1463:
1321:
1036:. There are several archetypal jaw suspensions: amphistyly, orbitostyly, hyostyly, and euhyostyly. In amphistyly, the palatoquadrate has a postorbital articulation with the chondrocranium from which ligaments primarily suspend it anteriorly. The hyoid articulates with the mandibular arch posteriorly, but it appears to provide little support to the upper and lower jaws. In orbitostyly, the orbital process hinges with the orbital wall and the hyoid provides the majority of suspensory support. In contrast, hyostyly involves an ethmoid articulation between the upper jaw and the cranium, while the hyoid most likely provides vastly more jaw support compared to the anterior ligaments. Finally, in euhyostyly, also known as true hyostyly, the mandibular cartilages lack a ligamentous connection to the cranium. Instead, the hyomandibular cartilages provide the only means of jaw support, while the ceratohyal and basihyal elements articulate with the lower jaw, but are disconnected from the rest of the hyoid.
890:
60:
1476:
35:
610:
591:
1217:
1274:
1248:
721:
705:
1387:
1183:
857:
1045:
629:
1233:
329:, there has also been considerable modification from the primitive pattern. The roof of the skull is generally well formed, and although the exact relationship of its bones to those of tetrapods is unclear, they are usually given similar names for convenience. Other elements of the skull, however, may be reduced; there is little cheek region behind the enlarged orbits, and little, if any bone in between them. The upper jaw is often formed largely from the
1633:
374:
1201:
1657:
848:. This fish can extend its jaws up to 65% the length of its head. This species utilizes its quick and extreme jaw protrusion to capture smaller fishes and crustaceans. The genus this species belongs to possess one unique ligament (vomero-interopercular) and two enlarged ligaments (interoperculo-mandibular and premaxilla-maxilla), which along with a few changes to the form of cranial bones, allow it to achieve extreme jaw protrusion.
5417:
5405:
5639:
1367:
735:
6631:
6613:
1445:
1543:
1678:
6643:
837:" has the property of allowing numerous arrangements to achieve a given mechanical result (fast jaw protrusion or a forceful bite), thus decoupling morphology from function. The actual morphology of wrasses reflects this, with many lineages displaying different jaw morphology that results in the same functional output in a similar or identical ecological niche.
247:
1282:
182:
to pump water across the gills. The familiar use of jaws for feeding would then have developed as a secondary function before becoming the primary function in many vertebrates. All vertebrate jaws, including the human jaw, evolved from early fish jaws. The appearance of the early vertebrate jaw has
1349:
forms. One morph has its jaw twisted to the left, allowing it to eat scales more readily on its victim's right flank. The other morph has its jaw twisted to the right, which makes it easier to eat scales on its victim's left flank. The relative abundance of the two morphs in populations is regulated
914:
in the mouth. Instead, when the moray bites prey, it first bites normally with its oral jaws, capturing the prey. Immediately thereafter, the pharyngeal jaws are brought forward and bite down on the prey to grip it; they then retract, pulling the prey down the moray eel's gullet, allowing it to be
1357:
In cichlids generally, the oral and pharyngeal teeth differ with different species in ways that allow them to process different kinds of prey. Primary oral jaws contain teeth which are used to capture and hold food, while pharyngeal jaws have pharyngeal teeth which function as a chewing tool.
1783:
were another class of fish which appeared also in the fossil records during the
Silurian at about the same time as the placoderms. They were smaller than most placoderms, usually under 20 centimetres. Spiny sharks did not diversify as much as placoderms, but survived much longer into the
1799:, that uses "breathing with the cheeks" to pump water across the gills of fish or air into the lungs in the case of amphibians. Over evolutionary time the more familiar use of jaws (to humans), in feeding, was selected for and became a very important function in vertebrates. Many
694:. By contrast, mere closure of the jaws would risk pushing food out of the mouth. In more advanced teleosts, the premaxilla is enlarged and has teeth, while the maxilla is toothless. The maxilla functions to push both the premaxilla and the lower jaw forward. To open the mouth, an
150:
and replace teeth as they wear by moving new teeth laterally from the medial jaw surface in a conveyor-belt fashion. Teeth are replaced multiple times also in most bony fishes, but unlike cartilaginous fishes, the new tooth erupts only after the old one has fallen out.
1490:
are small fish found worldwide in the deep sea. Relative to their size they have one of the widest gapes of any fish. The lower jaw has no ethmoid membrane (floor) and is attached only by the hinge and a modified tongue bone. There are several large, fang-like
1422:), have molariform teeth and a strengthened jawbone bone. To grab and bite prey not armoured with shells, predators need conical, bent back teeth. Herbivorous cichlids also have structural differences in their teeth. Cichlids that specialise in algae (e.g.
910:. The pharyngeal jaws of most fishes are not mobile. The pharyngeal jaws of the moray are highly mobile, perhaps as an adaptation to the constricted nature of the burrows they inhabit which inhibits their ability to swallow as other fishes do by creating a
1403:
This allows for different nutritional strategies, and because of this, cichlids are able to colonize different habitats. The structural diversity of the lower pharyngeal jaw could be one of the reasons for the occurrence of so many cichlid species.
1826:, which braces the jaw against the braincase and increases mechanical efficiency. While there is no fossil evidence directly to support this theory, it makes sense in light of the numbers of pharyngeal arches that are visible in extant jawed (the
1412:
niches. The pharyngeal jaw apparatus consists of two upper and one single lower plate, all of which have dentations that differ in size and type. The structure of the lower pharynx is often associated with the species of food of the species.
1848:
evolved. Originally it was the lower of two cartilages which supported the first gill arch (nearest the front) in early fish. Then it grew longer and stronger, and acquired muscles capable of closing the developing jaw. In early fish and in
1462:
922:
on the lateral sides of the head. The pharyngeal arches give rise to a number of different structures in the skeletal, muscular and circulatory systems in a manner which varies across the vertebrates. Pharyngeal arches trace back through
775:
Decoupled mechanism: Protrusion of the premaxilla is accomplished through elevation of the neurocranium causing the premaxilla to move anteriorly. Movements of the neurocranium are not coupled with the kinematics of the upper jaw (e.g.
813:
mouths, usually with separate jaw teeth that jut outwards. Many species can be readily recognized by their thick lips, the inside of which is sometimes curiously folded, a peculiarity which gave rise the German name of "lip-fishes"
4238:
tissue like most other bones); (2) both structures form the upper and lower bars that bend forward and are hinged in the middle; and (3) the musculature of the jaw seem homologous to the gill arches of jawless fishes. (Gilbert
785:
Suspensorial abduction mechanism: The lateral expansion of the suspensorium (a combination of the palatine, pterygoid series, and quadrate bones) pulls on a ligament which causes the premaxilla to protrude anteriorly (e.g.
1320:
494:. This is similar to the mandible (lower jaw), which is also a fusion of two halves at the mandibular symphysis. In bony fish, the maxilla is called the "upper maxilla," with the mandible being the "lower maxilla". The
5471:
Zhu, Min; Yu, Xiaobo; Erik
Ahlberg, Per; Choo, Brian; Lu, Jing; Qiao, Tuo; Qu, Qingming; Zhao, Wenjin; Jia, Liantao; Blom, Henning; Zhu, You'an (2013). "A Silurian placoderm with osteichthyan-like marginal jaw bones".
1133:. Some sharks lose 30,000 or more teeth in their lifetime. The rate of tooth replacement varies from once every 8 to 10 days to several months, although few studies have been able to quantify this. In most species of
670:
teleosts, the enlarged premaxilla is the main tooth-bearing bone, and the maxilla, which is attached to the lower jaw, acts as a lever, pushing and pulling the premaxilla as the mouth is opened and closed. These
752:
Mandibular depression mechanism: The depression of the lower jaw (mandible) pulls or pushes the premaxilla into protrusion via force transmission through ligaments and tendons connected to the upper jaws (e.g.
442:
lie above the prearticular bone. As the name implies, the majority of the teeth are attached to the dentary, but there are commonly also teeth on the coronoid bones, and sometimes on the prearticular as well.
284:, in which the cranium is represented by a trough-like basket of cartilaginous elements only partially enclosing the brain, and associated with the capsules for the inner ears and the single nostril.
4656:
Smith, M.M.; Coates, M.I. (2000). "10. Evolutionary origins of teeth and jaws: developmental models and phylogenetic patterns". In
Teaford, Mark F.; Smith, Moya Meredith; Ferguson, Mark W.J. (eds.).
886:
which no longer has a respiratory function. The first four arches still function as gills. Unlike the oral jaw, the pharyngeal jaw has no jaw joint, but is supported instead by a sling of muscles.
294:, also have simple skulls. The cranium is a single structure forming a case around the brain, enclosing the lower surface and the sides, but always at least partially open at the top as a large
104:
are positioned at the back of the throat. The oral jaws are used to capture and manipulate prey by biting and crushing. The pharyngeal jaws, so-called because they are positioned within the
178:, about 430 million years ago. The original selective advantage offered by the jaw was probably not related to feeding, but to increased respiration efficiency—the jaws were used in the
3901:
Burress, Edward D.; Duarte, Alejandro; Gangloff, Michael M.; Siefferman, Lynn (January 2013). "Isotopic trophic guild structure of a diverse subtropical South
American fish community".
510:, both maxilla and premaxilla are relatively plate-like bones, forming only the sides of the upper jaw, and part of the face, with the premaxilla also forming the lower boundary of the
590:
1604:
elements. The first set of these elements surrounded the mouth to form the jaw. The upper portion of the second embryonic arch supporting the gill became the hyomandibular bone of
698:
pulls back the top of the maxilla, pushing the lower jaw forward. In addition, the maxilla rotates slightly, which pushes forward a bony process that interlocks with the premaxilla.
234:, leading to three main four-bar linkage systems to generally describe the lateral and anterior expansion of the buccal cavity in fishes. The most thorough overview of the different
1569:
The appearance of the early vertebrate jaw has been described as "a crucial innovation" and "perhaps the most profound and radical evolutionary step in the vertebrate history".
1247:
3503:
686:(braincase); it plays a role in protruding the mouth and creating a circular opening. This lowers the pressure inside the mouth, sucking the prey inside. The lower jaw and
1749:
to achieve a high speed of jaw opening, opening their jaws in 20 milliseconds and completing the whole process in 50-60 milliseconds, comparable to modern fishes that use
1117:
rather than directly affixed to the jaw as in some fish. Shark teeth form within the jaw move outward in rows until they are eventually dislodged in a manner similar to a
863:
have two sets of jaws: the oral jaws that capture prey and the pharyngeal jaws that advance into the mouth and move prey from the oral jaws to the esophagus for swallowing
446:
This complex primitive pattern has, however, been simplified to various degrees in the great majority of vertebrates, as bones have either fused or vanished entirely. In
4811:
Compagnucci, C; Debiais-Thibaud, M; Coolen, M; Fish, J; Griffin, J N; Bertocchini, F; Minoux, M; Rijli, F M; Borday-Birraux, V; Casane, D; Mazanc, S; Depew, M J (2013).
1216:
628:
4092:
3323:
Hulsey, C Darrin; Cohen, Karly E; Johanson, Zerina; Karagic, Nidal; Meyer, Axel; Miller, Craig T; Sadier, Alexa; Summers, Adam P; Fraser, Gareth J (1 September 2020).
766:
Twisting maxilla mechanism: The depression of the mandible causes the maxilla to twist about the longitudinal axis resulting in the protrusion of the premaxilla (e.g.
3928:
Genner, Martin J.; Turner, George F.; Hawkins, Stephen J. (1999). "Foraging of Rocky
Habitat Cichlid Fishes in Lake Malawi: Coexistence through Niche Partitioning?".
348:
is not fully formed, and consists of multiple, somewhat irregularly shaped bones with no direct relationship to those of tetrapods. The upper jaw is formed from the
3725:"Evolution of a unique predatory feeding apparatus: functional anatomy, development and a genetic locus for jaw laterality in Lake Tanganyika scale-eating cichlids"
4471:
2674:
Westneat, Mark W.; Wainwright, Peter C. (November 1989). "Feeding mechanism ofEpibulus insidiator (Labridae; Teleostei): Evolution of a novel functional system".
1510:, has jaws larger than its body. The jaws are lined with small teeth and are loosely hinged. They open wide enough to swallow a fish larger than the eel itself.
918:
All vertebrates have a pharynx, used in both feeding and respiration. The pharynx arises during development through a series of six or more outpocketings called
609:
4929:
1200:
889:
1791:
The original selective advantage offered by the jaw may not be related to feeding, but rather to increased respiration efficiency. The jaws were used in the
1182:
6343:
5540:
2659:
1156:
have dense and flattened teeth used for crushing, those that feed on fish have needle-like teeth for gripping, and those that feed on larger prey such as
1232:
6085:
4813:"Pattern and polarity in the development and evolution of the gnathostome jaw: Both conservation and heterotopy in the branchial arches of the shark,
931:
who also share endodermal outpocketings of the pharyngeal apparatus. Similar patterns of gene expression can be detected in the developing pharynx of
498:
of the maxilla holds the upper teeth, and is referred to as the maxillary arch. In most vertebrates, the foremost part of the upper jaw, to which the
1585:
that did survive, have yielded little insight into the deep remodelling of the vertebrate skull that must have taken place as early jaws evolved.
238:
in animals has been provided by M. Muller, who also designed a new classification system, which is especially well suited for biological systems.
4028:"Trophic ecology of the deep-sea fish Malacosteus niger (Pisces: Stomiidae): An enigmatic feeding ecology to facilitate a unique visual system?"
3278:"Structure, attachment, replacement and growth of teeth in bluefish, Pomatomus saltatrix (Linnaeus, 1766), a teleost with deeply socketed teeth"
2264:
Muller, M (29 May 1996). "A novel classification of planar four-bar linkages and its application to the mechanical analysis of animal systems".
1308:. The purpose of the kype is not altogether clear, though they can be used to establish dominance by clamping them around the base of the tail (
5344:
5311:
5245:
5081:
5058:
4908:
4756:
4673:
4510:
4180:
4076:
3592:
2974:
2830:
2506:
2161:
261:
and sharks only possess a cartilaginous endocranium, with both the upper and lower jaws being separate elements. Bony fishes have additional
4965:
Hulsey, CD; Fraser, GJ; Streelman, JT (2005). "Evolution and development of complex biomechanical systems: 300 million years of fish jaws".
4603:
Anderson, P. S. L.; Westneat, M. (2009). "A biomechanical model of feeding kinematics for
Dunkleosteus terrelli (Arthrodira, Placodermi)".
1573:
had more difficulty surviving than fish with jaws, and most jawless fish became extinct during the
Triassic period. However studies of the
5181:
Oisi, Y; Ota, K G; Kuraku, S; Fujimoto, S; Kuratani, S (2013). "Craniofacial development of hagfishes and the evolution of vertebrates".
4953:
3421:
Kolmann, Matthew A.; Cohen, Karly E.; Bemis, Katherine E.; Summers, Adam P.; Irish, Frances J.; Hernandez, L. Patricia (September 2019).
5912:
1032:
with the upper. The arrangement of soft tissue and any additional articulations connecting these elements is collectively known as the
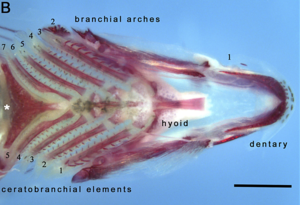
77:) arches and ceratobrachial elements (arch bones). The white asterisk indicates the toothed pharyngeal jaw. Scale bar represents 500 μm.
2180:
Westneat, Mark W. (September 1990). "Feeding mechanics of teleost fishes (Labridae; Perciformes): A test of four-bar linkage models".
1548:
Spindle diagram for the evolution of fish and other vertebrate classes. The earliest classes that developed jaws were the now extinct
1416:
In order to crack shellfish considerable force must be generated, which is why cichlids that feed on molluscs (e.g. the cichlid bass,
833:
are joined to the anterior tips of these two bones, respectively, creating a loop of 4 rigid bones connected by moving joints. This "
2992:"Evolutionary history of Otophysi (Teleostei), a major clade of the modern freshwater fishes: Pangaean origin and Mesozoic radiation"
1765:) at the blade edge in the largest individuals. The pressures generated in those regions were high enough to puncture or cut through
340:
Although the skulls of fossil lobe-finned fish resemble those of the early tetrapods, the same cannot be said of those of the living
5942:
5321:
4526:
4441:
3991:(Teleostei: Stomiidae: Malacosteinae), with Description of a New Species from the Temperate Southern Hemisphere and Indian Ocean".
3866:
Burress, Edward D. (April 2015). "Cichlid fishes as models of ecological diversification: patterns, mechanisms, and consequences".
1475:
3478:
1861:(bony fish) and their descendants (amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals) the cartilage was covered in bone – although in their
1692:
It is now accepted that the precursors of the jawed vertebrates are the long extinct bony (armoured) jawless fish, the so-called
701:
Teleosts achieve this jaw protrusion using one of four different mechanisms involving the ligamentous linkages within the skull.
5596:
5533:
654:(a bone at the tip of the upper jaw) and corresponding modifications in the jaw musculature which make it possible for them to
4027:
4196:
Khonsari, R. H.; Li, B.; Vernier, P.; Northcutt, R. G.; Janvier, P. (2009). "Agnathan brain anatomy and craniate phylogeny".
2717:
Mehta, Rita S.; Wainwright, Peter C. (6 September 2007). "Raptorial jaws in the throat help moray eels swallow large prey".
3237:"The fine structure of initial mineralisation during tooth development in the gummy shark, Mustelus manazo, Elasmobranchia"
2225:"The opercular mouth-opening mechanism of largemouth bass functions as a 3D four-bar linkage with three degrees of freedom"
1426:) tend to have small conical teeth. Species that feed on pods or seeds require large conical teeth for chewing their food.
1351:
322:
for the cranial nerves. The jaws consist of separate hoops of cartilage, almost always distinct from the cranium proper.
6647:
5681:
5128:
Mehta, Rita S.; Wainwright, Peter C. (May 2008). "Functional morphology of the pharyngeal jaw apparatus in moray eels".
4479:
5581:
5430:
1818:
that support the gills in fish. The two most anterior of these arches are thought to have become the jaw itself (see
462:, do not have any of the bones found in the lower jaw of other vertebrates. Instead, their lower jaw is composed of a
4766:
Botella, H.; Blom, H.; Dorka, M.; Ahlberg, P. E.; Janvier, P. (2007). "Jaws and teeth of the earliest bony fishes".
6333:
6060:
6030:
5917:
5526:
1901:
691:
5091:
Mallatt, J. (2008). "The origin of the vertebrate jaw: Neoclassical ideas versus newer, development-based ideas".
6606:
6599:
6566:
6308:
5980:
5661:
5457:
337:
itself located further back, and an additional bone, the symplectic, linking the jaw to the rest of the cranium.
1777:
was perfectly adapted to prey on free-swimming, armoured prey like arthropods, ammonites, and other placoderms.
59:
6616:
6375:
5420:
2533:
Motta, Philip Jay (23 February 1984). "Mechanics and
Functions of Jaw Protrusion in Teleost Fishes: A Review".
1057:
788:
34:
5638:
4266:
Clack, J. A. (1994). "Earliest known tetrapod braincase and the evolution of the stapes and fenestra ovalis".
3613:"Handed Foraging Behavior in Scale-Eating Cichlid Fish: Its Potential Role in Shaping Morphological Asymmetry"
3192:
Boyne, Philip J. (March 1970). "Study of the
Chronologic Development and Eruption of Teeth in Elasmobranchs".
2108:"The origin of the vertebrate jaw: Intersection between developmental biology-based model and fossil evidence"
4004:
3823:
Casciotta, Jorge R.; Arratia, Gloria (July 1993). "Jaws and teeth of american cichlids (Pisces: Labroidei)".
414:
to the mandible of mammals is merely the largest of several bones in the lower jaw. It is referred to as the
6594:
6576:
6138:
5887:
4921:
4551:"Feeding mechanics and bite force modelling of the skull of Dunkleosteus terrelli, an ancient apex predator"
2573:"Adaptive Significance of Intra- and Interspecific Differences in the Feeding Repertoires of Cichlid Fishes"
1715:
of fish, heavily armoured at the front of their body, which first appeared in the fossil records during the
1273:
1137:, teeth are replaced one at a time as opposed to the simultaneous replacement of an entire row. However, in
306:
organs. Behind these are the orbits, and then an additional pair of capsules enclosing the structure of the
3075:
Fraser GJ, Hulsey CD, Bloomquist RF, Uyesugi K, Manley NR, Streelman JT (February 2009). Jernvall J (ed.).
978:
and gill arches) needs extra strength due to its heavy exposure to physical stress. It has a layer of tiny
6556:
6380:
6365:
6188:
5907:
5796:
4974:
1516:
are a family of fresh water fishes which can be divided into genera with protractile upper jaws which are
1029:
131:
3670:
Hori, M. (1993). "Frequency-dependent natural selection in the handedness of scale-eating cichlid fish".
2054:"Does evolutionary innovation in pharyngeal jaws lead to rapid lineage diversification in labrid fishes?"
1109:
and bony fish continuously produce new teeth throughout their lives, they do so via different mechanism.
470:
of other groups. This also remains a significant element of the jaw in some primitive bony fish, such as
6669:
6586:
6571:
6080:
5897:
1725:
1665:
1644:
1341:
1190:
379:
5408:
1837:
1281:
738:
720:
704:
467:
310:. Finally, the skull tapers towards the rear, where the foramen magnum lies immediately above a single
183:
been described as "perhaps the most profound and radical evolutionary step in the vertebrate history".
5442:
4690:
3277:
1950:
Fraser, G. J.; Hulsey, C. D.; Bloomquist, R. F.; Uyesugi, K.; Manley, N. R.; Streelman, J. T. (2009).
882:. They are believed to have originated, in a similar way to oral jaws, as a modification of the fifth
6581:
5877:
5483:
5190:
4775:
4353:
4275:
4039:
3937:
3681:
3624:
2728:
2498:
2273:
2119:
1878:
1857:), Meckel's cartilage continued to be the main component of the lower jaw. But in the adult forms of
1723:. They became extinct by the end of that period, about 360 million years ago. Their largest species,
1719:
about 430 million years ago. Initially they were very successful, diversifying remarkably during the
1405:
1346:
1277:
Open mouth of a salmon showing the second set of pharyngeal jaws positioned at the back of the throat
778:
235:
191:
4979:
2855:
1745:
shield, the lower jaw and the jaw muscles joined together by movable joints. This mechanism allowed
1386:
994:. This gives these areas much of the same strength found in the bony tissue found in other animals.
6370:
6313:
6113:
6000:
5789:
4309:
Donoghue, P. C.; Purnell, M. A. (2005). "Genome duplication, extinction and vertebrate evolution".
4066:
1223:
222:
is responsible for the coordinated opening of the mouth and the three-dimensional expansion of the
4711:
3423:"Tooth and consequences: Heterodonty and dental replacement in piranhas and pacus (Serrasalmidae)"
2990:
Nakatani, Masanori; Miya, Masaki; Mabuchi, Kohji; Saitoh, Kenji; Nishida, Mutsumi (22 June 2011).
5952:
5507:
5224:
5153:
5116:
5029:
4881:
4799:
4620:
4369:
4291:
4213:
4086:
4008:
3969:
3953:
3883:
3848:
3805:
3705:
3460:
3217:
2902:
2752:
2699:
2550:
2205:
1589:
1487:
1451:
1374:
1329:
955:
782:), allowing for more versatility and modularity of the jaws during prey capture and manipulation.
577:
in front of the fish. In the case of hammerheads the rostrum (hammer) extends both ventrally and
573:
have rostrums (saws) which are both electro-sensitive and used for slashing. The rostrums extend
523:
411:
287:
111:
2003:"Independent evolution of the specialized pharyngeal jaw apparatus in cichlid and labrid fishes"
1044:
856:
5069:
4665:
997:
Generally sharks have only one layer of tesserae, but the jaws of large specimens, such as the
6298:
6203:
6108:
6020:
6015:
5962:
5769:
5576:
5566:
5499:
5447:
5377:
5340:
5307:
5286:
5241:
5216:
5145:
5108:
5077:
5054:
5021:
4992:
4904:
4898:
4873:
4838:
4791:
4752:
4742:
4669:
4580:
4506:
4326:
4176:
4149:
4072:
3961:
3840:
3797:
3756:
3697:
3672:
3652:
3588:
3582:
3563:
3452:
3444:
3403:
3354:
3305:
3297:
3258:
3209:
3159:
3108:
3031:
3013:
2970:
2962:
2943:
2894:
2836:
2826:
2803:
2744:
2691:
2630:
2502:
2490:
2471:
2430:
2330:
2289:
2246:
2197:
2157:
2085:
2034:
1983:
1564:
1014:
1010:
1006:
919:
578:
530:
373:
319:
311:
299:
227:
215:
211:
207:
5332:
5299:
4168:
518:, such as sharks and rays also lack a true maxilla. Their upper jaw is instead formed from a
6040:
5985:
5947:
5902:
5860:
5784:
5571:
5491:
5474:
5462:
5367:
5276:
5268:
5206:
5198:
5166:
5137:
5100:
5046:
5013:
4984:
4893:
Forey, Peter; Janvier, Philippe (2000). "Agnathans and the origin of jawed vertebrates". In
4863:
4828:
4783:
4657:
4612:
4570:
4562:
4414:
4387:
4361:
4318:
4283:
4205:
4139:
4131:
4047:
4000:
3945:
3910:
3875:
3832:
3787:
3746:
3736:
3689:
3642:
3632:
3553:
3545:
3434:
3393:
3385:
3344:
3336:
3289:
3248:
3201:
3149:
3139:
3098:
3088:
3021:
3003:
2933:
2886:
2793:
2783:
2736:
2719:
2683:
2620:
2584:
2542:
2461:
2420:
2281:
2236:
2189:
2127:
2075:
2065:
2024:
2014:
1973:
1963:
1738:
1632:
1617:
1513:
1496:
1130:
899:
834:
727:
558:
495:
403:
219:
5041:
Lingham-Soliar, Theagarten (2014). "The First
Vertebrates, Jawless Fishes, the Agnathans".
4638:
2877:
Wilga, C. D. (2005). "Morphology and evolution of the jaw suspension in lamniform sharks".
1495:
in the front of the jaws, followed by many small barbed teeth. There are several groups of
6257:
6237:
6065:
6052:
6035:
5990:
5872:
5811:
5735:
5730:
5666:
5653:
5623:
5325:
1895:
1890:
1850:
1815:
1808:
1804:
1750:
1712:
1656:
1309:
1297:
1122:
867:
841:
709:
672:
663:
655:
620:
562:
418:, and forms the body of the outer surface of the jaw. It is bordered below by a number of
326:
155:
74:
66:
5318:
690:(main upper fixed bone of the jaw) are then pulled back to close the mouth, and the fish
187:
had more difficulty surviving than fish with jaws, and most jawless fish became extinct.
5487:
5194:
4779:
4449:
4357:
4279:
4043:
3941:
3685:
3628:
3324:
2732:
2607:
Wainwright, Peter C.; Alfaro, Michael E.; Bolnick, Daniel I.; Hulsey, C. Darrin (2005).
2329:, though this is an outdated term which goes back to at least the 1858 first edition of
2277:
2266:
Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B: Biological Sciences
2123:
6533:
6506:
6398:
6390:
6323:
6293:
6232:
6214:
6168:
6158:
5762:
5715:
5281:
5256:
4575:
4550:
4144:
4119:
3751:
3724:
3647:
3612:
3558:
3529:
3398:
3373:
3349:
3253:
3236:
3154:
3127:
3103:
3076:
3026:
2991:
2798:
2771:
2080:
2053:
2029:
2002:
1978:
1951:
1928:
1423:
1366:
515:
349:
70:
48:
2653:
6663:
6635:
6538:
6452:
6272:
6247:
6242:
6198:
6193:
6148:
6143:
6123:
5995:
5774:
5693:
5272:
4658:
4209:
3549:
3464:
2648:
1912:
1827:
1785:
1605:
1409:
1393:
1254:
1207:
1165:
1118:
971:
936:
928:
455:
223:
5157:
5033:
4885:
4624:
4373:
4295:
4217:
3973:
3887:
3852:
3809:
3709:
3221:
2906:
2703:
2609:"Many-to-One Mapping of Form to Function: A General Principle in Organismal Design?"
2407:
Wueringer, B. E.; Squire, L. Jr; Kajiura, S. M.; Hart, N. S.; Collin, S. P. (2012).
2374:
2209:
734:
6528:
6352:
6267:
6227:
6128:
6070:
6010:
5937:
5932:
5922:
5838:
5828:
5757:
5740:
5647:
5608:
5601:
5511:
5228:
5120:
4803:
4344:
Forey, P. L.; Janvier, P. (1993). "Agnathans and the origin of jawed vertebrates".
4231:
4012:
3176:
2756:
1923:
1858:
1819:
1609:
1574:
1134:
1063:
1021:
967:
944:
940:
826:
810:
806:
798:
683:
667:
554:
507:
451:
423:
298:. The most anterior part of the cranium includes a forward plate of cartilage, the
281:
163:
1017:(snout), the cartilage can be spongy and flexible to absorb the power of impacts.
108:, are used to further process the food and move it from the mouth to the stomach.
5211:
5167:"Pharyngeal jaws and their evolutionary, ecological and behavioural significance"
4903:. US: University of Chicago Press; Nature/Macmillan Magazines. pp. 251–266.
4746:
3693:
3637:
3205:
3093:
3050:
2151:
1968:
438:
bone forms the articulation with the skull proper. Finally a set of three narrow
6511:
6499:
6425:
6183:
6178:
6153:
6133:
6075:
5970:
5865:
5843:
5833:
5806:
5676:
5628:
5050:
4833:
4812:
1845:
1792:
1780:
1705:
1693:
1553:
1507:
1480:
1444:
1418:
1408:
took place over the course of the cichlid radiation, synchronous with different
1238:
1169:
1110:
1053:
1009:, have two to three layers or more, depending on body size. The jaws of a large
1002:
874:
distinct from the primary (oral) jaws. They are contained within the throat, or
427:
262:
195:
179:
171:
4322:
4250:
3293:
1741:
mechanism for jaw opening that incorporated connections between the skull, the
1048:
Inside of a shark jaw where new teeth move forward as though on a conveyor belt
6561:
6328:
6262:
6252:
6173:
6163:
5848:
5816:
5801:
5747:
5720:
5703:
4135:
4051:
3879:
3792:
3775:
2425:
2408:
2132:
2107:
1907:
1823:
1796:
1754:
1697:
1616:
region in most fishes. It usually plays a role in suspending the jaws or the
1301:
1153:
998:
963:
895:
860:
651:
616:
550:
503:
345:
330:
295:
266:
231:
17:
3448:
3301:
3017:
3008:
6318:
6303:
6288:
6118:
5779:
5725:
5710:
5688:
5671:
5618:
5431:"Moray Eels Are Uniquely Equipped to Pack Big Prey Into Their Narrow Bodies"
5017:
4894:
4868:
4851:
3836:
2840:
2687:
2223:
Olsen, Aaron M.; Camp, Ariel L.; Brainerd, Elizabeth L. (15 December 2017).
2193:
2070:
1874:
1866:
1841:
1800:
1734:
1701:
1639:
1621:
1601:
1593:
1549:
1542:
1521:
1517:
1500:
1333:
1161:
1079:
1075:
975:
932:
924:
907:
883:
879:
659:
542:
519:
463:
435:
357:
318:. There are, in addition, at various points throughout the cranium, smaller
307:
303:
203:
167:
159:
139:
135:
123:
85:
5503:
5381:
5372:
5355:
5290:
5220:
5149:
5112:
5025:
4996:
4988:
4955:
Figure 1.14. Jaw structure in the fish, reptile, and mammal. (illustration)
4877:
4842:
4795:
4584:
4566:
4330:
4153:
3965:
3844:
3801:
3760:
3701:
3656:
3567:
3456:
3407:
3358:
3309:
3163:
3144:
3112:
3035:
2947:
2898:
2807:
2788:
2748:
2695:
2634:
2625:
2608:
2589:
2572:
2475:
2466:
2449:
2434:
2285:
2250:
2201:
2089:
2038:
2019:
1987:
1677:
1608:, which supports the skull and therefore links the jaw to the cranium. The
637:
have an electro-sensitive rostrum (saw) which is also used to slash at prey
4503:
The Marshall Illustrated Encyclopedia of Dinosaurs and Prehistoric Animals
3949:
3741:
3340:
3262:
3213:
2293:
6521:
6462:
6408:
6403:
6222:
6090:
5698:
5613:
5438:
4922:"The anatomical tradition: Evolutionary Embryology: Embryonic homologies"
4235:
3774:
Muschick, Moritz; Indermaur, Adrian; Salzburger, Walter (December 2012).
2938:
2921:
1918:
1870:
1742:
1720:
1716:
1095:
1087:
1083:
983:
822:
755:
600:
596:
566:
546:
534:
471:
419:
407:
391:
341:
315:
270:
175:
119:
5495:
5202:
4787:
2740:
2663:. Vol. 28 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 839.
6494:
6489:
6467:
6440:
6435:
6430:
5975:
5927:
5821:
5591:
5586:
5141:
5104:
4716:
4419:
4392:
3957:
3389:
2890:
2554:
2241:
2224:
2052:
Alfaro, M. E.; Brock, C. D.; Banbury, B. L.; Wainwright, P. C. (2009).
1862:
1831:
1766:
1582:
1578:
1570:
1337:
1324:
Dorsal view of right-bending (left) and left-bending (right) jaw morphs
1149:
1138:
1114:
1025:
987:
979:
911:
875:
830:
687:
676:
647:
634:
574:
570:
565:
which signal the presence of prey by detecting weak electrical fields.
511:
499:
483:
447:
384:
334:
258:
246:
199:
184:
105:
44:
5356:"Evolution of levers and linkages in the feeding mechanisms of fishes"
5174:
Convergence and plasticity in the adaptive radiation of cichlid fishes
3914:
3439:
3422:
3276:
Bemis, William E.; Giuliano, Anne; McGuire, Betty (20 November 2005).
2450:"Evolution of Levers and Linkages in the Feeding Mechanisms of Fishes"
1160:
have pointed lower teeth for gripping and triangular upper teeth with
6413:
4365:
4287:
4169:"Homologies and Evolutionary Transitions in Early Vertebrate History"
3776:"Convergent Evolution within an Adaptive Radiation of Cichlid Fishes"
3530:"Seasonal changes in the lower jaw skeleton in male Atlantic salmon (
1770:
1293:
1157:
991:
959:
939:. However, the vertebrate pharynx is unique in that it gives rise to
759:
695:
538:
487:
274:
194:. These linkages can be especially common and complex in the head of
4616:
2772:"Developmental and evolutionary origins of the pharyngeal apparatus"
2546:
3077:"An Ancient Gene Network Is Co-opted for Teeth on Old and New Jaws"
1952:"An ancient gene network is co-opted for teeth on old and new jaws"
1830:), which have seven arches, and primitive jawless vertebrates (the
6516:
6445:
5855:
5306:. Fish Physiology. Vol. 23. Academic Press. pp. 77–102.
1854:
1811:, resulting in highly complex jaws with dozens of bones involved.
1730:
1613:
1492:
1474:
1319:
1304:
so they have a pronounced curvature. These hooked jaws are called
1280:
1126:
1106:
1099:
1067:
1043:
888:
855:
768:
703:
502:
are attached in mammals consists of a separate pair of bones, the
459:
399:
372:
353:
291:
254:
143:
115:
40:
5339:. Fish Physiology. Vol. 23. Academic Press. pp. 29–76.
3987:
Kenaley, C. P. (2007). "Revision of the Stoplight Loosejaw Genus
356:
alone, all of which bear teeth. Much of the skull is formed from
6418:
6360:
6005:
5558:
5549:
1877:
bone, which forms part of the jaw joint in all tetrapods except
1597:
1305:
1285:
1257:
has knife-like teeth with main cusps flanked by lateral cusplets
1142:
1091:
1071:
395:
93:
65:
Dorsal view of the lower pharyngeal and oral jaws of a juvenile
5522:
5433:(Press release). National Science Foundation. 5 September 2007.
3374:"Evolution and development of Hertwig's epithelial root sheath"
2963:"Prey Capture Behavior and Feeding Mechanisms of Elasmobranchs"
1145:, all the teeth on one side of the jaw are replaced at a time.
430:
bone just above it. The inner surface of the jaw is lined by a
6457:
6025:
5409:
Video of a slingjaw wrasse catching prey by protruding its jaw
2360:
2325:
The mandible is also in some sources still referred to as the
1757:
when closing the jaw, estimated at 6,000 N (1,350 lb
871:
840:
The most extreme jaw protrusion found in fishes occurs in the
491:
257:
of fishes is formed from a series of loosely connected bones.
127:
89:
4900:
Shaking the tree: readings from Nature in the history of life
2652:
1873:(changes to bone) at the rear end of the jaw and becomes the
1729:, measured up to 10 m (33 ft) and weighed 3.6
1600:
opened behind the mouth, and these gills became supported by
1164:
edges for cutting. The teeth of plankton-feeders such as the
4598:
4596:
4594:
4544:
4542:
4540:
3479:"How big are whale sharks? And four other whale shark facts"
2965:. In Carrier, J. C.; Musick, J. A.; Heithaus, M. R. (eds.).
1148:
Tooth shape depends on the shark's diet: those that feed on
805:
Wrasses have become a primary study species in fish-feeding
603:, have a rostrum (bill) which evolved from the upper jawbone
529:
Some fish have permanently protruding upper jawbones called
245:
5257:"Development and evolution of the vertebrate primary mouth"
2823:
Sharks, Skates and Rays: The Biology of Elasmobranch Fishes
1210:
has teeth adapted to feed on crabs, shrimps and small fish.
47:, showing a lateral view of the oral jaws (purple) and the
4527:"Monster fish crushed opposition with strongest bite ever"
796:
Some teleosts use more than one of these mechanisms (e.g.
5421:
Video of a red bay snook catching prey by suction feeding
3534:): remodelling and regression of the kype after spawning"
1865:
the jaw initially develops as the Meckel's cartilage. In
825:
bones are connected at their posterior ends to the rigid
4005:
10.1643/0045-8511(2007)7[886:ROTSLG]2.0.CO;2
1753:
to assist in prey capture. They could also produce high
5518:
5300:"Functional Morphology of the Pharyngeal Jaw Apparatus"
4032:
Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers
422:
bones, while the angle of the jaw is formed by a lower
5004:
Koentges, G; Matsuoka, T (2002). "Jaws of the fates".
4120:"Neural crest patterning and the evolution of the jaw"
2001:
Mabuchi, K.; Miya, M.; Azuma, Y.; Nishida, M. (2007).
1520:, and genera with nonprotractile upper jaws which are
1328:
Fish jaws, like vertebrates in general, normally show
1070:, however, there are many exceptions. Some fish like
829:, and the superior and inferior articulations of the
4118:
Kimmel, C. B.; Miller, C. T.; Keynes, R. J. (2001).
210:. Especially advanced are the linkage mechanisms of
6549:
6482:
6389:
6351:
6342:
6281:
6212:
6099:
6051:
5961:
5886:
5646:
5556:
5397:
5236:Romer, Alfred Sherwood; Parsons, Thomas S. (1977).
4706:
4704:
3128:"A periodic pattern generator for dental diversity"
2922:"Evolution and ecology of feeding in elasmobranchs"
2920:Wilga, C. D.; Motta, P. J.; Sanford, C. P. (2007).
1241:
teeth are oblique and serrated to saw through flesh
5333:"Skull Biomechanics and Suction Feeding in Fishes"
5176:(PhD thesis). University of Basel. pp. 13–37.
5070:"The Earliest Jawed Vertebrates, the Gnathostomes"
4230:For example: (1) both sets of bones are made from
730:has the most extreme jaw protrusion of all fishes.
5240:. Philadelphia, PA: Holt-Saunders International.
4664:. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p.
4852:"Specification of jaw subdivisions by Dlx genes"
2969:(Second ed.). CRC Press. pp. 153–210.
679:that evolved independently at least five times.
4850:Depew, M J; Lufkin, T; Rubenstein, J L (2002).
3325:"Grand Challenges in Comparative Tooth Biology"
3126:Fraser GJ, Bloomquist RF, Streelman JT (2008).
658:. This is of great advantage, enabling them to
549:) use rostrums (bills) to slash and stun prey.
226:. The four-bar linkage is also responsible for
3051:"Do Carp Have Teeth? (Interesting Fish Facts)"
1345:. The jaws of this fish occur in two distinct
974:jaws. The jaw's surface (in comparison to the
126:. They do not have pharyngeal jaws. Generally
100:open and close the mouth, and a second set of
5534:
5458:"Ancient fish face shows roots of modern jaw"
4928:. Sunderland (MA): Sinauer Associates, Inc. (
4175:. Indiana University Press. pp. 57–121.
3372:Luan, X.; Ito, Y.; Diekwisch, T.G.H. (2005).
2602:
2600:
1648:, which lived about 380–360 million years ago
8:
5335:. In Shadwick, R. E.; Lauder, G. V. (eds.).
5302:. In Shadwick, R. E.; Lauder, G. V. (eds.).
4660:Development, function and evolution of teeth
4091:: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (
2528:
2526:
2524:
2522:
2520:
2518:
2491:"The Evolution of Fishes After the Devonian"
2394:
2347:
2313:
2145:
2143:
1945:
1943:
1761:) at the tip and 7,400 N (1,660 lb
763:). This is the most commonly used mechanism.
585:Fish with rostrums (extended upper jawbones)
166:. The earliest jaws appeared in now extinct
2961:Motta, Philip J.; Huber, Daniel R. (2012).
1226:lunges vertically and tears flesh from prey
656:protrude their jaws outwards from the mouth
122:, have one set of oral jaws made mainly of
6348:
5541:
5527:
5519:
4171:. In Anderson, J. S.; Sues, H.-D. (eds.).
3611:Lee, H. J.; Kusche, H.; Meyer, A. (2012).
3606:
3604:
1803:fish have substantially modified jaws for
526:with the bone found in other vertebrates.
146:. Cartilaginous fishes grow multiple sets
6086:Tradeoffs for locomotion in air and water
5371:
5280:
5210:
5076:. Vol. 1. Springer. pp. 33–58.
4978:
4867:
4832:
4691:"Prehistoric Fish Had Most Powerful Jaws"
4574:
4505:. London: Marshall Editions. p. 33.
4173:Major Transitions in Vertebrate Evolution
4143:
3791:
3750:
3740:
3723:Stewart, T. A.; Albertson, R. C. (2010).
3646:
3636:
3557:
3438:
3397:
3348:
3252:
3153:
3143:
3102:
3092:
3025:
3007:
2937:
2797:
2787:
2624:
2588:
2465:
2424:
2240:
2131:
2101:
2099:
2079:
2069:
2028:
2018:
1977:
1967:
1844:from which the mandibles (lower jaws) of
5255:Soukup, V; Horácek, I; Cerny, R (2013).
2770:Graham, Anthony; Richardson, Jo (2012).
2390:
2388:
2343:
2341:
2339:
1272:
360:, and its overall structure is reduced.
4751:(3rd ed.). John Wiley & Sons.
4549:Anderson, P.S.L.; Westneat, M. (2007).
2566:
2564:
2309:
2307:
2305:
2303:
1939:
1454:has one of the widest gapes of any fish
1175:
583:
5394:
4689:Britt, Robert Roy (28 November 2006).
4639:"More About Acanthodians (spiny fins)"
4105:
4084:
1638:↑ Skull diagram of the huge predatory
1524:or predators of very small organisms.
990:blocks of calcium salts arranged as a
809:due to their jaw structure. They have
5165:Muschick, M.; Salzburger, W. (2013).
4712:"The Gill Arches: Meckel's Cartilage"
2967:Biology of Sharks and Their Relatives
2858:. ReefQuest Centre for Shark Research
1372:Lower jawbone with molariform teeth (
134:and oppose vertically, comprising an
7:
5456:Barford, Eliot (25 September 2013).
2175:
2173:
1814:Jaws are thought to derive from the
1795:still observable in modern fish and
1588:The customary view is that jaws are
1098:expression regulates mechanisms for
943:support through the contribution of
682:The premaxilla is unattached to the
6642:
5913:Electroreception and electrogenesis
5360:Integrative and Comparative Biology
4944:One of the most celebrated cases...
4026:Sutton, Tracey T. (November 2005).
3528:Witten, P. E.; Hall, B. K. (2003).
3329:Integrative and Comparative Biology
2926:Integrative and Comparative Biology
2613:Integrative and Comparative Biology
2454:Integrative and Comparative Biology
2448:Westneat, M. W. (1 November 2004).
2409:"The function of the sawfish's saw"
1499:that serve to direct food down the
1013:may have up to five layers. In the
486:is a fusion of two bones along the
450:, only the dentary, articular, and
5043:The Vertebrate Integument Volume 1
2825:. Johns Hopkins University Press.
2156:. Westview Press. pp. 1–223.
1392:Lower jawbone with conical teeth (
1188:Jaw reconstruction of the extinct
1177:Cartilaginous jaws and their teeth
1024:the upper jaw is not fused to the
906:A notable example occurs with the
739:Slingjaw wrasse protruding its jaw
280:The simpler structure is found in
265:, forming a more or less coherent
25:
4311:Trends in Ecology & Evolution
2379:Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary
6641:
6630:
6629:
6612:
6611:
5637:
5415:
5403:
5273:10.1111/j.1469-7580.2012.01540.x
4210:10.1111/j.1463-6395.2008.00388.x
3581:Groot, C.; Margolis, L. (1991).
3550:10.1046/j.1469-7580.2003.00239.x
1676:
1655:
1631:
1596:. In jawless fishes a series of
1541:
1461:
1443:
1385:
1365:
1246:
1231:
1215:
1199:
1181:
1062:Jaws provide a platform in most
733:
719:
627:
608:
589:
377:Oral jaw from side and above of
154:Jaws probably originated in the
58:
33:
5597:Environmental impact of fishing
4472:"Ancient Fish With Killer Bite"
3049:Loesche, Max (1 October 2020).
2571:Liem, Karel F (February 1980).
2229:Journal of Experimental Biology
1612:is a set of bones found in the
1332:. An exception occurs with the
390:In vertebrates, the lower jaw (
4071:. John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
1483:jaws are larger than its body.
1090:have no teeth of any type. In
675:are evolutionary novelties in
569:and the critically endangered
466:structure homologous with the
314:, articulating with the first
302:, and capsules to enclose the
142:and can bear numerous ordered
1:
5172:. In Muschick, Moritz (ed.).
4478:. 19 May 2009. Archived from
4448:. 9 July 2005. Archived from
3584:Pacific salmon life histories
1788:about 290 million years ago.
1352:frequency-dependent selection
5682:intramembranous ossification
3694:10.1126/science.260.5105.216
3638:10.1371/journal.pone.0044670
3206:10.1177/00220345700490031501
3094:10.1371/journal.pbio.1000031
1969:10.1371/journal.pbio.1000031
1853:(cartilaginous fish such as
1078:have pharyngeal teeth only.
490:fissure that form the upper
5068:Lingham-Soliar, T. (2014).
5051:10.1007/978-3-642-53748-6_2
4834:10.1016/j.ydbio.2013.02.022
4065:Nelson, Joseph, S. (2006).
3427:Evolution & Development
1506:Another deep sea fish, the
1020:In sharks and other extant
6686:
6061:Fin and flipper locomotion
6031:Sequential hermaphroditism
5918:Jamming avoidance response
5635:
5354:Westneat, Mark W. (2004).
5298:Wainwright, P. C. (2006).
4920:Gilbert, Scott F. (2000).
4323:10.1016/j.tree.2005.04.008
3903:Ecology of Freshwater Fish
3587:. UBC Press. p. 143.
3294:10.1016/j.zool.2005.09.004
3194:Journal of Dental Research
1902:Entelognathus primordialis
1562:
1051:
619:has a rostrum packed with
561:have rostrums packed with
6625:
5414:
5402:
5074:The Vertebrate Integument
4531:The Sydney Morning Herald
4136:10.1017/S0021878201008068
4052:10.1016/j.dsr.2005.06.011
3880:10.1007/s10750-014-1960-z
3793:10.1016/j.cub.2012.10.048
2426:10.1016/j.cub.2012.01.055
2153:Discovering Fossil Fishes
2133:10.1007/s11434-012-5372-z
2106:Gai, Z.; Zhu, M. (2012).
1450:Relative to its size the
1288:of a spawning male salmon
692:is able to grasp the prey
5331:Westneat, M. W. (2006).
4748:Vertebrate Palaeontology
4501:Palmer, D., ed. (1999).
3235:Sasagawa I (June 1989).
3009:10.1186/1471-2148-11-177
2996:BMC Evolutionary Biology
2856:"Skeleton in the Corset"
2821:Hamlett, W. C. (1999f).
2495:Vertebrate Palaeontology
2489:Benton, Michael (2005).
2395:Romer & Parsons 1977
2348:Romer & Parsons 1977
2314:Romer & Parsons 1977
2112:Chinese Science Bulletin
2058:BMC Evolutionary Biology
2007:BMC Evolutionary Biology
1869:the cartilage partially
1058:Animal tooth development
789:Petrotilapia tridentiger
6577:Glossary of ichthyology
6139:Diel vertical migration
5018:10.1126/science.1077706
4869:10.1126/science.1075703
4442:"More About Placoderms"
4252:Evolutionary Embryology
3837:10.1002/jmor.1052170102
2688:10.1002/jmor.1052020202
2660:Encyclopædia Britannica
2327:inferior maxillary bone
2194:10.1002/jmor.1052050304
2071:10.1186/1471-2148-9-255
1773:armour suggesting that
1121:. Their scales, called
1028:, and the lower jaw is
5943:Surface wave detection
5908:Hydrodynamic reception
5582:Diseases and parasites
5443:"Evolution of the jaw"
4989:10.1089/zeb.2005.2.243
4567:10.1098/rsbl.2006.0569
4388:"Placodermi: Overview"
3508:Basking Shark Scotland
3378:Developmental Dynamics
3145:10.1186/1741-7007-6-32
2789:10.1186/2041-9139-3-24
2286:10.1098/rstb.1996.0065
2150:Maisey, J. G. (2000).
2020:10.1186/1471-2148-7-10
1484:
1325:
1289:
1278:
1049:
903:
864:
712:
664:draw it into the mouth
387:
383:, a close relative of
250:
6081:Undulatory locomotion
5898:Ampullae of Lorenzini
5212:20.500.14094/D1005717
5130:Journal of Morphology
4926:Developmental Biology
4821:Developmental Biology
4815:Scyliorhinus canicula
3950:10.1007/s004420050930
3825:Journal of Morphology
3742:10.1186/1741-7007-8-8
2879:Journal of Morphology
2676:Journal of Morphology
2499:John Wiley & Sons
2182:Journal of Morphology
1775:Dunkleosteus terrelli
1747:Dunkleosteus terrelli
1726:Dunkleosteus terrelli
1696:. The earliest known
1666:Dunkleosteus terrelli
1645:Dunkleosteus terrelli
1478:
1342:Perissodus microlepis
1323:
1284:
1276:
1191:Carcharodon megalodon
1047:
894:Pharyngeal jaw of an
892:
859:
707:
406:and the early fossil
402:with the cranium. In
380:Piaractus brachypomus
376:
249:
6309:Genetically modified
5373:10.1093/icb/44.5.378
5324:5 March 2016 at the
4942:(3rd and 4th paras,
4482:on 29 September 2012
4167:Janvier, P. (2007).
4130:(1&2): 105–119.
2626:10.1093/icb/45.2.256
2590:10.1093/icb/20.1.295
2467:10.1093/icb/44.5.378
1834:), which have nine.
1700:are the now extinct
1663:↑ Reconstruction of
1406:Convergent evolution
1113:are embedded in the
956:Cartilaginous fishes
870:are a second set of
846:Epibulus insidiator
779:Spathodus erythrodon
112:Cartilaginous fishes
6114:Aquatic respiration
6001:Life history theory
5496:10.1038/nature12617
5488:2013Natur.502..188Z
5238:The Vertebrate Body
5203:10.1038/nature11794
5195:2013Natur.493..175O
4788:10.1038/nature05989
4780:2007Natur.448..583B
4533:. 30 November 2006.
4358:1993Natur.361..129F
4280:1994Natur.369..392C
4234:cells (rather than
4068:Fishes of the World
4044:2005DSRI...52.2065S
3942:1999Oecol.121..283G
3686:1993Sci...260..216H
3629:2012PLoSO...744670L
3483:World Wildlife Fund
3341:10.1093/icb/icaa038
2741:10.1038/nature06062
2733:2007Natur.449...79M
2501:. pp. 175–84.
2278:1996RSPTB.351..689M
2124:2012ChSBu..57.3819G
1915:(jawed vertebrates)
1488:Stoplight loosejaws
1419:Crenicichla minuano
1224:shortfin mako shark
1066:for simple pointed
218:a system of linked
5953:Weberian apparatus
5261:Journal of Anatomy
5142:10.1002/jmor.10612
5105:10.2108/zsj.25.990
5093:Zoological Science
5045:. pp. 11–31.
4124:Journal of Anatomy
3538:Journal of Anatomy
3390:10.1002/dvdy.20674
3241:Journal of Anatomy
2939:10.1093/icb/icm029
2891:10.1002/jmor.10342
2854:Martin, R. Aidan.
2577:American Zoologist
2397:, pp. 217–243
2364:2nd edition, 1989.
2350:, pp. 244–247
2316:, pp. 173–177
2242:10.1242/jeb.159079
1838:Meckel's cartilage
1737:). It possessed a
1711:Placoderms were a
1535:Vertebrate classes
1485:
1452:stoplight loosejaw
1437:Stoplight loosejaw
1375:Ctenochromis horei
1330:bilateral symmetry
1326:
1312:) of an opponent.
1300:their jaws during
1290:
1279:
1050:
951:Cartilaginous jaws
904:
865:
713:
516:Cartilaginous fish
482:The upper jaw, or
468:Meckel's cartilage
456:Cartilaginous fish
404:lobe-finned fishes
388:
288:Cartilaginous fish
251:
208:feeding mechanisms
192:linkage mechanisms
6657:
6656:
6567:Fish common names
6478:
6477:
6109:Aquatic predation
5933:Capacity for pain
5662:Age determination
5482:(7470): 188–193.
5441:(13 March 2007).
5426:
5425:
5346:978-0-08-047776-3
5337:Fish Biomechanics
5313:978-0-08-047776-3
5304:Fish Biomechanics
5247:978-0-03-910284-5
5189:(7431): 175–180.
5083:978-3-642-53748-6
5060:978-3-642-53747-9
5012:(5592): 371–373.
4910:978-0-226-28497-2
4862:(5592): 381–385.
4774:(7153): 583–586.
4758:978-1-4051-4449-0
4743:Benton, Michael J
4675:978-0-521-57011-4
4512:978-1-84028-152-1
4352:(6408): 129–134.
4274:(6479): 392–394.
4182:978-0-253-34926-2
4078:978-0-471-25031-9
4038:(11): 2065–2076.
3915:10.1111/eff.12002
3786:(24): 2362–2368.
3680:(5105): 216–219.
3594:978-0-7748-0359-5
3440:10.1111/ede.12306
2976:978-1-4398-3924-9
2832:978-0-8018-6048-5
2508:978-1-4051-4449-0
2333:, if not earlier.
2272:(1340): 689–720.
2235:(24): 4612–4623.
2163:978-0-8133-3807-1
2118:(30): 3819–3828.
1816:pharyngeal arches
1571:Fish without jaws
1565:Evolution of fish
1131:homologous organs
1011:great white shark
1007:great white shark
920:pharyngeal arches
912:negative pressure
559:hammerhead sharks
394:or jawbone) is a
327:ray-finned fishes
236:types of linkages
220:four-bar linkages
206:many specialized
185:Fish without jaws
156:pharyngeal arches
88:have two sets of
43:of a generalized
16:(Redirected from
6677:
6645:
6644:
6633:
6632:
6615:
6614:
6349:
5641:
5572:Ethnoichthyology
5543:
5536:
5529:
5520:
5515:
5467:
5452:
5434:
5419:
5418:
5407:
5406:
5395:
5385:
5375:
5350:
5317:
5294:
5284:
5251:
5232:
5214:
5177:
5171:
5161:
5124:
5087:
5064:
5037:
5000:
4982:
4959:
4952:Gilbert (2000).
4941:
4939:
4937:
4914:
4889:
4871:
4846:
4836:
4807:
4762:
4729:
4728:
4726:
4724:
4708:
4699:
4698:
4686:
4680:
4679:
4663:
4653:
4647:
4646:
4635:
4629:
4628:
4600:
4589:
4588:
4578:
4546:
4535:
4534:
4523:
4517:
4516:
4498:
4492:
4491:
4489:
4487:
4468:
4462:
4461:
4459:
4457:
4438:
4432:
4431:
4429:
4427:
4411:
4405:
4404:
4402:
4400:
4384:
4378:
4377:
4366:10.1038/361129a0
4341:
4335:
4334:
4306:
4300:
4299:
4288:10.1038/369392a0
4263:
4257:
4256:
4249:Gilbert (2000).
4246:
4240:
4228:
4222:
4221:
4193:
4187:
4186:
4164:
4158:
4157:
4147:
4115:
4109:
4103:
4097:
4096:
4090:
4082:
4062:
4056:
4055:
4023:
4017:
4016:
3984:
3978:
3977:
3925:
3919:
3918:
3898:
3892:
3891:
3863:
3857:
3856:
3820:
3814:
3813:
3795:
3771:
3765:
3764:
3754:
3744:
3720:
3714:
3713:
3667:
3661:
3660:
3650:
3640:
3608:
3599:
3598:
3578:
3572:
3571:
3561:
3525:
3519:
3518:
3516:
3514:
3504:"Basking Sharks"
3500:
3494:
3493:
3491:
3489:
3475:
3469:
3468:
3442:
3418:
3412:
3411:
3401:
3384:(5): 1167–1180.
3369:
3363:
3362:
3352:
3320:
3314:
3313:
3273:
3267:
3266:
3256:
3232:
3226:
3225:
3189:
3183:
3174:
3168:
3167:
3157:
3147:
3123:
3117:
3116:
3106:
3096:
3072:
3066:
3065:
3063:
3061:
3055:Strike and Catch
3046:
3040:
3039:
3029:
3011:
2987:
2981:
2980:
2958:
2952:
2951:
2941:
2917:
2911:
2910:
2874:
2868:
2867:
2865:
2863:
2851:
2845:
2844:
2818:
2812:
2811:
2801:
2791:
2767:
2761:
2760:
2714:
2708:
2707:
2671:
2665:
2664:
2656:
2645:
2639:
2638:
2628:
2604:
2595:
2594:
2592:
2568:
2559:
2558:
2530:
2513:
2512:
2497:(3rd ed.).
2486:
2480:
2479:
2469:
2445:
2439:
2438:
2428:
2419:(5): R150–R151.
2404:
2398:
2392:
2383:
2382:
2371:
2365:
2357:
2351:
2345:
2334:
2323:
2317:
2311:
2298:
2297:
2261:
2255:
2254:
2244:
2220:
2214:
2213:
2177:
2168:
2167:
2147:
2138:
2137:
2135:
2103:
2094:
2093:
2083:
2073:
2049:
2043:
2042:
2032:
2022:
1998:
1992:
1991:
1981:
1971:
1947:
1739:four bar linkage
1680:
1659:
1635:
1545:
1514:Distichodontidae
1497:pharyngeal teeth
1465:
1447:
1389:
1369:
1250:
1235:
1219:
1203:
1185:
1172:are very small.
1123:dermal denticles
900:pharyngeal teeth
835:four-bar linkage
737:
728:sling-jaw wrasse
723:
673:protrusible jaws
631:
621:electroreceptors
612:
593:
563:electroreceptors
522:bar that is not
496:alveolar process
434:bone, while the
62:
37:
21:
6685:
6684:
6680:
6679:
6678:
6676:
6675:
6674:
6660:
6659:
6658:
6653:
6621:
6545:
6474:
6385:
6338:
6277:
6208:
6101:
6095:
6047:
5991:Ichthyoplankton
5957:
5889:
5882:
5878:Digital Library
5873:Teleost leptins
5812:Shark cartilage
5736:pharyngeal slit
5731:pharyngeal arch
5667:Anguilliformity
5652:
5650:
5642:
5633:
5552:
5547:
5470:
5455:
5437:
5429:
5416:
5404:
5398:External videos
5393:
5388:
5353:
5347:
5330:
5326:Wayback Machine
5314:
5297:
5254:
5248:
5235:
5180:
5169:
5164:
5127:
5099:(10): 990–998.
5090:
5084:
5067:
5061:
5040:
5003:
4980:10.1.1.210.7203
4964:
4951:
4935:
4933:
4919:
4911:
4892:
4849:
4810:
4765:
4759:
4741:
4737:
4735:Further reading
4732:
4722:
4720:
4710:
4709:
4702:
4688:
4687:
4683:
4676:
4655:
4654:
4650:
4637:
4636:
4632:
4617:10.1666/08011.1
4602:
4601:
4592:
4555:Biology Letters
4548:
4547:
4538:
4525:
4524:
4520:
4513:
4500:
4499:
4495:
4485:
4483:
4470:
4469:
4465:
4455:
4453:
4452:on 6 March 2018
4440:
4439:
4435:
4425:
4423:
4413:
4412:
4408:
4398:
4396:
4386:
4385:
4381:
4343:
4342:
4338:
4308:
4307:
4303:
4265:
4264:
4260:
4248:
4247:
4243:
4229:
4225:
4195:
4194:
4190:
4183:
4166:
4165:
4161:
4117:
4116:
4112:
4104:
4100:
4083:
4079:
4064:
4063:
4059:
4025:
4024:
4020:
3986:
3985:
3981:
3927:
3926:
3922:
3900:
3899:
3895:
3865:
3864:
3860:
3822:
3821:
3817:
3780:Current Biology
3773:
3772:
3768:
3722:
3721:
3717:
3669:
3668:
3664:
3610:
3609:
3602:
3595:
3580:
3579:
3575:
3527:
3526:
3522:
3512:
3510:
3502:
3501:
3497:
3487:
3485:
3477:
3476:
3472:
3420:
3419:
3415:
3371:
3370:
3366:
3322:
3321:
3317:
3275:
3274:
3270:
3234:
3233:
3229:
3191:
3190:
3186:
3175:
3171:
3125:
3124:
3120:
3074:
3073:
3069:
3059:
3057:
3048:
3047:
3043:
2989:
2988:
2984:
2977:
2960:
2959:
2955:
2919:
2918:
2914:
2876:
2875:
2871:
2861:
2859:
2853:
2852:
2848:
2833:
2820:
2819:
2815:
2769:
2768:
2764:
2727:(7158): 79–82.
2716:
2715:
2711:
2673:
2672:
2668:
2647:
2646:
2642:
2606:
2605:
2598:
2570:
2569:
2562:
2547:10.2307/1445030
2532:
2531:
2516:
2509:
2488:
2487:
2483:
2447:
2446:
2442:
2413:Current Biology
2406:
2405:
2401:
2393:
2386:
2373:
2372:
2368:
2358:
2354:
2346:
2337:
2324:
2320:
2312:
2301:
2263:
2262:
2258:
2222:
2221:
2217:
2179:
2178:
2171:
2164:
2149:
2148:
2141:
2105:
2104:
2097:
2051:
2050:
2046:
2000:
1999:
1995:
1962:(2): e1000031.
1949:
1948:
1941:
1937:
1896:DLX gene family
1891:Cranial kinesis
1887:
1851:chondrichthyans
1805:suction feeding
1764:
1760:
1751:suction feeding
1690:
1689:
1688:
1687:
1686:
1685:
1681:
1672:
1671:
1670:
1669:
1660:
1651:
1650:
1649:
1636:
1620:in the case of
1567:
1561:
1560:
1559:
1558:
1557:
1546:
1537:
1536:
1530:
1473:
1472:
1471:
1470:
1469:
1466:
1457:
1456:
1455:
1448:
1439:
1438:
1432:
1401:
1400:
1399:
1398:
1397:
1390:
1381:
1380:
1379:
1370:
1318:
1310:caudal peduncle
1271:
1266:
1261:
1258:
1251:
1242:
1236:
1227:
1220:
1211:
1204:
1195:
1186:
1060:
1042:
982:plates called "
953:
902:
868:Pharyngeal jaws
854:
852:Pharyngeal jaws
842:slingjaw wrasse
749:
748:
747:
746:
745:
732:
731:
724:
710:humphead wrasse
696:adductor muscle
650:have a movable
645:
638:
632:
623:
613:
604:
594:
480:
371:
366:
244:
216:suction feeding
158:supporting the
102:pharyngeal jaws
92:made mainly of
82:
81:
80:
79:
78:
67:Malawi eyebiter
63:
54:
53:
52:
49:pharyngeal jaws
38:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
6683:
6681:
6673:
6672:
6662:
6661:
6655:
6654:
6652:
6651:
6639:
6626:
6623:
6622:
6620:
6619:
6609:
6604:
6603:
6602:
6597:
6589:
6584:
6579:
6574:
6569:
6564:
6559:
6553:
6551:
6547:
6546:
6544:
6543:
6542:
6541:
6536:
6526:
6525:
6524:
6519:
6514:
6504:
6503:
6502:
6497:
6486:
6484:
6480:
6479:
6476:
6475:
6473:
6472:
6471:
6470:
6465:
6460:
6450:
6449:
6448:
6443:
6438:
6433:
6423:
6422:
6421:
6416:
6411:
6406:
6395:
6393:
6391:Wild fisheries
6387:
6386:
6384:
6383:
6378:
6373:
6368:
6363:
6357:
6355:
6346:
6340:
6339:
6337:
6336:
6331:
6326:
6321:
6316:
6314:Hallucinogenic
6311:
6306:
6301:
6296:
6291:
6285:
6283:
6279:
6278:
6276:
6275:
6270:
6265:
6260:
6255:
6250:
6245:
6240:
6235:
6230:
6225:
6219:
6217:
6210:
6209:
6207:
6206:
6201:
6196:
6191:
6189:Schooling fish
6186:
6181:
6176:
6171:
6166:
6161:
6156:
6151:
6149:Filter feeders
6146:
6141:
6136:
6131:
6126:
6124:Bottom feeders
6121:
6116:
6111:
6105:
6103:
6097:
6096:
6094:
6093:
6088:
6083:
6078:
6073:
6068:
6063:
6057:
6055:
6049:
6048:
6046:
6045:
6044:
6043:
6033:
6028:
6023:
6018:
6013:
6008:
6003:
5998:
5993:
5988:
5983:
5978:
5973:
5967:
5965:
5959:
5958:
5956:
5955:
5950:
5945:
5940:
5935:
5930:
5925:
5920:
5915:
5910:
5905:
5900:
5894:
5892:
5884:
5883:
5881:
5880:
5875:
5870:
5869:
5868:
5863:
5853:
5852:
5851:
5846:
5836:
5831:
5826:
5825:
5824:
5814:
5809:
5804:
5799:
5794:
5793:
5792:
5782:
5777:
5772:
5770:Leydig's organ
5767:
5766:
5765:
5763:pharyngeal jaw
5760:
5750:
5745:
5744:
5743:
5738:
5733:
5728:
5723:
5718:
5716:branchial arch
5708:
5707:
5706:
5696:
5691:
5686:
5685:
5684:
5679:
5669:
5664:
5658:
5656:
5644:
5643:
5636:
5634:
5632:
5631:
5626:
5621:
5616:
5611:
5606:
5605:
5604:
5599:
5594:
5584:
5579:
5574:
5569:
5563:
5561:
5554:
5553:
5548:
5546:
5545:
5538:
5531:
5523:
5517:
5516:
5468:
5453:
5435:
5424:
5423:
5412:
5411:
5400:
5399:
5392:
5391:External links
5389:
5387:
5386:
5366:(5): 378–389.
5351:
5345:
5328:
5312:
5295:
5252:
5246:
5233:
5178:
5162:
5136:(5): 604–619.
5125:
5088:
5082:
5065:
5059:
5038:
5001:
4973:(4): 243–257.
4961:
4960:
4948:
4947:
4916:
4915:
4909:
4890:
4847:
4827:(2): 428–448.
4808:
4763:
4757:
4738:
4736:
4733:
4731:
4730:
4700:
4681:
4674:
4648:
4645:. 9 July 2005.
4643:Devonian Times
4630:
4611:(2): 251–269.
4590:
4536:
4518:
4511:
4493:
4463:
4446:Devonian Times
4433:
4406:
4379:
4336:
4317:(6): 312–319.
4301:
4258:
4241:
4223:
4198:Acta Zoologica
4188:
4181:
4159:
4110:
4098:
4077:
4057:
4018:
3999:(4): 886–900.
3979:
3936:(2): 283–292.
3920:
3893:
3858:
3815:
3766:
3715:
3662:
3600:
3593:
3573:
3544:(5): 435–450.
3532:Salmo salar L.
3520:
3495:
3470:
3433:(5): 247–262.
3413:
3364:
3335:(3): 563–580.
3315:
3288:(4): 317–327.
3268:
3227:
3200:(3): 556–560.
3184:
3169:
3118:
3067:
3041:
2982:
2975:
2953:
2912:
2885:(1): 102–119.
2869:
2846:
2831:
2813:
2762:
2709:
2682:(2): 129–150.
2666:
2654:"Wrasse"
2651:, ed. (1911).
2649:Chisholm, Hugh
2640:
2619:(2): 256–262.
2596:
2583:(1): 295–314.
2560:
2514:
2507:
2481:
2460:(5): 378–389.
2440:
2399:
2384:
2366:
2352:
2335:
2331:Gray's Anatomy
2318:
2299:
2256:
2215:
2188:(3): 269–295.
2169:
2162:
2139:
2095:
2044:
1993:
1938:
1936:
1933:
1932:
1931:
1929:Palatoquadrate
1926:
1921:
1916:
1910:
1905:
1898:
1893:
1886:
1883:
1840:is a piece of
1809:jaw protrusion
1762:
1758:
1698:fish with jaws
1683:
1682:
1675:
1674:
1673:
1662:
1661:
1654:
1653:
1652:
1637:
1630:
1629:
1628:
1627:
1626:
1577:, the jawless
1547:
1540:
1539:
1538:
1534:
1533:
1532:
1531:
1529:
1526:
1468:Closeup of jaw
1467:
1460:
1459:
1458:
1449:
1442:
1441:
1440:
1436:
1435:
1434:
1433:
1431:
1428:
1424:Pseudotropheus
1391:
1384:
1383:
1382:
1371:
1364:
1363:
1362:
1361:
1360:
1317:
1314:
1270:
1267:
1265:
1262:
1260:
1259:
1252:
1245:
1243:
1237:
1230:
1228:
1221:
1214:
1212:
1205:
1198:
1196:
1187:
1180:
1178:
1174:
1041:
1038:
1034:jaw suspension
952:
949:
898:carrying some
893:
853:
850:
821:The nasal and
794:
793:
783:
773:
764:
725:
718:
717:
716:
715:
714:
644:
643:Jaw protrusion
641:
640:
639:
633:
626:
624:
614:
607:
605:
595:
588:
586:
479:
476:
454:bones remain.
440:coronoid bones
370:
367:
365:
362:
243:
240:
212:jaw protrusion
148:(polyphyodont)
96:. The primary
64:
57:
56:
55:
39:
32:
31:
30:
29:
28:
24:
18:Upper fish jaw
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
6682:
6671:
6668:
6667:
6665:
6650:
6649:
6640:
6638:
6637:
6628:
6627:
6624:
6618:
6617:more lists...
6610:
6608:
6605:
6601:
6598:
6596:
6593:
6592:
6590:
6588:
6585:
6583:
6580:
6578:
6575:
6573:
6572:Fish families
6570:
6568:
6565:
6563:
6560:
6558:
6557:Aquarium life
6555:
6554:
6552:
6548:
6540:
6539:fleshy-finned
6537:
6535:
6532:
6531:
6530:
6527:
6523:
6520:
6518:
6515:
6513:
6510:
6509:
6508:
6507:Cartilaginous
6505:
6501:
6498:
6496:
6493:
6492:
6491:
6488:
6487:
6485:
6481:
6469:
6466:
6464:
6461:
6459:
6456:
6455:
6454:
6451:
6447:
6444:
6442:
6439:
6437:
6434:
6432:
6429:
6428:
6427:
6424:
6420:
6417:
6415:
6412:
6410:
6407:
6405:
6402:
6401:
6400:
6397:
6396:
6394:
6392:
6388:
6382:
6379:
6377:
6374:
6372:
6369:
6367:
6364:
6362:
6359:
6358:
6356:
6354:
6350:
6347:
6345:
6341:
6335:
6332:
6330:
6327:
6325:
6322:
6320:
6317:
6315:
6312:
6310:
6307:
6305:
6302:
6300:
6297:
6295:
6292:
6290:
6287:
6286:
6284:
6280:
6274:
6271:
6269:
6266:
6264:
6261:
6259:
6256:
6254:
6251:
6249:
6246:
6244:
6241:
6239:
6236:
6234:
6231:
6229:
6226:
6224:
6221:
6220:
6218:
6216:
6211:
6205:
6202:
6200:
6197:
6195:
6192:
6190:
6187:
6185:
6182:
6180:
6177:
6175:
6172:
6170:
6167:
6165:
6162:
6160:
6157:
6155:
6152:
6150:
6147:
6145:
6144:Electric fish
6142:
6140:
6137:
6135:
6132:
6130:
6127:
6125:
6122:
6120:
6117:
6115:
6112:
6110:
6107:
6106:
6104:
6098:
6092:
6089:
6087:
6084:
6082:
6079:
6077:
6074:
6072:
6069:
6067:
6064:
6062:
6059:
6058:
6056:
6054:
6050:
6042:
6039:
6038:
6037:
6034:
6032:
6029:
6027:
6024:
6022:
6019:
6017:
6014:
6012:
6009:
6007:
6004:
6002:
5999:
5997:
5994:
5992:
5989:
5987:
5984:
5982:
5979:
5977:
5974:
5972:
5969:
5968:
5966:
5964:
5960:
5954:
5951:
5949:
5946:
5944:
5941:
5939:
5936:
5934:
5931:
5929:
5926:
5924:
5921:
5919:
5916:
5914:
5911:
5909:
5906:
5904:
5901:
5899:
5896:
5895:
5893:
5891:
5885:
5879:
5876:
5874:
5871:
5867:
5864:
5862:
5859:
5858:
5857:
5854:
5850:
5847:
5845:
5842:
5841:
5840:
5837:
5835:
5832:
5830:
5827:
5823:
5820:
5819:
5818:
5815:
5813:
5810:
5808:
5805:
5803:
5800:
5798:
5795:
5791:
5788:
5787:
5786:
5783:
5781:
5778:
5776:
5775:Mauthner cell
5773:
5771:
5768:
5764:
5761:
5759:
5756:
5755:
5754:
5751:
5749:
5746:
5742:
5739:
5737:
5734:
5732:
5729:
5727:
5724:
5722:
5719:
5717:
5714:
5713:
5712:
5709:
5705:
5702:
5701:
5700:
5697:
5695:
5694:Chromatophore
5692:
5690:
5687:
5683:
5680:
5678:
5675:
5674:
5673:
5670:
5668:
5665:
5663:
5660:
5659:
5657:
5655:
5649:
5645:
5640:
5630:
5627:
5625:
5622:
5620:
5617:
5615:
5612:
5610:
5607:
5603:
5600:
5598:
5595:
5593:
5590:
5589:
5588:
5585:
5583:
5580:
5578:
5575:
5573:
5570:
5568:
5565:
5564:
5562:
5560:
5555:
5551:
5544:
5539:
5537:
5532:
5530:
5525:
5524:
5521:
5513:
5509:
5505:
5501:
5497:
5493:
5489:
5485:
5481:
5477:
5476:
5469:
5465:
5464:
5459:
5454:
5450:
5449:
5444:
5440:
5436:
5432:
5428:
5427:
5422:
5413:
5410:
5401:
5396:
5390:
5383:
5379:
5374:
5369:
5365:
5361:
5357:
5352:
5348:
5342:
5338:
5334:
5329:
5327:
5323:
5320:
5315:
5309:
5305:
5301:
5296:
5292:
5288:
5283:
5278:
5274:
5270:
5266:
5262:
5258:
5253:
5249:
5243:
5239:
5234:
5230:
5226:
5222:
5218:
5213:
5208:
5204:
5200:
5196:
5192:
5188:
5184:
5179:
5175:
5168:
5163:
5159:
5155:
5151:
5147:
5143:
5139:
5135:
5131:
5126:
5122:
5118:
5114:
5110:
5106:
5102:
5098:
5094:
5089:
5085:
5079:
5075:
5071:
5066:
5062:
5056:
5052:
5048:
5044:
5039:
5035:
5031:
5027:
5023:
5019:
5015:
5011:
5007:
5002:
4998:
4994:
4990:
4986:
4981:
4976:
4972:
4968:
4963:
4962:
4957:
4956:
4950:
4949:
4945:
4931:
4927:
4923:
4918:
4917:
4912:
4906:
4902:
4901:
4896:
4891:
4887:
4883:
4879:
4875:
4870:
4865:
4861:
4857:
4853:
4848:
4844:
4840:
4835:
4830:
4826:
4822:
4818:
4816:
4809:
4805:
4801:
4797:
4793:
4789:
4785:
4781:
4777:
4773:
4769:
4764:
4760:
4754:
4750:
4749:
4744:
4740:
4739:
4734:
4719:
4718:
4713:
4707:
4705:
4701:
4696:
4692:
4685:
4682:
4677:
4671:
4667:
4662:
4661:
4652:
4649:
4644:
4640:
4634:
4631:
4626:
4622:
4618:
4614:
4610:
4606:
4599:
4597:
4595:
4591:
4586:
4582:
4577:
4572:
4568:
4564:
4560:
4556:
4552:
4545:
4543:
4541:
4537:
4532:
4528:
4522:
4519:
4514:
4508:
4504:
4497:
4494:
4481:
4477:
4473:
4467:
4464:
4451:
4447:
4443:
4437:
4434:
4422:
4421:
4416:
4410:
4407:
4395:
4394:
4389:
4383:
4380:
4375:
4371:
4367:
4363:
4359:
4355:
4351:
4347:
4340:
4337:
4332:
4328:
4324:
4320:
4316:
4312:
4305:
4302:
4297:
4293:
4289:
4285:
4281:
4277:
4273:
4269:
4262:
4259:
4254:
4253:
4245:
4242:
4237:
4233:
4227:
4224:
4219:
4215:
4211:
4207:
4204:(s1): 52–68.
4203:
4199:
4192:
4189:
4184:
4178:
4174:
4170:
4163:
4160:
4155:
4151:
4146:
4141:
4137:
4133:
4129:
4125:
4121:
4114:
4111:
4107:
4102:
4099:
4094:
4088:
4080:
4074:
4070:
4069:
4061:
4058:
4053:
4049:
4045:
4041:
4037:
4033:
4029:
4022:
4019:
4014:
4010:
4006:
4002:
3998:
3994:
3990:
3983:
3980:
3975:
3971:
3967:
3963:
3959:
3955:
3951:
3947:
3943:
3939:
3935:
3931:
3924:
3921:
3916:
3912:
3908:
3904:
3897:
3894:
3889:
3885:
3881:
3877:
3873:
3869:
3868:Hydrobiologia
3862:
3859:
3854:
3850:
3846:
3842:
3838:
3834:
3830:
3826:
3819:
3816:
3811:
3807:
3803:
3799:
3794:
3789:
3785:
3781:
3777:
3770:
3767:
3762:
3758:
3753:
3748:
3743:
3738:
3734:
3730:
3726:
3719:
3716:
3711:
3707:
3703:
3699:
3695:
3691:
3687:
3683:
3679:
3675:
3674:
3666:
3663:
3658:
3654:
3649:
3644:
3639:
3634:
3630:
3626:
3623:(9): e44670.
3622:
3618:
3614:
3607:
3605:
3601:
3596:
3590:
3586:
3585:
3577:
3574:
3569:
3565:
3560:
3555:
3551:
3547:
3543:
3539:
3535:
3533:
3524:
3521:
3509:
3505:
3499:
3496:
3484:
3480:
3474:
3471:
3466:
3462:
3458:
3454:
3450:
3446:
3441:
3436:
3432:
3428:
3424:
3417:
3414:
3409:
3405:
3400:
3395:
3391:
3387:
3383:
3379:
3375:
3368:
3365:
3360:
3356:
3351:
3346:
3342:
3338:
3334:
3330:
3326:
3319:
3316:
3311:
3307:
3303:
3299:
3295:
3291:
3287:
3283:
3279:
3272:
3269:
3264:
3260:
3255:
3250:
3246:
3242:
3238:
3231:
3228:
3223:
3219:
3215:
3211:
3207:
3203:
3199:
3195:
3188:
3185:
3182:
3180:
3177:Dave Abbott,
3173:
3170:
3165:
3161:
3156:
3151:
3146:
3141:
3137:
3133:
3129:
3122:
3119:
3114:
3110:
3105:
3100:
3095:
3090:
3086:
3082:
3078:
3071:
3068:
3056:
3052:
3045:
3042:
3037:
3033:
3028:
3023:
3019:
3015:
3010:
3005:
3001:
2997:
2993:
2986:
2983:
2978:
2972:
2968:
2964:
2957:
2954:
2949:
2945:
2940:
2935:
2931:
2927:
2923:
2916:
2913:
2908:
2904:
2900:
2896:
2892:
2888:
2884:
2880:
2873:
2870:
2857:
2850:
2847:
2842:
2838:
2834:
2828:
2824:
2817:
2814:
2809:
2805:
2800:
2795:
2790:
2785:
2781:
2777:
2773:
2766:
2763:
2758:
2754:
2750:
2746:
2742:
2738:
2734:
2730:
2726:
2722:
2721:
2713:
2710:
2705:
2701:
2697:
2693:
2689:
2685:
2681:
2677:
2670:
2667:
2662:
2661:
2655:
2650:
2644:
2641:
2636:
2632:
2627:
2622:
2618:
2614:
2610:
2603:
2601:
2597:
2591:
2586:
2582:
2578:
2574:
2567:
2565:
2561:
2556:
2552:
2548:
2544:
2540:
2536:
2529:
2527:
2525:
2523:
2521:
2519:
2515:
2510:
2504:
2500:
2496:
2492:
2485:
2482:
2477:
2473:
2468:
2463:
2459:
2455:
2451:
2444:
2441:
2436:
2432:
2427:
2422:
2418:
2414:
2410:
2403:
2400:
2396:
2391:
2389:
2385:
2380:
2376:
2370:
2367:
2363:
2362:
2356:
2353:
2349:
2344:
2342:
2340:
2336:
2332:
2328:
2322:
2319:
2315:
2310:
2308:
2306:
2304:
2300:
2295:
2291:
2287:
2283:
2279:
2275:
2271:
2267:
2260:
2257:
2252:
2248:
2243:
2238:
2234:
2230:
2226:
2219:
2216:
2211:
2207:
2203:
2199:
2195:
2191:
2187:
2183:
2176:
2174:
2170:
2165:
2159:
2155:
2154:
2146:
2144:
2140:
2134:
2129:
2125:
2121:
2117:
2113:
2109:
2102:
2100:
2096:
2091:
2087:
2082:
2077:
2072:
2067:
2063:
2059:
2055:
2048:
2045:
2040:
2036:
2031:
2026:
2021:
2016:
2012:
2008:
2004:
1997:
1994:
1989:
1985:
1980:
1975:
1970:
1965:
1961:
1957:
1953:
1946:
1944:
1940:
1934:
1930:
1927:
1925:
1922:
1920:
1917:
1914:
1913:Gnathostomata
1911:
1909:
1906:
1904:
1903:
1899:
1897:
1894:
1892:
1889:
1888:
1884:
1882:
1880:
1876:
1872:
1868:
1864:
1860:
1859:osteichthyans
1856:
1852:
1847:
1843:
1839:
1835:
1833:
1829:
1825:
1821:
1817:
1812:
1810:
1806:
1802:
1798:
1794:
1789:
1787:
1786:Early Permian
1782:
1778:
1776:
1772:
1768:
1756:
1752:
1748:
1744:
1740:
1736:
1732:
1728:
1727:
1722:
1718:
1714:
1709:
1707:
1703:
1699:
1695:
1684:↑ Spiny shark
1679:
1668:
1667:
1658:
1647:
1646:
1641:
1634:
1625:
1623:
1619:
1615:
1611:
1607:
1603:
1602:cartilaginous
1599:
1595:
1591:
1586:
1584:
1580:
1576:
1572:
1566:
1555:
1551:
1544:
1527:
1525:
1523:
1519:
1515:
1511:
1509:
1504:
1502:
1498:
1494:
1489:
1482:
1477:
1464:
1453:
1446:
1429:
1427:
1425:
1421:
1420:
1414:
1411:
1407:
1395:
1394:giant cichlid
1388:
1377:
1376:
1368:
1359:
1355:
1353:
1348:
1347:morphological
1344:
1343:
1339:
1336:scale-eating
1335:
1331:
1322:
1315:
1313:
1311:
1307:
1303:
1302:spawning runs
1299:
1295:
1287:
1283:
1275:
1268:
1263:
1256:
1255:prickly shark
1249:
1244:
1240:
1234:
1229:
1225:
1218:
1213:
1209:
1208:thornback ray
1202:
1197:
1193:
1192:
1184:
1179:
1176:
1173:
1171:
1167:
1166:basking shark
1163:
1159:
1155:
1151:
1146:
1144:
1140:
1136:
1132:
1128:
1124:
1120:
1119:conveyor belt
1116:
1112:
1108:
1103:
1101:
1097:
1093:
1089:
1085:
1081:
1077:
1073:
1069:
1065:
1059:
1055:
1046:
1039:
1037:
1035:
1031:
1027:
1023:
1022:elasmobranchs
1018:
1016:
1012:
1008:
1004:
1000:
995:
993:
989:
986:", which are
985:
981:
977:
973:
972:cartilaginous
969:
965:
961:
957:
950:
948:
946:
942:
938:
937:hemichordates
934:
930:
929:deuterostomes
926:
921:
916:
913:
909:
901:
897:
891:
887:
885:
881:
877:
873:
869:
862:
858:
851:
849:
847:
843:
838:
836:
832:
828:
824:
819:
817:
812:
808:
803:
801:
800:
791:
790:
784:
781:
780:
774:
771:
770:
765:
762:
761:
757:
751:
750:
744:
740:
736:
729:
722:
711:
706:
702:
699:
697:
693:
689:
685:
680:
678:
674:
669:
665:
661:
657:
653:
649:
642:
636:
630:
625:
622:
618:
611:
606:
602:
598:
592:
587:
584:
582:
580:
576:
572:
568:
564:
560:
556:
555:goblin sharks
552:
548:
544:
540:
536:
532:
527:
525:
521:
520:cartilagenous
517:
513:
509:
505:
501:
497:
493:
489:
485:
477:
475:
473:
469:
465:
464:cartilaginous
461:
457:
453:
449:
444:
441:
437:
433:
429:
425:
421:
417:
413:
409:
405:
401:
397:
393:
386:
382:
381:
375:
368:
363:
361:
359:
355:
351:
347:
343:
338:
336:
332:
328:
323:
321:
317:
313:
309:
305:
301:
297:
293:
289:
285:
283:
278:
276:
272:
268:
264:
260:
256:
248:
241:
239:
237:
233:
229:
225:
224:buccal cavity
221:
217:
213:
209:
205:
202:, which have
201:
197:
193:
188:
186:
181:
177:
173:
169:
165:
161:
157:
152:
149:
145:
141:
137:
133:
129:
125:
121:
117:
113:
109:
107:
103:
99:
95:
91:
87:
76:
72:
68:
61:
50:
46:
42:
36:
27:
19:
6670:Fish anatomy
6646:
6634:
6534:spiny-finned
6483:Major groups
6204:Intelligence
6184:Scale eaters
6129:Cleaner fish
6011:Mouthbrooder
5963:Reproduction
5938:Schreckstoff
5923:Lateral line
5839:Swim bladder
5829:Spiral valve
5758:hyomandibula
5752:
5741:pseudobranch
5624:Hypoxia in -
5479:
5473:
5461:
5446:
5363:
5359:
5336:
5303:
5267:(1): 79–99.
5264:
5260:
5237:
5186:
5182:
5173:
5133:
5129:
5096:
5092:
5073:
5042:
5009:
5005:
4970:
4966:
4954:
4943:
4934:. Retrieved
4925:
4899:
4859:
4855:
4824:
4820:
4814:
4771:
4767:
4747:
4721:. Retrieved
4715:
4695:Live Science
4694:
4684:
4659:
4651:
4642:
4633:
4608:
4605:Paleobiology
4604:
4561:(1): 76–79.
4558:
4554:
4530:
4521:
4502:
4496:
4484:. Retrieved
4480:the original
4476:Science News
4475:
4466:
4454:. Retrieved
4450:the original
4445:
4436:
4424:. Retrieved
4418:
4415:"Acanthodii"
4409:
4397:. Retrieved
4391:
4382:
4349:
4345:
4339:
4314:
4310:
4304:
4271:
4267:
4261:
4251:
4244:
4232:neural crest
4226:
4201:
4197:
4191:
4172:
4162:
4127:
4123:
4113:
4101:
4067:
4060:
4035:
4031:
4021:
3996:
3992:
3988:
3982:
3933:
3929:
3923:
3909:(1): 66–72.
3906:
3902:
3896:
3871:
3867:
3861:
3828:
3824:
3818:
3783:
3779:
3769:
3732:
3728:
3718:
3677:
3671:
3665:
3620:
3616:
3583:
3576:
3541:
3537:
3531:
3523:
3511:. Retrieved
3507:
3498:
3486:. Retrieved
3482:
3473:
3430:
3426:
3416:
3381:
3377:
3367:
3332:
3328:
3318:
3285:
3281:
3271:
3244:
3240:
3230:
3197:
3193:
3187:
3181:, found here
3178:
3172:
3135:
3131:
3121:
3084:
3081:PLOS Biology
3080:
3070:
3058:. Retrieved
3054:
3044:
2999:
2995:
2985:
2966:
2956:
2932:(1): 55–69.
2929:
2925:
2915:
2882:
2878:
2872:
2860:. Retrieved
2849:
2822:
2816:
2779:
2775:
2765:
2724:
2718:
2712:
2679:
2675:
2669:
2658:
2643:
2616:
2612:
2580:
2576:
2538:
2534:
2494:
2484:
2457:
2453:
2443:
2416:
2412:
2402:
2378:
2369:
2359:
2355:
2326:
2321:
2269:
2265:
2259:
2232:
2228:
2218:
2185:
2181:
2152:
2115:
2111:
2061:
2057:
2047:
2010:
2006:
1996:
1959:
1956:PLOS Biology
1955:
1924:Hyomandibula
1900:
1836:
1828:Gnathostomes
1820:hyomandibula
1813:
1790:
1781:Spiny sharks
1779:
1774:
1746:
1724:
1710:
1706:spiny sharks
1694:ostracoderms
1691:
1664:
1643:
1610:hyomandibula
1606:jawed fishes
1587:
1568:
1554:spiny sharks
1512:
1505:
1486:
1417:
1415:
1402:
1373:
1356:
1340:
1327:
1291:
1189:
1170:whale sharks
1147:
1104:
1102:initiation.
1086:, and adult
1061:
1033:
1019:
996:
954:
945:neural crest
941:endoskeletal
917:
905:
866:
845:
839:
827:neurocranium
820:
815:
807:biomechanics
804:
799:Petrotilapia
797:
795:
787:
777:
767:
754:
742:
700:
684:neurocranium
681:
646:
581:(sideways).
528:
481:
445:
439:
432:prearticular
431:
424:angular bone
416:dentary bone
415:
398:forming the
389:
378:
339:
324:
286:
282:jawless fish
279:
252:
189:
172:spiny sharks
164:jawless fish
153:
147:
110:
101:
97:
83:
69:showing the
26:
6648:WikiProject
6607:Prehistoric
6591:Threatened
6282:Other types
6179:Sardine run
6154:Forage fish
6134:Corallivory
5986:Development
5971:Bubble nest
5844:physoclisti
5834:Suckermouth
5807:Root effect
5629:Ichthyology
4426:10 December
4399:10 December
4106:Benton 2005
3989:Malacosteus
3874:(1): 7–27.
3831:(1): 1–36.
3729:BMC Biology
3132:BMC Biology
2541:(1): 1–18.
1846:vertebrates
1793:buccal pump
1755:bite forces
1594:gill arches
1575:cyclostomes
1508:pelican eel
1481:pelican eel
1239:Tiger shark
1154:crustaceans
1111:Shark teeth
1105:While both
1054:Shark tooth
1030:articulated
1003:tiger shark
915:swallowed.
811:protractile
599:, like all
504:premaxillae
428:suprangular
410:, the bone
333:, with the
263:dermal bone
196:bony fishes
180:buccal pump
174:during the
132:articulated
86:bony fishes
6263:Groundfish
6258:Freshwater
6253:Euryhaline
6238:Coral reef
6174:Salmon run
6164:Paedophagy
6066:Amphibious
6053:Locomotion
5861:pharyngeal
5849:physostome
5802:Photophore
5748:Glossohyal
5721:gill raker
5704:dorsal fin
5654:physiology
5448:Pharyngula
4895:Gee, Henry
4723:4 December
4486:2 December
4456:9 December
4236:mesodermal
3247:: 175–87.
3087:(2): e31.
3002:(1): 177.
2064:(1): 255.
1935:References
1908:Glossohyal
1824:hyoid arch
1822:) and the
1797:amphibians
1735:short tons
1702:placoderms
1590:homologous
1563:See also:
1550:placoderms
1522:herbivores
1518:carnivores
1080:Sea horses
1052:See also:
1005:, and the
999:bull shark
878:, of most
861:Moray eels
823:mandibular
816:Lippfische
708:Lips of a
666:. In more
652:premaxilla
617:paddlefish
551:Paddlefish
524:homologous
458:, such as
412:homologous
350:pterygoids
346:skull roof
342:lungfishes
331:premaxilla
296:fontanelle
290:, such as
267:skull roof
232:premaxilla
228:protrusion
198:, such as
168:placoderms
114:, such as
75:pharyngeal
6512:chimaeras
6399:Predatory
6376:Salmonids
6334:Whitefish
6324:Poisonous
6299:Diversity
6233:Coldwater
6169:Predatory
6159:Migratory
6119:Bait ball
6102:behaviour
6021:Pregnancy
6016:Polyandry
5790:papillare
5785:Operculum
5780:Meristics
5726:gill slit
5689:Cleithrum
5619:Fish kill
5609:Fear of -
5602:- as food
5592:Fisheries
5577:Evolution
5567:Diversity
5439:Myers, PZ
5319:Full view
4975:CiteSeerX
4967:Zebrafish
4087:cite book
3930:Oecologia
3513:25 August
3488:25 August
3465:201732743
3449:1520-541X
3302:0944-2006
3060:25 August
3018:1471-2148
2862:21 August
2782:(1): 24.
2375:"maxilla"
2013:(1): 10.
1875:articular
1867:tetrapods
1842:cartilage
1640:placoderm
1618:operculum
1579:hagfishes
1528:Evolution
1501:esophagus
1334:parasitic
1135:bony fish
1076:zebrafish
1064:bony fish
980:hexagonal
976:vertebrae
933:amphioxus
927:to basal
925:chordates
908:moray eel
884:gill arch
880:bony fish
660:grab prey
579:laterally
575:ventrally
567:Sawsharks
543:swordfish
508:bony fish
472:sturgeons
436:articular
408:tetrapods
364:Oral jaws
358:cartilage
308:inner ear
304:olfactory
190:Jaws use
140:lower jaw
136:upper jaw
124:cartilage
98:oral jaws
71:branchial
6664:Category
6636:Category
6587:Smallest
6500:lampreys
6463:flatfish
6453:Demersal
6409:mackerel
6404:billfish
6344:Commerce
6273:Tropical
6248:Demersal
6243:Deep-sea
6199:Venomous
6091:RoboTuna
6041:triggers
6036:Spawning
5996:Juvenile
5981:Egg case
5614:FishBase
5504:24067611
5460:. News.
5382:21676723
5322:Archived
5291:22804777
5221:23254938
5158:17013964
5150:18196573
5113:19267635
5034:20212436
5026:12376690
4997:18248183
4886:10274300
4878:12193642
4843:23473983
4796:17671501
4745:(2009).
4625:86203770
4585:17443970
4374:43389789
4331:16701387
4296:33913758
4218:56425436
4154:11523812
3974:13285836
3966:28308568
3888:15963069
3853:46927413
3845:29865430
3810:18363916
3802:23159601
3761:20102595
3735:(1): 8.
3710:33113282
3702:17807183
3657:22970282
3617:PLOS ONE
3568:14635799
3457:31449734
3408:16450392
3359:32533826
3310:16351980
3222:34954175
3164:18625062
3113:19215146
3036:21693066
2948:21672820
2907:45227734
2899:15880740
2841:39217534
2808:23020903
2749:17805293
2704:46933765
2696:29865677
2635:21676769
2476:21676723
2435:22401891
2251:29237766
2210:46933606
2202:29865760
2090:19849854
2039:17263894
1988:19215146
1919:Hox gene
1885:See also
1871:ossifies
1743:thoracic
1721:Devonian
1717:Silurian
1622:teleosts
1583:lampreys
1552:and the
1316:Cichlids
1264:Examples
1162:serrated
1150:mollusks
1139:piranhas
1096:Hox gene
1088:sturgeon
1084:pipefish
984:tesserae
756:Cyprinus
677:teleosts
648:Teleosts
601:billfish
597:Sailfish
547:sailfish
535:Billfish
531:rostrums
512:nostrils
500:incisors
448:teleosts
420:splenial
392:mandible
385:piranhas
320:foramina
316:vertebra
271:lungfish
259:Lampreys
176:Silurian
6582:Largest
6495:hagfish
6490:Jawless
6468:pollock
6441:sardine
6436:herring
6431:anchovy
6381:Tilapia
6371:Octopus
6366:Catfish
6353:Farming
6268:Pelagic
6228:Coastal
6215:habitat
6071:Walking
5976:Clasper
5928:Otolith
5890:systems
5888:Sensory
5822:ganoine
5797:Papilla
5648:Anatomy
5587:Fishing
5512:4462506
5484:Bibcode
5282:3552417
5229:4403344
5191:Bibcode
5121:3104126
5006:Science
4936:9 April
4897:(ed.).
4856:Science
4804:4337868
4776:Bibcode
4717:palaeos
4576:2373817
4420:Palaeos
4393:Palaeos
4354:Bibcode
4276:Bibcode
4145:1594948
4040:Bibcode
4013:1038874
3958:4222466
3938:Bibcode
3752:2828976
3682:Bibcode
3673:Science
3648:3435272
3625:Bibcode
3559:1571185
3399:2734338
3350:7821850
3282:Zoology
3263:2606790
3254:1256608
3214:5269110
3155:2496899
3104:2637924
3027:3141434
2799:3564725
2776:EvoDevo
2757:4384411
2729:Bibcode
2555:1445030
2294:8927640
2274:Bibcode
2120:Bibcode
2081:2779191
2030:1797158
1979:2637924
1879:mammals
1863:embryos
1832:Agnatha
1801:teleost
1767:cuticle
1592:to the
1410:trophic
1338:cichlid
1298:remodel
1158:mammals
1026:cranium
1015:rostrum
988:crystal
970:) have
947:cells.
876:pharynx
831:maxilla
743:YouTube
688:maxilla
668:derived
635:Sawfish
571:sawfish
488:palatal
484:maxilla
452:angular
335:maxilla
312:condyle
300:rostrum
230:of the
204:evolved
200:wrasses
106:pharynx
45:cichlid
6600:sharks
6517:sharks
6446:sprats
6426:Forage
6414:salmon
6294:Coarse
6076:Flying
5948:Vision
5903:Barbel
5817:Scales
5677:dermal
5557:About
5510:
5502:
5475:Nature
5463:Nature
5380:
5343:
5310:
5289:
5279:
5244:
5227:
5219:
5183:Nature
5156:
5148:
5119:
5111:
5080:
5057:
5032:
5024:
4995:
4977:
4907:
4884:
4876:
4841:
4802:
4794:
4768:Nature
4755:
4672:
4623:
4583:
4573:
4509:
4372:
4346:Nature
4329:
4294:
4268:Nature
4216:
4179:
4152:
4142:
4075:
4011:
3993:Copeia
3972:
3964:
3956:
3886:
3851:
3843:
3808:
3800:
3759:
3749:
3708:
3700:
3655:
3645:
3591:
3566:
3556:
3463:
3455:
3447:
3406:
3396:
3357:
3347:
3308:
3300:
3261:
3251:
3220:
3212:
3179:Sharks
3162:
3152:
3138:: 32.
3111:
3101:
3034:
3024:
3016:
2973:
2946:
2905:
2897:
2839:
2829:
2806:
2796:
2755:
2747:
2720:Nature
2702:
2694:
2633:
2553:
2535:Copeia
2505:
2474:
2433:
2292:
2249:
2208:
2200:
2160:
2088:
2078:
2037:
2027:
1986:
1976:
1855:sharks
1771:dermal
1296:often
1294:salmon
1269:Salmon
1194:, 1909
1125:, and
1107:sharks
992:mosaic
968:skates
960:sharks
760:Labrus
539:marlin
460:sharks
426:and a
354:vomers
344:. The
292:sharks
277:fish.
275:holost
214:. For
138:and a
116:sharks
51:(blue)
6562:Blind
6550:Lists
6329:Rough
6194:Sleep
6100:Other
5866:shark
5856:Teeth
5508:S2CID
5225:S2CID
5170:(PDF)
5154:S2CID
5117:S2CID
5030:S2CID
4882:S2CID
4800:S2CID
4621:S2CID
4370:S2CID
4292:S2CID
4239:2000)
4214:S2CID
4009:S2CID
3970:S2CID
3954:JSTOR
3884:S2CID
3849:S2CID
3806:S2CID
3706:S2CID
3461:S2CID
3218:S2CID
2903:S2CID
2753:S2CID
2700:S2CID
2551:JSTOR
2206:S2CID
1733:(4.0
1713:class
1642:fish
1614:hyoid
1598:gills
1493:teeth
1430:Other
1306:kypes
1292:Male
1143:pacus
1127:teeth
1100:tooth
1068:teeth
1040:Teeth
769:Mugil
506:. In
478:Upper
400:skull
369:Lower
255:skull
242:Skull
160:gills
144:teeth
84:Most
41:Skull
6595:rays
6529:Bony
6522:rays
6419:tuna
6361:Carp
6319:Oily
6304:Game
6289:Bait
6223:Cave
6006:Milt
5711:Gill
5699:Fins
5672:Bone
5559:fish
5550:Fish
5500:PMID
5378:PMID
5341:ISBN
5308:ISBN
5287:PMID
5242:ISBN
5217:PMID
5146:PMID
5109:PMID
5078:ISBN
5055:ISBN
5022:PMID
4993:PMID
4938:2018
4930:NCBI
4905:ISBN
4874:PMID
4839:PMID
4792:PMID
4753:ISBN
4725:2014
4670:ISBN
4581:PMID
4507:ISBN
4488:2014
4458:2014
4428:2014
4401:2014
4327:PMID
4177:ISBN
4150:PMID
4093:link
4073:ISBN
3997:2007
3962:PMID
3841:PMID
3798:PMID
3757:PMID
3698:PMID
3653:PMID
3589:ISBN
3564:PMID
3515:2022
3490:2022
3453:PMID
3445:ISSN
3404:PMID
3355:PMID
3306:PMID
3298:ISSN
3259:PMID
3210:PMID
3160:PMID
3109:PMID
3062:2022
3032:PMID
3014:ISSN
2971:ISBN
2944:PMID
2895:PMID
2864:2009
2837:OCLC
2827:ISBN
2804:PMID
2745:PMID
2692:PMID
2631:PMID
2539:1984
2503:ISBN
2472:PMID
2431:PMID
2290:PMID
2247:PMID
2198:PMID
2158:ISBN
2086:PMID
2035:PMID
1984:PMID
1807:and
1704:and
1581:and
1479:The
1286:Kype
1253:The
1222:The
1206:The
1168:and
1152:and
1141:and
1129:are
1115:gums
1092:fish
1074:and
1072:carp
1056:and
966:and
964:rays
935:and
872:jaws
726:The
662:and
615:The
557:and
545:and
396:bone
352:and
273:and
253:The
170:and
130:are
128:jaws
120:rays
118:and
94:bone
90:jaws
6458:cod
6213:By
6026:Roe
5753:Jaw
5651:and
5492:doi
5480:502
5368:doi
5277:PMC
5269:doi
5265:222
5207:hdl
5199:doi
5187:493
5138:doi
5134:269
5101:doi
5047:doi
5014:doi
5010:298
4985:doi
4864:doi
4860:298
4829:doi
4825:377
4784:doi
4772:448
4666:145
4613:doi
4571:PMC
4563:doi
4362:doi
4350:361
4319:doi
4284:doi
4272:369
4206:doi
4140:PMC
4132:doi
4128:199
4048:doi
4001:doi
3946:doi
3934:121
3911:doi
3876:doi
3872:748
3833:doi
3829:217
3788:doi
3747:PMC
3737:doi
3690:doi
3678:260
3643:PMC
3633:doi
3554:PMC
3546:doi
3542:203
3435:doi
3394:PMC
3386:doi
3382:235
3345:PMC
3337:doi
3290:doi
3286:108
3249:PMC
3245:164
3202:doi
3150:PMC
3140:doi
3099:PMC
3089:doi
3022:PMC
3004:doi
2934:doi
2887:doi
2883:265
2794:PMC
2784:doi
2737:doi
2725:449
2684:doi
2680:202
2621:doi
2585:doi
2543:doi
2462:doi
2421:doi
2361:OED
2282:doi
2270:351
2237:doi
2233:220
2190:doi
2186:205
2128:doi
2076:PMC
2066:doi
2025:PMC
2015:doi
1974:PMC
1964:doi
1769:or
1350:by
896:asp
818:).
802:).
492:jaw
325:In
269:in
162:of
6666::
5506:.
5498:.
5490:.
5478:.
5445:.
5376:.
5364:44
5362:.
5358:.
5285:.
5275:.
5263:.
5259:.
5223:.
5215:.
5205:.
5197:.
5185:.
5152:.
5144:.
5132:.
5115:.
5107:.
5097:25
5095:.
5072:.
5053:.
5028:.
5020:.
5008:.
4991:.
4983:.
4969:.
4924:.
4880:.
4872:.
4858:.
4854:.
4837:.
4823:.
4819:.
4798:.
4790:.
4782:.
4770:.
4714:.
4703:^
4693:.
4668:.
4641:.
4619:.
4609:35
4607:.
4593:^
4579:.
4569:.
4557:.
4553:.
4539:^
4529:.
4474:.
4444:.
4417:.
4390:.
4368:.
4360:.
4348:.
4325:.
4315:20
4313:.
4290:.
4282:.
4270:.
4212:.
4202:90
4200:.
4148:.
4138:.
4126:.
4122:.
4089:}}
4085:{{
4046:.
4036:52
4034:.
4030:.
4007:.
3995:.
3968:.
3960:.
3952:.
3944:.
3932:.
3907:22
3905:.
3882:.
3870:.
3847:.
3839:.
3827:.
3804:.
3796:.
3784:22
3782:.
3778:.
3755:.
3745:.
3731:.
3727:.
3704:.
3696:.
3688:.
3676:.
3651:.
3641:.
3631:.
3619:.
3615:.
3603:^
3562:.
3552:.
3540:.
3536:.
3506:.
3481:.
3459:.
3451:.
3443:.
3431:21
3429:.
3425:.
3402:.
3392:.
3380:.
3376:.
3353:.
3343:.
3333:60
3331:.
3327:.
3304:.
3296:.
3284:.
3280:.
3257:.
3243:.
3239:.
3216:.
3208:.
3198:49
3196:.
3158:.
3148:.
3134:.
3130:.
3107:.
3097:.
3083:.
3079:.
3053:.
3030:.
3020:.
3012:.
3000:11
2998:.
2994:.
2942:.
2930:47
2928:.
2924:.
2901:.
2893:.
2881:.
2835:.
2802:.
2792:.
2778:.
2774:.
2751:.
2743:.
2735:.
2723:.
2698:.
2690:.
2678:.
2657:.
2629:.
2617:45
2615:.
2611:.
2599:^
2581:20
2579:.
2575:.
2563:^
2549:.
2537:.
2517:^
2493:.
2470:.
2458:44
2456:.
2452:.
2429:.
2417:22
2415:.
2411:.
2387:^
2377:.
2338:^
2302:^
2288:.
2280:.
2268:.
2245:.
2231:.
2227:.
2204:.
2196:.
2184:.
2172:^
2142:^
2126:.
2116:57
2114:.
2110:.
2098:^
2084:.
2074:.
2060:.
2056:.
2033:.
2023:.
2009:.
2005:.
1982:.
1972:.
1958:.
1954:.
1942:^
1881:.
1708:.
1624:.
1503:.
1354:.
1094:,
1082:,
1001:,
962:,
844:,
792:).
772:).
758:,
741:–
553:,
541:,
533:.
514:.
474:.
5542:e
5535:t
5528:v
5514:.
5494::
5486::
5466:.
5451:.
5384:.
5370::
5349:.
5316:.
5293:.
5271::
5250:.
5231:.
5209::
5201::
5193::
5160:.
5140::
5123:.
5103::
5086:.
5063:.
5049::
5036:.
5016::
4999:.
4987::
4971:2
4958:.
4946:)
4940:.
4932:)
4913:.
4888:.
4866::
4845:.
4831::
4817:"
4806:.
4786::
4778::
4761:.
4727:.
4697:.
4678:.
4627:.
4615::
4587:.
4565::
4559:3
4515:.
4490:.
4460:.
4430:.
4403:.
4376:.
4364::
4356::
4333:.
4321::
4298:.
4286::
4278::
4255:.
4220:.
4208::
4185:.
4156:.
4134::
4108:.
4095:)
4081:.
4054:.
4050::
4042::
4015:.
4003::
3976:.
3948::
3940::
3917:.
3913::
3890:.
3878::
3855:.
3835::
3812:.
3790::
3763:.
3739::
3733:8
3712:.
3692::
3684::
3659:.
3635::
3627::
3621:7
3597:.
3570:.
3548::
3517:.
3492:.
3467:.
3437::
3410:.
3388::
3361:.
3339::
3312:.
3292::
3265:.
3224:.
3204::
3166:.
3142::
3136:6
3115:.
3091::
3085:7
3064:.
3038:.
3006::
2979:.
2950:.
2936::
2909:.
2889::
2866:.
2843:.
2810:.
2786::
2780:3
2759:.
2739::
2731::
2706:.
2686::
2637:.
2623::
2593:.
2587::
2557:.
2545::
2511:.
2478:.
2464::
2437:.
2423::
2381:.
2296:.
2284::
2276::
2253:.
2239::
2212:.
2192::
2166:.
2136:.
2130::
2122::
2092:.
2068::
2062:9
2041:.
2017::
2011:7
1990:.
1966::
1960:7
1763:f
1759:f
1731:t
1556:.
1396:)
1378:)
958:(
814:(
537:(
73:(
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.