425:
one-time loss of 500 sheep was reported in 1964 and in 1987, 250 sheep died from death camas poisoning. Poisonings generally occur in the early spring when the death camas plant is most abundant and other food sources for livestock are limited. Sheep seem to be poisoned most often due to their grazing behavior as they pull up and consume the entire plant. Moist conditions are more conducive to cattle poisoning as it makes it easier to extract the plant from the soil. Humans have also fallen victim to zygacine poisoning by mistaking the death camas for other edible plants. In 1994, a man presented to the emergency department with gastrointestinal symptoms, a depressed heart rate and low blood pressure after inadvertently eating plant material derived from a species of
202:
103:
33:
24:
367:. Death camas is prevalent throughout North America and is frequently the source of poisoning for outdoor enthusiasts and livestock due to its resemblance to other edible plants such as the wild onion. Despite this resemblance, the death camas plant lacks the distinct onion odor and is bitter to taste.
505:
Initial signs of zygacine poisoning in animals include frothy salivation around the mouth, followed by nausea and vomiting. Severely poisoned animals will suffer from a loss in appetite, lack of coordination and depression. Sheep, in particular, will stand with their heads and ears dropped with their
424:
Zygacine poisoning via ingestion of death camas had been reported in both livestock and humans as early as the nineteenth century. It has been for many years - and continues to be - responsible for the poisonings and deaths of many types of livestock including sheep, cattle, horses, pigs and fowl. A
551:
For animals, reported effective treatment of zygacine poisoning consists of injection of 2 mg of atropine sulfate and 8 mg of picrotoxin per 45 kg of body weight. Intravenous fluid therapy is used to increase blood pressure. A stomach tube can be used to relieve stomach pressure in
522:
compounds act by attaching to voltage-gated sodium ion channels, altering their permeability. Veratrum alkaloids cause affected sodium channels to reactivate 1000x slower than unaffected channels. They also block inactivation of sodium channels and change their activation threshold so they remain
510:, a condition characterized by involuntary movement of the muscles in the digestive tract, results in frequent defecation and urination. Fatally poisoned animals develop a weak and rapid pulse and labored breathing. The shuddering struggle to breathe may be confused with convulsions.
523:
open even at resting potential. As a result, sodium concentrations within the cell rise, leading to increased nerve and muscle excitability. This biochemical activity causes muscle contractions, repetitive firing of the nerves and an irregular heart rhythm from stimulation of
225:
InChI=1S/C29H45NO8/c1-14-5-8-20-26(4,34)22-16(13-30(20)12-14)17-11-27-19(28(17,35)24(33)23(22)32)7-6-18-25(27,3)10-9-21(37-15(2)31)29(18,36)38-27/h14,16-24,32-36H,5-13H2,1-4H3/t14-,16-,17?,18?,19?,20-,21?,22+,23?,24?,25-,26+,27?,28?,29?/m0/s1
444:
of 2.0 +/- 0.2 mg/kg when administered intravenously and 132 +/- 21 mg/kg when administered orally to mice. The lethal dose conversions for a 60 kg human, 600 kg cow and 80 kg sheep are included in the table below.
501:
Within an hour of ingesting the toxic death camas plant, a human will begin to experience nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramping and diarrhea. Other symptoms include low heart rate and blood pressure as well as ataxia and muscle spasms.
539:
There is no antidote for zygacine poisoning so only the symptoms arising from poisoning in humans are usually treated, of which bradycardia and hypotension are prioritized. These symptoms are initially treated with
497:
General symptoms of zygacine poisoning among humans and animals alike include but are not limited to gastrointestinal and cardiovascular ailments such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and irregular heartbeat.
548:. In a case study in which atropine was not sufficient, hypotension and bradycardia were successfully treated using dopamine. Dopamine increases renal sodium excretion, blood pressure and the heart rate.
605:
Stegelmeier, Bryan L., Reuel Field, Kip E. Panter, Jeffery O. Hall, Kevin D. Welch, James A. Pfister, Dale R. Gardner et al. "Selected poisonous plants affecting animal and human health." In
421:
which revealed that zygacine was one of the primary toxic components. Although it was first isolated in 1913, the structure and configuration of zygacine weren't reported until 1959.
760:"The acute toxicity of the death camas (Zigadenus species) alkaloid zygacine in mice, including the effect of methyllycaconitine coadministration on zygacine toxicity"
374:. Poisoned animals suffer from loss of appetite, lack of coordination, digestive and excretory disorders, labored breathing, racing heartbeat and frequently death.
983:
691:
Majak, Walter, Ruth E. McDiarmid, Walter
Cristofoli, Fang Sun, and Michael Benn. "Content of zygacine in Zygadenus venenosus at different stages of growth."
241:
745:
Panter, K.E., M.H. Raiphs, R.A. Smart, and B. Duelke. 1987. Death camas poisoning in sheep: A case report. Vet, and Human Tox. 29:45-48.
370:
The effects of zygacine consumption are lethal. Symptoms in humans include nausea, vomiting, slowed heart rate, low blood pressure and
216:
390:
988:
528:
920:
McLendon K, Preuss CV. Atropine. . In: StatPearls . Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls
Publishing; 2024 Jan-. Available from:
316:
968:
159:
758:
Welch, K. D.; Panter, K. E.; Gardner, D. R.; Stegelmeier, B. L.; Green, B. T.; Pfister, J. A.; Cook, D. (2011-05-01).
180:
417:
759:
651:"Guide to Poisonous Plants – College of Veterinary Medicine and Biomedical Sciences – Colorado State University"
411:
524:
978:
545:
45:
865:
Panter, Kip E., Kevin D. Welch, and Dale R. Gardner. "Poisonous plants: biomarkers for diagnosis." In
405:
plants in 1913. They were able to isolate zygadenine, the alkamine present in alkaloids of the genus
945:
Bhatt-Mehta, Varsha; Nahata, Milap C. (1989-09-10). "Dopamine and
Dobutamine in Pediatric Therapy".
879:
197:
69:
650:
795:
678:
Kupchan, S. Morris. "Veratrum alkaloids. XXX. 1 The structure and configuration of zygadenine2."
519:
438:
332:
932:
West, Patrick, and B. Zane
Horowitz. "Zigadenus poisoning treated with atropine and dopamine."
841:
787:
779:
619:
123:
833:
771:
355:
264:
168:
973:
201:
79:
409:. The minimal pharmacological activity of zygadenine led to subsequent investigations of
401:
Scientists first attempted to determine the toxic ingredient(s) of alkaloid extracts of
337:
310:
837:
962:
360:
148:
799:
705:
Chesnut, Victor King (1898). "Preliminary
Catalogue of Plants Poisonous to Stock".
571:
921:
507:
349:
719:
Panter, K. E., and L. F. James. "Death camas--early grazing can be hazardous."
386:
364:
295:
114:
783:
343:
32:
791:
845:
775:
707:
Fifteenth Annual report of the Bureau of Animal
Industry for the Year 1898
607:
Haschek and
Rousseaux's Handbook of Toxicologic Pathology (Third Edition)
541:
382:
378:
49:(5ξ,8ξ,9ξ,12ξ,14ξ)-4,14,15,16,20-Pentahydroxy-4,9-epoxycevan-3-yl acetate
732:
Kingsbury, John M. "Poisonous plants of the United States and Canada."
135:
371:
309:
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their
23:
947:
Pharmacotherapy: the
Journal of Human Pharmacology and Drug Therapy
249:
12C34O5(O)(CC3(C)5()CC4()1(O)(O)(O)1()2()CN2C(C)CC2()1(C)O)OC(C)=O
102:
92:
377:
Suggested treatment of poisoning in humans include administering
363:. These plants are commonly known and generally referred to as
909:
385:
to the patient. For animals, treatment consists of atropine,
185:
824:
Heilpern, Katherine L (1995-02-01). "Zigadenus
Poisoning".
518:
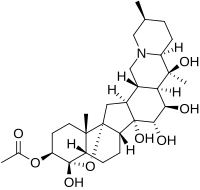
Zygacine is a steroidal alkaloid of the veratrum type.
57:
Cevane-3β,4β,14,15α,16β,20-hexol, 4,9-epoxy-, 3-acetate
531:functions of the heart, lungs and digestive tract.
753:
751:
880:"Cornell University Department of Animal Science"
147:
78:
922:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470551/
437:Zygacine is a highly potent compound with an
8:
709:. Government Printing Office. p. 396.
200:
122:
15:
167:
680:Journal of the American Chemical Society
447:
907:Furbee, Brent. "Neurotoxic plants." In
572:"Death Camas, Toxicoscordion venenosum"
560:
246:
221:
196:
903:
901:
899:
861:
859:
857:
855:
819:
817:
815:
813:
811:
809:
228:Key: IGDRXLIXNAWBBF-UFWHGLMDSA-N
7:
674:
672:
670:
645:
643:
641:
639:
601:
599:
597:
595:
593:
591:
566:
564:
429:. He recovered after being treated.
984:Heterocyclic compounds with 6 rings
138:
14:
884:poisonousplants.ansci.cornell.edu
282:
276:
31:
22:
313:(at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
546:muscarinic receptor antagonist
285:
270:
1:
934:Journal of Medical Toxicology
838:10.1016/S0196-0644(95)70336-5
695:31, no. 10 (1992): 3417-3418.
506:backs are arched. Intestinal
826:Annals of Emergency Medicine
682:81, no. 8 (1959): 1925-1928.
1005:
723:11, no. 4 (1989): 147-149.
477:144 mg - 176 mg
471:108 mg - 132 mg
764:Journal of Animal Science
307:
257:
237:
212:
62:
54:
44:
39:
30:
21:
867:Biomarkers in Toxicology
911:. Elsevier Inc., 2009.
736:98, no. 5 (1964): 349.
609:, pp. 1259-1314. 2013.
989:Nitrogen heterocycles
936:5, no. 4 (2009): 214.
776:10.2527/jas.2010-3444
460:Cattle (600 kg)
418:Zygadenus paniculatus
869:, pp. 563-589. 2014.
655:csuvth.colostate.edu
482:Oral Administration
412:Zygadenus venenosus
969:Steroidal alkaloids
721:Rangelands Archives
463:Sheep (80 kg)
457:Human (60 kg)
450:
303: g·mol
18:
527:which control the
488:66.60 g - 91.80 g
468:IV Administration
448:
391:activated charcoal
333:steroidal alkaloid
317:Infobox references
16:
552:bloated animals.
520:Veratrum alkaloid
495:
494:
491:8.88 g - 12.24 g
449:LD50 of Zygacine
325:Chemical compound
323:
322:
181:CompTox Dashboard
104:Interactive image
996:
954:
943:
937:
930:
924:
918:
912:
905:
894:
893:
891:
890:
876:
870:
863:
850:
849:
821:
804:
803:
770:(5): 1650–1657.
755:
746:
743:
737:
730:
724:
717:
711:
710:
702:
696:
689:
683:
676:
665:
664:
662:
661:
647:
634:
633:
631:
630:
624:www.uptodate.com
616:
610:
603:
586:
585:
583:
582:
568:
485:6.66 g - 9.18 g
474:1.08 g - 1.32 g
451:
302:
287:
284:
278:
272:
265:Chemical formula
205:
204:
189:
187:
171:
151:
140:
126:
106:
82:
35:
26:
19:
1004:
1003:
999:
998:
997:
995:
994:
993:
959:
958:
957:
944:
940:
931:
927:
919:
915:
906:
897:
888:
886:
878:
877:
873:
864:
853:
823:
822:
807:
757:
756:
749:
744:
740:
731:
727:
718:
714:
704:
703:
699:
690:
686:
677:
668:
659:
657:
649:
648:
637:
628:
626:
618:
617:
613:
604:
589:
580:
578:
570:
569:
562:
558:
537:
529:parasympathetic
516:
442:
435:
399:
326:
319:
314:
300:
290:
281:
275:
267:
253:
250:
245:
244:
233:
230:
229:
226:
220:
219:
208:
190:
183:
174:
154:
141:
129:
109:
96:
85:
72:
58:
50:
12:
11:
5:
1002:
1000:
992:
991:
986:
981:
976:
971:
961:
960:
956:
955:
938:
925:
913:
895:
871:
851:
832:(2): 259–262.
805:
747:
738:
725:
712:
697:
693:Phytochemistry
684:
666:
635:
611:
587:
559:
557:
554:
536:
533:
515:
512:
493:
492:
489:
486:
483:
479:
478:
475:
472:
469:
465:
464:
461:
458:
455:
440:
434:
431:
398:
395:
359:of the family
338:Toxicoscordion
335:of the genera
324:
321:
320:
315:
311:standard state
308:
305:
304:
298:
292:
291:
288:
279:
273:
268:
263:
260:
259:
255:
254:
252:
251:
248:
240:
239:
238:
235:
234:
232:
231:
227:
224:
223:
215:
214:
213:
210:
209:
207:
206:
198:DTXSID00950455
193:
191:
179:
176:
175:
173:
172:
164:
162:
156:
155:
153:
152:
144:
142:
134:
131:
130:
128:
127:
119:
117:
111:
110:
108:
107:
99:
97:
90:
87:
86:
84:
83:
75:
73:
68:
65:
64:
60:
59:
56:
52:
51:
48:
42:
41:
37:
36:
28:
27:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1001:
990:
987:
985:
982:
980:
977:
975:
972:
970:
967:
966:
964:
953:(5): 303–314.
952:
948:
942:
939:
935:
929:
926:
923:
917:
914:
910:
904:
902:
900:
896:
885:
881:
875:
872:
868:
862:
860:
858:
856:
852:
847:
843:
839:
835:
831:
827:
820:
818:
816:
814:
812:
810:
806:
801:
797:
793:
789:
785:
781:
777:
773:
769:
765:
761:
754:
752:
748:
742:
739:
735:
729:
726:
722:
716:
713:
708:
701:
698:
694:
688:
685:
681:
675:
673:
671:
667:
656:
652:
646:
644:
642:
640:
636:
625:
621:
615:
612:
608:
602:
600:
598:
596:
594:
592:
588:
577:
573:
567:
565:
561:
555:
553:
549:
547:
543:
534:
532:
530:
526:
521:
513:
511:
509:
503:
499:
490:
487:
484:
481:
480:
476:
473:
470:
467:
466:
462:
459:
456:
453:
452:
446:
443:
432:
430:
428:
422:
420:
419:
414:
413:
408:
404:
396:
394:
392:
388:
384:
380:
375:
373:
368:
366:
362:
361:Melanthiaceae
358:
357:
352:
351:
346:
345:
340:
339:
334:
330:
318:
312:
306:
299:
297:
294:
293:
269:
266:
262:
261:
256:
247:
243:
236:
222:
218:
211:
203:
199:
195:
194:
192:
182:
178:
177:
170:
166:
165:
163:
161:
158:
157:
150:
146:
145:
143:
137:
133:
132:
125:
121:
120:
118:
116:
113:
112:
105:
101:
100:
98:
94:
89:
88:
81:
77:
76:
74:
71:
67:
66:
61:
53:
47:
43:
38:
34:
29:
25:
20:
979:Plant toxins
950:
946:
941:
933:
928:
916:
908:
887:. Retrieved
883:
874:
866:
829:
825:
767:
763:
741:
734:Soil Science
733:
728:
720:
715:
706:
700:
692:
687:
679:
658:. Retrieved
654:
627:. Retrieved
623:
614:
606:
579:. Retrieved
576:calscape.org
575:
550:
538:
525:vagal nerves
517:
504:
500:
496:
436:
426:
423:
416:
410:
406:
402:
400:
376:
369:
354:
348:
342:
336:
328:
327:
63:Identifiers
55:Other names
508:peristalsis
365:death camas
350:Stenanthium
258:Properties
963:Categories
889:2018-05-15
660:2018-05-15
629:2018-05-15
620:"UpToDate"
581:2018-05-15
556:References
387:picrotoxin
296:Molar mass
169:BAY5Z5MC9Z
115:ChemSpider
91:3D model (
70:CAS Number
46:IUPAC name
784:1525-3163
535:Treatment
514:Mechanism
427:Zigadenus
407:Zigadenus
403:Zygadenus
344:Zigadenus
80:2777-79-9
17:Zygacine
792:21521823
542:atropine
454:Subject
433:Toxicity
383:atropine
379:dopamine
356:Anticlea
329:Zygacine
124:10181195
846:7832360
800:4693834
397:History
301:535.678
149:3083781
136:PubChem
974:Toxins
844:
798:
790:
782:
372:ataxia
242:SMILES
40:Names
796:S2CID
331:is a
217:InChI
93:JSmol
842:PMID
788:PMID
780:ISSN
544:, a
415:and
389:and
381:and
353:and
160:UNII
834:doi
772:doi
186:EPA
139:CID
965::
949:.
898:^
882:.
854:^
840:.
830:25
828:.
808:^
794:.
786:.
778:.
768:89
766:.
762:.
750:^
669:^
653:.
638:^
622:.
590:^
574:.
563:^
441:50
439:LD
393:.
347:,
341:,
280:45
274:29
951:9
892:.
848:.
836::
802:.
774::
663:.
632:.
584:.
289:8
286:O
283:N
277:H
271:C
188:)
184:(
95:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.