245:
159:
506:
392:
2235:
235:
Other evidence is extremely sparse, and is limited to peculiarities in the
Chinese language of Goguryeo inscriptions and a very few Goguryeo words glossed in Chinese texts. Vovin and Unger suggest that it was the original form of Koreanic, which subsequently replaced Japonic languages in the south of
497:. By the 5th century, Goguryeo ruled a huge area encompassing many ethnic groups and languages. These authors suggest that the place names reflect the languages of those states rather than that of Goguryeo. This would explain why they seem to reflect multiple language groups.
563:
Beckwith identified a dozen names of places and people in
Chinese histories that he argued were Goguryeo words. In his review of Beckwith's book, Byington criticized the historical basis of these identifications, as well as Beckwith's theories of Goguryeo origins in western
232:. Lee and Ramsey suggest that the language was intermediate between the two families. Other authors suggest that these placenames reflect the languages of other peoples in the part of central Korea captured by Goguryeo in the 5th century, rather than Goguryeo itself.
483:
pointed out similarities to
Japanese, particularly in the only attested numerals, 3, 5, 7 and 10. Beckwith proposed Japonic etymologies for most of the words, and argued that Koguryoan was Japonic. Beckwith's linguistic analysis has been criticized for the
488:
nature of his
Chinese reconstructions, for his handling of Japonic material and for hasty rejection of possible cognates in other languages. Lee and Ramsey argue that Koguryoan was somehow intermediate between Koreanic and Japonic.
492:
Other authors point out that most of the place names come from central Korea, an area captured by
Goguryeo from Baekje and other states in the 5th century, and none from the historical homeland of Goguryeo north of the
263:
in the early centuries of the common era. They contain impressionistic remarks about the languages of the area based on second-hand reports, and sometimes contradict one another. Later Korean histories, such as the
451:
means '-fold, layer', while the 'county' part of the gloss is not represented. In this way, a vocabulary of 80 to 100 words has been extracted from these place names. Although the pronunciations recorded using
1706:
Koguryo, the
Language of Japan's Continental Relatives: An Introduction to the Historical-Comparative Study of the Japanese-Koguryoic Languages with a Preliminary Description of Archaic Northeastern Middle
357:
in the same area was different from that of
Goguryeo. These languages are completely unattested, but are believed, on the basis of their location and the description of the people, to have been
468:
words. It is generally agreed that these glosses demonstrate that
Japonic languages were once spoken in part of the Korean peninsula, but there is no consensus on the identity of the speakers.
340:
described in quite different terms from Buyeo and
Goguryeo. Based on this text, Lee Ki-Moon divided the languages spoken on the Korean peninsula at that time into Puyŏ and Han groups.
2689:
471:
Scholars who take these words as representing the language of
Goguryeo have come to a range of conclusions about the language. Most Korean scholars view it as a form of
2755:
2760:
374:
was the same as that of Goguryeo. According to Korean traditional history, the kingdom of Baekje was founded by immigrants from Goguryeo who took over Mahan.
313:, believed themselves to be a southern offshoot of Buyeo. Over the next few centuries they would expand to rule much of eastern Manchuria and northern Korea.
1988:
1844:
1792:
1619:
2662:
2684:
2061:
1989:"The Ethnolinguistic History of the Early Korean Peninsula Region: Japanese-Koguryŏic and other Languages in the Koguryŏ, Paekche, and Silla kingdoms"
409:
and compiled in 1145 from earlier records that are no longer extant. This chapter surveys the part of Goguryeo annexed by Silla, with entries like
2750:
2725:
1974:
Beckwith, Christopher I. (2006), "Methodological Observations on Some Recent Studies of the Early Ethnolinguistic History of Korea and Vicinity",
2679:
2030:
1956:
1830:
1781:
1762:
1743:
1692:
1673:
1654:
1605:
1502:
794:, and argued that the Goguryeo language was the ancestor of Koreanic, and spread southwards to replace the Japonic languages of the Samhan.
386:
218:
439:
is meaningless, and hence seems to use Chinese characters to represent the sound of the name. From other examples, scholars infer that
2720:
2468:
1513:
349:
1520:
Byington, Mark E. (2006), "Christopher I. Beckwith—Koguryo, the Language of Japan's Continental Relatives (Leiden: Brill, 2004)",
310:
2544:
2270:
2256:
840:
2054:
283:
236:
the peninsula. Others maintain that it was Tungusic, or that there is insufficient evidence to establish its affiliation.
2740:
537:
533:
810:
2745:
2730:
2549:
281:
basin, was known to the Chinese from the 3rd century BCE. Chapter 30 "Description of the Eastern Barbarians" of the
2735:
529:
1891:
Whitman, John (2011), "Northeast Asian Linguistic Ecology and the Advent of Rice Agriculture in Korea and Japan",
1859:
2507:
1870:——— (2013), "From Koguryo to Tamna: Slowly riding to the South with speakers of Proto-Korean",
2414:
2378:
2047:
214:. All of these languages are unattested except for Goguryeo, for which evidence is limited and controversial.
2534:
2517:
1490:
187:
133:
2694:
2672:
2521:
2003:
1807:
1634:
723:
590:
2539:
532:(590s). All are written in Chinese, but some of them contain irregularities, including a few examples of
297:
475:
and focus on Korean interpretations of the data. In the early 20th century, Japanese scholars such as
2603:
2593:
1900:
1818:
795:
329:
2502:
2345:
2299:
586:
295:
in 244. Another version of this report, likely from a common source, is found in chapter 85 of the
2657:
2473:
2428:
2322:
2087:
672:
513:
Other data on the language of Goguryeo is extremely sparse, and its affiliation remains unclear.
465:
453:
358:
333:
81:
2715:
2618:
2583:
2578:
2100:
2078:
2026:
1952:
1826:
1777:
1758:
1739:
1688:
1669:
1650:
1601:
1509:
1498:
406:
325:
317:
229:
203:
158:
87:
228:, have treated these words as Korean, while other scholars have emphasized similarities with
2572:
2350:
2317:
2157:
1935:
1908:
1879:
1720:
1575:
1548:
787:
613:
536:
order (as found in Korean and other northeast Asian languages) instead of the usual Chinese
525:
517:
461:
256:
244:
164:
61:
2641:
2598:
2588:
2446:
2355:
2304:
2282:
2204:
2122:
2070:
2014:
1840:
1535:
Gardiner, Kenneth H. J. (2012a), "An Introductory Study of the 'Annals of Koguryŏ' in the
830:
791:
622:
609:
457:
73:
1562:——— (2012b), "Chinese Accounts of Koguryŏ and its Neighbours: From the
521:
309:
was only slightly different from them. Goguryeo, originally inhabiting the valley of the
1904:
552:, which some authors have connected to their use to represent Korean particles in later
2563:
2458:
2327:
2147:
2142:
2127:
719:'elder brother', but this has a limited distribution in Japonic, and may be a loanword.
594:
505:
480:
476:
195:
191:
149:
2709:
2626:
2436:
2360:
2167:
2132:
2095:
1615:
1593:
802:
557:
494:
366:
278:
224:. Most researchers in Korea, assuming that the people of Goguryeo spoke a dialect of
126:
1947:——— (2015), "Old Korean", in Brown, Lucien; Yeon, Jaehoon (eds.),
516:
A small number of inscriptions have been found in Goguryeo territory, including the
391:
2608:
2529:
2388:
1589:
1522:
818:
761:
711:
700:
602:) is the Goguryeo word for 'castle'. Beckwith compared this word with Old Japanese
1580:
1553:
255:
Chinese histories provide the only contemporaneous descriptions of peoples of the
206:. The histories also stated that these languages were different from those of the
776:'ceremonial headgear', which Vovin compared with the first part of Middle Korean
2337:
2291:
2264:
2250:
1703:
639:
401:
354:
266:
211:
2234:
248:
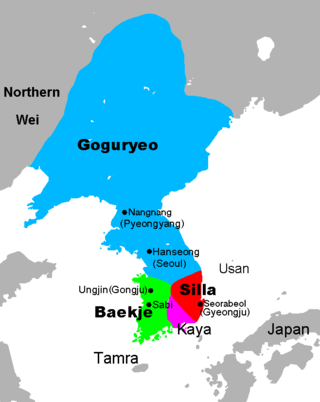
Chinese commanderies (in purple) and their eastern neighbours mentioned in the
2495:
2152:
2110:
1913:
1566:
Ch. 30, Description of the Eastern Barbarians (SGZ 30 pp. 20B-31B; 35A-36B)",
845:
553:
472:
302:
225:
199:
777:
751:
675:
347:
to the northeast differed from that of Buyeo and Goguryeo. Chapter 94 of the
2490:
2396:
260:
142:
110:
50:
301:(5th century). The report states that the languages of Buyeo, Goguryeo and
1939:
1883:
801:
Other authors suggest that the Goguryeo language was a Tungusic language.
738:), glossed as 'good archer'. This name appears in the Gwanggaeto Stele as
190:. Early Chinese histories state that the language was similar to those of
117:
2667:
1725:
806:
565:
427:'one calls' separates two alternative names for a place. The first part,
292:
183:
35:
821:
that rose from the former territory of Goguryeo were Tungusic speakers.
805:
argues for a Tungusic affiliation based on historical evidence that the
2631:
2485:
2025:, Tunguso Sibirica, vol. 20, Otto Harrassowitz, pp. 255–266,
2021:, in Pozzi, Alessandra; Janhunen, Juha Antero; Weiers, Michael (eds.),
1823:
The role of contact in the origins of the Japanese and Korean languages
814:
288:
2463:
1845:"Koguryŏ and Paekche: different languages or dialects of Old Korean?"
835:
371:
321:
39:
2023:
Tumen Jalafun Jecen Aku: Manchu Studies in Honour of Giovanni Stary
2018:
456:
are difficult to interpret, some of these words appear to resemble
2480:
2406:
2370:
2039:
756:'be good', but was unable to identify a match for the second part.
504:
390:
344:
306:
274:
243:
207:
54:
1793:"About Early Paekche language mistaken as being Koguryŏ language"
771:
745:
733:
705:
687:
681:
666:
660:
649:
597:
399:
The most widely cited evidence for Goguryeo is chapter 37 of the
2636:
1683:
Nam, Pung-hyun (2012), "Old Korean", in Tranter, Nicolas (ed.),
2043:
686:
with an Early Middle Korean word 'small, young' transcribed as
616:
163:
The Three Kingdoms of Korea, with Goguryeo and Buyeo in blue (
879:
877:
571:
Chinese histories contain a few glosses of Goguryeo words:
1034:
1032:
995:
993:
991:
909:
907:
714:
603:
1645:
Kim, Nam-Kil (1987), "Korean", in Comrie, Bernard (ed.),
1121:
1119:
963:
961:
894:
892:
750:). Vovin compared the first syllable with Middle Korean
433:, can be read in Chinese as 'seven-fold county', while
270:, do not describe the languages of the three kingdoms.
1495:
Koguryo, the Language of Japan's Continental Relatives
924:
922:
287:
records a survey carried out by the Chinese state of
978:
976:
798:
has proposed a similar model on historical grounds.
625:
405:, a history of the Three Kingdoms period written in
2650:
2617:
2562:
2516:
2445:
2427:
2405:
2387:
2369:
2336:
2290:
2281:
2263:
2249:
2242:
2203:
2189:
2166:
2109:
2086:
2077:
140:
124:
108:
103:
70:
60:
46:
31:
21:
766:
739:
727:
693:
655:
644:
580:
547:
541:
446:
440:
434:
353:(compiled in 659) states that the language of the
1592:(2017), "Other isolated languages of Asia", in
411:
2690:North–South differences in the Korean language
343:The same text states that the language of the
2055:
2019:"Why Manchu and Jurchen Look so Un-Tungusic?"
1649:, Oxford University Press, pp. 881–898,
744:(Eastern Han Chinese *dẓo-mu, Middle Chinese
428:
422:
413:
182:, was the language of the ancient kingdom of
8:
786:Vovin also pointed to Koreanic loanwords in
395:The Korean peninsula in the late 5th century
524:in 414), four inscriptions on the walls of
2663:International Circle of Korean Linguistics
2451:
2287:
2246:
2083:
2062:
2048:
2040:
1738:(3rd ed.), Rowman & Littlefield,
157:
18:
2685:National Institute of the Korean Language
1912:
1776:, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press,
1724:
1579:
1552:
1389:
1269:
1233:
1137:
1110:
1098:
1074:
1050:
1038:
1023:
1011:
999:
967:
952:
898:
883:
868:
1825:, Honolulu: University of Hawaii Press,
1664:Lee, Ki-Moon; Ramsey, S. Robert (2011),
1473:
1401:
1377:
1365:
1245:
1197:
1185:
726:, the legendary founder of Goguryeo, as
202:. Lee Ki-Moon grouped these four as the
2756:Languages attested from the 7th century
1996:Journal of Inner and East Asian Studies
1852:Journal of Inner and East Asian Studies
1800:Journal of Inner and East Asian Studies
1627:Journal of Inner and East Asian Studies
1305:
1293:
1209:
1125:
861:
665:'little elder brother'. Vovin compared
630:'fortified town', but with lenition of
540:order, and some uses of the characters
305:were similar, and that the language of
16:Speculated language of ancient Goguryeo
2680:List of English words of Korean origin
167:is not included in the Three Kingdoms)
2761:Languages extinct in the 10th century
1926:, by Ki-Moon Lee and Robert Ramsey",
1449:
1437:
1425:
1413:
1341:
1317:
1257:
1221:
1086:
928:
913:
509:Goguryeo monument in Jungwon, Chungju
217:The most cited evidence is a body of
7:
1461:
1062:
982:
940:
387:Placename glosses in the Samguk sagi
1353:
1329:
1281:
1173:
1161:
1149:
722:The same chapter gives the name of
1949:The Handbook of Korean Linguistics
370:(635) states that the language of
14:
1368:, pp. 32, 37–46, 52–53, 250.
350:History of the Northern Dynasties
2233:
1924:A History of the Korean Language
1685:The Languages of Japan and Korea
1666:A History of the Korean Language
1922:——— (2013), "
1620:"The lost languages of Koguryŏ"
1600:, Routledge, pp. 139–161,
767:
740:
728:
694:
656:
645:
581:
579:(late 3rd century) states that
548:
542:
447:
441:
435:
240:Descriptions in Chinese sources
2751:Unclassified languages of Asia
2726:History of the Korean language
1987:——— (2005),
1757:, Cambridge University Press,
1753:Shin, Michael D., ed. (2014),
1668:, Cambridge University Press,
841:History of the Korean language
186:(37 BCE – 668 CE), one of the
1:
1687:, Routledge, pp. 41–72,
1581:10.25024/review.2012.15.2.004
1554:10.25024/review.2012.15.1.001
577:Records of the Three Kingdoms
338:Records of the Three Kingdoms
284:Records of the Three Kingdoms
250:Records of the Three Kingdoms
1858:(2): 107–140, archived from
1568:The Review of Korean Studies
1541:The Review of Korean Studies
1452:, pp. 224–226, 237–238.
778:
772:
752:
746:
734:
715:
706:
688:
682:
676:
667:
661:
650:
626:
617:
604:
598:
316:To the south of the Chinese
1951:, Wiley, pp. 421–438,
1709:By Christopher I. Beckwith"
1647:The World's Major Languages
2777:
2469:Consonant and vowel tables
2002:(2): 33–64, archived from
1806:(2): 13–31, archived from
1736:A Concise History of Korea
1633:(2): 67–86, archived from
765:(early 7th century) gives
384:
2721:Extinct languages of Asia
2508:Transcription into Korean
2454:
2231:
1914:10.1007/s12284-011-9080-0
1734:Seth, Michael J. (2020),
530:stele in Jungwon, Chungju
429:
423:
414:
378:Placename glosses in the
219:placename glosses in the
156:
26:
1702:Pellard, Thomas (2005),
1491:Beckwith, Christopher I.
1380:, pp. 148–150, 153.
654:'big elder brother' and
643:(mid-6th century) gives
2535:Cyrillization of Korean
1516:, Second edition, 2007.
1270:Lee & Ramsey (2011)
1234:Lee & Ramsey (2011)
1138:Lee & Ramsey (2011)
1111:Lee & Ramsey (2011)
1099:Lee & Ramsey (2011)
1075:Lee & Ramsey (2011)
1051:Lee & Ramsey (2011)
1039:Lee & Ramsey (2011)
1000:Lee & Ramsey (2011)
968:Lee & Ramsey (2011)
953:Lee & Ramsey (2011)
899:Lee & Ramsey (2011)
884:Lee & Ramsey (2011)
869:Lee & Ramsey (2011)
188:Three Kingdoms of Korea
2695:Sino-Korean vocabulary
2673:List of Konglish terms
2318:Gyeonggi/Seoul dialect
2209:(19th century–present)
1755:Korean History in Maps
782:'ceremonial headgear'.
710:is closely matched by
704:(1103–1104). The word
510:
419:
396:
291:after their defeat of
252:
1940:10.1075/kl.15.2.05whi
1884:10.1075/kl.15.2.03vov
1791:Toh, Soo Hee (2005),
1772:Sohn, Ho-Min (1999),
1152:, pp. 51, 53–54.
508:
394:
298:Book of the Later Han
247:
1726:10.1353/ks.2006.0008
2741:Languages of Russia
2300:Chungcheong dialect
2190:Early modern Korean
1905:2011Rice....4..149W
1774:The Korean Language
1428:, pp. 228–230.
1416:, pp. 230–231.
1344:, pp. 117–119.
1296:, pp. 251–252.
1212:, pp. 168–169.
1026:, pp. 98, 108.
916:, pp. 231–232.
637:Chapter 100 of the
587:Eastern Han Chinese
2746:Languages of China
2731:Languages of Korea
2658:Koreanic languages
2429:Koreanic languages
2323:Gyeongsang dialect
1928:Korean Linguistics
1872:Korean Linguistics
1819:Unger, J. Marshall
1356:, pp. 42, 49.
943:, pp. 16, 19.
759:Chapter 41 of the
673:Late Middle Korean
575:Chapter 30 of the
511:
454:Chinese characters
445:means 'seven' and
397:
253:
2703:
2702:
2558:
2557:
2540:McCune-Reischauer
2423:
2422:
2309:Yeongdong dialect
2277:
2276:
2229:
2228:
2210:
2194:
2193:(17–18th century)
2173:
2172:(10–16th century)
2116:
2032:978-3-447-05378-5
1958:978-1-118-35491-9
1832:978-0-8248-3279-7
1783:978-0-521-36123-1
1764:978-1-107-09846-6
1745:978-1-5381-2897-8
1694:978-0-415-46287-7
1675:978-1-139-49448-9
1656:978-0-19-520521-3
1607:978-1-317-61090-8
1598:Language Isolates
1504:978-90-04-13949-7
1284:, pp. 23–26.
1248:, pp. 67–68.
1236:, pp. 40–41.
1224:, pp. 74–80.
1200:, pp. 27–28.
1113:, pp. 37–44.
1053:, pp. 34–36.
886:, pp. 43–44.
871:, pp. 34–35.
612:compared it with
407:Classical Chinese
318:Lelang Commandery
230:Japonic languages
176:Goguryeo language
172:
171:
66:7th–10th century?
2768:
2452:
2351:Hwanghae dialect
2346:Hamgyŏng dialect
2312:Yeongseo dialect
2288:
2247:
2237:
2208:
2192:
2171:
2115:(?–10th century)
2114:
2084:
2064:
2057:
2050:
2041:
2036:
2015:Vovin, Alexander
2010:
2008:
1993:
1983:
1962:
1943:
1918:
1916:
1899:(3–4): 149–158,
1887:
1866:
1864:
1849:
1841:Vovin, Alexander
1836:
1814:
1812:
1797:
1787:
1768:
1749:
1730:
1728:
1698:
1679:
1660:
1641:
1639:
1624:
1611:
1585:
1583:
1558:
1556:
1531:
1508:
1477:
1471:
1465:
1459:
1453:
1447:
1441:
1435:
1429:
1423:
1417:
1411:
1405:
1399:
1393:
1390:Gardiner (2012b)
1387:
1381:
1375:
1369:
1363:
1357:
1351:
1345:
1339:
1333:
1327:
1321:
1315:
1309:
1303:
1297:
1291:
1285:
1279:
1273:
1267:
1261:
1255:
1249:
1243:
1237:
1231:
1225:
1219:
1213:
1207:
1201:
1195:
1189:
1183:
1177:
1171:
1165:
1159:
1153:
1147:
1141:
1135:
1129:
1123:
1114:
1108:
1102:
1096:
1090:
1084:
1078:
1072:
1066:
1060:
1054:
1048:
1042:
1036:
1027:
1024:Gardiner (2012b)
1021:
1015:
1012:Gardiner (2012a)
1009:
1003:
997:
986:
980:
971:
965:
956:
950:
944:
938:
932:
926:
917:
911:
902:
896:
887:
881:
872:
866:
781:
775:
770:
769:
755:
749:
743:
742:
737:
732:(Middle Chinese
731:
730:
718:
709:
697:
696:
691:
685:
679:
670:
664:
659:
658:
653:
648:
647:
629:
620:
614:Middle Mongolian
607:
601:
592:
584:
583:
551:
550:
545:
544:
526:Pyongyang Castle
518:Gwanggaeto Stele
450:
449:
444:
443:
438:
437:
432:
431:
426:
425:
417:
416:
257:Korean peninsula
161:
152:
136:
120:
113:
76:
19:
2776:
2775:
2771:
2770:
2769:
2767:
2766:
2765:
2706:
2705:
2704:
2699:
2646:
2642:Yongbieocheonga
2613:
2554:
2512:
2441:
2419:
2415:Zainichi Korean
2401:
2383:
2365:
2356:Pyongan dialect
2332:
2305:Gangwon dialect
2273:
2259:
2238:
2225:
2207:
2199:
2191:
2185:
2170:
2162:
2113:
2105:
2073:
2071:Korean language
2068:
2033:
2013:
2006:
1991:
1986:
1973:
1970:
1968:Further reading
1965:
1959:
1946:
1921:
1890:
1869:
1862:
1847:
1839:
1833:
1817:
1810:
1795:
1790:
1784:
1771:
1765:
1752:
1746:
1733:
1701:
1695:
1682:
1676:
1663:
1657:
1644:
1637:
1622:
1614:
1608:
1588:
1561:
1534:
1519:
1505:
1489:
1485:
1480:
1474:Janhunen (2005)
1472:
1468:
1460:
1456:
1448:
1444:
1436:
1432:
1424:
1420:
1412:
1408:
1402:Beckwith (2004)
1400:
1396:
1388:
1384:
1378:Byington (2006)
1376:
1372:
1366:Beckwith (2004)
1364:
1360:
1352:
1348:
1340:
1336:
1328:
1324:
1316:
1312:
1304:
1300:
1292:
1288:
1280:
1276:
1268:
1264:
1256:
1252:
1246:Janhunen (2005)
1244:
1240:
1232:
1228:
1220:
1216:
1208:
1204:
1198:Beckwith (2004)
1196:
1192:
1186:Beckwith (2004)
1184:
1180:
1172:
1168:
1160:
1156:
1148:
1144:
1136:
1132:
1124:
1117:
1109:
1105:
1097:
1093:
1085:
1081:
1073:
1069:
1061:
1057:
1049:
1045:
1037:
1030:
1022:
1018:
1010:
1006:
998:
989:
981:
974:
966:
959:
951:
947:
939:
935:
927:
920:
912:
905:
897:
890:
882:
875:
867:
863:
859:
854:
831:Baekje language
827:
610:Alexander Vovin
503:
389:
383:
324:('three Han'),
277:, in the upper
242:
168:
148:
132:
129:
116:
109:
99:
77:
74:Language family
72:
17:
12:
11:
5:
2774:
2772:
2764:
2763:
2758:
2753:
2748:
2743:
2738:
2736:Puyŏ languages
2733:
2728:
2723:
2718:
2708:
2707:
2701:
2700:
2698:
2697:
2692:
2687:
2682:
2677:
2676:
2675:
2665:
2660:
2654:
2652:
2648:
2647:
2645:
2644:
2639:
2634:
2629:
2623:
2621:
2615:
2614:
2612:
2611:
2606:
2601:
2596:
2591:
2586:
2581:
2576:
2568:
2566:
2560:
2559:
2556:
2555:
2553:
2552:
2547:
2542:
2537:
2532:
2526:
2524:
2514:
2513:
2511:
2510:
2505:
2500:
2499:
2498:
2493:
2488:
2478:
2477:
2476:
2471:
2461:
2459:Korean Braille
2455:
2449:
2447:Writing system
2443:
2442:
2440:
2439:
2433:
2431:
2425:
2424:
2421:
2420:
2418:
2417:
2411:
2409:
2403:
2402:
2400:
2399:
2393:
2391:
2385:
2384:
2382:
2381:
2379:Chinese Korean
2375:
2373:
2367:
2366:
2364:
2363:
2361:Yukjin dialect
2358:
2353:
2348:
2342:
2340:
2334:
2333:
2331:
2330:
2328:Jeolla dialect
2325:
2320:
2315:
2314:
2313:
2310:
2302:
2296:
2294:
2285:
2279:
2278:
2275:
2274:
2269:
2267:
2261:
2260:
2255:
2253:
2244:
2240:
2239:
2232:
2230:
2227:
2226:
2224:
2223:
2220:
2217:
2213:
2211:
2201:
2200:
2197:
2195:
2187:
2186:
2184:
2183:
2180:
2176:
2174:
2164:
2163:
2161:
2160:
2155:
2150:
2145:
2140:
2135:
2130:
2125:
2119:
2117:
2107:
2106:
2104:
2103:
2098:
2092:
2090:
2088:Proto-Koreanic
2081:
2075:
2074:
2069:
2067:
2066:
2059:
2052:
2044:
2038:
2037:
2031:
2011:
2009:on 2009-02-26.
1984:
1969:
1966:
1964:
1963:
1957:
1944:
1934:(2): 246–260,
1919:
1888:
1878:(2): 222–240,
1867:
1865:on 2009-02-26.
1837:
1831:
1815:
1813:on 2009-02-26.
1788:
1782:
1769:
1763:
1750:
1744:
1731:
1713:Korean Studies
1699:
1693:
1680:
1674:
1661:
1655:
1642:
1640:on 2009-02-26.
1616:Janhunen, Juha
1612:
1606:
1594:Campbell, Lyle
1586:
1559:
1532:
1517:
1503:
1486:
1484:
1481:
1479:
1478:
1466:
1454:
1442:
1440:, p. 230.
1430:
1418:
1406:
1394:
1382:
1370:
1358:
1346:
1334:
1322:
1320:, p. 151.
1310:
1308:, p. 423.
1306:Whitman (2015)
1298:
1294:Whitman (2013)
1286:
1274:
1262:
1250:
1238:
1226:
1214:
1210:Pellard (2005)
1202:
1190:
1178:
1166:
1164:, p. 883.
1154:
1142:
1130:
1128:, p. 154.
1126:Whitman (2011)
1115:
1103:
1091:
1079:
1067:
1055:
1043:
1028:
1016:
1004:
987:
972:
957:
945:
933:
918:
903:
888:
873:
860:
858:
855:
853:
850:
849:
848:
843:
838:
833:
826:
823:
813:and later the
784:
783:
757:
720:
635:
608:'storehouse'.
595:Middle Chinese
502:
499:
481:Shinmura Izuru
385:Main article:
382:
376:
241:
238:
204:Puyŏ languages
170:
169:
162:
154:
153:
146:
138:
137:
130:
125:
122:
121:
114:
106:
105:
104:Language codes
101:
100:
98:
97:
96:
95:
80:
78:
71:
68:
67:
64:
58:
57:
48:
44:
43:
33:
32:Native to
29:
28:
24:
23:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2773:
2762:
2759:
2757:
2754:
2752:
2749:
2747:
2744:
2742:
2739:
2737:
2734:
2732:
2729:
2727:
2724:
2722:
2719:
2717:
2714:
2713:
2711:
2696:
2693:
2691:
2688:
2686:
2683:
2681:
2678:
2674:
2671:
2670:
2669:
2666:
2664:
2661:
2659:
2656:
2655:
2653:
2649:
2643:
2640:
2638:
2635:
2633:
2630:
2628:
2625:
2624:
2622:
2620:
2616:
2610:
2607:
2605:
2604:Speech levels
2602:
2600:
2597:
2595:
2594:Postpositions
2592:
2590:
2587:
2585:
2582:
2580:
2577:
2575:
2574:
2570:
2569:
2567:
2565:
2561:
2551:
2548:
2546:
2543:
2541:
2538:
2536:
2533:
2531:
2528:
2527:
2525:
2523:
2519:
2518:Cyrillization
2515:
2509:
2506:
2504:
2501:
2497:
2494:
2492:
2489:
2487:
2484:
2483:
2482:
2479:
2475:
2472:
2470:
2467:
2466:
2465:
2462:
2460:
2457:
2456:
2453:
2450:
2448:
2444:
2438:
2437:Jeju language
2435:
2434:
2432:
2430:
2426:
2416:
2413:
2412:
2410:
2408:
2404:
2398:
2395:
2394:
2392:
2390:
2386:
2380:
2377:
2376:
2374:
2372:
2368:
2362:
2359:
2357:
2354:
2352:
2349:
2347:
2344:
2343:
2341:
2339:
2335:
2329:
2326:
2324:
2321:
2319:
2316:
2311:
2308:
2307:
2306:
2303:
2301:
2298:
2297:
2295:
2293:
2289:
2286:
2284:
2280:
2272:
2268:
2266:
2262:
2258:
2254:
2252:
2248:
2245:
2241:
2236:
2221:
2218:
2215:
2214:
2212:
2206:
2205:Modern Korean
2202:
2196:
2188:
2181:
2178:
2177:
2175:
2169:
2168:Middle Korean
2165:
2159:
2156:
2154:
2151:
2149:
2146:
2144:
2141:
2139:
2136:
2134:
2131:
2129:
2126:
2124:
2121:
2120:
2118:
2112:
2108:
2102:
2099:
2097:
2094:
2093:
2091:
2089:
2085:
2082:
2080:
2076:
2072:
2065:
2060:
2058:
2053:
2051:
2046:
2045:
2042:
2034:
2028:
2024:
2020:
2016:
2012:
2005:
2001:
1997:
1990:
1985:
1981:
1977:
1972:
1971:
1967:
1960:
1954:
1950:
1945:
1941:
1937:
1933:
1929:
1925:
1920:
1915:
1910:
1906:
1902:
1898:
1894:
1889:
1885:
1881:
1877:
1873:
1868:
1861:
1857:
1853:
1846:
1842:
1838:
1834:
1828:
1824:
1820:
1816:
1809:
1805:
1801:
1794:
1789:
1785:
1779:
1775:
1770:
1766:
1760:
1756:
1751:
1747:
1741:
1737:
1732:
1727:
1722:
1718:
1714:
1710:
1708:
1700:
1696:
1690:
1686:
1681:
1677:
1671:
1667:
1662:
1658:
1652:
1648:
1643:
1636:
1632:
1628:
1621:
1617:
1613:
1609:
1603:
1599:
1595:
1591:
1590:Georg, Stefan
1587:
1582:
1577:
1574:(2): 91–113,
1573:
1569:
1565:
1560:
1555:
1550:
1546:
1542:
1538:
1533:
1530:(1): 141–166.
1529:
1525:
1524:
1518:
1515:
1514:90-04-13949-4
1511:
1506:
1500:
1496:
1492:
1488:
1487:
1482:
1476:, p. 84.
1475:
1470:
1467:
1464:, p. 39.
1463:
1458:
1455:
1451:
1446:
1443:
1439:
1434:
1431:
1427:
1422:
1419:
1415:
1410:
1407:
1404:, p. 41.
1403:
1398:
1395:
1392:, p. 98.
1391:
1386:
1383:
1379:
1374:
1371:
1367:
1362:
1359:
1355:
1350:
1347:
1343:
1338:
1335:
1332:, p. 42.
1331:
1326:
1323:
1319:
1314:
1311:
1307:
1302:
1299:
1295:
1290:
1287:
1283:
1278:
1275:
1272:, p. 40.
1271:
1266:
1263:
1260:, p. 28.
1259:
1254:
1251:
1247:
1242:
1239:
1235:
1230:
1227:
1223:
1218:
1215:
1211:
1206:
1203:
1199:
1194:
1191:
1187:
1182:
1179:
1176:, p. 12.
1175:
1170:
1167:
1163:
1158:
1155:
1151:
1146:
1143:
1140:, p. 43.
1139:
1134:
1131:
1127:
1122:
1120:
1116:
1112:
1107:
1104:
1101:, p. 39.
1100:
1095:
1092:
1089:, p. 73.
1088:
1083:
1080:
1077:, p. 37.
1076:
1071:
1068:
1065:, p. 38.
1064:
1059:
1056:
1052:
1047:
1044:
1041:, p. 35.
1040:
1035:
1033:
1029:
1025:
1020:
1017:
1014:, p. 24.
1013:
1008:
1005:
1002:, p. 34.
1001:
996:
994:
992:
988:
985:, p. 20.
984:
979:
977:
973:
970:, p. 36.
969:
964:
962:
958:
955:, p. 31.
954:
949:
946:
942:
937:
934:
931:, p. 87.
930:
925:
923:
919:
915:
910:
908:
904:
901:, p. 44.
900:
895:
893:
889:
885:
880:
878:
874:
870:
865:
862:
856:
851:
847:
844:
842:
839:
837:
834:
832:
829:
828:
824:
822:
820:
816:
812:
808:
804:
803:Juha Janhunen
799:
797:
793:
789:
780:
774:
764:
763:
758:
754:
748:
736:
725:
721:
717:
713:
708:
703:
702:
690:
684:
678:
674:
669:
663:
652:
642:
641:
636:
634:as in Korean.
633:
628:
624:
619:
615:
611:
606:
600:
596:
588:
578:
574:
573:
572:
569:
567:
561:
559:
558:Unified Silla
555:
539:
535:
531:
527:
523:
519:
514:
507:
500:
498:
496:
495:Taedong River
490:
487:
482:
478:
474:
469:
467:
463:
459:
455:
418:
410:
408:
404:
403:
393:
388:
381:
377:
375:
373:
369:
368:
367:Book of Liang
362:
360:
356:
352:
351:
346:
341:
339:
335:
331:
327:
323:
319:
314:
312:
308:
304:
300:
299:
294:
290:
286:
285:
280:
276:
273:The state of
271:
269:
268:
262:
258:
251:
246:
239:
237:
233:
231:
227:
223:
222:
215:
213:
209:
205:
201:
197:
193:
189:
185:
181:
177:
166:
160:
155:
151:
147:
145:
144:
139:
135:
131:
128:
127:Linguist List
123:
119:
115:
112:
107:
102:
94:
91:
90:
89:
86:
85:
83:
79:
75:
69:
65:
63:
59:
56:
52:
49:
45:
41:
37:
34:
30:
25:
20:
2651:Other topics
2571:
2530:ISO/TR 11941
2522:Romanization
2503:Mixed script
2389:Central Asia
2137:
2022:
2004:the original
1999:
1995:
1979:
1975:
1948:
1931:
1927:
1923:
1896:
1892:
1875:
1871:
1860:the original
1855:
1851:
1822:
1808:the original
1803:
1799:
1773:
1754:
1735:
1716:
1712:
1705:
1684:
1665:
1646:
1635:the original
1630:
1626:
1597:
1571:
1567:
1563:
1547:(1): 15–58,
1544:
1540:
1536:
1527:
1523:Acta Koreana
1521:
1494:
1469:
1457:
1450:Vovin (2013)
1445:
1438:Vovin (2013)
1433:
1426:Vovin (2013)
1421:
1414:Vovin (2013)
1409:
1397:
1385:
1373:
1361:
1349:
1342:Vovin (2005)
1337:
1325:
1318:Georg (2017)
1313:
1301:
1289:
1277:
1265:
1258:Unger (2009)
1253:
1241:
1229:
1222:Unger (2009)
1217:
1205:
1193:
1188:, p. 9.
1181:
1169:
1157:
1145:
1133:
1106:
1094:
1087:Unger (2009)
1082:
1070:
1058:
1046:
1019:
1007:
948:
936:
929:Unger (2009)
914:Vovin (2013)
864:
819:Qing dynasty
800:
785:
762:Book of Zhou
760:
712:Old Japanese
701:Jilin leishi
699:
638:
631:
576:
570:
562:
520:(erected in
515:
512:
491:
485:
470:
420:
412:
400:
398:
379:
365:
363:
348:
342:
337:
315:
296:
282:
272:
265:
259:and eastern
254:
249:
234:
220:
216:
179:
175:
173:
141:
92:
2474:Punctuation
2338:North Korea
2292:South Korea
2265:North Korea
2251:South Korea
2222:South Korea
2219:North Korea
1976:Altai Hakpo
1719:: 167–170,
1537:Samguk Sagi
1462:Sohn (1999)
1063:Sohn (1999)
983:Seth (2020)
941:Shin (2014)
811:Jin dynasty
796:James Unger
747:tsrhju-mjuw
640:Book of Wei
556:texts from
538:verb–object
534:object–verb
477:Naitō Konan
421:The phrase
402:Samguk sagi
380:Samguk sagi
267:Samguk sagi
221:Samguk sagi
2710:Categories
2619:Literature
2584:Honorifics
2579:Count word
2111:Old Korean
1982:: 199–234.
1354:Nam (2012)
1330:Nam (2012)
1282:Toh (2005)
1174:Toh (2005)
1162:Kim (1987)
1150:Nam (2012)
852:References
846:Old Korean
735:tsyu-muwng
680:'old' and
501:Other data
473:Old Korean
336:, who the
226:Old Korean
2573:Phonology
2491:Hyangchal
2397:Koryo-mar
1564:Sanguozhi
1497:, Brill,
857:Citations
698:) in the
662:thaj-syae
311:Hun River
261:Manchuria
180:Koguryoan
143:Glottolog
111:ISO 639-3
51:Manchuria
2716:Goguryeo
2668:Konglish
2599:Pronouns
2589:Numerals
2283:Dialects
2257:Pyojuneo
2243:Standard
2138:Goguryeo
2017:(2006),
1843:(2005),
1821:(2009),
1618:(2005),
1493:(2004),
825:See also
807:Jurchens
689:ʔæ-thwoj
651:ʔjot-syæ
566:Liaoning
528:, and a
466:Tungusic
458:Koreanic
415:七重縣一云難隱別
359:Tungusic
330:Byeonhan
320:lay the
293:Goguryeo
184:Goguryeo
150:kogu1234
93:Goguryeo
82:Koreanic
36:Goguryeo
22:Goguryeo
2632:Hyangga
2564:Grammar
2545:Revised
2486:Gugyeol
2271:Munhwaŏ
2158:Ye-Maek
2079:History
1901:Bibcode
1707:Chinese
1596:(ed.),
1483:Sources
817:of the
815:Manchus
809:of the
788:Jurchen
779:kwoskál
773:kwot-su
599:kuw-luw
462:Japonic
279:Songhua
62:Extinct
27:Koguryŏ
2464:Hangul
2216:Joseon
2198:Joseon
2182:Joseon
2179:Goryeo
2123:Baekje
2029:
1955:
1829:
1780:
1761:
1742:
1691:
1672:
1653:
1604:
1512:
1501:
836:Balhae
792:Manchu
753:tywǒh-
724:Jumong
623:Manchu
618:qoto-n
486:ad hoc
372:Baekje
334:Jinhan
322:Samhan
47:Region
40:Balhae
2609:Verbs
2481:Hanja
2407:Japan
2371:China
2153:Silla
2148:Okjeo
2143:Mahan
2128:Buyeo
2007:(PDF)
1992:(PDF)
1863:(PDF)
1848:(PDF)
1811:(PDF)
1796:(PDF)
1638:(PDF)
1623:(PDF)
677:nyěys
671:with
627:hoton
522:Ji'an
345:Yilou
326:Mahan
307:Okjeo
275:Buyeo
208:Yilou
196:Okjeo
192:Buyeo
178:, or
55:Korea
2637:Sijo
2627:Gasa
2550:Yale
2520:and
2133:Gaya
2101:Puyŏ
2027:ISBN
1953:ISBN
1893:Rice
1827:ISBN
1778:ISBN
1759:ISBN
1740:ISBN
1689:ISBN
1670:ISBN
1651:ISBN
1602:ISBN
1510:ISBN
1499:ISBN
790:and
683:thaj
668:ʔjot
621:and
605:kura
591:koro
546:and
479:and
464:and
364:The
355:Mohe
332:and
212:Mohe
210:and
198:and
174:The
165:Kaya
88:Puyŏ
2496:Idu
2096:Han
1936:doi
1909:doi
1880:doi
1721:doi
1576:doi
1549:doi
1539:",
707:syæ
554:Idu
436:難隱別
430:七重縣
289:Wei
134:zkg
118:zkg
2712::
1998:,
1994:,
1980:16
1978:,
1932:15
1930:,
1907:,
1895:,
1876:15
1874:,
1854:,
1850:,
1802:,
1798:,
1717:29
1715:,
1711:,
1629:,
1625:,
1572:15
1570:,
1545:15
1543:,
1526:,
1118:^
1031:^
990:^
975:^
960:^
921:^
906:^
891:^
876:^
768:骨蘇
741:鶵牟
729:朱蒙
716:se
695:亞退
657:太奢
646:謁奢
593:,
582:溝漊
568:.
560:.
460:,
442:難隱
424:一云
361:.
328:,
303:Ye
200:Ye
194:,
84:?
53:,
38:,
2063:e
2056:t
2049:v
2035:.
2000:2
1961:.
1942:.
1938::
1917:.
1911::
1903::
1897:4
1886:.
1882::
1856:2
1835:.
1804:2
1786:.
1767:.
1748:.
1729:.
1723::
1704:"
1697:.
1678:.
1659:.
1631:2
1610:.
1584:.
1578::
1557:.
1551::
1528:9
1507:.
692:(
632:t
589:*
585:(
549:伊
543:之
448:別
42:?
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.