77:
128:
108:
68:. During endoscopic ear surgery the surgeon holds the endoscope in one hand while working in the ear with the other. To allow this kind of single-handed surgery, different surgical instruments have to be used. Endoscopic visualization has improved due to high-definition video imaging and wide-field endoscopy, and being less invasive, EES is gaining importance as an adjunct to microscopic ear surgery.
140:
Endoscopic ear surgery utilizes the ear canal as the access point for removal of cholesteatoma and therefore represent a minimally invasive alternative to traditional surgery that requires large incision behind the ear. The reduction in postoperative pain and cost that is usually associated with the use of minimally invasive techniques has been demonstrated in endoscopic ear surgery.
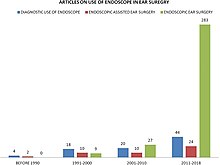
119:(observational EES), is increasing as optimized instrumentation and operative approaches become available. The number of citations published in the literature on this topic has skyrocketed recently with much of the interest focused on the use the endoscope as the main workhorse in otologic surgery rather than using the method for observation or as an adjunct to microscopic surgery.
180:
236:
104:
may reduce the need to drill for enhanced exposure of the operative field. The traditional otologic operating microscopes typically require larger portals (e.g., postauricular approaches) to enable adequate passage of light for intraoperative viewing and follow-up surveillance in the clinic. One handed dissection is cited as the main drawback to EES.
208:. To achieve that, using the microscope, an incision is made behind the ear using the "postauricular approach". The endoscope, with its ability to see around the corner, increases the likelihood of performing closures of perforations through the ear canal rather than making large incisions to access the whole perimeter of the perforation.
139:
cavity until the 1990s. The ability to see certain areas of the anatomy and to pursue disease was hampered by the straight line access when using the microscope. The endoscope allows the surgeon to look around the corners and to reach inaccessible areas like the sinus tympani through the ear canal.
99:
and the backlash he faced when he introduced FESS. Tarabichi and
Professor Stammberger persisted in their advocacy of their respective techniques and developed a friendship which resulted in the development of Tarabichi Stammberger Ear and Sinus Institute to train and educate surgeons in endoscopic
103:
One of the benefits of an endoscope compared to the microscope is the wide-field view of the middle ear afforded by the location of the light source at the tip of the instrument and the availability of various types of angled lenses. Middle ear procedures that utilize a rigid endoscope for viewing
191:
offers the most advantages for using the endoscope instead of the microscope. Failures in cholesteatoma surgery are most common in certain areas of the anatomy of the tympanic cavity, such as the facial recess, sinus tympani, anterior attic, and the protympanum which are poorly accessed with the
248:
plays the primary role in the pathophysiology of disorders of the middle ear. Access to the proximal part (ear side) of the eustachian tube is limited since most of the existing surgical access is posteriorly through the mastoid cavity. The endoscope allows the surgeon to reach the
227:, requires some removal of bone, and in some instances, an incision is made to facilitate access. The endoscope's ability to visualize around corners allows for better visualization of the stapes without needing any bone removal or making an incision.
239:
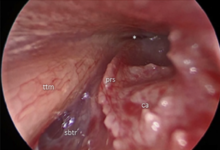
Using 30 degrees endoscope to look into the bony
Eustachian tube on a right ear. * indicates opening of the cartilaginous tube. ca: carotid artery. ttm: Tensor Tympani Muscle. prs: Protympanic spine. sbtr: Subtubal
88:
in Dubai during the late 1990s. His contributions to the field have led to him being recognized globally as the father of endoscopic ear surgery. He now lectures extensively on the topic worldwide.
80:
IWGEES Founding Board members paying tribute to Dr
Tarabichi. Left to right: Stephane Ayache, Dave Potheir, Seiji Kakehata, Daniele Marchioni, Joao Noqueira (top right), and Livio Presutti.
115:
The indications for this relatively new technique are evolving. The use of rigid endoscopes to perform ear surgery (operative EES), rather than just to visualize the contents of the
192:
microscope. The endoscope with its ability to see around the corners can visualize certain areas that are notorious for residual cholesteatoma such as the sinus tympani.
95:), EES has been controversial since early descriptions in the 1960s. Tarabichi's initial dissertations were met with skepticism in a very similar fashion to Professor
253:
or the bony
Eustachian tube and possibly carry out interventions to maintain an open eustachian tube by inserting a dilatation balloon catheter into that area.
389:
688:
Kinney SE (December 1982). "Five years experience using the intact canal wall tympanoplasty with mastoidectomy for cholesteatoma: preliminary report".
460:
Badr-El-Dine M, James AL, Panetti G, Marchioni D, Presutti L, Nogueira JF (April 2013). "Instrumentation and technologies in endoscopic ear surgery".
645:
Cohen MS, Landegger LD, Kozin ED, Lee DJ (March 2016). "Pediatric endoscopic ear surgery in clinical practice: Lessons learned and early outcomes".
92:
286:
136:
591:
111:
Number of publications categorized by the pattern of utilization of the endoscope in ear surgery per the last four decades
353:
Mer SB, Derbyshire AJ, Brushenko A, Pontarelli DA (April 1967). "Fiberoptic endotoscopes for examining the middle ear".
310:
Vining EM, Kennedy DW (July 1994). "The transmigration of endoscopic sinus surgery from Europe to the United States".
76:
149:
56:) is a minimally invasive alternative to traditional ear surgery and is defined as the use of the rigid
851:
61:
411:
Kozin ED, Gulati S, Kaplan AB, Lehmann AE, Remenschneider AK, Landegger LD, et al. (May 2015).
84:
Endoscopic ear surgery was first described in 1992 by
Professor Ahmed El-Guindy and pioneered by Dr
413:"Systematic review of outcomes following observational and operative endoscopic middle ear surgery"
841:
786:
713:
670:
627:
572:
335:
201:
826:
806:
767:
705:
662:
619:
611:
564:
529:
477:
442:
370:
327:
96:
27:
846:
798:
757:
749:
697:
654:
603:
556:
519:
511:
469:
432:
424:
362:
319:
152:
devised a classification system for the degree of use of the endoscope in otologic surgery:
65:
250:
245:
85:
366:
787:"The Role of Transtympanic Dilatation of the Eustachian Tube During Chronic Ear Surgery"
762:
737:
524:
499:
437:
412:
835:
701:
188:
717:
674:
576:
127:
631:
339:
224:
216:
107:
131:
Comparison between the field of view in endoscopic versus microscopic ear surgery
560:
323:
802:
753:
607:
473:
116:
615:
183:
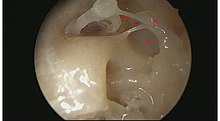
Sinus tympani: An area of the tympanic cavity that is hidden from microscope
57:
810:
771:
666:
623:
533:
481:
446:
179:
709:
568:
374:
331:
39:
272:
235:
658:
428:
205:
592:"Direct cost comparison of totally endoscopic versus open ear surgery"
515:
220:
135:
Ear surgery had been performed with the microscope and through the
234:
178:
126:
106:
75:
273:"IWGEES - International Working Group on Endoscopic Ear Surgery"
547:
Tarabichi M (January 1999). "Endoscopic middle ear surgery".
390:"Shifting paradigms – how a visionary can change a specialty"
742:
Indian
Journal of Otolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery
162:
Class 2: Mixed dissection with endoscope and microscope
204:
is essential for successful treatment of holes in the
223:, which conducts sound to the inner ear. Microscopic
785:Tarabichi, Muaaz; Kapadia, Mustafa (October 2016).
26:
21:
590:Patel, N; Mohammadi, A; Jufas, N (February 2018).
549:The Annals of Otology, Rhinology, and Laryngology
500:"An overview of endoscopic ear surgery in 2018"
64:, to visualize the middle and inner ear during
219:is a disease that results in fixation of the
8:
738:"Endoscopic transcanal middle ear surgery"
761:
523:
504:Laryngoscope Investigative Otolaryngology
436:
791:Otolaryngologic Clinics of North America
596:The Journal of Laryngology & Otology
462:Otolaryngologic Clinics of North America
267:
265:
261:
287:"In conversation with Muaaz Tarabichi"
18:
731:
729:
727:
498:Kapadiya M, Tarabichi M (June 2019).
200:Access to the whole perimeter of the
7:
493:
491:
367:10.1001/archotol.1967.00760040389009
91:Similar to the early years of FESS (
231:For access into the Eustachian tube
93:functional endoscopic sinus surgery
35:
159:Class 1: Inspection with endoscope
14:
702:10.1288/00005537-198212000-00011
312:Ear, Nose, & Throat Journal
170:Types of endoscopic ear surgery
156:Class 0: Microscopic only case
1:
388:Tarabichi, Muaaz (May 2019).
165:Class 3: Endoscopic only case
736:Tarabichi M (January 2010).
148:Cohen and his colleagues at
868:
827:Official website of IWGEES
561:10.1177/000348949910800106
355:Archives of Otolaryngology
324:10.1177/014556139407300708
803:10.1016/j.otc.2016.05.013
754:10.1007/s12070-010-0007-7
608:10.1017/S0022215117001694
474:10.1016/j.otc.2012.10.005
36:
291:ENT & Audiology News
394:ENT and Audiology News
241:
196:For perforated eardrum
184:
132:
112:
81:
50:Endoscopic ear surgery
22:Endoscopic ear surgery
238:
182:
130:
110:
79:
62:surgical microscope
659:10.1002/lary.25410
429:10.1002/lary.25048
242:
185:
133:
113:
82:
60:, as opposed to a
16:Surgical technique
318:(7): 456–8, 460.
175:For cholesteatoma
97:Heinz Stammberger
47:
46:
859:
815:
814:
797:(5): 1149–1162.
782:
776:
775:
765:
733:
722:
721:
696:(12): 1395–400.
690:The Laryngoscope
685:
679:
678:
647:The Laryngoscope
642:
636:
635:
587:
581:
580:
544:
538:
537:
527:
516:10.1002/lio2.276
495:
486:
485:
457:
451:
450:
440:
417:The Laryngoscope
408:
402:
401:
385:
379:
378:
350:
344:
343:
307:
301:
300:
298:
297:
283:
277:
276:
269:
212:For otosclerosis
66:otologic surgery
40:edit on Wikidata
19:
867:
866:
862:
861:
860:
858:
857:
856:
832:
831:
823:
818:
784:
783:
779:
735:
734:
725:
687:
686:
682:
644:
643:
639:
589:
588:
584:
546:
545:
541:
497:
496:
489:
459:
458:
454:
410:
409:
405:
387:
386:
382:
352:
351:
347:
309:
308:
304:
295:
293:
285:
284:
280:
271:
270:
263:
259:
246:Eustachian tube
233:
214:
198:
177:
172:
146:
125:
86:Muaaz Tarabichi
74:
43:
17:
12:
11:
5:
865:
863:
855:
854:
849:
844:
834:
833:
830:
829:
822:
821:External links
819:
817:
816:
777:
723:
680:
637:
602:(2): 122–128.
582:
539:
510:(3): 365–373.
487:
452:
423:(5): 1205–14.
403:
380:
345:
302:
278:
260:
258:
255:
232:
229:
213:
210:
197:
194:
176:
173:
171:
168:
167:
166:
163:
160:
157:
145:
144:Classification
142:
124:
121:
73:
70:
45:
44:
37:
34:
33:
32:otolaryngology
30:
24:
23:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
864:
853:
850:
848:
845:
843:
840:
839:
837:
828:
825:
824:
820:
812:
808:
804:
800:
796:
792:
788:
781:
778:
773:
769:
764:
759:
755:
751:
747:
743:
739:
732:
730:
728:
724:
719:
715:
711:
707:
703:
699:
695:
691:
684:
681:
676:
672:
668:
664:
660:
656:
652:
648:
641:
638:
633:
629:
625:
621:
617:
613:
609:
605:
601:
597:
593:
586:
583:
578:
574:
570:
566:
562:
558:
554:
550:
543:
540:
535:
531:
526:
521:
517:
513:
509:
505:
501:
494:
492:
488:
483:
479:
475:
471:
468:(2): 211–25.
467:
463:
456:
453:
448:
444:
439:
434:
430:
426:
422:
418:
414:
407:
404:
399:
395:
391:
384:
381:
376:
372:
368:
364:
361:(4): 387–93.
360:
356:
349:
346:
341:
337:
333:
329:
325:
321:
317:
313:
306:
303:
292:
288:
282:
279:
274:
268:
266:
262:
256:
254:
252:
247:
237:
230:
228:
226:
222:
218:
211:
209:
207:
203:
195:
193:
190:
189:cholesteatoma
181:
174:
169:
164:
161:
158:
155:
154:
153:
151:
143:
141:
138:
129:
122:
120:
118:
109:
105:
101:
98:
94:
89:
87:
78:
71:
69:
67:
63:
59:
55:
51:
41:
31:
29:
25:
20:
794:
790:
780:
745:
741:
693:
689:
683:
653:(3): 732–8.
650:
646:
640:
599:
595:
585:
555:(1): 39–46.
552:
548:
542:
507:
503:
465:
461:
455:
420:
416:
406:
397:
393:
383:
358:
354:
348:
315:
311:
305:
294:. Retrieved
290:
281:
243:
225:stapedectomy
217:Otosclerosis
215:
199:
187:Surgery for
186:
147:
134:
114:
102:
100:techniques.
90:
83:
53:
49:
48:
852:Ear surgery
748:(1): 6–24.
251:protympanum
202:perforation
836:Categories
296:2021-01-13
257:References
117:middle ear
842:Endoscopy
616:0022-2151
123:Rationale
58:endoscope
28:Specialty
811:27565385
772:23120674
718:19351570
675:33334597
667:26228434
624:28891461
577:40931362
534:31236473
482:23566907
447:25418475
847:Otology
763:3450149
710:7176793
632:4039791
569:9930539
525:6580051
438:4467784
375:6021747
340:2283335
332:8082598
240:Recess.
206:eardrum
137:mastoid
72:History
809:
770:
760:
716:
708:
673:
665:
630:
622:
614:
575:
567:
532:
522:
480:
445:
435:
373:
338:
330:
221:stapes
714:S2CID
671:S2CID
628:S2CID
573:S2CID
336:S2CID
38:[
807:PMID
768:PMID
706:PMID
663:PMID
620:PMID
612:ISSN
565:PMID
530:PMID
478:PMID
443:PMID
400:: 1.
398:28–2
371:PMID
328:PMID
244:The
150:MEEI
799:doi
758:PMC
750:doi
698:doi
655:doi
651:126
604:doi
600:132
557:doi
553:108
520:PMC
512:doi
470:doi
433:PMC
425:doi
421:125
363:doi
320:doi
54:EES
838::
805:.
795:49
793:.
789:.
766:.
756:.
746:62
744:.
740:.
726:^
712:.
704:.
694:92
692:.
669:.
661:.
649:.
626:.
618:.
610:.
598:.
594:.
571:.
563:.
551:.
528:.
518:.
506:.
502:.
490:^
476:.
466:46
464:.
441:.
431:.
419:.
415:.
396:.
392:.
369:.
359:85
357:.
334:.
326:.
316:73
314:.
289:.
264:^
813:.
801::
774:.
752::
720:.
700::
677:.
657::
634:.
606::
579:.
559::
536:.
514::
508:4
484:.
472::
449:.
427::
377:.
365::
342:.
322::
299:.
275:.
52:(
42:]
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.