
807:
805:
802:
800:
797:
796:
794:
790:
784:
781:
779:
776:
773:
770:
767:
764:
761:
758:
756:
755:Vapor barrier
753:
751:
748:
746:
743:
741:
738:
736:
733:
731:
730:Solar heating
728:
726:
725:Solar cooling
723:
721:
718:
716:
713:
711:
708:
706:
703:
701:
700:Refrigeration
698:
696:
693:
691:
688:
686:
683:
681:
678:
676:
673:
671:
670:Passive house
668:
666:
663:
661:
658:
656:
653:
651:
648:
646:
643:
641:
638:
636:
633:
631:
628:
625:
622:
620:
617:
615:
612:
610:
607:
605:
602:
599:
596:
594:
591:
589:
586:
584:
581:
579:
576:
573:
570:
568:
565:
562:
559:
557:
554:
552:
549:
546:
543:
541:
540:Chilled water
538:
536:
533:
531:
528:
526:
523:
521:
518:
516:
513:
511:
508:
506:
503:
501:
498:
496:
493:
491:
488:
486:
483:
482:
480:
476:
470:
467:
465:
462:
460:
457:
455:
452:
450:
447:
445:
442:
440:
439:Sensible heat
437:
435:
432:
430:
427:
425:
422:
420:
419:Noise control
417:
415:
412:
410:
407:
405:
402:
400:
399:Heat transfer
397:
395:
392:
390:
387:
385:
382:
380:
377:
375:
372:
370:
367:
365:
362:
360:
357:
355:
352:
350:
347:
346:
344:
338:
334:
327:
322:
320:
315:
313:
308:
307:
304:
298:
295:
294:
290:
273:
266:
260:
257:
241:
237:
230:
224:
221:
216:
214:9781401837655
210:
206:
205:
197:
194:
191:
186:
183:
176:
174:
170:
166:
163:
159:
150:
148:
144:
142:
136:
129:
123:
119:
115:
111:
107:
103:
101:
95:
93:
89:
85:
81:
73:
71:
67:
64:
60:
56:
52:
48:
44:
40:
33:valve output.
30:
21:
1661:Fireproofing
1445:and services
1441:Professions,
1339:Gas detector
1239:Trickle vent
1223:
1214:Smoke damper
1209:Smoke canopy
1204:Space heater
1134:Plenum space
1069:Heating film
949:Exhaust hood
919:Dehumidifier
859:Blast damper
854:Barrier pipe
829:Air purifier
740:Thermosiphon
619:Free cooling
535:Chilled beam
459:Thermal mass
444:Stack effect
429:Particulates
409:Infiltration
340:Fundamental
276:. Retrieved
271:
259:
247:. Retrieved
240:the original
235:
223:
203:
196:
185:
171:
167:
161:
157:
154:
145:
137:
133:
116:
112:
108:
104:
96:
77:
68:
54:
50:
46:
42:
38:
36:
1671:Warm Spaces
1313:Blower door
1291:and control
1289:Measurement
1270:Windcatcher
1244:Trombe wall
1184:Sail switch
1164:Refrigerant
1159:Recuperator
1034:Grease duct
994:Freeze stat
979:Fire damper
849:Back boiler
819:Air ionizer
814:Air handler
778:Ventilation
630:Hybrid heat
495:Air barrier
414:Latent heat
130:Description
100:isenthalpic
1723:Categories
1427:Thermostat
1349:Humidistat
1280:Zone valve
1249:TurboSwing
1124:Oil heater
1094:Humidifier
1024:Gas heater
974:Fan heater
944:Evaporator
929:Economizer
904:Compressor
809:Air filter
792:Components
609:Forced-air
505:Antifreeze
478:Technology
424:Outgassing
364:Convection
177:References
92:evaporator
84:compressor
24:superheat.
1537:Industry
1386:OpenTherm
1064:Heat pump
1059:Heat pipe
1009:Fume hood
984:Fireplace
889:Condenser
839:Attic fan
635:Hydronics
88:condenser
80:heat pump
1644:See also
1369:LonWorks
1303:Aquastat
1169:Register
1149:Radiator
804:Air door
604:Firestop
404:Humidity
379:Enthalpy
369:Dilution
354:Bake-out
342:concepts
141:nitrogen
55:TX valve
1443:trades,
1014:Furnace
879:Chiller
551:Coolant
278:16 June
249:16 June
1729:Valves
1713:Energy
1699:Portal
1596:SMACNA
1556:ASHRAE
1376:(MERV)
1330:(CADR)
1308:BACnet
1261:(ULPA)
1114:Louver
1039:Grille
914:Damper
864:Boiler
762:(VCRS)
563:(DOAS)
211:
162:outlet
118:value.
1636:(VOC)
1630:(SBS)
1619:(IAQ)
1576:CIBSE
1571:BSRIA
1474:(BIM)
1418:(STP)
1382:(NTP)
1004:Freon
774:(VRF)
768:(VAV)
626:(HRV)
600:(ERV)
574:(DCV)
547:(CAV)
268:(PDF)
243:(PDF)
232:(PDF)
158:inlet
151:Types
53:, or
1591:LEED
1551:AMCA
1546:AHRI
1079:HEPA
999:Flue
924:Duct
280:2014
251:2014
209:ISBN
86:, a
61:and
1601:UMC
1586:IIR
1566:BRE
959:Fan
51:TXV
47:TEV
41:or
1725::
270:.
234:.
49:,
37:A
1701::
325:e
318:t
311:v
282:.
253:.
217:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.