676:, it can be reversed. This can be accomplished by stretching the lower back, hip-flexors, quads and strengthening the abdominal muscles, hamstrings, and glutes. Strengthening the gluteal complex is a commonly accepted practice to reverse excessive lumbar lordosis, as an increase in gluteal muscle tone assists in the reduction of excessive anterior pelvic tilt and lumbar hyperlordosis. Local intra-articular hip pain has been shown to inhibit gluteal contraction potential, meaning that hip pain could be a main contributing factor to gluteal inhibition. Dancers should ensure that they don't strain themselves during dance rehearsals and performances. To help with lifts, the concept of isometric contraction, during which the length of the muscle remains the same during contraction, is important for stability and posture.
67:
533:– Another odd body formation is when an individual has a leg shorter than the other, which can be an immediate cause for the imbalance of hips then putting strain on the posture of the back which an individual has to adjust into vulnerable positions to meet aesthetic appearances. This can lead to permanent damage to the back. Genu recurvatum (swaying back knees) is also a factor that forces a dancer to adjust to unstable postures.
39:
543:, which causes poor lifting posture, hip flexion contracture, which means the lack of postural awareness, and thoracic hyperkyphosis, which causes the individual to compensate for limited hip turn out (which is essential to dances such as ballet). Weak psoas (short for iliopsoas-muscle that controls the hip flexor) forces the dancer to lift from the strength of their back instead of from the hip when lifting their leg into
606:
643:. The Scoliosis Research Society has proposed a range of 40° and 60° as measured between the upper endplate of Th12 and the upper endplate of S1. Individual studies, although using other reference points, have found normal ranges up to approximately 85°. It is generally more pronounced in females. It is relatively constant through adolescence and young adulthood, but decreases in the elderly.
410:, where some joints throughout the body are so hyper-extensible that they can become unstable (i.e. problematically much more flexible than normal, frequently to the point of partial or full dislocation). With such hyper-extensibility, it is also quite common (if not the norm) for some of the muscles surrounding an unstable joint to compensate for that instability by contracting.
254:
346:
356:
458:
months and the growth plates of the patient were checked to make sure that they were closed to rule out natural growth. The height loss occurs in the torso region and once the person fixes their back, the person's Body Mass Index will reduce since the person is taller and the stomach will also appear to be slimmer.
614:
arthrodesis and contribute to normal lumbar lordosis, it is helpful to identify a reproducible and accurate means of measuring segmental lordosis at these levels. A visible sign of hyperlordosis is an abnormally large arch of the lower back and the person appears to be puffing out his or her stomach and buttocks.
402:(the most common bone disease in which bone density is lost resulting in bone weakness and increased likelihood of fracture) are some of the most common causes of hyperlordosis. Other causes include obesity, hyperkyphosis (spine curvature disorder in which the thoracic curvature is abnormally rounded),
613:
Measurement and diagnosis of lumbar hyperlordosis can be difficult. Obliteration of vertebral end-plate landmarks by interbody fusion may make the traditional measurement of segmental lumbar lordosis more difficult. Because the L4–L5 and L5–S1 levels are most commonly involved in fusion procedures or
441:
Being less common than lumbar hyperlordosis, hypolordosis (also known as flatback) occurs when there's less of a curve in the lower back or a flattening of the lower back. This occurs because the vertebrae are oriented toward the back of the spine, stretching the disc towards the back and compressing
651:
Bone scans are conducted to rule out possible fractures and infections, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is used to eliminate the possibility of the spinal cord or nerve abnormalities, and computed tomography scans (CT scans) are used to get a more detailed image of the bones, muscles, and organs of
370:
region (lower back) experiences stress or extra weight and becomes arched more than normal, sometimes leading to muscle pain or spasms. It is a common postural position in which the natural curve of the lumbar region of the back is slightly or dramatically accentuated. Commonly known as swayback, it
682:
Only the muscles on the front and the back of the thighs can rotate the pelvis forward or backward while in a standing position because they can discharge the force on the ground through the legs and feet. Abdominal muscles and erector spinae can't discharge force on an anchor point while standing,
484:
pain. The most problematic symptom is that of a herniated disc where the individual has put so much strain on the back that the discs between the vertebrae have been damaged or have ruptured. Technical problems with dancing such as difficulty in the positions of attitude and arabesque can be a sign
727:
calls for adjusting the lower back curvature (as well as the rest of the spinal curvatures) through specific re-alignments of the pelvis to the thighs, it's referred to in shorthand as 'dropping the tailbone'. The specifics of the structural change are school specific and are part of the jibengong
476:
Merely slouching doesn't cause height loss, even though it may make a person look shorter, slouching may lead to perceived height loss, whereas lumbar hyperlordosis leads to actual and measured height loss. To make it easier to understand the difference, people losing a vertebra (which is around 2
178:, whose inflexible spines cause them to resort to an inefficient forward-leaning "bent-knee, bent-waist" gait. As such, lordosis in the human spine is considered one of the primary physiological adaptations of the human skeleton that allows for human gait to be as energetically efficient as it is.
595:
sites of injury in dancers are in the lower back. This can be attributed to the strains of repetitive dance training which may lead to minor trauma. If the damaged site is not given time to heal the damage of the injury will increase. Abrupt increases in dance intensity or sudden changes in dance
457:
For example, the height loss was measured by measuring the patient's height while standing straight (with exaggerated curves in the upper and lower back) and again after the patient fixed this issue (with no exaggerated curves), both of these measurements were taken in the morning with a gap of 6
698:
Controversy regarding the degree to which manipulative therapy can help a patient still exists. If therapeutic measures reduce symptoms, but not the measurable degree of lordotic curvature, this could be viewed as a successful outcome of treatment, though based solely on subjective data. The
1461:
Harrison, DD; Jackson, BL; Troyanovich, S; Robertson, G; de George, D; Barker, WF (September 1994). "The efficacy of cervical extension-compression traction combined with diversified manipulation and drop table adjustments in the rehabilitation of cervical lordosis: a pilot study".
1852:
553:– One of the greatest contributors is uneven muscles. Because all muscles have a muscle that works in opposition to it. It is imperative that to keep all muscles protected, the opposite muscle is not stronger than the muscle at risk. In the situation of lumbar lordosis,
497:
being tight are signs that improper muscles are being worked while dancing which leads to lumbar hyperlordosis. The most obvious signs of lumbar hyperlordosis are lower back pain in dancing and pedestrian activities as well as having the appearance of a swayed back.
1845:
1838:
477:
inches or 5 centimeters in height) in the spine will be shorter regardless of posture. Lumbar hyperlordosis, of course, doesn't make you lose a vertebra but it bends them in such a way that your spine's vertical height is reduced.
1215:
1157:
468:
However, the cause of height loss in both situations is a little different even though the impact is similar. In the first scenario, it can be due to a genetic condition, trauma to the spine, pregnancy in women, increased
584:
with another dancer they are extremely prone to lift in the incorrect posture, pushing their arms up to lift the other dancer, while letting their core and spine curve which is easy to then hyperlordosis in a dancer's
665:
Some corrective exercises can be done to alleviate this issue, but it may take several months to fix (provided that the person sits less, stands with a neutral pelvis, and sleeps on their back).
567:– Younger dancers are more at risk for the development of lumbar hyperlordosis because the lumbar fascia and hamstrings tighten when a child starts to experience a growth spurt into adolescence.
473:, or a sedentary lifestyle (sitting too much causes muscle imbalances and is the most common reason for this issue) and in the second scenario, the estrogen weakens the muscles in the area.
596:
choreography do not allow the body to adapt to the new stresses. New styles of dance, returning to dance, or increasing dance time by a great deal will result in exhaustion of the body.
2544:
515:– Natural factors of how spines are formed greatly increase certain individuals' likelihood to experience a strain or sprain in their back or neck. Factors such as having more lumbar
1251:
1193:
2549:
1406:
Freeman, Stephanie; Mascia, Anthony; McGill, Stuart (February 2013). "Arthrogenic neuromusculature inhibition: A foundational investigation of existence in the hip joint".
1371:
Choi, Sil-ah (April 2015). "Isometric hip abduction using a Thera-Band alters gluteus maximus muscle activity and the anterior pelvic tilt angle during bridging exercise".
264:
679:
Lumbar hyperlordosis may be treated by strengthening the hip extensors on the back of the thighs, and by stretching the hip flexors on the front of the thighs.
711:
is a plastic exterior that can be made with a small amount of lordosis to minimize stresses on discs that have experienced herniated discs. In the case where
413:
Excessive lordotic curvature – lumbar hyperlordosis, is also called "hollow back", and "saddle back" (after a similar condition that affects some horses);
406:(inflammation of the intervertebral disc space caused by infection), and benign juvenile lordosis. Other factors may also include rare diseases, including
2432:
417:
usually refers to a nearly opposite postural misalignment that can initially look quite similar. Common causes of lumbar hyperlordosis include tight
1925:
1830:
1575:
691:
and will treat hyperlordosis. So too will stiff-legged deadlifts and supine hip lifts and any other similar movement strengthen the posterior chain
631:
are used to measure the lumbar curvature. On a lateral X-ray, a normal range of the lordotic curvature of between 20° and 60° has been proposed by
454:) has a noticeable impact on the height of individuals with this medical issue, a height loss of 0.5–2.5 inches (1.27–6.35 centimeters) is common.
547:
or attitude. This causes great stress and risk of injury, especially because the dancer will have to compensate to obtain the positions required.
489:. Tightness of the iliopsoas results in a dancer having difficulty lifting their leg into high positions. Abdominal muscles being weak and the
1005:
728:(essential technique) of these schools. The adjustment is referred to in tai chi literature as 'when the lowest vertebrae are plumb erect...'
715:(EDS) is responsible, being properly fitted with a customized brace may be a solution to avoid strain and limit the frequency of instability.
1355:
854:
683:
unless one is holding his hands somewhere, hence their function will be to flex or extend the torso, not the hip. Back hyper-extensions on a
695:
in the front of the thighs. Abdominal exercises could be avoided altogether if they stimulate too much the psoas and the other hip flexors.
2373:
946:
1298:
371:
is common in dancers. Imbalances in muscle strength and length are one cause of this excessive stress to the lower back, such as weak
780:
1061:
Shimizu, Mutsuya; Kobayashi, Tetsuya; Chiba, Hisashi; Senoo, Issei; Ito, Hiroshi; Matsukura, Keisuke; Saito, Senri (2020-07-01).
2327:
523:, and then in cases of less lumbar the individual not reaching their necessity for flexibility and then pushing their bodies to
2539:
2046:
46:
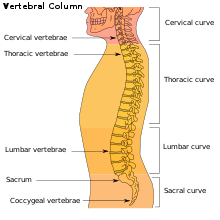
Diagram showing normal curvature (posterior concavity) of the cervical (neck) and lumbar (lower back) vertebral column (spine)
1449:
Arnheim, Daniel D.. Dance
Injuries:Their Prevention and Care. Second Edition. St. Louis, Missouri: C. V. Mosby Company, 1980.
805:
200:
is a different condition with a different cause, that at a glance can mimic the outward appearance of lumbar hyperlordosis.
1120:
Solomon, Ruth. Preventing Dance
Injuries: An Interdisciplinary Perspective. Reston, VA: American Alliance for Health, 1990.
971:
Solomon, Ruth. Preventing Dance
Injuries: An Interdisciplinary Perspective. Reston, VA: American Alliance for Health, 1990.
627:
Precise diagnosis is done by looking at a complete medical history, physical examination, and other tests of the patient.
2162:
1865:
1568:
898:
668:
Since lumbar hyperlordosis is usually caused by habitual poor posture, rather than by an inherent physical defect like
561:. The muscular imbalance results in pulling down the pelvis in the front of the body, creating a swayback in the spine.
407:
325:
2332:
2051:
1881:
1869:
544:
297:
2363:
2417:
2337:
1809:
272:
304:
2272:
1915:
628:
1633:
2309:
1943:
1920:
1561:
283:
268:
1814:
1672:
1488:
T'ai Chi Ch'uan: A Simplified Method of
Calisthenics for Health & Self Defence. By Manqing Zheng p. 10
1036:
983:
712:
311:
205:
185:
163:
1216:"Segmental Lumbar Lordosis: Manual Versus Computer-Assisted Measurement Using Seven Different Techniques"
1158:"Segmental Lumbar Lordosis: Manual Versus Computer-Assisted Measurement Using Seven Different Techniques"
1132:
Howse, Justin. Dance
Technique and Injury Prevention. Third Edition. London: A&C Black Limited, 2000.
2212:
1877:
1819:
834:
520:
480:
Although lumbar hyperlordosis gives an impression of a stronger back, it can lead to moderate to severe
19:
This article is about the human spinal shape and related disorders. For the animal sexual posture, see
465:
who have weaker muscles in the lower back due to increased estrogen intake and other such treatments.
442:
it in the front. This can cause a narrowing of the opening for the nerves, potentially pinching them.
2427:
293:
699:
presence of measurable abnormality does not automatically equate with a level of reported symptoms.
229:. Lordosis may also increase at puberty, sometimes not becoming evident until the early or mid-20s.
2534:
2245:
1861:
1796:
1533:
1063:"Adult spinal deformity and its relationship with height loss: a 34-year longitudinal cohort study"
1013:
226:
66:
1543:
2107:
1431:
1243:
1185:
636:
120:
1804:
950:
2442:
2422:
1720:
1694:
1538:
1471:
1423:
1388:
1351:
1319:
1294:
1280:
1235:
1177:
1102:
1084:
921:
850:
801:
776:
752:
747:
640:
558:
554:
470:
395:
75:
51:
20:
2489:
2484:
2405:
2397:
2317:
2281:
2089:
2041:
1998:
1689:
1599:
1415:
1380:
1227:
1169:
1092:
1074:
913:
842:
511:
394:(a disorder where bones grow abnormally, which can result in short stature as in dwarfism),
225:
curvatures, result in a difference in the thickness between the front and back parts of the
124:
60:
2505:
2240:
2070:
2036:
1989:
1764:
1732:
1332:
688:
632:
1511:
2368:
2299:
2263:
2235:
2157:
2061:
1935:
1737:
1725:
1584:
1231:
1173:
1097:
1062:
846:
742:
605:
490:
391:
152:
1419:
506:
Possible causes that lead to the condition of lumbar hyperlordosis are the following:
318:
38:
2528:
2378:
2322:
2289:
2172:
1993:
1786:
1769:
1715:
1652:
737:
673:
1435:
1247:
1189:
2460:
2353:
2195:
2167:
1953:
1948:
1679:
917:
708:
422:
399:
171:
104:
56:
1384:
2383:
2150:
2141:
2026:
1958:
1710:
1667:
1638:
684:
540:
462:
451:
380:
376:
1548:
1079:
2358:
2294:
2207:
2201:
2177:
2145:
2112:
2081:
2031:
2003:
1774:
592:
581:
494:
481:
418:
1088:
929:
135:
convex curvature of the spine. The normal outward (convex) curvature in the
2465:
2410:
2217:
2102:
2095:
2076:
2008:
1972:
1759:
1751:
1617:
1144:
Brinson, Peter. Fit to Dance?. London: Calouste
Gulbenkian Foundation, 1996.
669:
516:
486:
430:
372:
233:
1427:
1392:
1239:
1181:
1106:
925:
1475:
1907:
1903:
1885:
1779:
1684:
1607:
1286:
899:"The natural history of human gait and posture. Part 1. Spine and pelvis"
414:
403:
175:
136:
128:
875:
2475:
2133:
724:
426:
282:
if you can. Unsourced or poorly sourced material may be challenged and
88:
1350:(Ninth ed.). New Zealand: Spinal Publications New Zealand, Ltd.
524:
367:
167:
140:
116:
355:
166:
makes it easier for humans to bring the bulk of their mass over the
604:
384:
354:
80:
1553:
2018:
1834:
1557:
390:
Other health conditions and disorders can cause hyperlordosis.
379:(psoai). A major feature of lumbar hyperlordosis is a forward
2451:
1981:
1894:
247:
84:
115:
are also used to refer to the normal inward curvature of the
1291:
Spinal
Disorders: Fundamentals of Diagnosis and Treatment
557:
are weaker than the muscles in the lumbar spine and the
433:
deficiency in children, can cause lumbar hyperlordosis.
279:
1464:
196:(after a similar condition that affects some horses).
800:(23 ed.). Williams & Wilkins. p. 807.
2498:
2474:
2450:
2441:
2396:
2346:
2308:
2280:
2271:
2262:
2228:
2188:
2132:
2125:
2060:
2017:
1980:
1971:
1934:
1902:
1893:
1876:
1795:
1750:
1703:
1660:
1651:
1626:
1598:
1591:
1073:(1). Springer Science and Business Media LLC: 422.
723:While not really a 'treatment', the martial art of
398:(a condition in which vertebrae slip forward), and
74:
50:
31:
635:et al., as measured from the inferior endplate of
240:is an X-ray taken of a patient leaning backward.
1037:"Strategies for Correcting Bad Posture – Part 4"
383:, resulting in the pelvis resting on top of the
170:. This allows for a much more efficient walking
1314:"Lordosis". Lucile Packard Children's Hospital.
687:or the inflatable ball will strengthen all the
2545:Congenital disorders of musculoskeletal system
1502:Gylys, Barbara A.; Mary Ellen Wedding (2005),
839:Deep Tissue Massage Treatment (Second Edition)
820:Medical Systems: A Body Systems Approach, 2005
278:Please review the contents of the section and
204:is an abnormally straight (or in severe cases
1846:
1569:
188:of the lumbar region, and is commonly called
8:
16:Abnormal inward curvature of the lower spine
1373:Journal of Electromyography and Kinesiology
1276:
1274:
1272:
1270:
1268:
2550:Symptoms and signs: musculoskeletal system
2447:
2277:
2268:
2129:
1977:
1899:
1890:
1853:
1839:
1831:
1657:
1595:
1576:
1562:
1554:
461:A similar impact has also been noticed in
221:Normal lordotic curvatures, also known as
65:
37:
28:
1293:. Springer Science & Business Media.
1096:
1078:
798:Stedman's Medical Dictionary, Illustrated
833:Simancek, Jeffrey A., ed. (2013-01-01),
773:Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary
539:– Common problems in the hips are tight
1448:
1143:
1131:
1119:
970:
763:
1328:
1317:
841:, St. Louis: Mosby, pp. 116–133,
775:(24 ed.). Saunders. p. 851.
7:
2374:Greig cephalopolysyndactyly syndrome
984:"Types of Spine Curvature Disorders"
828:
826:
450:Lumbar hyperlordosis (also known as
366:is a condition that occurs when the
580:– When male dancers are performing
1864:malformations and deformations of
1232:10.1097/01.bsd.0000109836.59382.47
1174:10.1097/01.bsd.0000109836.59382.47
847:10.1016/b978-0-323-07759-0.00031-6
14:
1539:Lordosis - MedlinePlus definition
1420:10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2012.11.014
835:"Chapter 8 - Back and Abdominals"
693:without involving the hip flexors
344:
252:
2047:Congenital patellar dislocation
1926:Wallis–Zieff–Goldblatt syndrome
1010:lower-back-pain-management.com/
918:10.1016/j.gaitpost.2004.01.001
280:add the appropriate references
99:is historically defined as an
1:
1385:10.1016/j.jelekin.2014.09.005
1156:Schuler Thomas C (Oct 2004).
1067:BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders
609:X-ray of lumbar hyperlordosis
1797:Intervertebral disc disorder
1035:Cressey, Eric (2010-12-09).
639:to the inferior endplate of
408:Ehlers–Danlos syndrome (EDS)
2333:Oto-palato-digital syndrome
2328:Hallermann–Streiff syndrome
2052:Congenital knee dislocation
1870:musculoskeletal abnormality
1504:Medical Terminology Systems
1214:Subach Brian R (Oct 2004).
265:reliable medical references
151:. The term comes from
2566:
2364:Craniodiaphyseal dysplasia
1080:10.1186/s12891-020-03464-2
947:"Lordotic Chest Technique"
18:
2338:Treacher Collins syndrome
2189:reduction deficits / limb
1810:Degenerative disc disease
771:Dorland, William (1965).
271:or relies too heavily on
45:
36:
2163:Cenani–Lenz syndactylism
1916:Cleidocranial dysostosis
1544:Lordosis - SpineUniverse
1346:McKenzie, Robin (2011).
796:Stedman, Thomas (1976).
103:inward curvature of the
2310:Craniofacial dysostosis
1512:"Osteoporosis-overview"
159: 'bent backward'.
143:regions is also termed
131:historically refers to
2540:Deforming dorsopathies
1866:musculoskeletal system
1815:Spinal disc herniation
1673:Ankylosing spondylitis
1549:Ways To Treat Lordosis
713:Ehlers Danlos syndrome
610:
519:allowing for too much
360:
107:. However, the terms
2418:Klippel–Feil syndrome
1820:Facet joint arthrosis
1634:Scheuermann's disease
1408:Clinical Biomechanics
608:
358:
123:regions of the human
2428:Spina bifida occulta
1944:Madelung's deformity
1921:Sprengel's deformity
1506:, F.A. Davis Company
1220:J Spinal Disord Tech
1162:J Spinal Disord Tech
452:anterior pelvic tilt
364:Lumbar hyperlordosis
359:Lumbar hyperlordosis
244:Lumbar hyperlordosis
182:Lumbar hyperlordosis
2246:RAPADILINO syndrome
1348:Treat Your Own Back
1016:on 2 September 2017
1006:"Sway back posture"
897:Lovejoy CO (2005).
652:the lumbar region.
437:Lumbar hypolordosis
421:muscles, excessive
227:intervertebral disc
174:than that of other
2108:Rocker bottom foot
906:Gait & Posture
611:
446:Signs and symptoms
361:
2522:
2521:
2518:
2517:
2514:
2513:
2443:Thoracic skeleton
2423:Spondylolisthesis
2392:
2391:
2258:
2257:
2254:
2253:
2121:
2120:
1967:
1966:
1828:
1827:
1746:
1745:
1721:Spondylolisthesis
1647:
1646:
1534:What is Lordosis?
1357:978-0-9876504-0-5
1327:Missing or empty
856:978-0-323-07759-0
748:Lordosis behavior
572:Technical factors
559:hamstring muscles
555:abdominal muscles
425:, and pregnancy.
396:spondylolisthesis
353:
352:
329:
208:) lumbar region.
94:
93:
76:Diagnostic method
26:Medical condition
21:Lordosis behavior
2557:
2490:Pectus carinatum
2485:Pectus excavatum
2448:
2406:Spinal curvature
2398:Vertebral column
2318:Crouzon syndrome
2282:Craniosynostosis
2278:
2269:
2134:fingers and toes
2130:
2042:Discoid meniscus
1999:Upington disease
1978:
1900:
1891:
1855:
1848:
1841:
1832:
1704:non inflammatory
1690:Spondylodiscitis
1658:
1600:Spinal curvature
1596:
1578:
1571:
1564:
1555:
1523:
1521:
1519:
1507:
1489:
1486:
1480:
1479:
1458:
1452:
1446:
1440:
1439:
1403:
1397:
1396:
1368:
1362:
1361:
1343:
1337:
1336:
1330:
1325:
1323:
1315:
1311:
1305:
1304:
1278:
1263:
1262:
1260:
1259:
1250:. Archived from
1211:
1205:
1204:
1202:
1201:
1192:. Archived from
1153:
1147:
1141:
1135:
1129:
1123:
1117:
1111:
1110:
1100:
1082:
1058:
1052:
1051:
1049:
1047:
1032:
1026:
1025:
1023:
1021:
1012:. Archived from
1002:
996:
995:
993:
991:
980:
974:
968:
962:
961:
959:
958:
949:. Archived from
943:
937:
936:
934:
928:. Archived from
903:
894:
888:
887:
885:
883:
872:
866:
865:
864:
863:
830:
821:
818:
812:
811:
793:
787:
786:
768:
348:
347:
339:
336:
330:
328:
287:
256:
255:
248:
162:Lordosis in the
70:
69:
61:medical genetics
41:
29:
2565:
2564:
2560:
2559:
2558:
2556:
2555:
2554:
2525:
2524:
2523:
2510:
2506:Poland syndrome
2494:
2470:
2437:
2388:
2342:
2304:
2250:
2241:Larsen syndrome
2229:multiple joints
2224:
2184:
2117:
2056:
2037:Genu recurvatum
2013:
1990:Hip dislocation
1963:
1930:
1880:
1872:
1859:
1829:
1824:
1805:Schmorl's nodes
1791:
1765:Upper back pain
1742:
1733:Spinal stenosis
1699:
1643:
1622:
1587:
1582:
1530:
1517:
1515:
1510:
1501:
1497:
1492:
1487:
1483:
1460:
1459:
1455:
1447:
1443:
1405:
1404:
1400:
1370:
1369:
1365:
1358:
1345:
1344:
1340:
1326:
1316:
1313:
1312:
1308:
1301:
1284:
1279:
1266:
1257:
1255:
1213:
1212:
1208:
1199:
1197:
1155:
1154:
1150:
1142:
1138:
1130:
1126:
1118:
1114:
1060:
1059:
1055:
1045:
1043:
1041:EricCressey.com
1034:
1033:
1029:
1019:
1017:
1004:
1003:
999:
989:
987:
982:
981:
977:
969:
965:
956:
954:
945:
944:
940:
932:
901:
896:
895:
891:
881:
879:
874:
873:
869:
861:
859:
857:
832:
831:
824:
819:
815:
808:
795:
794:
790:
783:
770:
769:
765:
761:
734:
721:
705:
689:posterior chain
663:
658:
649:
625:
620:
603:
504:
448:
439:
349:
345:
340:
334:
331:
288:
277:
273:primary sources
257:
253:
246:
219:
217:Lumbar lordosis
214:
202:Lumbar kyphosis
64:
27:
24:
17:
12:
11:
5:
2563:
2561:
2553:
2552:
2547:
2542:
2537:
2527:
2526:
2520:
2519:
2516:
2515:
2512:
2511:
2509:
2508:
2502:
2500:
2496:
2495:
2493:
2492:
2487:
2481:
2479:
2472:
2471:
2469:
2468:
2463:
2457:
2455:
2445:
2439:
2438:
2436:
2435:
2430:
2425:
2420:
2415:
2414:
2413:
2402:
2400:
2394:
2393:
2390:
2389:
2387:
2386:
2381:
2376:
2371:
2369:Dolichocephaly
2366:
2361:
2356:
2350:
2348:
2344:
2343:
2341:
2340:
2335:
2330:
2325:
2320:
2314:
2312:
2306:
2305:
2303:
2302:
2300:Trigonocephaly
2297:
2292:
2286:
2284:
2275:
2273:Skull and face
2266:
2260:
2259:
2256:
2255:
2252:
2251:
2249:
2248:
2243:
2238:
2236:Arthrogryposis
2232:
2230:
2226:
2225:
2223:
2222:
2221:
2220:
2215:
2210:
2198:
2192:
2190:
2186:
2185:
2183:
2182:
2181:
2180:
2170:
2165:
2160:
2158:Arachnodactyly
2155:
2154:
2153:
2138:
2136:
2127:
2123:
2122:
2119:
2118:
2116:
2115:
2110:
2105:
2100:
2099:
2098:
2086:
2085:
2084:
2079:
2066:
2064:
2062:foot deformity
2058:
2057:
2055:
2054:
2049:
2044:
2039:
2034:
2029:
2023:
2021:
2015:
2014:
2012:
2011:
2006:
2001:
1996:
1986:
1984:
1975:
1969:
1968:
1965:
1964:
1962:
1961:
1956:
1951:
1946:
1940:
1938:
1936:hand deformity
1932:
1931:
1929:
1928:
1923:
1918:
1912:
1910:
1897:
1888:
1874:
1873:
1860:
1858:
1857:
1850:
1843:
1835:
1826:
1825:
1823:
1822:
1817:
1812:
1807:
1801:
1799:
1793:
1792:
1790:
1789:
1784:
1783:
1782:
1777:
1767:
1762:
1756:
1754:
1748:
1747:
1744:
1743:
1741:
1740:
1738:Facet syndrome
1735:
1730:
1729:
1728:
1726:Retrolisthesis
1718:
1713:
1707:
1705:
1701:
1700:
1698:
1697:
1695:Pott's disease
1692:
1687:
1682:
1677:
1676:
1675:
1664:
1662:
1655:
1649:
1648:
1645:
1644:
1642:
1641:
1636:
1630:
1628:
1624:
1623:
1621:
1620:
1615:
1610:
1604:
1602:
1593:
1589:
1588:
1585:Spinal disease
1583:
1581:
1580:
1573:
1566:
1558:
1552:
1551:
1546:
1541:
1536:
1529:
1528:External links
1526:
1525:
1524:
1508:
1496:
1493:
1491:
1490:
1481:
1453:
1441:
1398:
1363:
1356:
1338:
1306:
1300:978-3540690917
1299:
1285:Norbert Boos,
1264:
1206:
1148:
1136:
1124:
1112:
1053:
1027:
997:
975:
963:
938:
935:on 2012-01-21.
889:
867:
855:
822:
813:
806:
788:
781:
762:
760:
757:
756:
755:
753:Pott's disease
750:
745:
743:Kyphoscoliosis
740:
733:
730:
720:
717:
704:
701:
662:
659:
657:
654:
648:
645:
624:
621:
619:
616:
602:
599:
598:
597:
591:– Over 45% of
586:
578:Improper lifts
569:
568:
562:
548:
534:
528:
503:
500:
491:rectus femoris
447:
444:
438:
435:
392:Achondroplasia
351:
350:
343:
341:
335:September 2016
260:
258:
251:
245:
242:
218:
215:
213:
210:
127:. Similarly,
92:
91:
78:
72:
71:
54:
48:
47:
43:
42:
34:
33:
25:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2562:
2551:
2548:
2546:
2543:
2541:
2538:
2536:
2533:
2532:
2530:
2507:
2504:
2503:
2501:
2497:
2491:
2488:
2486:
2483:
2482:
2480:
2477:
2473:
2467:
2464:
2462:
2459:
2458:
2456:
2453:
2449:
2446:
2444:
2440:
2434:
2433:Sacralization
2431:
2429:
2426:
2424:
2421:
2419:
2416:
2412:
2409:
2408:
2407:
2404:
2403:
2401:
2399:
2395:
2385:
2382:
2380:
2379:Plagiocephaly
2377:
2375:
2372:
2370:
2367:
2365:
2362:
2360:
2357:
2355:
2352:
2351:
2349:
2345:
2339:
2336:
2334:
2331:
2329:
2326:
2324:
2323:Hypertelorism
2321:
2319:
2316:
2315:
2313:
2311:
2307:
2301:
2298:
2296:
2293:
2291:
2290:Scaphocephaly
2288:
2287:
2285:
2283:
2279:
2276:
2274:
2270:
2267:
2265:
2261:
2247:
2244:
2242:
2239:
2237:
2234:
2233:
2231:
2227:
2219:
2216:
2214:
2211:
2209:
2206:
2205:
2204:
2203:
2199:
2197:
2194:
2193:
2191:
2187:
2179:
2176:
2175:
2174:
2173:Brachydactyly
2171:
2169:
2166:
2164:
2161:
2159:
2156:
2152:
2149:
2148:
2147:
2143:
2140:
2139:
2137:
2135:
2131:
2128:
2126:Either / both
2124:
2114:
2111:
2109:
2106:
2104:
2101:
2097:
2094:
2093:
2092:
2091:
2087:
2083:
2080:
2078:
2075:
2074:
2073:
2072:
2068:
2067:
2065:
2063:
2059:
2053:
2050:
2048:
2045:
2043:
2040:
2038:
2035:
2033:
2030:
2028:
2025:
2024:
2022:
2020:
2016:
2010:
2007:
2005:
2002:
2000:
1997:
1995:
1994:Hip dysplasia
1991:
1988:
1987:
1985:
1983:
1979:
1976:
1974:
1970:
1960:
1957:
1955:
1952:
1950:
1947:
1945:
1942:
1941:
1939:
1937:
1933:
1927:
1924:
1922:
1919:
1917:
1914:
1913:
1911:
1909:
1905:
1901:
1898:
1896:
1892:
1889:
1887:
1883:
1879:
1875:
1871:
1867:
1863:
1856:
1851:
1849:
1844:
1842:
1837:
1836:
1833:
1821:
1818:
1816:
1813:
1811:
1808:
1806:
1803:
1802:
1800:
1798:
1794:
1788:
1787:Radiculopathy
1785:
1781:
1778:
1776:
1773:
1772:
1771:
1770:Low back pain
1768:
1766:
1763:
1761:
1758:
1757:
1755:
1753:
1749:
1739:
1736:
1734:
1731:
1727:
1724:
1723:
1722:
1719:
1717:
1716:Spondylolysis
1714:
1712:
1709:
1708:
1706:
1702:
1696:
1693:
1691:
1688:
1686:
1683:
1681:
1678:
1674:
1671:
1670:
1669:
1666:
1665:
1663:
1659:
1656:
1654:
1653:Spondylopathy
1650:
1640:
1637:
1635:
1632:
1631:
1629:
1625:
1619:
1616:
1614:
1611:
1609:
1606:
1605:
1603:
1601:
1597:
1594:
1590:
1586:
1579:
1574:
1572:
1567:
1565:
1560:
1559:
1556:
1550:
1547:
1545:
1542:
1540:
1537:
1535:
1532:
1531:
1527:
1513:
1509:
1505:
1499:
1498:
1494:
1485:
1482:
1477:
1473:
1470:(7): 454–64.
1469:
1465:
1457:
1454:
1450:
1445:
1442:
1437:
1433:
1429:
1425:
1421:
1417:
1414:(5): 171–77.
1413:
1409:
1402:
1399:
1394:
1390:
1386:
1382:
1379:(2): 310–15.
1378:
1374:
1367:
1364:
1359:
1353:
1349:
1342:
1339:
1334:
1321:
1310:
1307:
1302:
1296:
1292:
1288:
1282:
1277:
1275:
1273:
1271:
1269:
1265:
1254:on 2013-07-21
1253:
1249:
1245:
1241:
1237:
1233:
1229:
1226:(5): 372–79.
1225:
1221:
1217:
1210:
1207:
1196:on 2013-07-21
1195:
1191:
1187:
1183:
1179:
1175:
1171:
1168:(5): 372–79.
1167:
1163:
1159:
1152:
1149:
1145:
1140:
1137:
1133:
1128:
1125:
1121:
1116:
1113:
1108:
1104:
1099:
1094:
1090:
1086:
1081:
1076:
1072:
1068:
1064:
1057:
1054:
1042:
1038:
1031:
1028:
1015:
1011:
1007:
1001:
998:
985:
979:
976:
972:
967:
964:
953:on 2020-02-13
952:
948:
942:
939:
931:
927:
923:
919:
915:
912:(1): 95–112.
911:
907:
900:
893:
890:
877:
871:
868:
858:
852:
848:
844:
840:
836:
829:
827:
823:
817:
814:
809:
803:
799:
792:
789:
784:
782:9780721631462
778:
774:
767:
764:
758:
754:
751:
749:
746:
744:
741:
739:
738:Hyperkyphosis
736:
735:
731:
729:
726:
718:
716:
714:
710:
702:
700:
696:
694:
690:
686:
680:
677:
675:
674:hyperkyphosis
671:
666:
660:
655:
653:
646:
644:
642:
638:
634:
630:
622:
617:
615:
607:
600:
594:
590:
587:
583:
579:
576:
575:
574:
573:
566:
563:
560:
556:
552:
549:
546:
542:
538:
535:
532:
529:
526:
522:
518:
514:
513:
509:
508:
507:
501:
499:
496:
492:
488:
483:
478:
474:
472:
471:abdominal fat
466:
464:
459:
455:
453:
445:
443:
436:
434:
432:
428:
424:
420:
416:
411:
409:
405:
401:
397:
393:
388:
386:
382:
378:
374:
369:
365:
357:
342:
338:
327:
324:
320:
317:
313:
310:
306:
303:
299:
296: –
295:
291:
290:Find sources:
285:
281:
275:
274:
270:
266:
261:This section
259:
250:
249:
243:
241:
239:
238:lordotic view
235:
230:
228:
224:
216:
211:
209:
207:
203:
199:
195:
191:
187:
184:is excessive
183:
179:
177:
173:
169:
165:
160:
158:
154:
150:
146:
142:
138:
134:
130:
126:
122:
118:
114:
110:
106:
102:
98:
90:
86:
82:
79:
77:
73:
68:
62:
58:
55:
53:
49:
44:
40:
35:
30:
22:
2354:Macrocephaly
2200:
2196:Acheiropodia
2168:Ectrodactyly
2088:
2069:
1954:Oligodactyly
1949:Clinodactyly
1878:Appendicular
1680:Sacroiliitis
1661:inflammatory
1612:
1516:. Retrieved
1503:
1484:
1467:
1463:
1456:
1444:
1411:
1407:
1401:
1376:
1372:
1366:
1347:
1341:
1309:
1290:
1256:. Retrieved
1252:the original
1223:
1219:
1209:
1198:. Retrieved
1194:the original
1165:
1161:
1151:
1139:
1127:
1115:
1070:
1066:
1056:
1044:. Retrieved
1040:
1030:
1018:. Retrieved
1014:the original
1009:
1000:
988:. Retrieved
978:
966:
955:. Retrieved
951:the original
941:
930:the original
909:
905:
892:
882:December 15,
880:. Retrieved
870:
860:, retrieved
838:
816:
797:
791:
772:
766:
722:
709:Boston brace
706:
697:
692:
681:
678:
667:
664:
650:
626:
612:
588:
577:
571:
570:
565:Growth spurt
564:
550:
536:
530:
510:
505:
479:
475:
467:
460:
456:
449:
440:
423:visceral fat
412:
400:osteoporosis
389:
363:
362:
332:
322:
315:
308:
301:
289:
269:verification
262:
237:
231:
222:
220:
201:
197:
193:
189:
181:
180:
161:
156:
148:
144:
132:
112:
108:
105:lumbar spine
100:
96:
95:
57:Rheumatology
2384:Saddle nose
2151:Webbed toes
2142:Polydactyly
2027:Genu valgum
1959:Polydactyly
1711:Spondylosis
1668:Spondylitis
1639:Torticollis
685:Roman chair
582:dance lifts
541:hip flexors
521:flexibility
463:trans women
381:pelvic tilt
377:hip flexors
263:needs more
194:saddle back
190:hollow back
164:human spine
2535:Human back
2529:Categories
2359:Platybasia
2295:Oxycephaly
2208:Phocomelia
2202:Ectromelia
2178:Stub thumb
2146:Syndactyly
2113:Hammer toe
2082:Pigeon toe
2032:Genu varum
2004:Coxa valga
1862:Congenital
1775:Coccydynia
1518:8 December
1495:References
1329:|url=
1258:2009-12-10
1200:2009-12-10
990:8 December
957:2009-11-14
876:"Lordosis"
862:2020-11-03
807:0683079247
647:MRI and CT
593:anatomical
495:quadriceps
482:lower back
375:and tight
373:hamstrings
305:newspapers
294:"Lordosis"
2411:Scoliosis
2218:Hemimelia
2103:Pes cavus
2096:Flat feet
2077:Club foot
2009:Coxa vara
1760:Neck pain
1752:Back pain
1618:Scoliosis
1592:Deforming
1514:. A.D.A.M
1089:1471-2474
1046:17 August
1020:17 August
878:. Wordnik
759:Footnotes
670:scoliosis
661:Exercises
656:Treatment
601:Diagnosis
545:arabesque
517:vertebrae
487:iliopsoas
431:vitamin D
234:radiology
223:secondary
198:Sway back
186:extension
52:Specialty
2461:Cervical
1908:shoulder
1904:clavicle
1886:dysmelia
1780:Sciatica
1685:Discitis
1613:Lordosis
1608:Kyphosis
1436:23316030
1428:23261019
1393:25262160
1320:cite web
1289:(2008).
1287:Max Aebi
1248:23503809
1240:15385876
1190:23503809
1182:15385876
1107:32611342
926:15536039
732:See also
633:Stagnara
618:Scanning
485:of weak
419:low back
415:swayback
404:discitis
176:primates
149:kyphotic
145:kyphosis
137:thoracic
133:abnormal
129:kyphosis
121:cervical
113:lordotic
109:lordosis
101:abnormal
97:Lordosis
32:Lordosis
2476:sternum
1476:7989879
1098:7331160
986:. WebMD
725:tai chi
719:Tai chi
589:Overuse
551:Muscles
493:of the
427:Rickets
319:scholar
284:removed
89:CT Scan
2499:other:
2213:Amelia
2090:valgus
1474:
1434:
1426:
1391:
1354:
1297:
1281:p. 769
1246:
1238:
1188:
1180:
1134:p. 193
1122:p. 122
1105:
1095:
1087:
924:
853:
804:
779:
703:Braces
629:X-rays
525:injury
502:Causes
385:thighs
368:lumbar
321:
314:
307:
300:
292:
206:flexed
168:pelvis
157:lordos
141:sacral
117:lumbar
63:
2466:Bifid
2347:other
2264:Axial
2071:varus
1627:Other
1451:p. 36
1432:S2CID
1244:S2CID
1186:S2CID
1146:p. 45
973:p. 85
933:(PDF)
902:(PDF)
623:X-ray
585:back.
512:Spine
326:JSTOR
312:books
212:Types
155:
153:Greek
125:spine
81:X-ray
2452:ribs
2019:knee
1895:Arms
1882:limb
1520:2013
1472:PMID
1424:PMID
1389:PMID
1352:ISBN
1333:help
1295:ISBN
1283:in:
1236:PMID
1178:PMID
1103:PMID
1085:ISSN
1048:2014
1022:2014
992:2013
922:PMID
884:2013
851:ISBN
802:ISBN
777:ISBN
707:The
537:Hips
531:Legs
429:, a
298:news
267:for
236:, a
192:or
172:gait
139:and
119:and
111:and
1982:hip
1973:Leg
1416:doi
1381:doi
1228:doi
1170:doi
1093:PMC
1075:doi
914:doi
843:doi
672:or
637:T12
232:In
147:or
85:MRI
2531::
2144:/
1992:/
1906:/
1884:/
1868:/
1500:*
1468:17
1466:.
1430:.
1422:.
1412:28
1410:.
1387:.
1377:25
1375:.
1324::
1322:}}
1318:{{
1267:^
1242:.
1234:.
1224:17
1222:.
1218:.
1184:.
1176:.
1166:17
1164:.
1160:.
1101:.
1091:.
1083:.
1071:21
1069:.
1065:.
1039:.
1008:.
920:.
910:21
908:.
904:.
849:,
837:,
825:^
641:L5
387:.
286:.
87:,
83:,
59:,
2478::
2454::
1854:e
1847:t
1840:v
1577:e
1570:t
1563:v
1522:.
1478:.
1438:.
1418::
1395:.
1383::
1360:.
1335:)
1331:(
1303:.
1261:.
1230::
1203:.
1172::
1109:.
1077::
1050:.
1024:.
994:.
960:.
916::
886:.
845::
810:.
785:.
527:.
337:)
333:(
323:·
316:·
309:·
302:·
276:.
23:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.