111:
88:
149:, which uses chloroform as the formylating agent. Protonated hexamine ring-opens to expose an iminium group. Addition to the aromatic ring results in an intermediate at the oxidation state of a benzylamine. An intramolecular redox reaction then ensues, raising the benzylic carbon to the oxidation state of an aldehyde. The oxygen atom is provided by water on acid hydrolysis in the final step.
378:
Duff, J. C.; Bills, E. J. (1932). "273. Reactions between hexamethylenetetramine and phenolic compounds. Part I. A new method for the preparation of 3- and 5-aldehydosalicylic acids".
153:
170:
Duff, J. C.; Bills, E. J. (1934). "282. Reactions between hexamethylenetetramine and phenolic compounds. Part II. Formation of phenolic aldehydes. Distinctive behaviour of
546:
Anderson, Andrew A.; Goetzen, Thomas; Shackelford, Scott A.; Tsank, Stella (September 2000). "A Convenient One-Step
Synthesis of 2-Hydroxy-1,3,5-Benzenetricarbaldehyde".
300:
352:
110:
87:
77:
589:
152:
295:
146:
579:
438:-butylsalicylaldehyde)-1,2-cyclohexanediamino Manganese(III) Chloride, a Highly Enantioselective Epoxidation Catalyst"
53:
40:
as the formyl carbon source. The method is generally inefficient. The reaction is named after James Cooper Duff.
315:
584:
305:
103:
can also be prepared by the Duff reaction. In this example, formylation occurs at the position para to the
516:
519:(July 1998). "Mono- and Diformylation of 4-Substituted Phenols: A New Application of the Duff Reaction".
118:
Unlike other formylation reactions the Duff reaction is able to attach multiple aldehyde groups. If both
268:
25:
233:
142:
482:
442:
358:
348:
342:
310:
254:
29:
555:
528:
491:
451:
385:
277:
246:
221:
200:
179:
74:
123:
100:
281:
573:
380:
133:. Conversion of phenol to the corresponding 1,3,5-trialdehyde has also been reported
191:
Duff, J. C.; Bills, E. J. (1941). "96. A new general method for the preparation of
165:
Duff was a chemist at the
College of Technology, Birmingham, around 1920–1950. who
44:
33:
477:
417:
338:
559:
266:
Ogata, Y.; Sugiura, F. (1968). "Kinetics and mechanism of the Duff reaction".
238:
122:
positions are vacant then a diformylation is possible, as in the formation of
495:
455:
362:
344:
Advanced
Organic Chemistry: Reactions, Mechanisms, and Structure, 3rd edition
258:
212:
Duff, J. C.; Bills, E. J. (1945). "71. A new method for the preparation of
389:
225:
204:
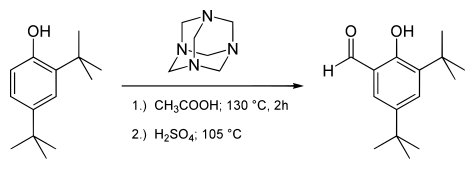
183:
127:
37:
532:
250:
104:
48:
402:
Mundy, Bradford P.; Ellerd, Michael G.; Favaloro, Frank G. (2005).
61:
positions are blocked, in which case the formylation occurs at the
57:
to the electron donating substituent preferentially, unless the
195:-hydroxyaldehydes from phenols and hexamethylenetetramine".
151:
109:
86:
406:, 2nd Edition, John Wiley & Sons, pp. 222 – 223.
404:Name Reactions and Reagents in Organic Synthesis
236:(1946). "The Synthesis of Aromatic Aldehydes".
47:substituents on the aromatic ring such as in a
476:Allen, C. F. H.; Leubner, Gerhard W. (1951).
8:
416:Larrow, Jay F.; Jacobsen, Eric N. (1998).
333:
331:
327:
373:
371:
301:Bodroux-Chichibabin aldehyde synthesis
7:
84:is prepared by the Duff reaction:
14:
347:, New York: Wiley, p. 727,
43:The reaction requires strongly
1:
282:10.1016/S0040-4020(01)88408-8
216:-dialkylaminobenzaldehydes".
22:hexamine aromatic formylation
296:Bouveault aldehyde synthesis
114:Duff reaction syringaldehyde
145:is related to that for the
606:
504:, vol. 4, p. 866
464:, vol. 10, p. 96
560:10.1080/00397910008086933
548:Synthetic Communications
496:10.15227/orgsyn.031.0092
456:10.15227/orgsyn.075.0001
316:Vilsmeier-Haack reaction
306:Reimer-Tiemann reaction
156:Duff reaction mechanism
147:Reimer–Tiemann reaction
157:
115:
96:
590:Formylation reactions
161:Historical references
155:
113:
95:-butylsalicylaldehyde
91:Duff reaction 3,5-di-
90:
82:-butylsalicylaldehyde
51:. Formylation occurs
32:for the synthesis of
390:10.1039/jr9320001987
226:10.1039/jr9450000276
205:10.1039/jr9410000547
184:10.1039/jr9340001305
99:The natural product
26:formylation reaction
533:10.1055/s-1998-2110
478:"Syringic aldehyde"
251:10.1021/cr60120a002
234:Lloyd Noel Ferguson
580:Addition reactions
517:Lindoy, Leonard F.
158:
143:reaction mechanism
137:Reaction mechanism
116:
97:
554:(17): 3227–3232.
502:Collected Volumes
483:Organic Syntheses
462:Collected Volumes
443:Organic Syntheses
311:Sommelet reaction
45:electron donating
30:organic chemistry
597:
564:
563:
543:
537:
536:
527:(7): 1029–1032.
513:
507:
505:
498:
473:
467:
465:
458:
413:
407:
400:
394:
393:
375:
366:
365:
335:
285:
262:
229:
208:
187:
605:
604:
600:
599:
598:
596:
595:
594:
570:
569:
568:
567:
545:
544:
540:
515:
514:
510:
500:
475:
474:
470:
460:
415:
414:
410:
401:
397:
377:
376:
369:
355:
337:
336:
329:
324:
292:
265:
232:
211:
190:
174:-nitrophenol".
169:
163:
139:
75:salicylaldehyde
71:
12:
11:
5:
603:
601:
593:
592:
587:
585:Name reactions
582:
572:
571:
566:
565:
538:
508:
468:
408:
395:
367:
353:
326:
325:
323:
320:
319:
318:
313:
308:
303:
298:
291:
288:
287:
286:
263:
245:(2): 227–254.
230:
209:
188:
162:
159:
138:
135:
124:diformylcresol
101:syringaldehyde
70:
67:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
602:
591:
588:
586:
583:
581:
578:
577:
575:
561:
557:
553:
549:
542:
539:
534:
530:
526:
522:
518:
512:
509:
503:
497:
493:
489:
485:
484:
479:
472:
469:
463:
457:
453:
449:
445:
444:
439:
437:
433:
429:
425:
421:
412:
409:
405:
399:
396:
391:
387:
383:
382:
381:J. Chem. Soc.
374:
372:
368:
364:
360:
356:
354:9780471854722
350:
346:
345:
340:
334:
332:
328:
321:
317:
314:
312:
309:
307:
304:
302:
299:
297:
294:
293:
289:
283:
279:
275:
271:
270:
264:
260:
256:
252:
248:
244:
241:
240:
235:
231:
227:
223:
219:
218:J. Chem. Soc.
215:
210:
206:
202:
198:
197:J. Chem. Soc.
194:
189:
185:
181:
177:
176:J. Chem. Soc.
173:
168:
167:
166:
160:
154:
150:
148:
144:
136:
134:
132:
130:
125:
121:
112:
108:
106:
102:
94:
89:
85:
83:
81:
76:
73:The modified
68:
66:
64:
60:
56:
55:
50:
46:
41:
39:
35:
34:benzaldehydes
31:
27:
23:
19:
18:Duff reaction
551:
547:
541:
524:
520:
511:
501:
487:
481:
471:
461:
447:
441:
435:
434:-Bis(3,5-di-
431:
427:
423:
419:
411:
403:
398:
379:
343:
339:March, Jerry
276:(14): 5001.
273:
267:
242:
237:
217:
213:
196:
192:
175:
171:
164:
140:
128:
119:
117:
98:
92:
79:
72:
62:
58:
52:
42:
21:
17:
15:
269:Tetrahedron
574:Categories
322:References
239:Chem. Rev.
65:position.
521:Synthesis
363:642506595
384:: 1987.
341:(1985),
290:See also
259:21024865
178:: 1305.
105:phenolic
69:Examples
38:hexamine
28:used in
220:: 276.
199:: 547.
131:-cresol
78:3,5-di-
490:: 92.
361:
351:
257:
49:phenol
450:: 1.
126:from
120:ortho
59:ortho
54:ortho
36:with
24:is a
525:1998
436:tert
359:OCLC
349:ISBN
255:PMID
141:The
107:OH.
93:tert
80:tert
63:para
16:The
556:doi
529:doi
492:doi
452:doi
386:doi
278:doi
247:doi
222:doi
201:doi
180:doi
20:or
576::
552:30
550:.
523:.
499:;
488:31
486:.
480:.
459:;
448:75
446:.
440:.
432:N'
426:)-
418:"(
370:^
357:,
330:^
274:24
272:.
253:.
243:38
562:.
558::
535:.
531::
506:.
494::
466:.
454::
430:,
428:N
424:R
422:,
420:R
392:.
388::
284:.
280::
261:.
249::
228:.
224::
214:p
207:.
203::
193:o
186:.
182::
172:p
129:p
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.