73:
292:
502:, which leads from the oviduct to the dorsal surface of the body. The function of this canal is debated, but it may be used for insemination in some species or for disposal of waste products from reproduction in other species. Most trematodes possess an ovicapt, an enlarged portion of the oviduct where it joins the ovary. It probably controls the release of ova and spaces out their descent down the uterus.
38:
1920:
of the definitive host. Humans become infected after free-swimming cercaria liberated from infected snails penetrate the skin. These dioecious worms are long and thin, ranging in size from 10 to 30 mm in length to 0.2 to 1.0 mm in diameter. Adult males are shorter and thicker than females,
737:
The evolutionary origins of the
Digenea have been debated for some time, but there appears general agreement that the proto-digenean was a parasite of a mollusc, possibly of the mantle cavity. Evidence for this comes from the ubiquity of molluscs as first intermediate hosts for digeneans, and the
1921:
and have a long groove along one side of the body in which the female is clasped. Females reach sexual maturity after they have been united with a male. After mating the two remain locked together for the rest of their lives. They can live for several years and produce many thousands of eggs.
505:
The uterus typically opens into a common genital atrium that also received the distal male copulatory organ (cirrus) before immediately opening onto the outer surface of the worm. The distal part of the uterus may be expanded into a metraterm, set off from the proximal uterus by a muscular
351:
are flukes with an oral sucker and a ventral sucker, but the ventral sucker is somewhere other than posterior. These terms are common in older literature, when they were thought to reflect systematic relationships within the groups. They have fallen out of use in modern digenean taxonomy.
745:
It is likely that more complex life cycles evolved through a process of terminal addition, whereby digeneans survived predation of their mollusc host, probably by a fish. Other hosts were added by the same process until the modern bewildering diversity of life cycle patterns developed.
466:
and a cirrus (analogous to a penis) usually (but not always) enclosed in a cirrus sac. The cirrus may or may not be covered in proteinaceous spines. The exact conformation of these organs within the male terminal genitalia is taxonomically important at the familial and generic levels.
2073:
The seven major species of non-schistosomes that infect humans are listed below. People become infected after ingesting metacercarial cysts on plants or in undercooked animal flesh. Most species inhabit the human gastrointestinal tract, where they shed eggs along with host feces.
616:
There is a bewildering array of variation on the complex digenean life cycle, and plasticity in this trait is probably a key to the group's success. In general, the life cycles may have two, three, or four obligate (necessary) hosts, sometimes with transport or
251:
Characteristic features of the
Digenea include a syncytial tegument; that is, a tegument where the junctions between cells are broken down and a single continuous cytoplasm surrounds the entire animal. A similar tegument is found in other members of the
738:
fact that most aspidogastreans (the sister group to the
Digenea) also have mollusc associations. It is thought that the early trematodes (the collective name for digeneans and aspidogastreans) likely evolved from rhabdocoel
518:
As adults, most digeneans possess a terminal or subterminal mouth, a muscular pharynx that provides the force for ingesting food, and a forked, blind digestive system consisting of two tubular sacs called caeca (sing.
717:. Transmission occurs when the definitive host preys upon an infected second intermediate host. Metacercariae excyst in the definitive host's gut in response to a variety of physical and chemical signals, such as gut
607:
cells. Larval stages have many kinds of sensory receptors, including light receptors and chemoreceptors. Chemoreception plays an important role in the free-living miracidial larva recognising and locating its host.
693:
The life cycles of some digeneans include only two hosts, the second being a vertebrate. In these groups, sexual maturity occurs after the cercaria penetrates the second host, which is in this case also the
685:
environment, often using a whip-like tail, though a tremendous diversity of tail morphology is seen. Cercariae are infective to the second host in the life cycle, and infection may occur passively (e.g., a
674:. The second generation is thus the daughter parthenita sequence. These in turn undergo further asexual reproduction, ultimately yielding large numbers of the second free-living stage, the
628:
The alternation of sexual and asexual generations is an important feature of digeneans. This phenomenon involves the presence of several discrete generations in one life-cycle.
364:. This is likely to be an adaptation to low abundance within hosts, allowing the life cycle to continue when only one individual successfully infects the final host.
332:, on the ventral surface. The oral sucker surrounds the mouth, while the ventral sucker is a blind muscular organ with no connection to any internal structure.
2651:
2422:
Olson P. D., Cribb T. H., Tkach V. V., Bray R. A. & Littlewood D. T. J. (2003). "Phylogeny and classification of the
Digenea (Platyhelminthes: Trematoda)".
559:, where they most often graze on contents of the lumen (e.g., food ingested by the host, bile, mucus), but they may also feed across the mucosal wall (e.g.,
2638:
2492:
571:
stage found in some groups does have a mouth, pharynx and simple gut and may actively consume host tissue or even other parasites. Encysted
1908:
afflicting over 200 million people. The species that infect humans can be divided into groups, the schistosomes and the non-schistosomes.
621:
hosts in between. The three-host life cycle is probably the most common. In almost all species, the first host in the life cycle is a
625:. This has led to the inference that the ancestral digenean was a mollusc parasite and that vertebrate hosts were added subsequently.
563:, host blood). The blood flukes, such as schistosomes, spirorchiids and sanguinicolids, feed exclusively on blood. Asexual stages in
222:, one ventral and one oral. Adults commonly live within the digestive tract, but occur throughout the organ systems of all classes of
2470:
2457:
651:
worm), in which they proceed to hatch. Alternatively, eggs may hatch in water to release an actively swimming, ciliated larva, the
2687:
647:) by either passive or active means. The eggs of some digeneans, for example, are (passively) eaten by snails (or, rarely, by an
729:, etc. Once excysted, adult digeneans migrate to more or less specific sites in the definitive host and the life cycle repeats.
491:
and egg-shell production) with ducts, the ootype (a chamber where eggs are formed), a complex collection of glands cells called
2343:"A review of the Zoogonidae (Digenea: Microphalloidea) from fishes of the waters around New Caledonia, with the description of
2720:
713:
of host and parasite origin, or encapsulated in a layer of tissue derived from the host only. This stage is infective to the
2643:
2560:
2604:
568:
2656:
2617:
2399:
658:
After post-ingestion hatching or penetration of the snail, the miracidium metamorphoses into a simple, sac-like
72:
2046:
2210:
2179:
2137:
1990:
1737:
1582:
1232:
1205:
1154:
1005:
329:
643:, in which sexual reproduction does not occur. Digeneans may infect the first intermediate host (usually a
2513:
2296:
2502:
297:
2016:
714:
695:
640:
404:
705:
In three-host life cycles, cercariae develop in the second intermediate host into a resting stage, the
2692:
2573:
1541:
825:
663:
2243:
1956:
1872:
1247:
604:
408:
215:
2082:. These flukes generally cause mild pathology in humans, but more serious effects may also occur.
702:, or secondary (there was at one time in evolutionary history a third host but it has been lost).
2108:
1917:
1578:
67:
2217:
2144:
524:
2664:
2466:
2453:
2378:
2272:
1856:
1840:
1645:
1504:
1456:
1105:
785:
536:
499:
377:
2679:
2715:
2669:
2430:
2368:
2358:
2279:
1832:
1824:
1776:
1725:
1464:
1297:
1239:
1060:
1028:
857:
552:
463:
373:
310:
291:
219:
1816:
1800:
1784:
1768:
1709:
1677:
1613:
1589:
1562:
1512:
1419:
1403:
1353:
1321:
1228:
1220:
1212:
1020:
964:
809:
556:
459:
451:
257:
194:
186:
2612:
2599:
2475:
2373:
2342:
2186:
2163:
1848:
1808:
1760:
1693:
1621:
1570:
1520:
1345:
1329:
1201:
1150:
1084:
980:
972:
956:
849:
777:
420:
59:
2434:
2709:
2551:
2264:
2150:
1974:
1880:
1792:
1717:
1701:
1496:
1488:
1440:
1411:
1374:
1337:
1305:
1169:
1142:
1068:
1012:
940:
911:
893:
879:
865:
817:
699:
443:
396:
365:
361:
261:
231:
114:
51:
523:). In some species the two gut caeca join posteriorly to make a ring-shaped gut or
1963:
1864:
1653:
1629:
1448:
1382:
1255:
1185:
1177:
1076:
1052:
932:
763:
572:
544:
507:
455:
343:
with an oral sucker and an acetabulum at the posterior end of the body are called
2625:
2545:
2303:
2235:
2171:
2038:
2023:
2008:
1982:
1929:
1733:
1685:
1669:
1597:
1480:
1313:
1276:
1161:
1044:
1036:
1001:
801:
739:
726:
540:
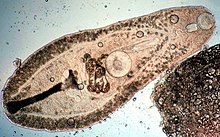
539:. Digeneans are also capable of direct nutrient uptake through the tegument by
389:
281:
223:
55:
46:
2565:
2497:
754:
Digenea includes about 80 families. They are listed below, organised by order.
698:. Two-host life cycles can be primary (there never was a third host) as in the
2115:
1744:
1193:
833:
652:
632:
428:
412:
302:
277:
253:
124:
2536:
681:
Free-swimming cercariae leave the snail host and move through the aquatic or
2586:
2260:
2034:
1978:
1901:
1126:
682:
618:
560:
548:
385:
340:
273:
265:
227:
212:
201:
190:
134:
84:
2382:
2084:
1935:
317:
2530:
2314:
576:
314:
204:
104:
20:
603:
are, for the most part, lacking among the adults, although they do have
37:
2250:
2231:
2202:
2154:
2053:
1997:
1924:
The four species of schistosomes that infect humans are members of the
1905:
648:
631:
A typical digenean trematode life cycle is as follows. Eggs leave the
622:
588:
564:
480:
432:
416:
381:
325:
269:
235:
2630:
2363:
450:
are present, but some flukes can have more than 100. Also present are
2079:
2060:
2004:
1970:
722:
690:
consumes a cercaria) or actively (the cercaria penetrates the fish).
636:
596:
528:
520:
447:
431:
that become included in these embryonic stages. Since the absence of
424:
285:
197:
94:
2507:
2591:
655:, which must locate and penetrate the body wall of the snail host.
2288:
2227:
2197:
2167:
2129:
2030:
1925:
644:
600:
592:
567:
intermediate hosts feed mostly by direct absorption, although the
484:
476:
400:
369:
321:
290:
149:
2578:
2319:
2310:
2193:
2159:
2125:
710:
687:
532:
488:
392:. Asexual reproduction in the first larval stage is ubiquitous.
2511:
495:, which is believed to lubricate the uterus for egg passage.
531:
may fuse with the body wall posteriorly to make one or more
718:
742:
that colonised the open mantle cavity of early molluscs.
234:
and that the
Monogenea are more closely allied with the
2078:, which colonizes the lungs, can also pass its eggs in
506:
sphincter, or it may be lined with spines, as in the
435:
is not proven, the exact definition remains doubtful.
2498:
Parasitic Worms at the
Natural History Museum, London
662:. The mother sporocyst undergoes a round of internal
238:. Around 6,000 species have been described to date.
230:, it is now recognised that they are closest to the
2520:
1904:to humans, but some of these species are important
498:In addition, some digeneans possess a canal called
446:is the general rule among the Digenea. Usually two
2449:Gibson, D.I., Jones, A. & Bray, R.A. (2002).
2480:Synopsis of digenetic trematodes of vertebrates.
2493:Cambridge University Schistosome Research Group
639:and use various strategies to infect the first
551:. Most adult digeneans occur in the vertebrate
1900:Only about 12 of the 6,000 known species are
591:at the anterior end of the body serve as the
8:
403:stage (miracidium) is widely reported, the
395:While the sexual formation of the digenean
2508:
2464:Interrelationships of the Platyhelminthes.
535:, or with the excretory vesicle to form a
487:, a pair of vitelline glands (involved in
36:
27:
2462:Littlewood D.T.J. & Bray R.A. (2001)
2372:
2362:
407:of the asexual stages remains a problem.
276:, unsegmented body-plan and have a solid
2333:
164:
2424:International Journal for Parasitology
399:and asexual reproduction in the first
384:. A key group of digeneans which are
7:
2618:c9f009d2-64cc-4f76-8af8-4ed93b6b10f4
2394:
2392:
226:. Once thought to be related to the
2400:"Principles of Parasitism: Digenea"
599:extend anteriorly and posteriorly.
360:The vast majority of digeneans are
1796:Krasnolobova & Timofeeva, 1965
339:is a worm with one sucker (oral).
14:
2341:Bray, RA.; Justine, J-L. (2014).
1189:Skrjabin & Guschanskaja, 1955
1173:Skrjabin & Guschanskaja, 1955
709:, which is usually encysted in a
71:
2482:Keigaku Publishing Co., Tokyo.
1916:The Schistosomes occur in the
843:Superfamily Schistosomatoidea
415:visible germ balls consist of
1:
2435:10.1016/S0020-7519(03)00049-3
771:Superfamily Brachylaimoidea
411:studies have shown that the
328:sucker sometimes termed the
288:) as in all platyhelminths.
2451:Key to the Trematoda, vol.1
1836:Fischthal & Kuntz, 1981
1828:Fischthal & Kuntz, 1981
795:Superfamily Diplostomoidea
2737:
1309:Cable & Hunninen, 1942
861:Stiles & Hassall, 1898
845:Stiles & Hassall, 1898
475:Usually there is a single
372:being transferred via the
58:) from the intestine of a
18:
1896:Human digenean infections
1876:Jue Sue & Platt, 1999
1788:Jue Sue & Platt, 1998
510:and some other families.
162:
157:
68:Scientific classification
66:
44:
35:
30:
2099:Mode of Human Infection
2096:First Intermediate Host
2047:Schistosoma intercalatum
1947:First Intermediate Host
781:Joyeux & Foley, 1930
773:Joyeux & Foley, 1930
666:, giving rise to either
309:There are typically two
260:comprising the Digenea,
19:For the bird genus, see
2404:www.biology.ualberta.ca
2211:Gastrodiscoides hominis
2138:Heterophyes heterophyes
1991:Schistosoma haematobium
1251:Gibson & Bray, 1979
575:stages and free-living
320:sucker surrounding the
272:. Digeneans possess a
2297:Paragonimus westermani
2180:Metagonimus yokogawaii
2087:Human non-Schistosomes
2076:Paragonimus westermani
1535:Transversotrematoidea
768:Suborder Diplostomata
306:
2721:Protostome subclasses
2017:Schistosoma japonicum
427:and to a line of new
413:light microscopically
405:developmental biology
294:
2613:Fauna Europaea (new)
1585:& Williams, 1966
1542:Transversotrematidae
826:Proterodiplostomidae
664:asexual reproduction
579:stages do not feed.
409:Electron microscopic
2345:Overstreetia cribbi
2244:Clonorchis sinensis
2089:
1957:Schistosoma mansoni
1940:
1873:Thrinascotrematidae
1248:Sclerodistomoididae
1099:Haplosplanchnoidea
672:daughter sporocysts
423:which give rise to
356:Reproductive system
298:Overstreetia cribbi
295:Anterior sucker of
2109:Fasciolopsis buski
2085:
1938:Human Schistosomes
1936:
1918:circulatory system
1579:Batrachotrematidae
1532:Transversotremata
1434:Paramphistomoidea
995:Echinostomatoidea
750:Important families
721:levels, digestive
555:or its associated
485:seminal receptacle
368:is internal, with
307:
218:and, usually, two
2703:
2702:
2665:Open Tree of Life
2514:Taxon identifiers
2364:10.7717/peerj.292
2325:
2324:
2273:Fasciola hepatica
2066:
2065:
1885:
1877:
1869:
1861:
1857:Styphlotrematidae
1853:
1845:
1841:Orientocreadiidae
1837:
1829:
1821:
1813:
1805:
1797:
1789:
1781:
1773:
1765:
1757:
1749:
1741:
1730:
1722:
1714:
1706:
1698:
1690:
1682:
1674:
1666:
1658:
1650:
1646:Atractotrematidae
1642:
1634:
1626:
1618:
1610:
1602:
1594:
1586:
1575:
1567:
1559:
1546:
1538:
1525:
1517:
1509:
1505:Opisthotrematidae
1501:
1493:
1485:
1477:
1474:Pronocephaloidea
1469:
1461:
1457:Microscaphidiidae
1453:
1445:
1437:
1424:
1416:
1408:
1400:
1397:Opisthorchioidea
1387:
1379:
1371:
1358:
1350:
1342:
1334:
1326:
1318:
1310:
1302:
1294:
1281:
1273:
1260:
1252:
1244:
1236:
1225:
1217:
1209:
1198:
1190:
1182:
1174:
1166:
1158:
1147:
1139:
1131:
1123:
1110:
1106:Haplosplanchnidae
1102:
1096:Haplosplanchnata
1089:
1081:
1073:
1065:
1057:
1049:
1041:
1033:
1025:
1017:
1009:
998:
985:
977:
969:
961:
953:
945:
937:
929:
916:
898:
890:
870:
862:
854:
846:
838:
830:
822:
814:
806:
798:
790:
786:Leucochloridiidae
782:
774:
678:(pl. cercariae).
670:(sing. redia) or
641:intermediate host
601:Sensory receptors
527:. In others the
433:meiotic processes
172:
171:
153:
2728:
2696:
2695:
2683:
2682:
2673:
2672:
2660:
2659:
2647:
2646:
2634:
2633:
2621:
2620:
2608:
2607:
2595:
2594:
2582:
2581:
2569:
2568:
2556:
2555:
2554:
2541:
2540:
2539:
2509:
2437:
2420:
2414:
2413:
2411:
2410:
2396:
2387:
2386:
2376:
2366:
2338:
2280:Galba truncatula
2093:Scientific Name
2090:
2069:Non-schistosomes
1944:Scientific Name
1941:
1883:
1875:
1867:
1859:
1851:
1843:
1835:
1833:Ocadiatrematidae
1827:
1825:Meristocotylidae
1819:
1811:
1803:
1795:
1787:
1779:
1777:Cephalogonimidae
1771:
1763:
1755:
1754:Plagiorchioidea
1747:
1736:
1728:
1726:Prosthogonimidae
1720:
1712:
1704:
1696:
1688:
1680:
1672:
1664:
1663:Microphalloidea
1656:
1648:
1640:
1632:
1624:
1616:
1608:
1600:
1592:
1581:
1573:
1565:
1557:
1556:Allocreadioidea
1544:
1536:
1523:
1515:
1507:
1499:
1491:
1483:
1475:
1468:Fischoeder, 1901
1467:
1465:Paramphistomidae
1459:
1451:
1444:Fischoeder, 1901
1443:
1436:Fischoeder, 1901
1435:
1422:
1414:
1406:
1398:
1385:
1377:
1369:
1356:
1348:
1340:
1332:
1324:
1316:
1308:
1300:
1298:Aephnidiogenidae
1292:
1291:Lepocreadioidea
1279:
1271:
1258:
1250:
1242:
1240:Sclerodistomidae
1231:
1223:
1215:
1204:
1196:
1188:
1181:Monticelli, 1888
1180:
1172:
1164:
1153:
1145:
1137:
1129:
1121:
1108:
1100:
1087:
1079:
1071:
1063:
1061:Philophthalmidae
1055:
1047:
1039:
1031:
1029:Echinostomatidae
1023:
1015:
1004:
996:
983:
975:
967:
959:
951:
950:Gymnophalloidea
943:
935:
927:
914:
896:
888:
868:
860:
858:Schistosomatidae
852:
844:
836:
828:
820:
812:
804:
796:
788:
780:
772:
660:mother sporocyst
553:alimentary canal
514:Digestive system
464:ejaculatory duct
382:genital aperture
200:, consisting of
148:
76:
75:
40:
28:
2736:
2735:
2731:
2730:
2729:
2727:
2726:
2725:
2706:
2705:
2704:
2699:
2691:
2686:
2678:
2676:
2668:
2663:
2655:
2650:
2642:
2637:
2629:
2624:
2616:
2611:
2603:
2598:
2590:
2585:
2577:
2572:
2564:
2559:
2550:
2549:
2544:
2535:
2534:
2529:
2516:
2503:Fishdisease.net
2489:
2446:
2441:
2440:
2421:
2417:
2408:
2406:
2398:
2397:
2390:
2340:
2339:
2335:
2330:
2071:
1914:
1898:
1817:Macroderoididae
1801:Encyclometridae
1785:Choanocotylidae
1769:Brachycoeliidae
1710:Phaneropsolidae
1678:Exotidendriidae
1614:Callodistomidae
1590:Brachycladiidae
1563:Acanthocolpidae
1545:Witenberg, 1944
1537:Witenberg, 1944
1513:Pronocephalidae
1431:Pronocephalata
1420:Opisthorchiidae
1404:Cryptogonimidae
1394:Opisthorchiata
1354:Liliatrematidae
1322:Gorgocephalidae
1229:Ptychogonimidae
1221:Lecithasteridae
1216:Travassos, 1922
1213:Isoparorchiidae
1021:Echinochasmidae
965:Fellodistomidae
944:Kurochkin, 1975
908:Bivesiculoidea
887:Apocreadioidea
810:Cyathocotylidae
752:
735:
715:definitive host
696:definitive host
614:
585:
516:
473:
460:seminal vesicle
452:vasa efferentia
441:
358:
249:
244:
195:Platyhelminthes
147:
105:Platyhelminthes
70:
24:
17:
16:Class of flukes
12:
11:
5:
2734:
2732:
2724:
2723:
2718:
2708:
2707:
2701:
2700:
2698:
2697:
2684:
2674:
2661:
2648:
2635:
2622:
2609:
2600:Fauna Europaea
2596:
2583:
2570:
2557:
2542:
2526:
2524:
2518:
2517:
2512:
2506:
2505:
2500:
2495:
2488:
2487:External links
2485:
2484:
2483:
2473:
2460:
2445:
2442:
2439:
2438:
2429:(7): 733–755.
2415:
2388:
2332:
2331:
2329:
2326:
2323:
2322:
2317:
2308:
2300:
2292:
2291:
2286:
2283:
2276:
2268:
2267:
2258:
2255:
2247:
2239:
2238:
2225:
2222:
2214:
2206:
2205:
2200:
2191:
2187:Semisulcospira
2183:
2175:
2174:
2164:Eastern Europe
2157:
2148:
2141:
2133:
2132:
2123:
2120:
2112:
2104:
2103:
2100:
2097:
2094:
2070:
2067:
2064:
2063:
2058:
2050:
2042:
2041:
2028:
2020:
2012:
2011:
2002:
1994:
1986:
1985:
1968:
1960:
1952:
1951:
1948:
1945:
1913:
1910:
1897:
1894:
1893:
1892:
1891:
1890:
1889:
1888:
1887:
1886:
1878:
1870:
1862:
1854:
1849:Plagiorchiidae
1846:
1844:Yamaguti, 1958
1838:
1830:
1822:
1820:McMullen, 1937
1814:
1809:Leptophallidae
1806:
1798:
1790:
1782:
1774:
1766:
1761:Auridistomidae
1752:
1751:
1750:
1742:
1731:
1723:
1715:
1707:
1705:Yamaguti, 1958
1699:
1694:Microphallidae
1691:
1683:
1675:
1673:Yamaguti, 1971
1661:
1660:
1659:
1651:
1649:Yamaguti, 1939
1639:Haploporoidea
1637:
1636:
1635:
1627:
1622:Dicrocoeliidae
1619:
1607:Gorgoderoidea
1605:
1604:
1603:
1595:
1587:
1576:
1571:Allocreadiidae
1568:
1551:
1550:
1549:
1548:
1547:
1530:
1529:
1528:
1527:
1526:
1521:Rhabdiopoeidae
1518:
1510:
1502:
1494:
1486:
1472:
1471:
1470:
1462:
1454:
1446:
1429:
1428:
1427:
1426:
1425:
1417:
1409:
1392:
1391:
1390:
1389:
1388:
1380:
1368:Monorchioidea
1363:
1362:
1361:
1360:
1359:
1351:
1346:Lepocreadiidae
1343:
1341:Yamaguti, 1958
1335:
1330:Gyliauchenidae
1327:
1319:
1317:Yamaguti, 1958
1311:
1303:
1301:Yamaguti, 1934
1288:Lepocreadiata
1286:
1285:
1284:
1283:
1282:
1265:
1264:
1263:
1262:
1261:
1253:
1245:
1237:
1226:
1218:
1210:
1202:Hirudinellidae
1199:
1191:
1183:
1175:
1167:
1159:
1151:Bathycotylidae
1148:
1134:
1133:
1132:
1115:
1114:
1113:
1112:
1111:
1094:
1093:
1092:
1091:
1090:
1085:Typhlocoelidae
1082:
1074:
1066:
1058:
1050:
1048:Railliet, 1895
1042:
1034:
1026:
1018:
1016:Stossich, 1902
1010:
992:Echinostomata
990:
989:
988:
987:
986:
984:Johnston, 1927
981:Tandanicolidae
978:
973:Gymnophallidae
970:
962:
960:Yamaguti, 1971
957:Botulisaccidae
948:
947:
946:
938:
926:Bucephaloidea
921:
920:
919:
918:
917:
915:Yamaguti, 1934
903:
902:
901:
900:
899:
897:Skrjabin, 1942
889:Skrjabin, 1942
877:
876:
875:
874:
873:
872:
871:
869:Stunkard, 1921
863:
855:
850:Aporocotylidae
841:
840:
839:
837:Railliet, 1919
831:
823:
815:
807:
793:
792:
791:
783:
778:Brachylaimidae
751:
748:
734:
731:
613:
610:
584:
583:Nervous system
581:
515:
512:
500:Laurer's Canal
472:
469:
440:
437:
378:Laurer's Canal
362:hermaphrodites
357:
354:
258:platyhelminths
248:
245:
243:
240:
170:
169:
160:
159:
155:
154:
142:
138:
137:
132:
128:
127:
122:
118:
117:
112:
108:
107:
102:
98:
97:
92:
88:
87:
82:
78:
77:
64:
63:
60:Flame Cardinal
42:
41:
33:
32:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2733:
2722:
2719:
2717:
2714:
2713:
2711:
2694:
2689:
2685:
2681:
2675:
2671:
2666:
2662:
2658:
2653:
2649:
2645:
2640:
2636:
2632:
2627:
2623:
2619:
2614:
2610:
2606:
2601:
2597:
2593:
2588:
2584:
2580:
2575:
2571:
2567:
2562:
2558:
2553:
2547:
2543:
2538:
2532:
2528:
2527:
2525:
2523:
2519:
2515:
2510:
2504:
2501:
2499:
2496:
2494:
2491:
2490:
2486:
2481:
2477:
2474:
2472:
2471:0-7484-0903-3
2468:
2465:
2461:
2459:
2458:0-85199-547-0
2455:
2452:
2448:
2447:
2443:
2436:
2432:
2428:
2425:
2419:
2416:
2405:
2401:
2395:
2393:
2389:
2384:
2380:
2375:
2370:
2365:
2360:
2356:
2352:
2348:
2346:
2337:
2334:
2327:
2321:
2318:
2316:
2312:
2309:
2306:
2305:
2301:
2299:
2298:
2294:
2293:
2290:
2287:
2284:
2282:
2281:
2277:
2275:
2274:
2270:
2269:
2266:
2265:North America
2262:
2259:
2256:
2253:
2252:
2248:
2246:
2245:
2241:
2240:
2237:
2233:
2229:
2226:
2223:
2220:
2219:
2215:
2213:
2212:
2208:
2207:
2204:
2201:
2199:
2195:
2192:
2189:
2188:
2184:
2182:
2181:
2177:
2176:
2173:
2169:
2165:
2161:
2158:
2156:
2152:
2149:
2147:
2146:
2142:
2140:
2139:
2135:
2134:
2131:
2127:
2124:
2121:
2118:
2117:
2113:
2111:
2110:
2106:
2105:
2102:Endemic Area
2101:
2098:
2095:
2092:
2091:
2088:
2083:
2081:
2077:
2068:
2062:
2059:
2056:
2055:
2051:
2049:
2048:
2044:
2043:
2040:
2036:
2032:
2029:
2026:
2025:
2021:
2019:
2018:
2014:
2013:
2010:
2006:
2003:
2000:
1999:
1995:
1993:
1992:
1988:
1987:
1984:
1980:
1976:
1975:South America
1972:
1969:
1966:
1965:
1961:
1959:
1958:
1954:
1953:
1950:Endemic Area
1949:
1946:
1943:
1942:
1939:
1934:
1932:
1931:
1927:
1922:
1919:
1911:
1909:
1907:
1903:
1895:
1882:
1881:Urotrematidae
1879:
1874:
1871:
1866:
1863:
1858:
1855:
1850:
1847:
1842:
1839:
1834:
1831:
1826:
1823:
1818:
1815:
1810:
1807:
1802:
1799:
1794:
1793:Echinoporidae
1791:
1786:
1783:
1778:
1775:
1770:
1767:
1762:
1759:
1758:
1753:
1746:
1743:
1739:
1735:
1732:
1727:
1724:
1719:
1718:Pleurogenidae
1716:
1711:
1708:
1703:
1702:Pachypsolidae
1700:
1695:
1692:
1687:
1684:
1679:
1676:
1671:
1668:
1667:
1662:
1655:
1652:
1647:
1644:
1643:
1638:
1631:
1628:
1623:
1620:
1615:
1612:
1611:
1606:
1599:
1596:
1591:
1588:
1584:
1580:
1577:
1572:
1569:
1564:
1561:
1560:
1555:
1554:
1552:
1543:
1540:
1539:
1534:
1533:
1531:
1522:
1519:
1514:
1511:
1506:
1503:
1498:
1497:Nudacotylidae
1495:
1490:
1489:Notocotylidae
1487:
1482:
1479:
1478:
1473:
1466:
1463:
1458:
1455:
1450:
1447:
1442:
1441:Cladorchiidae
1439:
1438:
1433:
1432:
1430:
1421:
1418:
1413:
1412:Heterophyidae
1410:
1405:
1402:
1401:
1396:
1395:
1393:
1384:
1381:
1376:
1375:Lissorchiidae
1373:
1372:
1367:
1366:
1364:
1357:Gubanov, 1953
1355:
1352:
1347:
1344:
1339:
1338:Lepidapedidae
1336:
1331:
1328:
1323:
1320:
1315:
1312:
1307:
1306:Deropristidae
1304:
1299:
1296:
1295:
1290:
1289:
1287:
1278:
1275:
1274:
1270:Heronimoidea
1269:
1268:
1266:
1257:
1254:
1249:
1246:
1241:
1238:
1234:
1230:
1227:
1222:
1219:
1214:
1211:
1207:
1203:
1200:
1195:
1192:
1187:
1184:
1179:
1176:
1171:
1170:Dictysarcidae
1168:
1163:
1160:
1156:
1152:
1149:
1144:
1143:Accacoeliidae
1141:
1140:
1135:
1128:
1125:
1124:
1119:
1118:
1116:
1107:
1104:
1103:
1098:
1097:
1095:
1086:
1083:
1078:
1075:
1070:
1069:Psilostomidae
1067:
1062:
1059:
1054:
1051:
1046:
1043:
1038:
1035:
1030:
1027:
1022:
1019:
1014:
1013:Cyclocoelidae
1011:
1007:
1003:
1000:
999:
994:
993:
991:
982:
979:
974:
971:
966:
963:
958:
955:
954:
949:
942:
941:Nuitrematidae
939:
934:
931:
930:
925:
924:
922:
913:
912:Bivesiculidae
910:
909:
907:
906:
905:Bivesiculata
904:
895:
894:Apocreadiidae
892:
891:
886:
885:
884:Apocreadiata
883:
882:
881:
880:Plagiorchiida
878:
867:
866:Spirorchiidae
864:
859:
856:
851:
848:
847:
842:
835:
832:
827:
824:
821:Poirier, 1886
819:
818:Diplostomidae
816:
813:Mühling, 1898
811:
808:
803:
800:
799:
797:Poirier, 1886
794:
787:
784:
779:
776:
775:
770:
769:
767:
766:
765:
762:
761:
760:
759:
755:
749:
747:
743:
741:
740:turbellarians
732:
730:
728:
724:
720:
716:
712:
708:
703:
701:
700:Bivesiculidae
697:
691:
689:
684:
679:
677:
673:
669:
665:
661:
656:
654:
650:
646:
642:
638:
634:
629:
626:
624:
620:
611:
609:
606:
605:tangoreceptor
602:
598:
594:
590:
582:
580:
578:
574:
573:metacercarial
570:
566:
562:
558:
554:
550:
546:
542:
538:
534:
530:
526:
522:
513:
511:
509:
503:
501:
496:
494:
493:Mehlis’ gland
490:
486:
482:
478:
471:Female organs
470:
468:
465:
461:
457:
453:
449:
445:
438:
436:
434:
430:
426:
422:
418:
414:
410:
406:
402:
398:
393:
391:
387:
383:
379:
375:
371:
367:
366:Fertilisation
363:
355:
353:
350:
346:
342:
338:
333:
331:
327:
323:
319:
316:
312:
304:
300:
299:
293:
289:
287:
283:
279:
275:
271:
267:
263:
262:Aspidogastrea
259:
256:; a group of
255:
246:
241:
239:
237:
233:
232:Aspidogastrea
229:
225:
221:
217:
214:
210:
206:
203:
199:
196:
192:
188:
185:– race) is a
184:
180:
176:
168:
166:
161:
156:
151:
146:
143:
140:
139:
136:
133:
130:
129:
126:
123:
120:
119:
116:
115:Rhabditophora
113:
110:
109:
106:
103:
100:
99:
96:
93:
90:
89:
86:
83:
80:
79:
74:
69:
65:
61:
57:
53:
52:Plagiorchiida
49:
48:
43:
39:
34:
29:
26:
22:
2521:
2479:
2476:Yamaguti, S.
2463:
2450:
2426:
2423:
2418:
2407:. Retrieved
2403:
2354:
2350:
2344:
2336:
2302:
2295:
2278:
2271:
2249:
2242:
2216:
2209:
2185:
2178:
2143:
2136:
2114:
2107:
2086:
2075:
2072:
2052:
2045:
2022:
2015:
1996:
1989:
1964:Biomphalaria
1962:
1955:
1937:
1928:
1923:
1915:
1912:Schistosomes
1899:
1865:Telorchiidae
1748:Odhner, 1902
1657:Nicoll, 1914
1654:Haploporidae
1641:Nicoll, 1914
1630:Gorgoderidae
1617:Odhner, 1910
1593:Odhner, 1905
1500:Barker, 1916
1449:Mesometridae
1415:Leiper, 1909
1386:Odhner, 1911
1383:Monorchiidae
1378:Magath, 1917
1370:Odhner, 1911
1365:Monorchiata
1349:Odhner, 1905
1325:Manter, 1966
1293:Odhner, 1905
1256:Syncoeliidae
1243:Odhner, 1927
1224:Odhner, 1905
1186:Gonocercidae
1178:Didymozoidae
1165:Nicoll, 1910
1146:Odhner, 1911
1136:Hemiuroidea
1088:Harrah, 1922
1080:Odhner, 1926
1077:Rhytidodidae
1056:Odhner, 1910
1053:Himasthlidae
1024:Odhner, 1910
976:Odhner, 1905
968:Nicoll, 1909
952:Odhner, 1905
933:Bucephalidae
923:Bucephalata
853:Odhner, 1912
829:Dubois, 1936
764:Diplostomida
757:
756:
753:
744:
736:
707:metacercaria
706:
704:
692:
680:
675:
671:
667:
659:
657:
630:
627:
615:
595:. From this
586:
545:phagocytosis
517:
508:Monorchiidae
504:
497:
492:
474:
456:vas deferens
442:
394:
390:schistosomes
359:
348:
344:
336:
334:
308:
296:
250:
247:Key features
208:
182:
178:
174:
173:
163:
144:
121:Superclass:
45:
25:
2626:iNaturalist
2546:Wikispecies
2304:Oncomelania
2236:Philippines
2172:Middle East
2039:Philippines
2024:Oncomelania
2009:Middle East
1983:Middle East
1930:Schistosoma
1884:Poche, 1926
1868:Looss, 1899
1812:Dayal, 1938
1804:Mehra, 1931
1780:Looss, 1899
1772:Looss, 1899
1734:Renicolidae
1721:Looss, 1899
1713:Mehra, 1935
1689:Poche, 1926
1686:Faustulidae
1681:Mehra, 1935
1670:Diplangidae
1633:Looss, 1899
1625:Looss, 1899
1609:Looss, 1901
1601:Ozaki, 1925
1598:Opecoelidae
1574:Looss, 1902
1558:Looss, 1902
1553:Xiphidiata
1524:Poche, 1926
1516:Looss, 1899
1508:Poche, 1926
1484:Blair, 1979
1481:Labicolidae
1476:Looss, 1899
1460:Looss, 1900
1452:Poche, 1926
1423:Looss, 1899
1399:Braun, 1901
1333:Fukui, 1929
1314:Enenteridae
1277:Heronimidae
1267:Heronimata
1259:Looss, 1899
1197:Looss, 1899
1162:Derogenidae
1138:Looss, 1899
1120:Azygioidea
1109:Poche, 1926
1101:Poche, 1925
1072:Looss, 1900
1064:Looss, 1899
1045:Fasciolidae
1037:Eucotylidae
1032:Looss, 1899
1002:Calycodidae
997:Looss, 1902
936:Poche, 1907
928:Poche, 1907
802:Brauninidae
789:Poche, 1907
727:temperature
612:Life cycles
541:pinocytosis
439:Male organs
417:mitotically
345:Amphistomes
282:body cavity
224:vertebrates
111:Subphylum:
56:Opecoelidae
47:Helicometra
2710:Categories
2409:2020-01-09
2328:References
2218:Helicorbis
2116:Segmentina
1902:infectious
1860:Baer, 1924
1852:Lühe, 1901
1764:Lühe, 1901
1756:Lühe, 1901
1745:Zoogonidae
1729:Lühe, 1909
1697:Ward, 1901
1665:Ward, 1901
1566:Lühe, 1906
1492:Lühe, 1909
1407:Ward, 1917
1280:Ward, 1918
1272:Ward, 1918
1194:Hemiuridae
1130:Lühe, 1909
1122:Lühe, 1909
1117:Hemiurata
1040:Cohn, 1904
834:Strigeidae
805:Wolf, 1903
653:miracidium
633:vertebrate
429:germ cells
330:acetabulum
278:parenchyma
254:Neodermata
242:Morphology
207:(known as
191:trematodes
181:– double,
141:Subclass:
125:Neodermata
2289:Worldwide
2261:East Asia
2145:Pirinella
2035:East Asia
1979:Caribbean
1127:Azygiidae
733:Evolution
619:paratenic
577:cercarial
561:submucosa
549:syncitium
525:cyclocoel
444:Protandry
419:dividing
386:dioecious
337:monostome
274:vermiform
266:Monogenea
228:Monogenea
213:syncytial
211:) with a
205:flatworms
202:parasitic
158:Families
135:Trematoda
91:Kingdom:
85:Eukaryota
2579:46487208
2531:Wikidata
2478:(1971).
2383:24688868
2357:: e292.
2315:crayfish
1906:diseases
676:cercaria
635:host in
537:uroproct
479:with an
388:are the
349:Distomes
324:, and a
315:anterior
305:digenean
303:zoogonid
280:with no
216:tegument
165:See text
101:Phylum:
95:Animalia
81:Domain:
31:Digenea
21:Anthipes
2716:Digenea
2680:4143360
2566:Digenea
2552:Digenea
2537:Q132650
2522:Digenea
2374:3961169
2285:Plants
2251:Bulinus
2232:Vietnam
2224:Plants
2203:Siberia
2155:Tilapia
2122:Plants
2054:Bulinus
1998:Bulinus
1738:Dollfus
1583:Dollfus
1233:Dollfus
1206:Dollfus
1155:Dollfus
1006:Dollfus
758:Digenea
723:enzymes
649:annelid
623:mollusc
589:ganglia
587:Paired
565:mollusc
547:by the
481:oviduct
425:embryos
376:to the
326:ventral
311:suckers
270:Cestoda
236:Cestoda
220:suckers
193:in the
175:Digenea
145:Digenea
131:Class:
2693:108400
2677:uBio:
2670:407244
2631:244536
2592:1STRGO
2469:
2456:
2381:
2371:
2347:n. sp"
2151:Mullet
2080:saliva
2061:Africa
2005:Africa
1971:Africa
1740:, 1939
1235:, 1937
1208:, 1932
1157:, 1932
1008:, 1929
683:marine
668:rediae
637:faeces
597:nerves
557:organs
533:anuses
521:caecum
448:testes
401:larval
374:cirrus
341:Flukes
286:coelom
209:flukes
198:phylum
152:, 1863
2688:WoRMS
2644:55189
2605:16240
2444:Notes
2351:PeerJ
2311:Crabs
2257:Fish
2228:India
2198:Trout
2168:Egypt
2130:India
2057:spp.
2031:China
2027:spp.
2001:spp.
1967:spp.
1926:genus
645:snail
593:brain
569:redia
529:caeca
477:ovary
421:cells
370:sperm
322:mouth
313:, an
187:class
183:Genos
177:(Gr.
150:Carus
62:fish
50:sp. (
2657:6179
2652:NCBI
2639:ITIS
2587:EPPO
2467:ISBN
2454:ISBN
2379:PMID
2320:Asia
2307:sp.
2254:sp.
2221:sp.
2194:Carp
2190:sp.
2160:Asia
2126:Asia
2119:sp.
711:cyst
688:fish
543:and
489:yolk
483:, a
454:, a
397:eggs
318:oral
268:and
2574:EoL
2561:AFD
2431:doi
2369:PMC
2359:doi
380:or
189:of
179:Dis
2712::
2690::
2667::
2654::
2641::
2628::
2615::
2602::
2589::
2576::
2563::
2548::
2533::
2427:33
2402:.
2391:^
2377:.
2367:.
2353:.
2349:.
2313:,
2263:,
2234:,
2230:,
2196:,
2170:,
2166:,
2162:,
2153:,
2128:,
2037:,
2033:,
2007:,
1981:,
1977:,
1973:,
1933:.
725:,
719:pH
462:,
458:,
347:.
335:A
301:a
264:,
167:.
54::
2433::
2412:.
2385:.
2361::
2355:2
284:(
23:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.