743:
844:
908:
relationship between stress and plastic strain, the
Ramberg–Osgood model implies that plastic strain is present even for very low levels of stress. Nevertheless, for low applied stresses and for the commonly used values of the material constants
1586:
1347:
Several slightly different alternative formulations of the
Ramberg-Osgood equation can be found. As the models are purely empirical, it is often useful to try different models and check which has the best fit with the chosen material.
1460:
123:
365:
1081:
646:
1322:
762:
634:
1014:
1219:
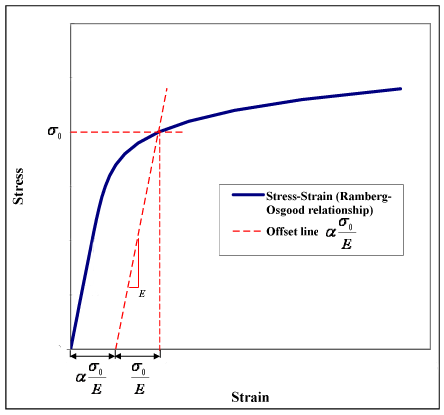
1338:: Generic representation of the stress–strain curve by means of the Ramberg–Osgood equation. Strain corresponding to the yield point is the sum of the elastic and plastic components.
451:
1167:
1115:
317:
290:
400:
1520:
149:
1489:
974:
526:
1268:
881:
927:
546:
175:
1247:
902:
1509:
1389:
1369:
947:
566:
491:
471:
247:
227:
201:
1396:
64:
1673:
Gadamchetty, Geethanjali; Pandey, Abhijeet; Gawture, Majnoo (2016-01-05). "On
Practical Implementation of the Ramberg-Osgood Model for FE Simulation".
1249:
are ~5 or greater, although more precise values are usually obtained by fitting of tensile (or compressive) experimental data. Values for
1332:
738:{\displaystyle \ K\left({\frac {\sigma }{E}}\right)^{n}=\alpha {\frac {\sigma }{E}}\left({\frac {\sigma }{\sigma _{0}}}\right)^{n-1}}
324:
1023:
1270:
can also be found by means of fitting to experimental data, although for some materials, it can be fixed in order to have the
839:{\displaystyle \varepsilon ={\frac {\sigma }{E}}+\alpha {\frac {\sigma }{E}}\left({\frac {\sigma }{\sigma _{0}}}\right)^{n-1}}
1284:
571:
949:, the plastic strain remains negligible compared to the elastic strain. On the other hand, for stress levels higher than
982:
55:, checking the fit of the model with actual experimental data for the particular material of interest is essential.
1741:
152:
28:
1512:
1177:
32:
1619:
405:
1130:
1086:
319:, can be modeled with a power law. The elastic and plastic components are summed to find the total strain.
52:
1630:
1581:{\displaystyle \varepsilon ={\frac {\sigma }{E}}+0.002\left({\frac {\sigma }{\sigma _{y}}}\right)^{n}}
295:
268:
372:
1491:, is assumed to be at the 0.2% offset strain, the following relationship can be derived. Note that
36:
1614:
Ramberg, W., & Osgood, W. R. (1943). Description of stress–strain curves by three parameters.
134:
1736:
1467:
952:
504:
204:
1252:
865:
1713:
1690:
912:
531:
160:
1682:
265:
The equation is essentially assuming the elastic strain portion of the stress-strain curve,
178:
24:
1596:
1455:{\displaystyle \varepsilon ={\frac {\sigma }{E}}+\left({\frac {\sigma }{K}}\right)^{1/n}}
1231:
886:
118:{\displaystyle \varepsilon ={\frac {\sigma }{E}}+K\left({\frac {\sigma }{E}}\right)^{n}}
1494:
1374:
1354:
932:
551:
476:
456:
258:
232:
212:
186:
44:
1511:
is again as defined in the original
Ramberg-Osgood equation and is the inverse of the
1351:
The
Ramberg-Osgood equation can also be expressed using the Hollomon parameters where
1730:
752:
Replacing in the first expression, the
Ramberg–Osgood equation can be written as
1331:
1717:
1694:
636:, it is convenient to rewrite the term on the extreme right side as follows:
1710:
Determination of stress-strain relations from "offset" yield strength values
905:
249:
are constants that depend on the material being considered. In this form,
1686:
402:, is equal to the elastic part of the strain, while the second term,
976:, plastic strain becomes progressively larger than elastic strain.
1330:
58:
In its original form, the equation for strain (deformation) is
1618:, National Advisory Committee For Aeronautics, Washington DC.
360:{\displaystyle \varepsilon =\varepsilon _{e}+\varepsilon _{p}}
1076:{\displaystyle \varepsilon =(1+\alpha ){{\sigma _{0}}/{E}}\,}
1274:
equal to the accepted value of strain of 0.2%, which means:
23:
was created to describe the nonlinear relationship between
292:, can be modeled with a line, while the plastic portion,
1675:
SAE International
Journal of Materials and Manufacturing
257:
are not the same as the constants commonly seen in the
1020:, as shown in figure 1. This comes from the fact that
1523:
1497:
1470:
1399:
1377:
1357:
1317:{\displaystyle \alpha {\frac {\sigma _{0}}{E}}=0.002}
1287:
1255:
1234:
1180:
1133:
1089:
1026:
985:
955:
935:
915:
889:
868:
765:
649:
574:
554:
534:
507:
479:
459:
408:
375:
327:
298:
271:
235:
215:
189:
163:
137:
67:
629:{\displaystyle \alpha =K({\sigma _{0}}/{E})^{n-1}\,}
1631:"Mechanical Properties of Materials | MechaniCalc"
1580:
1503:
1483:
1454:
1383:
1363:
1316:
1262:
1241:
1213:
1161:
1109:
1075:
1008:
968:
941:
921:
896:
875:
862:of the material depends on the material constants
858:In the last form of the Ramberg–Osgood model, the
838:
737:
628:
560:
540:
520:
485:
465:
445:
394:
359:
311:
284:
241:
221:
195:
169:
143:
117:
1391:is the strain hardening coefficient (no units).
453:, accounts for the plastic part, the parameters
16:Nonlinear relationship between stress and strain
1712:. National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics.
1654:Hollomon, J. R. (1945). "Tensile Deformation".
1009:{\displaystyle \alpha {\frac {\sigma _{0}}{E}}}
1597:Viscoplasticity#Johnson–Cook flow stress model
39:. It is especially applicable to metals that
8:
1214:{\displaystyle \alpha ({\sigma _{0}}/E)\,}
1572:
1560:
1551:
1530:
1522:
1496:
1475:
1469:
1442:
1438:
1424:
1406:
1398:
1376:
1356:
1297:
1291:
1286:
1259:
1254:
1238:
1233:
1210:
1199:
1192:
1187:
1179:
1158:
1152:
1147:
1140:
1135:
1134:
1132:
1106:
1100:
1088:
1072:
1066:
1061:
1054:
1049:
1048:
1025:
995:
989:
984:
960:
954:
934:
914:
893:
888:
872:
867:
824:
812:
803:
788:
772:
764:
723:
711:
702:
687:
675:
661:
648:
625:
613:
604:
599:
592:
587:
573:
553:
533:
512:
506:
478:
458:
437:
428:
423:
418:
407:
391:
386:
381:
376:
374:
351:
338:
326:
303:
297:
276:
270:
234:
214:
188:
162:
136:
109:
95:
74:
66:
1607:
1513:Hollomon's strain hardening coefficient
51:elastic-plastic transition. As it is a
446:{\displaystyle \ K({\sigma }/{E})^{n}}
1371:is the strength coefficient (Pa) and
1162:{\displaystyle {{\sigma _{0}}/{E}}\,}
1110:{\displaystyle \sigma =\sigma _{0}\,}
7:
1464:Alternatively, if the yield stress,
854:Hardening behavior and yield offset
369:The first term on the right side,
14:
497:of the material. Introducing the
528:, and defining a new parameter,
312:{\displaystyle \varepsilon _{p}}
285:{\displaystyle \varepsilon _{e}}
395:{\displaystyle {\sigma }/{E}\,}
1207:
1184:
1045:
1033:
610:
584:
434:
415:
43:with plastic deformation (see
1:
1120:Accordingly, (see Figure 1):
144:{\displaystyle \varepsilon }
1484:{\displaystyle \sigma _{y}}
969:{\displaystyle \sigma _{0}}
521:{\displaystyle \sigma _{0}}
1758:
1263:{\displaystyle \alpha \,}
1228:Commonly used values for
876:{\displaystyle \alpha \,}
35:—in materials near their
1343:Alternative Formulations
1172:plastic strain at yield
1125:elastic strain at yield
922:{\displaystyle \alpha }
541:{\displaystyle \alpha }
170:{\displaystyle \sigma }
21:Ramberg–Osgood equation
1616:Technical Note No. 902
1582:
1505:
1485:
1456:
1385:
1365:
1339:
1318:
1264:
1243:
1215:
1163:
1111:
1077:
1010:
970:
943:
923:
898:
877:
840:
739:
630:
562:
542:
522:
487:
467:
447:
396:
361:
313:
286:
243:
223:
197:
171:
145:
119:
53:phenomenological model
1583:
1506:
1486:
1457:
1386:
1366:
1334:
1319:
1265:
1244:
1216:
1164:
1112:
1078:
1011:
971:
944:
924:
899:
878:
841:
740:
631:
563:
543:
523:
488:
468:
448:
397:
362:
314:
287:
244:
224:
198:
172:
146:
120:
1708:Hill, H. N. (1944).
1687:10.4271/2015-01-9086
1656:Transactions of AIME
1521:
1495:
1468:
1397:
1375:
1355:
1285:
1253:
1232:
1178:
1131:
1087:
1024:
983:
953:
933:
913:
887:
866:
763:
647:
572:
552:
532:
505:
477:
457:
406:
373:
325:
296:
269:
233:
213:
187:
161:
135:
65:
1242:{\displaystyle n\,}
897:{\displaystyle n\,}
33:stress–strain curve
1578:
1501:
1481:
1452:
1381:
1361:
1340:
1314:
1260:
1239:
1211:
1159:
1107:
1073:
1006:
966:
939:
919:
894:
873:
860:hardening behavior
836:
735:
626:
558:
538:
518:
495:hardening behavior
483:
463:
443:
392:
357:
309:
282:
239:
219:
193:
167:
141:
115:
1742:Materials science
1566:
1538:
1504:{\displaystyle n}
1432:
1414:
1384:{\displaystyle n}
1364:{\displaystyle K}
1306:
1016:can be seen as a
1004:
942:{\displaystyle n}
818:
796:
780:
717:
695:
669:
652:
561:{\displaystyle K}
501:of the material,
486:{\displaystyle n}
466:{\displaystyle K}
411:
259:Hollomon equation
242:{\displaystyle n}
222:{\displaystyle K}
196:{\displaystyle E}
103:
82:
1749:
1722:
1721:
1705:
1699:
1698:
1670:
1664:
1663:
1651:
1645:
1644:
1642:
1641:
1627:
1621:
1612:
1587:
1585:
1584:
1579:
1577:
1576:
1571:
1567:
1565:
1564:
1552:
1539:
1531:
1510:
1508:
1507:
1502:
1490:
1488:
1487:
1482:
1480:
1479:
1461:
1459:
1458:
1453:
1451:
1450:
1446:
1437:
1433:
1425:
1415:
1407:
1390:
1388:
1387:
1382:
1370:
1368:
1367:
1362:
1323:
1321:
1320:
1315:
1307:
1302:
1301:
1292:
1269:
1267:
1266:
1261:
1248:
1246:
1245:
1240:
1220:
1218:
1217:
1212:
1203:
1198:
1197:
1196:
1168:
1166:
1165:
1160:
1157:
1156:
1151:
1146:
1145:
1144:
1116:
1114:
1113:
1108:
1105:
1104:
1082:
1080:
1079:
1074:
1071:
1070:
1065:
1060:
1059:
1058:
1015:
1013:
1012:
1007:
1005:
1000:
999:
990:
975:
973:
972:
967:
965:
964:
948:
946:
945:
940:
928:
926:
925:
920:
903:
901:
900:
895:
882:
880:
879:
874:
845:
843:
842:
837:
835:
834:
823:
819:
817:
816:
804:
797:
789:
781:
773:
744:
742:
741:
736:
734:
733:
722:
718:
716:
715:
703:
696:
688:
680:
679:
674:
670:
662:
650:
635:
633:
632:
627:
624:
623:
608:
603:
598:
597:
596:
567:
565:
564:
559:
547:
545:
544:
539:
527:
525:
524:
519:
517:
516:
492:
490:
489:
484:
472:
470:
469:
464:
452:
450:
449:
444:
442:
441:
432:
427:
422:
409:
401:
399:
398:
393:
390:
385:
380:
366:
364:
363:
358:
356:
355:
343:
342:
318:
316:
315:
310:
308:
307:
291:
289:
288:
283:
281:
280:
256:
252:
248:
246:
245:
240:
228:
226:
225:
220:
202:
200:
199:
194:
176:
174:
173:
168:
150:
148:
147:
142:
124:
122:
121:
116:
114:
113:
108:
104:
96:
83:
75:
1757:
1756:
1752:
1751:
1750:
1748:
1747:
1746:
1727:
1726:
1725:
1707:
1706:
1702:
1672:
1671:
1667:
1653:
1652:
1648:
1639:
1637:
1635:mechanicalc.com
1629:
1628:
1624:
1613:
1609:
1605:
1593:
1556:
1547:
1546:
1519:
1518:
1493:
1492:
1471:
1466:
1465:
1420:
1419:
1395:
1394:
1373:
1372:
1353:
1352:
1345:
1293:
1283:
1282:
1251:
1250:
1230:
1229:
1188:
1176:
1175:
1136:
1129:
1128:
1096:
1085:
1084:
1050:
1022:
1021:
991:
981:
980:
956:
951:
950:
931:
930:
911:
910:
885:
884:
864:
863:
856:
808:
799:
798:
761:
760:
707:
698:
697:
657:
656:
645:
644:
609:
588:
570:
569:
550:
549:
530:
529:
508:
503:
502:
493:describing the
475:
474:
455:
454:
433:
404:
403:
371:
370:
347:
334:
323:
322:
299:
294:
293:
272:
267:
266:
254:
250:
231:
230:
211:
210:
205:Young's modulus
185:
184:
159:
158:
133:
132:
91:
90:
63:
62:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1755:
1753:
1745:
1744:
1739:
1729:
1728:
1724:
1723:
1700:
1681:(1): 200–205.
1665:
1646:
1622:
1606:
1604:
1601:
1600:
1599:
1592:
1589:
1575:
1570:
1563:
1559:
1555:
1550:
1545:
1542:
1537:
1534:
1529:
1526:
1500:
1478:
1474:
1449:
1445:
1441:
1436:
1431:
1428:
1423:
1418:
1413:
1410:
1405:
1402:
1380:
1360:
1344:
1341:
1329:
1328:
1327:
1326:
1325:
1324:
1313:
1310:
1305:
1300:
1296:
1290:
1258:
1237:
1226:
1225:
1209:
1206:
1202:
1195:
1191:
1186:
1183:
1169:
1155:
1150:
1143:
1139:
1103:
1099:
1095:
1092:
1069:
1064:
1057:
1053:
1047:
1044:
1041:
1038:
1035:
1032:
1029:
1003:
998:
994:
988:
963:
959:
938:
918:
892:
871:
855:
852:
851:
850:
849:
848:
847:
846:
833:
830:
827:
822:
815:
811:
807:
802:
795:
792:
787:
784:
779:
776:
771:
768:
750:
749:
748:
747:
746:
745:
732:
729:
726:
721:
714:
710:
706:
701:
694:
691:
686:
683:
678:
673:
668:
665:
660:
655:
622:
619:
616:
612:
607:
602:
595:
591:
586:
583:
580:
577:
557:
537:
515:
511:
499:yield strength
482:
462:
440:
436:
431:
426:
421:
417:
414:
389:
384:
379:
354:
350:
346:
341:
337:
333:
330:
306:
302:
279:
275:
263:
262:
238:
218:
208:
192:
182:
166:
156:
140:
126:
125:
112:
107:
102:
99:
94:
89:
86:
81:
78:
73:
70:
45:work hardening
31:—that is, the
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1754:
1743:
1740:
1738:
1735:
1734:
1732:
1719:
1715:
1711:
1704:
1701:
1696:
1692:
1688:
1684:
1680:
1676:
1669:
1666:
1661:
1657:
1650:
1647:
1636:
1632:
1626:
1623:
1620:
1617:
1611:
1608:
1602:
1598:
1595:
1594:
1590:
1588:
1573:
1568:
1561:
1557:
1553:
1548:
1543:
1540:
1535:
1532:
1527:
1524:
1516:
1514:
1498:
1476:
1472:
1462:
1447:
1443:
1439:
1434:
1429:
1426:
1421:
1416:
1411:
1408:
1403:
1400:
1392:
1378:
1358:
1349:
1342:
1337:
1333:
1311:
1308:
1303:
1298:
1294:
1288:
1281:
1280:
1279:
1278:
1277:
1276:
1275:
1273:
1256:
1235:
1224:
1204:
1200:
1193:
1189:
1181:
1173:
1170:
1153:
1148:
1141:
1137:
1126:
1123:
1122:
1121:
1118:
1101:
1097:
1093:
1090:
1067:
1062:
1055:
1051:
1042:
1039:
1036:
1030:
1027:
1019:
1001:
996:
992:
986:
977:
961:
957:
936:
916:
907:
904:. Due to the
890:
869:
861:
853:
831:
828:
825:
820:
813:
809:
805:
800:
793:
790:
785:
782:
777:
774:
769:
766:
759:
758:
757:
756:
755:
754:
753:
730:
727:
724:
719:
712:
708:
704:
699:
692:
689:
684:
681:
676:
671:
666:
663:
658:
653:
643:
642:
641:
640:
639:
638:
637:
620:
617:
614:
605:
600:
593:
589:
581:
578:
575:
555:
548:, related to
535:
513:
509:
500:
496:
480:
460:
438:
429:
424:
419:
412:
387:
382:
377:
367:
352:
348:
344:
339:
335:
331:
328:
320:
304:
300:
277:
273:
260:
236:
216:
209:
206:
190:
183:
180:
164:
157:
154:
138:
131:
130:
129:
110:
105:
100:
97:
92:
87:
84:
79:
76:
71:
68:
61:
60:
59:
56:
54:
50:
47:), showing a
46:
42:
38:
34:
30:
26:
22:
1709:
1703:
1678:
1674:
1668:
1659:
1655:
1649:
1638:. Retrieved
1634:
1625:
1615:
1610:
1517:
1463:
1393:
1350:
1346:
1335:
1272:yield offset
1271:
1227:
1223:yield offset
1222:
1171:
1124:
1119:
1018:yield offset
1017:
978:
859:
857:
751:
498:
494:
368:
321:
264:
127:
57:
48:
40:
37:yield points
20:
18:
1731:Categories
1662:: 268–277.
1640:2020-05-27
1603:References
979:The value
1737:Mechanics
1718:647978489
1695:1946-3987
1558:σ
1554:σ
1533:σ
1525:ε
1473:σ
1427:σ
1409:σ
1401:ε
1295:σ
1289:α
1257:α
1190:σ
1182:α
1138:σ
1098:σ
1091:σ
1052:σ
1043:α
1028:ε
993:σ
987:α
958:σ
917:α
906:power-law
870:α
829:−
810:σ
806:σ
791:σ
786:α
775:σ
767:ε
728:−
709:σ
705:σ
690:σ
685:α
664:σ
618:−
590:σ
576:α
536:α
510:σ
420:σ
378:σ
349:ε
336:ε
329:ε
301:ε
274:ε
165:σ
139:ε
98:σ
77:σ
69:ε
1591:See also
1336:Figure 1
1083:, when
1716:
1693:
651:
410:
179:stress
153:strain
49:smooth
41:harden
29:strain
25:stress
1544:0.002
1312:0.002
207:, and
128:here
1714:OCLC
1691:ISSN
929:and
883:and
473:and
253:and
229:and
27:and
19:The
1683:doi
1660:162
568:as
203:is
177:is
151:is
1733::
1689:.
1677:.
1658:.
1633:.
1515:.
1221:=
1174:=
1127:=
1117:.
1720:.
1697:.
1685::
1679:9
1643:.
1574:n
1569:)
1562:y
1549:(
1541:+
1536:E
1528:=
1499:n
1477:y
1448:n
1444:/
1440:1
1435:)
1430:K
1422:(
1417:+
1412:E
1404:=
1379:n
1359:K
1309:=
1304:E
1299:0
1236:n
1208:)
1205:E
1201:/
1194:0
1185:(
1154:E
1149:/
1142:0
1102:0
1094:=
1068:E
1063:/
1056:0
1046:)
1040:+
1037:1
1034:(
1031:=
1002:E
997:0
962:0
937:n
891:n
832:1
826:n
821:)
814:0
801:(
794:E
783:+
778:E
770:=
731:1
725:n
720:)
713:0
700:(
693:E
682:=
677:n
672:)
667:E
659:(
654:K
621:1
615:n
611:)
606:E
601:/
594:0
585:(
582:K
579:=
556:K
514:0
481:n
461:K
439:n
435:)
430:E
425:/
416:(
413:K
388:E
383:/
353:p
345:+
340:e
332:=
305:p
278:e
261:.
255:n
251:K
237:n
217:K
191:E
181:,
155:,
111:n
106:)
101:E
93:(
88:K
85:+
80:E
72:=
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.