629:(RA). The fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) play a key role in the pathogenesis of RA, and the aggressive phenotype of FLS in RA and the effect these cells have on the microenvironment in the joint can be summarized into hallmarks that distinguish them from healthy FLS. These hallmark features of FLS in RA are divided into seven cell-intrinsic hallmarks (such as reduced apoptosis and impaired contact inhibition) and four cell-extrinsic hallmarks (such as their ability to recruit and stimulate immune cells).
305:
652:. When this happens, the synovium can interfere with the normal functioning of the joint. Excessive thickened synovium, filled with cells and fibrotic collagenous tissue, can physically restrict joint movement. The synovial fibroblasts may make smaller hyaluronan so it is a less effective lubricant of the cartilage surfaces. Under stimulation from invading inflammatory cells, the synovial cells may also produce
495:
208:
29:
390:
in nature which facilitates continuous exchange of oxygen, carbon dioxide and metabolites between blood and synovial fluid. This is especially important since it is the major source of metabolic support for articular cartilage. Under normal conditions synovial fluid contain <100/mL of leucocytes
41:
354:
This membrane, together with the cells of the intima, provides something like an inner tube, sealing the synovial fluid from the surrounding tissue (effectively stopping the joints from being squeezed dry when subject to impact, such as running).
843:
597:
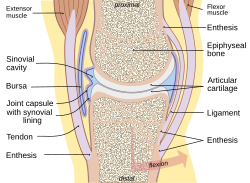
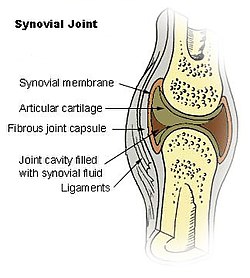
Providing a plane of separation, or disconnection, between solid tissues so that movement can occur with minimum bending of solid components. If this separation is lost, as in a 'frozen shoulder', the joint cannot
604:
Controlling the volume of fluid in the cavity so that it is just enough to allow the solid components to move over each other freely. This volume is normally so small that the joint is under slight suction.
593:
is filled with pliable solid tissue. The fluid-filled gap is at most only a twentieth of a millimetre thick. This means that synovium has certain jobs to do. These may include:
567:, the engineering problems that nature must solve are very different because the joint works within an almost completely solid structure, with no wheels or nuts and bolts.
430:
The macrophage-like synovial cells (derived from monocytes in blood) are responsible for the removal of undesirable substances from the synovial fluid (hence are rich in
376:
Some areas of cartilage have to obtain nutrients indirectly and may do so either from diffusion through cartilage or possibly by 'stirring' of synovial fluid.
114:
427:, which lubricates the joint surfaces. The water of synovial fluid is not secreted as such but is effectively trapped in the joint space by the hyaluronan.
386:
The synovial fluid can be thought of as a specialized fluid form of synovial extracellular matrix rather than a secretion in the usual sense. The fluid is
407:-like type A synovial cells. Surface cells have no basement membrane or junctional complexes denoting an epithelium despite superficial resemblance.
1419:
773:
90:
516:
225:
827:
802:
748:
542:
291:
951:
Townsend MJ (2014). "Molecular and cellular heterogeneity in the
Rheumatoid Arthritis synovium: clinical correlates of synovitis".
1120:
272:
570:
In general, the bearing surfaces of manmade joints interlock, as in a hinge. This is rare for biological joints (although the
244:
908:
Suhrbier A, La Linn M (2004). "Clinical and pathologic aspects of arthritis due to Ross River virus and other alphaviruses".
520:
229:
109:
251:
1037:"Utility of arthroscopic guided synovial biopsy in understanding synovial tissue pathology in health and disease states"
601:
Providing a packing that can change shape in whatever way is needed to allow the bearing surfaces to move on each other.
187:
505:
1285:
258:
524:
509:
383:, which, it is presumed, help to allow the soft tissue to change shape as the joint surfaces move one on another.
218:
317:
1358:
1344:
190:(FLS). Type A cells maintain the synovial fluid by removing wear-and-tear debris. As for the FLS, they produce
73:
240:
1390:
1340:
1326:
1317:
325:
182:
lubricant on the inside surface. In contact with the synovial fluid at the tissue surface are many rounded
1386:
121:
97:
85:
1233:
1163:
420:
1476:
1113:
665:
626:
1294:
1170:
344:
988:"Restoring synovial homeostasis in rheumatoid arthritis by targeting fibroblast-like synoviocytes"
304:
1440:
933:
265:
1335:
1331:
1068:
1017:
968:
925:
890:
823:
798:
769:
744:
556:
155:
1290:
1058:
1048:
1007:
999:
960:
917:
880:
622:
175:
1218:
1106:
711:
564:
431:
191:
167:
739:
Young, Barbara; Lowe, James S.; Stevens, Alan; Heath, John W.; Deakin, Philip J. (2006).
423:); which makes the synovial fluid "ropy"-like egg-white, together with a molecule called
1436:
1431:
1426:
1377:
1264:
1259:
1190:
1153:
1063:
1036:
1012:
987:
921:
885:
868:
698:
689:
618:
336:
321:
179:
171:
163:
379:
The surface of synovium may be flat or may be covered with finger-like projections or
1470:
1409:
1175:
1143:
159:
937:
1381:
1254:
1223:
649:
359:
40:
78:
1354:
1280:
1208:
1203:
1195:
1158:
869:"Osteoarthritis pathogenesis - a complex process that involves the entire joint"
641:
494:
316:
The outer layer, or subintima, can be of almost any type of connective tissue –
207:
964:
1363:
1243:
1003:
693:
685:
657:
637:
633:
416:
412:
404:
403:
The intimal cells are of two types, fibroblast-like type B synovial cells and
387:
183:
186:-like synovial cells (type A) and also type B cells, which are also known as
102:
1367:
1322:
1180:
1148:
661:
645:
614:
590:
370:
358:
Just beneath the intima, most synovium has a dense net of fenestrated small
1072:
1021:
972:
929:
894:
1053:
1455:
1450:
578:
424:
392:
363:
478:
Secrete hyaluronic acid, and proteins complex (mucin) of synovial fluid
380:
1313:
822:. India: Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers Pvt. Limited. p. 12.
343:
Where the underlying subintima is loose, the intima sits on a pliable
127:
653:
582:
571:
332:
194:, as well as other extracellular components in the synovial fluid.
1129:
560:
434:). It accounts for approximately 25% of cells lining the synovium.
303:
61:
586:
28:
1102:
797:(13th ed.). McGraw-Hill Education / Medical. 2013-02-13.
488:
201:
373:
is close enough to get nutrition directly from the synovium.
1087:
640:
proliferation and an influx of inflammatory cells including
366:
not only for synovium but also for the avascular cartilage.
312:
The synovial membrane is variable but often has two layers:
16:
Connective tissue present within and around synovial joints
1098:
1089:
The
American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language
844:"Synovial Membrane - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics"
820:
Handbook of Joint
Disorders Arthroscopy & Pathology
764:
Nelson, Fred R T; Blauvelt, Carolyn
Taliaferro (2015).
741:
Wheater's
Functional Histology: A Text and Colour Atlas
577:
More often the surfaces are held together by cord-like
632:
In general, inflamed synovium is accompanied by extra
331:
The inner layer (in contact with synovial fluid), or
636:
recruitment (as well as the existing type A cells),
1399:
1303:
1273:
1136:
232:. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
108:
96:
84:
72:
60:
55:
50:
21:
415:) manufacture a long-chain sugar polymer called
308:Histology of a synovial membrane. H&E stain.
411:The fibroblast-like synoviocytes (derived from
1114:
613:Synovium can become irritated and thickened (
324:(fatty; e.g. in intra-articular fat pads) or
8:
699:Synovial fluid § Etymology and pronunciation
795:Junqueira's Basic Histology: Text and Atlas
555:Although a biological joint can resemble a
523:. Unsourced material may be challenged and
1121:
1107:
1099:
818:Afroz, T; Radha, S; Vidyasagar, J (2012).
39:
27:
1062:
1052:
1011:
884:
543:Learn how and when to remove this message
292:Learn how and when to remove this message
668:can then further irritate the synovium.
437:
67:membrana synovialis capsulae articularis
743:(5th ed.). Churchill Livingstone.
722:
986:Nygaard, G.; Firestein, G. S. (2020).
768:(8th ed.). Elsevier. p. 70.
125:
18:
7:
789:
787:
785:
734:
732:
730:
728:
726:
521:adding citations to reliable sources
230:adding citations to reliable sources
178:on the outside surface and with the
664:extracellular matrix. Fragments of
174:. It makes direct contact with the
922:10.1097/01.bor.0000130537.76808.26
766:A Manual of Orthopedic Terminology
581:. Virtually all the space between
14:
369:In any one position, much of the
1035:Wechalekar MD, Smith MD (2014).
953:Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol
493:
206:
158:that lines the inner surface of
696:. More information is given at
217:needs additional citations for
339:thinner than a piece of paper.
1:
867:Man GS, Mologhianu G (2014).
1092:, Houghton Mifflin Harcourt.
692:". The latter was coined by
188:fibroblast-like synoviocytes
1086:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt,
992:Nature Reviews Rheumatology
672:Etymology and pronunciation
1493:
1286:Anatomical terms of motion
965:10.1016/j.berh.2014.10.024
347:, giving rise to the term
320:(dense collagenous type),
1004:10.1038/s41584-020-0413-5
335:, consists of a sheet of
328:(loose collagenous type).
120:
38:
26:
1375:specialized/lower limbs:
1352:specialized/upper limbs:
617:) in conditions such as
680:is related to the word
660:) that can digest the
391:in which majority are
309:
122:Anatomical terminology
1234:Ball and socket joint
1164:Interosseous membrane
1054:10.5312/wjo.v5.i5.566
910:Curr. Opin. Rheumatol
848:www.sciencedirect.com
475:Endoplasmic reticulum
421:endoplasmic reticulum
307:
666:extracellular matrix
627:rheumatoid arthritis
574:'s jaw interlocks).
517:improve this section
226:improve this article
1252:by range of motion:
447:Prominent organelle
241:"Synovial membrane"
154:) is a specialized
142:(also known as the
310:
1464:
1463:
1415:Synovial membrane
1336:External rotation
1332:Internal rotation
775:978-0-323-22158-0
553:
552:
545:
482:
481:
349:synovial membrane
302:
301:
294:
276:
156:connective tissue
152:stratum synoviale
140:synovial membrane
136:
135:
131:
22:Synovial membrane
1484:
1420:Fibrous membrane
1123:
1116:
1109:
1100:
1094:
1093:
1083:
1077:
1076:
1066:
1056:
1032:
1026:
1025:
1015:
983:
977:
976:
948:
942:
941:
905:
899:
898:
888:
864:
858:
857:
855:
854:
840:
834:
833:
815:
809:
808:
791:
780:
779:
761:
755:
754:
736:
623:Ross River virus
548:
541:
537:
534:
528:
497:
489:
438:
297:
290:
286:
283:
277:
275:
234:
210:
202:
176:fibrous membrane
144:synovial stratum
128:edit on Wikidata
43:
31:
19:
1492:
1491:
1487:
1486:
1485:
1483:
1482:
1481:
1467:
1466:
1465:
1460:
1395:
1299:
1269:
1219:Condyloid joint
1132:
1127:
1097:
1085:
1084:
1080:
1041:World J. Orthop
1034:
1033:
1029:
985:
984:
980:
950:
949:
945:
907:
906:
902:
866:
865:
861:
852:
850:
842:
841:
837:
830:
817:
816:
812:
805:
793:
792:
783:
776:
763:
762:
758:
751:
738:
737:
724:
720:
712:Synovial sheath
708:
674:
611:
565:ball and socket
549:
538:
532:
529:
514:
498:
487:
432:Golgi apparatus
419:(hence rich in
401:
298:
287:
281:
278:
235:
233:
223:
211:
200:
172:synovial bursas
164:synovial joints
132:
46:
34:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1490:
1488:
1480:
1479:
1469:
1468:
1462:
1461:
1459:
1458:
1453:
1448:extracapsular:
1444:
1443:
1437:Articular disk
1434:
1432:Synovial bursa
1429:
1427:Synovial fluid
1424:
1423:
1422:
1417:
1403:
1401:
1397:
1396:
1394:
1393:
1384:
1378:Plantarflexion
1371:
1370:
1361:
1348:
1347:
1338:
1329:
1320:
1307:
1305:
1301:
1300:
1298:
1297:
1288:
1283:
1277:
1275:
1271:
1270:
1268:
1267:
1262:
1260:Amphiarthrosis
1257:
1248:
1247:
1239:
1238:
1237:
1236:
1228:
1227:
1226:
1221:
1213:
1212:
1211:
1206:
1198:
1186:
1185:
1184:
1183:
1178:
1168:
1167:
1166:
1161:
1156:
1151:
1140:
1138:
1134:
1133:
1128:
1126:
1125:
1118:
1111:
1103:
1096:
1095:
1078:
1027:
998:(6): 316–333.
978:
943:
900:
859:
835:
828:
810:
803:
781:
774:
756:
749:
721:
719:
716:
715:
714:
707:
704:
690:synovial fluid
673:
670:
619:osteoarthritis
610:
607:
606:
605:
602:
599:
557:man-made joint
551:
550:
501:
499:
492:
486:
483:
480:
479:
476:
473:
470:
466:
465:
462:
459:
456:
452:
451:
448:
445:
442:
436:
435:
428:
400:
399:Synovial cells
397:
341:
340:
329:
300:
299:
214:
212:
205:
199:
196:
180:synovial fluid
168:tendon sheaths
134:
133:
124:
118:
117:
112:
106:
105:
100:
94:
93:
88:
82:
81:
76:
70:
69:
64:
58:
57:
53:
52:
48:
47:
45:Synovial joint
44:
36:
35:
32:
24:
23:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1489:
1478:
1475:
1474:
1472:
1457:
1454:
1452:
1449:
1446:
1445:
1442:
1438:
1435:
1433:
1430:
1428:
1425:
1421:
1418:
1416:
1413:
1412:
1411:
1410:Joint capsule
1408:
1405:
1404:
1402:
1398:
1392:
1388:
1385:
1383:
1379:
1376:
1373:
1372:
1369:
1365:
1362:
1360:
1356:
1353:
1350:
1349:
1346:
1342:
1339:
1337:
1333:
1330:
1328:
1324:
1321:
1319:
1315:
1312:
1309:
1308:
1306:
1302:
1296:
1292:
1289:
1287:
1284:
1282:
1279:
1278:
1276:
1272:
1266:
1263:
1261:
1258:
1256:
1253:
1250:
1249:
1246:
1245:
1241:
1240:
1235:
1232:
1231:
1229:
1225:
1222:
1220:
1217:
1216:
1214:
1210:
1207:
1205:
1202:
1201:
1199:
1197:
1194:
1192:
1188:
1187:
1182:
1179:
1177:
1176:Synchondrosis
1174:
1173:
1172:
1171:Cartilaginous
1169:
1165:
1162:
1160:
1157:
1155:
1152:
1150:
1147:
1146:
1145:
1142:
1141:
1139:
1135:
1131:
1124:
1119:
1117:
1112:
1110:
1105:
1104:
1101:
1091:
1090:
1082:
1079:
1074:
1070:
1065:
1060:
1055:
1050:
1047:(5): 566–73.
1046:
1042:
1038:
1031:
1028:
1023:
1019:
1014:
1009:
1005:
1001:
997:
993:
989:
982:
979:
974:
970:
966:
962:
959:(4): 539–49.
958:
954:
947:
944:
939:
935:
931:
927:
923:
919:
915:
911:
904:
901:
896:
892:
887:
882:
878:
874:
870:
863:
860:
849:
845:
839:
836:
831:
829:9789350257234
825:
821:
814:
811:
806:
804:9780071780339
800:
796:
790:
788:
786:
782:
777:
771:
767:
760:
757:
752:
750:9780443068508
746:
742:
735:
733:
731:
729:
727:
723:
717:
713:
710:
709:
705:
703:
701:
700:
695:
691:
687:
683:
679:
671:
669:
667:
663:
659:
655:
651:
647:
643:
639:
635:
630:
628:
624:
620:
616:
608:
603:
600:
596:
595:
594:
592:
588:
585:, ligaments,
584:
580:
575:
573:
568:
566:
562:
558:
547:
544:
536:
526:
522:
518:
512:
511:
507:
502:This section
500:
496:
491:
490:
484:
477:
474:
471:
468:
467:
464:Phagocytosis
463:
460:
457:
454:
453:
449:
446:
443:
441:Synovial cell
440:
439:
433:
429:
426:
422:
418:
414:
410:
409:
408:
406:
398:
396:
394:
389:
384:
382:
377:
374:
372:
367:
365:
362:that provide
361:
360:blood vessels
356:
352:
350:
346:
338:
334:
330:
327:
323:
319:
315:
314:
313:
306:
296:
293:
285:
274:
271:
267:
264:
260:
257:
253:
250:
246:
243: –
242:
238:
237:Find sources:
231:
227:
221:
220:
215:This article
213:
209:
204:
203:
197:
195:
193:
189:
185:
181:
177:
173:
169:
165:
161:
157:
153:
149:
145:
141:
129:
123:
119:
116:
113:
111:
107:
104:
101:
99:
95:
92:
89:
87:
83:
80:
77:
75:
71:
68:
65:
63:
59:
54:
49:
42:
37:
33:Typical joint
30:
25:
20:
1447:
1414:
1406:
1382:Dorsiflexion
1374:
1351:
1310:
1255:Synarthrosis
1251:
1242:
1224:Saddle joint
1189:
1088:
1081:
1044:
1040:
1030:
995:
991:
981:
956:
952:
946:
916:(4): 374–9.
913:
909:
903:
879:(1): 37–41.
876:
873:J. Med. Life
872:
862:
851:. Retrieved
847:
838:
819:
813:
794:
765:
759:
740:
697:
681:
677:
675:
650:plasma cells
631:
612:
576:
569:
554:
539:
530:
515:Please help
503:
461:Mitochondria
402:
388:transudative
385:
378:
375:
368:
357:
353:
348:
342:
311:
288:
279:
269:
262:
255:
248:
236:
224:Please help
219:verification
216:
151:
147:
143:
139:
137:
91:A03.0.00.028
66:
1477:Soft tissue
1355:Protraction
1281:Kinesiology
1274:Terminology
1265:Diarthrosis
1209:Pivot joint
1204:Hinge joint
1196:Plane joint
1159:Syndesmosis
658:proteinases
642:lymphocytes
559:in being a
56:Identifiers
1400:Components
1364:Supination
1359:Retraction
1345:Depression
1295:Antagonist
1244:synostosis
853:2023-05-04
718:References
694:Paracelsus
638:fibroblast
634:macrophage
472:Fibroblast
458:Macrophage
417:hyaluronan
413:mesenchyme
405:macrophage
282:March 2023
252:newspapers
192:hyaluronan
184:macrophage
1407:capsular:
1391:Inversion
1368:Pronation
1341:Elevation
1327:Abduction
1323:Adduction
1318:Extension
1181:Symphysis
1149:Gomphosis
688:meaning "
676:The word
662:cartilage
646:monocytes
615:synovitis
609:Pathology
591:cartilage
579:ligaments
504:does not
485:Mechanics
450:Function
393:monocytes
371:cartilage
364:nutrients
198:Structure
1471:Category
1456:Enthesis
1451:Ligament
1441:Meniscus
1387:Eversion
1311:general:
1191:synovial
1073:25405084
1022:32393826
973:25481548
938:12045116
930:15201600
895:24653755
706:See also
678:synovium
533:May 2015
444:Resemble
425:lubricin
345:membrane
160:capsules
148:synovium
1314:Flexion
1304:Motions
1291:Agonist
1144:Fibrous
1064:4133463
1013:7987137
886:3956093
684:in its
682:synovia
654:enzymes
583:muscles
525:removed
510:sources
326:areolar
322:adipose
318:fibrous
266:scholar
79:D013583
51:Details
1154:Suture
1130:Joints
1071:
1061:
1020:
1010:
971:
936:
928:
893:
883:
826:
801:
772:
747:
589:, and
572:badger
469:Type B
455:Type A
333:intima
268:
261:
254:
247:
239:
170:, and
1137:Types
934:S2CID
686:sense
598:move.
587:bones
563:or a
561:hinge
381:villi
337:cells
273:JSTOR
259:books
126:[
115:66762
62:Latin
1069:PMID
1018:PMID
969:PMID
926:PMID
891:PMID
824:ISBN
799:ISBN
770:ISBN
745:ISBN
648:and
508:any
506:cite
245:news
138:The
103:1538
86:TA98
74:MeSH
1230:3°
1215:2°
1200:1°
1059:PMC
1049:doi
1008:PMC
1000:doi
961:doi
918:doi
881:PMC
625:or
519:by
228:by
162:of
150:or
110:FMA
98:TA2
1473::
1067:.
1057:.
1043:.
1039:.
1016:.
1006:.
996:16
994:.
990:.
967:.
957:28
955:.
932:.
924:.
914:16
912:.
889:.
875:.
871:.
846:.
784:^
725:^
702:.
644:,
621:,
395:.
351:.
166:,
146:,
1439:/
1389:/
1380:/
1366:/
1357:/
1343:/
1334:/
1325:/
1316:/
1293:/
1193::
1122:e
1115:t
1108:v
1075:.
1051::
1045:5
1024:.
1002::
975:.
963::
940:.
920::
897:.
877:7
856:.
832:.
807:.
778:.
753:.
656:(
546:)
540:(
535:)
531:(
527:.
513:.
295:)
289:(
284:)
280:(
270:·
263:·
256:·
249:·
222:.
130:]
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.