41:
147:
If the cemental union between affected teeth is slight, the teeth may separate during extraction of one of the teeth and may never be noticed. If the union is large or firm, the planned extraction of one of the teeth may inadvertently result in the removal of its mate. A clinician’s awareness of the
105:
The postinflammatory pattern frequently involves carious molars in which the root ends (apices) overlie the roots of impacted third molars, most common with the distally angulated third molars. The resultant large pulpal exposure often permits pulpal drainage, leading to a resolution of a portion of
101:
The exact cause of concrescence is unknown. However, it may develop during root formation (true/primary concrescence) or after root formation (acquired/secondary concrescence). Factors that may cause concrescence include injuries (trauma), crowding of teeth, inflammation, or infection. Concrescence
143:
Post-inflammatory concrescence must be kept in mind whenever extraction is planned for non-vital teeth with apices that overlie the roots of an adjacent tooth. Significant difficulties with extraction can be experienced during removal of a tooth that is unexpectedly joined to its neighbor.
118:
taken at different angles can aid in the detection of concrescence, since the condition may be misdiagnosed as radiographic overlap of superimposed teeth. Radiographically, teeth appear joined together with the absence of periodontal ligament or interdental bone between them. Cone beam computed
485:
470:
123:
examination of extracted teeth is necessary to confirm the diagnosis and distinguishing concrescence from differential diagnoses of gemination or fusion by observing lack of dentinal confluence between fused teeth.
140:
should be considered to prevent further periodontal destruction leading to tooth loss. However, a consequence of extraction is that the conjoined tooth also must often be removed.
528:
59:
overlying the roots of at least two teeth fuse together without the involvement of dentin. Usually, two teeth are involved with the upper second and third
250:
Gunduz, K; Sumer, M; Sumer, A P; Gunhan, O (2006). "Concrescence of a mandibular third molar and a supernumerary fourth molar: Report of a rare case".
521:
63:
being most commonly fused together. The prevalence ranges 0.04–0.8% in permanent teeth, with the incidence being highest in the posterior maxilla.
214:
Delanora, Leonardo Alan; Simon, Maria Eloise de Sá; Rodriguez, Eder
Alberto Sigua; Faverani, Leonardo Perez; Pavan, Angelo Jose (10 August 2020).
744:
114:
Clinically, concrescence is difficult to diagnose due to lack of involvement of tooth enamel resulting in a tooth crown that appears normal.
82:
Possible gum disease (localized periodontal destruction due to aetiological factors, e.g. funnel development leading to plaque accumulation)
514:
435:
132:
If the condition is not affecting the patient, no treatment is needed. Concrescence teeth could be reshaped and replaced with full
144:
Surgical separation often is required to complete the procedure without loss of a significant portion of the surrounding bone.
216:"Can concrescence diagnosis be obtained merely by clinical and imaging examination? from clinical case to histology"
148:
characteristics of this odontogenic anomaly may help avert adverse outcomes in the treatment of concrescent teeth.
692:
702:
651:
119:
tomography (CBCT) may assist in diagnosis and treatment planning, but cannot provide a definitive diagnosis.
687:
656:
430:. Chichester, West Sussex Oxford Ames, Iowa: Wiley-Blackwell, A John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., Publication.
615:
489:
630:
275:
506:
661:
542:
431:
380:
267:
137:
133:
27:
718:
697:
605:
591:
370:
360:
318:
259:
227:
179:
723:
596:
89:
402:
136:. If the teeth are having recurrent problems, are non-restorable, or are painful, tooth
666:
375:
348:
76:
40:
494:
738:
671:
538:
60:
279:
646:
625:
610:
586:
120:
303:
183:
620:
565:
115:
600:
560:
479:
172:
Oral
Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology, Oral Radiology, and Endodontology
365:
323:
556:
102:
appears to have no particular predisposition for age, gender, or ethnicity.
85:
Cavities (caries) due to predisposition from crowded teeth and misalignment.
32:
401:
Neville, Brad W.; Damm, Douglas D.; Allen, Carl M.; Chi, Angela C. (2019),
384:
271:
263:
232:
215:
72:
Problems with tooth positioning causing cheek biting and traumatic ulcers.
56:
462:
170:
Romito, Laura M. (March 2004). "Concrescence: report of a rare case".
474:
44:
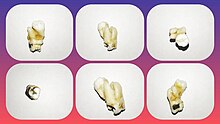
Dental concrescence between a 2M (erupted) and a higher 3M (retained)
52:
39:
297:
295:
293:
291:
289:
510:
347:
Venugopal, Sanjay; Smitha, BV; Saurabh, Sprithyani (2013).
342:
340:
338:
336:
334:
106:
the intrabony pathosis. Cemental repair then occurs.
304:"Endodontic Miscellany: Concrescence - a case report"
88:
May cause fracture of the tuberosity or floor of the
452:
711:
680:
639:
574:
549:
456:
245:
243:
26:
21:
407:Color Atlas of Oral and Maxillofacial Diseases
522:
8:
353:Journal of Indian Society of Periodontology
529:
515:
507:
453:
349:"Paramolar concrescence and periodontitis"
51:is an uncommon developmental condition of
18:
374:
364:
322:
231:
165:
163:
161:
157:
209:
207:
205:
203:
201:
199:
197:
195:
193:
7:
428:Pathology of the hard dental tissues
396:
394:
302:Fernandes, A; Sar Dessai, G (1999).
75:Involved teeth may have difficulty
14:
220:Research, Society and Development
1:
745:Developmental tooth pathology
184:10.1016/j.tripleo.2003.10.015
409:, Elsevier, pp. 367–410
79:or may not erupt completely.
761:
226:(9): e41996893–e41996893.
693:Dentinogenesis imperfecta
703:Regional odontodysplasia
652:Regional odontodysplasia
426:Schuurs, Albert (2013).
366:10.4103/0972-124X.115647
324:10.4103/0970-7212.347464
688:Amelogenesis imperfecta
264:10.1038/sj.bdj.4813191
252:British Dental Journal
233:10.33448/rsd-v9i9.6893
45:
43:
657:Turner's hypoplasia
631:Supernumerary roots
67:Signs and symptoms
46:
732:
731:
662:Enamel hypoplasia
543:tooth abnormality
504:
503:
38:
37:
16:Medical condition
752:
719:Dental fluorosis
698:Dentin dysplasia
681:Other hereditary
606:Dens invaginatus
531:
524:
517:
508:
454:
442:
441:
423:
417:
416:
415:
414:
403:"Bone Pathology"
398:
389:
388:
378:
368:
344:
329:
328:
326:
308:
299:
284:
283:
247:
238:
237:
235:
211:
188:
187:
167:
19:
760:
759:
755:
754:
753:
751:
750:
749:
735:
734:
733:
728:
724:Tooth impaction
707:
676:
635:
597:Dens evaginatus
570:
545:
535:
505:
500:
499:
465:
451:
446:
445:
438:
425:
424:
420:
412:
410:
400:
399:
392:
346:
345:
332:
306:
301:
300:
287:
249:
248:
241:
213:
212:
191:
169:
168:
159:
154:
130:
112:
99:
90:maxillary sinus
69:
17:
12:
11:
5:
758:
756:
748:
747:
737:
736:
730:
729:
727:
726:
721:
715:
713:
709:
708:
706:
705:
700:
695:
690:
684:
682:
678:
677:
675:
674:
669:
667:Ectopic enamel
664:
659:
654:
649:
643:
641:
637:
636:
634:
633:
628:
623:
618:
613:
608:
603:
594:
589:
584:
578:
576:
575:Shape and size
572:
571:
569:
568:
563:
553:
551:
547:
546:
537:Developmental
536:
534:
533:
526:
519:
511:
502:
501:
498:
497:
482:
466:
461:
460:
458:
457:Classification
450:
449:External links
447:
444:
443:
436:
418:
390:
330:
285:
239:
189:
178:(3): 325–327.
156:
155:
153:
150:
129:
126:
111:
108:
98:
95:
94:
93:
86:
83:
80:
73:
68:
65:
36:
35:
30:
24:
23:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
757:
746:
743:
742:
740:
725:
722:
720:
717:
716:
714:
710:
704:
701:
699:
696:
694:
691:
689:
686:
685:
683:
679:
673:
672:Ectopic tooth
670:
668:
665:
663:
660:
658:
655:
653:
650:
648:
645:
644:
642:
638:
632:
629:
627:
624:
622:
619:
617:
614:
612:
609:
607:
604:
602:
598:
595:
593:
590:
588:
585:
583:
580:
579:
577:
573:
567:
564:
562:
558:
555:
554:
552:
548:
544:
540:
539:tooth disease
532:
527:
525:
520:
518:
513:
512:
509:
496:
492:
491:
487:
483:
481:
477:
476:
472:
468:
467:
464:
459:
455:
448:
439:
437:9781405153652
433:
429:
422:
419:
408:
404:
397:
395:
391:
386:
382:
377:
372:
367:
362:
358:
354:
350:
343:
341:
339:
337:
335:
331:
325:
320:
316:
312:
311:Endodontology
305:
298:
296:
294:
292:
290:
286:
281:
277:
273:
269:
265:
261:
257:
253:
246:
244:
240:
234:
229:
225:
221:
217:
210:
208:
206:
204:
202:
200:
198:
196:
194:
190:
185:
181:
177:
173:
166:
164:
162:
158:
151:
149:
145:
141:
139:
135:
127:
125:
122:
117:
109:
107:
103:
96:
91:
87:
84:
81:
78:
74:
71:
70:
66:
64:
62:
58:
54:
50:
42:
34:
31:
29:
25:
20:
647:Dilaceration
626:Taurodontism
611:Enamel pearl
582:Concrescence
581:
484:
469:
427:
421:
411:, retrieved
406:
359:(3): 383–6.
356:
352:
314:
310:
258:(3): 141–2.
255:
251:
223:
219:
175:
171:
146:
142:
131:
121:Histological
113:
104:
100:
49:Concrescence
48:
47:
22:Concrescence
621:Microdontia
616:Macrodontia
566:Hyperdontia
317:(2): 65–6.
116:Radiographs
601:Talon cusp
592:Gemination
561:Hypodontia
413:2023-12-20
152:References
138:extraction
55:where the
640:Formation
557:Anodontia
128:Treatment
110:Diagnosis
33:Dentistry
28:Specialty
739:Category
550:Quantity
385:24049342
280:20376985
272:16474352
77:erupting
57:cementum
376:3768192
587:Fusion
434:
383:
373:
278:
270:
134:crowns
61:molars
712:Other
495:520.2
480:K00.2
307:(PDF)
276:S2CID
97:Cause
53:teeth
490:9-CM
432:ISBN
381:PMID
268:PMID
486:ICD
471:ICD
371:PMC
361:doi
319:doi
260:doi
256:200
228:doi
180:doi
741::
493::
478::
475:10
405:,
393:^
379:.
369:.
357:17
355:.
351:.
333:^
315:11
313:.
309:.
288:^
274:.
266:.
254:.
242:^
222:.
218:.
192:^
176:97
174:.
160:^
599:/
559:/
541:/
530:e
523:t
516:v
488:-
473:-
463:D
440:.
387:.
363::
327:.
321::
282:.
262::
236:.
230::
224:9
186:.
182::
92:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.