3335:
3252:
3297:
3267:
3222:
3350:
3380:
3365:
369:
3207:
3237:
1252:
1243:
1234:
3862:
3282:
1011:
1040:
1031:
1020:
945:
936:
927:
661:
3884:
580:
571:
820:
653:
27:
473:
1089:
Qaidam, Alex, and Tarim – along the
Central China orogen to form a combined East Asian continent. The northern margins of the northern continent collided with Baltica and Siberia 310–250 Ma, and thus the formation of the East Asian continent marked Pangaea at its greatest extent. By this time, the rifting of western Pangaea had already begun.
636:, Afghanistan, Iran, and Turkey – were still attached to the Indian–Australian margin of Gondwana. Other blocks that now form part of southwestern Europe and North America from New England to Florida were still attached to the African-South American margin of Gondwana. This northward drift of terranes across the Tethys also included the
1143:
diversity reach a maximum in the Late
Jurassic—Early Cretaceous and plate tectonic didn't affect the distribution of these flying reptiles. Crocodilian ancestors also diversified during the Early Cretaceous but were divided into Laurasian and Gondwanan populations; true crocodilians evolved from the
1057:
split the Asian blocks – Tarim, Qaidam, Alex, North China, and South China – from the northern shores of
Gondwana (north of Australia in modern coordinates) and the closure of the same ocean reassembled them along the same shores 500–460 Mya resulting in Gondwana at its largest extent.
996:
Laurasia and
Gondwana were equal in size but had distinct geological histories. Gondwana was assembled before the formation of Pangaea, but the assembly of Laurasia occurred during and after the formation of the supercontinent. These differences resulted in different patterns of basin formation and
849:
During the
Cambrian and Early Ordovician, when wide oceans separated all major continents, only pelagic marine organisms, such as plankton, could move freely across the open ocean and therefore the oceanic gaps between continents are easily detected in the fossil records of marine bottom dwellers and
783:
Continent stretched across northern
Laurentia and into Avalonia and Baltica but for most of the Devonian a narrow seaway formed a barrier where the North Atlantic would later open. Tetrapods evolved from fish in the Late Devonian, with the oldest known fossils from Greenland. Low sea-levels during
497:
Siberia was located near but at some distance from
Laurentia's northern margin in most reconstructions. In the reconstruction of some Russian geologists, however, the southern margin (modern coordinates) of Siberia merged with the northern margin of Laurentia, and these two continents broke up along
1194:
In the early Eocene a peak in global warming led to a pan-Arctic fauna with alligators and amphibians present north of the Arctic Circle. In the early
Palaeogene, landbridges still connected continents, allowing land animals to migrate between them. On the other hand, submerged areas occasionally
1080:
During the
Carboniferous and Permian, Baltica first collided with Kazakhstania and Siberia, then North China with Mongolia and Siberia. By the middle Carboniferous, however, South China had already been in contact with North China long enough to allow floral exchange between the two continents. The
2002:
Eckelmann, K.; Nesbor, H. D.; Königshof, P.; Linnemann, U.; Hofmann, M.; Lange, J. M.; Sagawe, A. (2014). "Plate interactions of
Laurussia and Gondwana during the formation of Pangaea—Constraints from U–Pb LA–SF–ICP–MS detrital zircon ages of Devonian and Early Carboniferous siliciclastics of the
1088:
When the eastern Palaeo-Tethys closed 250–230 Mya, a series of Asian blocks – Sibumasu, Indochina, South China, Qiantang, and Lhasa – formed a separate southern Asian continent. This continent collided 240–220 Mya with a northern continent – North China, Qinling, Qilian,
796:
into two provinces, with one of them confined to a large embayment west of the Appalachians. By the Middle Devonian, these two provinces had been united into one and the closure of the Rheic Ocean finally united faunas across Laurussia. High plankton productivity from the Devonian-Carboniferous
1056:
During the assembly of Pangaea Laurasia grew as continental blocks broke off Gondwana's northern margin; pulled by old closing oceans in front of them and pushed by new opening oceans behind them. During the Neoproterozoic-Early Paleozoic break-up of Rodinia the opening of the Proto-Tethys Ocean
1084:
In the early Permian, the Neo-Tethys Ocean opened behind the Cimmerian terranes (Sibumasu, Qiantang, Lhasa) and, in the late Carboniferous, the Palaeo-Tethys Ocean closed in front. The eastern branch of the Palaeo-Tethys Ocean, however, remained opened while Siberia was added to Laurussia and
411:
1,800—1,300 Mya, especially along the Laurentia—Greenland—Baltica margin. Laurentia and Baltica formed a coherent continental mass with southern Greenland and Labrador adjacent to the Arctic margin of Baltica. A magmatic arc extended from Laurentia through southern Greenland to northern
858:
and fishes remained isolated. As Laurussia formed during the Devonian and Pangaea formed, fish species in both Laurussia and Gondwana began to migrate between continents and before the end of the Devonian similar species were found on both sides of what remained of the Variscan barrier.
997:
transport of sediments. East Antarctica was the highest ground within Pangaea and produced sediments that were transported across eastern Gondwana but never reached Laurasia. During the Palaeozoic, c. 30–40% of Laurasia but only 10–20% of Gondwana was covered by shallow marine water.
521:(c. 750–600 Mya) as Australia-Antarctica (East Gondwana) rifted from the western margin of Laurentia, while the rest of Rodinia (West Gondwana and Laurasia) rotated clockwise and drifted south. Earth subsequently underwent a series of glaciations – the
1213:(an order of birds including kingfishers) evolved in Laurasia. While this group now has a mostly tropical distribution, they originated in the Arctic in the late Eocene c. 35 Mya from where they diversified across Laurasia and farther south across the Equator.
2146:
Li, Z. X.; Bogdanova, S. V.; Collins, A. S.; Davidson, A.; De Waele, B.; Ernst, R. E.; Fitzsimons, I. C. W.; Fuck, R. A.; Gladkochub, D. P.; Jacobs, J.; Karlstrom, K. E.; Lul, S.; Natapov, L. M.; Pease, V.; Pisarevsky, S. A.; Thrane, K.; Vernikovsky, V. (2008).
968:
The Palaezoic-Mesozoic transition was marked by the reorganisation of Earth's tectonic plates which resulted in the assembly of Pangaea, and eventually its break-up. Caused by the detachment of subducted mantle slabs, this reorganisation resulted in rising
350:
Several earlier supercontinents proposed and debated in the 1990s and later (e.g. Rodinia, Nuna, Nena) included earlier connections between Laurentia, Baltica, and Siberia. These original connections apparently survived through one and possibly even two
643:
Pannotia broke apart in the late Precambrian into Laurentia, Baltica, Siberia, and Gondwana. A series of continental blocks – the Cadomian–Avalonian, Cathaysian, and Cimmerian terranes – broke away from Gondwana and began to drift north.
537:
glaciations (c. 610-590 Mya) – both Laurentia and Baltica were located south of 30°S, with the South Pole located in eastern Baltica, and glacial deposits from this period have been found in Laurentia and Baltica but not in Siberia.
1101:
opened between Gondwana and Laurasia in the Late Jurassic. The fossil record, however, suggests the intermittent presence of a Trans-Tethys land bridge, though the location and duration of such a land bridge remains enigmatic.
412:
Baltica. The breakup of Columbia began 1,600 Mya, including along the western margin of Laurentia and northern margin of Baltica (modern coordinates), and was completed c. 1,300—1,200 Mya, a period during which mafic
1068:
North China, South China, Indochina, and Tarim broke off Gondwana during the Silurian-Devonian; Palaeo-Tethys opened behind them. Sibumasu and Qiantang and other Cimmerian continental fragments broke off in the Early Permian.
346:
in 1988 as the merger between Laurentia and Baltica along the northern Caledonian suture. The "Old Red Continent" is an informal name often used for the Silurian-Carboniferous deposits in the central landmass of Laurussia.
1116:. Pines adapted to cold and arid climates in environments where the growing season was shorter or wildfire common; this evolution limited pine range to between 31° and 50° north and resulted in a split into two subgenera:
2933:
Torsvik, T. H.; Van der Voo, R.; Preeden, U.; Mac Niocaill, C.; Steinberger, B.; Doubrovine, P. V.; van Hinsbergen, D. J. J.; Domeier, M.; Gaina, C.; Tohver, E.; Meert, J. G.; McCausland, P. J. A.; Cocks, R. M. (2012).
1060:
The break-up of Rodinia also resulted in the opening of the long-lived Paleo-Asian Ocean between Baltica and Siberia in the north and Tarim and North China in the south. The closure of this ocean is preserved in the
839:(between Armorica and Gondwana) to form the supercontinent Pangaea. The Variscan orogeny is complex and the exact timing and the order of the collisions between involved microcontinents has been debated for decades.
1199:
separated Europe and Asia from the Middle Jurassic to the Oligocene and as this sea or strait dried out, a massive faunal interchange took place and the resulting extinction event in Europe is known as the
842:
Pangaea was completely assembled by the Permian except for the Asian blocks. The supercontinent was centred on the Equator during the Triassic and Jurassic, a period that saw the emergence of the
767:
During the Devonian (416-359 Mya) the combined landmass of Baltica and Avalonia rotated around Laurentia, which remained static near the Equator. The Laurentian warm, shallow seas and on
869:
in central Laurussia (today New York, United States). In the late Carboniferous, Laurussia was centred on the Equator and covered by tropical rainforests, commonly referred to as the
486:, but the exact fit of various continents within Rodinia is debated. In some reconstructions, Baltica was attached to Greenland along its Scandinavian or Caledonide margin while
1288:, a continental fragment sitting on top of the Eurasian Plate, and North America. By 56 Mya Greenland had become an independent plate, separated from North America by the
339:
proposed that Pangaea was divided into two larger landmasses, Laurasia in the Northern Hemisphere and Gondwana in the Southern Hemisphere, separated by the Tethys Ocean.
288:
were then added to Pangaea 290–300 Ma to form Laurasia. Laurasia finally became an independent continental mass when Pangaea broke up into Gondwana and Laurasia.
324:
finally collided with Baltica in the Late Permian to form Laurasia. A series of continental blocks that now form East and Southeast Asia were later added to Laurasia.
699:(480–420 Mya). Baltica-Avalonia was then rotated and pushed north towards Laurentia. The collision between these continents closed the Iapetus Ocean and formed
3170:
2987:"Late Riphean rifting and breakup of Laurasia: data on geochronological studies of ultramafic alkaline complexes in the southern framing of the Siberian craton"
827:
The subduction of the Iapetus Ocean resulted in the first contact between Laurussia and Gondwana in the Late Devonian and terminated in full collision or the
668:
Laurentia remained almost static near the Equator throughout the early Palaeozoic, separated from Baltica by the up to 3,000 km (1,900 mi)-wide
3124:. Devonian of the World: Proceedings of the 2nd International Symposium on the Devonian System — Memoir 14, Volume I: Regional Syntheses. pp. 15–48.
696:
2404:
Milner, A. C.; Milner, A. R.; Evans, S. E. (2000). "Amphibians, reptiles and birds: a biogeographical review". In Culver, S. J.; Rawson, P. F. (eds.).
3944:
549:
opened between them. Laurentia then began to move quickly (20 cm/year (7.9 in/year)) north towards the Equator where it got stuck over a
331:
proposed that the continents in the Southern Hemisphere were once merged into a larger continent called Gondwana. In 1915 German meteorologist
672:. In the Late Cambrian, the mid-ocean ridge in the Iapetus Ocean subducted beneath Gondwana which resulted in the opening of a series of large
1722:, Assembly of Western Pangaea: Carboniferous–Permian, pp. 453–454; Assembly of Eastern Pangaea: Late Permian–Jurassic, p. 454; Fig. 10, p. 454
978:
719:
during the Devonian. The continent covered 37,000,000 km (14,000,000 sq mi) including several large Arctic continental blocks.
3924:
3010:
Zhao, G.; Cawood, P. A.; Wilde, S. A.; Sun, M. (2002). "Review of global 2.1–1.8 Ga orogens: implications for a pre-Rodinia supercontinent".
1942:
Cocks, L. R. M.; Torsvik, T. H. (2011). "The Palaeozoic geography of Laurentia and western Laurussia: a stable craton with mobile margins".
1274:, between eastern North America, from what is today the Gulf of Mexico to Nova Scotia, and in Africa and Europe, from Morocco to Greenland.
449:
a major large igneous province 1,380 Mya during the breakup of the Nuna/Columbia supercontinent connects Laurentia, Baltica, Siberia,
2890:
Torsvik, T. H.; Smethurst, M. A.; Meert, J. G.; Van der Voo, R.; McKerrow, W. S.; Brasier, M. D.; Sturt, B. A.; Walderhaug, H. J. (1996).
763:
where the northward directed subduction of the ocean floor between Gondwana and Laurussia pushed continental fragments towards the latter.
1293:
1135:(crurotarsans, pterosaurs and dinosaurs including birds) had a global distribution, especially crurotarsans, the group ancestral to the
246:
3974:
2713:
Seton, M.; Müller, R. D.; Zahirovic, S.; Gaina, C.; Torsvik, T.; Shephard, G.; Talsma, A.; Gurnis, M.; Maus, S.; Chandler, M. (2012).
3959:
3939:
3163:
3138:
2635:
2421:
2394:
1992:
874:
542:
901: – evolved and diversified, alongside other arthropods who were herbivorous and carnivorous, and tetrapods –
1128:
to fire-prone landscapes. By the end of the Cretaceous, pines were established across Laurasia, from North America to East Asia.
981:. Tentional stresses across Eurasia developed into a large system of rift basins (Urengoy, East Uralian-Turgay and Khudosey) and
3979:
3934:
3949:
3929:
3914:
616:
or Greater Gondwana. At this time a series of continental blocks – Peri-Gondwana – that now form part of Asia, the
400:) and the Volhyn—Central Russia and Pachelma orogenies (across western Russia) in Baltica; and the Akitkan Orogen in Siberia.
3919:
1900:
3954:
3872:
986:
3778:
3156:
1594:, Closure of Proto-Tethys Ocean and the first assembly of East Asian blocks at the northern margin of Gondwana, pp. 7-10
1289:
846:. Heavy rainfall resulted in high groundwater tables, in turn resulting in peat formation and extensive coal deposits.
2192:"Geochemical evidence of First Forestation in the southernmost euramerica from Upper Devonian (Famennian) Black shales"
3738:
1062:
2840:
3964:
2291:"A Laurasian origin for a pantropical bird radiation is supported by genomic and fossil data (Aves: Coraciiformes)"
1175:
slowly settled in Laurasia from Gondwana in the Triassic, the latter of which was the living area of their Permian
1077:, Sikuleh, southwest Sumatra, West Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo broke off during the Late Triassic-Late Jurassic.
850:
non-marine species. By the Late Ordovician, when continents were pushed closer together closing the oceanic gaps,
823:
Pangaea formed during the closure of the Rheic Ocean 330 Mya (early Carboniferous) (view centred on 30°S,30°E)
656:
Laurussia (left) during the closure of the Iapetus Ocean 430 Mya (middle Silurian) (view centred on 0°,-60°).
439:(Ukraine), southern Siberia, northern Laurentia, and West Africa indicate these cratons were linked to each other;
3683:
3673:
3426:
377:
2891:
2433:"Permo–Triassic intraplate magmatism and rifting in Eurasia: implications for mantle plumes and mantle dynamics"
1775:, Closure of Paleo-Asian Ocean: collision of Tarim, Alex and North China with East Europe and Siberia, pp. 11-14
280:
c. 400 Ma to form Laurussia/Euramerica. Laurussia/Euramerica then collided with Gondwana to form Pangaea.
3969:
3892:
3658:
2985:
Yarmolyuk, V. V.; Kovalenko, V. I.; Sal'nikova, E. B.; Nikiforov, A. V.; Kotov, A. B.; Vladykin, N. V. (2006).
245:
period) during the breakup of Pangaea, drifting farther north after the split and finally broke apart with the
2072:
Gheerbrant, E.; Rage, J. C. (2006). "Paleobiogeography of Africa: how distinct from Gondwana and Laurasia?".
1160: – was similar to that of the crocodilians. East Asia remained isolated with endemic species including
3715:
3710:
3074:"Geological reconstructions of the East Asian blocks: From the breakup of Rodinia to the assembly of Pangea"
1886:
Blakey, R. C. (2003). Wong, T. E. (ed.). "Carboniferous–Permian paleogeography of the assembly of Pangaea".
393:
376:
Laurentia and Baltica first formed a continental mass known as Proto-Laurasia as part of the supercontinent
2667:"Late Proterozoic plate tectonics and palaeogeography: a tale of two supercontinents, Rodinia and Pannotia"
3653:
1959:
974:
534:
499:
428:
368:
2892:"Continental break-up and collision in the Neoproterozoic and Palaeozoic—a tale of Baltica and Laurentia"
431:
provide evidences for continental mergers during this period. Those related to Proto-Laurasia includes:
3538:
3446:
3256:
3251:
2935:
2190:
Lu, M.; Lu, Y.; Ikejiri, T.; Hogancamp, N.; Sun, Y.; Wu, Q.; Carroll, R.; Çemen, I.; Pashin, J. (2019).
1292:. By 33 Mya spreading had ceased in the Labrador Sea and relocated to the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. The
1109:
789:
530:
482:
In the vast majority of plate tectonic reconstructions, Laurentia formed the core of the supercontinent
2241:
McKerrow, W. S.; Mac Niocaill, C.; Ahlberg, P. E.; Clayton, G.; Cleal, C. J.; Eagar, R. M. C. (2000).
3877:
3632:
3523:
3085:
3052:
3019:
2950:
2906:
2855:
2804:
2789:
2726:
2678:
2615:
2575:
2527:
2487:
2444:
2350:
2254:
2203:
2163:
2081:
2045:
2012:
1951:
1915:
866:
621:
417:
397:
389:
157:
2377:
Metcalfe, I. (1999). "Gondwana dispersion and Asian accretion: an overview". In Metcalfe, I. (ed.).
1964:
3887:
3834:
3624:
3583:
2473:"Stratigraphic record of the early Mesozoic breakup of Pangea in the Laurasia-Gondwana rift system"
1251:
1242:
1233:
843:
745:
727:
522:
503:
454:
446:
in southern Siberia that can be connected to the Melville Bugt dyke swarm in western Greenland; and
408:
317:
285:
121:
80:
1112:
originated in Laurasia in the Early Cretaceous c. 130 Mya in competition with faster growing
3742:
3588:
3568:
3101:
2871:
2820:
2694:
2645:
2591:
2543:
2270:
2127:
990:
836:
637:
442:
a 1,630–1,640 Mya-old continent composed of Siberia, Laurentia, and Baltica is suggested by
421:
309:
277:
131:
126:
3861:
1982:
2413:
3809:
3663:
3628:
3134:
2631:
2417:
2390:
2322:
2229:
2034:"Large Igneous Provinces and supercontinents: Toward completing the plate tectonic revolution"
1988:
785:
780:
768:
716:
689:
629:
336:
84:
3824:
3488:
3093:
3060:
3027:
2966:
2958:
2914:
2863:
2812:
2769:
2734:
2686:
2623:
2583:
2535:
2495:
2452:
2405:
2382:
2358:
2312:
2302:
2262:
2219:
2211:
2171:
2117:
2089:
2053:
2020:
1969:
1923:
1180:
1074:
828:
487:
436:
385:
335:
proposed the existence of a supercontinent called Pangaea. In 1937 South African geologist
174:
2472:
2431:
Nikishin, A. M.; Ziegler, P. A.; Abbott, D.; Brunet, M. F.; Cloetingh, S. A. P. L. (2002).
476:
Rodinia 900 Mya centred on Laurentia with Baltica and Amazonia on its southern margin.
3814:
3784:
3725:
3548:
2657:
2148:
1285:
962:
749:
300:
of North America and continental fragments that now make up part of Europe, collided with
695:
Avalonia rifted from Gondwana in the Early Ordovician and collided with Baltica near the
604:
Laurentia, Baltica, and Siberia remained connected to each other within the short-lived,
3089:
3056:
3023:
2954:
2910:
2859:
2808:
2730:
2682:
2619:
2579:
2531:
2491:
2448:
2354:
2258:
2207:
2167:
2085:
2049:
2016:
1955:
1919:
1888:
Proceedings of the XVTH International Congress on Carboniferous and Permian Stratigraphy
1763:, Closure of Paleo-Tethys Ocean and assembly of Pangea with East Asian blocks, pp. 14-16
31:
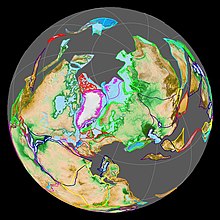
Laurasia (centre) and Gondwana (bottom) as part of Pangaea 200 Mya (Early Jurassic)
3746:
3466:
3420:
2317:
2290:
2224:
2191:
1305:
1267:
1217:
1202:
1165:
1161:
1010:
738:
673:
526:
518:
491:
443:
332:
152:
53:
3031:
2627:
2456:
1187:
staying in Laurasia (until further descendants switched to Gondwana starting from the
1039:
1030:
1019:
944:
935:
926:
3908:
3763:
3301:
3296:
3286:
3281:
3105:
3073:
2986:
2918:
2875:
2824:
2754:
2714:
2698:
2666:
2563:
2547:
2515:
2432:
2406:
2274:
2242:
2033:
1310:
1210:
1184:
1098:
1070:
760:
669:
633:
553:
in the Proto-pacific. Baltica remained near Gondwana in southern latitudes into the
546:
343:
313:
90:
3097:
3064:
2962:
2755:"Rainforest collapse triggered Pennsylvanian tetrapod diversification in Euramerica"
2738:
2595:
2175:
2131:
1973:
660:
3866:
3819:
3553:
3528:
3339:
3334:
2499:
1271:
1157:
1136:
982:
970:
863:
798:
731:
507:
450:
352:
328:
321:
281:
116:
2816:
2587:
2266:
1139:. This cosmopolitanism ended as Gondwana fragmented and Laurasia was assembled.
961:
During the Carboniferous–Permian Siberia, Kazakhstan, and Baltica collided in the
2093:
2057:
1927:
1048:
Journey of the Asian blocks from Gondwana to Laurasia 450, 350, 300, and 200 Mya.
3720:
3688:
3678:
2841:"Earth geography from 400 to 250 Ma: a palaeomagnetic, faunal and facies review"
902:
886:
870:
832:
802:
737:
the western margin were the western shelves of Laurentia, later affected by the
677:
605:
514:
502:
no later than 570 Mya and traces of this breakup can still be found in the
404:
250:
136:
3040:
2215:
2102:
3758:
3668:
3648:
3498:
3226:
3221:
2386:
2122:
1196:
1176:
1113:
898:
882:
793:
554:
550:
413:
227:
2362:
2024:
1811:, Introduction, pp. 445–446; Mesozoic origin and diversification, pp. 450–451
1266:
In the Triassic–Early Jurassic (c. 200 Mya), the opening of the Central
494:. Australia and East Antarctica were located on Laurentia's western margin.
3829:
3798:
3693:
3643:
3563:
3558:
3503:
3436:
3179:
2867:
1526:, Abstract; Initial break-up of Rodinia and Vendian glaciations, pp. 237–240
1270:
was preceded by the formation of a series of large rift basins, such as the
1153:
1149:
1140:
1132:
906:
831:
in the early Carboniferous (340 Mya). The Variscan orogeny closed the
819:
784:
the Early Devonian produced natural barriers in Laurussia which resulted in
776:
685:
652:
617:
579:
570:
254:
106:
26:
3072:
Zhao, G.; Wang, Y.; Huang, B.; Dong, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, G.; Yu, S. (2018).
2335:
2326:
2307:
2233:
472:
2564:"The Scandinavian Caledonides and their relationship to the Variscan belt"
977:
when they reached the crust. This tectonic activity also resulted in the
380:
which was assembled 2,100—1,800 Mya to encompass virtually all known
3753:
3638:
3518:
3508:
3471:
3456:
3431:
3354:
3349:
1508:
1188:
1145:
1131:
From the Triassic to the Early Jurassic, before the break-up of Pangaea,
1105:
894:
878:
855:
681:
625:
613:
609:
599:
305:
265:
242:
236:
231:
221:
953:
The Uralian orogeny and the formation of Laurasia 300, 280, and 240 Mya.
545:) forced Laurentia and Baltica to separate ca. 650–600 Mya and the
215:) was the more northern of two large landmasses that formed part of the
3773:
3768:
3533:
3513:
3493:
3461:
3451:
3384:
3379:
3369:
3364:
2970:
2289:
McCullough, J. M.; Moyle, R. G.; Smith, B. T.; Andersen, M. J. (2019).
2149:"Assembly, configuration, and break-up history of Rodinia: A synthesis"
1172:
1118:
910:
890:
851:
814:
772:
753:
483:
467:
381:
301:
273:
269:
216:
111:
70:
3148:
3041:"A Paleo-Mesoproterozoic supercontinent: assembly, growth and breakup"
2379:
Gondwana Dispersion and Asian Accretion. IGCP 321 final results volume
3804:
3573:
3271:
3266:
3211:
3206:
2773:
1984:
Our wandering continents : an hypothesis of continental drifting
1574:
1367:
297:
66:
2690:
722:
With the Caledonian orogeny completed Laurussia was delimited thus:
676:. During the Ordovician, these basins evolved into a new ocean, the
2539:
2336:"What's in a name? The Columbia (Paleopangaea/Nuna) supercontinent"
1746:, Differences Between Gondwana and Laurasia in Pangea, pp. 127, 130
1183:
returning to Gondwana (and stayed there after Pangaea split) while
854:(brachiopods and trilobites) could spread between continents while
620:
terranes – Indochina, North China, and South China – and
355:, though their intermittent duration and recurrent fit is debated.
3578:
3183:
3131:
Evolution of Laurussia: A study in Late Palaeozoic plate tectonics
1678:
1450:, Laurentia (North America and Greenland) and Baltica, pp. 145-149
1124:
818:
659:
651:
471:
367:
1642:
1081:
Cimmerian blocks rifted from Gondwana in the Late Carboniferous.
3241:
3236:
2715:"Global continental and ocean basin reconstructions since 200Ma"
1523:
1484:
258:
76:
16:
Northern landmass that formed part of the Pangaea supercontinent
3152:
590:
Right: Laurasia during the breakup of Pannotia at 550 Mya.
2243:"The late Palaeozoic relations between Gondwana and Laurussia"
2032:
Ernst, R. E.; Bleeker, W.; Söderlund, U.; Kerr, A. C. (2013).
192:
752:
orogeny which marked the collision between Laurussia and the
396:
in Greenland; the Kola-Karelian (the northwest margin of the
180:
1844:
1519:
1517:
1731:
207:
204:
195:
189:
1496:
1472:
1370:, From Laurentia to Laurussia and Laurasia: Overview, p. 6
201:
1868:
1459:
873:. By the Permian, the climate had become arid and these
2936:"Phanerozoic polar wander, palaeogeography and dynamics"
1669:, Geological Evidence of the Pangean Megamonsoon, p. 223
1570:
1568:
2408:
Biotic Response to Global Change-The Last Million Years
1702:
1260:
Opening of the North Atlantic Ocean 90, 50, and 30 Mya.
1144:
former. The distribution of the three major groups of
2753:
Sahney, S.; Benton, M. J.; Falcon-Lang, H. J. (2010).
1284:
spreading had begun in the North Atlantic between the
1108:
evolved in the early Mesozoic c. 250 Mya and the
2614:. Vol. 7. Oxford University Press. p. 653.
1419:
1417:
1415:
862:
The oldest tree fossils are from the Middle Devonian
1901:"The late Archean record: a puzzle in ca. 35 pieces"
1756:
1754:
1752:
1690:
1587:
1585:
1583:
312:
c. 430–420 Mya to form Laurussia. In the Late
186:
177:
2003:Rhenohercynian zone, Central European Variscides".
498:what is now the 3,000 km (1,900 mi)-long
183:
145:
99:
59:
49:
41:
36:
1462:, Progress on continental reconstructions, pp. 8–9
1447:
707:Another historical term for this continent is the
2074:Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology
1832:
1820:
1772:
1760:
1591:
3039:Zhao, G.; Sun, M.; Wilde, S. A.; Li, S. (2004).
2797:Geological Society, London, Special Publications
2671:Geological Society, London, Special Publications
2568:Geological Society, London, Special Publications
2247:Geological Society, London, Special Publications
588:Left: Laurasia as part of Pannotia 600 Mya.
1602:
1600:
779:exceeding 1 m (3 ft 3 in). The
517:opened and Rodinia began to breakup during the
435:1,750 Mya extensive magmatism in Baltica,
2103:"Ecology and evolution of pine life histories"
1796:
1715:
1713:
1711:
1435:
1423:
680:, which separated a series of terranes –
3164:
2480:Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences
1743:
1657:, Paleogeographic Evolution of Pangea, p. 216
8:
1630:
1618:
1378:
1376:
1355:
788:within the benthic fauna. In Laurentia the
759:and the southern margin was a Pacific-style
19:
715:, in reference to abundant red beds of the
342:"Laurussia" was defined by Swiss geologist
3612:
3607:
3407:
3402:
3324:
3319:
3196:
3191:
3171:
3157:
3149:
2381:. Rotterdam: A.A. Balkema. pp. 9–28.
25:
3543:
2316:
2306:
2223:
2121:
1963:
1871:, Rockall–North America/Greenland, p. 222
2839:Torsvik, T. H.; Cocks, L. R. M. (2004).
2562:Rey, P.; Burg, J. P.; Casey, M. (1997).
1784:
1547:
1296:had effectively broken Laurasia in two.
835:(between Avalonia and Armorica) and the
316:Laurussia and Gondwana formed Pangaea.
2412:. Cambridge University Press. pp.
1666:
1654:
1606:
1559:
1535:
1406:
1394:
1343:
1327:
45:1,071 Mya (Proto-Laurasia) 253 Mya
2653:
2643:
2516:"Climate of the supercontinent Pangea"
1808:
1719:
1499:, Siberia–Laurentia connection, p. 189
1358:, Laurussia and Laurasia, pp. 558, 560
1122:adapted to stressful environments and
18:
1856:
1734:, Introduction, pp. 4–5; Fig. 4, p. 8
1703:Sahney, Benton & Falcon-Lang 2010
1438:, Summary and Discussion, pp. 114–115
1382:
292:Terminology and origin of the concept
7:
2610:Rogers, J. J.; Santosh, M. (2004).
1294:opening of the North Atlantic Ocean
1168:(club-tailed, armoured dinosaurs).
640:, now spread from Europe to China.
247:opening of the North Atlantic Ocean
2295:Proceedings of the Royal Society B
14:
2848:Journal of the Geological Society
1681:, The narrowing oceans, pp. 10–11
1562:, The break-up of Pannotia, p. 78
1179:. They split in two groups, with
1085:Gondwana collided with Laurasia.
979:Permian–Triassic extinction event
543:Central Iapetus Magmatic Province
398:Svecokarelian/Svecofennian orogen
3945:Natural history of North America
3883:
3882:
3860:
3378:
3363:
3348:
3333:
3295:
3280:
3265:
3250:
3235:
3220:
3205:
1471:"Consensus" reconstruction from
1250:
1241:
1232:
1038:
1029:
1018:
1009:
943:
934:
925:
881:(giant mosses) were replaced by
578:
569:
525:(c. 650 Mya, also known as
327:In 1904–1909 Austrian geologist
173:
3706:Possible future supercontinents
3122:Laurussia—the old red continent
3098:10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.10.003
3065:10.1016/j.earscirev.2004.02.003
2963:10.1016/j.earscirev.2012.06.007
2739:10.1016/j.earscirev.2012.03.002
2176:10.1016/j.precamres.2007.04.021
1974:10.1016/j.earscirev.2011.01.007
1833:Milner, Milner & Evans 2000
1821:Milner, Milner & Evans 2000
1065:, the largest orogen on Earth.
775:evolved, including the largest
592:View centred on the South Pole.
384:continental blocks. Surviving
2612:Continents and supercontinents
2500:10.1146/annurev.earth.25.1.337
1987:. Edinburgh: Oliver and Boyd.
1621:, Facies and faunas, pp. 10–11
1216:The placental mammal group of
1:
3032:10.1016/S0012-8252(02)00073-9
2817:10.1144/GSL.SP.2000.173.01.01
2628:10.1016/S1342-937X(05)70827-3
2588:10.1144/GSL.SP.1997.121.01.08
2457:10.1016/S0040-1951(02)00123-3
2267:10.1144/GSL.SP.2000.179.01.03
1645:, Introduction, pp. 1484–1486
1278:
909:such as amphibians and early
889:fauna – including
234:. It separated from Gondwana
3925:Carboniferous paleogeography
3484:Other prehistoric continents
2919:10.1016/0012-8252(96)00008-6
2094:10.1016/j.palaeo.2006.03.016
2058:10.1016/j.lithos.2013.02.017
1928:10.1016/j.lithos.2003.07.003
1290:Labrador Sea-Baffin Bay Rift
1097:Pangaea split in two as the
805:in the basins of Laurentia.
744:the northern margin was the
726:The eastern margin were the
697:Ordovician–Silurian boundary
372:Columbia/Nuna 1,590 Mya
1063:Central Asian Orogenic Belt
713:Old Red Sandstone Continent
506:in northern Canada and the
490:was docked along Baltica's
478:View centred on 30°S,130°E.
388:from this assembly are the
219:supercontinent from around
3996:
2216:10.1038/s41598-019-43993-y
1797:Gheerbrant & Rage 2006
1631:Rey, Burg & Casey 1997
1511:, p. 1031; Fig. 1, p. 1032
1050:View centred on 0°S,105°E.
955:View centred on 25°N,35°E.
829:Hercynian/Variscan orogeny
812:
664:Euramerica in the Devonian
597:
465:
296:Laurentia, the Palaeozoic
272:, and a series of smaller
3975:Natural history of Europe
3852:
3610:
3606:
3405:
3401:
3322:
3318:
3194:
3190:
2387:10.1080/08120099608728282
2123:10.1007/s13595-012-0201-8
1744:Rogers & Santosh 2004
1334:Oxford English Dictionary
1220:is named after Laurasia.
416:were emplaced, including
249:c. 56 Mya. The name is a
24:
3960:Geology of North America
3940:Paleocene paleogeography
3893:Chronology of continents
2788:Stampfli, G. M. (2000).
2363:10.1016/j.gr.2011.12.002
2110:Annals of Forest Science
2025:10.1016/j.gr.2013.05.018
1619:Cocks & Torsvik 2011
1356:Torsvik & Cocks 2004
1195:divided continents: the
885:. In the dry climate a
771:a diverse assemblage of
3980:Natural history of Asia
3935:Mesozoic paleogeography
3129:Ziegler, P. A. (2012).
3120:Ziegler, P. A. (1988).
2868:10.1144/0016-764903-098
2665:Scotese, C. R. (2009).
2514:Parrish, J. T. (1993).
1981:Du Toit, A. L. (1937).
1705:, Introduction, p. 1079
1633:, Introduction, pp. 1–2
1609:, Introduction, pp. 1–4
1164:(horned dinosaurs) and
975:large igneous provinces
692: – from Gondwana.
429:large igneous provinces
241:(beginning in the late
3950:Mesozoic North America
3930:Permian paleogeography
3915:Former supercontinents
3654:Great Australian Bight
2991:Doklady Earth Sciences
2520:The Journal of Geology
2308:10.1098/rspb.2019.0122
2101:Keeley, J. E. (2012).
1859:, Introduction, p. 338
1845:McCullough et al. 2019
1799:, Introduction, p. 225
1487:, Rodinia, pp. 236–237
824:
665:
657:
500:Central Asian Foldbelt
479:
394:Nagssugtoqidian orogen
373:
3920:Historical continents
3078:Earth-Science Reviews
3045:Earth-Science Reviews
3012:Earth-Science Reviews
2943:Earth-Science Reviews
2899:Earth-Science Reviews
2719:Earth-Science Reviews
2471:Olsen, P. E. (1997).
2334:Meert, J. G. (2012).
1944:Earth-Science Reviews
1643:Eckelmann et al. 2014
1509:Yarmolyuk et al. 2006
875:rainforests collapsed
822:
797:boundary resulted in
790:Transcontinental Arch
663:
655:
475:
371:
3955:Geology of Greenland
3878:Continental fragment
3873:Regions of the world
2156:Precambrian Research
1899:Bleeker, W. (2003).
1732:Nikishin et al. 2002
1679:McKerrow et al. 2000
1550:, Palaeotethys, p. 3
844:Pangaean megamonsoon
648:Euramerica/Laurussia
541:A mantle plume (the
237:215 to 175
222:335 to 175
158:North American Plate
85:Arabian subcontinent
37:Historical continent
3835:Indian Subcontinent
3625:Submerged continent
3090:2018ESRv..186..262Z
3057:2004ESRv...67...91Z
3024:2002ESRv...59..125Z
2955:2012ESRv..114..325T
2911:1996ESRv...40..229T
2860:2004JGSoc.161..555T
2809:2000GSLSP.173....1S
2731:2012ESRv..113..212S
2683:2009GSLSP.326...67S
2620:2004GondR...7..653R
2580:1997GSLSP.121..179R
2532:1993JG....101..215P
2492:1997AREPS..25..337O
2449:2002Tectp.351....3N
2355:2012GondR..21..987M
2259:2000GSLSP.179....9M
2208:2019NatSR...9.7581L
2168:2008PreR..160..179L
2086:2006PPP...241..224G
2050:2013Litho.174....1E
2017:2014GondR..25.1484E
1956:2011ESRv..106....1C
1920:2003Litho..71...99B
1894:. Utrecht: 443–456.
1575:Torsvik et al. 2012
1524:Torsvik et al. 1996
1485:Torsvik et al. 1996
1368:Torsvik et al. 2012
993:, and South China.
987:West Siberian Basin
504:Franklin dike swarm
390:Trans-Hudson orogen
230:), the other being
81:Indian subcontinent
21:
3616:
3411:
3328:
3200:
2301:(1910): 20190122.
2196:Scientific Reports
1847:, Conclusion, p. 7
1385:, pp. 991–992
1282: 83 Mya
965:to form Laurasia.
837:Proto-Tethys Ocean
825:
666:
658:
480:
374:
310:Caledonian orogeny
278:Caledonian orogeny
276:, collided in the
100:Smaller continents
3965:Geology of Europe
3902:
3901:
3848:
3847:
3843:
3842:
3664:Kerguelen Plateau
3602:
3601:
3597:
3596:
3397:
3396:
3392:
3391:
3314:
3313:
3309:
3308:
2768:(12): 1079–1082.
2343:Gondwana Research
2005:Gondwana Research
1869:Seton et al. 2012
1460:Ernst et al. 2013
781:Old Red Sandstone
717:Old Red Sandstone
709:Old Red Continent
337:Alexander du Toit
224:million years ago
166:
165:
3987:
3886:
3885:
3867:World portal
3865:
3864:
3802:
3751:
3708:
3636:
3613:
3608:
3486:
3424:
3408:
3403:
3382:
3367:
3352:
3337:
3325:
3320:
3299:
3284:
3269:
3254:
3239:
3224:
3209:
3197:
3192:
3173:
3166:
3159:
3150:
3144:
3125:
3116:
3114:
3112:
3068:
3035:
3018:(1–4): 125–162.
3006:
3004:
3002:
2981:
2979:
2977:
2949:(3–4): 325–368.
2940:
2929:
2927:
2925:
2905:(3–4): 229–258.
2896:
2886:
2884:
2882:
2845:
2835:
2833:
2831:
2794:
2790:"Tethyan oceans"
2784:
2782:
2780:
2774:10.1130/G31182.1
2759:
2749:
2747:
2745:
2709:
2707:
2705:
2661:
2655:
2651:
2649:
2641:
2606:
2604:
2602:
2558:
2556:
2554:
2510:
2508:
2506:
2477:
2467:
2465:
2463:
2427:
2411:
2400:
2373:
2371:
2369:
2340:
2330:
2320:
2310:
2285:
2283:
2281:
2237:
2227:
2186:
2184:
2182:
2162:(1–2): 179–210.
2153:
2142:
2140:
2138:
2125:
2107:
2097:
2068:
2066:
2064:
2028:
2011:(4): 1484–1500.
1998:
1977:
1967:
1938:
1936:
1934:
1905:
1895:
1872:
1866:
1860:
1854:
1848:
1842:
1836:
1830:
1824:
1818:
1812:
1806:
1800:
1794:
1788:
1787:, pp. 15–16
1782:
1776:
1773:Zhao et al. 2018
1770:
1764:
1761:Zhao et al. 2018
1758:
1747:
1741:
1735:
1729:
1723:
1717:
1706:
1700:
1694:
1688:
1682:
1676:
1670:
1664:
1658:
1652:
1646:
1640:
1634:
1628:
1622:
1616:
1610:
1604:
1595:
1592:Zhao et al. 2018
1589:
1578:
1572:
1563:
1557:
1551:
1545:
1539:
1533:
1527:
1521:
1512:
1506:
1500:
1494:
1488:
1482:
1476:
1469:
1463:
1457:
1451:
1448:Zhao et al. 2002
1445:
1439:
1436:Zhao et al. 2004
1433:
1427:
1424:Zhao et al. 2004
1421:
1410:
1404:
1398:
1392:
1386:
1380:
1371:
1365:
1359:
1353:
1347:
1341:
1335:
1332:
1283:
1280:
1254:
1245:
1236:
1114:flowering plants
1042:
1033:
1022:
1013:
947:
938:
929:
703:, also known as
624:terranes –
582:
573:
492:Tornquist margin
240:
225:
214:
213:
210:
209:
206:
203:
198:
197:
194:
191:
188:
185:
182:
179:
71:Balkan Peninsula
29:
22:
3995:
3994:
3990:
3989:
3988:
3986:
3985:
3984:
3970:Geology of Asia
3905:
3904:
3903:
3898:
3897:
3859:
3844:
3839:
3825:Eastern Siberia
3815:Central America
3803:
3796:
3790:
3785:Terra Australis
3752:
3736:
3730:
3726:Pangaea Proxima
3709:
3704:
3698:
3637:
3633:microcontinents
3622:
3598:
3593:
3539:East Antarctica
3487:
3482:
3476:
3425:
3421:supercontinents
3417:
3393:
3388:
3383:
3373:
3368:
3358:
3353:
3343:
3338:
3310:
3305:
3300:
3290:
3285:
3275:
3270:
3260:
3255:
3245:
3240:
3230:
3225:
3215:
3210:
3186:
3177:
3147:
3141:
3128:
3119:
3110:
3108:
3071:
3051:(1–2): 91–123.
3038:
3009:
3000:
2998:
2984:
2975:
2973:
2938:
2932:
2923:
2921:
2894:
2889:
2880:
2878:
2843:
2838:
2829:
2827:
2792:
2787:
2778:
2776:
2757:
2752:
2743:
2741:
2712:
2703:
2701:
2691:10.1144/SP326.4
2664:
2652:
2642:
2638:
2609:
2600:
2598:
2561:
2552:
2550:
2513:
2504:
2502:
2475:
2470:
2461:
2459:
2430:
2424:
2403:
2397:
2376:
2367:
2365:
2338:
2333:
2288:
2279:
2277:
2240:
2189:
2180:
2178:
2151:
2145:
2136:
2134:
2105:
2100:
2071:
2062:
2060:
2031:
2001:
1995:
1980:
1965:10.1.1.663.2972
1941:
1932:
1930:
1914:(2–4): 99–134.
1903:
1898:
1885:
1881:
1876:
1875:
1867:
1863:
1855:
1851:
1843:
1839:
1831:
1827:
1819:
1815:
1807:
1803:
1795:
1791:
1783:
1779:
1771:
1767:
1759:
1750:
1742:
1738:
1730:
1726:
1718:
1709:
1701:
1697:
1689:
1685:
1677:
1673:
1665:
1661:
1653:
1649:
1641:
1637:
1629:
1625:
1617:
1613:
1605:
1598:
1590:
1581:
1573:
1566:
1558:
1554:
1546:
1542:
1534:
1530:
1522:
1515:
1507:
1503:
1495:
1491:
1483:
1479:
1470:
1466:
1458:
1454:
1446:
1442:
1434:
1430:
1422:
1413:
1405:
1401:
1393:
1389:
1381:
1374:
1366:
1362:
1354:
1350:
1342:
1338:
1333:
1329:
1324:
1319:
1302:
1286:Rockall Plateau
1281:
1264:
1263:
1262:
1261:
1257:
1256:
1255:
1247:
1246:
1238:
1237:
1226:
1095:
1093:Flora and fauna
1054:
1053:
1052:
1051:
1049:
1045:
1044:
1043:
1035:
1034:
1025:
1024:
1023:
1015:
1014:
1003:
963:Uralian orogeny
959:
958:
957:
956:
954:
950:
949:
948:
940:
939:
931:
930:
919:
817:
811:
732:Moscow Platform
674:back-arc basins
650:
612:supercontinent
602:
596:
595:
594:
593:
591:
589:
585:
584:
583:
575:
574:
563:
477:
470:
464:
427:Traces left by
366:
361:
294:
235:
220:
200:
176:
172:
162:
146:Tectonic plates
141:
95:
32:
17:
12:
11:
5:
3993:
3991:
3983:
3982:
3977:
3972:
3967:
3962:
3957:
3952:
3947:
3942:
3937:
3932:
3927:
3922:
3917:
3907:
3906:
3900:
3899:
3896:
3895:
3890:
3880:
3875:
3870:
3854:
3853:
3850:
3849:
3846:
3845:
3841:
3840:
3838:
3837:
3832:
3827:
3822:
3820:Eastern Africa
3817:
3812:
3807:
3793:
3791:
3789:
3788:
3781:
3776:
3771:
3766:
3761:
3756:
3733:
3731:
3729:
3728:
3723:
3718:
3713:
3701:
3699:
3697:
3696:
3691:
3686:
3681:
3676:
3671:
3666:
3661:
3656:
3651:
3646:
3641:
3619:
3617:
3611:
3604:
3603:
3600:
3599:
3595:
3594:
3592:
3591:
3586:
3581:
3576:
3571:
3566:
3561:
3556:
3551:
3546:
3541:
3536:
3531:
3526:
3521:
3516:
3511:
3506:
3501:
3496:
3491:
3479:
3477:
3475:
3474:
3469:
3464:
3459:
3454:
3449:
3444:
3439:
3434:
3429:
3414:
3412:
3406:
3399:
3398:
3395:
3394:
3390:
3389:
3376:
3374:
3361:
3359:
3346:
3344:
3331:
3329:
3323:
3316:
3315:
3312:
3311:
3307:
3306:
3293:
3291:
3278:
3276:
3263:
3261:
3248:
3246:
3233:
3231:
3218:
3216:
3203:
3201:
3195:
3188:
3187:
3178:
3176:
3175:
3168:
3161:
3153:
3146:
3145:
3139:
3126:
3117:
3069:
3036:
3007:
2997:(7): 1031–1036
2982:
2930:
2887:
2854:(4): 555–572.
2836:
2785:
2750:
2725:(3): 212–270.
2710:
2662:
2654:|journal=
2636:
2607:
2574:(1): 179–200.
2559:
2540:10.1086/648217
2526:(2): 215–233.
2511:
2486:(1): 337–401.
2468:
2437:Tectonophysics
2428:
2422:
2401:
2395:
2374:
2349:(4): 987–993.
2331:
2286:
2238:
2187:
2143:
2116:(4): 445–453.
2098:
2080:(2): 224–246.
2069:
2029:
1999:
1993:
1978:
1939:
1896:
1882:
1880:
1877:
1874:
1873:
1861:
1849:
1837:
1825:
1813:
1801:
1789:
1777:
1765:
1748:
1736:
1724:
1707:
1695:
1693:, pp. 1–2
1691:Lu et al. 2019
1683:
1671:
1659:
1647:
1635:
1623:
1611:
1596:
1579:
1564:
1552:
1540:
1528:
1513:
1501:
1497:Li et al. 2008
1489:
1477:
1473:Li et al. 2008
1464:
1452:
1440:
1428:
1411:
1399:
1387:
1372:
1360:
1348:
1336:
1326:
1325:
1323:
1320:
1318:
1315:
1314:
1313:
1308:
1306:Laurasiatheria
1301:
1298:
1268:Atlantic Ocean
1259:
1258:
1249:
1248:
1240:
1239:
1231:
1230:
1229:
1228:
1227:
1225:
1222:
1218:Laurasiatheria
1203:Grande Coupure
1166:Ankylosauridae
1158:ornithischians
1094:
1091:
1047:
1046:
1037:
1036:
1028:
1027:
1026:
1017:
1016:
1008:
1007:
1006:
1005:
1004:
1002:
999:
973:that produced
952:
951:
942:
941:
933:
932:
924:
923:
922:
921:
920:
918:
915:
813:Main article:
810:
807:
765:
764:
757:
742:
739:Antler orogeny
735:
649:
646:
638:Hunic terranes
598:Main article:
587:
586:
577:
576:
568:
567:
566:
565:
564:
562:
559:
527:Snowball Earth
519:Neoproterozoic
466:Main article:
463:
460:
459:
458:
447:
440:
424:in Laurentia.
392:in Laurentia;
365:
362:
360:
359:Proto-Laurasia
357:
333:Alfred Wegener
293:
290:
164:
163:
161:
160:
155:
153:Eurasian Plate
149:
147:
143:
142:
140:
139:
134:
129:
124:
119:
114:
109:
103:
101:
97:
96:
94:
93:
88:
74:
63:
61:
57:
56:
54:Supercontinent
51:
47:
46:
43:
39:
38:
34:
33:
30:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
3992:
3981:
3978:
3976:
3973:
3971:
3968:
3966:
3963:
3961:
3958:
3956:
3953:
3951:
3948:
3946:
3943:
3941:
3938:
3936:
3933:
3931:
3928:
3926:
3923:
3921:
3918:
3916:
3913:
3912:
3910:
3894:
3891:
3889:
3881:
3879:
3876:
3874:
3871:
3869:
3868:
3863:
3856:
3855:
3851:
3836:
3833:
3831:
3828:
3826:
3823:
3821:
3818:
3816:
3813:
3811:
3808:
3806:
3801:
3800:
3799:Subcontinents
3795:
3794:
3792:
3787:
3786:
3782:
3780:
3777:
3775:
3772:
3770:
3767:
3765:
3764:Kumari Kandam
3762:
3760:
3757:
3755:
3750:
3748:
3744:
3740:
3735:
3734:
3732:
3727:
3724:
3722:
3719:
3717:
3714:
3712:
3707:
3703:
3702:
3700:
3695:
3692:
3690:
3687:
3685:
3682:
3680:
3677:
3675:
3672:
3670:
3667:
3665:
3662:
3660:
3657:
3655:
3652:
3650:
3647:
3645:
3642:
3640:
3635:
3634:
3630:
3626:
3621:
3620:
3618:
3615:
3614:
3609:
3605:
3590:
3587:
3585:
3582:
3580:
3577:
3575:
3572:
3570:
3567:
3565:
3562:
3560:
3557:
3555:
3552:
3550:
3547:
3545:
3542:
3540:
3537:
3535:
3532:
3530:
3527:
3525:
3522:
3520:
3517:
3515:
3512:
3510:
3507:
3505:
3502:
3500:
3497:
3495:
3492:
3490:
3485:
3481:
3480:
3478:
3473:
3470:
3468:
3465:
3463:
3460:
3458:
3455:
3453:
3450:
3448:
3445:
3443:
3440:
3438:
3435:
3433:
3430:
3428:
3423:
3422:
3416:
3415:
3413:
3410:
3409:
3404:
3400:
3387:
3386:
3381:
3375:
3372:
3371:
3366:
3360:
3357:
3356:
3351:
3345:
3342:
3341:
3336:
3330:
3327:
3326:
3321:
3317:
3304:
3303:
3302:South America
3298:
3292:
3289:
3288:
3287:North America
3283:
3277:
3274:
3273:
3268:
3262:
3259:
3258:
3253:
3247:
3244:
3243:
3238:
3232:
3229:
3228:
3223:
3217:
3214:
3213:
3208:
3202:
3199:
3198:
3193:
3189:
3185:
3181:
3174:
3169:
3167:
3162:
3160:
3155:
3154:
3151:
3142:
3140:9789400904699
3136:
3132:
3127:
3123:
3118:
3107:
3103:
3099:
3095:
3091:
3087:
3083:
3079:
3075:
3070:
3066:
3062:
3058:
3054:
3050:
3046:
3042:
3037:
3033:
3029:
3025:
3021:
3017:
3013:
3008:
2996:
2992:
2988:
2983:
2972:
2968:
2964:
2960:
2956:
2952:
2948:
2944:
2937:
2931:
2920:
2916:
2912:
2908:
2904:
2900:
2893:
2888:
2877:
2873:
2869:
2865:
2861:
2857:
2853:
2849:
2842:
2837:
2826:
2822:
2818:
2814:
2810:
2806:
2802:
2798:
2791:
2786:
2775:
2771:
2767:
2763:
2756:
2751:
2740:
2736:
2732:
2728:
2724:
2720:
2716:
2711:
2700:
2696:
2692:
2688:
2684:
2680:
2676:
2672:
2668:
2663:
2659:
2647:
2639:
2637:9780195347333
2633:
2629:
2625:
2621:
2617:
2613:
2608:
2597:
2593:
2589:
2585:
2581:
2577:
2573:
2569:
2565:
2560:
2549:
2545:
2541:
2537:
2533:
2529:
2525:
2521:
2517:
2512:
2501:
2497:
2493:
2489:
2485:
2481:
2474:
2469:
2458:
2454:
2450:
2446:
2443:(1–2): 3–39.
2442:
2438:
2434:
2429:
2425:
2423:0-511-04068-7
2419:
2415:
2410:
2409:
2402:
2398:
2396:90-5410-446-5
2392:
2388:
2384:
2380:
2375:
2364:
2360:
2356:
2352:
2348:
2344:
2337:
2332:
2328:
2324:
2319:
2314:
2309:
2304:
2300:
2296:
2292:
2287:
2276:
2272:
2268:
2264:
2260:
2256:
2252:
2248:
2244:
2239:
2235:
2231:
2226:
2221:
2217:
2213:
2209:
2205:
2201:
2197:
2193:
2188:
2177:
2173:
2169:
2165:
2161:
2157:
2150:
2144:
2133:
2129:
2124:
2119:
2115:
2111:
2104:
2099:
2095:
2091:
2087:
2083:
2079:
2075:
2070:
2059:
2055:
2051:
2047:
2043:
2039:
2035:
2030:
2026:
2022:
2018:
2014:
2010:
2006:
2000:
1996:
1994:9780598627582
1990:
1986:
1985:
1979:
1975:
1971:
1966:
1961:
1957:
1953:
1950:(1–2): 1–51.
1949:
1945:
1940:
1929:
1925:
1921:
1917:
1913:
1909:
1902:
1897:
1893:
1889:
1884:
1883:
1878:
1870:
1865:
1862:
1858:
1853:
1850:
1846:
1841:
1838:
1835:, p. 328
1834:
1829:
1826:
1823:, p. 319
1822:
1817:
1814:
1810:
1805:
1802:
1798:
1793:
1790:
1786:
1785:Metcalfe 1999
1781:
1778:
1774:
1769:
1766:
1762:
1757:
1755:
1753:
1749:
1745:
1740:
1737:
1733:
1728:
1725:
1721:
1716:
1714:
1712:
1708:
1704:
1699:
1696:
1692:
1687:
1684:
1680:
1675:
1672:
1668:
1663:
1660:
1656:
1651:
1648:
1644:
1639:
1636:
1632:
1627:
1624:
1620:
1615:
1612:
1608:
1603:
1601:
1597:
1593:
1588:
1586:
1584:
1580:
1576:
1571:
1569:
1565:
1561:
1556:
1553:
1549:
1548:Stampfli 2000
1544:
1541:
1537:
1532:
1529:
1525:
1520:
1518:
1514:
1510:
1505:
1502:
1498:
1493:
1490:
1486:
1481:
1478:
1474:
1468:
1465:
1461:
1456:
1453:
1449:
1444:
1441:
1437:
1432:
1429:
1425:
1420:
1418:
1416:
1412:
1409:, p. 108
1408:
1403:
1400:
1396:
1391:
1388:
1384:
1379:
1377:
1373:
1369:
1364:
1361:
1357:
1352:
1349:
1345:
1340:
1337:
1331:
1328:
1321:
1316:
1312:
1311:Laurasiformes
1309:
1307:
1304:
1303:
1299:
1297:
1295:
1291:
1287:
1275:
1273:
1269:
1253:
1244:
1235:
1223:
1221:
1219:
1214:
1212:
1211:Coraciiformes
1207:
1205:
1204:
1198:
1192:
1190:
1186:
1182:
1178:
1174:
1169:
1167:
1163:
1162:psittacosaurs
1159:
1155:
1151:
1147:
1142:
1138:
1134:
1129:
1127:
1126:
1121:
1120:
1115:
1111:
1107:
1103:
1100:
1099:Tethys Seaway
1092:
1090:
1086:
1082:
1078:
1076:
1072:
1066:
1064:
1058:
1041:
1032:
1021:
1012:
1000:
998:
994:
992:
991:Pechora Basin
988:
984:
983:flood basalts
980:
976:
972:
971:mantle plumes
966:
964:
946:
937:
928:
916:
914:
912:
908:
904:
900:
896:
892:
888:
887:detritivorous
884:
880:
876:
872:
868:
867:Gilboa forest
865:
860:
857:
853:
847:
845:
840:
838:
834:
830:
821:
816:
808:
806:
804:
800:
799:anoxic events
795:
791:
787:
786:provincialism
782:
778:
774:
770:
762:
761:active margin
758:
755:
754:Arctic Craton
751:
747:
743:
740:
736:
733:
729:
728:Barents Shelf
725:
724:
723:
720:
718:
714:
710:
706:
702:
698:
693:
691:
687:
683:
679:
675:
671:
670:Iapetus Ocean
662:
654:
647:
645:
641:
639:
635:
631:
627:
623:
619:
615:
611:
607:
601:
581:
572:
560:
558:
556:
552:
548:
547:Iapetus Ocean
544:
539:
536:
532:
528:
524:
520:
516:
515:Proto-Pacific
511:
509:
505:
501:
495:
493:
489:
485:
474:
469:
461:
456:
452:
448:
445:
441:
438:
434:
433:
432:
430:
425:
423:
419:
415:
410:
406:
401:
399:
395:
391:
387:
383:
379:
370:
363:
358:
356:
354:
353:Wilson Cycles
348:
345:
344:Peter Ziegler
340:
338:
334:
330:
325:
323:
319:
315:
314:Carboniferous
311:
307:
303:
299:
291:
289:
287:
283:
279:
275:
271:
267:
262:
260:
256:
252:
248:
244:
238:
233:
229:
223:
218:
212:
170:
159:
156:
154:
151:
150:
148:
144:
138:
135:
133:
130:
128:
125:
123:
120:
118:
115:
113:
110:
108:
105:
104:
102:
98:
92:
91:North America
89:
86:
82:
79:(without the
78:
75:
72:
69:(without the
68:
65:
64:
62:
60:Today part of
58:
55:
52:
48:
44:
40:
35:
28:
23:
3858:
3797:
3783:
3747:hypothesised
3737:
3705:
3623:
3554:Kazakhstania
3529:Congo Craton
3483:
3441:
3419:Prehistoric
3418:
3377:
3362:
3347:
3340:Afro-Eurasia
3332:
3294:
3279:
3264:
3249:
3234:
3219:
3204:
3133:. Springer.
3130:
3121:
3109:. Retrieved
3081:
3077:
3048:
3044:
3015:
3011:
2999:. Retrieved
2994:
2990:
2974:. Retrieved
2946:
2942:
2922:. Retrieved
2902:
2898:
2879:. Retrieved
2851:
2847:
2828:. Retrieved
2800:
2796:
2777:. Retrieved
2765:
2761:
2742:. Retrieved
2722:
2718:
2702:. Retrieved
2677:(1): 67–83.
2674:
2670:
2611:
2599:. Retrieved
2571:
2567:
2551:. Retrieved
2523:
2519:
2503:. Retrieved
2483:
2479:
2460:. Retrieved
2440:
2436:
2407:
2378:
2366:. Retrieved
2346:
2342:
2298:
2294:
2278:. Retrieved
2250:
2246:
2199:
2195:
2179:. Retrieved
2159:
2155:
2135:. Retrieved
2113:
2109:
2077:
2073:
2061:. Retrieved
2041:
2037:
2008:
2004:
1983:
1947:
1943:
1931:. Retrieved
1911:
1907:
1891:
1887:
1864:
1852:
1840:
1828:
1816:
1804:
1792:
1780:
1768:
1739:
1727:
1698:
1686:
1674:
1667:Parrish 1993
1662:
1655:Parrish 1993
1650:
1638:
1626:
1614:
1607:Ziegler 2012
1577:, p. 16
1560:Scotese 2009
1555:
1543:
1538:, p. 71
1536:Scotese 2009
1531:
1504:
1492:
1480:
1467:
1455:
1443:
1431:
1407:Bleeker 2003
1402:
1395:Ziegler 1988
1390:
1363:
1351:
1346:, p. 40
1344:Du Toit 1937
1339:
1330:
1276:
1272:Newark Basin
1265:
1215:
1208:
1201:
1193:
1170:
1148: – the
1137:crocodilians
1130:
1123:
1117:
1104:
1096:
1087:
1083:
1079:
1067:
1059:
1055:
1001:Asian blocks
995:
967:
960:
903:insectivores
891:ringed worms
864:pteridophyte
861:
848:
841:
826:
803:black shales
766:
721:
712:
708:
704:
700:
694:
667:
642:
603:
540:
512:
510:in Siberia.
508:Aldan Shield
496:
481:
426:
402:
375:
349:
341:
329:Eduard Suess
326:
322:Kazakhstania
295:
282:Kazakhstania
263:
168:
167:
117:Kazakhstania
3721:Novopangaea
3589:South China
3569:North China
3084:: 262–286.
2971:10852/62957
2924:22 December
2830:30 November
2803:(1): 1–23.
2704:10 November
2601:23 November
2553:26 November
2462:15 February
2368:22 December
2253:(1): 9–20.
2202:(1): 7581.
2137:22 February
2063:28 December
1933:22 December
1809:Keeley 2012
1720:Blakey 2003
1224:Final split
1171:Meanwhile,
897:, and some
871:coal forest
833:Rheic Ocean
794:brachiopods
705:Euramerica.
678:Rheic Ocean
606:Precambrian
455:West Africa
414:dike swarms
405:Proterozoic
403:Additional
364:Pre–Rodinia
264:Laurentia,
251:portmanteau
132:South China
127:North China
3909:Categories
3857:See also:
3759:Hyperborea
3749:continents
3684:Seychelles
3669:Madagascar
3649:Doggerland
3544:Euramerica
3499:Asiamerica
3227:Antarctica
3180:Continents
3111:7 December
3001:1 December
2976:9 November
2881:25 January
2744:1 December
2505:1 December
2280:18 January
1857:Olsen 1997
1426:, Abstract
1397:, Abstract
1383:Meert 2012
1317:References
1197:Turgai Sea
1133:archosaurs
1110:pine genus
1106:Pine trees
1075:West Burma
907:piscivores
899:arthropods
801:that left
777:trilobites
618:Cathaysian
555:Ordovician
529:) and the
407:crust was
3830:Greenland
3694:Zealandia
3659:Jan Mayen
3644:Cathaysia
3564:Laurentia
3559:Laramidia
3549:Kalaharia
3504:Atlantica
3437:Kenorland
3257:Australia
3106:134171828
2876:128812370
2825:219202298
2699:128845353
2656:ignored (
2646:cite book
2548:128757269
2275:129789533
1960:CiteSeerX
1185:the other
1177:ancestors
1154:theropods
1150:sauropods
1146:dinosaurs
1141:Pterosaur
883:treeferns
879:lycopsids
856:ostracods
750:Lomonosov
746:Innuitian
701:Laurussia
686:Carolinia
630:Qiangtang
622:Cimmerian
551:cold spot
535:Ice Brook
418:MacKenzie
255:Laurentia
107:Laurentia
3888:Category
3754:Atlantis
3739:Mythical
3674:Mauritia
3639:Beringia
3524:Cimmeria
3519:Chilenia
3509:Avalonia
3489:Amazonia
3472:Vaalbara
3457:Pannotia
3442:Laurasia
3432:Gondwana
3427:Columbia
3355:Americas
2779:22 March
2596:49353621
2327:31506056
2234:31110279
2181:10 April
2132:18013787
2044:: 1–14.
1300:See also
1189:Jurassic
917:Laurasia
911:amniotes
895:molluscs
792:divided
690:Armorica
682:Avalonia
626:Sibumasu
614:Pannotia
610:Cambrian
600:Pannotia
561:Pannotia
523:Varanger
488:Amazonia
437:Sarmatia
409:accreted
382:Archaean
378:Columbia
306:Avalonia
274:terranes
266:Avalonia
243:Triassic
232:Gondwana
169:Laurasia
83:and the
20:Laurasia
3774:Meropis
3769:Lemuria
3584:Siberia
3534:Cuyania
3514:Baltica
3494:Arctica
3462:Rodinia
3452:Pangaea
3385:Oceania
3370:Eurasia
3086:Bibcode
3053:Bibcode
3020:Bibcode
2951:Bibcode
2907:Bibcode
2856:Bibcode
2805:Bibcode
2762:Geology
2727:Bibcode
2679:Bibcode
2616:Bibcode
2576:Bibcode
2528:Bibcode
2488:Bibcode
2445:Bibcode
2351:Bibcode
2318:6742990
2255:Bibcode
2225:6527553
2204:Bibcode
2164:Bibcode
2082:Bibcode
2046:Bibcode
2013:Bibcode
1952:Bibcode
1916:Bibcode
1879:Sources
1173:mammals
1119:Strobus
985:in the
852:benthos
815:Pangaea
809:Pangaea
773:benthos
769:shelves
531:Rapitan
484:Rodinia
468:Rodinia
462:Rodinia
422:Sudbury
386:sutures
318:Siberia
308:in the
302:Baltica
286:Siberia
270:Baltica
217:Pangaea
122:Siberia
112:Baltica
3810:Arabia
3805:Alaska
3745:, and
3716:Aurica
3711:Amasia
3574:Pampia
3272:Europe
3212:Africa
3137:
3104:
2874:
2823:
2697:
2634:
2594:
2546:
2420:
2416:–332.
2393:
2325:
2315:
2273:
2232:
2222:
2130:
2038:Lithos
1991:
1962:
1908:Lithos
1156:, and
989:, the
688:, and
453:, and
67:Europe
42:Formed
3689:Sunda
3679:Sahul
3629:lands
3579:Sahul
3184:Earth
3102:S2CID
2939:(PDF)
2895:(PDF)
2872:S2CID
2844:(PDF)
2821:S2CID
2793:(PDF)
2758:(PDF)
2695:S2CID
2592:S2CID
2544:S2CID
2476:(PDF)
2339:(PDF)
2271:S2CID
2152:(PDF)
2128:S2CID
2106:(PDF)
1904:(PDF)
1322:Notes
1125:Pinus
1071:Lhasa
634:Lhasa
451:Congo
444:sills
137:Tarim
3743:lost
3631:and
3447:Nena
3242:Asia
3135:ISBN
3113:2019
3003:2019
2978:2019
2926:2019
2883:2020
2832:2019
2781:2020
2746:2019
2706:2019
2658:help
2632:ISBN
2603:2019
2555:2019
2507:2019
2464:2020
2418:ISBN
2391:ISBN
2370:2019
2323:PMID
2282:2020
2230:PMID
2183:2020
2139:2020
2065:2019
1989:ISBN
1935:2019
1209:The
905:and
730:and
533:and
513:The
420:and
320:and
304:and
298:core
284:and
259:Asia
257:and
77:Asia
50:Type
3182:of
3094:doi
3082:186
3061:doi
3028:doi
2995:404
2967:hdl
2959:doi
2947:114
2915:doi
2864:doi
2852:161
2813:doi
2801:173
2770:doi
2735:doi
2723:113
2687:doi
2675:326
2624:doi
2584:doi
2572:121
2536:doi
2524:101
2496:doi
2453:doi
2441:351
2414:316
2383:doi
2359:doi
2313:PMC
2303:doi
2299:286
2263:doi
2251:179
2220:PMC
2212:doi
2172:doi
2160:160
2118:doi
2090:doi
2078:241
2054:doi
2042:174
2021:doi
1970:doi
1948:106
1924:doi
1277:By
1191:).
1181:one
711:or
253:of
239:Mya
228:Mya
3911::
3779:Mu
3741:,
3467:Ur
3100:.
3092:.
3080:.
3076:.
3059:.
3049:67
3047:.
3043:.
3026:.
3016:59
3014:.
2993:.
2989:.
2965:.
2957:.
2945:.
2941:.
2913:.
2903:40
2901:.
2897:.
2870:.
2862:.
2850:.
2846:.
2819:.
2811:.
2799:.
2795:.
2766:38
2764:.
2760:.
2733:.
2721:.
2717:.
2693:.
2685:.
2673:.
2669:.
2650::
2648:}}
2644:{{
2630:.
2622:.
2590:.
2582:.
2570:.
2566:.
2542:.
2534:.
2522:.
2518:.
2494:.
2484:25
2482:.
2478:.
2451:.
2439:.
2435:.
2389:.
2357:.
2347:21
2345:.
2341:.
2321:.
2311:.
2297:.
2293:.
2269:.
2261:.
2249:.
2245:.
2228:.
2218:.
2210:.
2198:.
2194:.
2170:.
2158:.
2154:.
2126:.
2114:69
2112:.
2108:.
2088:.
2076:.
2052:.
2040:.
2036:.
2019:.
2009:25
2007:.
1968:.
1958:.
1946:.
1922:.
1912:71
1910:.
1906:.
1892:10
1890:.
1751:^
1710:^
1599:^
1582:^
1567:^
1516:^
1414:^
1375:^
1279:c.
1206:.
1152:,
1073:,
913:.
893:,
877:,
684:,
632:,
628:,
557:.
268:,
261:.
199:,-
190:eɪ
181:ɔː
3627:/
3172:e
3165:t
3158:v
3143:.
3115:.
3096::
3088::
3067:.
3063::
3055::
3034:.
3030::
3022::
3005:.
2980:.
2969::
2961::
2953::
2928:.
2917::
2909::
2885:.
2866::
2858::
2834:.
2815::
2807::
2783:.
2772::
2748:.
2737::
2729::
2708:.
2689::
2681::
2660:)
2640:.
2626::
2618::
2605:.
2586::
2578::
2557:.
2538::
2530::
2509:.
2498::
2490::
2466:.
2455::
2447::
2426:.
2399:.
2385::
2372:.
2361::
2353::
2329:.
2305::
2284:.
2265::
2257::
2236:.
2214::
2206::
2200:9
2185:.
2174::
2166::
2141:.
2120::
2096:.
2092::
2084::
2067:.
2056::
2048::
2027:.
2023::
2015::
1997:.
1976:.
1972::
1954::
1937:.
1926::
1918::
1475:.
756:;
748:-
741:;
734:;
608:-
457:.
226:(
211:/
208:ə
205:i
202:ʃ
196:ə
193:ʒ
187:r
184:ˈ
178:l
175:/
171:(
87:)
73:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.