266:
142:
942:
255:
169:
32:
462:
After the death of the normal intermediate host, its body can be eaten by carnivores suitable as definitive hosts. In their small intestines, protoscoleces turn inside out, attach, and give rise to adult tapeworms, completing the lifecycle. In humans, the cysts persist and grow for years. They are
450:
are infected by ingesting eggs. Sheep, goats, cattle, camels, pigs, wild herbivores, and rodents are the usual intermediate hosts, but humans can also be infected. Humans are dead-end hosts, since their corpses are nowadays seldom eaten by carnivorous predators.
454:
The egg hatches in the digestive system of the intermediate host, producing a planula larva. It penetrates the intestinal wall and is carried by bloodstream to liver, lung, brain, or another organ. It settles there and turns into a bladder-like structure called
463:
regularly found in the liver (and every possible organ: spleen, kidney, bone, brain, tongue and skin) and are asymptomatic until their growing size produces symptoms or are accidentally discovered. Disruption of the cysts (spontaneous or
613:
In 2020, an international effort of scientists from 16 countries lead to a detailed consensus on terminology, i.e. the terms to be used or rejected for the genetics, epidemiology, biology, immunology and clinical aspects linked with
956:
1148:
575:
The origin of these parasites based on host-parasite co-evolution comparisons was North
America or Asia, depending on whether the ancestral definitive hosts were
265:
1200:
1122:
459:. From the inner lining of its wall, protoscoleces (i.e. scoleces with invaginated tissue layers) bud and protrude into the fluid filling the cyst.
446:
predators – dogs, wolves, foxes, and lions. The adult tapeworm lives in their small intestines and delivers eggs to be excreted with the stool. The
1174:
141:
1261:
706:
Thompson RC, McManus DP (2001). "Chapter 1: Aetiology: parasites and life cycles". In Eckert J, Gemmell MA, Meslin FX, Pawłowski ZS (eds.).
713:
721:
115:
1179:
53:
96:
1187:
479:
49:
68:
168:
1161:
1057:
1034:
628:
512:
302:
155:
75:
1256:
1101:
846:
Knapp J, Nakao M, Yanagida T, Okamoto M, Saarma U, Lavikainen A, Ito A (2011). "Phylogenetic relationships within
42:
1205:
1114:
475:
387:
is usually long and can be up to 50 years. Cystic echinococcosis is mostly found in South and
Central America,
372:
500:
82:
314:
1251:
796:
536:
364:
296:
941:
530:
974:
524:
518:
64:
1062:
356:
478:, or other imaging techniques. Antiechinococcus antibodies can be detected with serodiagnostic tests –
1215:
1070:
1021:
1266:
506:
337:
308:
828:
709:
WHO/OIE Manual on
Echinococcosis in Humans and Animals: a Public Health Problem of Global Concern
447:
163:
1012:
632:. However, it is possible to protect humans from the fox tapeworm by deworming the main hosts.
1223:
1153:
930:
912:
871:
820:
777:
717:
595:
384:
254:
1228:
1271:
920:
902:
863:
812:
767:
757:
651:
89:
1109:
1096:
925:
890:
889:
Vuitton DA, McManus DP, Rogan MT, Romig T, Gottstein B, Naidich A, et al. (2020).
772:
745:
439:
352:
291:
220:
20:
1245:
1026:
707:
680:
416:
1039:
832:
487:
468:
456:
891:"International consensus on terminology to be used in the field of echinococcoses"
854:
tapeworms (Cestoda: Taeniidae): an inference from nuclear protein-coding genes".
1192:
1135:
1006:
867:
443:
392:
341:
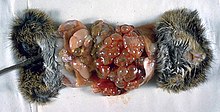
31:
907:
816:
464:
428:
424:
150:
997:
916:
1166:
1083:
336:. An anus is absent, and it has no digestive system. Its body is covered by
230:
180:
934:
875:
824:
781:
762:
1049:
991:
498:
A phylogenetic tree has been created for several species in this genus –
435:
333:
329:
325:
287:
200:
1127:
420:
283:
210:
1140:
685:
DPDx - Laboratory
Identification of Parasites of Public Health Concern
340:
and the worm is divided into a scolex, a short neck, and three to six
605:
412:
408:
388:
190:
968:
746:"Immunology and Immunodiagnosis of Cystic Echinococcosis: An Update"
1088:
580:
576:
540:. The first diverging species are the neotropical endemic species
483:
404:
400:
396:
264:
253:
599:
from which it diverged more than 10 million years ago. The genus
1075:
972:
25:
593:
are basal in this genus. The genus is a sister to the genus
19:
This article is about the organism. For the infection, see
687:. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 15 July 2019
603:
evolved in North
America in canids and began to diversify
294:
is an infectious disease caused by the following species:
795:
Nakao M, McManus DP, Schantz PM, Craig PS, Ito A (2007).
471:) can be life-threatening due to anaphylactic shock.
981:
324:is triploblastic – it has three layers – outermost
56:. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
650:
269:General description of the egg and oncosphere of
958:How To Exterminate The Fox Tapeworm In Your Area
744:Zhang W, Wen H, Li J, Lin R, McManus DP (2012).
290:phylum (colloquially known as flatworms). Human
258:schematic representation of the life cycle of
801:inferred from complete mitochondrial genomes"
8:
969:
140:
129:
924:
906:
771:
761:
116:Learn how and when to remove this message
355:. The three types of echinococcosis are
641:
733:– via World Health Organization.
675:
673:
856:Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution
750:Clinical and Developmental Immunology
7:
1216:34200b0b-9568-4c56-bc97-04e57cd70b0a
1115:18bc2ba3-aa34-408f-8cce-af1a49268979
797:"A molecular phylogeny of the genus
474:Cysts are detected with ultrasound,
54:adding citations to reliable sources
714:Office International des Epizooties
14:
344:. Its body shape is ribbon-like.
961:– via Amazon Kindle Store.
940:
167:
30:
41:needs additional citations for
1:
480:indirect fluorescent antibody
1262:Parasitic animals of mammals
626:There is no vaccine against
351:spp. cause a disease called
868:10.1016/j.ympev.2011.07.022
649:Dandan, Imad (7 May 2019).
629:Echinococcus multilocularis
556:are sister species, as are
513:Echinococcus multilocularis
286:, a parasitic class of the
156:Echinococcus multilocularis
1288:
18:
955:Grabs A (November 2016).
817:10.1017/s0031182006001934
476:X-ray computed tomography
373:polycystic echinococcosis
164:Scientific classification
162:
148:
139:
132:
908:10.1051/parasite/2020024
587:Echinococcus oligarthrus
501:Echinococcus oligarthrus
608: million years ago
537:Echinococcus granulosus
482:, complement fixation,
365:alveolar echinococcosis
519:Echinococcus shiquicus
274:
262:
531:Echinococcus ortleppi
490:, and other methods.
357:cystic echinococcosis
268:
257:
1110:Fauna Europaea (new)
525:Echinococcus equinus
434:Echinococcosis is a
50:improve this article
763:10.1155/2012/101895
591:Echinococcus vogeli
507:Echinococcus vogeli
448:intermediate hosts
415:, and the western
282:is a genus within
275:
263:
1257:Parasites of dogs
1239:
1238:
1224:Open Tree of Life
975:Taxon identifiers
937:. Article No. 41.
716:. pp. 1–19.
558:E. multilocularis
385:incubation period
369:E. multilocularis
303:E. multilocularis
252:
251:
248:
126:
125:
118:
100:
1279:
1232:
1231:
1219:
1218:
1209:
1208:
1196:
1195:
1193:NHMSYS0020706654
1183:
1182:
1170:
1169:
1157:
1156:
1144:
1143:
1131:
1130:
1118:
1117:
1105:
1104:
1092:
1091:
1079:
1078:
1066:
1065:
1053:
1052:
1043:
1042:
1030:
1029:
1017:
1016:
1015:
1002:
1001:
1000:
970:
963:
962:
952:
946:
945:
944:
938:
928:
910:
886:
880:
879:
843:
837:
836:
792:
786:
785:
775:
765:
741:
735:
734:
732:
730:
703:
697:
696:
694:
692:
681:"Echinococcosis"
677:
668:
667:
665:
663:
654:
646:
609:
440:definitive hosts
246:
172:
171:
144:
130:
121:
114:
110:
107:
101:
99:
58:
34:
26:
1287:
1286:
1282:
1281:
1280:
1278:
1277:
1276:
1242:
1241:
1240:
1235:
1227:
1222:
1214:
1212:
1204:
1199:
1191:
1186:
1178:
1173:
1165:
1160:
1152:
1147:
1139:
1134:
1126:
1121:
1113:
1108:
1100:
1095:
1087:
1082:
1074:
1069:
1061:
1056:
1048:
1046:
1038:
1033:
1025:
1020:
1011:
1010:
1005:
996:
995:
990:
977:
967:
966:
954:
953:
949:
939:
888:
887:
883:
845:
844:
840:
794:
793:
789:
743:
742:
738:
728:
726:
724:
705:
704:
700:
690:
688:
679:
678:
671:
661:
659:
652:"Hydatid Cysts"
648:
647:
643:
638:
624:
604:
496:
288:platyhelminthes
245:
201:Platyhelminthes
166:
122:
111:
105:
102:
59:
57:
47:
35:
24:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1285:
1283:
1275:
1274:
1269:
1264:
1259:
1254:
1252:Cestoda genera
1244:
1243:
1237:
1236:
1234:
1233:
1220:
1210:
1197:
1184:
1171:
1158:
1145:
1132:
1119:
1106:
1097:Fauna Europaea
1093:
1080:
1067:
1054:
1044:
1031:
1018:
1003:
987:
985:
979:
978:
973:
965:
964:
947:
881:
862:(3): 628–638.
838:
811:(5): 713–722.
787:
736:
722:
698:
669:
640:
639:
637:
634:
623:
620:
568:is related to
542:E. oligarthrus
495:
492:
381:E. oligarthrus
353:echinococcosis
315:E. oligarthrus
292:echinococcosis
250:
249:
247:Rudolphi, 1801
238:
234:
233:
228:
224:
223:
221:Cyclophyllidea
218:
214:
213:
208:
204:
203:
198:
194:
193:
188:
184:
183:
178:
174:
173:
160:
159:
153:infected with
149:Necropsy of a
146:
145:
137:
136:
124:
123:
65:"Echinococcus"
38:
36:
29:
21:Echinococcosis
16:Genus of worms
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1284:
1273:
1270:
1268:
1265:
1263:
1260:
1258:
1255:
1253:
1250:
1249:
1247:
1230:
1225:
1221:
1217:
1211:
1207:
1202:
1198:
1194:
1189:
1185:
1181:
1176:
1172:
1168:
1163:
1159:
1155:
1150:
1146:
1142:
1137:
1133:
1129:
1124:
1120:
1116:
1111:
1107:
1103:
1098:
1094:
1090:
1085:
1081:
1077:
1072:
1068:
1064:
1059:
1055:
1051:
1045:
1041:
1036:
1032:
1028:
1023:
1019:
1014:
1008:
1004:
999:
993:
989:
988:
986:
984:
980:
976:
971:
960:
959:
951:
948:
943:
936:
932:
927:
922:
918:
914:
909:
904:
900:
896:
892:
885:
882:
877:
873:
869:
865:
861:
857:
853:
849:
842:
839:
834:
830:
826:
822:
818:
814:
810:
806:
802:
800:
791:
788:
783:
779:
774:
769:
764:
759:
755:
751:
747:
740:
737:
725:
723:92-9044-522-X
719:
715:
711:
710:
702:
699:
686:
682:
676:
674:
670:
658:
653:
645:
642:
635:
633:
631:
630:
621:
619:
617:
616:Echinococcus
611:
607:
602:
598:
597:
592:
588:
584:
582:
578:
573:
571:
570:E. granulosus
567:
566:E. canadensis
563:
559:
555:
554:E. canadensis
551:
547:
543:
539:
538:
533:
532:
527:
526:
521:
520:
515:
514:
509:
508:
503:
502:
493:
491:
489:
485:
481:
477:
472:
470:
466:
460:
458:
452:
449:
445:
441:
437:
432:
430:
426:
422:
418:
417:United States
414:
410:
406:
402:
398:
394:
390:
386:
382:
378:
374:
370:
366:
362:
361:E. granulosus
358:
354:
350:
345:
343:
339:
335:
331:
327:
323:
319:
317:
316:
311:
310:
305:
304:
299:
298:
297:E. granulosus
293:
289:
285:
281:
280:
272:
267:
261:
256:
244:
243:
239:
236:
235:
232:
229:
226:
225:
222:
219:
216:
215:
212:
209:
206:
205:
202:
199:
196:
195:
192:
189:
186:
185:
182:
179:
176:
175:
170:
165:
161:
158:
157:
152:
147:
143:
138:
135:
131:
128:
120:
117:
109:
106:December 2009
98:
95:
91:
88:
84:
81:
77:
74:
70:
67: –
66:
62:
61:Find sources:
55:
51:
45:
44:
39:This article
37:
33:
28:
27:
22:
1040:Echinococcus
1027:Echinococcus
1013:Echinococcus
983:Echinococcus
982:
957:
950:
898:
894:
884:
859:
855:
851:
848:Echinococcus
847:
841:
808:
805:Parasitology
804:
799:Echinococcus
798:
790:
753:
749:
739:
727:. Retrieved
708:
701:
689:. Retrieved
684:
660:. Retrieved
656:
644:
627:
625:
615:
612:
601:Echinococcus
600:
594:
590:
586:
585:
574:
569:
565:
562:E. shiquicus
561:
557:
553:
549:
545:
541:
535:
529:
523:
517:
511:
505:
499:
497:
488:Western blot
473:
469:liver biopsy
461:
457:hydatid cyst
453:
433:
380:
376:
368:
360:
349:Echinococcus
348:
346:
332:, and inner
322:Echinococcus
321:
320:
313:
307:
301:
295:
279:Echinococcus
278:
277:
276:
271:Echinococcus
270:
260:Echinococcus
259:
242:Echinococcus
241:
240:
154:
134:Echinococcus
133:
127:
112:
103:
93:
86:
79:
72:
60:
48:Please help
43:verification
40:
1136:iNaturalist
1007:Wikispecies
729:24 November
691:24 November
662:24 November
550:E. ortleppi
444:carnivorous
393:Middle East
383:. A worm's
347:In humans,
342:proglottids
1267:Hepatology
1246:Categories
636:References
622:Prevention
465:iatrogenic
429:California
425:New Mexico
375:caused by
367:caused by
359:caused by
151:cotton rat
76:newspapers
917:1776-1042
712:. Paris:
618:species.
546:E. vogeli
377:E. vogeli
328:, middle
309:E. vogeli
231:Taeniidae
187:Kingdom:
181:Eukaryota
1047:BioLib:
992:Wikidata
935:32500855
895:Parasite
876:21907295
833:42494141
825:17156584
782:22235225
756:: 1–10.
657:Medscape
494:Taxonomy
436:zoonosis
338:tegument
334:endoderm
330:mesoderm
326:ectoderm
227:Family:
197:Phylum:
191:Animalia
177:Domain:
1272:Cestoda
1229:1021829
1180:1059442
1154:1308129
1128:3268465
1076:2923036
998:Q344662
926:7273836
773:3253442
421:Arizona
284:Cestoda
237:Genus:
217:Order:
211:Cestoda
207:Class:
90:scholar
1213:NZOR:
1167:103070
1141:171456
1089:1ECHNG
933:
923:
915:
901:: 41.
874:
852:Taenia
831:
823:
780:
770:
720:
596:Taenia
581:felids
577:canids
534:, and
438:. The
427:, and
413:Russia
409:Greece
391:, the
389:Africa
371:, and
92:
85:
78:
71:
63:
1149:IRMNG
1102:98526
1063:29694
1050:43812
829:S2CID
484:ELISA
467:e.g.
405:Spain
401:Italy
397:China
97:JSTOR
83:books
1206:6209
1201:NCBI
1175:ITIS
1123:GBIF
1084:EPPO
1058:BOLD
931:PMID
913:ISSN
872:PMID
850:and
821:PMID
778:PMID
754:2012
731:2023
718:ISBN
693:2023
664:2023
589:and
560:and
552:and
544:and
442:are
273:spp.
69:news
1188:NBN
1162:ISC
1071:EoL
1035:AFD
1022:ADW
921:PMC
903:doi
864:doi
813:doi
809:134
768:PMC
758:doi
606:5.8
579:or
564:.
431:).
379:or
312:or
52:by
1248::
1226::
1203::
1190::
1177::
1164::
1151::
1138::
1125::
1112::
1099::
1086::
1073::
1060::
1037::
1024::
1009::
994::
929:.
919:.
911:.
899:27
897:.
893:.
870:.
860:61
858:.
827:.
819:.
807:.
803:.
776:.
766:.
752:.
748:.
683:.
672:^
655:.
610:.
583:.
572:.
548:.
528:,
522:,
516:,
510:,
504:,
486:,
423:,
411:,
407:,
403:,
399:,
395:,
363:,
318:.
306:,
300:,
905::
878:.
866::
835:.
815::
784:.
760::
695:.
666:.
419:(
119:)
113:(
108:)
104:(
94:·
87:·
80:·
73:·
46:.
23:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.