31:
1204:
1305:
1317:
98:) producing a clear image of the plane of the sample the microscope is focused on. Unfortunately a microscope is not this specific and light from sources outside the focal plane also reaches the detector; in a thick sample there may be a significant amount of material, and so spurious signal, between the focal plane and the
364:
Lightsheet based fluorescence microscopy illuminates the sample with excitation light under an angle of 90° to the direction of observation, i.e. only the focal plane is illuminated using a laser that is only focused in one direction (lightsheet). This method effectively reduces out-of focus light
420:
Optical sectioning can be enhanced by the use of clearing agents possessing a high refractive index (>1.4) such as Benzyl-Alcohol/Benzyl
Benzoate (BABB) or Benzyl-ether which render specimens transparent and therefore allow for observation of internal structures.
307:
Beyond increasing numerical aperture, there are few techniques available to improve optical sectioning in bright-field light microscopy. Most microscopes with oil immersion objectives are reaching the limits of numerical aperture possible due to
321:
Differential interference contrast (DIC) provides modest improvements to optical sectioning. In DIC the sample is effectively illuminated by two slightly offset light sources which then interfere to produce an image resulting from the
390:"-dependent effect of requiring multiple photons to simultaneously interact with a fluorophore gives stimulation only very close to the focal plane. These techniques are normally used in conjunction with confocal microscopy.
338:
objects out of the focal plane only interfere with the image if they are illuminated and fluoresce. This adds an extra way in which optical sectioning can be improved by making illumination specific to only the focal plane.
293:
209:
459:
3D imaging using a combination of focal sectioning and tilting has been demonstrated theoretically and experimentally in order to provide exceptional 3D resolution over large fields of view.
393:
Further improvements in optical sectioning are under active development, these principally work through methods to circumvent the diffraction limit of light. Examples include single photon
144:
in the depth direction (the "z resolution") of a standard wide field microscope depends on the numerical aperture and the wavelength of the light and can be approximated as:
456:
is a fluorescent microscopy technique, which intentionally restricts observation to either the top or bottom surfaces of a sample, but with extremely high depth resolution.
1247:
942:
628:
Huisken, J.; Swoger, J.; Bene, F. Del; Wittbrodt, J.; Stelzer, E. H. (2004). "Optical sectioning deep inside live embryos by selective plane illumination microscopy".
1158:
1015:
Hovden, R; Ercius, P (2014). "Breaking the
Crowther Limit: Combining Depth-Sectioning and Tilt Tomography for High-Resolution, Wide-Field 3D Reconstructions".
1086:
326:
of the two sources. As the offset in the light sources is small the only difference in phase results from the material close to the focal plane.
1290:
1285:
1153:
859:
453:
1252:
373:
359:
235:
1188:
1168:
316:
450:
are not typically discussed in the context of optical sectioning as these microscopes only interact with the surface of the sample.
149:
1232:
1228:
1079:
369:
133:
objective lenses typically have higher numerical apertures (and so better optical sectioning) than low magnification objectives.
1257:
378:
Dual and multi-photon excitation techniques take advantage of the fact that fluorophores can be excited not just by a single
439:
typically have a large depth of field (poor optical sectioning), and thus thin sectioning of samples is still widely used.
397:
through two objective lenses to give extremely accurate depth information about a single fluorophore and three-dimensional
72:
Good optical sectioning, often referred to as good depth or z resolution, is popular in modern microscopy as it allows the
1321:
447:
398:
506:
Qian, Jia; Lei, Ming; Dan, Dan; Yao, Baoli; Zhou, Xing; Yang, Yanlong; Yan, Shaohui; Min, Junwei; Yu, Xianghua (2015).
1309:
1072:
365:
and may in addition lead to a modest improvement in longitudinal resolution, compared to epi fluorescence microscopy.
1275:
1148:
443:
1236:
1218:
1133:
335:
1138:
647:
1143:
936:
409:
352:
95:
573:
562:
351:
uses a scanning point or points of light to illuminate the sample. In conjunction with a pinhole at a
969:
896:
751:
639:
519:
475:
652:
408:, an image processing technique to remove blur from the image according to a measured or calculated
1343:
1223:
1163:
485:
436:
348:
343:
799:"Three-dimensional structured illumination microscopy and its application to chromosome structure"
355:
this acts to filter out light from sources outside the focal plane to improve optical sectioning.
1114:
1050:
1024:
720:
673:
610:
141:
118:
30:
1042:
997:
924:
865:
855:
820:
779:
712:
665:
630:
602:
545:
227:
740:"Interferometric fluorescent super-resolution microscopy resolves 3D cellular ultrastructure"
1203:
1193:
1034:
987:
977:
914:
904:
847:
810:
769:
759:
704:
657:
594:
535:
527:
432:
323:
106:
73:
1280:
958:"Depth sectioning with the aberration-corrected scanning transmission electron microscope"
137:
objectives typically have even larger numerical apertures so improved optical sectioning.
404:
The optical sectioning of normal wide field microscopes can be improved significantly by
386:
but also by multiple photons, which together provide the correct energy. The additional "
973:
900:
755:
643:
523:
1173:
992:
957:
919:
884:
774:
739:
540:
507:
394:
110:
99:
85:
90:
In an ideal microscope, only light from the focal plane would be allowed to reach the
1337:
1242:
405:
387:
134:
130:
126:
1054:
614:
1038:
677:
471:
69:
techniques are specifically designed to improve the quality of optical sectioning.
58:
35:
724:
909:
114:
54:
1178:
1107:
1095:
815:
798:
481:
309:
66:
50:
17:
883:
Becker, K., Jährling, N., Saghafi, S., Weiler, R., & Dodt, H. U. (2012).
982:
764:
692:
661:
585:
Conchello JA, Lichtman JW (December 2005). "Optical sectioning microscopy".
62:
1046:
1001:
928:
869:
824:
783:
716:
708:
669:
606:
549:
109:, the quality of optical sectioning is governed by the same physics as the
76:
reconstruction of a sample from images captured at different focal planes.
42:
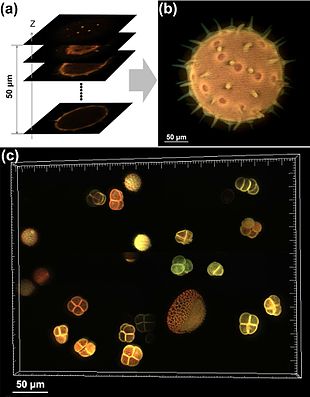
grain. (b) Combined image. (c) Combined image of a group of pollen grains.
122:
91:
65:. Many different techniques for optical sectioning are used and several
956:
Borisevich, A. Y.; Lupini, A. R.; Pennycook, S. J. (21 February 2006).
531:
105:
With no modification to the microscope, i.e. with a simple wide field
1183:
1064:
598:
383:
379:
39:
851:
1029:
885:"Chemical clearing and dehydration of GFP expressing mouse brains"
738:
Shtengel G, Galbraith JA, Galbraith CG, et al. (March 2009).
508:"Full-color structured illumination optical sectioning microscopy"
29:
288:{\displaystyle D_{x}=D_{y}={\frac {0.61\lambda }{\mathrm {NA} }}}
57:
deep within a thick sample. This is used to reduce the need for
1068:
429:
Optical sectioning is underdeveloped in non-light microscopes.
219:
the refractive index of the objective lens immersion media and
204:{\displaystyle D_{z}={\frac {\lambda n}{(\mathrm {NA} )^{2}}}}
691:
Gratton E, Barry NP, Beretta S, Celli A (September 2001).
1248:
Total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy (TIRF)
442:
Although similar physics guides the focusing process,
842:. Advances in Biochemical Engineering/Biotechnology.
563:
Nikon
MicroscopyU – Depth of Field and Depth of Focus
238:
152:
1286:
Photo-activated localization microscopy (PALM/STORM)
467:
The primary alternatives to optical sectioning are:
1266:
1211:
1124:
80:
Optical sectioning in traditional light microscopes
287:
203:
838:Sibarita JB (2005). "Deconvolution microscopy".
962:Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
1189:Interference reflection microscopy (IRM/RICM)
1080:
27:Imaging of focal planes within a thick sample
8:
941:: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (
49:is the process by which a suitably designed
484:, which is particularly well developed for
298:Techniques for improving optical sectioning
1087:
1073:
1065:
129:) and gives good optical sectioning. High
1028:
991:
981:
918:
908:
814:
773:
763:
651:
539:
275:
265:
256:
243:
237:
192:
180:
166:
157:
151:
1159:Differential interference contrast (DIC)
498:
1154:Quantitative phase-contrast microscopy
934:
474:of the sample, for example as used in
693:"Multiphoton fluorescence microscopy"
7:
1316:
1281:Stimulated emission depletion (STED)
454:Total internal reflection microscopy
374:multiphoton fluorescence microscope
360:Light sheet fluorescence microscopy
399:structured illumination microscopy
317:differential interference contrast
279:
276:
184:
181:
25:
1253:Lightsheet microscopy (LSFM/SPIM)
1315:
1304:
1303:
1202:
486:transmission electron microscopy
370:two-photon excitation microscopy
125:, the depth of field is small (
1258:Lattice light-sheet microscopy
1169:Second harmonic imaging (SHIM)
1039:10.1016/j.ultramic.2014.01.013
574:Nikon MicroscopyU – Resolution
189:
177:
61:using instruments such as the
1:
840:Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol
448:scanning electron microscopes
303:Bright-field light microscopy
910:10.1371/journal.pone.0033916
744:Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A
94:(typically an observer or a
53:can produce clear images of
121:lens, equivalent to a wide
1360:
444:Scanning probe microscopes
367:
357:
341:
314:
83:
1299:
1200:
1102:
816:10.1007/s10577-008-1231-9
230:can be approximated as:
223:the numerical aperture.
34:(a) Optically sectioned
1219:Fluorescence microscopy
1179:Structured illumination
1134:Bright-field microscopy
983:10.1073/pnas.0507105103
765:10.1073/pnas.0813131106
662:10.1126/science.1100035
336:fluorescence microscopy
330:Fluorescence microscopy
1291:Near-field (NSOM/SNOM)
1229:Multiphoton microscopy
709:10.1006/meth.2001.1219
289:
205:
43:
1144:Dark-field microscopy
410:point spread function
353:conjugate focal plane
290:
206:
33:
1212:Fluorescence methods
437:electron microscopes
236:
150:
1243:Image deconvolution
1224:Confocal microscopy
1164:Dispersion staining
1139:Köhler illumination
974:2006PNAS..103.3044B
901:2012PLoSO...733916B
797:Carlton PM (2008).
756:2009PNAS..106.3125S
644:2004Sci...305.1007H
638:(5686): 1007–1009.
524:2015NatSR...514513Q
349:Confocal microscopy
344:confocal microscopy
226:In comparison, the
215:is the wavelength,
1115:Optical microscopy
1096:Optical microscopy
512:Scientific Reports
285:
228:lateral resolution
201:
119:numerical aperture
47:Optical sectioning
44:
1331:
1330:
1276:Diffraction limit
861:978-3-540-23698-6
532:10.1038/srep14513
324:phase differences
283:
199:
74:three-dimensional
16:(Redirected from
1351:
1319:
1318:
1307:
1306:
1269:limit techniques
1206:
1127:contrast methods
1125:Illumination and
1089:
1082:
1075:
1066:
1059:
1058:
1032:
1012:
1006:
1005:
995:
985:
968:(9): 3044–3048.
953:
947:
946:
940:
932:
922:
912:
880:
874:
873:
835:
829:
828:
818:
794:
788:
787:
777:
767:
735:
729:
728:
688:
682:
681:
655:
625:
619:
618:
599:10.1038/nmeth815
582:
576:
571:
565:
560:
554:
553:
543:
503:
294:
292:
291:
286:
284:
282:
274:
266:
261:
260:
248:
247:
210:
208:
207:
202:
200:
198:
197:
196:
187:
175:
167:
162:
161:
107:light microscope
21:
1359:
1358:
1354:
1353:
1352:
1350:
1349:
1348:
1334:
1333:
1332:
1327:
1295:
1268:
1267:Sub-diffraction
1262:
1207:
1198:
1126:
1120:
1098:
1093:
1063:
1062:
1017:Ultramicroscopy
1014:
1013:
1009:
955:
954:
950:
933:
882:
881:
877:
862:
852:10.1007/b102215
837:
836:
832:
796:
795:
791:
737:
736:
732:
690:
689:
685:
653:10.1.1.456.2250
627:
626:
622:
584:
583:
579:
572:
568:
561:
557:
505:
504:
500:
495:
472:Thin sectioning
465:
427:
418:
416:Clearing agents
382:of the correct
376:
368:Main articles:
362:
346:
332:
319:
305:
300:
267:
252:
239:
234:
233:
188:
176:
168:
153:
148:
147:
88:
82:
59:thin sectioning
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1357:
1355:
1347:
1346:
1336:
1335:
1329:
1328:
1326:
1325:
1313:
1300:
1297:
1296:
1294:
1293:
1288:
1283:
1278:
1272:
1270:
1264:
1263:
1261:
1260:
1255:
1250:
1245:
1240:
1226:
1221:
1215:
1213:
1209:
1208:
1201:
1199:
1197:
1196:
1191:
1186:
1181:
1176:
1174:4Pi microscope
1171:
1166:
1161:
1156:
1151:
1149:Phase contrast
1146:
1141:
1136:
1130:
1128:
1122:
1121:
1119:
1118:
1111:
1103:
1100:
1099:
1094:
1092:
1091:
1084:
1077:
1069:
1061:
1060:
1007:
948:
875:
860:
830:
803:Chromosome Res
789:
750:(9): 3125–30.
730:
683:
620:
593:(12): 920–31.
577:
566:
555:
497:
496:
494:
491:
490:
489:
479:
464:
461:
426:
423:
417:
414:
395:interferometry
358:Main article:
342:Main article:
331:
328:
315:Main article:
304:
301:
299:
296:
281:
278:
273:
270:
264:
259:
255:
251:
246:
242:
195:
191:
186:
183:
179:
174:
171:
165:
160:
156:
111:depth of field
100:objective lens
86:Depth of field
81:
78:
26:
24:
18:Clearing agent
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1356:
1345:
1342:
1341:
1339:
1324:
1323:
1314:
1312:
1311:
1302:
1301:
1298:
1292:
1289:
1287:
1284:
1282:
1279:
1277:
1274:
1273:
1271:
1265:
1259:
1256:
1254:
1251:
1249:
1246:
1244:
1241:
1238:
1234:
1230:
1227:
1225:
1222:
1220:
1217:
1216:
1214:
1210:
1205:
1195:
1192:
1190:
1187:
1185:
1182:
1180:
1177:
1175:
1172:
1170:
1167:
1165:
1162:
1160:
1157:
1155:
1152:
1150:
1147:
1145:
1142:
1140:
1137:
1135:
1132:
1131:
1129:
1123:
1117:
1116:
1112:
1110:
1109:
1105:
1104:
1101:
1097:
1090:
1085:
1083:
1078:
1076:
1071:
1070:
1067:
1056:
1052:
1048:
1044:
1040:
1036:
1031:
1026:
1022:
1018:
1011:
1008:
1003:
999:
994:
989:
984:
979:
975:
971:
967:
963:
959:
952:
949:
944:
938:
930:
926:
921:
916:
911:
906:
902:
898:
895:(3): e33916.
894:
890:
886:
879:
876:
871:
867:
863:
857:
853:
849:
845:
841:
834:
831:
826:
822:
817:
812:
809:(3): 351–65.
808:
804:
800:
793:
790:
785:
781:
776:
771:
766:
761:
757:
753:
749:
745:
741:
734:
731:
726:
722:
718:
714:
710:
706:
703:(1): 103–10.
702:
698:
694:
687:
684:
679:
675:
671:
667:
663:
659:
654:
649:
645:
641:
637:
633:
632:
624:
621:
616:
612:
608:
604:
600:
596:
592:
588:
581:
578:
575:
570:
567:
564:
559:
556:
551:
547:
542:
537:
533:
529:
525:
521:
517:
513:
509:
502:
499:
492:
487:
483:
480:
477:
473:
470:
469:
468:
462:
460:
457:
455:
451:
449:
445:
440:
438:
434:
430:
424:
422:
415:
413:
411:
407:
406:deconvolution
402:
400:
396:
391:
389:
388:concentration
385:
381:
375:
371:
366:
361:
356:
354:
350:
345:
340:
337:
329:
327:
325:
318:
313:
311:
302:
297:
295:
271:
268:
262:
257:
253:
249:
244:
240:
231:
229:
224:
222:
218:
214:
193:
172:
169:
163:
158:
154:
145:
143:
138:
136:
135:Oil immersion
132:
131:magnification
128:
127:shallow focus
124:
120:
117:. For a high
116:
112:
108:
103:
101:
97:
93:
87:
79:
77:
75:
70:
68:
64:
60:
56:
52:
48:
41:
37:
32:
19:
1320:
1308:
1237:Three-photon
1113:
1106:
1020:
1016:
1010:
965:
961:
951:
937:cite journal
892:
888:
878:
843:
839:
833:
806:
802:
792:
747:
743:
733:
700:
696:
686:
635:
629:
623:
590:
587:Nat. Methods
586:
580:
569:
558:
515:
511:
501:
466:
463:Alternatives
458:
452:
441:
431:
428:
419:
403:
392:
377:
363:
347:
333:
320:
306:
232:
225:
220:
216:
212:
146:
139:
104:
89:
71:
55:focal planes
46:
45:
38:images of a
36:fluorescence
115:photography
1344:Microscopy
1233:Two-photon
1108:Microscope
846:: 201–43.
493:References
482:Tomography
310:refraction
142:resolution
113:effect in
84:See also:
67:microscopy
51:microscope
1030:1402.0028
1023:: 26–31.
648:CiteSeerX
518:: 14513.
476:histology
272:λ
170:λ
63:microtome
1338:Category
1310:Category
1055:41919418
1047:24636875
1002:16492746
929:22479475
889:PLOS ONE
870:16080270
825:18461477
784:19202073
717:11559001
670:15310904
615:17722926
607:16299477
550:26415516
312:limits.
123:aperture
92:detector
1322:Commons
993:1413870
970:Bibcode
920:3316521
897:Bibcode
775:2637278
752:Bibcode
697:Methods
678:3213175
640:Bibcode
631:Science
541:4586488
520:Bibcode
1184:Sarfus
1053:
1045:
1000:
990:
927:
917:
868:
858:
823:
782:
772:
725:822155
723:
715:
676:
668:
650:
613:
605:
548:
538:
384:energy
380:photon
213:λ
211:where
40:pollen
1194:Raman
1051:S2CID
1025:arXiv
721:S2CID
674:S2CID
611:S2CID
433:X-ray
425:Other
1043:PMID
998:PMID
943:link
925:PMID
866:PMID
856:ISBN
821:PMID
780:PMID
713:PMID
666:PMID
603:PMID
546:PMID
446:and
435:and
372:and
269:0.61
140:The
1035:doi
1021:140
988:PMC
978:doi
966:103
915:PMC
905:doi
848:doi
811:doi
770:PMC
760:doi
748:106
705:doi
658:doi
636:305
595:doi
536:PMC
528:doi
334:In
96:CCD
1340::
1235:,
1049:.
1041:.
1033:.
1019:.
996:.
986:.
976:.
964:.
960:.
939:}}
935:{{
923:.
913:.
903:.
891:.
887:.
864:.
854:.
844:95
819:.
807:16
805:.
801:.
778:.
768:.
758:.
746:.
742:.
719:.
711:.
701:25
699:.
695:.
672:.
664:.
656:.
646:.
634:.
609:.
601:.
589:.
544:.
534:.
526:.
514:.
510:.
412:.
401:.
221:NA
102:.
1239:)
1231:(
1088:e
1081:t
1074:v
1057:.
1037::
1027::
1004:.
980::
972::
945:)
931:.
907::
899::
893:7
872:.
850::
827:.
813::
786:.
762::
754::
727:.
707::
680:.
660::
642::
617:.
597::
591:2
552:.
530::
522::
516:5
488:.
478:.
280:A
277:N
263:=
258:y
254:D
250:=
245:x
241:D
217:n
194:2
190:)
185:A
182:N
178:(
173:n
164:=
159:z
155:D
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.