54:
256:
228:
670:. Traits that are dominantly inherited cannot skip generations, meaning that two nonroan parents cannot produce a roan offspring. In cases where roan has appeared to skip generations, one of the parents is usually discovered to be slightly roaned. A roan can also be born from two seemingly nonroan parents if the roan coat is "masked" by extensive white markings or gray. In some cases, the supposedly roan offspring is not true roan at all, but rabicano, sabino, or influenced by some other genetic factor.
433:
414:, also called white ticking. While true roans have an even intermixture of white hairs throughout the body, except the extremities, the white hairs of a rabicano are densest around the base of the tail and the flank. Rabicano roaning frequently forms rings of white hair around the base of the tail, and in extensively roaned rabicanos, the white hairs may converge to form vertical stripes over the ribcage. Rabicano is found in many breeds, and may account for some "roan"
212:
483:, one type of leopard complex coat color also called "marble", is an all-over blend of white and colored hairs. Patches of skin that lie close to the bone, such as on the face and legs, and the point of shoulder and point of hip, do not grow as much white hair. These darker patches are called "varnish marks" and are not found in true roans. Varnish roans can also be distinguished from true roans by the presence of leopard complex characteristics, such as the white
200:
193:, the coat grows back in solid-colored without any white hairs. These regions of solid-colored coat are called "corn spots" or "corn marks", and can appear even without the horse having had a visible injury. Another trait is reverse dappling; many horses develop rings of hair that appear slightly different-colored, called dapples, which often indicate good health. Usually dapples are darker than the surrounding coat, but on a roan, the dapples are lighter.
300:
38:
244:
46:
2287:
460:
397:
355:
1869:"The paper by Hintz and Van Vleck caused all this commotion, but there were earlier mentions of a roan cross being lethal, too," Penedo explained. "But it was never fully established by any molecular analysis that homozygous roan horses would not be produced from matings of two roan parents." in Overton, 2004.
181:
Some roan horses have more white hair than others, and even individual horses may look lighter or darker based on the season, and their coats may vary from year to year. While roan is always present at birth, the soft first coat of newborn foals may not show the white hairs well. Some roan horses get
748:
The belief in "lethal roan" persisted until recently, when homozygous roan stallions with large numbers of offspring - all roan - were satisfactorily identified. Homozygous roan stallions were identified in both
European populations of Belgian horses in 1977, and in North American, in Quarter Horse
636:
as a mixture of white with red or brown hairs, but which researchers identify as chestnuts turning gray. The
Arabian Horse Association defines "roan" as an even mixture of white and colored, usually chestnut, hairs, but researchers suggest most animals so classified are probably either rabicano, or
110:
Horses with the roan pattern have an even mixture of white and colored hairs in the coat. These interspersed white hairs are more scattered or absent on the horse's head, mane, tail, and lower legs. The unaffected color on the legs often forms a sharp, inverted "V" above the knee and hock, not seen
444:
white spotting patterns. Many patterns in many breeds are called "sabino", and these patterns usually feature irregular, rough-edged patches of white that originate from the lower legs, face, and ventral midline. The borders of these white patches can be heavily roaned, and some sabinos can be
279:
indicates that "true roan" or "classic roan" is distinct from several similar patterns that are collectively called "roaning". In studies of the white patterning genotypes of laboratory mice, no fewer than four produced roaning or flecking. Therefore, the existence of other types of roaning
227:
907:), it will outwardly appear blue roan, barring the influence of other genes. Normally, the chestnut and roan alleles would be separated during chromosomal crossover, but these two linked genes usually remain together. Such a horse will produce sex cells that are either
311:. However, grays lighten with age, while roans do not. Gray is one of the most common coat colors found in horses, and is found in almost all breeds. The defining characteristic of the gray coat is that it becomes progressively lighter over time. Gray
704:
3 (ECA3) in the KIT sequence. A roan zygosity test is reliable for
American Quarter Horse, American Paint Horse, Welsh Pony, and Gypsy Cob. Until a direct test is developed, the roan zygosity test may enable breeders to produce roans more reliably.
101:
coat color, which also begins with intermixed white and colored hairs, roans do not become progressively lighter in color as they age. The silvering effect of mixed white and colored hairs can create coats that look bluish or pinkish.
625:-patterned stallion Catch A Bird phenotypically appear to be true roan, and though few of those reproduced, some offspring of his daughter Slip Catch, though registered as bay, have apparently been verified as carrying the roan gene.
323:
is unchanged. The first white hairs are usually seen around the muzzle and eyes. As a gray may go from entirely colored to entirely white over the course of its life, the process of "graying out" can, at times, closely resemble roan.
76:, and tail—are mostly solid-colored. Horses with roan coats have white hairs evenly intermingled throughout any other color. The head, legs, mane, and tail have fewer scattered white hairs or none at all. The roan pattern is
255:
1385:
The progressive loss of colour in the hair of grey horses is controlled by a dominantly inherited allele at the Grey locus (G^G). Foals are born any colour depending on the alleles present at other colour determining
842:, and roan. Research since equine linkage group II was defined has identified the exact location of the tobiano allele and the chestnut allele. The region of the chromosome that harbors the roan gene is
96:
for roan in several breeds. True roan is always present at birth, though it may be hard to see until after the foal coat sheds out. The coat may lighten or darken from winter to summer, but unlike the
2032:
Marklund, L; Moller MJ; Sandberg K; Andersson L (Dec 1996). "A missense mutation in the gene for melanocyte-stimulating hormone receptor (MC1R) is associated with the chestnut coat color in horses".
677:
182:
darker with age. Generally, roans appear to have more white hair when they have their short summer coats and darker when they have their winter coats. These peculiar tendencies of roans led to the
199:
211:
1705:
280:
conditions not covered by those mentioned here is possible and likely. The patterns identified as "roaning" have particular qualities that can be used to tell them apart from true roan.
2126:
Haase, B; SA Brooks; T Tozaki; D Burger; P-A Poncet; S Rieder; T Hasegawa; C Penedo; T Leeb (2009). "Seven novel KIT mutations in horses with white coat colour phenotypes".
797:
are located physically close together on a chromosome, they tend to be exchanged together. The rate at which two genes are passed on together can be used to calculate their
133:
is loosely applied to any roan with a dark underlying coat that gives it a bluish cast. In the strictest sense, though, "blue roan" is a common synonym for a roan with a
53:
927:
were on the same chromosome, though, the horse would be expected to produce primarily chestnut roans and nonchestnut nonroans with chestnut, nonroan partners.
315:
may be born any color, and there may be no indication of the future gray coat at birth. Mature grays may retain none of their original coat color, and have a "
2228:
1997:
Haase, B; Jude R; Brooks SA; Leeb T (June 2008). "An equine chromosome 3 inversion is associated with the tobiano spotting pattern in German horse breeds".
1055:
Marklund, S; M Moller; K Sandberg; L Andersson (1999). "Close association between sequence polymorphism in the KIT gene and the roan coat color in horses".
147:
Association changed its coat color descriptions; roans with a chestnut background coat are registered "red roan", while "bay roan" is its own category. The
1694:
Overton, Rebecca (2004). "Other studies discovered them in two other equine breeds, the
Ardennais, found in France, and the Hokkaido, which live in Japan."
374:
base coat, and is a coat color with a bluish cast and darker points. Unlike blue roans, grullos are solid color and appear bluish due to low amounts of
1359:
Locke, MM; MCT Penedo; SJ Brickker; LV Millon; JD Murray (2002). "Linkage of the grey coat colour locus to microsatellites on horse chromosome 25".
1248:
1713:
262:
275:
In the most general sense, the word "roan" refers to any animal with a mixture of white and colored hairs in the coat. Recent research into
1811:
1970:
Andersson, L; Sandberg, K (Mar–Apr 1982). "A linkage group composed of three coat color genes and three serum protein loci in horses".
1664:
919:), the horse would produce primarily blue roans, or chestnut nonroans, but few chestnut roans and few black nonroans. If the recessive
1023:
1619:
1586:
1510:
1426:
1231:
1168:
118:
Often, the background coat color is used in combination with the word "roan" to describe the shade of a roan horse's coat, such as
939:
during the late 17th-early 18th century. He was known as the "Blue Horse Rider" or "One Who Rides the Blue Horse" during his time.
336:
turning gray. Unlike grays, roans do not develop more white hair with age, and without white markings, roans retain colored heads.
233:
This strawberry roan mare, though very light-colored, is still identifiable as a roan by the dark color of her extremities and the
741:", so roan was believed to follow a similar pattern. Genetic science in the 1970s could not provide a clear answer, as methods of
2221:
1116:
674:
721:
trait. Finding neither stillborn nor sickly, short-lived foals from these roan parents, the researchers concluded that in the
733:. Other studies at the time were using progeny ratios to identify potential lethality related to other coat colors, such as "
948:
1529:
Brooks, Samantha A.; Bailey, Ernest (2005). "Exon skipping in the KIT gene causes a Sabino spotting pattern in horses".
1635:
1467:
is the
Spanish name for the crane bird, and these horses are similar to the bluish color of the sandhill crane." p. 37.
2214:
2193:
Our association analysis indicated that the putative major gene for white markings is located at or near the KIT locus
243:
2757:
2738:
2707:
2697:
2672:
789:
as is, but a mixture of DNA from each parent. Paired chromosomes exchange parallel pieces of DNA, a process called
650:
276:
112:
887:
The effect of linkage between roan and chestnut is readily observed. If a horse possesses one chromosome with the
1295:
846:
to parts of chromosomes in other species that also control coat color, even some similar to roan. Presently, the
824:
524:
654:
205:
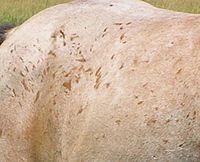
Corn marks or corn spots occur where a roan's skin has been damaged. The hair grows back in without any white.
126:
roan, but colloquial terms also are used for some colors. The most common terms for various roan colors are:
2727:
1299:
556:
111:
in other roan-like coat patterns. The nonwhite background coat may be any color, as determined by unrelated
436:
A Paso Fino with both roan and sabino patterning: The white at the end of the tail indicates gray, as well.
2646:
1900:
Trommerhausen-Smith, Ann (1978). "Linkage of tobiano coat spotting and albumin markers in a pony family".
953:
714:
660:
528:
148:
2479:
2435:
1259:
853:
790:
738:
628:
Nonetheless, most
Thoroughbreds and Arabians with roan-like coats are most likely related to graying or
899:), while the other chromosome contains the recessive chestnut allele and the recessive nonroan allele (
432:
189:
Roans have other unusual characteristics. If the skin is damaged by even a very minor scrape, cut, or
2161:
Rieder, Stefan; Christian Hagger; Gabriela Obexer-Ruff; Tosso Leeb; Pierre-André Poncet (2008-02-21).
1935:
Sandberg, Kaj; Juneja, R. Kumar (2009). "Close linkage between the albumin and Gc loci in the horse".
801:
from each other on the chromosome. Genes that tend to be passed on as a group form what is called a "
718:
552:
532:
144:
77:
68:
pattern characterized by an even mixture of colored and white hairs on the body, while the head and "
613:
To date, only one
Thoroughbred family has been genetically verified as true roan, and there are no
2532:
2339:
1316:
Bennett, Dorothy C.; M. Lynn
Lamoreux (August 2003). "The Color Loci of Mice - A Genetic Century".
599:
520:
445:
mistaken for roans. The roaning of sabinos originates in a white patch, and the roaning is uneven.
378:
in each hair, not interspersed white hairs. Like other dun coat colors, grullos have dark or black
2636:
2409:
2275:
2057:
1554:
1341:
1080:
843:
571:
379:
234:
190:
183:
27:
Horse coat color pattern characterized by an even mixture of colored and white hairs on the body
2163:"Genetic Analysis of White Facial and Leg Markings in the Swiss Franches-Montagnes Horse Breed"
1819:
1418:
1303:
2245:
2237:
2184:
2143:
2108:
2049:
2014:
1979:
1952:
1917:
1615:
1582:
1546:
1506:
1422:
1376:
1333:
1227:
1164:
1072:
936:
835:
299:
2631:
2329:
2174:
2135:
2098:
2088:
2041:
2006:
1944:
1909:
1852:
1671:
1603:
1538:
1410:
1368:
1325:
1064:
742:
512:
69:
65:
2286:
1611:
1027:
880:
spotting, and is thought to be a major contributor to many other forms of less distinctive
700:
responsible for true roan has not yet been identified exactly, but been assigned to equine
2546:
2258:
1913:
1856:
839:
808:
Equine linkage group II includes a number of genes. The first linkage was found between a
802:
776:
591:
587:
583:
548:
508:
472:
333:
1783:
1734:
1160:
1153:
221:
of this bay roan show the characteristic inverted "V" of dark hair not affected by roan.
2474:
2445:
2425:
2384:
2263:
2103:
2076:
1948:
881:
877:
812:
753:
734:
685:
638:
579:
479:
breed, have several manifestations that feature mixtures of white and colored hairs. A
156:
123:
37:
1127:
467:
is showing white sclera, mottled skin, and darker bony regions such as the cheekbones.
2751:
2651:
2621:
2606:
2418:
2307:
2139:
2010:
1755:
1411:
1372:
1329:
828:
614:
603:
575:
536:
516:
415:
404:
371:
329:
320:
316:
134:
2061:
1558:
1443:
1084:
785:, DNA is "reshuffled" to ensure that the next generation does not inherit ancestral
2682:
2564:
2554:
2484:
2430:
2299:
1480:
1345:
873:
618:
544:
480:
454:
441:
427:
325:
308:
294:
98:
73:
31:
1604:
1577:
Sponenberg, Dan
Phillip (2003). "5 / Patterns Characterized by Patches of White".
1501:
Sponenberg, Dan
Phillip (2003). "4 / Patterns of White Occurring on Base Colors".
2093:
2677:
2641:
2457:
2346:
2270:
2253:
798:
633:
504:
119:
81:
1879:
1642:. Tennessee Walking Horse Breeders' and Exhibitors' Association. Archived from
998:
2626:
2511:
2404:
2369:
2364:
2359:
2316:
1542:
809:
786:
701:
567:
563:
488:
2687:
2656:
2560:
2179:
2162:
2077:"Allelic Heterogeneity at the Equine KIT Locus in Dominant White (W) Horses"
1643:
782:
595:
540:
476:
464:
2188:
2147:
2112:
2018:
1550:
1380:
1337:
1076:
396:
45:
2053:
2045:
1983:
1175:...blue roan comes on a dark (black, brown, or liver chestnut) background.
1068:
2722:
2586:
2527:
2389:
2334:
2075:
Haase B, Brooks SA, Schlumbaum A, Azor PJ, Bailey E, et al. (2007).
1956:
1921:
935:
The Blue Roan was a popular horse kept and ridden by the 10th Sikh Guru,
888:
757:
722:
717:
found fewer roan offspring from roan-to-roan matings than expected for a
697:
681:
629:
492:
411:
401:
391:
367:
349:
168:
93:
89:
85:
17:
763:, produce 100% roan offspring. Homozygous roans and heterozygous roans (
459:
2692:
2616:
2611:
2522:
2491:
861:
831:
820:
816:
622:
375:
218:
827:. In 1982, a linkage grouping was proposed, including three genes for
358:
A blue dun or grullo has no intermingled white hairs in its body coat.
2496:
2394:
2206:
869:
726:
667:
484:
363:
345:
354:
177:
replaced red roan as the term for a roan with a bay background coat.
1126:. American Quarter Horse Association. pp. 24–6. Archived from
793:, prior to being passed on to the next generation. When particular
57:
Red roan, roaning over chestnut, sometimes called "strawberry roan"
2702:
2469:
848:
752:
In some breeds, homozygous roans can be identified by an indirect
730:
607:
527:. It is also found regularly in North American breeds such as the
458:
431:
395:
353:
303:
A young gray horse may appear roan, but becomes lighter with age.
298:
52:
44:
36:
1756:"2021 AUGUST (Late) Online Sale | Inglis Digital Online Auctions"
237:
on her hindquarters, which has grown back in without white hairs.
2717:
2712:
794:
312:
2210:
261:
This dark bay roan, painted in the 18th century carrying the
1304:
http://0-dictionary.oed.com.helin.uri.edu/cgi/entry/50207603
186:
word for roan, which translates as "always changing color."
1843:
Hintz; van Vleck (1979). "Lethal dominant roan in horses".
1151:
Evans, James Warren (1990). "Breeds in the United States".
632:
characteristics. Thoroughbred "roans" are described by the
1735:"(Phenotypically) True Roan Thoroughbreds: A New Mutation"
143:
used to include both chestnut and bay roans. In 1999, the
151:
Association followed suit in 2003. Previously, the term
88:
responsible for roan has not been exactly identified, a
1788:
The American Stud Book Principal Rules and Requirements
1712:. Lexington: Thoroughbred Times Co. Inc. Archived from
1670:. American Saddlebred Horse Association. Archived from
876:
spotting, no fewer than eleven alleles responsible for
1026:. New Jersey Pony Breeders and Owners. Archived from
852:
gene is the primary candidate gene for roan. While a
637:
have a partially-spotted pattern that results from a
1572:
1570:
1568:
819:
white spotting in 1978. The same blood type marker,
366:(also grulla, mouse dun) coloring is created by the
2665:
2599:
2574:
2545:
2505:
2456:
2443:
2417:
2315:
2306:
2294:
2244:
155:described the pinkish color of a light chestnut or
1152:
891:nonchestnut allele and the dominant roan allele (
332:registered as "roan" are often gray, especially
1226:(2 ed.). Wiley-Blackwell. pp. 65–68.
2173:(2). The American Genetic Association: 130–6.
1050:
1048:
1046:
1044:
2222:
1524:
1522:
1446:. The Regents of the University of California
1217:
1215:
1213:
1211:
1209:
1207:
1205:
1203:
993:
991:
989:
823:, was linked to another blood protein called
49:A "blue roan", roaning over a black base coat
8:
1908:(4). American Genetic Association: 214–216.
1838:
1836:
1475:
1473:
1404:
1402:
1400:
1398:
1396:
1394:
1201:
1199:
1197:
1195:
1193:
1191:
1189:
1187:
1185:
1183:
987:
985:
983:
981:
979:
977:
975:
973:
971:
969:
495:skin around the eyes, muzzle, and genitals.
440:Roaning is also associated with some of the
163:may be applied to a dark chestnut roan, and
1818:. Arabian Horse Association. Archived from
1602:Bowling, Ann T.; Ruvinsky, Anatoly (2000).
1581:(2 ed.). Wiley-Blackwell. p. 91.
1505:(2 ed.). Wiley-Blackwell. p. 69.
1409:Bowling, Ann T.; Ruvinsky, Anatoly (2000).
503:True or classic roan is common in European
382:, always including a stripe down the back.
2462:
2453:
2321:
2312:
2229:
2215:
2207:
725:condition the roan gene was lethal to the
2178:
2102:
2092:
1483:. UC Davis Veterinary Genetics Laboratory
1110:
1108:
1106:
1104:
1102:
1100:
1098:
1096:
1094:
319:" coat, while the color of the skin and
1003:Veterinary Genetics Laboratory Services
965:
195:
1806:
1804:
915:. Mated to chestnut nonroan partners (
688:to indirectly determine the number of
617:that are true roan. A small number of
265:, has dark extremities and corn spots.
41:Bay roan (sometimes called "red roan")
1914:10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a108933
1857:10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a109213
1778:
1776:
1444:"Introduction to Coat Color Genetics"
680:'s genetics services has developed a
7:
1706:"A roan by any other name is a roan"
1949:10.1111/j.1365-2052.1978.tb01430.x
1159:(2 ed.). Macmillan. pp.
159:roan. While less common, the term
25:
1640:The Tennessee Walking Horse Breed
1463:Sponenberg, Dan Phillip (2003). "
1247:Overton, Rebecca (January 2002).
307:Roans are sometimes mistaken for
2285:
2140:10.1111/j.1365-2052.2009.01893.x
2011:10.1111/j.1365-2052.2008.01715.x
1442:Veterinary Genetics Laboratory.
1373:10.1046/j.1365-2052.2002.00885.x
1330:10.1034/j.1600-0749.2003.00067.x
1298:. 2nd edition 1989. OED Online.
1222:Sponenberg, Dan Phillip (2003).
999:"Roan Zygosity Test Information"
254:
242:
226:
210:
198:
1115:Overton, Rebecca (2004-12-15).
767:) are identical in appearance.
675:University of California, Davis
30:For Roan in other animals, see
931:Cultural/Historical References
713:A 1979 study of American-bred
475:colors, characteristic of the
1:
949:Strawberry roan (horse color)
678:School of Veterinary Medicine
249:Reverse dapples on a bay roan
2094:10.1371/journal.pgen.0030195
756:test. Such horses, with the
745:had not yet been developed.
594:may also be roan. Some roan
1704:Peters, Anne (2002-05-04).
2774:
2739:Category:Horse coat colors
2708:Endothelin receptor type B
2673:Equine coat color genetics
774:
651:Equine coat color genetics
648:
452:
425:
410:One pattern of roaning is
389:
343:
292:
277:equine coat color genetics
29:
2736:
2465:
2355:
2324:
2283:
1812:"What color is my horse?"
1784:"Section IV: Color Guide"
1606:The genetics of the horse
1543:10.1007/s00335-005-2472-y
1413:The genetics of the horse
1296:Oxford English Dictionary
1258:: 106–111. Archived from
868:also harbors one or more
825:vitamin D-binding protein
781:During the production of
696:alleles a horse has. The
525:Rhenish-German Cold-Blood
400:An extensively expressed
663:trait symbolized by the
655:Introduction to genetics
171:or the lightest sorrels.
2728:Melanocortin 1 receptor
1665:"Conformation Brochure"
1636:"Coat Color: Modifiers"
1300:Oxford University Press
771:Equine linkage group II
562:British ponies such as
557:Tennessee Walking Horse
80:, and is found in many
954:Chestnut (horse color)
468:
437:
407:
359:
304:
149:American Quarter Horse
84:. While the specific
58:
50:
42:
2666:Genetics and breeding
2507:Base color variations
2436:Lethal white syndrome
2180:10.1093/jhered/esm115
2046:10.1007/s003359900264
1816:Purebred Registration
1579:Equine color genetics
1503:Equine color genetics
1318:Pigment Cell Research
1224:Equine color genetics
1069:10.1007/s003359900987
854:chromosomal inversion
791:chromosomal crossover
586:ponies may be roan.
462:
449:Varnish roan vs. roan
435:
399:
357:
302:
56:
48:
40:
838:: tobiano spotting,
715:Belgian draft horses
600:American Saddlebreds
553:Missouri Fox Trotter
145:American Paint Horse
78:dominantly inherited
2167:Journal of Heredity
1972:Journal of Heredity
1902:Journal of Heredity
1845:Journal of Heredity
1481:"Dun Zygosity Test"
1302:. 3 June 2008. <
1256:Paint Horse Journal
521:Italian Heavy Draft
507:breeds such as the
263:Duke of Württemberg
2637:Primitive markings
2238:Equine coat colors
1880:"Homozygous Roans"
1710:Thoroughbred Times
1124:Quarter Horse News
743:molecular analysis
610:may also be roan.
469:
438:
408:
380:primitive markings
360:
305:
59:
51:
43:
2758:Horse coat colors
2745:
2744:
2595:
2594:
2541:
2540:
2381:
2380:
2377:
2376:
2357:double dilution:
2326:single dilution:
1790:. The Jockey Club
1760:inglisdigital.com
1610:. CABI. pp.
1249:"The White Stuff"
937:Guru Gobind Singh
659:Roan is a simple
621:offspring of the
487:, finely striped
386:Rabicano vs. roan
16:(Redirected from
2765:
2632:Point coloration
2575:Roaning patterns
2515:
2463:
2454:
2401:
2343:
2322:
2313:
2289:
2278:
2267:
2246:Base coat colors
2231:
2224:
2217:
2208:
2196:
2195:
2182:
2158:
2152:
2151:
2123:
2117:
2116:
2106:
2096:
2072:
2066:
2065:
2034:Mammalian Genome
2029:
2023:
2022:
1994:
1988:
1987:
1967:
1961:
1960:
1932:
1926:
1925:
1897:
1891:
1890:
1888:
1887:
1882:. Hancock Horses
1876:
1870:
1867:
1861:
1860:
1840:
1831:
1830:
1828:
1827:
1808:
1799:
1798:
1796:
1795:
1780:
1771:
1770:
1768:
1766:
1752:
1746:
1745:
1743:
1741:
1731:
1725:
1724:
1722:
1721:
1701:
1695:
1692:
1686:
1685:
1683:
1682:
1676:
1669:
1661:
1655:
1654:
1652:
1651:
1632:
1626:
1625:
1609:
1599:
1593:
1592:
1574:
1563:
1562:
1531:Mammalian Genome
1526:
1517:
1516:
1498:
1492:
1491:
1489:
1488:
1477:
1468:
1461:
1455:
1454:
1452:
1451:
1439:
1433:
1432:
1417:. CABI. p.
1416:
1406:
1389:
1388:
1356:
1350:
1349:
1313:
1307:
1280:
1274:
1273:
1271:
1270:
1264:
1253:
1244:
1238:
1237:
1219:
1178:
1177:
1158:
1148:
1142:
1141:
1139:
1138:
1132:
1121:
1112:
1089:
1088:
1057:Mammalian Genome
1052:
1039:
1038:
1036:
1035:
1020:
1014:
1013:
1011:
1010:
995:
872:responsible for
864:white spotting,
834:, and three for
592:Miniature Horses
588:Icelandic Horses
258:
246:
230:
214:
202:
137:background coat.
66:horse coat color
21:
2773:
2772:
2768:
2767:
2766:
2764:
2763:
2762:
2748:
2747:
2746:
2741:
2732:
2661:
2591:
2570:
2557:
2547:Leopard complex
2537:
2516:
2509:
2508:
2501:
2450:
2448:
2439:
2413:
2392:
2373:
2351:
2338:(also known as
2337:
2302:
2290:
2281:
2273:
2262:(also known as
2261:
2240:
2235:
2205:
2200:
2199:
2160:
2159:
2155:
2128:Animal Genetics
2125:
2124:
2120:
2074:
2073:
2069:
2031:
2030:
2026:
1999:Animal Genetics
1996:
1995:
1991:
1969:
1968:
1964:
1937:Animal Genetics
1934:
1933:
1929:
1899:
1898:
1894:
1885:
1883:
1878:
1877:
1873:
1868:
1864:
1842:
1841:
1834:
1825:
1823:
1810:
1809:
1802:
1793:
1791:
1782:
1781:
1774:
1764:
1762:
1754:
1753:
1749:
1739:
1737:
1733:
1732:
1728:
1719:
1717:
1703:
1702:
1698:
1693:
1689:
1680:
1678:
1674:
1667:
1663:
1662:
1658:
1649:
1647:
1634:
1633:
1629:
1622:
1601:
1600:
1596:
1589:
1576:
1575:
1566:
1537:(11): 893–902.
1528:
1527:
1520:
1513:
1500:
1499:
1495:
1486:
1484:
1479:
1478:
1471:
1462:
1458:
1449:
1447:
1441:
1440:
1436:
1429:
1408:
1407:
1392:
1361:Animal Genetics
1358:
1357:
1353:
1315:
1314:
1310:
1281:
1277:
1268:
1266:
1262:
1251:
1246:
1245:
1241:
1234:
1221:
1220:
1181:
1171:
1150:
1149:
1145:
1136:
1134:
1130:
1119:
1114:
1113:
1092:
1054:
1053:
1042:
1033:
1031:
1022:
1021:
1017:
1008:
1006:
997:
996:
967:
962:
945:
933:
779:
777:Genetic linkage
773:
719:simple dominant
711:
709:Homozygous roan
686:genetic markers
657:
647:
602:are known. The
549:Spanish Mustang
501:
473:leopard complex
463:A varnish roan
457:
451:
430:
424:
422:Sabino vs. roan
394:
388:
352:
344:Main articles:
342:
297:
291:
286:
273:
266:
259:
250:
247:
238:
231:
222:
215:
206:
203:
153:strawberry roan
113:genetic factors
108:
35:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
2771:
2769:
2761:
2760:
2750:
2749:
2743:
2742:
2737:
2734:
2733:
2731:
2730:
2725:
2720:
2715:
2710:
2705:
2700:
2695:
2690:
2685:
2680:
2675:
2669:
2667:
2663:
2662:
2660:
2659:
2654:
2649:
2644:
2639:
2634:
2629:
2624:
2619:
2614:
2609:
2603:
2601:
2597:
2596:
2593:
2592:
2590:
2589:
2584:
2578:
2576:
2572:
2571:
2569:
2568:
2551:
2549:
2543:
2542:
2539:
2538:
2536:
2535:
2530:
2525:
2519:
2517:
2506:
2503:
2502:
2500:
2499:
2494:
2489:
2488:
2487:
2482:
2477:
2475:Splashed white
2466:
2460:
2458:Pinto patterns
2451:
2446:Horse markings
2444:
2441:
2440:
2438:
2433:
2428:
2426:Dominant white
2423:
2421:
2415:
2414:
2412:
2407:
2402:
2387:
2382:
2379:
2378:
2375:
2374:
2372:
2367:
2362:
2356:
2353:
2352:
2350:
2349:
2344:
2332:
2325:
2319:
2310:
2308:Dilution genes
2304:
2303:
2298:
2296:
2292:
2291:
2284:
2282:
2280:
2279:
2268:
2256:
2250:
2248:
2242:
2241:
2236:
2234:
2233:
2226:
2219:
2211:
2204:
2203:External links
2201:
2198:
2197:
2153:
2118:
2067:
2024:
2005:(3): 306–309.
1989:
1962:
1943:(3): 169–173.
1927:
1892:
1871:
1862:
1832:
1800:
1772:
1747:
1726:
1696:
1687:
1656:
1627:
1620:
1594:
1587:
1564:
1518:
1511:
1493:
1469:
1456:
1434:
1427:
1390:
1367:(5): 329–337.
1351:
1324:(4): 333–344.
1308:
1275:
1239:
1232:
1179:
1169:
1143:
1117:"In The Genes"
1090:
1063:(3): 283–288.
1040:
1015:
964:
963:
961:
958:
957:
956:
951:
944:
941:
932:
929:
882:white markings
878:dominant white
772:
769:
735:dominant white
710:
707:
646:
643:
639:dominant white
500:
497:
453:Main article:
450:
447:
426:Main article:
423:
420:
390:Main article:
387:
384:
341:
338:
330:Arabian Horses
293:Main article:
290:
287:
285:
282:
272:
269:
268:
267:
260:
253:
251:
248:
241:
239:
232:
225:
223:
216:
209:
207:
204:
197:
179:
178:
172:
138:
124:gold champagne
107:
106:Identification
104:
92:can determine
72:"—lower legs,
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2770:
2759:
2756:
2755:
2753:
2740:
2735:
2729:
2726:
2724:
2721:
2719:
2716:
2714:
2711:
2709:
2706:
2704:
2701:
2699:
2696:
2694:
2691:
2689:
2686:
2684:
2681:
2679:
2676:
2674:
2671:
2670:
2668:
2664:
2658:
2655:
2653:
2650:
2648:
2645:
2643:
2640:
2638:
2635:
2633:
2630:
2628:
2625:
2623:
2620:
2618:
2615:
2613:
2610:
2608:
2607:Bend-Or spots
2605:
2604:
2602:
2598:
2588:
2585:
2583:
2580:
2579:
2577:
2573:
2567:
2566:
2562:
2556:
2553:
2552:
2550:
2548:
2544:
2534:
2531:
2529:
2526:
2524:
2521:
2520:
2518:
2513:
2504:
2498:
2495:
2493:
2490:
2486:
2483:
2481:
2478:
2476:
2473:
2472:
2471:
2468:
2467:
2464:
2461:
2459:
2455:
2452:
2447:
2442:
2437:
2434:
2432:
2429:
2427:
2424:
2422:
2420:
2416:
2411:
2410:Silver dapple
2408:
2406:
2403:
2399:
2398:
2391:
2388:
2386:
2383:
2371:
2368:
2366:
2363:
2361:
2358:
2354:
2348:
2345:
2341:
2336:
2333:
2331:
2328:
2327:
2323:
2320:
2318:
2314:
2311:
2309:
2305:
2301:
2297:
2293:
2288:
2277:
2272:
2269:
2265:
2260:
2257:
2255:
2252:
2251:
2249:
2247:
2243:
2239:
2232:
2227:
2225:
2220:
2218:
2213:
2212:
2209:
2202:
2194:
2190:
2186:
2181:
2176:
2172:
2168:
2164:
2157:
2154:
2149:
2145:
2141:
2137:
2133:
2129:
2122:
2119:
2114:
2110:
2105:
2100:
2095:
2090:
2086:
2082:
2078:
2071:
2068:
2063:
2059:
2055:
2051:
2047:
2043:
2040:(12): 895–9.
2039:
2035:
2028:
2025:
2020:
2016:
2012:
2008:
2004:
2000:
1993:
1990:
1985:
1981:
1977:
1973:
1966:
1963:
1958:
1954:
1950:
1946:
1942:
1938:
1931:
1928:
1923:
1919:
1915:
1911:
1907:
1903:
1896:
1893:
1881:
1875:
1872:
1866:
1863:
1858:
1854:
1850:
1846:
1839:
1837:
1833:
1822:on 2008-05-14
1821:
1817:
1813:
1807:
1805:
1801:
1789:
1785:
1779:
1777:
1773:
1761:
1757:
1751:
1748:
1736:
1730:
1727:
1716:on 2010-02-28
1715:
1711:
1707:
1700:
1697:
1691:
1688:
1677:on 2011-07-23
1673:
1666:
1660:
1657:
1646:on 2011-07-17
1645:
1641:
1637:
1631:
1628:
1623:
1621:0-85199-429-6
1617:
1613:
1608:
1607:
1598:
1595:
1590:
1588:0-8138-0759-X
1584:
1580:
1573:
1571:
1569:
1565:
1560:
1556:
1552:
1548:
1544:
1540:
1536:
1532:
1525:
1523:
1519:
1514:
1512:0-8138-0759-X
1508:
1504:
1497:
1494:
1482:
1476:
1474:
1470:
1466:
1460:
1457:
1445:
1438:
1435:
1430:
1428:0-85199-429-6
1424:
1420:
1415:
1414:
1405:
1403:
1401:
1399:
1397:
1395:
1391:
1387:
1382:
1378:
1374:
1370:
1366:
1362:
1355:
1352:
1347:
1343:
1339:
1335:
1331:
1327:
1323:
1319:
1312:
1309:
1305:
1301:
1297:
1293:
1289:
1285:
1279:
1276:
1265:on 2008-08-07
1261:
1257:
1250:
1243:
1240:
1235:
1233:0-8138-0759-X
1229:
1225:
1218:
1216:
1214:
1212:
1210:
1208:
1206:
1204:
1202:
1200:
1198:
1196:
1194:
1192:
1190:
1188:
1186:
1184:
1180:
1176:
1172:
1170:0-7167-1811-1
1166:
1162:
1157:
1156:
1147:
1144:
1133:on 2007-09-27
1129:
1125:
1118:
1111:
1109:
1107:
1105:
1103:
1101:
1099:
1097:
1095:
1091:
1086:
1082:
1078:
1074:
1070:
1066:
1062:
1058:
1051:
1049:
1047:
1045:
1041:
1030:on 2009-10-14
1029:
1025:
1019:
1016:
1004:
1000:
994:
992:
990:
988:
986:
984:
982:
980:
978:
976:
974:
972:
970:
966:
959:
955:
952:
950:
947:
946:
942:
940:
938:
930:
928:
926:
923:and dominant
922:
918:
914:
910:
906:
902:
898:
894:
890:
885:
883:
879:
875:
871:
867:
863:
859:
855:
851:
850:
845:
841:
837:
833:
830:
826:
822:
818:
814:
811:
806:
804:
803:linkage group
800:
796:
792:
788:
784:
778:
770:
768:
766:
762:
759:
755:
750:
746:
744:
740:
736:
732:
728:
724:
720:
716:
708:
706:
703:
699:
695:
691:
687:
683:
679:
676:
671:
669:
666:
662:
656:
652:
644:
642:
640:
635:
631:
626:
624:
620:
616:
611:
609:
605:
604:Hokkaido Pony
601:
597:
593:
589:
585:
581:
577:
573:
569:
565:
560:
558:
554:
550:
546:
542:
538:
537:Peruvian Paso
534:
530:
529:Quarter Horse
526:
522:
518:
517:Trait Du Nord
514:
510:
506:
498:
496:
494:
490:
486:
482:
478:
474:
466:
461:
456:
448:
446:
443:
434:
429:
421:
419:
417:
413:
406:
405:Arabian horse
403:
398:
393:
385:
383:
381:
377:
373:
369:
365:
356:
351:
347:
339:
337:
335:
331:
327:
322:
318:
314:
310:
301:
296:
289:Gray vs. roan
288:
283:
281:
278:
270:
264:
257:
252:
245:
240:
236:
229:
224:
220:
213:
208:
201:
196:
194:
192:
187:
185:
176:
173:
170:
166:
162:
158:
154:
150:
146:
142:
139:
136:
132:
129:
128:
127:
125:
121:
116:
114:
105:
103:
100:
95:
91:
87:
83:
79:
75:
71:
67:
63:
55:
47:
39:
33:
19:
2723:STX17 (Gray)
2683:Horse genome
2581:
2565:Knabstrupper
2558:
2555:Varnish roan
2449:and patterns
2431:Sabino-white
2396:
2395:Blue dun or
2192:
2170:
2166:
2156:
2134:(5): 623–9.
2131:
2127:
2121:
2087:(11): e195.
2084:
2080:
2070:
2037:
2033:
2027:
2002:
1998:
1992:
1975:
1971:
1965:
1940:
1936:
1930:
1905:
1901:
1895:
1884:. Retrieved
1874:
1865:
1851:(2): 145–6.
1848:
1844:
1824:. Retrieved
1820:the original
1815:
1792:. Retrieved
1787:
1763:. Retrieved
1759:
1750:
1738:. Retrieved
1729:
1718:. Retrieved
1714:the original
1709:
1699:
1690:
1679:. Retrieved
1672:the original
1659:
1648:. Retrieved
1644:the original
1639:
1630:
1605:
1597:
1578:
1534:
1530:
1502:
1496:
1485:. Retrieved
1464:
1459:
1448:. Retrieved
1437:
1412:
1384:
1364:
1360:
1354:
1321:
1317:
1311:
1291:
1287:
1283:
1278:
1267:. Retrieved
1260:the original
1255:
1242:
1223:
1174:
1154:
1146:
1135:. Retrieved
1128:the original
1123:
1060:
1056:
1032:. Retrieved
1028:the original
1018:
1007:. Retrieved
1002:
934:
924:
920:
916:
912:
908:
904:
900:
896:
892:
886:
865:
857:
847:
807:
780:
764:
760:
751:
747:
739:lethal white
712:
693:
689:
672:
664:
658:
627:
619:Thoroughbred
612:
561:
545:Standardbred
502:
481:varnish roan
470:
455:Varnish roan
439:
428:Sabino horse
409:
370:acting on a
362:Blue dun or
361:
340:Dun vs. roan
326:Thoroughbred
306:
295:Gray (horse)
274:
188:
180:
174:
164:
160:
152:
140:
130:
117:
109:
82:horse breeds
61:
60:
32:Roan (color)
2678:Color breed
2533:Tricoloured
2510:(primarily
2370:Smoky cream
2347:Smoky black
1978:(2): 91–4.
1765:20 November
787:chromosomes
749:stallions.
634:Jockey Club
533:Paint Horse
284:Roan mimics
271:Terminology
2512:UK English
2393:(see also
2340:Isabelline
2276:Seal brown
2081:PLOS Genet
1886:2008-06-04
1826:2009-10-01
1794:2009-10-01
1720:2008-06-04
1681:2009-10-01
1650:2009-10-01
1487:2009-05-27
1450:2008-06-04
1269:2009-10-06
1137:2008-06-04
1034:2009-10-06
1024:"Articles"
1009:2009-10-01
1005:. UC Davis
960:References
844:homologous
836:coat color
810:blood type
775:See also:
754:DNA marker
723:homozygous
702:chromosome
684:that uses
649:See also:
596:Trakehners
584:New Forest
499:Prevalence
165:honey roan
161:lilac roan
2657:Tiger eye
2561:Appaloosa
2559:See also
2385:Champagne
2274:included
1155:The Horse
783:sex cells
580:Connemara
572:Gypsy Cob
541:Paso Fino
477:Appaloosa
465:Appaloosa
334:chestnuts
184:Icelandic
169:palominos
131:Blue roan
18:Blue roan
2752:Category
2703:KIT gene
2688:Wildtype
2652:Mushroom
2587:Rabicano
2528:Skewbald
2360:Cremello
2335:Palomino
2330:Buckskin
2259:Chestnut
2189:18296388
2148:19456317
2113:17997609
2062:29095360
2019:18410476
1559:32782072
1551:16284805
1381:12354140
1338:12859616
1085:32790547
1077:10051325
943:See also
889:wildtype
840:chestnut
832:proteins
799:distance
758:genotype
698:mutation
682:DNA test
661:dominant
645:Genetics
641:allele.
630:rabicano
615:Arabians
576:Shetland
513:Ardennes
416:Arabians
412:rabicano
402:rabicano
392:Rabicano
368:dun gene
350:Dun gene
219:forelegs
175:Bay roan
141:Red roan
122:roan or
94:zygosity
90:DNA test
86:mutation
2693:Melanin
2627:Pangaré
2617:Cropout
2612:Brindle
2523:Piebald
2492:Tobiano
2365:Perlino
2104:2065884
2054:8995760
1984:7096983
1740:Nov 18,
1346:3904358
870:alleles
862:tobiano
860:causes
821:albumin
817:tobiano
737:" and "
623:brindle
509:Brabant
493:mottled
376:pigment
2698:Agouti
2647:Flaxen
2497:Tovero
2485:Sabino
2397:Grullo
2264:Sorrel
2187:
2146:
2111:
2101:
2060:
2052:
2017:
1982:
1957:751533
1955:
1922:569673
1920:
1618:
1585:
1557:
1549:
1509:
1465:Grullo
1425:
1379:
1344:
1336:
1290:. and
1230:
1167:
1083:
1075:
874:sabino
813:marker
727:embryo
668:allele
582:, and
523:, and
491:, and
489:hooves
485:sclera
442:sabino
364:grullo
346:Grullo
157:sorrel
70:points
2642:Sooty
2622:Liver
2600:Other
2480:Frame
2470:Overo
2419:White
2405:Pearl
2317:Cream
2254:Black
2058:S2CID
1675:(PDF)
1668:(PDF)
1555:S2CID
1386:loci.
1342:S2CID
1306:>.
1263:(PDF)
1252:(PDF)
1131:(PDF)
1120:(PDF)
1081:S2CID
829:serum
795:genes
765:Rn/rn
761:Rn/Rn
731:fetus
608:Japan
590:and
568:Welsh
564:Dales
505:draft
372:black
317:white
313:foals
309:grays
235:brand
191:brand
135:black
64:is a
2718:PAX3
2713:MITF
2582:Roan
2563:and
2300:Gray
2295:Gray
2185:PMID
2144:PMID
2109:PMID
2050:PMID
2015:PMID
1980:PMID
1953:PMID
1918:PMID
1767:2021
1742:2021
1616:ISBN
1614:–5.
1583:ISBN
1547:PMID
1507:ISBN
1423:ISBN
1377:PMID
1334:PMID
1284:roan
1228:ISBN
1165:ISBN
1073:PMID
917:e/rn
913:e/rn
909:E/Rn
903:and
895:and
815:and
673:The
653:and
598:and
555:and
471:The
348:and
328:and
321:eyes
217:The
99:gray
74:mane
62:Roan
2390:Dun
2271:Bay
2175:doi
2136:doi
2099:PMC
2089:doi
2042:doi
2007:doi
1945:doi
1910:doi
1853:doi
1539:doi
1369:doi
1326:doi
1292:n.1
1065:doi
911:or
866:KIT
858:KIT
856:of
849:KIT
805:".
729:or
692:or
606:of
167:to
120:bay
2754::
2191:.
2183:.
2171:99
2169:.
2165:.
2142:.
2132:40
2130:.
2107:.
2097:.
2083:.
2079:.
2056:.
2048:.
2036:.
2013:.
2003:39
2001:.
1976:73
1974:.
1951:.
1939:.
1916:.
1906:69
1904:.
1849:70
1847:.
1835:^
1814:.
1803:^
1786:.
1775:^
1758:.
1708:.
1638:.
1612:64
1567:^
1553:.
1545:.
1535:16
1533:.
1521:^
1472:^
1421:.
1419:57
1393:^
1383:.
1375:.
1365:33
1363:.
1340:.
1332:.
1322:16
1320:.
1294:"
1286:,
1254:.
1182:^
1173:.
1163:.
1161:81
1122:.
1093:^
1079:.
1071:.
1061:10
1059:.
1043:^
1001:.
968:^
925:Rn
905:rn
897:Rn
884:.
694:rn
690:Rn
665:Rn
578:,
574:,
570:,
566:,
559:.
551:,
547:,
543:,
539:,
535:,
531:,
519:,
515:,
511:,
418:.
115:.
2514:)
2400:)
2342:)
2266:)
2230:e
2223:t
2216:v
2177::
2150:.
2138::
2115:.
2091::
2085:3
2064:.
2044::
2038:7
2021:.
2009::
1986:.
1959:.
1947::
1941:9
1924:.
1912::
1889:.
1859:.
1855::
1829:.
1797:.
1769:.
1744:.
1723:.
1684:.
1653:.
1624:.
1591:.
1561:.
1541::
1515:.
1490:.
1453:.
1431:.
1371::
1348:.
1328::
1288:a
1282:"
1272:.
1236:.
1140:.
1087:.
1067::
1037:.
1012:.
921:e
901:e
893:E
34:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.