74:
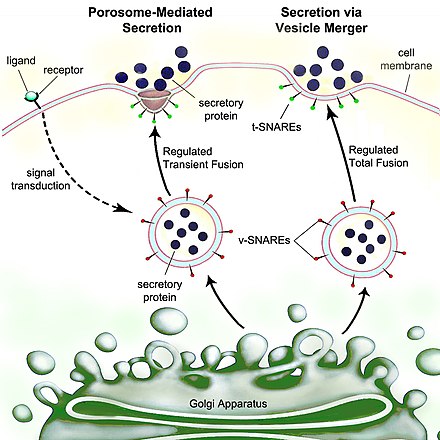
vesicle containing v-SNARE docks at the porosome base containing t-SNARE, membrane continuity (ring complex) is formed between the two. The size of the t/v-SNARE complex is directly proportional to the size of the vesicle. These vesicles contain dehydrated proteins (non-active) which are activated once they are hydrated. GTP is required for the transport of water through the water channels or
Aquaporins, and ions through ion channels to hydrate the vesicle. Once the vesicle fuses at the porosome base, the contents of the vesicle at high pressure are ejected from the cell.
70:
microscopy, demonstrate increased presence of partially empty vesicles following secretion. This suggested that during the secretory process, only a portion of the vesicular contents are able to exit the cell. This could only be possible if the vesicle were to temporarily establish continuity with the cell plasma membrane, expel a portion of its contents, then detach, reseal, and withdraw into the cytosol (endocytose). In this way, the secretory vesicle could be reused for subsequent rounds of exo-endocytosis, until completely empty of its contents.
27:
20:
69:
with the cell membrane. Once the vesicles have docked with the SNARE proteins, they swell, which increases their internal pressure. They then transiently fuse at the base of the porosome, and these pressurized contents are ejected from the cell. Examination of cells following secretion using electron
73:
Porosomes vary in size depending on the cell type. Porosome in the exocrine pancreas and in endocrine and neuroendocrine cells range from 100 nm to 180 nm in diameter while in neurons they range from 10 nm to 15 nm (about 1/10 the size of pancreatic porosomes). When a secretory
60:
or continuity for the release of intravesicular contents from the cell. After secretion is complete, the fusion pore temporarily formed at the base of the porosome is sealed. Porosomes are few nanometers in size and contain many different types of protein, especially chloride and calcium channels,
77:
Generally, the porosomes are opened and closed by actin, however, neurons require a fast response therefore they have central plugs that open to release contents and close to stop the release (the composition of the central plug is yet to be discovered). Porosomes have been demonstrated to be the
78:
universal secretory machinery in cells. The neuronal porosome proteome has been solved, providing the possible molecular architecture and the complete composition of the machinery.
292:
323:
463:
266:
435:
418:
299:
66:
337:
56:. The transient fusion of secretory vesicle membrane at a porosome, base via SNARE proteins, results in the formation of a
456:
541:
637:
532:
449:
95:
545:
527:
632:
581:
536:
210:"Discovery of the Porosome: revealing the molecular mechanism of secretion and membrane fusion in cells"
280:
586:
414:
382:
317:
262:
239:
190:
149:
87:
45:
601:
519:
372:
364:
229:
221:
180:
139:
131:
596:
91:
62:
481:
377:
352:
234:
225:
209:
144:
135:
119:
49:
37:
626:
606:
566:
489:
473:
407:
504:
494:
26:
19:
441:
86:
The porosome was discovered in the early to mid-1990s by a team led by
Professor
499:
368:
576:
571:
259:
NanoCellBiology of
Secretion. Imaging its cellular and molecular underpinnings
53:
41:
386:
243:
194:
153:
185:
168:
561:
120:"Discovery of the 'porosome'; the universal secretory machinery in cells"
591:
509:
261:, vol. 1, Springer Briefs in Biological Imaging, pp. 1–70,
405:
Walter F. Boron, Emile L. Boulpaep (2017). ""Search: Porosome"".
353:"Neuronal porosome proteome: Molecular dynamics and architecture"
445:
281:
http://joe.endocrinology-journals.org/cgi/reprint/176/2/169.pdf
351:
Lee JS, Jeremic A, Shin L, Cho WJ, Chen X, Jena BP (2012).
438:
Jena Lab at Wayne State
University School of Medicine
436:
Molecular
Machinery & Mechanism of Cell Secretion
554:
518:
480:
406:
169:"Fusion pore or porosome: structure and dynamics"
36:are cup-shaped supramolecular structures in the
457:
8:
65:that mediate the docking and fusion of the
464:
450:
442:
113:
111:
376:
233:
184:
143:
25:
18:
107:
322:: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (
315:
16:Structure in eukaryotic cell membrane
7:
48:transiently dock in the process of
226:10.1111/j.1582-4934.2004.tb00255.x
136:10.1111/j.1582-4934.2006.tb00294.x
14:
1:
542:Peripheral membrane protein
369:10.1016/j.jprot.2012.05.017
654:
533:Integral membrane proteins
413:(3rd ed.). Elsevier.
94:School of Medicine, using
577:Lipid raft/microdomains
96:atomic force microscopy
582:Membrane contact sites
546:Lipid-anchored protein
528:Membrane glycoproteins
30:
23:
537:transmembrane protein
338:"Unsupported Browser"
186:10.1677/joe.0.1760169
29:
22:
562:Caveolae/Coated pits
118:Anderson LL (2006).
82:History of discovery
257:Jena, B.P. (2012),
587:Membrane nanotubes
472:Structures of the
409:Medical Physiology
46:secretory vesicles
31:
24:
620:
619:
520:Membrane proteins
268:978-1-4614-2437-6
214:J. Cell. Mol. Med
124:J. Cell. Mol. Med
88:Bhanu Pratap Jena
645:
638:Membrane biology
602:Nuclear envelope
597:Nodes of Ranvier
466:
459:
452:
443:
424:
412:
391:
390:
380:
348:
342:
341:
334:
328:
327:
321:
313:
311:
310:
304:
298:. Archived from
297:
289:
283:
278:
272:
271:
254:
248:
247:
237:
208:Jena BP (2004).
205:
199:
198:
188:
167:Jena BP (2003).
164:
158:
157:
147:
115:
653:
652:
648:
647:
646:
644:
643:
642:
623:
622:
621:
616:
550:
514:
482:Membrane lipids
476:
470:
432:
427:
421:
404:
400:
398:Further reading
395:
394:
363:(13): 3952–62.
350:
349:
345:
336:
335:
331:
314:
308:
306:
302:
295:
293:"Archived copy"
291:
290:
286:
279:
275:
269:
256:
255:
251:
207:
206:
202:
166:
165:
161:
117:
116:
109:
104:
92:Yale University
84:
17:
12:
11:
5:
651:
649:
641:
640:
635:
625:
624:
618:
617:
615:
614:
609:
607:Phycobilisomes
604:
599:
594:
589:
584:
579:
574:
569:
567:Cell junctions
564:
558:
556:
552:
551:
549:
548:
539:
530:
524:
522:
516:
515:
513:
512:
507:
502:
497:
492:
486:
484:
478:
477:
471:
469:
468:
461:
454:
446:
440:
439:
431:
430:External links
428:
426:
425:
419:
401:
399:
396:
393:
392:
343:
329:
284:
273:
267:
249:
200:
159:
106:
105:
103:
100:
83:
80:
63:SNARE proteins
50:vesicle fusion
38:cell membranes
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
650:
639:
636:
634:
631:
630:
628:
613:
610:
608:
605:
603:
600:
598:
595:
593:
592:Myelin sheath
590:
588:
585:
583:
580:
578:
575:
573:
570:
568:
565:
563:
560:
559:
557:
553:
547:
543:
540:
538:
534:
531:
529:
526:
525:
523:
521:
517:
511:
508:
506:
505:Sphingolipids
503:
501:
498:
496:
495:Phospholipids
493:
491:
490:Lipid bilayer
488:
487:
485:
483:
479:
475:
474:cell membrane
467:
462:
460:
455:
453:
448:
447:
444:
437:
434:
433:
429:
422:
420:9781455743773
416:
411:
410:
403:
402:
397:
388:
384:
379:
374:
370:
366:
362:
358:
354:
347:
344:
339:
333:
330:
325:
319:
305:on 2016-03-03
301:
294:
288:
285:
282:
277:
274:
270:
264:
260:
253:
250:
245:
241:
236:
231:
227:
223:
219:
215:
211:
204:
201:
196:
192:
187:
182:
179:(2): 169–74.
178:
174:
173:J. Endocrinol
170:
163:
160:
155:
151:
146:
141:
137:
133:
130:(1): 126–31.
129:
125:
121:
114:
112:
108:
101:
99:
97:
93:
89:
81:
79:
75:
71:
68:
64:
59:
55:
51:
47:
43:
39:
35:
28:
21:
633:Cell anatomy
611:
500:Lipoproteins
408:
360:
357:J Proteomics
356:
346:
332:
307:. Retrieved
300:the original
287:
276:
258:
252:
217:
213:
203:
176:
172:
162:
127:
123:
85:
76:
72:
57:
44:cells where
33:
32:
220:(1): 1–21.
61:actin, and
58:fusion pore
627:Categories
572:Glycocalyx
309:2010-02-21
102:References
42:eukaryotic
612:Porosomes
54:secretion
34:Porosomes
387:22659300
318:cite web
244:15090256
195:12553865
154:16563225
67:vesicles
510:Sterols
378:4580231
235:6740243
145:3933105
417:
385:
375:
265:
242:
232:
193:
152:
142:
555:Other
303:(PDF)
296:(PDF)
415:ISBN
383:PMID
324:link
263:ISBN
240:PMID
191:PMID
150:PMID
52:and
373:PMC
365:doi
230:PMC
222:doi
181:doi
177:176
140:PMC
132:doi
90:at
40:of
629::
381:.
371:.
361:75
359:.
355:.
320:}}
316:{{
238:.
228:.
216:.
212:.
189:.
175:.
171:.
148:.
138:.
128:10
126:.
122:.
110:^
98:.
544:/
535:/
465:e
458:t
451:v
423:.
389:.
367::
340:.
326:)
312:.
246:.
224::
218:8
197:.
183::
156:.
134::
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.