462:
1055:. This may be caused by a slowed signal from the sinus node (sinus bradycardia), by a pause in the normal activity of the sinus node (sinus arrest), or by blocking of the electrical impulse on its way from the atria to the ventricles (AV block or heart block). Heart block comes in varying degrees and severity. It may be caused by reversible poisoning of the AV node (with drugs that impair conduction) or by irreversible damage to the node. Bradycardias may also be present in the normally functioning heart of endurance athletes or other well-conditioned persons. Bradycardia may also occur in
229:
64:
791:. The normal heart rate of the fetus is between 110 and 160 beats per minute. Any rhythm beyond these limits is abnormal and classed as a fetal arrhythmia. These are mainly the result of premature atrial contractions, usually give no symptoms, and have little consequence. However, around one percent of these will be the result of significant structural damage to the heart.
904:. These cannot usually diagnose specific arrhythmia but can give a general indication of the heart rate and whether it is regular or irregular. Not all the electrical impulses of the heart produce audible or palpable beats; in many cardiac arrhythmias, the premature or abnormal beats do not produce an effective pumping action and are experienced as "skipped" beats.
1043:
1117:
Congenital heart defects are structural or electrical pathway problems in the heart that are present at birth. Anyone can be affected by this because overall health does not play a role in the problem. Problems with the electrical pathway of the heart can cause very fast or even deadly arrhythmias.
1126:
tachycardia is the most common type of ventricular tachycardia in otherwise healthy individuals. This defect is due to an electrical node in the right ventricle just before the pulmonary artery. When the node is stimulated, the patient will go into ventricular tachycardia, which does not allow the
1046:
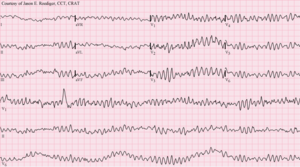
Normal sinus rhythm, with solid black arrows pointing to normal P waves representative of normal sinus node function, followed by a pause in sinus node activity (resulting in a transient loss of heartbeats). Note that the P wave that disrupts the pause (indicated by the dashed arrow) does not look
1208:
or if conduction is abnormally slow in some areas (for example in heart damage) so the myocardial cells are unable to activate the fast sodium channel, part of the impulse will arrive late and potentially be treated as a new impulse. Depending on the timing, this can produce a sustained abnormal
443:
Arrhythmia affects millions of people. In Europe and North
America, as of 2014, atrial fibrillation affects about 2% to 3% of the population. Atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter resulted in 112,000 deaths in 2013, up from 29,000 in 1990. However, in most recent cases concerning the SARS-CoV‑2
1436:
differs in that the shock is not synchronized. It is needed for the chaotic rhythm of ventricular fibrillation and is also used for pulseless ventricular tachycardia. Often, more electricity is required for defibrillation than for cardioversion. In most defibrillation, the recipient has lost
452:
and about 15% of all deaths globally. About 80% of sudden cardiac death is the result of ventricular arrhythmias. Arrhythmias may occur at any age but are more common among older people. Arrhythmias may also occur in children; however, the normal range for the heart rate varies with age.
1322:
Triggered beats occur when problems at the level of the ion channels in individual heart cells result in abnormal propagation of electrical activity and can lead to a sustained abnormal rhythm. They are relatively rare and can result from the action of anti-arrhythmic drugs, or after
751:
Approximately 180,000 to 250,000 people die suddenly of this cause every year in the US. SADS may occur from other causes. There are many inherited conditions and heart diseases that can affect young people which can subsequently cause sudden death without advance symptoms.
1375:
There are many classes of antiarrhythmic medications, with different mechanisms of action and many different individual drugs within these classes. Although the goal of drug therapy is to prevent arrhythmia, nearly every antiarrhythmic drug has the potential to act as a
1479:, they use fine probes inserted through the blood vessels to map electrical activity from within the heart. This allows abnormal areas of conduction to be located very accurately and subsequently destroyed by heat, cold, electrical, or laser probes in a process called
1174:, are the least dangerous dysrhythmias; but they can still produce a decrease in the heart's pumping efficiency because the signal reaches the various parts of the heart muscle with different timing than usual and can be responsible for poorly coordinated contraction.
1313:
in the lack of a normal pulse, but defibrillation is the only intervention that can restore a healthy heart rhythm. Defibrillation is performed by applying an electric shock to the heart, which resets the cells, permitting a normal beat to re-establish itself.
424:, which attempt to restore a normal heart rhythm. This latter group may have more significant side effects, especially if taken for a long period of time. Pacemakers are often used for slow heart rates. Those with an irregular heartbeat are often treated with
1131:
is another complex problem in the heart and has been labeled as an independent factor in mortality. There are multiple methods of treatment for these including cardiac ablations, medication treatment, or lifestyle changes to have less stress and exercise.
1348:
Several physical acts can increase parasympathetic nervous supply to the heart, resulting in blocking of electrical conduction through the AV node. This can slow down or stop several arrhythmias that originate above or at the AV node (see main article:
1029:
refers to a normal phenomenon of alternating mild acceleration and slowing of the heart rate that occurs with breathing in and out respectively. It is usually quite pronounced in children and steadily decreases with age. This can also be present during
3036:
3017:
1021:
In adults, the normal resting heart rate ranges from 60 to 90 beats per minute. The resting heart rate in children is much faster. In athletes, however, the resting heart rate can be as slow as 40 beats per minute, and be considered normal.
934:
that uses a catheter to "listen" to the electrical activity from within the heart, additionally if the source of the arrhythmias is found, often the abnormal cells can be ablated and the arrhythmia can be permanently corrected.
825:
associated with adverse events. Examples include a higher risk of blood clotting within the heart and a higher risk of insufficient blood being transported to the heart because of a weak heartbeat. Other increased risks are of
1158:
is a single specialized location in the atrium that has a higher automaticity (a faster pacemaker) than the rest of the heart and, therefore, is usually responsible for setting the heart rate and initiating each heartbeat.
833:
If an arrhythmia results in a heartbeat that is too fast, too slow, or too weak to supply the body's needs, this manifests as lower blood pressure and may cause lightheadedness, dizziness, syncope, loss of consciousness,
1335:
The method of cardiac rhythm management depends firstly on whether the affected person is stable or unstable. Treatments may include physical maneuvers, medications, electricity conversion, or electro- or cryo-cautery.
1154:; however, only some of these cells are designed to routinely trigger heartbeats. These cells are found in the conduction system of the heart and include the SA node, AV node, Bundle of His, and Purkinje fibers. The
444:
pandemic, cardiac arrhythmias are commonly developed and associated with high morbidity and mortality among patients hospitalized with the COVID-19 infection, due to the infection's ability to cause myocardial injury.
2585:"Clinical value of transesophageal atrial stimulation and recording in patients with arrhythmia-related symptoms or documented supraventricular tachycardia--correlation to clinical history and invasive studies"
1388:
Several groups of drugs slow conduction through the heart, without actually preventing an arrhythmia. These drugs can be used to "rate control" a fast rhythm and make it physically tolerable for the patient.
2734:"Circus movement in rabbit atrial muscle as a mechanism of tachycardia. II. The role of nonuniform recovery of excitability in the occurrence of unidirectional block, as studied with multiple microelectrodes"
1339:
In the United States, people admitted to the hospital with cardiac arrhythmia and conduction disorders with and without complications were admitted to the intensive care unit more than half the time in 2011.
1185:. The resulting heart rhythm depends on where the first signal begins: If it is the sinoatrial node, the rhythm remains normal but rapid; if it is an ectopic focus, many types of dysrhythmia may ensue.
1106:. Abnormal impulses can begin by one of three mechanisms: automaticity, re-entry, or triggered activity. A specialized form of re-entry which is both common and problematic is termed fibrillation.
246:
1122:
is due to an extra pathway in the heart that is made up of electrical muscle tissue. This tissue allows the electrical impulse, which stimulates the heartbeat, to happen very rapidly. Right
1953:"Global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013"
1193:
Re-entrant arrhythmias occur when an electrical impulse recurrently travels in a tight circle within the heart, rather than moving from one end of the heart to the other and then stopping.
2702:
Wiener N, Rosenblueth A (July 1946). "The mathematical formulation of the problem of conduction of impulses in a network of connected excitable elements, specifically in cardiac muscle".
1259:
When an entire chamber of the heart is involved in multiple micro-re-entry circuits and is, therefore, quivering with chaotic electrical impulses, it is said to be in fibrillation.
1416:
Arrhythmias may also be treated electrically, by applying a shock across the heart – either externally to the chest wall, or internally to the heart via implanted electrodes.
3805:
768:
2856:
247:
1426:
to the underlying heartbeat. It is used for the treatment of supraventricular tachycardias. In elective cardioversion, the recipient is usually sedated or lightly
1083:
and called sinus tachycardia. Other conditions that increase sympathetic nervous system activity in the heart include ingested or injected substances, such as
951:
is only approximately 5–6 mm (remaining constant in people of different age and weight). Transesophageal atrial stimulation can differentiate between
3446:
776:
635:
1638:
989:
739:
occasioned by an arrhythmia in the presence or absence of any structural heart disease on autopsy. The most common cause of sudden death in the US is
394:
181:
428:
to reduce the risk of complications. Those who have severe symptoms from an arrhythmia or are medically unstable may receive urgent treatment with a
3136:
1170:
fires more often than the sinoatrial node, it can produce a sustained abnormal rhythm. Rhythms produced by an ectopic focus in the atria, or by the
1293:(VF, or V-fib) can lead to death within minutes. When a heart goes into V-fib, effective pumping of the blood stops. V-fib is considered a form of
3863:
1229:
1204:
impulse will spread through the heart quickly enough that each cell will respond only once. However, if there is some essential heterogeneity of
1119:
964:
374:
1786:
1747:
1514:. In the 1960s and 1970s problems with antihistamines and antipsychotics were discovered. It was not until the 1980s that the underlying issue,
3180:
1441:
960:
238:
2782:
1718:
598:
1681:
1599:
3858:
3667:
3504:
2439:"Continuous ECG monitoring versus mobile telemetry: A comparison of arrhythmia diagnostics in human- versus algorithmic-dependent systems"
1951:
Naghavi M, Wang H, Lozano R, Davis A, Liang X, Zhou M, et al. (GBD 2013 Mortality and Causes of Death
Collaborators) (January 2015).
1109:
Although the term "tachycardia" has been known for over 160 years, bases for the classification of arrhythmias are still being discussed.
2667:
Peressutti C, Martín-González JM, M García-Manso J, Mesa D (November 2010). "Heart rate dynamics in different levels of Zen meditation".
3672:
3662:
3251:
620:
3105:
2545:
Anier A, Kaik J, Meigas K (2008). "Device and methods for performing transesophageal stimulation at reduced pacing current threshold".
1642:
3969:
3800:
3414:
610:
3840:
1810:"Sudden cardiac death and inherited channelopathy: the basic electrophysiology of the myocyte and myocardium in ion channel disease"
1047:
like the previous (normal) P waves – this last P wave is arising from a different part of the atrium, representing an escape rhythm.
582:
362:
358:
2945:"Osborn waves following out-of-hospital cardiac arrest—Effect of level of temperature management and risk of arrhythmia and death"
3835:
2632:
Yasuma F, Hayano J (February 2004). "Respiratory sinus arrhythmia: why does the heartbeat synchronize with respiratory rhythm?".
724:
687:
674:
570:
319:
124:
1486:
This procedure may be completely curative for some forms of arrhythmia, but for others, the success rate remains disappointing.
821:
Some arrhythmias do not cause symptoms and are not associated with increased mortality. However, some asymptomatic arrhythmias
3704:
3485:
2840:
1531:
640:
919:
is an EKG recorded over a 24-hour period, to detect arrhythmias that may happen briefly and unpredictably throughout the day.
3780:
3775:
3699:
2119:
1487:
1205:
956:
555:
543:
3499:
1075:
an arrhythmia. Increased heart rate is a normal response to physical exercise or emotional stress. This is mediated by the
4126:
4002:
3931:
3763:
1298:
864:
Cardiac arrhythmia are caused by one of two major mechanism. The first of arrhythmia is a result of enhanced or abnormal
523:
248:
4224:
4121:
3914:
3897:
3830:
3750:
3129:
1350:
1166:
focus and is, by definition, a pathological phenomenon. This may cause a single premature beat now and then, or, if the
1026:
968:
528:
508:
461:
408:
Many arrhythmias can be effectively treated. Treatments may include medications, medical procedures such as inserting a
354:
342:
162:
3964:
4219:
3409:
1547:
839:
772:
708:
First, second, and third-degree blocks also can occur at the level of the sinoatrial junction. This is referred to as
35:
3946:
3434:
3419:
1178:
1076:
594:
PVCs that occur at intervals of 2 normal beats to 1 PVC, or 1 normal beat to 2 PVCs, are termed "PVCs in trigeminy"
3721:
4024:
3689:
3616:
3343:
1123:
669:
481:; couplets; runs, that is 3 or more beats; non-sustained = less than 30 seconds or sustained= over 30 seconds).
3974:
4148:
3904:
3694:
3591:
3572:
3402:
3175:
3051:
1290:
1267:
1102:
Tachycardia that is not sinus tachycardia usually results from the addition of abnormal impulses to the normal
865:
698:
663:
625:
378:
71:
2498:"Multimodal Neural Network for Recognition of Cardiac Arrhythmias Based on 12-Load Electrocardiogram Signals"
4181:
4155:
4143:
4131:
4116:
3850:
3792:
3596:
3577:
3229:
3169:
3122:
1563:
1233:
927:
740:
615:
602:
382:
131:
3770:
3736:
3679:
3657:
3479:
3461:
3397:
3264:
3217:
3145:
1568:
1543:
931:
565:
449:
390:
386:
346:
166:
3534:
3529:
3424:
3234:
1491:
1460:
1370:
1221:
1171:
1141:
1003:
748:
656:
652:
1392:
Some arrhythmias promote blood clotting within the heart and increase the risk of embolus and stroke.
1278:. Atrial fibrillation may be due to serious underlying medical conditions and should be evaluated by a
1220:) are considered to be the main mechanism of life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias. In particular, the
1150:
cell firing off an impulse on its own. All of the cells in the heart have the ability to initiate an
922:
A more advanced study of the heart's electrical activity can be performed to assess the source of the
4030:
3558:
3539:
3439:
3350:
3293:
2509:
1782:
1743:
1464:
1162:
Any part of the heart that initiates an impulse without waiting for the sinoatrial node is called an
702:
589:
478:
445:
417:
338:
158:
322:. While most cases of arrhythmia are not serious, some predispose a person to complications such as
4035:
3892:
3887:
3810:
3714:
3684:
3643:
3269:
3186:
3040:
1523:
1495:
1263:
815:
806:. These may be infrequent, frequent, or continuous. Some of these arrhythmias are harmless (though
744:
630:
538:
513:
366:
311:
116:
2943:
Hadziselimovic E, Thomsen JH, Kjaergaard J, Køber L, Graff C, Pehrson S, et al. (July 2018).
2274:
Winkel BG, Holst AG, Theilade J, Kristensen IB, Thomsen JL, Ottesen GL, et al. (April 2011).
1714:
597:
Groups of three premature ventricular beats are called triplets and are considered a brief run of
4138:
3936:
3758:
3709:
3334:
3281:
3191:
2980:
2614:
2562:
1882:
1685:
1595:
1244:
972:
923:
518:
307:
112:
95:
2367:
1067:
In adults and children over 15, resting heart rate faster than 100 beats per minute is labeled
465:
Broad classification of arrhythmias according to region of heart required to sustain the rhythm
4198:
4049:
4007:
3922:
3740:
3638:
3355:
3298:
3196:
3091:
3062:
2972:
2964:
2922:
2848:
2821:
2778:
2755:
2711:
2684:
2649:
2606:
2527:
2478:
2460:
2419:
2349:
2297:
2256:
2207:
2158:
2115:
2092:
2069:
2031:
1982:
1933:
1874:
1839:
1480:
1286:
1182:
1056:
1007:
912:
869:
853:
756:
713:
560:
503:
493:
398:
193:
188:
83:
75:
4171:
4063:
3956:
3652:
2956:
2912:
2811:
2745:
2729:
2676:
2641:
2596:
2554:
2517:
2468:
2450:
2409:
2401:
2339:
2331:
2287:
2246:
2238:
2197:
2189:
2148:
2061:
2021:
2013:
1972:
1964:
1923:
1913:
1866:
1829:
1821:
1201:
1151:
1128:
994:
Each heartbeat originates as an electrical impulse from a small area of tissue in the right
764:
760:
709:
498:
1634:
4193:
3585:
3566:
3553:
3360:
3239:
1155:
1092:
1015:
999:
877:
350:
170:
63:
1857:
Vogler J, Breithardt G, Eckardt L (July 2012). "Bradyarrhythmias and conduction blocks".
2960:
2513:
4186:
4094:
3992:
3984:
3882:
3392:
3385:
3372:
2473:
2438:
2414:
2389:
2344:
2319:
2251:
2226:
2225:
Chugh SS, Reinier K, Teodorescu C, Evanado A, Kehr E, Al Samara M, et al. (2008).
2202:
2177:
2065:
2026:
2001:
1977:
1952:
1928:
1901:
1834:
1809:
1551:
1535:
1499:
1448:
1433:
1377:
1358:
1324:
1302:
1294:
1275:
1225:
1163:
1147:
995:
952:
916:
846:
802:
The most common symptom of arrhythmia is an awareness of an abnormal heartbeat, called
736:
533:
437:
429:
402:
370:
331:
197:
2944:
2917:
2900:
2193:
1968:
1451:. Temporary pacing may be necessary for reversible causes of very slow heartbeats, or
810:
for patients) but some of them predispose to adverse outcomes. Arrhythmias also cause
4213:
4176:
4087:
3222:
1456:
1419:
1393:
1167:
1103:
1011:
873:
799:
The term cardiac arrhythmia covers a very large number of very different conditions.
433:
425:
413:
327:
279:
140:
3045:
2984:
2816:
2799:
2798:
Den
Ruijter HM, Berecki G, Opthof T, Verkerk AO, Zock PL, Coronel R (January 2007).
2566:
1886:
1289:(lower chambers) of the heart; it is always a medical emergency. If left untreated,
290:, and a resting heart rate that is too slow – below 60 beats per minute – is called
4108:
4082:
3926:
3874:
3547:
3523:
3493:
3470:
3339:
3329:
2618:
1251:
can be protective against arrhythmias, they can facilitate re-entrant arrhythmias.
1088:
1010:(main pumping chambers). The impulse then spreads through both ventricles via the
893:
827:
601:(NSVT); if the grouping lasts for more than 30 seconds, it is considered sustained
421:
299:
100:
1510:
Arrhythmias due to medications have been reported since the 1920s with the use of
1475:
Some cardiologists further sub-specialize into electrophysiology. In specialized
3114:
3056:
2680:
1825:
245:
4043:
3941:
3731:
3648:
3630:
3456:
3429:
3380:
3321:
3086:
2522:
2497:
2088:
1515:
1452:
1354:
1068:
1052:
948:
897:
807:
803:
474:
470:
291:
287:
3067:
2455:
2405:
2335:
2292:
2275:
2242:
2017:
1200:
in every direction but will do so only once within a short time. Normally, the
74:(VF) showing disorganized electrical activity producing a spiked tracing on an
4071:
2870:
2153:
2136:
1870:
1467:
may be placed in situations where the bradycardia is not expected to recover.
1427:
1080:
1031:
842:, or brain death due to insufficient supply of blood and oxygen to the brain.
811:
682:
315:
303:
283:
263:
120:
108:
88:
2968:
2583:
Pehrson SM, Blomström-Lundqvist C, Ljungström E, Blomström P (October 1994).
2531:
2464:
1018:
causing a synchronized contraction of the heart muscle and, thus, the pulse.
1006:, which is normally the only electrical connection between the atria and the
3030:
3026:
2750:
2733:
2645:
1279:
1034:
breathing exercises that involve deep inhaling and breath holding patterns.
944:
892:
Cardiac arrhythmia is often first detected by simple but nonspecific means:
691:
409:
208:
104:
2976:
2926:
2852:
2839:
Barrett ML, Smith MW, Elizhauser A, Honigman LS, Pines JM (December 2014).
2825:
2715:
2688:
2653:
2601:
2584:
2482:
2423:
2353:
2301:
2260:
2211:
2096:
2073:
2035:
1986:
1937:
1878:
1843:
302:
or feeling a pause between heartbeats. In more serious cases, there may be
30:
This article is about the irregular heartbeat. For the skin condition, see
2610:
2558:
2227:"Epidemiology of sudden cardiac death: clinical and research implications"
2162:
1274:
Atrial fibrillation affects the upper chambers of the heart, known as the
1002:. The impulse initially causes both atria to contract, then activates the
3997:
3154:
2759:
1684:. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. July 1, 2011. Archived from
1476:
1397:
1248:
1217:
1197:
1084:
678:
588:
Premature ventricular beats occurring after every normal beat are termed
295:
31:
17:
2052:
Mehra R (2007). "Global public health problem of sudden cardiac death".
1918:
1380:, and so must be carefully selected and used under medical supervision.
1042:
1511:
1422:
is either achieved pharmacologically or via the application of a shock
1405:
1401:
477:), mechanism (automaticity, re-entry, triggered) or duration (isolated
3009:
1071:. Tachycardia may result in palpitation; however, tachycardia is not
743:
specifically because of poor oxygenation of the heart muscle, that is
655:
blocks, because the vast majority of them arise from pathology at the
57:
Cardiac arrhythmia, heart arrhythmia, dysrhythmia, irregular heartbeat
4077:
4057:
3212:
3109:
3021:
2276:"Nationwide study of sudden cardiac death in persons aged 1-35 years"
1539:
1519:
1096:
323:
136:
856:
is one way to diagnose and assess the risk of any given arrhythmia.
286:
that is too fast – above 100 beats per minute in adults – is called
2496:
Kiladze MR, Lyakhova UA, Lyakhov PA, Nagornov NN, Vahabi M (2023).
2847:(185). Rockville, MD: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.
1310:
1041:
901:
788:
732:
460:
1224:
is common in the thin walls of the atria, sometimes resulting in
2775:
Cardiac
Arrhythmias: Their Mechanisms, Diagnosis, and Management
2578:
2576:
835:
254:
Heart sounds of a girl experiencing arrhythmia after exercising.
27:
Group of medical conditions characterized by irregular heartbeat
3118:
2800:"Pro- and antiarrhythmic properties of a diet rich in fish oil"
2002:"Arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death in the COVID-19 pandemic"
1527:
1237:
412:, and surgery. Medications for a fast heart rate may include
1900:
Zoni-Berisso M, Lercari F, Carazza T, Domenicucci S (2014).
1270:): ventricular fibrillation is imminently life-threatening.
227:
2114:(10th ed.). Philadelphia, PA: Williams & Wilkins.
1902:"Epidemiology of atrial fibrillation: European perspective"
1785:. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. July 1, 2011.
1746:. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. July 1, 2011.
1717:. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. July 1, 2011.
1598:. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. July 1, 2011.
1353:). Parasympathetic nervous supply to the heart is via the
712:
typically manifesting with various degrees and patterns of
1440:
Defibrillation or cardioversion may be accomplished by an
947:
to a part where the distance to the posterior wall of the
397:. A number of tests can help with diagnosis, including an
1490:
is often curable by ablating one of the pathways in the
585:(PVCs), sometimes called ventricular extra beats (VEBs)
1240:
syndromes, which utilize abnormal conduction pathways.
282:, including when it is too fast or too slow. A resting
1236:. These types of re-entry circuits are different from
911:
diagnostic test for assessment of heart rhythm is the
943:(TAS) instead uses an electrode inserted through the
830:
and stroke, heart failure, and sudden cardiac death.
769:
Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia
2999:
2390:"Overview of Basic Mechanisms of Cardiac Arrhythmia"
1538:, particularly in patients treated with 33 °C.
337:
Arrhythmias are often categorized into four groups:
4164:
4107:
4016:
3983:
3955:
3913:
3872:
3849:
3823:
3791:
3749:
3730:
3629:
3615:
3515:
3469:
3455:
3371:
3320:
3313:
3250:
3205:
3162:
3153:
3077:
3003:
2178:"Epidemiology and genetics of sudden cardiac death"
1596:"What Are the Signs and Symptoms of an Arrhythmia?"
1051:A slow rhythm (less than 60 beats/min) is labelled
659:. They are the most common causes of bradycardia:
484:Arrhythmias are also classified by site of origin:
215:
203:
187:
176:
154:
146:
130:
94:
82:
53:
48:
1447:Electrical treatment of arrhythmias also includes
2871:"AED Buyer's Guide | AED Prices & Comparison"
2777:(3 ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
1297:. An affected individual will not survive unless
1550:physiological phenomenon, associated with lower
1437:consciousness so there is no need for sedation.
1357:, and these maneuvers are collectively known as
1127:heart to fill with blood before beating again.
2704:Archivos del Instituto de Cardiologia de Mexico
2437:Willcox ME, Compton SJ, Bardy GH (2021-12-01).
1808:Martin CA, Matthews GD, Huang CL (April 2012).
963:. It can also evaluate the risk in people with
852:Medical assessment of the abnormality using an
2841:"Utilization of Intensive Care Services, 2011"
1502:isolation, but the results are less reliable.
1177:Conditions that increase automaticity include
3130:
2368:"Passing Out (Syncope) Caused by Arrhythmias"
2320:"Fetal arrhythmias: Diagnosis and management"
1738:
1736:
1709:
1707:
1705:
1703:
1676:
1674:
1672:
1670:
1668:
1666:
1664:
1662:
1660:
8:
2388:Antzelevitch C, Burashnikov A (March 2011).
1629:
1627:
1625:
1623:
1621:
1619:
1617:
1590:
1588:
1586:
1584:
1216:, vortices of excitation in the myocardium (
926:heart beats. This can be accomplished in an
448:is the cause of about half of deaths due to
2324:Indian Pacing and Electrophysiology Journal
1777:
1775:
1773:
1771:
1769:
1767:
1765:
393:. Arrhythmias are due to problems with the
3746:
3626:
3466:
3447:Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia
3317:
3159:
3137:
3123:
3115:
3000:
2894:
2892:
2890:
2047:
2045:
1542:are not associated with increased risk of
1282:. It is not typically a medical emergency.
777:arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia
636:Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia
45:
2916:
2815:
2749:
2600:
2521:
2472:
2454:
2413:
2343:
2291:
2250:
2201:
2152:
2025:
1976:
1927:
1917:
1833:
1639:National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute
990:Electrical conduction system of the heart
395:electrical conduction system of the heart
182:electrical conduction system of the heart
2313:
2311:
2112:Marriott's Practical Electrocardiography
1228:. Re-entry is also responsible for most
391:atrioventricular conduction disturbances
365:. Supraventricular tachycardias include
2732:, Bonke FI, Schopman FJ (August 1976).
1580:
1285:Ventricular fibrillation occurs in the
1230:paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia
1000:sinus node or sinoatrial node (SA node)
755:Causes of SADS in young people include
375:paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia
3181:Spontaneous coronary artery dissection
2135:Zipes DP, Wellens HJ (November 1998).
1442:implantable cardioverter-defibrillator
961:atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia
469:Arrhythmia may be classified by rate (
298:. Symptoms, when present, may include
261:
2938:
2936:
1789:from the original on 17 February 2015
1750:from the original on 18 February 2015
1602:from the original on 19 February 2015
1532:targeted temperature management (TTM)
1498:can also be treated, by performing a
599:non-sustained ventricular tachycardia
7:
3505:Nonbacterial thrombotic endocarditis
2899:Heist EK, Ruskin JN (October 2010).
2087:Farzam K, Richards JR (2022-12-27).
1309:CPR can prolong the survival of the
1262:Fibrillation can affect the atrium (
666:, which manifests as PR prolongation
509:Premature atrial contractions (PACs)
294:. Some types of arrhythmias have no
2961:10.1016/j.resuscitation.2018.04.037
2669:International Journal of Cardiology
2231:Progress in Cardiovascular Diseases
2089:"Premature ventricular contraction"
1715:"Who Is at Risk for an Arrhythmia?"
1091:, and an overactive thyroid gland (
845:Some types of arrhythmia result in
621:Polymorphic ventricular tachycardia
616:Monomorphic ventricular tachycardia
3801:Accelerated idioventricular rhythm
2066:10.1016/j.jelectrocard.2007.06.023
1404:, and anti-platelet drugs such as
939:Transesophageal atrial stimulation
787:Arrhythmias may also occur in the
727:(SADS), is a term used as part of
611:Accelerated idioventricular rhythm
583:Premature ventricular contractions
529:Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT)
377:. Ventricular arrhythmias include
359:premature ventricular contractions
25:
2918:10.1161/circulationaha.109.894725
2394:Cardiac Electrophysiology Clinics
2194:10.1161/circulationaha.111.023838
2176:Deo R, Albert CM (January 2012).
1721:from the original on 3 March 2015
1645:from the original on 2 March 2015
1408:can reduce the risk of clotting.
363:premature junctional contractions
207:Medications, medical procedures (
2859:from the original on 2015-04-02.
1744:"How Are Arrhythmias Diagnosed?"
1196:Every cardiac cell can transmit
729:sudden unexpected death syndrome
725:Sudden arrhythmic death syndrome
720:Sudden arrhythmic death syndrome
688:Type 2 Second degree heart block
675:Type 1 Second degree heart block
571:Premature junctional contraction
320:decreased level of consciousness
262:Problems playing this file? See
243:
125:decreased level of consciousness
62:
3486:Subacute bacterial endocarditis
2817:10.1016/j.cardiores.2006.06.014
2547:Estonian Journal of Engineering
1859:Revista Espanola de Cardiologia
1004:atrioventricular node (AV node)
641:Re-entry ventricular arrhythmia
1783:"How Are Arrhythmias Treated?"
1488:AV nodal reentrant tachycardia
1120:Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome
965:Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome
957:AV nodal reentrant tachycardia
880:network. The second is due to
556:AV nodal reentrant tachycardia
544:AV nodal reentrant tachycardia
385:. Bradyarrhythmias are due to
1:
4003:Pulseless electrical activity
3932:Multifocal atrial tachycardia
3806:Catecholaminergic polymorphic
1969:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61682-2
1351:supraventricular tachycardias
1299:cardiopulmonary resuscitation
881:
868:formation originating at the
524:Multifocal atrial tachycardia
355:premature atrial contractions
343:supraventricular tachycardias
163:supraventricular tachycardias
2681:10.1016/j.ijcard.2009.06.058
2054:Journal of Electrocardiology
1826:10.1136/heartjnl-2011-300953
1494:(usually the slow pathway).
969:supraventricular tachycardia
915:(abbreviated ECG or EKG). A
900:, or feeling for peripheral
278:, are irregularities in the
2523:10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3335176
2318:Batra AS, Balaji S (2019).
840:persistent vegetative state
773:hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
36:arrhythmia (disambiguation)
4241:
3947:Wandering atrial pacemaker
3494:non-infective endocarditis
3435:Endocardial fibroelastosis
2456:10.1016/j.hroo.2021.09.008
2406:10.1016/j.ccep.2010.10.012
2336:10.1016/j.ipej.2019.02.007
2243:10.1016/j.pcad.2008.06.003
2018:10.1007/s00059-020-04924-0
1546:, and may be considered a
1368:
1179:sympathetic nervous system
1139:
1077:sympathetic nervous system
987:
984:Normal electrical activity
539:Atrial fibrillation (Afib)
514:Wandering atrial pacemaker
239:Emma's irregular heartbeat
29:
4025:hexaxial reference system
3970:Jervell and Lange-Nielsen
3500:Libman–Sacks endocarditis
2901:"Drug-induced arrhythmia"
2154:10.1161/01.CIR.98.21.2334
1871:10.1016/j.rec.2012.01.027
1554:in univariable analyses.
1305:are provided immediately.
1146:Automaticity refers to a
1124:ventricular outflow tract
884:conduction disturbances.
670:Second-degree heart block
430:controlled electric shock
70:
61:
3905:Ventricular fibrillation
3176:Coronary artery aneurysm
2293:10.1093/eurheartj/ehq428
1291:ventricular fibrillation
1268:ventricular fibrillation
998:of the heart called the
896:of the heartbeat with a
699:Third-degree heart block
664:First-degree heart block
651:These are also known as
626:Ventricular fibrillation
379:ventricular fibrillation
72:Ventricular fibrillation
4182:Diastolic heart failure
4156:Athletic heart syndrome
4117:Ventricular hypertrophy
3851:Pre-excitation syndrome
3705:Left posterior fascicle
3230:Acute coronary syndrome
3170:Coronary artery disease
2804:Cardiovascular Research
2773:Mandel WJ, ed. (1995).
2751:10.1161/01.RES.39.2.168
2646:10.1378/chest.125.2.683
1564:Pre-excitation syndrome
1234:ventricular tachycardia
967:, as well as terminate
928:electrophysiology study
741:coronary artery disease
603:ventricular tachycardia
383:ventricular tachycardia
347:ventricular arrhythmias
330:. Others may result in
167:ventricular arrhythmias
3700:Left anterior fascicle
3480:infective endocarditis
3265:Hibernating myocardium
3146:Cardiovascular disease
2845:HCUP Statistical Brief
2602:10.1002/clc.4960171004
2449:(6, Part A): 543–559.
2280:European Heart Journal
2137:"Sudden cardiac death"
2060:(6 Suppl): S118–S122.
1569:Holiday heart syndrome
1544:ventricular arrhythmia
1530:) are frequent during
1198:impulses of excitation
1057:some types of seizures
1048:
979:Differential diagnosis
932:endovascular procedure
577:Ventricular arrhythmia
566:Junctional tachycardia
466:
450:cardiovascular disease
387:sinus node dysfunction
353:. Extra beats include
232:
34:. For other uses, see
3864:Wolff–Parkinson–White
3824:Premature contraction
3722:Adams–Stokes syndrome
3425:Loeffler endocarditis
3235:Myocardial infarction
2559:10.3176/eng.2008.2.05
2000:Kuck KH (June 2020).
1906:Clinical Epidemiology
1682:"Types of Arrhythmia"
1635:"What Is Arrhythmia?"
1477:catheter laboratories
1461:myocardial infarction
1371:Antiarrhythmic agents
1222:autowave reverberator
1172:atrioventricular node
1142:Automatic tachycardia
1045:
657:atrioventricular node
550:Junctional arrhythmia
464:
418:antiarrhythmic agents
231:
4031:Right axis deviation
3993:Sudden cardiac death
3351:Pericardial effusion
3294:Ventricular aneurysm
2738:Circulation Research
1396:medications such as
1365:Antiarrhythmic drugs
1266:) or the ventricle (
703:complete heart block
590:ventricular bigeminy
446:Sudden cardiac death
4225:Medical emergencies
4036:Left axis deviation
3893:Atrial fibrillation
3888:Ventricular flutter
3811:Torsades de pointes
3685:Bundle branch block
3644:Sick sinus syndrome
3430:Cardiac amyloidosis
3415:Tachycardia-induced
3270:Myocardial stunning
3218:Prinzmetal's angina
3187:Coronary thrombosis
2589:Clinical Cardiology
2514:2023IEEEA..11m3744K
1919:10.2147/CLEP.S47385
1496:Atrial fibrillation
1455:(for example, from
1430:for the procedure.
1264:atrial fibrillation
1245:omega-3 fatty acids
849:, or sudden death.
816:shortness of breath
745:myocardial ischemia
731:to describe sudden
631:Torsades de pointes
367:atrial fibrillation
312:shortness of breath
276:cardiac arrhythmias
117:shortness of breath
4220:Cardiac arrhythmia
4139:Atrial enlargement
3937:Pacemaker syndrome
3859:Lown–Ganong–Levine
3781:Junctional ectopic
3776:AV nodal reentrant
3282:Myocardial rupture
3192:Coronary vasospasm
3078:External resources
2110:Wagner GS (2001).
1471:Electrical cautery
1344:Physical maneuvers
1049:
795:Signs and symptoms
519:Atrial tachycardia
467:
233:
180:Problems with the
4207:
4206:
4199:Obstructive shock
4103:
4102:
4050:Short QT syndrome
4017:Other / ungrouped
4008:Sinoatrial arrest
3923:Ectopic pacemaker
3819:
3818:
3639:Sinus bradycardia
3611:
3610:
3607:
3606:
3356:Cardiac tamponade
3309:
3308:
3299:Dressler syndrome
3197:Myocardial bridge
3101:
3100:
2911:(14): 1426–1435.
2784:978-0-397-51185-3
2508:: 133744–133754.
2147:(21): 2334–2351.
1963:(9963): 117–171.
1524:electrocardiogram
1481:catheter ablation
1218:autowave vortices
1206:refractory period
913:electrocardiogram
854:electrocardiogram
757:viral myocarditis
714:sinus bradycardia
561:Junctional rhythm
504:Sinus tachycardia
494:Sinus bradycardia
488:Atrial arrhythmia
399:electrocardiogram
249:
223:
222:
194:Electrocardiogram
189:Diagnostic method
76:electrocardiogram
43:Medical condition
16:(Redirected from
4232:
4172:Cardiac fibrosis
4064:T wave alternans
3957:Long QT syndrome
3751:Supraventricular
3747:
3680:Intraventricular
3627:
3467:
3318:
3163:Coronary disease
3160:
3139:
3132:
3125:
3116:
3001:
2989:
2988:
2940:
2931:
2930:
2920:
2896:
2885:
2884:
2882:
2881:
2867:
2861:
2860:
2836:
2830:
2829:
2819:
2795:
2789:
2788:
2770:
2764:
2763:
2753:
2726:
2720:
2719:
2699:
2693:
2692:
2664:
2658:
2657:
2629:
2623:
2622:
2604:
2580:
2571:
2570:
2542:
2536:
2535:
2525:
2493:
2487:
2486:
2476:
2458:
2434:
2428:
2427:
2417:
2385:
2379:
2378:
2376:
2374:
2364:
2358:
2357:
2347:
2315:
2306:
2305:
2295:
2271:
2265:
2264:
2254:
2222:
2216:
2215:
2205:
2173:
2167:
2166:
2156:
2132:
2126:
2125:
2107:
2101:
2100:
2084:
2078:
2077:
2049:
2040:
2039:
2029:
1997:
1991:
1990:
1980:
1948:
1942:
1941:
1931:
1921:
1897:
1891:
1890:
1854:
1848:
1847:
1837:
1805:
1799:
1798:
1796:
1794:
1779:
1760:
1759:
1757:
1755:
1740:
1731:
1730:
1728:
1726:
1711:
1698:
1697:
1695:
1693:
1678:
1655:
1654:
1652:
1650:
1641:. July 1, 2011.
1631:
1612:
1611:
1609:
1607:
1592:
1518:was determined.
1516:QTc prolongation
1232:, and dangerous
1209:circuit rhythm.
1202:action potential
1181:stimulation and
1152:action potential
1129:Long QT syndrome
1027:sinus arrhythmia
959:and orthodromic
941:
940:
783:Fetal arrhythmia
765:Brugada syndrome
761:long QT syndrome
710:sinoatrial block
701:, also known as
690:, also known as
677:, also known as
499:Sinus arrhythmia
351:bradyarrhythmias
274:, also known as
251:
250:
230:
171:bradyarrhythmias
66:
46:
21:
4240:
4239:
4235:
4234:
4233:
4231:
4230:
4229:
4210:
4209:
4208:
4203:
4194:Rheumatic fever
4160:
4099:
4012:
3979:
3951:
3909:
3868:
3845:
3815:
3787:
3734:
3726:
3620:
3603:
3511:
3460:
3451:
3367:
3361:Hemopericardium
3305:
3246:
3240:Unstable angina
3213:Angina pectoris
3206:Active ischemia
3201:
3149:
3143:
3102:
3097:
3096:
3073:
3072:
3012:
2998:
2993:
2992:
2942:
2941:
2934:
2898:
2897:
2888:
2879:
2877:
2869:
2868:
2864:
2838:
2837:
2833:
2797:
2796:
2792:
2785:
2772:
2771:
2767:
2728:
2727:
2723:
2701:
2700:
2696:
2666:
2665:
2661:
2631:
2630:
2626:
2595:(10): 528–534.
2582:
2581:
2574:
2544:
2543:
2539:
2495:
2494:
2490:
2443:Heart Rhythm O2
2436:
2435:
2431:
2387:
2386:
2382:
2372:
2370:
2366:
2365:
2361:
2317:
2316:
2309:
2273:
2272:
2268:
2224:
2223:
2219:
2175:
2174:
2170:
2134:
2133:
2129:
2122:
2109:
2108:
2104:
2086:
2085:
2081:
2051:
2050:
2043:
1999:
1998:
1994:
1950:
1949:
1945:
1899:
1898:
1894:
1856:
1855:
1851:
1807:
1806:
1802:
1792:
1790:
1781:
1780:
1763:
1753:
1751:
1742:
1741:
1734:
1724:
1722:
1713:
1712:
1701:
1691:
1689:
1680:
1679:
1658:
1648:
1646:
1633:
1632:
1615:
1605:
1603:
1594:
1593:
1582:
1577:
1560:
1508:
1473:
1463:). A permanent
1414:
1386:
1373:
1367:
1359:vagal maneuvers
1346:
1333:
1325:depolarizations
1320:
1318:Triggered beats
1257:
1191:
1156:sinoatrial node
1144:
1138:
1115:
1093:hyperthyroidism
1065:
1040:
1016:Purkinje fibers
992:
986:
981:
938:
937:
890:
862:
797:
785:
722:
649:
579:
552:
490:
479:premature beats
459:
432:in the form of
304:lightheadedness
269:
268:
260:
258:
257:
256:
255:
252:
244:
241:
234:
228:
109:lightheadedness
44:
39:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
4238:
4236:
4228:
4227:
4222:
4212:
4211:
4205:
4204:
4202:
4201:
4196:
4191:
4190:
4189:
4187:Cardiac asthma
4184:
4174:
4168:
4166:
4162:
4161:
4159:
4158:
4153:
4152:
4151:
4146:
4136:
4135:
4134:
4129:
4124:
4113:
4111:
4105:
4104:
4101:
4100:
4098:
4097:
4095:Strain pattern
4092:
4091:
4090:
4085:
4080:
4068:
4067:
4066:
4054:
4053:
4052:
4040:
4039:
4038:
4033:
4020:
4018:
4014:
4013:
4011:
4010:
4005:
4000:
3995:
3989:
3987:
3985:Cardiac arrest
3981:
3980:
3978:
3977:
3972:
3967:
3965:Andersen–Tawil
3961:
3959:
3953:
3952:
3950:
3949:
3944:
3939:
3934:
3929:
3919:
3917:
3911:
3910:
3908:
3907:
3902:
3901:
3900:
3890:
3885:
3883:Atrial flutter
3879:
3877:
3870:
3869:
3867:
3866:
3861:
3855:
3853:
3847:
3846:
3844:
3843:
3838:
3833:
3827:
3825:
3821:
3820:
3817:
3816:
3814:
3813:
3808:
3803:
3797:
3795:
3789:
3788:
3786:
3785:
3784:
3783:
3778:
3768:
3767:
3766:
3755:
3753:
3744:
3728:
3727:
3725:
3724:
3719:
3718:
3717:
3712:
3707:
3702:
3697:
3692:
3682:
3677:
3676:
3675:
3670:
3665:
3655:
3646:
3641:
3635:
3633:
3624:
3613:
3612:
3609:
3608:
3605:
3604:
3602:
3601:
3600:
3599:
3594:
3582:
3581:
3580:
3575:
3563:
3562:
3561:
3556:
3544:
3543:
3542:
3537:
3532:
3519:
3517:
3513:
3512:
3510:
3509:
3508:
3507:
3502:
3490:
3489:
3488:
3475:
3473:
3464:
3453:
3452:
3450:
3449:
3444:
3443:
3442:
3437:
3432:
3427:
3422:
3417:
3412:
3407:
3406:
3405:
3393:Cardiomyopathy
3390:
3389:
3388:
3386:Chagas disease
3377:
3375:
3369:
3368:
3366:
3365:
3364:
3363:
3358:
3348:
3347:
3346:
3337:
3326:
3324:
3315:
3311:
3310:
3307:
3306:
3304:
3303:
3302:
3301:
3296:
3286:
3285:
3284:
3274:
3273:
3272:
3267:
3256:
3254:
3248:
3247:
3245:
3244:
3243:
3242:
3237:
3227:
3226:
3225:
3220:
3209:
3207:
3203:
3202:
3200:
3199:
3194:
3189:
3184:
3178:
3173:
3166:
3164:
3157:
3151:
3150:
3144:
3142:
3141:
3134:
3127:
3119:
3113:
3112:
3099:
3098:
3095:
3094:
3082:
3081:
3079:
3075:
3074:
3071:
3070:
3059:
3048:
3033:
3013:
3008:
3007:
3005:
3004:Classification
2997:
2996:External links
2994:
2991:
2990:
2932:
2886:
2862:
2831:
2810:(2): 316–325.
2790:
2783:
2765:
2744:(2): 168–177.
2721:
2710:(3): 205–265.
2694:
2675:(1): 142–146.
2659:
2640:(2): 683–690.
2624:
2572:
2537:
2488:
2429:
2380:
2359:
2330:(3): 104–109.
2307:
2286:(8): 983–990.
2266:
2237:(3): 213–228.
2217:
2188:(4): 620–637.
2168:
2127:
2120:
2102:
2091:. StatPearls.
2079:
2041:
2012:(4): 325–326.
1992:
1943:
1892:
1865:(7): 656–667.
1849:
1820:(7): 536–543.
1800:
1761:
1732:
1699:
1688:on 7 June 2015
1656:
1613:
1579:
1578:
1576:
1573:
1572:
1571:
1566:
1559:
1556:
1536:cardiac arrest
1507:
1504:
1500:pulmonary vein
1472:
1469:
1449:cardiac pacing
1434:Defibrillation
1413:
1410:
1385:
1382:
1378:pro-arrhythmic
1369:Main article:
1366:
1363:
1345:
1342:
1332:
1329:
1319:
1316:
1307:
1306:
1303:defibrillation
1295:cardiac arrest
1283:
1256:
1253:
1226:atrial flutter
1190:
1187:
1148:cardiac muscle
1140:Main article:
1137:
1134:
1114:
1111:
1064:
1061:
1039:
1036:
988:Main article:
985:
982:
980:
977:
953:atrial flutter
917:Holter monitor
889:
886:
861:
858:
847:cardiac arrest
796:
793:
784:
781:
737:cardiac arrest
721:
718:
706:
705:
696:
695:
694:
685:
667:
648:
645:
644:
643:
638:
633:
628:
623:
618:
613:
608:
607:
606:
595:
592:
578:
575:
574:
573:
568:
563:
558:
551:
548:
547:
546:
541:
536:
534:Atrial flutter
531:
526:
521:
516:
511:
506:
501:
496:
489:
486:
458:
457:Classification
455:
438:defibrillation
426:blood thinners
403:Holter monitor
371:atrial flutter
259:
253:
242:
237:
236:
235:
226:
225:
224:
221:
220:
217:
213:
212:
205:
201:
200:
198:Holter monitor
191:
185:
184:
178:
174:
173:
156:
152:
151:
148:
144:
143:
134:
128:
127:
98:
92:
91:
86:
80:
79:
68:
67:
59:
58:
55:
51:
50:
42:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
4237:
4226:
4223:
4221:
4218:
4217:
4215:
4200:
4197:
4195:
4192:
4188:
4185:
4183:
4180:
4179:
4178:
4177:Heart failure
4175:
4173:
4170:
4169:
4167:
4163:
4157:
4154:
4150:
4147:
4145:
4142:
4141:
4140:
4137:
4133:
4130:
4128:
4125:
4123:
4120:
4119:
4118:
4115:
4114:
4112:
4110:
4106:
4096:
4093:
4089:
4088:ST depression
4086:
4084:
4081:
4079:
4076:
4075:
4074:
4073:
4069:
4065:
4062:
4061:
4060:
4059:
4055:
4051:
4048:
4047:
4046:
4045:
4041:
4037:
4034:
4032:
4029:
4028:
4027:
4026:
4022:
4021:
4019:
4015:
4009:
4006:
4004:
4001:
3999:
3996:
3994:
3991:
3990:
3988:
3986:
3982:
3976:
3973:
3971:
3968:
3966:
3963:
3962:
3960:
3958:
3954:
3948:
3945:
3943:
3940:
3938:
3935:
3933:
3930:
3928:
3924:
3921:
3920:
3918:
3916:
3912:
3906:
3903:
3899:
3896:
3895:
3894:
3891:
3889:
3886:
3884:
3881:
3880:
3878:
3876:
3871:
3865:
3862:
3860:
3857:
3856:
3854:
3852:
3848:
3842:
3839:
3837:
3834:
3832:
3829:
3828:
3826:
3822:
3812:
3809:
3807:
3804:
3802:
3799:
3798:
3796:
3794:
3790:
3782:
3779:
3777:
3774:
3773:
3772:
3769:
3765:
3762:
3761:
3760:
3757:
3756:
3754:
3752:
3748:
3745:
3742:
3738:
3733:
3729:
3723:
3720:
3716:
3715:Trifascicular
3713:
3711:
3708:
3706:
3703:
3701:
3698:
3696:
3693:
3691:
3688:
3687:
3686:
3683:
3681:
3678:
3674:
3671:
3669:
3666:
3664:
3661:
3660:
3659:
3656:
3654:
3650:
3647:
3645:
3642:
3640:
3637:
3636:
3634:
3632:
3628:
3625:
3623:
3618:
3614:
3598:
3597:regurgitation
3595:
3593:
3590:
3589:
3588:
3587:
3583:
3579:
3578:regurgitation
3576:
3574:
3571:
3570:
3569:
3568:
3564:
3560:
3559:regurgitation
3557:
3555:
3552:
3551:
3550:
3549:
3545:
3541:
3540:regurgitation
3538:
3536:
3533:
3531:
3528:
3527:
3526:
3525:
3521:
3520:
3518:
3514:
3506:
3503:
3501:
3498:
3497:
3496:
3495:
3491:
3487:
3484:
3483:
3482:
3481:
3477:
3476:
3474:
3472:
3468:
3465:
3463:
3458:
3454:
3448:
3445:
3441:
3438:
3436:
3433:
3431:
3428:
3426:
3423:
3421:
3418:
3416:
3413:
3411:
3408:
3404:
3401:
3400:
3399:
3396:
3395:
3394:
3391:
3387:
3384:
3383:
3382:
3379:
3378:
3376:
3374:
3370:
3362:
3359:
3357:
3354:
3353:
3352:
3349:
3345:
3341:
3338:
3336:
3333:
3332:
3331:
3328:
3327:
3325:
3323:
3319:
3316:
3312:
3300:
3297:
3295:
3292:
3291:
3290:
3287:
3283:
3280:
3279:
3278:
3275:
3271:
3268:
3266:
3263:
3262:
3261:
3258:
3257:
3255:
3253:
3249:
3241:
3238:
3236:
3233:
3232:
3231:
3228:
3224:
3223:Stable angina
3221:
3219:
3216:
3215:
3214:
3211:
3210:
3208:
3204:
3198:
3195:
3193:
3190:
3188:
3185:
3182:
3179:
3177:
3174:
3171:
3168:
3167:
3165:
3161:
3158:
3156:
3152:
3147:
3140:
3135:
3133:
3128:
3126:
3121:
3120:
3117:
3111:
3107:
3104:
3103:
3093:
3089:
3088:
3084:
3083:
3080:
3076:
3069:
3065:
3064:
3060:
3058:
3054:
3053:
3049:
3047:
3043:
3042:
3038:
3034:
3032:
3028:
3024:
3023:
3019:
3015:
3014:
3011:
3006:
3002:
2995:
2986:
2982:
2978:
2974:
2970:
2966:
2962:
2958:
2954:
2950:
2949:Resuscitation
2946:
2939:
2937:
2933:
2928:
2924:
2919:
2914:
2910:
2906:
2902:
2895:
2893:
2891:
2887:
2876:
2872:
2866:
2863:
2858:
2854:
2850:
2846:
2842:
2835:
2832:
2827:
2823:
2818:
2813:
2809:
2805:
2801:
2794:
2791:
2786:
2780:
2776:
2769:
2766:
2761:
2757:
2752:
2747:
2743:
2739:
2735:
2731:
2725:
2722:
2717:
2713:
2709:
2705:
2698:
2695:
2690:
2686:
2682:
2678:
2674:
2670:
2663:
2660:
2655:
2651:
2647:
2643:
2639:
2635:
2628:
2625:
2620:
2616:
2612:
2608:
2603:
2598:
2594:
2590:
2586:
2579:
2577:
2573:
2568:
2564:
2560:
2556:
2552:
2548:
2541:
2538:
2533:
2529:
2524:
2519:
2515:
2511:
2507:
2503:
2499:
2492:
2489:
2484:
2480:
2475:
2470:
2466:
2462:
2457:
2452:
2448:
2444:
2440:
2433:
2430:
2425:
2421:
2416:
2411:
2407:
2403:
2399:
2395:
2391:
2384:
2381:
2369:
2363:
2360:
2355:
2351:
2346:
2341:
2337:
2333:
2329:
2325:
2321:
2314:
2312:
2308:
2303:
2299:
2294:
2289:
2285:
2281:
2277:
2270:
2267:
2262:
2258:
2253:
2248:
2244:
2240:
2236:
2232:
2228:
2221:
2218:
2213:
2209:
2204:
2199:
2195:
2191:
2187:
2183:
2179:
2172:
2169:
2164:
2160:
2155:
2150:
2146:
2142:
2138:
2131:
2128:
2123:
2117:
2113:
2106:
2103:
2098:
2094:
2090:
2083:
2080:
2075:
2071:
2067:
2063:
2059:
2055:
2048:
2046:
2042:
2037:
2033:
2028:
2023:
2019:
2015:
2011:
2007:
2003:
1996:
1993:
1988:
1984:
1979:
1974:
1970:
1966:
1962:
1958:
1954:
1947:
1944:
1939:
1935:
1930:
1925:
1920:
1915:
1911:
1907:
1903:
1896:
1893:
1888:
1884:
1880:
1876:
1872:
1868:
1864:
1860:
1853:
1850:
1845:
1841:
1836:
1831:
1827:
1823:
1819:
1815:
1811:
1804:
1801:
1788:
1784:
1778:
1776:
1774:
1772:
1770:
1768:
1766:
1762:
1749:
1745:
1739:
1737:
1733:
1720:
1716:
1710:
1708:
1706:
1704:
1700:
1687:
1683:
1677:
1675:
1673:
1671:
1669:
1667:
1665:
1663:
1661:
1657:
1644:
1640:
1636:
1630:
1628:
1626:
1624:
1622:
1620:
1618:
1614:
1601:
1597:
1591:
1589:
1587:
1585:
1581:
1574:
1570:
1567:
1565:
1562:
1561:
1557:
1555:
1553:
1549:
1545:
1541:
1537:
1533:
1529:
1525:
1521:
1517:
1513:
1505:
1503:
1501:
1497:
1493:
1489:
1484:
1482:
1478:
1470:
1468:
1466:
1462:
1458:
1457:drug overdose
1454:
1450:
1445:
1443:
1438:
1435:
1431:
1429:
1425:
1421:
1420:Cardioversion
1417:
1411:
1409:
1407:
1403:
1399:
1395:
1394:Anticoagulant
1390:
1383:
1381:
1379:
1372:
1364:
1362:
1360:
1356:
1352:
1343:
1341:
1337:
1330:
1328:
1326:
1317:
1315:
1312:
1304:
1300:
1296:
1292:
1288:
1284:
1281:
1277:
1273:
1272:
1271:
1269:
1265:
1260:
1254:
1252:
1250:
1246:
1241:
1239:
1235:
1231:
1227:
1223:
1219:
1215:
1212:As a sort of
1210:
1207:
1203:
1199:
1194:
1188:
1186:
1184:
1180:
1175:
1173:
1169:
1168:ectopic focus
1165:
1160:
1157:
1153:
1149:
1143:
1135:
1133:
1130:
1125:
1121:
1113:Heart defects
1112:
1110:
1107:
1105:
1104:cardiac cycle
1100:
1098:
1094:
1090:
1086:
1082:
1078:
1074:
1070:
1062:
1060:
1058:
1054:
1044:
1037:
1035:
1033:
1028:
1023:
1019:
1017:
1013:
1012:bundle of His
1009:
1005:
1001:
997:
991:
983:
978:
976:
974:
970:
966:
962:
958:
954:
950:
946:
942:
933:
929:
925:
920:
918:
914:
910:
907:The simplest
905:
903:
899:
895:
887:
885:
883:
879:
875:
871:
867:
859:
857:
855:
850:
848:
843:
841:
837:
831:
829:
824:
819:
817:
813:
809:
805:
800:
794:
792:
790:
782:
780:
778:
774:
770:
766:
762:
758:
753:
750:
746:
742:
738:
734:
730:
726:
719:
717:
715:
711:
704:
700:
697:
693:
689:
686:
684:
680:
676:
673:
672:
671:
668:
665:
662:
661:
660:
658:
654:
646:
642:
639:
637:
634:
632:
629:
627:
624:
622:
619:
617:
614:
612:
609:
604:
600:
596:
593:
591:
587:
586:
584:
581:
580:
576:
572:
569:
567:
564:
562:
559:
557:
554:
553:
549:
545:
542:
540:
537:
535:
532:
530:
527:
525:
522:
520:
517:
515:
512:
510:
507:
505:
502:
500:
497:
495:
492:
491:
487:
485:
482:
480:
476:
472:
463:
456:
454:
451:
447:
441:
439:
435:
434:cardioversion
431:
427:
423:
419:
415:
414:beta blockers
411:
406:
404:
400:
396:
392:
388:
384:
380:
376:
372:
368:
364:
360:
356:
352:
348:
344:
340:
335:
333:
329:
328:heart failure
325:
321:
317:
313:
309:
305:
301:
297:
293:
289:
285:
281:
277:
273:
267:
265:
240:
218:
214:
210:
206:
202:
199:
195:
192:
190:
186:
183:
179:
175:
172:
168:
164:
160:
157:
153:
149:
145:
142:
141:heart failure
138:
135:
133:
132:Complications
129:
126:
122:
118:
114:
110:
106:
102:
99:
97:
93:
90:
87:
85:
81:
77:
73:
69:
65:
60:
56:
52:
47:
41:
37:
33:
19:
4109:Cardiomegaly
4083:ST elevation
4070:
4056:
4042:
4023:
3927:Ectopic beat
3875:fibrillation
3710:Bifascicular
3621:
3584:
3565:
3546:
3522:
3492:
3478:
3471:Endocarditis
3410:Hypertrophic
3344:Constrictive
3330:Pericarditis
3288:
3276:
3259:
3085:
3061:
3050:
3035:
3016:
2952:
2948:
2908:
2904:
2878:. Retrieved
2874:
2865:
2844:
2834:
2807:
2803:
2793:
2774:
2768:
2741:
2737:
2724:
2707:
2703:
2697:
2672:
2668:
2662:
2637:
2633:
2627:
2592:
2588:
2550:
2546:
2540:
2505:
2501:
2491:
2446:
2442:
2432:
2400:(1): 23–45.
2397:
2393:
2383:
2371:. Retrieved
2362:
2327:
2323:
2283:
2279:
2269:
2234:
2230:
2220:
2185:
2181:
2171:
2144:
2140:
2130:
2111:
2105:
2082:
2057:
2053:
2009:
2005:
1995:
1960:
1956:
1946:
1909:
1905:
1895:
1862:
1858:
1852:
1817:
1813:
1803:
1791:. Retrieved
1752:. Retrieved
1723:. Retrieved
1690:. Retrieved
1686:the original
1647:. Retrieved
1604:. Retrieved
1540:Osborn waves
1520:Osborn waves
1509:
1485:
1474:
1446:
1439:
1432:
1428:anesthetized
1424:synchronized
1423:
1418:
1415:
1391:
1387:
1374:
1347:
1338:
1334:
1321:
1308:
1261:
1258:
1255:Fibrillation
1242:
1213:
1211:
1195:
1192:
1176:
1161:
1145:
1136:Automaticity
1116:
1108:
1101:
1089:amphetamines
1072:
1066:
1063:Tachycardias
1050:
1038:Bradycardias
1024:
1020:
993:
936:
921:
908:
906:
894:auscultation
891:
863:
851:
844:
832:
828:embolization
822:
820:
804:palpitations
801:
798:
786:
754:
749:heart attack
728:
723:
707:
650:
647:Heart blocks
483:
468:
442:
422:procainamide
407:
336:
332:sudden death
300:palpitations
275:
271:
270:
101:Palpitations
40:
3975:Romano–Ward
3942:Parasystole
3841:Ventricular
3793:Ventricular
3732:Tachycardia
3649:Heart block
3631:Bradycardia
3457:Endocardium
3420:Restrictive
3381:Myocarditis
3322:Pericardium
3087:MedlinePlus
2955:: 119–125.
2905:Circulation
2730:Allessie MA
2502:IEEE Access
2182:Circulation
2141:Circulation
1912:: 213–220.
1453:bradycardia
1412:Electricity
1384:Other drugs
1355:vagus nerve
1073:necessarily
1069:tachycardia
1053:bradycardia
949:left atrium
898:stethoscope
808:distracting
735:because of
475:bradycardia
471:tachycardia
339:extra beats
308:passing out
292:bradycardia
288:tachycardia
272:Arrhythmias
159:Extra beats
147:Usual onset
113:passing out
54:Other names
4214:Categories
3873:Flutter /
3836:Junctional
3771:Junctional
3764:Multifocal
3737:paroxysmal
3653:Sinoatrial
3622:arrhythmia
3617:Conduction
3373:Myocardium
3106:Arrhythmia
3063:DiseasesDB
2880:2021-08-13
2875:AED Brands
2553:(2): 154.
2121:0683307460
1575:References
1331:Management
1301:(CPR) and
1287:ventricles
1081:sinus node
1032:meditation
1008:ventricles
971:caused by
888:Diagnostic
812:chest pain
683:Wenckebach
401:(ECG) and
316:chest pain
284:heart rate
264:media help
211:), surgery
121:chest pain
89:Cardiology
49:Arrhythmia
4132:Pulmonary
3915:Pacemaker
3586:pulmonary
3567:tricuspid
3403:Alcoholic
2969:0300-9572
2532:2169-3536
2465:2666-5018
1552:mortality
1465:pacemaker
1280:physician
1243:Although
1025:The term
945:esophagus
870:pacemaker
860:Mechanism
692:Mobitz II
410:pacemaker
280:heartbeat
216:Frequency
209:pacemaker
204:Treatment
150:Older age
105:dizziness
84:Specialty
18:Trigeminy
3998:Asystole
3898:Familial
3592:stenosis
3573:stenosis
3554:stenosis
3535:stenosis
3530:prolapse
3252:Sequelae
3155:Ischemia
2985:19236851
2977:29723608
2927:20921449
2857:Archived
2853:25654157
2826:16859661
2716:20245817
2689:19631997
2654:14769752
2567:42055085
2483:34988499
2424:21892379
2373:13 April
2354:30817991
2302:21131293
2261:19026856
2212:22294707
2097:30422584
2074:17993308
2036:32333026
1987:25530442
1938:24966695
1887:18983179
1879:22627074
1844:22422742
1787:Archived
1748:Archived
1719:Archived
1643:Archived
1600:Archived
1558:See also
1506:Research
1402:heparins
1398:warfarin
1249:fish oil
1214:re-entry
1189:Re-entry
1085:caffeine
1014:and the
973:re-entry
924:aberrant
909:specific
882:re-entry
878:Purkinje
679:Mobitz I
420:such as
296:symptoms
219:Millions
96:Symptoms
32:erythema
3398:Dilated
3340:Chronic
3148:(heart)
3057:D001145
2619:7097362
2611:8001299
2510:Bibcode
2474:8703156
2415:3164530
2345:6531664
2252:2621010
2203:3399522
2163:9826323
2027:7181098
1978:4340604
1929:4064952
1835:3308472
1793:7 March
1754:7 March
1725:7 March
1692:7 March
1649:7 March
1606:7 March
1512:quinine
1492:AV node
1444:(ICD).
1406:aspirin
1183:hypoxia
1164:ectopic
1079:on the
872:or the
866:impulse
4078:J wave
3831:Atrial
3759:Atrial
3548:aortic
3524:mitral
3516:Valves
3462:valves
3314:Layers
3183:(SCAD)
3110:Curlie
3092:001101
2983:
2975:
2967:
2925:
2851:
2824:
2781:
2760:939001
2758:
2714:
2687:
2652:
2617:
2609:
2565:
2530:
2481:
2471:
2463:
2422:
2412:
2352:
2342:
2300:
2259:
2249:
2210:
2200:
2161:
2118:
2095:
2072:
2034:
2024:
1985:
1975:
1957:Lancet
1936:
1926:
1885:
1877:
1842:
1832:
1548:benign
1534:after
1097:anemia
996:atrium
902:pulses
324:stroke
177:Causes
137:Stroke
4165:Other
4149:Right
4127:Right
3741:sinus
3690:Right
3440:Viral
3335:Acute
3289:weeks
3260:hours
3172:(CAD)
3068:15206
2981:S2CID
2634:Chest
2615:S2CID
2563:S2CID
1883:S2CID
1814:Heart
1311:brain
1276:atria
1247:from
1095:) or
930:, an
789:fetus
747:or a
733:death
605:(VT).
416:, or
318:, or
155:Types
78:(ECG)
4144:Left
4122:Left
3739:and
3695:Left
3277:days
3052:MeSH
3041:9-CM
2973:PMID
2965:ISSN
2923:PMID
2849:PMID
2822:PMID
2779:ISBN
2756:PMID
2712:PMID
2685:PMID
2650:PMID
2607:PMID
2528:ISSN
2479:PMID
2461:ISSN
2420:PMID
2375:2020
2350:PMID
2298:PMID
2257:PMID
2208:PMID
2159:PMID
2116:ISBN
2093:PMID
2070:PMID
2032:PMID
2006:Herz
1983:PMID
1934:PMID
1875:PMID
1840:PMID
1795:2015
1756:2015
1727:2015
1694:2015
1651:2015
1608:2015
1400:and
836:coma
814:and
775:and
381:and
373:and
361:and
349:and
3108:at
3046:427
3037:ICD
3031:I49
3027:I47
3018:ICD
2957:doi
2953:128
2913:doi
2909:122
2812:doi
2746:doi
2677:doi
2673:145
2642:doi
2638:125
2597:doi
2555:doi
2518:doi
2469:PMC
2451:doi
2410:PMC
2402:doi
2340:PMC
2332:doi
2288:doi
2247:PMC
2239:doi
2198:PMC
2190:doi
2186:125
2149:doi
2062:doi
2022:PMC
2014:doi
1973:PMC
1965:doi
1961:385
1924:PMC
1914:doi
1867:doi
1830:PMC
1822:doi
1528:ECG
1522:on
1459:or
1238:WPW
1087:or
874:His
823:are
681:or
436:or
389:or
326:or
107:or
4216::
4072:ST
4044:QT
3925:/
3673:3°
3668:2°
3663:1°
3658:AV
3651::
3342:/
3090::
3066::
3055::
3044::
3029:–
3025::
3022:10
2979:.
2971:.
2963:.
2951:.
2947:.
2935:^
2921:.
2907:.
2903:.
2889:^
2873:.
2855:.
2843:.
2820:.
2808:73
2806:.
2802:.
2754:.
2742:39
2740:.
2736:.
2708:16
2706:.
2683:.
2671:.
2648:.
2636:.
2613:.
2605:.
2593:17
2591:.
2587:.
2575:^
2561:.
2551:57
2549:.
2526:.
2516:.
2506:11
2504:.
2500:.
2477:.
2467:.
2459:.
2445:.
2441:.
2418:.
2408:.
2396:.
2392:.
2348:.
2338:.
2328:19
2326:.
2322:.
2310:^
2296:.
2284:32
2282:.
2278:.
2255:.
2245:.
2235:51
2233:.
2229:.
2206:.
2196:.
2184:.
2180:.
2157:.
2145:98
2143:.
2139:.
2068:.
2058:40
2056:.
2044:^
2030:.
2020:.
2010:45
2008:.
2004:.
1981:.
1971:.
1959:.
1955:.
1932:.
1922:.
1908:.
1904:.
1881:.
1873:.
1863:65
1861:.
1838:.
1828:.
1818:98
1816:.
1812:.
1764:^
1735:^
1702:^
1659:^
1637:.
1616:^
1583:^
1483:.
1361:.
1327:.
1099:.
1059:.
975:.
955:,
838:,
818:.
779:.
771:,
767:,
763:,
759:,
716:.
653:AV
473:,
440:.
405:.
369:,
357:,
345:,
341:,
334:.
314:,
310:,
306:,
196:,
169:,
165:,
161:,
139:,
123:,
119:,
115:,
111:,
103:,
4058:T
3743:)
3735:(
3619:/
3459:/
3138:e
3131:t
3124:v
3039:-
3020:-
3010:D
2987:.
2959::
2929:.
2915::
2883:.
2828:.
2814::
2787:.
2762:.
2748::
2718:.
2691:.
2679::
2656:.
2644::
2621:.
2599::
2569:.
2557::
2534:.
2520::
2512::
2485:.
2453::
2447:2
2426:.
2404::
2398:3
2377:.
2356:.
2334::
2304:.
2290::
2263:.
2241::
2214:.
2192::
2165:.
2151::
2124:.
2099:.
2076:.
2064::
2038:.
2016::
1989:.
1967::
1940:.
1916::
1910:6
1889:.
1869::
1846:.
1824::
1797:.
1758:.
1729:.
1696:.
1653:.
1610:.
1526:(
876:-
266:.
38:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.