1249:
1259:
33:
198:
can distinguish between facultative anaerobes and aerotolerant organisms. If the organism is using fermentation in an anaerobic environment, the addition of oxygen will cause facultative anaerobes to suspend fermentation and begin using oxygen for respiration. Aerotolerant organisms must continue
95:
environment. The ability to exhibit aerobic respiration may yield benefits to the aerobic organism, as aerobic respiration yields more energy than anaerobic respiration. Energy production of the cell involves the synthesis of
62:
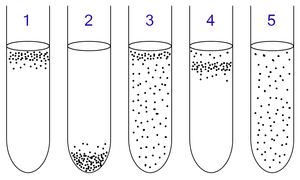
can grow with or without oxygen because they can metabolise energy aerobically or anaerobically. They gather mostly at the top because aerobic respiration generates more ATP than either fermentation or anaerobic respiration.
277:
In
Oxidative phosphorylation, ATP is synthesized from ADP and a phosphate using ATP synthase. ATP synthase is powered by a proton-motive force created by using the energy generated from the electron transport chain. A
345:
69:
need oxygen because they cannot ferment or respire anaerobically. However, they are poisoned by high concentrations of oxygen. They gather in the upper part of the test tube but not the very top.
75:
do not require oxygen as they metabolise energy anaerobically. Unlike obligate anaerobes however, they are not poisoned by oxygen. They can be found evenly spread throughout the test tube.
282:(H) has a positive charge and if separated by a cellular membrane, it creates a difference in charge between the inside and outside of the membrane. Oxidative phosphorylation occurs in the
452:"These Microbes May Have Survived 100 Million Years Beneath the Seafloor - Rescued from their cold, cramped and nutrient-poor homes, the bacteria awoke in the lab and grew"
104:. In aerobic respiration, ATP synthase is coupled with an electron transport chain in which oxygen acts as a terminal electron acceptor. In July 2020,
297:
because it acts as the terminal electron acceptor in prokaryotes' electron transport chain. Molecular Oxygen is reduced to water in this process.
50:
need oxygen because they cannot ferment or respire anaerobically. They gather at the top of the tube where the oxygen concentration is highest.
374:
350:
955:
695:
614:
574:
129:
945:
872:
1069:
800:
167:
1188:
1283:
1293:
326:
316:
199:
fermentation in the presence of oxygen. Facultative organisms grow in both oxygen rich media and oxygen free media.
910:
451:
235:
1064:
987:
950:
746:
56:
are poisoned by oxygen, so they gather at the bottom of the tube where the oxygen concentration is lowest.
1140:
1059:
1038:
688:
271:
97:
1288:
1180:
822:
259:
59:
1262:
1020:
895:
878:
716:
489:
145:
41:
1145:
1030:
1025:
918:
888:
741:
726:
311:
180:
require oxygen for energy production, but are harmed by atmospheric concentrations of oxygen (21% O
113:
1175:
1074:
883:
795:
788:
208:
171:
125:
72:
631:
1252:
1115:
1081:
1048:
905:
900:
858:
805:
681:
659:
651:
610:
580:
570:
515:
432:
380:
370:
321:
306:
231:
194:
When an organism is able to survive in both oxygen and anaerobic environments, the use of the
53:
967:
843:
643:
505:
497:
422:
414:
1193:
1092:
977:
853:
783:
736:
141:
47:
493:
848:
812:
510:
478:"Aerobic microbial life persists in oxic marine sediment as old as 101.5 million years"
477:
427:
402:
216:
195:
177:
105:
66:
630:
Borisov, Vitaliy B.; Verkhovsky, Michael I. (23 October 2015). Stewart, Valley (ed.).
1277:
1202:
1087:
1043:
1015:
1006:
996:
972:
868:
647:
283:
222:
This equation is a summary of what happens in three series of biochemical reactions:
109:
1232:
1217:
1097:
838:
756:
704:
279:
187:
101:
539:
476:
Morono Y, Ito M, Hoshino T, Terada T, Hori T, Ikehara M, et al. (July 2020).
569:(4 ed.). Galveston, Texas: University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston.
1120:
227:
17:
501:
1227:
1212:
1130:
863:
564:
563:
Hentges DJ (1996). "17: Anaerobes:General
Characteristics". In Baron S (ed.).
384:
223:
655:
1222:
1053:
1011:
923:
817:
403:"The aerobic mitochondrial ATP synthesis from a comprehensive point of view"
287:
149:
663:
584:
519:
436:
364:
731:
708:
673:
117:
88:
37:
418:
1161:
1125:
761:
212:
32:
1207:
962:
161:
121:
92:
1135:
153:
31:
366:
Metals, Microbes, and
Minerals - The Biogeochemical Side of Life
677:
157:
128:(SPG) ("the deadest spot in the ocean"), and could be the
369:(1st ed.). Berlin: de Gruyter GmbH & Co. KG.
219:) is oxidized to power the electron transport chain:
120:, up to 101.5 million years old, 250 feet below the
1174:
1154:
1106:
995:
986:
938:
831:
769:
755:
715:
40:can be identified by growing them in test tubes of
27:Organism that thrives in an oxygenated environment
401:Morelli AM, Ravera S, Panfoli I (October 2020).
689:
538:Todar K. "Nutrition and Growth of Bacteria".
170:use oxygen if it is available, but also have
8:
190:do not use oxygen but are not harmed by it.
144:need oxygen to grow. In a process known as
992:
766:
696:
682:
674:
607:Principles of Biochemistry and Biophysics
509:
426:
363:Kroneck PM, Sosa Torres ME, eds. (2021).
211:to create ATP from ADP and a phosphate.
541:Todar's Online Textbook of Bacteriology
533:
531:
529:
338:
207:Aerobic organisms use a process called
7:
1258:
396:
394:
609:. Laxmi Publications. p. 530.
25:
1257:
1248:
1247:
648:10.1128/ecosalplus.ESP-0012-2015
148:, these organisms use oxygen to
91:that can survive and grow in an
946:Bacterial cellular morphologies
642:(2): ecosalplus.ESP–0012–2015.
1:
174:methods of energy production.
351:Dorland's Medical Dictionary
327:Oxygenation (environmental)
317:Fermentation (biochemistry)
293:Aerobic respiration needs O
1310:
1189:Bacteria (classifications)
911:Primary nutritional groups
502:10.1038/s41467-020-17330-1
118:organically poor sediments
1243:
236:oxidative phosphorylation
130:longest-living life forms
114:quasi-suspended animation
1065:Bacterial outer membrane
152:substrates (for example
1060:Gram-negative bacteria
1039:Gram-positive bacteria
450:Wu KJ (28 July 2020).
262:+ 38 phosphate → 6 CO
188:Aerotolerant anaerobes
108:reported that aerobic
76:
73:Aerotolerant organisms
36:Aerobic and anaerobic
915:Substrate preference
482:Nature Communications
168:Facultative anaerobes
60:Facultative anaerobes
35:
1284:Cellular respiration
896:Microbial metabolism
632:"Oxygen as Acceptor"
566:Medical Microbiology
203:Aerobic Respiration
146:cellular respiration
100:by an enzyme called
42:thioglycollate broth
1294:Biology terminology
1146:Non-motile bacteria
742:Pathogenic bacteria
605:Chauhan BS (2008).
494:2020NatCo..11.3626M
419:10.1098/rsob.200224
312:Anaerobic digestion
230:(also known as the
209:aerobic respiration
1075:Lipopolysaccharide
456:The New York Times
126:South Pacific Gyre
77:
54:Obligate anaerobes
1271:
1270:
1170:
1169:
1116:Bacterial capsule
1082:Periplasmic space
1049:Lipoteichoic acid
934:
933:
906:Microbial ecology
901:Nitrogen fixation
376:978-3-11-058890-3
322:Aerobic vaginitis
307:Aerobic digestion
232:Citric acid cycle
116:", were found in
106:marine biologists
16:(Redirected from
1301:
1261:
1260:
1251:
1250:
1199:Former groupings
993:
844:Human microbiome
767:
698:
691:
684:
675:
668:
667:
627:
621:
620:
602:
596:
595:
593:
591:
560:
554:
553:
551:
549:
535:
524:
523:
513:
473:
467:
466:
464:
462:
447:
441:
440:
430:
398:
389:
388:
360:
354:
343:
142:Obligate aerobes
81:aerobic organism
48:Obligate aerobes
21:
18:Obligate aerobic
1309:
1308:
1304:
1303:
1302:
1300:
1299:
1298:
1274:
1273:
1272:
1267:
1239:
1194:Bacterial phyla
1178:
1166:
1150:
1108:
1102:
1093:Arabinogalactan
998:
982:
930:
827:
771:
759:
751:
737:Lysogenic cycle
718:
711:
702:
672:
671:
629:
628:
624:
617:
604:
603:
599:
589:
587:
577:
562:
561:
557:
547:
545:
537:
536:
527:
475:
474:
470:
460:
458:
449:
448:
444:
400:
399:
392:
377:
362:
361:
357:
344:
340:
335:
303:
296:
269:
265:
257:
253:
249:
245:
205:
183:
178:Microaerophiles
160:) and generate
138:
70:
67:Microaerophiles
64:
57:
51:
45:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1307:
1305:
1297:
1296:
1291:
1286:
1276:
1275:
1269:
1268:
1266:
1265:
1255:
1244:
1241:
1240:
1238:
1237:
1236:
1235:
1230:
1225:
1220:
1210:
1205:
1196:
1191:
1185:
1183:
1172:
1171:
1168:
1167:
1165:
1164:
1158:
1156:
1152:
1151:
1149:
1148:
1143:
1138:
1133:
1128:
1123:
1118:
1112:
1110:
1104:
1103:
1101:
1100:
1095:
1084:
1079:
1078:
1077:
1072:
1056:
1051:
1046:
1035:
1034:
1033:
1028:
1023:
1009:
1003:
1001:
990:
984:
983:
981:
980:
975:
970:
965:
960:
959:
958:
953:
951:cell structure
942:
940:
936:
935:
932:
931:
929:
928:
927:
926:
924:Saccharophilic
921:
913:
908:
903:
898:
893:
892:
891:
886:
881:
876:
866:
861:
856:
851:
841:
835:
833:
829:
828:
826:
825:
820:
815:
813:Microaerophile
810:
809:
808:
803:
793:
792:
791:
786:
775:
773:
764:
753:
752:
750:
749:
744:
739:
734:
729:
723:
721:
713:
712:
703:
701:
700:
693:
686:
678:
670:
669:
622:
616:978-8131803226
615:
597:
575:
555:
525:
468:
442:
413:(10): 200224.
390:
375:
355:
337:
336:
334:
331:
330:
329:
324:
319:
314:
309:
302:
299:
294:
275:
274:
267:
263:
255:
251:
247:
243:
217:monosaccharide
204:
201:
196:Pasteur effect
192:
191:
185:
181:
175:
165:
137:
134:
112:(mainly), in "
110:microorganisms
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1306:
1295:
1292:
1290:
1287:
1285:
1282:
1281:
1279:
1264:
1256:
1254:
1246:
1245:
1242:
1234:
1231:
1229:
1226:
1224:
1221:
1219:
1216:
1215:
1214:
1211:
1209:
1206:
1204:
1203:Schizomycetes
1200:
1197:
1195:
1192:
1190:
1187:
1186:
1184:
1182:
1177:
1173:
1163:
1160:
1159:
1157:
1153:
1147:
1144:
1142:
1139:
1137:
1134:
1132:
1129:
1127:
1124:
1122:
1119:
1117:
1114:
1113:
1111:
1105:
1099:
1096:
1094:
1091:
1089:
1085:
1083:
1080:
1076:
1073:
1071:
1068:
1067:
1066:
1063:
1061:
1057:
1055:
1052:
1050:
1047:
1045:
1044:Teichoic acid
1042:
1040:
1036:
1032:
1029:
1027:
1024:
1022:
1019:
1018:
1017:
1016:Peptidoglycan
1013:
1010:
1008:
1007:Cell membrane
1005:
1004:
1002:
1000:
994:
991:
989:
985:
979:
976:
974:
971:
969:
966:
964:
961:
957:
954:
952:
949:
948:
947:
944:
943:
941:
937:
925:
922:
920:
917:
916:
914:
912:
909:
907:
904:
902:
899:
897:
894:
890:
887:
885:
882:
880:
877:
874:
870:
867:
865:
862:
860:
857:
855:
852:
850:
847:
846:
845:
842:
840:
837:
836:
834:
830:
824:
821:
819:
816:
814:
811:
807:
804:
802:
799:
798:
797:
794:
790:
787:
785:
782:
781:
780:
777:
776:
774:
768:
765:
763:
758:
754:
748:
745:
743:
740:
738:
735:
733:
730:
728:
725:
724:
722:
720:
714:
710:
706:
699:
694:
692:
687:
685:
680:
679:
676:
665:
661:
657:
653:
649:
645:
641:
637:
633:
626:
623:
618:
612:
608:
601:
598:
586:
582:
578:
576:9780963117212
572:
568:
567:
559:
556:
543:
542:
534:
532:
530:
526:
521:
517:
512:
507:
503:
499:
495:
491:
487:
483:
479:
472:
469:
457:
453:
446:
443:
438:
434:
429:
424:
420:
416:
412:
408:
404:
397:
395:
391:
386:
382:
378:
372:
368:
367:
359:
356:
353:
352:
347:
342:
339:
332:
328:
325:
323:
320:
318:
315:
313:
310:
308:
305:
304:
300:
298:
291:
289:
285:
281:
273:
261:
241:
240:
239:
237:
233:
229:
225:
220:
218:
214:
210:
202:
200:
197:
189:
186:
179:
176:
173:
169:
166:
163:
159:
155:
151:
147:
143:
140:
139:
135:
133:
131:
127:
123:
119:
115:
111:
107:
103:
99:
94:
90:
86:
82:
74:
68:
61:
55:
49:
43:
39:
34:
30:
19:
1289:Microbiology
1233:Mendosicutes
1218:Gracilicutes
1198:
1098:Mycolic acid
1088:Mycobacteria
1086:
1058:
1037:
973:Coccobacilli
873:in pregnancy
839:Extremophile
823:Aerotolerant
778:
757:Biochemistry
719:microbiology
705:Microbiology
639:
635:
625:
606:
600:
588:. Retrieved
565:
558:
546:. Retrieved
540:
485:
481:
471:
459:. Retrieved
455:
445:
410:
407:Open Biology
406:
365:
358:
349:
341:
292:
284:mitochondria
280:hydrogen ion
276:
221:
206:
193:
132:ever found.
102:ATP synthase
84:
80:
78:
29:
1121:Slime layer
801:Facultative
789:Facultative
636:EcoSal Plus
544:. p. 4
488:(1): 3626.
228:Krebs cycle
1278:Categories
1228:Mollicutes
1223:Firmicutes
1213:Prokaryota
1131:Glycocalyx
956:plasticity
919:Lipophilic
772:preference
747:Resistance
385:1201187551
333:References
288:eukaryotes
224:glycolysis
93:oxygenated
1181:evolution
1155:Composite
1054:Endospore
1012:Cell wall
988:Structure
879:Placental
818:Nanaerobe
796:Anaerobic
727:Infection
656:2324-6200
172:anaerobic
1253:Category
1176:Taxonomy
1109:envelope
999:envelope
889:Salivary
806:Obligate
784:Obligate
732:Exotoxin
709:Bacteria
664:26734697
585:21413255
520:32724059
437:33081639
346:"aerobe"
301:See also
122:seafloor
89:organism
38:bacteria
1263:Commons
1162:Biofilm
1141:Fimbria
1126:S-layer
1107:Outside
968:Bacilli
884:Uterine
869:Vaginal
779:Aerobic
762:ecology
717:Medical
590:24 July
548:24 July
511:7387439
490:Bibcode
461:31 July
428:7653358
270:O + 38
234:), and
213:Glucose
150:oxidize
124:in the
1208:Monera
978:Spiral
770:Oxygen
662:
654:
613:
583:
573:
518:
508:
435:
425:
383:
373:
266:+ 44 H
226:, the
162:energy
154:sugars
87:is an
85:aerobe
1136:Pilus
1090:only:
1070:Porin
1062:only:
1041:only:
963:Cocci
939:Shape
859:Mouth
832:Other
258:+ 38
254:+ 6 O
136:Types
1179:and
997:Cell
864:Skin
854:Lung
760:and
660:PMID
652:ISSN
611:ISBN
592:2016
581:PMID
571:ISBN
550:2016
516:PMID
463:2020
433:PMID
381:OCLC
371:ISBN
158:fats
156:and
1031:DAP
1026:NAG
1021:NAM
849:Gut
644:doi
506:PMC
498:doi
423:PMC
415:doi
348:at
290:.
286:of
272:ATP
260:ADP
215:(a
98:ATP
83:or
79:An
71:5:
65:4:
58:3:
52:2:
46:1:
1280::
1201::
1014::
707::
658:.
650:.
638:.
634:.
579:.
528:^
514:.
504:.
496:.
486:11
484:.
480:.
454:.
431:.
421:.
411:10
409:.
405:.
393:^
379:.
248:12
238:.
184:).
44::
875:)
871:(
697:e
690:t
683:v
666:.
646::
640:6
619:.
594:.
552:.
522:.
500::
492::
465:.
439:.
417::
387:.
295:2
268:2
264:2
256:2
252:6
250:O
246:H
244:6
242:C
182:2
164:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.