40:
52:
411:
Wang, D; Uhrin, P; Mocan, A; Waltenberger, B; Breuss, J. M; Tewari, D; Mihaly-Bison, J; Huminiecki, Łukasz; Starzyński, R. R; Tzvetkov, N. T; Horbańczuk, J; Atanasov, A. G (2018). "Vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation as a therapeutic target. Part 1: Molecular targets and pathways".
225:
lead to powerful vasodilation, which causes a decrease in blood pressure by presynaptic activation of the receptors in the sympathetic ganglia. This presynaptic effect is predominant and completely overrides the vasoconstrictive effect of the alpha-2 receptors in the vascular smooth
195:(contraction of the vascular smooth muscle cells decreasing the diameter of the vessels). These receptors are activated in response to shock or low blood pressure as a defensive reaction trying to restore the normal blood pressure. Antagonists of alpha-1 receptors (
240:(i.e. the effect is opposite of the one resulting from activation of alpha-1 and alpha-2 receptors in the vascular smooth muscle cells). Usage of beta-2 receptor agonists as hypotensive agents is less widespread due to adverse effects such as unnecessary
261:, a mechanism that is responsible for the redistribution of the blood within the body to areas where it is needed (i.e. areas with temporarily enhanced oxygen consumption). Thus the main function of vascular smooth
221:
of alpha-2 receptors in the vascular smooth muscle lead to vasoconstriction. However, in clinical practice drugs applied intravenously that are agonists of alpha-2 receptors such as
295:, thus their greater wall thickness. This is because they have to carry pumped blood away from the heart to all the organs and tissues that need the oxygenated blood. The
538:
607:
924:
955:
302:
Excessive proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells contributes to the progression of pathological conditions, such as vascular
207:(a decrease in vascular smooth muscle tone with increase of vessel diameter and decrease of the blood pressure). (See also
625:
531:
163:
159:
960:
167:
151:
591:
506:
86:
1153:
1027:
1022:
184:
The adrenergic receptors exert opposite physiologic effects in the vascular smooth muscle under activation:
1111:
940:
580:
524:
319:
98:
56:
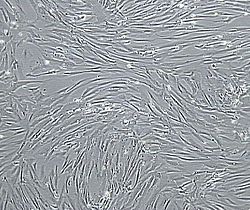
Vascular smooth muscle cells, isolated from human aorta, growing and forming a monolayer in cell culture.
327:
555:
307:
257:
Vascular smooth muscle contracts or relaxes to change both the volume of blood vessels and the local
740:
208:
155:
1178:
1073:
989:
896:
649:
486:
468:
429:
393:
689:
476:
460:
421:
383:
375:
266:
192:
39:
17:
1017:
909:
311:
974:
950:
481:
448:
388:
363:
258:
241:
178:
449:"The role of smooth muscle cells in plaque stability: Therapeutic targeting potential"
1172:
1039:
547:
425:
288:
135:
119:
70:
718:
671:
511:
303:
274:
270:
233:
204:
139:
123:
74:
379:
91:
1068:
1043:
862:
833:
634:
296:
278:
262:
245:
237:
51:
1138:
1099:
1094:
984:
945:
919:
914:
884:
879:
874:
802:
735:
713:
565:
343:
315:
472:
1143:
1048:
1034:
994:
904:
820:
772:
767:
684:
602:
222:
196:
490:
433:
397:
1133:
1104:
1064:
869:
323:
200:
171:
104:
1148:
853:
777:
265:
is to regulate the caliber of the blood vessels in the body. Excessive
218:
174:
464:
1089:
843:
331:
284:
848:
838:
760:
755:
750:
745:
797:
728:
723:
664:
659:
654:
644:
639:
516:
292:
520:
322:. Recent studies have shown that the majority of cells within
44:
Diagram showing the location of vascular smooth muscle cells.
447:
Harman, Jennifer L.; Jørgensen, Helle F. (October 2019).
138:
found within, and composing the majority of the wall of
134:
Vascular smooth muscle refers to the particular type of
150:
Vascular smooth muscle is innervated primarily by the
1124:
1082:
1057:
1010:
1003:
973:
933:
895:
819:
786:
702:
624:
615:
601:
590:
579:
554:
85:
80:
66:
61:
32:
27:Smooth muscle tissue in the walls of blood vessels
364:"Vascular smooth muscle cells in atherosclerosis"
158:(adrenoceptors). The three types present are:
532:
362:Bennett, M. R; Sinha, S; Owens, G. K (2016).
8:
507:Image of smooth muscle in the arterial walls
334:, are vascular smooth muscle cell derived.
191:. Under NE binding alpha-1 receptors cause
1007:
706:
621:
612:
598:
587:
539:
525:
517:
50:
38:
480:
387:
354:
102:
29:
232:. Agonism of beta-2 receptors causes
7:
925:Connective tissue in skeletal muscle
122:that makes up most of the walls of
25:
426:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2018.04.006
956:Excitation–contraction coupling
453:British Journal of Pharmacology
1:
512:Smooth muscle in stomach wall
380:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.306361
326:, the predominant cause of
299:lining of each is similar.
177:of these cell receptors is
168:beta-2 adrenergic receptors
18:Vascular smooth muscle cell
1195:
961:Sliding filament mechanism
152:sympathetic nervous system
709:
680:
244:in lungs and increase in
97:
49:
37:
291:within their walls than
1154:Fukutin-related protein
287:have a great deal more
1112:Sarcoplasmic reticulum
941:Neuromuscular junction
849:elastic filament/titin
571:Vascular smooth muscle
414:Biotechnology Advances
324:atherosclerotic plaque
320:pulmonary hypertension
116:Vascular smooth muscle
99:Anatomical terminology
33:Vascular smooth muscle
844:thick filament/myosin
277:as in shock leads to
368:Circulation Research
156:adrenergic receptors
839:thin filament/actin
825:(a, i, and h bands;
271:high blood pressure
209:receptor antagonist
279:low blood pressure
273:, while excessive
238:low blood pressure
1166:
1165:
1162:
1161:
1120:
1119:
1074:Myosatellite cell
990:Intercalated disc
969:
968:
897:Connective tissue
815:
814:
811:
810:
778:Synemin/desmuslin
698:
697:
465:10.1111/bph.14779
459:(19): 3741–3753.
215:alpha-2 receptors
189:alpha-1 receptors
113:
112:
108:
16:(Redirected from
1186:
1008:
791:
707:
690:Laminin, alpha 2
622:
613:
599:
588:
541:
534:
527:
518:
495:
494:
484:
444:
438:
437:
420:(6): 1586–1607.
408:
402:
401:
391:
359:
308:plaque formation
267:vasoconstriction
230:beta-2 receptors
193:vasoconstriction
105:edit on Wikidata
54:
42:
30:
21:
1194:
1193:
1189:
1188:
1187:
1185:
1184:
1183:
1169:
1168:
1167:
1158:
1126:
1116:
1078:
1053:
999:
976:
965:
929:
891:
826:
824:
807:
787:
782:
694:
676:
617:
606:
593:
582:
575:
557:
550:
545:
503:
498:
446:
445:
441:
410:
409:
405:
361:
360:
356:
352:
340:
312:atherosclerosis
255:
242:bronchodilation
148:
132:
118:is the type of
109:
57:
45:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1192:
1190:
1182:
1181:
1171:
1170:
1164:
1163:
1160:
1159:
1157:
1156:
1151:
1146:
1141:
1136:
1130:
1128:
1122:
1121:
1118:
1117:
1115:
1114:
1109:
1108:
1107:
1097:
1092:
1086:
1084:
1080:
1079:
1077:
1076:
1071:
1061:
1059:
1055:
1054:
1052:
1051:
1046:
1037:
1032:
1031:
1030:
1025:
1014:
1012:
1005:
1001:
1000:
998:
997:
992:
987:
981:
979:
971:
970:
967:
966:
964:
963:
958:
953:
951:Muscle spindle
948:
943:
937:
935:
931:
930:
928:
927:
922:
917:
912:
907:
901:
899:
893:
892:
890:
889:
888:
887:
882:
877:
866:
865:
859:
858:
857:
856:
851:
846:
841:
830:
828:
827:z and m lines)
817:
816:
813:
812:
809:
808:
806:
805:
800:
794:
792:
784:
783:
781:
780:
775:
770:
765:
764:
763:
758:
753:
748:
743:
733:
732:
731:
726:
716:
710:
704:
700:
699:
696:
695:
693:
692:
687:
681:
678:
677:
675:
674:
669:
668:
667:
662:
657:
652:
647:
642:
631:
629:
619:
610:
596:
585:
577:
576:
574:
573:
568:
562:
560:
552:
551:
546:
544:
543:
536:
529:
521:
515:
514:
509:
502:
501:External links
499:
497:
496:
439:
403:
374:(4): 692–702.
353:
351:
348:
347:
346:
339:
336:
259:blood pressure
254:
251:
250:
249:
227:
212:
179:norepinephrine
147:
144:
131:
128:
111:
110:
101:
95:
94:
89:
83:
82:
78:
77:
68:
64:
63:
59:
58:
55:
47:
46:
43:
35:
34:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1191:
1180:
1177:
1176:
1174:
1155:
1152:
1150:
1147:
1145:
1142:
1140:
1137:
1135:
1132:
1131:
1129:
1123:
1113:
1110:
1106:
1103:
1102:
1101:
1098:
1096:
1093:
1091:
1088:
1087:
1085:
1081:
1075:
1072:
1070:
1066:
1063:
1062:
1060:
1056:
1050:
1047:
1045:
1041:
1040:Microfilament
1038:
1036:
1033:
1029:
1026:
1024:
1021:
1020:
1019:
1016:
1015:
1013:
1009:
1006:
1002:
996:
993:
991:
988:
986:
983:
982:
980:
978:
972:
962:
959:
957:
954:
952:
949:
947:
944:
942:
939:
938:
936:
932:
926:
923:
921:
918:
916:
913:
911:
908:
906:
903:
902:
900:
898:
894:
886:
883:
881:
878:
876:
873:
872:
871:
868:
867:
864:
861:
860:
855:
852:
850:
847:
845:
842:
840:
837:
836:
835:
832:
831:
829:
822:
818:
804:
801:
799:
796:
795:
793:
790:
785:
779:
776:
774:
771:
769:
766:
762:
759:
757:
754:
752:
749:
747:
744:
742:
739:
738:
737:
734:
730:
727:
725:
722:
721:
720:
717:
715:
712:
711:
708:
705:
703:Intracellular
701:
691:
688:
686:
683:
682:
679:
673:
670:
666:
663:
661:
658:
656:
653:
651:
648:
646:
643:
641:
638:
637:
636:
633:
632:
630:
627:
623:
620:
618:extracellular
614:
611:
609:
604:
600:
597:
595:
589:
586:
584:
578:
572:
569:
567:
564:
563:
561:
559:
553:
549:
548:Muscle tissue
542:
537:
535:
530:
528:
523:
522:
519:
513:
510:
508:
505:
504:
500:
492:
488:
483:
478:
474:
470:
466:
462:
458:
454:
450:
443:
440:
435:
431:
427:
423:
419:
415:
407:
404:
399:
395:
390:
385:
381:
377:
373:
369:
365:
358:
355:
349:
345:
342:
341:
337:
335:
333:
329:
325:
321:
317:
313:
309:
305:
300:
298:
294:
290:
289:smooth muscle
286:
282:
280:
276:
272:
268:
264:
260:
252:
247:
243:
239:
235:
231:
228:
224:
220:
216:
213:
210:
206:
202:
198:
194:
190:
187:
186:
185:
182:
180:
176:
173:
169:
165:
161:
157:
153:
145:
143:
141:
140:blood vessels
137:
136:smooth muscle
129:
127:
125:
124:blood vessels
121:
120:smooth muscle
117:
106:
100:
96:
93:
90:
88:
84:
79:
76:
75:blood vessels
72:
71:smooth muscle
69:
65:
60:
53:
48:
41:
36:
31:
19:
1018:Muscle fiber
788:
719:Dystrobrevin
672:Dystroglycan
570:
456:
452:
442:
417:
413:
406:
371:
367:
357:
328:heart attack
304:inflammation
301:
283:
275:vasodilation
256:
234:vasodilation
229:
214:
205:vasodilation
188:
183:
170:|. The main
149:
146:Nerve supply
133:
115:
114:
1069:Muscle cell
1044:Myofilament
863:Tropomyosin
834:Myofilament
635:Sarcoglycan
297:endothelial
263:muscle tone
246:blood sugar
81:Identifiers
1139:Telethonin
1100:Sarcolemma
1095:Sarcoplasm
1028:extrafusal
1023:intrafusal
985:Myocardium
946:Motor unit
920:Endomysium
915:Perimysium
803:Caveolin 3
736:Syntrophin
714:Dystrophin
566:Calmodulin
350:References
344:Mural cell
316:restenosis
172:endogenous
1179:Angiology
1144:Dysferlin
1127:ungrouped
1049:Sarcomere
1035:Myofibril
995:Nebulette
905:Epimysium
821:Sarcomere
773:Dysbindin
768:Syncoilin
685:Sarcospan
616:Membrane/
603:Costamere
473:0007-1188
269:leads to
223:clonidine
197:doxazosin
130:Structure
1173:Category
1134:Myotilin
1105:T-tubule
1065:Myoblast
910:Fascicle
870:Troponin
789:related:
592:Skeletal
581:Striated
491:31254285
434:29684502
398:26892967
338:See also
285:Arteries
253:Function
219:Agonists
203:) cause
201:prazosin
154:through
73:wall of
1149:Fukutin
975:Cardiac
934:General
854:nebulin
482:6780045
389:4762053
248:levels.
226:muscle.
175:agonist
164:alpha-2
160:alpha-1
92:D009131
67:Part of
62:Details
1125:Other/
1090:Desmin
977:muscle
594:muscle
583:muscle
558:muscle
556:Smooth
489:
479:
471:
432:
396:
386:
332:stroke
318:, and
181:(NE).
1083:Other
1058:Cells
1011:Fiber
293:veins
103:[
1004:Both
798:NOS1
665:SGCZ
660:SGCG
655:SGCE
650:SGCD
645:SGCB
640:SGCA
608:DAPC
487:PMID
469:ISSN
430:PMID
394:PMID
330:and
236:and
166:and
87:MeSH
626:DAP
477:PMC
461:doi
457:176
422:doi
384:PMC
376:doi
372:118
1175::
761:G2
756:G1
751:B2
746:B1
485:.
475:.
467:.
455:.
451:.
428:.
418:36
416:.
392:.
382:.
370:.
366:.
314:,
310:,
306:,
281:.
217:.
199:,
162:,
142:.
126:.
1067:/
1042:/
885:I
880:C
875:T
823:/
741:A
729:B
724:A
628::
605:/
540:e
533:t
526:v
493:.
463::
436:.
424::
400:.
378::
211:)
107:]
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.