641:
105:
158:
171:
179:
Different aspects of the Earth's environment are shown next to the timescale for comparison, including Earth impacts, solar luminosity, carbon dioxide levels, and oxygen levels. Separately, a table lists the time estimates, downloadable as a spreadsheet, from each study along with references and links to the abstracts of the original articles. Users can download the original study data as
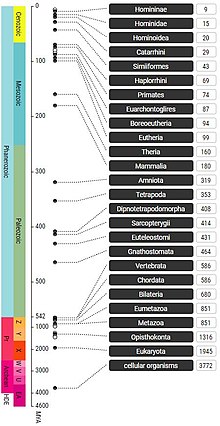
183:-formatted timetrees for further research. In the timeline search, users type the name of a taxon, and all divergences back to the origin of life are show with their taxon names, in a vertical ladder-like figure. Timepanels of Earth's environment also are shown next to the geological timescale, as in all three search options. The third search option,
212:
24:
153:
was brought to life using animated computer-generated imagery in scenes every 10 minutes during the 2-hour movie. The original development of TimeTree, by Hedges and Kumar, dates to the late 1990s, with initial support from NASA Astrobiology
Institute. Since then, it has been supported by additional
191:
by either specifying a taxon (group) name or uploading a list of species or other taxa. After specifying a group name, the user can choose which taxonomic level they prefer to view. For example, with a family group name, either a species-level or genus-level timetree can be selected. Then, the
178:
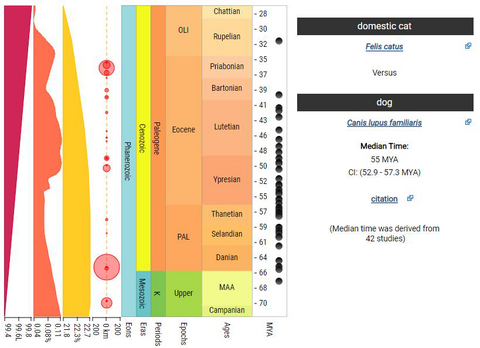
TimeTree users can search for the names of two species, such as cat and dog, to obtain the mean and median time estimates for their divergence, in millions of years. The results also show all individual time estimates, from each study, next to a geologic timescale, indicating geologic periods.
140:
of a chosen taxon or user-submitted group of taxa. TimeTree has been used in public education to conceptualize the evolution of life, such as in high school settings. David
Attenborough's Emmy Award-winning film and television program
142:
200:
file or image for publication. Times on the tree can be explored by clicking on nodes, and obtaining tables of data pertaining to the node. The database also allows search of
132:
of life from published studies, and allow easy access to that information on the web or mobile device. The database permits searching for average node times between two
447:
Kumar, Sudhir; Suleski, Michael; Craig, Jack; Kasprowicz, Adrienne; Sanderford, Maxwell; Li, Michael; Stecher, Glen; Hedges, S. Blair (2022).
154:
grants from NASA, and by NSF and NIH. The current version (v5) was released in 2022 and contains data from 4,075 studies and 137,306 species.
361:
136:
or higher taxa, viewing a timeline from the perspective of a taxon, which shows all divergences back to the origin of life, and building a
496:
Metzger KJ (2011). "Helping
Students Conceptualize Species Divergence Events using the Online Tool "TimeTree: The Timescale of Life"".
656:
161:
Results of a simple nodetime search in TimeTree database for the divergence time of cats and dogs in millions of years
53:
125:
117:
69:
611:
554:
513:
390:
603:
478:
426:
408:
357:
327:
309:
267:
259:
121:
593:
585:
544:
505:
468:
460:
416:
400:
317:
301:
249:
81:
377:
Hedges, S. Blair; Marin, Julie; Suleski, Michael; Paymer, Madeline; Kumar, Sudhir (2015).
157:
640:
104:
533:"Time travel and the naturalist's notebook: Vladimir Nabokov meets the TimeTree of Life"
598:
573:
473:
448:
421:
378:
322:
289:
74:
149:
of life, generated from the TimeTree database, as a framework for the production. The
650:
615:
197:
180:
558:
517:
305:
254:
128:. The basic concept has been to produce and present a community consensus of the
170:
589:
549:
532:
31:
464:
412:
313:
263:
509:
404:
607:
482:
430:
331:
271:
201:
193:
188:
184:
150:
146:
137:
129:
234:
235:"TimeTree: a public knowledge-base of divergence times among organisms"
133:
23:
211:
174:
Results from a timeline search in TimeTree for humans (Homo sapiens)
395:
210:
169:
156:
379:"Tree of Life Reveals Clock-Like Speciation and Diversification"
233:
Hedges, S. Blair; Dudley, Joel; Kumar, Sudhir (4 October 2006).
449:"TimeTree 5: An Expanded Resource for Species Divergence Times"
351:
634:
95:
215:
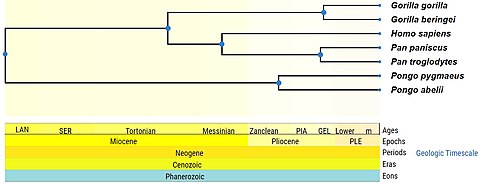
Results of a timetree search in TimeTree for
Hominidae.
204:
articles by author name. The entire open-access book
290:"TimeTree2: species divergence times on the iPhone"
90:
80:
68:
52:
40:
30:
350:Hedges, S. Blair; Kumar, Sudhir (2009-04-23).
288:Kumar, Sudhir; Hedges, S. Blair (2011-07-15).
8:
124:, for presenting times of divergence in the
16:
639:
248:(23). Oxford University Press: 2971–2972.
103:
36:S. Blair Hedges, Joel Dudley, Sudhir Kumar
15:
597:
574:"Molecular memories of a Cambrian fossil"
548:
472:
420:
394:
345:
343:
341:
321:
253:
356:. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press.
225:
116:is a free public database developed by
572:Babaian, Caryn; Kumar, Sudhir (2020).
531:Babaian, Caryn; Kumar, Sudhir (2018).
283:
281:
7:
442:
440:
14:
145:used Hedges and Kumar's circular
22:
453:Molecular Biology and Evolution
383:Molecular Biology and Evolution
196:is show and can be output as a
1:
306:10.1093/bioinformatics/btr315
255:10.1093/bioinformatics/btl505
578:The American Biology Teacher
537:The American Biology Teacher
498:The American Biology Teacher
187:search, involves building a
673:
208:is presented on the site.
590:10.1525/abt.2020.82.9.586
550:10.1525/abt.2018.80.9.650
120:and Sudhir Kumar, now at
64:
48:
21:
657:Bioinformatics software
510:10.1525/abt.2011.73.2.9
465:10.1093/molbev/msac174
216:
175:
162:
405:10.1093/molbev/msv037
214:
173:
160:
353:The Timetree of Life
18:
217:
176:
163:
32:Original author(s)
363:978-0-19-953503-3
300:(14): 2023–2024.
122:Temple University
111:
110:
664:
643:
638:
637:
635:Official website
620:
619:
601:
569:
563:
562:
552:
528:
522:
521:
493:
487:
486:
476:
444:
435:
434:
424:
398:
374:
368:
367:
347:
336:
335:
325:
285:
276:
275:
257:
239:
230:
206:Timetree of Life
107:
102:
99:
97:
26:
19:
672:
671:
667:
666:
665:
663:
662:
661:
647:
646:
633:
632:
629:
624:
623:
571:
570:
566:
530:
529:
525:
495:
494:
490:
446:
445:
438:
376:
375:
371:
364:
349:
348:
339:
287:
286:
279:
237:
232:
231:
227:
222:
168:
143:Rise of Animals
118:S. Blair Hedges
94:
60:
41:Initial release
12:
11:
5:
670:
668:
660:
659:
649:
648:
645:
644:
628:
627:External links
625:
622:
621:
584:(9): 586–595.
564:
543:(9): 650–658.
523:
504:(2): 106–108.
488:
436:
389:(4): 835–845.
369:
362:
337:
294:Bioinformatics
277:
242:Bioinformatics
224:
223:
221:
218:
167:
164:
109:
108:
92:
88:
87:
84:
78:
77:
75:Bioinformatics
72:
66:
65:
62:
61:
59:v5.0 / 2022
58:
56:
54:Stable release
50:
49:
46:
45:
42:
38:
37:
34:
28:
27:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
669:
658:
655:
654:
652:
642:
636:
631:
630:
626:
617:
613:
609:
605:
600:
595:
591:
587:
583:
579:
575:
568:
565:
560:
556:
551:
546:
542:
538:
534:
527:
524:
519:
515:
511:
507:
503:
499:
492:
489:
484:
480:
475:
470:
466:
462:
458:
454:
450:
443:
441:
437:
432:
428:
423:
418:
414:
410:
406:
402:
397:
392:
388:
384:
380:
373:
370:
365:
359:
355:
354:
346:
344:
342:
338:
333:
329:
324:
319:
315:
311:
307:
303:
299:
295:
291:
284:
282:
278:
273:
269:
265:
261:
256:
251:
247:
243:
236:
229:
226:
219:
213:
209:
207:
203:
199:
195:
190:
186:
182:
172:
165:
159:
155:
152:
148:
144:
139:
135:
131:
127:
123:
119:
115:
106:
101:
93:
89:
85:
83:
79:
76:
73:
71:
67:
63:
57:
55:
51:
47:
43:
39:
35:
33:
29:
25:
20:
581:
577:
567:
540:
536:
526:
501:
497:
491:
456:
452:
386:
382:
372:
352:
297:
293:
245:
241:
228:
205:
177:
126:tree of life
113:
112:
220:References
616:227304077
413:1537-1719
396:1412.4312
314:1367-4803
264:1367-4811
98:.timetree
651:Category
608:33967280
559:91951552
518:85026876
483:35932227
431:25739733
332:21622662
272:17021158
202:timetree
194:timetree
189:timetree
185:timetree
166:Features
151:timetree
147:timetree
138:timetree
130:timetree
114:TimeTree
86:Freeware
17:TimeTree
599:8104914
474:9400175
422:4379413
323:3129528
134:species
91:Website
82:License
614:
606:
596:
557:
516:
481:
471:
429:
419:
411:
360:
330:
320:
312:
270:
262:
198:Newick
181:Newick
612:S2CID
555:S2CID
514:S2CID
459:(8).
391:arXiv
238:(PDF)
604:PMID
479:PMID
427:PMID
409:ISSN
358:ISBN
328:PMID
310:ISSN
268:PMID
260:ISSN
100:.org
70:Type
44:2006
594:PMC
586:doi
545:doi
506:doi
469:PMC
461:doi
417:PMC
401:doi
318:PMC
302:doi
250:doi
96:www
653::
610:.
602:.
592:.
582:82
580:.
576:.
553:.
541:80
539:.
535:.
512:.
502:73
500:.
477:.
467:.
457:39
455:.
451:.
439:^
425:.
415:.
407:.
399:.
387:32
385:.
381:.
340:^
326:.
316:.
308:.
298:27
296:.
292:.
280:^
266:.
258:.
246:22
244:.
240:.
618:.
588::
561:.
547::
520:.
508::
485:.
463::
433:.
403::
393::
366:.
334:.
304::
274:.
252::
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.